Hidden Markov Models. A Specific Form of Process.. Doubly Stochastic Processes. What a sensible agent must do. A Common Trait
|
|
|
- Timothy Matthews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 -755 Mchne Lernng for Sgnl roceng Hdden Mrkov Model 04 Oc 0 redcon : holy grl hycl recore Auooble rocke hevenly bode Nurl phenoen Weher Fnncl d Sock rke World ffr Who gong o hve he ne prng? Sgnl Audo vdeo.. A Coon r Wh enble gen u do Lern bou he proce Sere d wh rend Sochc funcon of ochc funcon of ochc funcon of An underlyng proce h progree eengly rndoly E.g. Curren poon of vehcle E.g. curren enen n ock rke Curren e of ocl/econoc ndcor Rndo epreon of underlyng proce E.g wh you ee fro he vehcle E.g. curren ock prce of vrou ock E.g. do populce y que / proe on ree / opple dcor.. A B C 3 Fro whever hey know Bc requreen for oher procedure rck underlyng procee redc fuure vlue 4 A Specfc For of roce.. Doubly ochc procee One rndo proce genere n Rndo proce ; Q Second level proce genere obervon funcon of Rndo proce Y Y; f L Y Doubly Sochc rocee Doubly ochc procee re odel My no be rue repreenon of proce underlyng cul d Fr level vrble y be qunfble vrble oon/e of vehcle Second level vrble ochc funcon of poon Fr level vrble y no hve enng Senen of ock rke Confguron of vocl rc Y 5 6
2 Sochc Funcon of Mrkov Chn Mrkov Chn Fr level vrble uully brc S Y S S3 he fr level vrble ued o be he oupu of Mrkov Chn he econd level vrble funcon of he oupu of he Mrkov Chn Alo clled n HMM Anoher vrn ochc funcon of Mrkov proce Kln Flerng.. roce cn go hrough nuber of e Rndo wlk Brownn oon.. Fro ech e cn go o ny oher e wh probbly Whch only depend on he curren e Wlk goe on forever Or unl h n borbng wll Oupu of he proce equence of e he proce wen hrough 7 8 Sochc Funcon of Mrkov Chn Sochc funcon of Mrkov Chn HMMS S roble: S Oupu: Y Y ; f[ ] L Specfc o HMM: Y == Y Y Y Y ; f L S3 Lern he nure of he proce fro d rck he underlyng e Senc redc he fuure 9 0 Fun uff wh HMM.. he lle on beween he ll nd he cy A lle on beween he cy nd ll Inbound rn brng people bck fro he ll Mnly hopper Occonl ll eployee Who y hve hopped.. Oubound rn brng bck people fro he cy Mnly offce worker Bu lo he occonl hopper Who y be fro n offce..
3 he urnle One oble fernoon you ue yourelf by obervng he urnle he on Group of people e perodclly Soe people re werng cul oher re forlly dreed Soe re crryng hoppng bg oher hve brefce W he l rn n ncong rn or n ougong one he urnle One oble fernoon you ue yourelf by obervng he urnle he on. Wh you know: eople hop n cul re Unle hey hed o he hop fro work Shopper crry hoppng bg people fro offce crry brefce Uully here re ore hop hn offce he ll here re ore offce hn hop n he cy Oubound rn follow nbound rn Uully Modellng he proble Modellng he proble Inbound Oubound Inbound Oubound re luggge oubound =? Inbound rn fro he ll hve ore cully dreed people ore people crryng hoppng bg he nuber of people levng ny e y be ll Inuffcen o udge re luggge nbound =? oubound nbound =? nbound oubound =? If you know ll h how do you decde he drecon of he rn How do you ee hee er? 95 6 Wh n HMM A hough Eperen I u clled ou he 6 fro he blue guy.. go wch o pern.. robblc funcon of rkov chn Model dyncl ye Sye goe hrough nuber of e Followng Mrkov chn odel On rrvng ny e genere obervon ccordng o e pecfc probbly drbuon 7 wo hooer roll dce A cller cll ou he nuber rolled. We only ge o her wh he cll ou he cller behve rndoly If he h u clled nuber rolled by he blue hooer h ne cll h of he red hooer 70% of he e Bu f he h u clled he red hooer he h only 40% probbly of cllng he red hooer gn n he ne cll How do we chrcerze h? 8
4 blue red blue red A hough Eperen A hough Eperen he do nd rrow repreen he e of he cller When he on he blue crcle he cll ou he blue dce When he on he red crcle he cll ou he red dce he hogr repreen he probbly drbuon of he nuber for he blue nd red dce 9 When he cller n ny e he cll nuber bed on he probbly drbuon of h e We cll hee e oupu drbuon A ech ep he ove fro h curren e o noher e followng probbly drbuon We cll hee rnon probble he cller n HMM!!! 0 Wh n HMM Hdden Mrkov Model HMM re cl odel for cul procee he odel ue h he proce cn be n one of nuber of e ny e nn he e of he proce ny e nn depend only on he e he prevou nn culy Mrkovn A ech nn he proce genere n obervon fro probbly drbuon h pecfc o he curren e he genered obervon re ll h we ge o ee he cul e of he proce no drecly obervble Hence he qulfer hdden A Hdden Mrkov Model con of wo coponen A e/rnon bckbone h pecfe how ny e here re nd how hey cn follow one noher A e of probbly drbuon one for ech e whch pecfe he drbuon of ll vecor n h e h cn be fcored no wo epre probblc ene A probblc Mrkov chn wh e nd rnon A e of d probbly drbuon oced wh he e 755/8797 Mrkov chn D drbuon HMM ued o be generng d e equence e drbuon obervon equence How n HMM odel proce 3 HMM reer he opology of he HMM Nuber of e nd llowed rnon E.g. here we hve 3 e nd cnno go fro he blue e o he red he rnon probble Ofen repreened r here he probbly h when n e he proce wll ove o he probbly p of begnnng ny e he coplee e repreened p he e oupu drbuon
5 HMM e oupu drbuon he e oupu drbuon he drbuon of d produced fro ny e ypclly odelled Gun he Dgonl Covrnce Mr Full covrnce: ll eleen re non-zero Dgonl covrnce: off-dgonl eleen re zero p Gun ; Q e d Q 0.5 Q Q - - S - / he preeer re nd Q More ypclly odelled Gun ure K w Gun ; Q 0 Oher drbuon y lo be ued E.g. hogr n he dce ce 5 For GMM frequenly ued h he feure vecor denon re ll ndependen of ech oher Reul: he covrnce r reduced o dgonl for he deernn of he dgonl Q r ey o copue 6 hree Bc HMM roble Wh he probbly h wll genere pecfc obervon equence Gven obervon equence how do we deerne whch obervon w genered fro whch e he e egenon proble Copung he robbly of n Obervon Sequence wo pec o producng he obervon: rogreng hrough equence of e roducng obervon fro hee e How do we lern he preer of he HMM fro obervon equence 7 8 HMM ued o be generng d rogreng hrough e robbly h he HMM wll follow prculr e equence e equence he proce begn oe e red here Fro h e ke n llowed rnon o rrve he e or ny oher e Fro h e ke noher llowed rnon And o on he probbly h he proce wll nlly be n e he rnon probbly of ovng o e he ne e nn when he ye currenly n Alo denoed by erler 9 30
6 Generng Obervon fro Se HMM ued o be generng d robbly h he HMM wll genere prculr obervon equence gven e equence e equence known e equence o o o o o o e drbuon obervon equence Copued fro he Gun or Gun ure for e o he probbly of generng obervon o when he ye n e A ech e genere n obervon fro he e n h e 3 3 HMM ued o be generng d roceedng hrough Se nd roducng Obervon robbly h he HMM wll genere prculr e equence nd fro prculr obervon equence e equence e drbuon o o o o o o o o o obervon equence A ech e produce n obervon nd ke rnon robbly of Generng n Obervon Sequence he prece e equence no known All poble e equence u be condered Copung Effcenly Eplc ung over ll e equence no rcble A very lrge nuber of poble e equence o o o... 3 ll. poble e. equence o o o Ined we ue he forwrd lgorh A dync progrng echnque. ll. poble e. equence o o o
