Consider a Binary antipodal system which produces data of δ (t)
|
|
|
- Lesley Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modulaion Polem PSK: (inay Phae-hi keying) Conide a inay anipodal yem whih podue daa o δ ( o + δ ( o inay and epeively. Thi daa i paed o pule haping ile and he oupu o he pule haping ile i muliplied y o( π o have a pa-and peum in he hannel (up-onveion). o( π Mappe daa = ± δ ( Pule Shaping File p ( ( daa p( o(π a) valuae ime domain and equeny domain epeenaion o anmied ignal. Why pa-and ommuniaion i equied? Wha i he ignal andwidh a he anmie oupu i Squae-Roo-Raied Coine (SQRC) ile i ued a pule haping ile? ) Wha i he opimum eeive uue? Wha i he ane union o mahed ile? Diu he poailiy o eo o he pa-and yem. ) I he phae o he aie in he anmie and he eeive ae no he ame, wha happen? Can we eove he daa in hi ae? Soluion: Pa a) The anmie i anmiing eihe p( o(π o p( o(π o in ohe wod i i anmiing eihe p( o(π o p( o(π + π ). Thi i why we all hi yem inay phae hi keying (PSK). We eihe end he oine wih phae o o wih a phae oπ. Conide a pule haping ile o p( a hown elow: p ( T Then, he anmie uue and oupu o anmie in ime domain i a hown elow: Conodia Univeiy LC4
2 Modulaion,,,,,,,... + Mappe o [ π ] ( o [ π ] + o[π ] ( = o[π ],,,,,,,... The ignal a he oupu o he anmie in he equeny domain i:.p( + ) +.P( ) Thee ae wo eaon o having paand ommuniaion: - To divide he availale andpa andwidh eween eveal ue. - To have mall ize anenna due o having high equenie. The andwidh o he ignal a he oupu o he paand anmie i: W ignal = ( + β ) T whih i wie he aeand andwidh. Pa ) Opimum eeive i a ollow: o( π o o daa p( o(π x ( Mahed File p( T Reeive z ( Theeoe, he aove i he opimum andpa eeive. T Deeo daa + o(4π daa p( daa p( o(4π x( = daa p( o (π = daa p( = + Sine mahed ile i a law pa ile we have: daa z( = p( * p( T Theeoe, pa and yem i equivalen o aeand yem. The mahed ile ha he ame ane union a pule haping ile and heeoe i i SQRC. ) Conodia Univeiy LC4
3 Modulaion The poailiy o eo o he paand yem i he ame a aeand yem and heeoe he R would e a alulaed eoe: Pa ) Aume a phae dieene oϕ, x( = daa p( o(π o(π + ϕ) R( PSK ) = Q o(4π + ϕ) + o( ϕ) daa p( o( ϕ) daa p( o(4π + ϕ) = daa p( = + Sine mahed ile i a law pa ile we have: daa z ( = p( * p( T o( ϕ) Sine ϕ i a andom nume eween and π, we anno make a deiion uing maximum likelihood deeo. To e ale o eove he daa, we hould i indϕ. Conodia Univeiy 3 LC4
4 Modulaion Two dimenional modulaion heme: o( π o( π = T m Mappe I h ( ( ( m ( Î = T Deiion m ) Q h ( m ( Qˆ Tanmie in( π in( π Re eive andwidh: W= ( ) ( β ) + β = + T The onellaion diagam o i a ollow: R Le onide he yem elow, whee adjaen poin (hoizonally o veially) have equal diane om eah ohe. Deiion oundaie o maximum likelihood deeion ae hown y dahed line. 3 P ( ) = 4( ) Q P ( ) 3 P = = ( ) Q log 4 = 3Q Conodia Univeiy 4 LC4
5 Modulaion I Q The deiion lok wok aed on deiion egion. The onellaion diagam o PSK i a ollow: Le onide he PSK yem elow, whee adjaen poin have equal angula diane. Deiion oundaie o maximum likelihood deeion ae hown y dahed line. d θ θ = π /8 Fo PSK, we an ue Gay oding a hown in he onellaion diagam and heeoe: P 4 4P = = = in( /) = P Q in( π /) Q π Q log R in( π /) Anwe: P 8P = Q in( π / R,,,..., Gay oding i oviou. I 3 ae poin in he onellaion diagam in lok-wie ode, hen Gay oding an e hown in he mappe a ollow: I x.7 y -y -.7 -x - -x -.7 -y y.7 x Q y.7 x x.7 y -y -.7 -x - -x -.7 -y x = o(π / 8) y = in(π / 8) = an The deiion lok i evaluae he phae o he eeived veo ϕ and hen deiion Q I ae made a ollow: ( i ) π ( i + ) π I < ϕ <, deide ha i ha een anmied. (o i =,,3,.., ) Conodia Univeiy LC4
6 Modulaion Polem: Deign o Communiaion Syem A eam o digial daa wih daa ae o M/ i o e anmied in an addiive whie Gauian noie hannel wih powe peal deniy o Wa/Hz whee he availale andwidh i 4 MHz. The equied yem peomane i a i eo ae o. Conide M o MPSK and deign he e paand anmie and eeive y deemining all he paamee o he deign (inluding he eeived powe) and dawing a yem lok diagam. Soluion: = M ( ) R ( ) aume.3 DS R = + = +.3 =.3 log M log M 4 Hz log M 3.9, o we an hooe M = and oeponding heme ae - o -PSK. 3 = P ( ) = 4( ) Q 3Q P ( ) 3 P = = ( ) Q log 4 P ( ) = 3 = Q 4 = Q.33 4 = = Fom Q-union ale x 4. 7 and heeoe: 9 =. 9 P = R =. =.7mW π P ( PSK ) = P ( M ) Q in and M P P P = = π Q in log = Fom Q-union ale: π x = in = 4. P R R P log M = ( Gay oded ) = 8 = =.. 8 = = = =.8mW log M log Theeoe,- i ee, ine he eeived powe i 3 o -PSK. Conodia Univeiy LC4
7 Modulaion Polem (Analog Communiaion) The polem o he uue o polem. i he ue o ideal ile. We would like o deign anohe anmie whih ue no ile. Thi kind o modulao i alled Quadaue-Ampliude-Modulao (). Daw he uue o hi new anmie o anmi he inomaion aou m ( and m ( uh ha he oupu ignal x _ ou( ha he ame ene equeny and he ame andwidh a o polem.. Show ha you deign wok y howing he uue o he eeive and explaining he eovey o oh ignal m ( ) and m ( ). Daw he equeny peum o all he ignal in he anmie and he eeive a well. Soluion: Single ideand ignal ae had o geneae ine a hown in pa a o hi polem ideal ile ae equied. To anmi wo ignal m ( ) and m ( ), we an ue Quadaue Ampliude Modulaion () whih do no equie any ile a all and heeoe i i paial. Tanmie Reeive = m ( o π m ( in π and he aie ( + The anmie oupu i ϕ ( ) ( ) equeny i = 4 khz. To ind he andwidh and ene equeny o ϕ ( examine wo ignal m ( o( π 4 ) and m ( in( π 4 ), we hould. The ae-and andwidh o m ( and m ( i khz and a we know he andwidh o eah o he Doule Side-and modulaed m ( o 4 m ( in π 4 would e doule o ha whih i khz. The ignal ( π ) and ( ) ene equeny o eah o hee ignal would e he aie equeny o 4kHz. ϕ = m ( o π 4 + m ( in π will have ( 4 Theeoe, he anmied ignal ( ) ( ) ene equeny o 4kHz wih andwidh o khz. To eove m ( and m (, oheen eeive a hown aove ould e ued. Thi an e poved y alulaing x ( and x ( aed on he uue o he eeive. x = ϕ ( o(π 4 = m ( o(π 4 + m ( in π 4 o(π 4 [ ( )] ) ( + m ( in( [ m ( o(π 4 + m ( in( π 4 )] in( 4 ) = m ( + m ( o(π 9 π 9 x = ϕ ( in(π 4 = π ( ( = m m ( o(π 9 + m ( in π 9 ( Conodia Univeiy 7 LC4
8 The la wo em in oh equaion ae andpa ignal eneed a = 9kHz whih ae uppeed y he lowpa ile and heeoe, he oupu o hee ile will eove ( ) oe ha hee low-pa ile ae no ideal. Fequeny peum o all he ignal ae povided elow: M ( ) Modulaion m and m ( ). - [khz ] M ( ) - Re / [ ( )] Φ -4 4 Im / [ ( )] Φ -4 4 We noe ha he anmied equeny peum i omplex. Theeoe, Φ [ Φ ( )] + j Im[ Φ ( )] ( ) = Re Conideing ha low pa ile in he eeive have ane union o H( ) and H ( ), we an how he equeny peum o all he ignal in he eeive and alo ome up wih ane union o hee wo ile. Conodia Univeiy 8 LC4
9 [ X ( )] Re Modulaion [ X ( )] Im / H ( ) ˆ M ( ) [ X ( )] Re [ X ( )] Im / H ( ) M ( ) ˆ aed on he aove wo lowpa ile ae idenial wih pa and o o Kz, op-and o lage han 8 KHz and aniion and o KHz o 8 KHz. The hal ampliude u-o equeny i 4 KHz. oe ha uing hee ile and auming ha hee i no noie in he hannel, we have: M ˆ ˆ ( ) = M ( ) m ( = m ( M ˆ ( ) = M ( ) mˆ ( = m ( ) Conodia Univeiy 9 LC4
Control Systems -- Final Exam (Spring 2006)
 6.5 Conrol Syem -- Final Eam (Spring 6 There are 5 prolem (inluding onu prolem oal poin. (p Given wo marie: (6 Compue A A e e. (6 For he differenial equaion [ ] ; y u A wih ( u( wha i y( for >? (8 For
6.5 Conrol Syem -- Final Eam (Spring 6 There are 5 prolem (inluding onu prolem oal poin. (p Given wo marie: (6 Compue A A e e. (6 For he differenial equaion [ ] ; y u A wih ( u( wha i y( for >? (8 For
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum II
 DS-SS II 7. Dire Sequene Spread Speru II ER One igh hink ha DS-SS would have he following drawak. Sine he RF andwidh i ie ha needed for a narrowand PSK ignal a he ae daa rae R, here will e ie a uh noie
DS-SS II 7. Dire Sequene Spread Speru II ER One igh hink ha DS-SS would have he following drawak. Sine he RF andwidh i ie ha needed for a narrowand PSK ignal a he ae daa rae R, here will e ie a uh noie
6.302 Feedback Systems Recitation : Phase-locked Loops Prof. Joel L. Dawson
 6.32 Feedback Syem Phae-locked loop are a foundaional building block for analog circui deign, paricularly for communicaion circui. They provide a good example yem for hi cla becaue hey are an excellen
6.32 Feedback Syem Phae-locked loop are a foundaional building block for analog circui deign, paricularly for communicaion circui. They provide a good example yem for hi cla becaue hey are an excellen
Application of Combined Fourier Series Transform (Sampling Theorem)
 Applicaion o Combined Fourier Serie ranorm Sampling heorem x X[] m m Sampling Frequency Deparmen o Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Deparmen o Elecrical and Compuer Engineering X[] x We need Fourier Serie
Applicaion o Combined Fourier Serie ranorm Sampling heorem x X[] m m Sampling Frequency Deparmen o Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Deparmen o Elecrical and Compuer Engineering X[] x We need Fourier Serie
Multicode DS-CDMA With Joint Transmit/Receive Frequency-domain Equalization
 Muliode DS-CDMA Wih Join Tanmi/Reeive Fequeny-domain Equalizaion Kazuki TAKEDA iomihi TOMEBA and Fumiyuki ADACI Dep. of Eleial and Communiaion Engineeing, Gaduae Shool of Engineeing, Tohoku Univeiy 6-6-5,
Muliode DS-CDMA Wih Join Tanmi/Reeive Fequeny-domain Equalizaion Kazuki TAKEDA iomihi TOMEBA and Fumiyuki ADACI Dep. of Eleial and Communiaion Engineeing, Gaduae Shool of Engineeing, Tohoku Univeiy 6-6-5,
Final Exam. Tuesday, December hours, 30 minutes
 an Faniso ae Univesi Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 04 Final Exam Tuesda, Deembe 6 hous, 30 minues Name: Insuions. This is losed book, losed noes exam.. No alulaos of an kind ae allowed. 3. how all he alulaions.
an Faniso ae Univesi Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 04 Final Exam Tuesda, Deembe 6 hous, 30 minues Name: Insuions. This is losed book, losed noes exam.. No alulaos of an kind ae allowed. 3. how all he alulaions.
u(t) Figure 1. Open loop control system
 Open loop conrol v cloed loop feedbac conrol The nex wo figure preen he rucure of open loop and feedbac conrol yem Figure how an open loop conrol yem whoe funcion i o caue he oupu y o follow he reference
Open loop conrol v cloed loop feedbac conrol The nex wo figure preen he rucure of open loop and feedbac conrol yem Figure how an open loop conrol yem whoe funcion i o caue he oupu y o follow he reference
On The Estimation of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complete Block Designs
 Mahemaical Theoy and Modeling ISSN 45804 (Pape ISSN 505 (Online Vol.6, No.7, 06 www.iise.og On The Esimaion of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complee Bloc Designs EFFANGA, EFFANGA OKON AND BASSE, E.