7 Se nde Se nde Se nde Se nde Illurve Eple Dveron: he rell Eple: generc HMM wh 5 e nd ernng e. Lef o rgh opology = for e nd 0 for oher he rrow repreen rnon for whch he probbly no 0 Noon: = We repreen o = b for brevy 37 - Feure vecor e he rell grphcl repreenon of ll poble ph hrough he HMM o produce gven obervon he Y repreen HMM e repreen obervon Every edge n he grph repreen vld rnon n he HMM over ngle e ep Every node repreen he even of prculr obervon beng genered fro prculr e 38 he Forwrd Algorh he Forwrd Algorh... e... e - Cn be recurvely eed rng fro he fr e nn forwrd recuron - e he ol probbly of ALL e equence h end e e nd ll obervon unl - - ' ' ' e cn be recurvely copued n er of he forwrd probble e he Forwrd Algorh olprob he borbng e e In he fnl obervon he lph ech e gve he probbly of ll e equence endng h e Generl odel: he ol probbly of he obervon he u of he lph vlue ll e Obervon equence re ued o end only when he proce rrve n borbng e No obervon re produced fro he borbng e 4 4
8 Se nde he Forwrd Algorh olprob borbng roble : Se egenon Gven only equence of obervon how do we deerne whch equence of e w followed n producng? borbng ' borbng ' e ' Aborbng e odel: he ol probbly he lph copued he borbng e fer he fnl obervon he HMM generor Se re hdden HMM ued o be generng d HMM ued o be generng d e equence e equence e drbuon e drbuon obervon equence he proce goe hrough ere of e nd produce obervon fro he 45 obervon equence he obervon do no revel he underlyng e 46 HMM ued o be generng d e equence e drbuon obervon equence he e egenon proble Eng he Se Sequence Mny dfferen e equence re cpble of producng he obervon Soluon: Idenfy he o probble e equence he e equence for whch he probbly of progreng hrough h equence nd generng he obervon equence u.e u o o o Se egenon: Ee e equence gven obervon 47 48
9 Eng he e equence Eng he e equence Once gn ehuve evluon pobly epenve Bu once gn ple dync progrng Once gn ehuve evluon pobly epenve Bu once gn ple dync progrng oluon vlble o o o oluon vlble o o o o o o o o o Needed: Needed: rg... o o o rg... o o o he HMM generor he e equence HMM ued o be generng d e equence he probbly of e equence????y endng e nd producng ll obervon unl o o..-???? oy = o..-???? oyy e drbuon obervon equence he be e equence h end wh y wll hve probbly equl o he probbly of he be e equence endng - e oyy Ech encloed er repreen one forwrd rnon nd ubequen eon 5 5 e equence Eendng he e equence y rell he grph below how he e of ll poble e equence hrough h HMM n fve e nn e drbuon obervon equence he probbly of e equence????y endng e nd producng obervon unl o o..-o???? y = o..-???? oyy 53 e 54
10 he co of eendng e equence he co of eendng e equence endng only dependen on he rnon fro o y nd he obervon probbly y he co of eendng e equence he be ph o y hrough ply n eenon of he be ph o Beo..-???? oyy oyy y y e 55 e 56 he Recuron he overll be ph o y n eenon of he be ph o one of he e he prevou e he Recuron rob. of be ph o y = M Beo..-???? oyy y y e 57 e 58 Fndng he be e equence Verb Serch cond. he ple lgorh u preened clled he VIERBI lgorh n he lerure Afer A.J.Verb who nvened h dync progrng lgorh for copleely dfferen purpoe: decodng error correcon code! 59 Inl e nlzed wh ph-core = b e 5 Oc 0 All oher e hve core 0 nce = 0 for he 755/
11 Verb Serch cond. Verb Serch cond. Se wh be ph-core Se wh ph-core < be Se whou vld ph-core = [ - b ] Se rnon probbly o = [ - b ] Se rnon probbly o Score for e gven he npu e ol ph-core endng up e e Score for e gven he npu e ol ph-core endng up e e e e 6 6 Verb Serch cond. Verb Serch cond. e 63 e 64 Verb Serch cond. Verb Serch cond. e 65 e 66
12 Verb Serch cond. Verb Serch cond. e 67 e 68 Verb Serch cond. Verb Serch cond. HE BES SAE SEQUENCE IS HE ESIMAE OF HE SAE SEQUENCE FOLLOWED IN GENERAING HE OBSERVAION e 69 e 70 roble3: rnng HMM preer We cn copue he probbly of n obervon nd he be e equence gven n obervon ung he HMM preer Bu where do he HMM preer coe fro? hey u be lerned fro collecon of obervon equence Lernng HMM preer: Sple procedure counng Gven e of rnng nnce Iervely:. Inlze HMM preer. Segen ll rnng nnce 3. Ee rnon probble nd e oupu probbly preer by counng 7 7
13 Lernng by counng eple Eplnon by eple n ne few lde e HMM Gun DF e 3 obervon equence Eple how ONE eron How o coun fer e equence re obned Eple: Lernng HMM reer We hve n HMM wh wo e nd. Obervon re vecor h equence h vecor We re gven he followng hree obervon equence And hve lredy eed e equence Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c Eple: Lernng HMM reer Inl e probble uully denoed p: We hve 3 obervon of hee begn wh S nd one wh S ps = /3 ps = /3 Eple: Lernng HMM reer rnon probble: Se S occur e n non ernl locon Of hee followed by S e I followed by S Y e S S = / ; S S = y / Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c Eple: Lernng HMM reer rnon probble: Se S occur e n non ernl locon Of hee followed edely by S 6 e I followed by S Y e S S = / ; S S = y / Eple: Lernng HMM reer rnon probble: Se S occur e n non ernl locon Of hee followed edely by S 6 e I followed edely by S 5 e S S = / ; S S = y / Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c
14 Eple: Lernng HMM reer rnon probble: Se S occur e n non ernl locon Of hee followed edely by S 6 e I followed edely by S 5 e S S = 6/ ; S S = 5 / Eple: Lernng HMM reer rnon probble: Se S occur 3 e n non ernl locon Of hee followed edely by S 6 e I followed edely by S 5 e S S = 6/ ; S S = 5 / Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c Eple: Lernng HMM reer rnon probble: Se S occur 3 e n non ernl locon Of hee followed edely by S 5 e I followed edely by S 5 e S S = 6/ ; S S = 5 / Eple: Lernng HMM reer rnon probble: Se S occur 3 e n non ernl locon Of hee followed edely by S 5 e I followed edely by S 8 e S S = 6/ ; S S = 5 / Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 8 8 Eple: Lernng HMM reer rnon probble: Obervon Se S occur 3 e n non ernl locon Of hee followed edely by S 5 e I followed edely by S 8 e S S = 5 / 3; S S = 8 / 3 e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob S S = 6/ = 0.545; S S = 5/ = S S = 5/3 = 0.385; S S = 8/3 = 0.65 reer lern o fr Se nl probble ofen denoed p ps = /3 = 0.66 ps = /3 = 0.33 Se rnon probble Obervon Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 Repreened rnon r A S S S S S S Ech row of h r u u o.0 S S
15 Eple: Lernng HMM reer Se oupu probbly for S here re 3 obervon n S Se oupu probbly for S here re 3 obervon n S Segrege he ou nd coun Eple: Lernng HMM reer Copue preer en nd vrnce of Gun oupu deny for e S Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob e e S S S S S S Ob Q S ep d p Q Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 e e S S S Ob b3 b4 b9 3 b 4 b 9 6 c 7 c 9 c 4 0 c 5 b 3 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 e e S S S S Ob c c c4 c5 Q 3... b3 b3 b4 b c c c c Eple: Lernng HMM reer Se oupu probbly for S here re 4 obervon n S Se oupu probbly for S here re 4 obervon n S Segrege he ou nd coun Eple: Lernng HMM reer Copue preer en nd vrnce of Gun oupu deny for e S Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S S Ob e e S S S S Ob Q S ep d p Q Obervon e e S S S S S S S S S Ob b b b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 e e S S S S S S Ob b b b5 b6 b7 b8 Obervon 3 e e S S S S S S S S Ob c c c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 87 e e S S S S Ob c c6 c7 c b6 4 b7 5 b8 8 c b Q 88 c6 b c7 b5 c 8 We hve lern ll he HMM preer Upde rule ech eron Se nl probble ofen denoed p ps = 0.66 ps = /3 = 0.33 p No.of obervon equence h r e olno.of obervon equence Se rnon probble A Se oupu probble Se oupu probbly for S Se oupu probbly for S 0.5 Q S ep d p Q 0.5 Q S ep d p Q ob : e.&. e Q ob : e ob : e. Aue e oupu DF = Gun ob : e ob. ob ob : e ob : e ob. For GMM ee GMM preer fro collecon 89 of obervon ny e 90