Mahemaical Theoy and Modeling ISSN 45804 (Pape ISSN 505 (Online Vol.6, No.7, 06 www.iise.og On The Esimaion of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complee Bloc Designs EFFANGA, EFFANGA OKON AND BASSE, E.
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
156 There are 9 books stacked on a shelf. The thickness of each book is either 1 inch or 2
 156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
Let. x y. denote a bivariate time series with zero mean.
 Linear Filer Le x y : T denoe a bivariae ime erie wih zero mean. Suppoe ha he ime erie {y : T} i conruced a follow: y a x The ime erie {y : T} i aid o be conruced from {x : T} by mean of a Linear Filer.
Linear Filer Le x y : T denoe a bivariae ime erie wih zero mean. Suppoe ha he ime erie {y : T} i conruced a follow: y a x The ime erie {y : T} i aid o be conruced from {x : T} by mean of a Linear Filer.
Invert and multiply. Fractions express a ratio of two quantities. For example, the fraction
 Appendi E: Mnipuling Fions Te ules fo mnipuling fions involve lgei epessions e el e sme s e ules fo mnipuling fions involve numes Te fundmenl ules fo omining nd mnipuling fions e lised elow Te uses of
Appendi E: Mnipuling Fions Te ules fo mnipuling fions involve lgei epessions e el e sme s e ules fo mnipuling fions involve numes Te fundmenl ules fo omining nd mnipuling fions e lised elow Te uses of
CYCLOSTATIONARITY-BASED BLIND CLASSIFICATION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATIONS
 CYCLOSAIONARIY-BASED BLIND CLASSIFICAION OF ANALOG AND DIGIAL MODULAIONS Oavia A. Dobe Ali Abdi 2 Yehekel Ba-Ne 2 Wei Su 3 Fauly of Eng. Applied Siene Memoial Univeiy of Newfoundl S. John NL AB 3X5 Canada
CYCLOSAIONARIY-BASED BLIND CLASSIFICAION OF ANALOG AND DIGIAL MODULAIONS Oavia A. Dobe Ali Abdi 2 Yehekel Ba-Ne 2 Wei Su 3 Fauly of Eng. Applied Siene Memoial Univeiy of Newfoundl S. John NL AB 3X5 Canada
8.5 Circles and Lengths of Segments
 LenghofSegmen20052006.nb 1 8.5 Cicle and Lengh of Segmen In hi ecion we will how (and in ome cae pove) ha lengh of chod, ecan, and angen ae elaed in ome nal way. We will look a hee heoem ha ae hee elaionhip
LenghofSegmen20052006.nb 1 8.5 Cicle and Lengh of Segmen In hi ecion we will how (and in ome cae pove) ha lengh of chod, ecan, and angen ae elaed in ome nal way. We will look a hee heoem ha ae hee elaionhip
Add the transfer payments and subtract the total taxes from (1): Using these definitions, the above becomes: The Saving and Investment Equation:
 San Fanio Sae Univei Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 06 Poblem e 5 Conumpion-Saving Deiion and Riadian Equivalene. (0 poin. Saving and Invemen equaion. a. Deive he aving and invemen equaion. The fomula fo GDP uing
San Fanio Sae Univei Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 06 Poblem e 5 Conumpion-Saving Deiion and Riadian Equivalene. (0 poin. Saving and Invemen equaion. a. Deive he aving and invemen equaion. The fomula fo GDP uing
12. Nyquist Sampling, Pulse-Amplitude Modulation, and Time- Division Multiplexing
 Nyqui Sapling, Pule-Apliude Modulaion, and Tie Diviion Muliplexing on Mac 2. Nyqui Sapling, Pule-Apliude Modulaion, and Tie- Diviion Muliplexing Many analogue counicaion ye are ill in wide ue oday. Thee
Nyqui Sapling, Pule-Apliude Modulaion, and Tie Diviion Muliplexing on Mac 2. Nyqui Sapling, Pule-Apliude Modulaion, and Tie- Diviion Muliplexing Many analogue counicaion ye are ill in wide ue oday. Thee
Molecular Evolution and Phylogeny. Based on: Durbin et al Chapter 8
 Molecula Evoluion and hylogeny Baed on: Dubin e al Chape 8. hylogeneic Tee umpion banch inenal node leaf Topology T : bifucaing Leave - N Inenal node N+ N- Lengh { i } fo each banch hylogeneic ee Topology
Molecula Evoluion and hylogeny Baed on: Dubin e al Chape 8. hylogeneic Tee umpion banch inenal node leaf Topology T : bifucaing Leave - N Inenal node N+ N- Lengh { i } fo each banch hylogeneic ee Topology
Two figures are similar fi gures when they have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
 NDIN O PIION. o be poficient in math, ou need to ue clea definition in dicuion with othe and in ou own eaoning. imilait and anfomation ential uetion When a figue i tanlated, eflected, otated, o dilated
NDIN O PIION. o be poficient in math, ou need to ue clea definition in dicuion with othe and in ou own eaoning. imilait and anfomation ential uetion When a figue i tanlated, eflected, otated, o dilated
Fall 2004/05 Solutions to Assignment 5: The Stationary Phase Method Provided by Mustafa Sabri Kilic. I(x) = e ixt e it5 /5 dt (1) Z J(λ) =
 8.35 Fall 24/5 Solution to Aignment 5: The Stationay Phae Method Povided by Mutafa Sabi Kilic. Find the leading tem fo each of the integal below fo λ >>. (a) R eiλt3 dt (b) R e iλt2 dt (c) R eiλ co t dt
8.35 Fall 24/5 Solution to Aignment 5: The Stationay Phae Method Povided by Mutafa Sabi Kilic. Find the leading tem fo each of the integal below fo λ >>. (a) R eiλt3 dt (b) R e iλt2 dt (c) R eiλ co t dt
Addition & Subtraction of Polynomials
 Addiion & Sucion of Polynomil Addiion of Polynomil: Adding wo o moe olynomil i imly me of dding like em. The following ocedue hould e ued o dd olynomil 1. Remove enhee if hee e enhee. Add imil em. Wie
Addiion & Sucion of Polynomil Addiion of Polynomil: Adding wo o moe olynomil i imly me of dding like em. The following ocedue hould e ued o dd olynomil 1. Remove enhee if hee e enhee. Add imil em. Wie
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Estimation and Confidence Intervals: Additional Topics
 Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
#5 Demodulation and Detection Error due to Noise
 06 Q Wirele Communicaion Engineering #5 Demodulaion and Deecion Error due o Noie Kei Sakaguci akaguci@mobile.ee. Jul 8, 06 Coure Scedule Dae Tex Conen # June 7, 7 Inroducion o wirele communicaion em #
06 Q Wirele Communicaion Engineering #5 Demodulaion and Deecion Error due o Noie Kei Sakaguci akaguci@mobile.ee. Jul 8, 06 Coure Scedule Dae Tex Conen # June 7, 7 Inroducion o wirele communicaion em #
Chapter 19 Webassign Help Problems
 Chapte 9 Webaign Help Poblem 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Poblem 4: The pictue fo thi poblem i a bit mileading. They eally jut give you the pictue fo Pat b. So let fix that. Hee i the pictue fo Pat (a): Pat (a) imply
Chapte 9 Webaign Help Poblem 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Poblem 4: The pictue fo thi poblem i a bit mileading. They eally jut give you the pictue fo Pat b. So let fix that. Hee i the pictue fo Pat (a): Pat (a) imply
Low-complexity Algorithms for MIMO Multiplexing Systems
 Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
The Purpose of this talk The generation of the high-frequency resonant FEL wave by means of it s low-frequency wave as a pomp wave
 The Purpoe of hi alk The generaion of he high-frequency reonan FEL wave y mean of i low-frequency wave a a pomp wave A free elecron laer ha wo reonan frequencie wih : λ 1, = ( 1 ± β β ) λ w In a waveguide:
The Purpoe of hi alk The generaion of he high-frequency reonan FEL wave y mean of i low-frequency wave a a pomp wave A free elecron laer ha wo reonan frequencie wih : λ 1, = ( 1 ± β β ) λ w In a waveguide:
Frequency Response. We now know how to analyze and design ccts via s- domain methods which yield dynamical information
 Frequency Repone We now now how o analyze and deign cc via - domain mehod which yield dynamical informaion Zero-ae repone Zero-inpu repone Naural repone Forced repone The repone are decribed by he exponenial
Frequency Repone We now now how o analyze and deign cc via - domain mehod which yield dynamical informaion Zero-ae repone Zero-inpu repone Naural repone Forced repone The repone are decribed by he exponenial
, the. L and the L. x x. max. i n. It is easy to show that these two norms satisfy the following relation: x x n x = (17.3) max
 ecure 8 7. Sabiliy Analyi For an n dimenional vecor R n, he and he vecor norm are defined a: = T = i n i (7.) I i eay o how ha hee wo norm aify he following relaion: n (7.) If a vecor i ime-dependen, hen
ecure 8 7. Sabiliy Analyi For an n dimenional vecor R n, he and he vecor norm are defined a: = T = i n i (7.) I i eay o how ha hee wo norm aify he following relaion: n (7.) If a vecor i ime-dependen, hen
TRAVELING WAVES. Chapter Simple Wave Motion. Waves in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation are called the
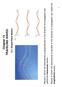 Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
General Non-Arbitrage Model. I. Partial Differential Equation for Pricing A. Traded Underlying Security
 1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
To become more mathematically correct, Circuit equations are Algebraic Differential equations. from KVL, KCL from the constitutive relationship
 Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Problem Set If all directed edges in a network have distinct capacities, then there is a unique maximum flow.
 CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
Solutions to the Exam Digital Communications I given on the 11th of June = 111 and g 2. c 2
 Soluions o he Exam Digial Communicaions I given on he 11h of June 2007 Quesion 1 (14p) a) (2p) If X and Y are independen Gaussian variables, hen E [ XY ]=0 always. (Answer wih RUE or FALSE) ANSWER: False.
Soluions o he Exam Digial Communicaions I given on he 11h of June 2007 Quesion 1 (14p) a) (2p) If X and Y are independen Gaussian variables, hen E [ XY ]=0 always. (Answer wih RUE or FALSE) ANSWER: False.
8.1. a) For step response, M input is u ( t) Taking inverse Laplace transform. as α 0. Ideal response, K c. = Kc Mτ D + For ramp response, 8-1
 8. a For ep repone, inpu i u, U Y a U α α Y a α α Taking invere Laplae ranform a α e e / α / α A α 0 a δ 0 e / α a δ deal repone, α d Y i Gi U i δ Hene a α 0 a i For ramp repone, inpu i u, U Soluion anual
8. a For ep repone, inpu i u, U Y a U α α Y a α α Taking invere Laplae ranform a α e e / α / α A α 0 a δ 0 e / α a δ deal repone, α d Y i Gi U i δ Hene a α 0 a i For ramp repone, inpu i u, U Soluion anual
EE Control Systems LECTURE 2
 Copyrigh F.L. Lewi 999 All righ reerved EE 434 - Conrol Syem LECTURE REVIEW OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM LAPLACE TRANSFORM The Laplace ranform i very ueful in analyi and deign for yem ha are linear and ime-invarian
Copyrigh F.L. Lewi 999 All righ reerved EE 434 - Conrol Syem LECTURE REVIEW OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM LAPLACE TRANSFORM The Laplace ranform i very ueful in analyi and deign for yem ha are linear and ime-invarian
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 30 Signal & Syem Prof. ark Fowler oe Se #34 C-T Tranfer Funcion and Frequency Repone /4 Finding he Tranfer Funcion from Differenial Eq. Recall: we found a DT yem Tranfer Funcion Hz y aking he ZT of
EECE 30 Signal & Syem Prof. ark Fowler oe Se #34 C-T Tranfer Funcion and Frequency Repone /4 Finding he Tranfer Funcion from Differenial Eq. Recall: we found a DT yem Tranfer Funcion Hz y aking he ZT of
Surface Contents Author Index
 uae onen Auho Inde IAP VOLUME IV PA 2 OMMIION II i an Aug.2-22 EM ALIBAION OF INELLIGEN PHOOGAMMEON Heping PAN 1 hunen HANG 2 1 Digial Inelligene eeah ene hool o emoe ening and Inomaion EngineeingWuhan
uae onen Auho Inde IAP VOLUME IV PA 2 OMMIION II i an Aug.2-22 EM ALIBAION OF INELLIGEN PHOOGAMMEON Heping PAN 1 hunen HANG 2 1 Digial Inelligene eeah ene hool o emoe ening and Inomaion EngineeingWuhan
Communications II Lecture 4: Effects of Noise on AM. Professor Kin K. Leung EEE and Computing Departments Imperial College London Copyright reserved
 Commuiaio II Leure 4: Effe of Noie o M Profeor Ki K. Leug EEE ad Compuig Deparme Imperial College Lodo Copyrigh reerved Noie i alog Commuiaio Syem How do variou aalog modulaio heme perform i he preee of
Commuiaio II Leure 4: Effe of Noie o M Profeor Ki K. Leug EEE ad Compuig Deparme Imperial College Lodo Copyrigh reerved Noie i alog Commuiaio Syem How do variou aalog modulaio heme perform i he preee of
An Automatic Door Sensor Using Image Processing
 An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
CONTROL SYSTEMS. Chapter 10 : State Space Response
 CONTROL SYSTEMS Chaper : Sae Space Repone GATE Objecive & Numerical Type Soluion Queion 5 [GATE EE 99 IIT-Bombay : Mark] Conider a econd order yem whoe ae pace repreenaion i of he form A Bu. If () (),
CONTROL SYSTEMS Chaper : Sae Space Repone GATE Objecive & Numerical Type Soluion Queion 5 [GATE EE 99 IIT-Bombay : Mark] Conider a econd order yem whoe ae pace repreenaion i of he form A Bu. If () (),
Circular Motion Problem Solving
 iula Motion Poblem Soling Aeleation o a hange in eloity i aued by a net foe: Newton nd Law An objet aeleate when eithe the magnitude o the dietion of the eloity hange We aw in the lat unit that an objet