16 rnng by egenon: Verb rnng Inl odel Segenon Model Converged? ye Inlze ll HMM preer no Alernve o counng: SOF counng Epecon zon Every obervon conrbue o every e Segen ll rnng obervon equence no e ung he Verb lgorh wh he curren odel Ung eed e equence nd rnng obervon equence reee he HMM preer h ehod lo clled egenl k-en lernng procedure 9 Upde rule ech eron Upde rule ech eron p Ob e olno. of Ob obervon equence p Ob e olno. of Ob obervon equence Ob Ob e Ob e Ob e Ob Ob Ob e e Ob Ob Ob Ob e Ob e Ob e Ob Ob Ob e e Ob Ob Q Ob e Ob Ob Ob e Every obervon conrbue o every e Ob Ob Q Ob e Ob Ob Ob e Where dd hee er coe fro? Ob Ob e Ob he probbly h he proce w when genered gven he enre obervon Droppng he Ob ubcrp for brevy e... he probbly h he HMM w n prculr e when generng he obervon equence he probbly h followed e equence h ped hrough e e... e... We wll copue e... fr h he probbly h he proce ved e whle producng he enre obervon e 95 96
17 e... h cn be decopoed no wo ulplcve econ he econ of he lce ledng no e e nd he econ ledng ou of he Forwrd h he probbly of he red econ he ol probbly of ll e equence endng e e h ply Cn be copued ung he forwrd lgorh e e he Bckwrd h he blue poron repreen he probbly of ll e equence h begn e e Lke he red poron cn be copued ung bckwrd recuron b he Bckwrd Recuron... e bn b b Cn be recurvely eed rng fro he fnl e e nn bckwrd recuron e b + b ' ' ' e b he ol probbly of ALL e equence h depr fro e nd ll obervon fer b = he fnl e nn for ll vld fnl e ' he coplee probbly oeror probbly of e b... e bn he probbly h he proce w n e e gven h we hve oberved he d obned by ple norlzon - b e e Ob ' e e h er ofen referred o he g er nd denoed by g ' ' b b ' 0 0
18 Upde rule ech eron Upde rule ech eron p Ob e olno. of Ob obervon equence p Ob e olno. of Ob obervon equence Ob Ob e Ob e Ob e Ob Ob Ob e e Ob Ob Ob Ob e Ob e Ob e Ob Ob Ob e e Ob Ob Q Ob hee hve been found e Ob Ob Ob e Ob Ob Q Ob e Ob Ob Ob e Where dd hee er coe fro? Ob Ob e e '... e e '... + e 05 + e 06 e e '... e e '... ' ' ' ' b ' + e 07 + e 08
19 he poeror probbly of rnon Upde rule ech eron p Ob e olno. of Ob obervon equence e e ' Ob b ' ' b ' Ob Ob e Ob e Ob e Ob Ob Ob e e Ob Ob he poeror probbly of rnon gven n obervon Q Ob hee hve been found e Ob Ob Ob e Ob Ob 09 0 rnng whou eplc egenon: Bu Welch rnng Every feure vecor oced wh every e of every HMM wh probbly Inl odel Se ocon probble Model Converged? ye no HMM Iue How o fnd he be e equence: Covered How o lern HMM preer: Covered How o copue he probbly of n obervon equence: Covered robble copued ung he forwrd-bckwrd lgorh Sof decon ken he level of HMM e In prcce he egenon bed Verb rnng uch eer o pleen nd uch fer he dfference n perfornce beween he wo ll epeclly f we hve lo of rnng d Mgc nuber How ny e: No nce uoc echnque o lern h You chooe For peech HMM opology uully lef o rgh no bckwrd rnon For oher cyclc procee opology u reflec nure of proce No. of e 3 per phonee n peech For oher procee depend on eed no. of dnc e n proce Applcon of HMM Clfcon: Lern HMM for he vrou cle of e ere fro rnng d Copue probbly of e e ere ung he HMM for ech cl Ue n Byen clfer Speech recognon von gene equencng chrcer recognon e nng redcon rckng 3 4
20 Applcon of HMM Segenon: Gven HMM for vrou even fnd even boundre Sply fnd he be e equence nd he locon where e dene chnge Auoc peech egenon e egenon by opc geneoe egenon 5
Supporting information How to concatenate the local attractors of subnetworks in the HPFP
 n Effcen lgorh for Idenfyng Prry Phenoype rcors of Lrge-Scle Boolen Newor Sng-Mo Choo nd Kwng-Hyun Cho Depren of Mhecs Unversy of Ulsn Ulsn 446 Republc of Kore Depren of Bo nd Brn Engneerng Kore dvnced
n Effcen lgorh for Idenfyng Prry Phenoype rcors of Lrge-Scle Boolen Newor Sng-Mo Choo nd Kwng-Hyun Cho Depren of Mhecs Unversy of Ulsn Ulsn 446 Republc of Kore Depren of Bo nd Brn Engneerng Kore dvnced
Multivariate Time Series Analysis
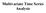 Mulvre me Sere Anl Le { : } be Mulvre me ere. Denon: () = men vlue uncon o { : } = E[ ] or. (,) = Lgged covrnce mr o { : } = E{[ - ()][ - ()]'} or, Denon: e me ere { : } onr e jon drbuon o,,, e me e jon
Mulvre me Sere Anl Le { : } be Mulvre me ere. Denon: () = men vlue uncon o { : } = E[ ] or. (,) = Lgged covrnce mr o { : } = E{[ - ()][ - ()]'} or, Denon: e me ere { : } onr e jon drbuon o,,, e me e jon
Introduction. Section 9: HIGHER ORDER TWO DIMENSIONAL SHAPE FUNCTIONS
 Secon 9: HIGHER ORDER TWO DIMESIO SHPE FUCTIOS Inroducon We ne conder hpe funcon for hgher order eleen. To do h n n orderl fhon we nroduce he concep of re coordne. Conder ere of rngulr eleen depced n he
Secon 9: HIGHER ORDER TWO DIMESIO SHPE FUCTIOS Inroducon We ne conder hpe funcon for hgher order eleen. To do h n n orderl fhon we nroduce he concep of re coordne. Conder ere of rngulr eleen depced n he
Hidden Markov Models
 11-755 Machne Learnng for Sgnal Processng Hdden Markov Models Class 15. 12 Oc 2010 1 Admnsrva HW2 due Tuesday Is everyone on he projecs page? Where are your projec proposals? 2 Recap: Wha s an HMM Probablsc
11-755 Machne Learnng for Sgnal Processng Hdden Markov Models Class 15. 12 Oc 2010 1 Admnsrva HW2 due Tuesday Is everyone on he projecs page? Where are your projec proposals? 2 Recap: Wha s an HMM Probablsc
Hidden Markov Model. a ij. Observation : O1,O2,... States in time : q1, q2,... All states : s1, s2,..., sn
 Hdden Mrkov Model S S servon : 2... Ses n me : 2... All ses : s s2... s 2 3 2 3 2 Hdden Mrkov Model Con d Dscree Mrkov Model 2 z k s s s s s s Degree Mrkov Model Hdden Mrkov Model Con d : rnson roly from
Hdden Mrkov Model S S servon : 2... Ses n me : 2... All ses : s s2... s 2 3 2 3 2 Hdden Mrkov Model Con d Dscree Mrkov Model 2 z k s s s s s s Degree Mrkov Model Hdden Mrkov Model Con d : rnson roly from
RL for Large State Spaces: Policy Gradient. Alan Fern
 RL for Lrge Se Spce: Polcy Grden Aln Fern RL v Polcy Grden Serch So fr ll of our RL echnque hve red o lern n ec or pprome uly funcon or Q-funcon Lern opml vlue of beng n e or kng n con from e. Vlue funcon
RL for Lrge Se Spce: Polcy Grden Aln Fern RL v Polcy Grden Serch So fr ll of our RL echnque hve red o lern n ec or pprome uly funcon or Q-funcon Lern opml vlue of beng n e or kng n con from e. Vlue funcon
Physics 15 Second Hour Exam
 hc 5 Second Hou e nwe e Mulle hoce / ole / ole /6 ole / ------------------------------- ol / I ee eone ole lee how ll wo n ode o ecee l ced. I ou oluon e llegle no ced wll e gen.. onde he collon o wo 7.
hc 5 Second Hou e nwe e Mulle hoce / ole / ole /6 ole / ------------------------------- ol / I ee eone ole lee how ll wo n ode o ecee l ced. I ou oluon e llegle no ced wll e gen.. onde he collon o wo 7.