iula Motion Poblem Soling Aeleation o a hange in eloity i aued by a net foe: Newton nd Law An objet aeleate when eithe the magnitude o the dietion of the eloity hange We aw in the lat unit that an objet
Interpolation and Pulse Shaping
 EE345S Real-Time Digial Signal Proceing Lab Spring 2006 Inerpolaion and Pule Shaping Prof. Brian L. Evan Dep. of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering The Univeriy of Texa a Auin Lecure 7 Dicree-o-Coninuou
EE345S Real-Time Digial Signal Proceing Lab Spring 2006 Inerpolaion and Pule Shaping Prof. Brian L. Evan Dep. of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering The Univeriy of Texa a Auin Lecure 7 Dicree-o-Coninuou
Sample Final Exam (finals03) Covering Chapters 1-9 of Fundamentals of Signals & Systems
 Sample Final Exam Covering Chaper 9 (final04) Sample Final Exam (final03) Covering Chaper 9 of Fundamenal of Signal & Syem Problem (0 mar) Conider he caual opamp circui iniially a re depiced below. I LI
Sample Final Exam Covering Chaper 9 (final04) Sample Final Exam (final03) Covering Chaper 9 of Fundamenal of Signal & Syem Problem (0 mar) Conider he caual opamp circui iniially a re depiced below. I LI
Lecture 8. Digital Communications Part III. Digital Demodulation
 Lecure 8. Digial Communicaions Par III. Digial Demodulaion Binary Deecion M-ary Deecion Lin Dai (Ciy Universiy of Hong Kong) EE38 Principles of Communicaions Lecure 8 Analog Signal Source SOURCE A-D Conversion
Lecure 8. Digial Communicaions Par III. Digial Demodulaion Binary Deecion M-ary Deecion Lin Dai (Ciy Universiy of Hong Kong) EE38 Principles of Communicaions Lecure 8 Analog Signal Source SOURCE A-D Conversion
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecture-V Stochastic Processes and the Basic Term-Structure Equation 1 Stochastic Processes Any variable whose value changes over time in an uncertain
 Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Tutorial 5 Drive dynamics & control
 UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES Electic Dive Sytem School o Electical Engineeing & Telecommunication ELEC463 Electic Dive Sytem Tutoial 5 Dive dynamic & contol. The ollowing paamete ae known o two high peomance
UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES Electic Dive Sytem School o Electical Engineeing & Telecommunication ELEC463 Electic Dive Sytem Tutoial 5 Dive dynamic & contol. The ollowing paamete ae known o two high peomance
2-d Motion: Constant Acceleration
 -d Moion: Consan Acceleaion Kinemaic Equaions o Moion (eco Fom Acceleaion eco (consan eloci eco (uncion o Posiion eco (uncion o The eloci eco and posiion eco ae a uncion o he ime. eloci eco a ime. Posiion
-d Moion: Consan Acceleaion Kinemaic Equaions o Moion (eco Fom Acceleaion eco (consan eloci eco (uncion o Posiion eco (uncion o The eloci eco and posiion eco ae a uncion o he ime. eloci eco a ime. Posiion
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Coupled Mass Transport and Reaction in LPCVD Reactors
 ople Ma Tanpo an eaion in LPV eao ile A in B e.g., SiH 4 in H Sepaae eao ino o egion, inaafe & annla b - oniniy Eqn: : onveion-iffion iffion-eaion Eqn Ampion! ile peie i in majo aie ga e.g., H isih 4!
ople Ma Tanpo an eaion in LPV eao ile A in B e.g., SiH 4 in H Sepaae eao ino o egion, inaafe & annla b - oniniy Eqn: : onveion-iffion iffion-eaion Eqn Ampion! ile peie i in majo aie ga e.g., H isih 4!
Physics 442. Electro-Magneto-Dynamics. M. Berrondo. Physics BYU
 Physis 44 Eleo-Magneo-Dynamis M. Beondo Physis BYU Paaveos Φ= V + Α Φ= V Α = = + J = + ρ J J ρ = J S = u + em S S = u em S Physis BYU Poenials Genealize E = V o he ime dependen E & B ase Podu of paaveos:
Physis 44 Eleo-Magneo-Dynamis M. Beondo Physis BYU Paaveos Φ= V + Α Φ= V Α = = + J = + ρ J J ρ = J S = u + em S S = u em S Physis BYU Poenials Genealize E = V o he ime dependen E & B ase Podu of paaveos:
Classification of Equations Characteristics
 Clssiiion o Eqions Cheisis Consie n elemen o li moing in wo imensionl spe enoe s poin P elow. The ph o P is inie he line. The posiion ile is s so h n inemenl isne long is s. Le he goening eqions e epesene
Clssiiion o Eqions Cheisis Consie n elemen o li moing in wo imensionl spe enoe s poin P elow. The ph o P is inie he line. The posiion ile is s so h n inemenl isne long is s. Le he goening eqions e epesene
Transmit Beamforming with Reduced Channel State Information in MIMO-OFDM Wireless Systems
 anmi Beamfoming wih Reduced Channel Sae Infomaion in MIMO-OFDM Wiele Syem Seung-Hyeon Yang, Jae-Yun Ko, and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Elecical Engineeing and INMC Seoul Naional Univeiy Seoul, Koea Email:
anmi Beamfoming wih Reduced Channel Sae Infomaion in MIMO-OFDM Wiele Syem Seung-Hyeon Yang, Jae-Yun Ko, and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Elecical Engineeing and INMC Seoul Naional Univeiy Seoul, Koea Email:
Non-sinusoidal Signal Generators
 Non-sinusoidal Signal Geneaos ecangle, iangle, saw ooh, pulse, ec. Muliibao cicuis: asable no sable saes (wo quasi-sable saes; i emains in each sae fo pedeemined imes) monosable one sable sae, one unsable
Non-sinusoidal Signal Geneaos ecangle, iangle, saw ooh, pulse, ec. Muliibao cicuis: asable no sable saes (wo quasi-sable saes; i emains in each sae fo pedeemined imes) monosable one sable sae, one unsable
Inference for A One Way Factorial Experiment. By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo
 Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Analysis of Members with Axial Loads and Moments. (Length effects Disregarded, Short Column )
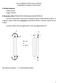 Analyi o emer wih Axial Loa an omen (Lengh ee Diregare, Shor Column ) A. Reaing Aignmen Chaper 9 o ex Chaper 10 o ACI B. reenaion o he INTERACTION DIAGRA or FAILURE ENVELO We have een ha a given eion an
Analyi o emer wih Axial Loa an omen (Lengh ee Diregare, Shor Column ) A. Reaing Aignmen Chaper 9 o ex Chaper 10 o ACI B. reenaion o he INTERACTION DIAGRA or FAILURE ENVELO We have een ha a given eion an
When analyzing an object s motion there are two factors to consider when attempting to bring it to rest. 1. The object s mass 2. The object s velocity
 SPH4U Momenum LoRuo Momenum i an exenion of Newon nd law. When analyzing an ojec moion here are wo facor o conider when aeming o ring i o re.. The ojec ma. The ojec velociy The greaer an ojec ma, he more
SPH4U Momenum LoRuo Momenum i an exenion of Newon nd law. When analyzing an ojec moion here are wo facor o conider when aeming o ring i o re.. The ojec ma. The ojec velociy The greaer an ojec ma, he more