(,,, ) (,,, ). In addition, there are three other consumers, -2, -1, and 0. Consumer -2 has the utility function
 MACROECONOMIC THEORY T J KEHOE ECON 87 SPRING 5 PROBLEM SET # Conder an overlappng generaon economy le ha n queon 5 on problem e n whch conumer lve for perod The uly funcon of he conumer born n perod,
MACROECONOMIC THEORY T J KEHOE ECON 87 SPRING 5 PROBLEM SET # Conder an overlappng generaon economy le ha n queon 5 on problem e n whch conumer lve for perod The uly funcon of he conumer born n perod,
ANOTHER CATEGORY OF THE STOCHASTIC DEPENDENCE FOR ECONOMETRIC MODELING OF TIME SERIES DATA
 Tn Corn DOSESCU Ph D Dre Cner Chrsn Unversy Buchres Consnn RAISCHI PhD Depren of Mhecs The Buchres Acdey of Econoc Sudes ANOTHER CATEGORY OF THE STOCHASTIC DEPENDENCE FOR ECONOMETRIC MODELING OF TIME SERIES
Tn Corn DOSESCU Ph D Dre Cner Chrsn Unversy Buchres Consnn RAISCHI PhD Depren of Mhecs The Buchres Acdey of Econoc Sudes ANOTHER CATEGORY OF THE STOCHASTIC DEPENDENCE FOR ECONOMETRIC MODELING OF TIME SERIES
8. INVERSE Z-TRANSFORM
 8. INVERSE Z-TRANSFORM The proce by whch Z-trnform of tme ere, nmely X(), returned to the tme domn clled the nvere Z-trnform. The nvere Z-trnform defned by: Computer tudy Z X M-fle trn.m ued to fnd nvere
8. INVERSE Z-TRANSFORM The proce by whch Z-trnform of tme ere, nmely X(), returned to the tme domn clled the nvere Z-trnform. The nvere Z-trnform defned by: Computer tudy Z X M-fle trn.m ued to fnd nvere
Normal Random Variable and its discriminant functions
 Noral Rando Varable and s dscrnan funcons Oulne Noral Rando Varable Properes Dscrnan funcons Why Noral Rando Varables? Analycally racable Works well when observaon coes for a corruped snle prooype 3 The
Noral Rando Varable and s dscrnan funcons Oulne Noral Rando Varable Properes Dscrnan funcons Why Noral Rando Varables? Analycally racable Works well when observaon coes for a corruped snle prooype 3 The
PHY2053 Summer C 2013 Exam 1 Solutions
 PHY053 Sue C 03 E Soluon. The foce G on o G G The onl cobnon h e '/ = doubln.. The peed of lh le 8fulon c 86,8 le 60 n 60n h 4h d 4d fonh.80 fulon/ fonh 3. The dnce eled fo he ene p,, 36 (75n h 45 The
PHY053 Sue C 03 E Soluon. The foce G on o G G The onl cobnon h e '/ = doubln.. The peed of lh le 8fulon c 86,8 le 60 n 60n h 4h d 4d fonh.80 fulon/ fonh 3. The dnce eled fo he ene p,, 36 (75n h 45 The
 ISSN 075-7 : (7) 0 007 C ( ), E-l: ssolos@glco FPGA LUT FPGA EM : FPGA, LUT, EM,,, () FPGA (feldprogrble ge rrs) [, ] () [], () [] () [5] [6] FPGA LUT (Look-Up-Tbles) EM (Ebedded Meor locks) [7, 8] LUT
ISSN 075-7 : (7) 0 007 C ( ), E-l: ssolos@glco FPGA LUT FPGA EM : FPGA, LUT, EM,,, () FPGA (feldprogrble ge rrs) [, ] () [], () [] () [5] [6] FPGA LUT (Look-Up-Tbles) EM (Ebedded Meor locks) [7, 8] LUT
1.B Appendix to Chapter 1
 Secon.B.B Append o Chper.B. The Ordnr Clcl Here re led ome mporn concep rom he ordnr clcl. The Dervve Conder ncon o one ndependen vrble. The dervve o dened b d d lm lm.b. where he ncremen n de o n ncremen
Secon.B.B Append o Chper.B. The Ordnr Clcl Here re led ome mporn concep rom he ordnr clcl. The Dervve Conder ncon o one ndependen vrble. The dervve o dened b d d lm lm.b. where he ncremen n de o n ncremen
Modeling and Predicting Sequences: HMM and (may be) CRF. Amr Ahmed Feb 25
 Modelg d redcg Sequeces: HMM d m be CRF Amr Ahmed 070 Feb 25 Bg cure redcg Sgle Lbel Ipu : A se of feures: - Bg of words docume - Oupu : Clss lbel - Topc of he docume - redcg Sequece of Lbels Noo Noe:
Modelg d redcg Sequeces: HMM d m be CRF Amr Ahmed 070 Feb 25 Bg cure redcg Sgle Lbel Ipu : A se of feures: - Bg of words docume - Oupu : Clss lbel - Topc of he docume - redcg Sequece of Lbels Noo Noe:
v v at 1 2 d vit at v v 2a d
 SPH3UW Unt. Accelerton n One Denon Pge o 9 Note Phyc Inventory Accelerton the rte o chnge o velocty. Averge ccelerton, ve the chnge n velocty dvded by the te ntervl, v v v ve. t t v dv Intntneou ccelerton
SPH3UW Unt. Accelerton n One Denon Pge o 9 Note Phyc Inventory Accelerton the rte o chnge o velocty. Averge ccelerton, ve the chnge n velocty dvded by the te ntervl, v v v ve. t t v dv Intntneou ccelerton
RL for Large State Spaces: Policy Gradient. Alan Fern
 RL for Lrge Se Spce: Polcy Grden Aln Fern Movon for Polcy Serch So fr ll of our RL echnque hve red o lern n ec or pprome vlue funcon or Q-funcon Lern opml vlue of beng n e or kng n con from e. Vlue funcon
RL for Lrge Se Spce: Polcy Grden Aln Fern Movon for Polcy Serch So fr ll of our RL echnque hve red o lern n ec or pprome vlue funcon or Q-funcon Lern opml vlue of beng n e or kng n con from e. Vlue funcon
THEORETICAL AUTOCORRELATIONS. ) if often denoted by γ. Note that
 THEORETICAL AUTOCORRELATIONS Cov( y, y ) E( y E( y))( y E( y)) ρ = = Var( y) E( y E( y)) =,, L ρ = and Cov( y, y ) s ofen denoed by whle Var( y ) f ofen denoed by γ. Noe ha γ = γ and ρ = ρ and because
THEORETICAL AUTOCORRELATIONS Cov( y, y ) E( y E( y))( y E( y)) ρ = = Var( y) E( y E( y)) =,, L ρ = and Cov( y, y ) s ofen denoed by whle Var( y ) f ofen denoed by γ. Noe ha γ = γ and ρ = ρ and because
Review: Transformations. Transformations - Viewing. Transformations - Modeling. world CAMERA OBJECT WORLD CSE 681 CSE 681 CSE 681 CSE 681
 Revew: Trnsforons Trnsforons Modelng rnsforons buld cople odels b posonng (rnsforng sple coponens relve o ech oher ewng rnsforons plcng vrul cer n he world rnsforon fro world coordnes o cer coordnes Perspecve
Revew: Trnsforons Trnsforons Modelng rnsforons buld cople odels b posonng (rnsforng sple coponens relve o ech oher ewng rnsforons plcng vrul cer n he world rnsforon fro world coordnes o cer coordnes Perspecve
( ) () we define the interaction representation by the unitary transformation () = ()
 Hgher Order Perurbaon Theory Mchael Fowler 3/7/6 The neracon Represenaon Recall ha n he frs par of hs course sequence, we dscussed he chrödnger and Hesenberg represenaons of quanum mechancs here n he chrödnger
Hgher Order Perurbaon Theory Mchael Fowler 3/7/6 The neracon Represenaon Recall ha n he frs par of hs course sequence, we dscussed he chrödnger and Hesenberg represenaons of quanum mechancs here n he chrödnger
Physics 120 Spring 2007 Exam #1 April 20, Name
 Phc 0 Spng 007 E # pl 0, 007 Ne P Mulple Choce / 0 Poble # / 0 Poble # / 0 Poble # / 0 ol / 00 In eepng wh he Unon College polc on cdec hone, ued h ou wll nehe ccep no pode unuhozed nce n he copleon o
Phc 0 Spng 007 E # pl 0, 007 Ne P Mulple Choce / 0 Poble # / 0 Poble # / 0 Poble # / 0 ol / 00 In eepng wh he Unon College polc on cdec hone, ued h ou wll nehe ccep no pode unuhozed nce n he copleon o