11.5 MAP Estimator MAP avoids this Computational Problem!
 .5 MAP timator ecall that the hit-or-mi cot function gave the MAP etimator it maimize the a oteriori PDF Q: Given that the MMS etimator i the mot natural one why would we conider the MAP etimator? A: If
.5 MAP timator ecall that the hit-or-mi cot function gave the MAP etimator it maimize the a oteriori PDF Q: Given that the MMS etimator i the mot natural one why would we conider the MAP etimator? A: If
Then the number of elements of S of weight n is exactly the number of compositions of n into k parts.
 Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Primal and Weakly Primal Sub Semi Modules
 Aein Inenionl Jounl of Conepoy eeh Vol 4 No ; Jnuy 204 Pil nd Wekly Pil ub ei odule lik Bineh ub l hei Depen Jodn Univeiy of iene nd Tehnology Ibid 220 Jodn Ab Le be ouive eiing wih ideniy nd n -ei odule
Aein Inenionl Jounl of Conepoy eeh Vol 4 No ; Jnuy 204 Pil nd Wekly Pil ub ei odule lik Bineh ub l hei Depen Jodn Univeiy of iene nd Tehnology Ibid 220 Jodn Ab Le be ouive eiing wih ideniy nd n -ei odule
Chapter 2: Problem Solutions
 Chapter 2: Solution Dicrete Time Proceing of Continuou Time Signal Sampling à 2.. : Conider a inuoidal ignal and let u ample it at a frequency F 2kHz. xt 3co000t 0. a) Determine and expreion for the ampled
Chapter 2: Solution Dicrete Time Proceing of Continuou Time Signal Sampling à 2.. : Conider a inuoidal ignal and let u ample it at a frequency F 2kHz. xt 3co000t 0. a) Determine and expreion for the ampled
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions -- ANSWERS -- Logarithms Practice Diploma ANSWERS 1
 Eponenial and Logarihmic Funcions -- ANSWERS -- Logarihms racice Diploma ANSWERS www.puremah.com Logarihms Diploma Syle racice Eam Answers. C. D 9. A 7. C. A. C. B 8. D. D. C NR. 8 9. C 4. C NR. NR 6.
Eponenial and Logarihmic Funcions -- ANSWERS -- Logarihms racice Diploma ANSWERS www.puremah.com Logarihms Diploma Syle racice Eam Answers. C. D 9. A 7. C. A. C. B 8. D. D. C NR. 8 9. C 4. C NR. NR 6.
Performance Comparison of LCMV-based Space-time 2D Array and Ambiguity Problem
 Inernaional journal of cience Commerce and umaniie Volume No 2 No 3 April 204 Performance Comparion of LCMV-baed pace-ime 2D Arra and Ambigui Problem 2 o uan Chang and Jin hinghia Deparmen of Communicaion
Inernaional journal of cience Commerce and umaniie Volume No 2 No 3 April 204 Performance Comparion of LCMV-baed pace-ime 2D Arra and Ambigui Problem 2 o uan Chang and Jin hinghia Deparmen of Communicaion
4/3/2017. PHY 712 Electrodynamics 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 103
 PHY 7 Eleodnais 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 0 Plan fo Leue 0: Coninue eading Chap Snhoon adiaion adiaion fo eleon snhoon deies adiaion fo asonoial objes in iula obis 0/05/07 PHY 7 Sping 07 -- Leue 0 0/05/07 PHY
PHY 7 Eleodnais 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 0 Plan fo Leue 0: Coninue eading Chap Snhoon adiaion adiaion fo eleon snhoon deies adiaion fo asonoial objes in iula obis 0/05/07 PHY 7 Sping 07 -- Leue 0 0/05/07 PHY
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
Network Flows: Introduction & Maximum Flow
 CSC 373 - lgorihm Deign, nalyi, and Complexiy Summer 2016 Lalla Mouaadid Nework Flow: Inroducion & Maximum Flow We now urn our aenion o anoher powerful algorihmic echnique: Local Search. In a local earch
CSC 373 - lgorihm Deign, nalyi, and Complexiy Summer 2016 Lalla Mouaadid Nework Flow: Inroducion & Maximum Flow We now urn our aenion o anoher powerful algorihmic echnique: Local Search. In a local earch
An Open cycle and Closed cycle Gas Turbine Engines. Methods to improve the performance of simple gas turbine plants
 An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
Logarithms Practice Exam - ANSWERS
 Logarihms racice Eam - ANSWERS Answers. C. D 9. A 9. D. A. C. B. B. D. C. B. B. C NR.. C. B. B. B. B 6. D. C NR. 9. NR. NR... C 7. B. C. B. C 6. C 6. C NR.. 7. B 7. D 9. A. D. C Each muliple choice & numeric
Logarihms racice Eam - ANSWERS Answers. C. D 9. A 9. D. A. C. B. B. D. C. B. B. C NR.. C. B. B. B. B 6. D. C NR. 9. NR. NR... C 7. B. C. B. C 6. C 6. C NR.. 7. B 7. D 9. A. D. C Each muliple choice & numeric
Chapter 6 Control Systems Design by Root-Locus Method. Lag-Lead Compensation. Lag lead Compensation Techniques Based on the Root-Locus Approach.