A. Inventory model. Why are we interested in it? What do we really study in such cases.
 Some general yem model.. Inenory model. Why are we nereed n? Wha do we really udy n uch cae. General raegy of machng wo dmlar procee, ay, machng a fa proce wh a low one. We need an nenory or a buffer or
Some general yem model.. Inenory model. Why are we nereed n? Wha do we really udy n uch cae. General raegy of machng wo dmlar procee, ay, machng a fa proce wh a low one. We need an nenory or a buffer or
Response of MDOF systems
 Response of MDOF syses Degree of freedo DOF: he nu nuber of ndependen coordnaes requred o deerne copleely he posons of all pars of a syse a any nsan of e. wo DOF syses hree DOF syses he noral ode analyss
Response of MDOF syses Degree of freedo DOF: he nu nuber of ndependen coordnaes requred o deerne copleely he posons of all pars of a syse a any nsan of e. wo DOF syses hree DOF syses he noral ode analyss
Forms of Energy. Mass = Energy. Page 1. SPH4U: Introduction to Work. Work & Energy. Particle Physics:
 SPH4U: Inroducion o ork ork & Energy ork & Energy Discussion Definiion Do Produc ork of consn force ork/kineic energy heore ork of uliple consn forces Coens One of he os iporn conceps in physics Alernive
SPH4U: Inroducion o ork ork & Energy ork & Energy Discussion Definiion Do Produc ork of consn force ork/kineic energy heore ork of uliple consn forces Coens One of he os iporn conceps in physics Alernive
Laplace Examples, Inverse, Rational Form
 Lecure 3 Ouline: Lplce Exple, Invere, Rionl For Announceen: Rein: 6: Lplce Trnfor pp. 3-33, 55.5-56.5, 7 HW 8 poe, ue nex We. Free -y exenion OcenOne Roo Tour will e fer cl y 7 (:3-:) Lunch provie ferwr.
Lecure 3 Ouline: Lplce Exple, Invere, Rionl For Announceen: Rein: 6: Lplce Trnfor pp. 3-33, 55.5-56.5, 7 HW 8 poe, ue nex We. Free -y exenion OcenOne Roo Tour will e fer cl y 7 (:3-:) Lunch provie ferwr.
Motion. Part 2: Constant Acceleration. Acceleration. October Lab Physics. Ms. Levine 1. Acceleration. Acceleration. Units for Acceleration.
 Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
II The Z Transform. Topics to be covered. 1. Introduction. 2. The Z transform. 3. Z transforms of elementary functions
 II The Z Trnsfor Tocs o e covered. Inroducon. The Z rnsfor 3. Z rnsfors of eleenry funcons 4. Proeres nd Theory of rnsfor 5. The nverse rnsfor 6. Z rnsfor for solvng dfference equons II. Inroducon The
II The Z Trnsfor Tocs o e covered. Inroducon. The Z rnsfor 3. Z rnsfors of eleenry funcons 4. Proeres nd Theory of rnsfor 5. The nverse rnsfor 6. Z rnsfor for solvng dfference equons II. Inroducon The
Calculus 241, section 12.2 Limits/Continuity & 12.3 Derivatives/Integrals notes by Tim Pilachowski r r r =, with a domain of real ( )
 Clculu 4, econ Lm/Connuy & Devve/Inel noe y Tm Plchow, wh domn o el Wh we hve o : veco-vlued uncon, ( ) ( ) ( ) j ( ) nume nd ne o veco The uncon, nd A w done wh eul uncon ( x) nd connuy e he componen
Clculu 4, econ Lm/Connuy & Devve/Inel noe y Tm Plchow, wh domn o el Wh we hve o : veco-vlued uncon, ( ) ( ) ( ) j ( ) nume nd ne o veco The uncon, nd A w done wh eul uncon ( x) nd connuy e he componen
graph of unit step function t
 .5 Piecewie coninuou forcing funcion...e.g. urning he forcing on nd off. The following Lplce rnform meril i ueful in yem where we urn forcing funcion on nd off, nd when we hve righ hnd ide "forcing funcion"
.5 Piecewie coninuou forcing funcion...e.g. urning he forcing on nd off. The following Lplce rnform meril i ueful in yem where we urn forcing funcion on nd off, nd when we hve righ hnd ide "forcing funcion"
4.8 Improper Integrals
 4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
グラフィカルモデルによる推論 確率伝搬法 (2) Kenji Fukumizu The Institute of Statistical Mathematics 計算推論科学概論 II (2010 年度, 後期 )
 グラフィカルモデルによる推論 確率伝搬法 Kenj Fukuzu he Insue of Sascal Maheacs 計算推論科学概論 II 年度 後期 Inference on Hdden Markov Model Inference on Hdden Markov Model Revew: HMM odel : hdden sae fne Inference Coue... for any Naïve
グラフィカルモデルによる推論 確率伝搬法 Kenj Fukuzu he Insue of Sascal Maheacs 計算推論科学概論 II 年度 後期 Inference on Hdden Markov Model Inference on Hdden Markov Model Revew: HMM odel : hdden sae fne Inference Coue... for any Naïve
Laplace Transform. Definition of Laplace Transform: f(t) that satisfies The Laplace transform of f(t) is defined as.
 Lplce Trfor The Lplce Trfor oe of he hecl ool for olvg ordry ler dfferel equo. - The hoogeeou equo d he prculr Iegrl re olved oe opero. - The Lplce rfor cover he ODE o lgerc eq. σ j ple do. I he pole o
Lplce Trfor The Lplce Trfor oe of he hecl ool for olvg ordry ler dfferel equo. - The hoogeeou equo d he prculr Iegrl re olved oe opero. - The Lplce rfor cover he ODE o lgerc eq. σ j ple do. I he pole o
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) j ( ) A. b) Theorem
 b) Theoe The u of he eco pojecon of eco n ll uull pependcul (n he ene of he cl poduc) decon equl o he eco. ( ) n e e o The pojecon conue he eco coponen of he eco. poof. n e ( ) ( ) ( ) e e e e e e e e
b) Theoe The u of he eco pojecon of eco n ll uull pependcul (n he ene of he cl poduc) decon equl o he eco. ( ) n e e o The pojecon conue he eco coponen of he eco. poof. n e ( ) ( ) ( ) e e e e e e e e
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. 1. Basic transforms
 LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. Bic rnform In hi coure, Lplce Trnform will be inroduced nd heir properie exmined; ble of common rnform will be buil up; nd rnform will be ued o olve ome dierenil equion by rnforming
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. Bic rnform In hi coure, Lplce Trnform will be inroduced nd heir properie exmined; ble of common rnform will be buil up; nd rnform will be ued o olve ome dierenil equion by rnforming
A New Translation Template Learning Based on Hidden Markov Modeling
 A New Trnslon Teple Lernng Bsed on Hdden Mrov Modelng NGUYEN MINH LE, AKIRA HIMAZU, nd UUMU HORIGUCHI Grdue chool of Inforon cence, JAIT IHIKAWA 93-9, JAPAN Absrc: Ths pper ddresses novel rnslon ehod bsed
A New Trnslon Teple Lernng Bsed on Hdden Mrov Modelng NGUYEN MINH LE, AKIRA HIMAZU, nd UUMU HORIGUCHI Grdue chool of Inforon cence, JAIT IHIKAWA 93-9, JAPAN Absrc: Ths pper ddresses novel rnslon ehod bsed
Maximum Likelihood Estimation
 Mau Lkelhood aon Beln Chen Depaen of Copue Scence & Infoaon ngneeng aonal Tawan oal Unvey Refeence:. he Alpaydn, Inoducon o Machne Leanng, Chape 4, MIT Pe, 4 Saple Sac and Populaon Paaee A Scheac Depcon
Mau Lkelhood aon Beln Chen Depaen of Copue Scence & Infoaon ngneeng aonal Tawan oal Unvey Refeence:. he Alpaydn, Inoducon o Machne Leanng, Chape 4, MIT Pe, 4 Saple Sac and Populaon Paaee A Scheac Depcon