 hapter 6 ontrol Sytem Deign by Root-Lou Method Lag-Lead ompenation Lag lead ompenation ehnique Baed on the Root-Lou Approah. γ β K, ( γ >, β > ) In deigning lag lead ompenator, we onider two ae where γ
hapter 6 ontrol Sytem Deign by Root-Lou Method Lag-Lead ompenation Lag lead ompenation ehnique Baed on the Root-Lou Approah. γ β K, ( γ >, β > ) In deigning lag lead ompenator, we onider two ae where γ
EE3723 : Digital Communications
 EE373 : Digial Communicaions Week 6-7: Deecion Error Probabiliy Signal Space Orhogonal Signal Space MAJU-Digial Comm.-Week-6-7 Deecion Mached filer reduces he received signal o a single variable zt, afer
EE373 : Digial Communicaions Week 6-7: Deecion Error Probabiliy Signal Space Orhogonal Signal Space MAJU-Digial Comm.-Week-6-7 Deecion Mached filer reduces he received signal o a single variable zt, afer
Detailed solution of IES 2014 (ECE) Conventional Paper II. solve I 0 and use same formula again. Saturation region
 etailed olution of IS 4 (C) Conventional Pape II qv qv Sol. (a) IC I e Ie K K 4 I =.7 Fo I C = m olve I and ue ame fomula again K IC V ln 5ln 4 q I.7 =.8576 Volt Sol. (b) VGS VS Vupply 5V N MOS channel,
etailed olution of IS 4 (C) Conventional Pape II qv qv Sol. (a) IC I e Ie K K 4 I =.7 Fo I C = m olve I and ue ame fomula again K IC V ln 5ln 4 q I.7 =.8576 Volt Sol. (b) VGS VS Vupply 5V N MOS channel,
International Journal of Mathematical Archive-5(6), 2014, Available online through ISSN
 Inenaional Jonal o Mahemaical Achive-6, 0, 09-8 Availale online hogh www.ijma.ino ISSN 9 06 EXISENCE OF NONOSCILLAORY SOLUIONS OF A CLASS OF NONLINEAR NEURAL DELAY DIFFERENIAL EQUAIONS OF HIRD ORDER K
Inenaional Jonal o Mahemaical Achive-6, 0, 09-8 Availale online hogh www.ijma.ino ISSN 9 06 EXISENCE OF NONOSCILLAORY SOLUIONS OF A CLASS OF NONLINEAR NEURAL DELAY DIFFERENIAL EQUAIONS OF HIRD ORDER K
Introduction to SLE Lecture Notes
 Inroducion o SLE Lecure Noe May 13, 16 - The goal of hi ecion i o find a ufficien condiion of λ for he hull K o be generaed by a imple cure. I urn ou if λ 1 < 4 hen K i generaed by a imple curve. We will
Inroducion o SLE Lecure Noe May 13, 16 - The goal of hi ecion i o find a ufficien condiion of λ for he hull K o be generaed by a imple cure. I urn ou if λ 1 < 4 hen K i generaed by a imple curve. We will
Drill Bit Hydraulics
 Drill i yraulic Aumpion ) Change of preure ue o elevaion i negligible. ) Velociy upream i negligible compare o nozzle. 3) reure ue o fricion i negligible. Δ Δ 8.075 4 E ρvn 0 reure rop acro bi, vn nozzle
Drill i yraulic Aumpion ) Change of preure ue o elevaion i negligible. ) Velociy upream i negligible compare o nozzle. 3) reure ue o fricion i negligible. Δ Δ 8.075 4 E ρvn 0 reure rop acro bi, vn nozzle
5.2.6 COMPARISON OF QUALITY CONTROL AND VERIFICATION TESTS
 5..6 COMPARISON OF QUALITY CONTROL AND VERIFICATION TESTS Thi proedure i arried out to ompare two different et of multiple tet reult for finding the ame parameter. Typial example would be omparing ontrator
5..6 COMPARISON OF QUALITY CONTROL AND VERIFICATION TESTS Thi proedure i arried out to ompare two different et of multiple tet reult for finding the ame parameter. Typial example would be omparing ontrator
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
How can you find the dimensions of a square or a circle when you are given its area? When you multiply a number by itself, you square the number.
 7. Finding Squae Root How can you find the dimenion of a quae o a cicle when you ae given it aea? When you multiply a numbe by itelf, you quae the numbe. Symbol fo quaing i the exponent. = = 6 quaed i
7. Finding Squae Root How can you find the dimenion of a quae o a cicle when you ae given it aea? When you multiply a numbe by itelf, you quae the numbe. Symbol fo quaing i the exponent. = = 6 quaed i
Question 1 Equivalent Circuits
 MAE 40 inear ircuit Fall 2007 Final Intruction ) Thi exam i open book You may ue whatever written material you chooe, including your cla note and textbook You may ue a hand calculator with no communication
MAE 40 inear ircuit Fall 2007 Final Intruction ) Thi exam i open book You may ue whatever written material you chooe, including your cla note and textbook You may ue a hand calculator with no communication
CROSSTALK ANALYSIS FOR HIGH-PRECISION OPTICAL PICKUP ACTUATOR SYSTEM
 Jounal o Theoeial and Applied Inomaion Tehnology h Apil 2. Vol. 5 No. 25-2 JATIT & LLS. All ighs eseved. ISSN: 992-8645 www.jai.og E-ISSN: 87-95 CROSSTALK ANALYSIS FOR HIGH-PRECISION OPTICAL PICKUP ACTUATOR
Jounal o Theoeial and Applied Inomaion Tehnology h Apil 2. Vol. 5 No. 25-2 JATIT & LLS. All ighs eseved. ISSN: 992-8645 www.jai.og E-ISSN: 87-95 CROSSTALK ANALYSIS FOR HIGH-PRECISION OPTICAL PICKUP ACTUATOR
Relative and Circular Motion
 Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Angle Modulation: NB (Sinusoid)
 gle Moulaio: NB Siuoi I uay, i he eage igal i a pue iuoi, ha i, a a i o o PM o FM The, i whee a p a o PM o FM : pea equey eviaio Noe ha i ow a oulaio ie o agle oulaio a i he aiu value o phae eviaio o boh
gle Moulaio: NB Siuoi I uay, i he eage igal i a pue iuoi, ha i, a a i o o PM o FM The, i whee a p a o PM o FM : pea equey eviaio Noe ha i ow a oulaio ie o agle oulaio a i he aiu value o phae eviaio o boh
EE 508 Lecture 16. Filter Transformations. Lowpass to Bandpass Lowpass to Highpass Lowpass to Band-reject
 EE 508 Lecture 6 Filter Tranformation Lowpa to Bandpa Lowpa to Highpa Lowpa to Band-reject Review from Lat Time Flat Paband/Stopband Filter T j T j Lowpa Bandpa T j T j Highpa Bandreject Review from Lat
EE 508 Lecture 6 Filter Tranformation Lowpa to Bandpa Lowpa to Highpa Lowpa to Band-reject Review from Lat Time Flat Paband/Stopband Filter T j T j Lowpa Bandpa T j T j Highpa Bandreject Review from Lat
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
EE202 Circuit Theory II
 EE202 Circui Theory II 2017-2018, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN I. Inroducion & eview of Fir Order Circui (Chaper 7 of Nilon - 3 Hr. Inroducion, C and L Circui, Naural and Sep epone of Serie and Parallel L/C
EE202 Circui Theory II 2017-2018, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN I. Inroducion & eview of Fir Order Circui (Chaper 7 of Nilon - 3 Hr. Inroducion, C and L Circui, Naural and Sep epone of Serie and Parallel L/C
SAMPLING. Sampling is the acquisition of a continuous signal at discrete time intervals and is a fundamental concept in real-time signal processing.