Physics 201 Lecture 2
 Physcs 1 Lecure Lecure Chper.1-. Dene Poson, Dsplcemen & Dsnce Dsngush Tme nd Tme Inerl Dene Velocy (Aerge nd Insnneous), Speed Dene Acceleron Undersnd lgebrclly, hrough ecors, nd grphclly he relonshps
Physcs 1 Lecure Lecure Chper.1-. Dene Poson, Dsplcemen & Dsnce Dsngush Tme nd Tme Inerl Dene Velocy (Aerge nd Insnneous), Speed Dene Acceleron Undersnd lgebrclly, hrough ecors, nd grphclly he relonshps
GMM parameter estimation. Xiaoye Lu CMPS290c Final Project
 GMM paraeer esaon Xaoye Lu M290c Fnal rojec GMM nroducon Gaussan ure Model obnaon of several gaussan coponens Noaon: For each Gaussan dsrbuon:, s he ean and covarance ar. A GMM h ures(coponens): p ( 2π
GMM paraeer esaon Xaoye Lu M290c Fnal rojec GMM nroducon Gaussan ure Model obnaon of several gaussan coponens Noaon: For each Gaussan dsrbuon:, s he ean and covarance ar. A GMM h ures(coponens): p ( 2π
A Demand System for Input Factors when there are Technological Changes in Production
 A Demand Syem for Inpu Facor when here are Technologcal Change n Producon Movaon Due o (e.g.) echnologcal change here mgh no be a aonary relaonhp for he co hare of each npu facor. When emang demand yem
A Demand Syem for Inpu Facor when here are Technologcal Change n Producon Movaon Due o (e.g.) echnologcal change here mgh no be a aonary relaonhp for he co hare of each npu facor. When emang demand yem
Chapter 6. Isoparametric Formulation
 ME 78 FIIE ELEME MEHOD Chper. Ioprerc Forlon Se fncon h ed o defne he eleen geoer ed o defne he dplceen whn he eleen ode r Eleen Lner geoer Lner dplceen ode Be Eleen Qdrc geoer Qdrc dplceen We gn he e
ME 78 FIIE ELEME MEHOD Chper. Ioprerc Forlon Se fncon h ed o defne he eleen geoer ed o defne he dplceen whn he eleen ode r Eleen Lner geoer Lner dplceen ode Be Eleen Qdrc geoer Qdrc dplceen We gn he e
Outline. Probabilistic Model Learning. Probabilistic Model Learning. Probabilistic Model for Time-series Data: Hidden Markov Model
 Probablsc Model for Tme-seres Daa: Hdden Markov Model Hrosh Mamsuka Bonformacs Cener Kyoo Unversy Oulne Three Problems for probablsc models n machne learnng. Compung lkelhood 2. Learnng 3. Parsng (predcon
Probablsc Model for Tme-seres Daa: Hdden Markov Model Hrosh Mamsuka Bonformacs Cener Kyoo Unversy Oulne Three Problems for probablsc models n machne learnng. Compung lkelhood 2. Learnng 3. Parsng (predcon
Let us look at a linear equation for a one-port network, for example some load with a reflection coefficient s, Figure L6.
 ECEN 5004, prng 08 Actve Mcrowve Crcut Zoy Popovc, Unverty of Colordo, Boulder LECURE 5 IGNAL FLOW GRAPH FOR MICROWAVE CIRCUI ANALYI In mny text on mcrowve mplfer (e.g. the clc one by Gonzlez), gnl flow-grph
ECEN 5004, prng 08 Actve Mcrowve Crcut Zoy Popovc, Unverty of Colordo, Boulder LECURE 5 IGNAL FLOW GRAPH FOR MICROWAVE CIRCUI ANALYI In mny text on mcrowve mplfer (e.g. the clc one by Gonzlez), gnl flow-grph
PROBABILISTIC EXTENTION OF THE CUMULATIVE PROSPECT THEORY
 Il Zuler PROBABILISTIC EXTENTION OF THE CUMULATIVE PROSPECT THEORY BASIC RESEARCH PROGRAM WORKING PAPERS SERIES: ECONOMICS WP BRP 33/EC/23 Th Worng Per n ouu of reerch roec leened he Nonl Reerch Unver
Il Zuler PROBABILISTIC EXTENTION OF THE CUMULATIVE PROSPECT THEORY BASIC RESEARCH PROGRAM WORKING PAPERS SERIES: ECONOMICS WP BRP 33/EC/23 Th Worng Per n ouu of reerch roec leened he Nonl Reerch Unver
Discrete Markov Process. Introduction. Example: Balls and Urns. Stochastic Automaton. INTRODUCTION TO Machine Learning 3rd Edition
 EHEM ALPAYDI he MI Press, 04 Lecure Sldes for IRODUCIO O Machne Learnng 3rd Edon alpaydn@boun.edu.r hp://www.cmpe.boun.edu.r/~ehem/ml3e Sldes from exboo resource page. Slghly eded and wh addonal examples
EHEM ALPAYDI he MI Press, 04 Lecure Sldes for IRODUCIO O Machne Learnng 3rd Edon alpaydn@boun.edu.r hp://www.cmpe.boun.edu.r/~ehem/ml3e Sldes from exboo resource page. Slghly eded and wh addonal examples
Remember: Project Proposals are due April 11.
 Bonformtcs ecture Notes Announcements Remember: Project Proposls re due Aprl. Clss 22 Aprl 4, 2002 A. Hdden Mrov Models. Defntons Emple - Consder the emple we tled bout n clss lst tme wth the cons. However,
Bonformtcs ecture Notes Announcements Remember: Project Proposls re due Aprl. Clss 22 Aprl 4, 2002 A. Hdden Mrov Models. Defntons Emple - Consder the emple we tled bout n clss lst tme wth the cons. However,
Rotations.
 oons j.lbb@phscs.o.c.uk To s summ Fmes of efeence Invnce une nsfomons oon of wve funcon: -funcons Eule s ngles Emple: e e - - Angul momenum s oon geneo Genec nslons n Noehe s heoem Fmes of efeence Conse
oons j.lbb@phscs.o.c.uk To s summ Fmes of efeence Invnce une nsfomons oon of wve funcon: -funcons Eule s ngles Emple: e e - - Angul momenum s oon geneo Genec nslons n Noehe s heoem Fmes of efeence Conse
E-Companion: Mathematical Proofs
 E-omnon: Mthemtcl Poo Poo o emm : Pt DS Sytem y denton o t ey to vey tht t ncee n wth d ncee n We dene } ] : [ { M whee / We let the ttegy et o ech etle n DS e ]} [ ] [ : { M w whee M lge otve nume oth
E-omnon: Mthemtcl Poo Poo o emm : Pt DS Sytem y denton o t ey to vey tht t ncee n wth d ncee n We dene } ] : [ { M whee / We let the ttegy et o ech etle n DS e ]} [ ] [ : { M w whee M lge otve nume oth
H = d d q 1 d d q N d d p 1 d d p N exp
 8333: Sacal Mechanc I roblem Se # 7 Soluon Fall 3 Canoncal Enemble Non-harmonc Ga: The Hamlonan for a ga of N non neracng parcle n a d dmenonal box ha he form H A p a The paron funcon gven by ZN T d d
8333: Sacal Mechanc I roblem Se # 7 Soluon Fall 3 Canoncal Enemble Non-harmonc Ga: The Hamlonan for a ga of N non neracng parcle n a d dmenonal box ha he form H A p a The paron funcon gven by ZN T d d
ESS 265 Spring Quarter 2005 Kinetic Simulations
 SS 65 Spng Quae 5 Knec Sulaon Lecue une 9 5 An aple of an lecoagnec Pacle Code A an eaple of a knec ulaon we wll ue a one denonal elecoagnec ulaon code called KMPO deeloped b Yohhau Oua and Hoh Mauoo.
SS 65 Spng Quae 5 Knec Sulaon Lecue une 9 5 An aple of an lecoagnec Pacle Code A an eaple of a knec ulaon we wll ue a one denonal elecoagnec ulaon code called KMPO deeloped b Yohhau Oua and Hoh Mauoo.
Graduate Macroeconomics 2 Problem set 5. - Solutions
 Graduae Macroeconomcs 2 Problem se. - Soluons Queson 1 To answer hs queson we need he frms frs order condons and he equaon ha deermnes he number of frms n equlbrum. The frms frs order condons are: F K
Graduae Macroeconomcs 2 Problem se. - Soluons Queson 1 To answer hs queson we need he frms frs order condons and he equaon ha deermnes he number of frms n equlbrum. The frms frs order condons are: F K
Notes on the stability of dynamic systems and the use of Eigen Values.