 SAMPLING Sampling i the acquiition of a continuou ignal at dicrete time interval and i a fundamental concept in real-time ignal proceing. he actual ampling operation can alo be defined by the figure belo
SAMPLING Sampling i the acquiition of a continuou ignal at dicrete time interval and i a fundamental concept in real-time ignal proceing. he actual ampling operation can alo be defined by the figure belo
Internal Model Control
 Internal Model Control Part o a et o leture note on Introdution to Robut Control by Ming T. Tham 2002 The Internal Model Prinile The Internal Model Control hiloohy relie on the Internal Model Prinile,
Internal Model Control Part o a et o leture note on Introdution to Robut Control by Ming T. Tham 2002 The Internal Model Prinile The Internal Model Control hiloohy relie on the Internal Model Prinile,
5.2 GRAPHICAL VELOCITY ANALYSIS Polygon Method
 ME 352 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS 52 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS olygon Mehod Velociy analyi form he hear of kinemaic and dynamic of mechanical yem Velociy analyi i uually performed following a poiion analyi; ie,
ME 352 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS 52 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS olygon Mehod Velociy analyi form he hear of kinemaic and dynamic of mechanical yem Velociy analyi i uually performed following a poiion analyi; ie,
ÖRNEK 1: THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MOMENTUM RELATION Calculate the linear momentum of a particle of mass m=10 kg which has a. kg m s
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
6 December 2013 H. T. Hoang - www4.hcmut.edu.vn/~hthoang/ 1
 Lecure Noe Fundamenal of Conrol Syem Inrucor: Aoc. Prof. Dr. Huynh Thai Hoang Deparmen of Auomaic Conrol Faculy of Elecrical & Elecronic Engineering Ho Chi Minh Ciy Univeriy of Technology Email: hhoang@hcmu.edu.vn
Lecure Noe Fundamenal of Conrol Syem Inrucor: Aoc. Prof. Dr. Huynh Thai Hoang Deparmen of Auomaic Conrol Faculy of Elecrical & Elecronic Engineering Ho Chi Minh Ciy Univeriy of Technology Email: hhoang@hcmu.edu.vn
Algorithmic Discrete Mathematics 6. Exercise Sheet
 Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
Optimal Waveform Design with Constant Modulus Constraint for Rank-One Target Detection
 Senor & Tranduer Vol. 63 Iue January 4 pp. 39-43 Senor & Tranduer 4 by IFSA Publihing S. L. p://www.enorporal.om Opimal Waveform Deign wih Conan odulu Conrain for Rank-One Targe Deeion Fengming XIN Bin
Senor & Tranduer Vol. 63 Iue January 4 pp. 39-43 Senor & Tranduer 4 by IFSA Publihing S. L. p://www.enorporal.om Opimal Waveform Deign wih Conan odulu Conrain for Rank-One Targe Deeion Fengming XIN Bin
QUASI-EXTREMUM SCALAR CONTROL FOR INDUCTION TRACTION MOTORS: RESULTS OF SIMULATION. Rodica Feştilă* Vasile Tulbure** Eva Dulf * Clement Feştilă*
 QUAI-EXEMUM CALA CONOL FO INDUCION ACION MOO: EUL OF IMULAION odia Feşilă aile ulbue Eva Dulf Cleen Feşilă Depaen of Auoai Conol, ehnial Univeiy of Cluj-Napoa, Fauly of Auoaion and Copue iene, 6-8 Baiiu,
QUAI-EXEMUM CALA CONOL FO INDUCION ACION MOO: EUL OF IMULAION odia Feşilă aile ulbue Eva Dulf Cleen Feşilă Depaen of Auoai Conol, ehnial Univeiy of Cluj-Napoa, Fauly of Auoaion and Copue iene, 6-8 Baiiu,
SYSTEMS OF NON-LINEAR EQUATIONS. Introduction Graphical Methods Close Methods Open Methods Polynomial Roots System of Multivariable Equations
 SYSTEMS OF NON-LINEAR EQUATIONS Itoduto Gaphal Method Cloe Method Ope Method Polomal Root Stem o Multvaale Equato Chapte Stem o No-Lea Equato /. Itoduto Polem volvg o-lea equato egeeg lude optmato olvg
SYSTEMS OF NON-LINEAR EQUATIONS Itoduto Gaphal Method Cloe Method Ope Method Polomal Root Stem o Multvaale Equato Chapte Stem o No-Lea Equato /. Itoduto Polem volvg o-lea equato egeeg lude optmato olvg
Part I. Labor- Leisure Decision (15 pts)
 Eon 509 Sping 204 Final Exam S. Paene Pa I. Labo- Leisue Deision (5 ps. Conside he following sai eonom given b he following equaions. Uili ln( H ln( l whee H sands fo he househ f f Poduion: Ah whee f sands
Eon 509 Sping 204 Final Exam S. Paene Pa I. Labo- Leisue Deision (5 ps. Conside he following sai eonom given b he following equaions. Uili ln( H ln( l whee H sands fo he househ f f Poduion: Ah whee f sands
Reinforcement learning
 Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Lectures 29 and 30 BIQUADRATICS AND STATE SPACE OP AMP REALIZATIONS. I. Introduction
 EE-202/445, 3/18/18 9-1 R. A. DeCarlo Lecures 29 and 30 BIQUADRATICS AND STATE SPACE OP AMP REALIZATIONS I. Inroducion 1. The biquadraic ransfer funcion has boh a 2nd order numeraor and a 2nd order denominaor:
EE-202/445, 3/18/18 9-1 R. A. DeCarlo Lecures 29 and 30 BIQUADRATICS AND STATE SPACE OP AMP REALIZATIONS I. Inroducion 1. The biquadraic ransfer funcion has boh a 2nd order numeraor and a 2nd order denominaor:
Combinatorial Approach to M/M/1 Queues. Using Hypergeometric Functions
 Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
AVS fiziks. Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