 Noes on he sabl of dnamc ssems and he use of Egen Values. Source: Macro II course noes, Dr. Davd Bessler s Tme Seres course noes, zarads (999) Ineremporal Macroeconomcs chaper 4 & Techncal ppend, and Hamlon
Noes on he sabl of dnamc ssems and he use of Egen Values. Source: Macro II course noes, Dr. Davd Bessler s Tme Seres course noes, zarads (999) Ineremporal Macroeconomcs chaper 4 & Techncal ppend, and Hamlon
Decompression diagram sampler_src (source files and makefiles) bin (binary files) --- sh (sample shells) --- input (sample input files)
 . Iroduco Probblsc oe-moh forecs gudce s mde b 50 esemble members mproved b Model Oupu scs (MO). scl equo s mde b usg hdcs d d observo d. We selec some prmeers for modfg forecs o use mulple regresso formul.
. Iroduco Probblsc oe-moh forecs gudce s mde b 50 esemble members mproved b Model Oupu scs (MO). scl equo s mde b usg hdcs d d observo d. We selec some prmeers for modfg forecs o use mulple regresso formul.
Variants of Pegasos. December 11, 2009
 Inroducon Varans of Pegasos SooWoong Ryu bshboy@sanford.edu December, 009 Youngsoo Cho yc344@sanford.edu Developng a new SVM algorhm s ongong research opc. Among many exng SVM algorhms, we wll focus on
Inroducon Varans of Pegasos SooWoong Ryu bshboy@sanford.edu December, 009 Youngsoo Cho yc344@sanford.edu Developng a new SVM algorhm s ongong research opc. Among many exng SVM algorhms, we wll focus on
( )a = "t = 1 E =" B E = 5016 V. E = BHv # 3. 2 %r. c.) direction of induced current in the loop for : i.) "t < 1
 99 3 c dr b a µ r.? d b µ d d cdr a r & b d & µ c µ c b dr µ c µ c b & ' ln' a +*+* b ln r ln a a r a ' µ c b 'b* µ c ln' * & ln, &a a+ ncreang no he page o nduced curren wll creae a - feldou of he page
99 3 c dr b a µ r.? d b µ d d cdr a r & b d & µ c µ c b dr µ c µ c b & ' ln' a +*+* b ln r ln a a r a ' µ c b 'b* µ c ln' * & ln, &a a+ ncreang no he page o nduced curren wll creae a - feldou of he page
In this Chapter. Chap. 3 Markov chains and hidden Markov models. Probabilistic Models. Example: CpG Islands
 In ths Chpter Chp. 3 Mrov chns nd hdden Mrov models Bontellgence bortory School of Computer Sc. & Eng. Seoul Ntonl Unversty Seoul 5-74, Kore The probblstc model for sequence nlyss HMM (hdden Mrov model)
In ths Chpter Chp. 3 Mrov chns nd hdden Mrov models Bontellgence bortory School of Computer Sc. & Eng. Seoul Ntonl Unversty Seoul 5-74, Kore The probblstc model for sequence nlyss HMM (hdden Mrov model)
Solution in semi infinite diffusion couples (error function analysis)
 Soluon n sem nfne dffuson couples (error funcon analyss) Le us consder now he sem nfne dffuson couple of wo blocks wh concenraon of and I means ha, n a A- bnary sysem, s bondng beween wo blocks made of
Soluon n sem nfne dffuson couples (error funcon analyss) Le us consder now he sem nfne dffuson couple of wo blocks wh concenraon of and I means ha, n a A- bnary sysem, s bondng beween wo blocks made of
Multiple Failures. Diverse Routing for Maximizing Survivability. Maximum Survivability Models. Minimum-Color (SRLG) Diverse Routing
 Mulple Falure Dvere Roung for Maxmzng Survvably One-falure aumpon n prevou work Mulple falure Hard o provde 100% proecon Maxmum urvvably Maxmum Survvably Model Mnmum-Color (SRLG) Dvere Roung Each lnk ha
Mulple Falure Dvere Roung for Maxmzng Survvably One-falure aumpon n prevou work Mulple falure Hard o provde 100% proecon Maxmum urvvably Maxmum Survvably Model Mnmum-Color (SRLG) Dvere Roung Each lnk ha
Matching. Lecture 13 Link Analysis ( ) 13.1 Link Analysis ( ) 13.2 Google s PageRank Algorithm The Top Ten Algorithms in Data Mining
 Lecture 13 Link Anlsis () 131 13.1 Serch Engine Indexing () 132 13.1 Link Anlsis () 13.2 Google s PgeRnk Algorith The Top Ten Algoriths in Dt Mining J. McCorick, Nine Algoriths Tht Chnged the Future, Princeton
Lecture 13 Link Anlsis () 131 13.1 Serch Engine Indexing () 132 13.1 Link Anlsis () 13.2 Google s PgeRnk Algorith The Top Ten Algoriths in Dt Mining J. McCorick, Nine Algoriths Tht Chnged the Future, Princeton
Chapter 6: AC Circuits
 Chaper 6: AC Crcus Chaper 6: Oulne Phasors and he AC Seady Sae AC Crcus A sable, lnear crcu operang n he seady sae wh snusodal excaon (.e., snusodal seady sae. Complee response forced response naural response.
Chaper 6: AC Crcus Chaper 6: Oulne Phasors and he AC Seady Sae AC Crcus A sable, lnear crcu operang n he seady sae wh snusodal excaon (.e., snusodal seady sae. Complee response forced response naural response.
Interval Estimation. Consider a random variable X with a mean of X. Let X be distributed as X X
 ECON 37: Ecoomercs Hypohess Tesg Iervl Esmo Wh we hve doe so fr s o udersd how we c ob esmors of ecoomcs reloshp we wsh o sudy. The queso s how comforble re we wh our esmors? We frs exme how o produce
ECON 37: Ecoomercs Hypohess Tesg Iervl Esmo Wh we hve doe so fr s o udersd how we c ob esmors of ecoomcs reloshp we wsh o sudy. The queso s how comforble re we wh our esmors? We frs exme how o produce
Physics 240: Worksheet 16 Name
 Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
_ J.. C C A 551NED. - n R ' ' t i :. t ; . b c c : : I I .., I AS IEC. r '2 5? 9
 C C A 55NED n R 5 0 9 b c c \ { s AS EC 2 5? 9 Con 0 \ 0265 o + s ^! 4 y!! {! w Y n < R > s s = ~ C c [ + * c n j R c C / e A / = + j ) d /! Y 6 ] s v * ^ / ) v } > { ± n S = S w c s y c C { ~! > R = n
C C A 55NED n R 5 0 9 b c c \ { s AS EC 2 5? 9 Con 0 \ 0265 o + s ^! 4 y!! {! w Y n < R > s s = ~ C c [ + * c n j R c C / e A / = + j ) d /! Y 6 ] s v * ^ / ) v } > { ± n S = S w c s y c C { ~! > R = n
Ordinary Differential Equations in Neuroscience with Matlab examples. Aim 1- Gain understanding of how to set up and solve ODE s
 Ordnary Dfferenal Equaons n Neuroscence wh Malab eamples. Am - Gan undersandng of how o se up and solve ODE s Am Undersand how o se up an solve a smple eample of he Hebb rule n D Our goal a end of class
Ordnary Dfferenal Equaons n Neuroscence wh Malab eamples. Am - Gan undersandng of how o se up and solve ODE s Am Undersand how o se up an solve a smple eample of he Hebb rule n D Our goal a end of class
Lecture 4: Trunking Theory and Grade of Service (GOS)
 Lecure 4: Trunkng Theory nd Grde of Servce GOS 4.. Mn Problems nd Defnons n Trunkng nd GOS Mn Problems n Subscrber Servce: lmed rdo specrum # of chnnels; mny users. Prncple of Servce: Defnon: Serve user
Lecure 4: Trunkng Theory nd Grde of Servce GOS 4.. Mn Problems nd Defnons n Trunkng nd GOS Mn Problems n Subscrber Servce: lmed rdo specrum # of chnnels; mny users. Prncple of Servce: Defnon: Serve user
Chebyshev Polynomial Solution of Nonlinear Fredholm-Volterra Integro- Differential Equations
 Çny Ünvee Fen-Edeby Füle Jounl of A nd Scence Sy : 5 y 6 Chebyhev Polynol Soluon of onlne Fedhol-Vole Inego- Dffeenl Equon Hndn ÇERDİK-YASA nd Ayşegül AKYÜZ-DAŞCIOĞU Abc In h ppe Chebyhev collocon ehod
Çny Ünvee Fen-Edeby Füle Jounl of A nd Scence Sy : 5 y 6 Chebyhev Polynol Soluon of onlne Fedhol-Vole Inego- Dffeenl Equon Hndn ÇERDİK-YASA nd Ayşegül AKYÜZ-DAŞCIOĞU Abc In h ppe Chebyhev collocon ehod
Quick Fuzzy Backpropagation Algorithm
 Publhed n Neurl Neork, 4(): 3-44, Quck Fuzzy Bckpropgon Algorh ALEXANDER NIKOV AND STEFKA STOEVA Techncl Unvery of Sof, Sof, Bulgr nd Bulgrn Nonl Lbrry, Sof, Bulgr Abrc - A odfcon of he fuzzy bckpropgon
Publhed n Neurl Neork, 4(): 3-44, Quck Fuzzy Bckpropgon Algorh ALEXANDER NIKOV AND STEFKA STOEVA Techncl Unvery of Sof, Sof, Bulgr nd Bulgrn Nonl Lbrry, Sof, Bulgr Abrc - A odfcon of he fuzzy bckpropgon
Chapter 6 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies
 Chpe 6 Pne oon of Rd ode 6. Equon of oon fo Rd bod. 6., 6., 6.3 Conde d bod ced upon b ee een foce,, 3,. We cn ume h he bod mde of e numbe n of pce of m Δm (,,, n). Conden f he moon of he m cene of he
Chpe 6 Pne oon of Rd ode 6. Equon of oon fo Rd bod. 6., 6., 6.3 Conde d bod ced upon b ee een foce,, 3,. We cn ume h he bod mde of e numbe n of pce of m Δm (,,, n). Conden f he moon of he m cene of he
Chapter 2: Evaluative Feedback
 Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Chapter Lagrangian Interpolation
 Chaper 5.4 agrangan Inerpolaon Afer readng hs chaper you should be able o:. dere agrangan mehod of nerpolaon. sole problems usng agrangan mehod of nerpolaon and. use agrangan nerpolans o fnd deraes and
Chaper 5.4 agrangan Inerpolaon Afer readng hs chaper you should be able o:. dere agrangan mehod of nerpolaon. sole problems usng agrangan mehod of nerpolaon and. use agrangan nerpolans o fnd deraes and
Bipartite Matching. Matching. Bipartite Matching. Maxflow Formulation
 Mching Inpu: undireced grph G = (V, E). Biprie Mching Inpu: undireced, biprie grph G = (, E).. Mching Ern Myr, Hrld äcke Biprie Mching Inpu: undireced, biprie grph G = (, E). Mflow Formulion Inpu: undireced,
Mching Inpu: undireced grph G = (V, E). Biprie Mching Inpu: undireced, biprie grph G = (, E).. Mching Ern Myr, Hrld äcke Biprie Mching Inpu: undireced, biprie grph G = (, E). Mflow Formulion Inpu: undireced,
The solution is often represented as a vector: 2xI + 4X2 + 2X3 + 4X4 + 2X5 = 4 2xI + 4X2 + 3X3 + 3X4 + 3X5 = 4. 3xI + 6X2 + 6X3 + 3X4 + 6X5 = 6.
 [~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
[~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
X-Ray Notes, Part III
 oll 6 X-y oe 3: Pe X-Ry oe, P III oe Deeo Coe oupu o x-y ye h look lke h: We efe ue of que lhly ffee efo h ue y ovk: Co: C ΔS S Sl o oe Ro: SR S Co o oe Ro: CR ΔS C SR Pevouly, we ee he SR fo ye hv pxel
oll 6 X-y oe 3: Pe X-Ry oe, P III oe Deeo Coe oupu o x-y ye h look lke h: We efe ue of que lhly ffee efo h ue y ovk: Co: C ΔS S Sl o oe Ro: SR S Co o oe Ro: CR ΔS C SR Pevouly, we ee he SR fo ye hv pxel
0 for t < 0 1 for t > 0
 8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
Hidden Markov Models
 Hdden Mkov Model Ronld J. Wllm CSG220 Spng 2007 Conn evel lde dped fom n Andew Mooe uol on h opc nd few fgue fom Ruell & ovg AIMA e nd Alpydn Inoducon o Mchne Lenng e. A Smple Mkov Chn /2 /3 /3 /3 3 2
Hdden Mkov Model Ronld J. Wllm CSG220 Spng 2007 Conn evel lde dped fom n Andew Mooe uol on h opc nd few fgue fom Ruell & ovg AIMA e nd Alpydn Inoducon o Mchne Lenng e. A Smple Mkov Chn /2 /3 /3 /3 3 2
Principle Component Analysis
 Prncple Component Anlyss Jng Go SUNY Bufflo Why Dmensonlty Reducton? We hve too mny dmensons o reson bout or obtn nsghts from o vsulze oo much nose n the dt Need to reduce them to smller set of fctors
Prncple Component Anlyss Jng Go SUNY Bufflo Why Dmensonlty Reducton? We hve too mny dmensons o reson bout or obtn nsghts from o vsulze oo much nose n the dt Need to reduce them to smller set of fctors
Introduction ( Week 1-2) Course introduction A brief introduction to molecular biology A brief introduction to sequence comparison Part I: Algorithms
 Course organzaon Inroducon Wee -2) Course nroducon A bref nroducon o molecular bology A bref nroducon o sequence comparson Par I: Algorhms for Sequence Analyss Wee 3-8) Chaper -3, Models and heores» Probably
Course organzaon Inroducon Wee -2) Course nroducon A bref nroducon o molecular bology A bref nroducon o sequence comparson Par I: Algorhms for Sequence Analyss Wee 3-8) Chaper -3, Models and heores» Probably
An Ising model on 2-D image
 School o Coputer Scence Approte Inerence: Loopy Bele Propgton nd vrnts Prolstc Grphcl Models 0-708 Lecture 4, ov 7, 007 Receptor A Knse C Gene G Receptor B Knse D Knse E 3 4 5 TF F 6 Gene H 7 8 Hetunndn
School o Coputer Scence Approte Inerence: Loopy Bele Propgton nd vrnts Prolstc Grphcl Models 0-708 Lecture 4, ov 7, 007 Receptor A Knse C Gene G Receptor B Knse D Knse E 3 4 5 TF F 6 Gene H 7 8 Hetunndn
Flow Networks Alon Efrat Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk. Flow networks. Flow networks CS 445
 CS 445 Flow Nework lon Efr Slide corey of Chrle Leieron wih mll chnge by Crol Wenk Flow nework Definiion. flow nework i direced grph G = (V, E) wih wo diingihed erice: orce nd ink. Ech edge (, ) E h nonnegie
CS 445 Flow Nework lon Efr Slide corey of Chrle Leieron wih mll chnge by Crol Wenk Flow nework Definiion. flow nework i direced grph G = (V, E) wih wo diingihed erice: orce nd ink. Ech edge (, ) E h nonnegie
CS434a/541a: Pattern Recognition Prof. Olga Veksler. Lecture 4
 CS434a/54a: Paern Recognon Prof. Olga Veksler Lecure 4 Oulne Normal Random Varable Properes Dscrmnan funcons Why Normal Random Varables? Analycally racable Works well when observaon comes form a corruped
CS434a/54a: Paern Recognon Prof. Olga Veksler Lecure 4 Oulne Normal Random Varable Properes Dscrmnan funcons Why Normal Random Varables? Analycally racable Works well when observaon comes form a corruped
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecure 9 Hamlonan Equaons of Moon (Chaper 8) Wha We Dd Las Tme Consruced Hamlonan formalsm H ( q, p, ) = q p L( q, q, ) H p = q H q = p H = L Equvalen o Lagrangan formalsm Smpler, bu
Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecure 9 Hamlonan Equaons of Moon (Chaper 8) Wha We Dd Las Tme Consruced Hamlonan formalsm H ( q, p, ) = q p L( q, q, ) H p = q H q = p H = L Equvalen o Lagrangan formalsm Smpler, bu
P441 Analytical Mechanics - I. Coupled Oscillators. c Alex R. Dzierba
 Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecure 9 Hamlonan Equaons of Moon (Chaper 8) Wha We Dd Las Tme Consruced Hamlonan formalsm Hqp (,,) = qp Lqq (,,) H p = q H q = p H L = Equvalen o Lagrangan formalsm Smpler, bu wce as
Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecure 9 Hamlonan Equaons of Moon (Chaper 8) Wha We Dd Las Tme Consruced Hamlonan formalsm Hqp (,,) = qp Lqq (,,) H p = q H q = p H L = Equvalen o Lagrangan formalsm Smpler, bu wce as
Fast Algorithm for Robust Template Matching with M-estimators
 Fs Algorh for Robus Tele Mchng wh M-esors Jun-Hung Chen Chu-Song Chen nd Yong-Sheng Chen nsue of nforon Scence Acde Snc Te Twn e-l: song@s.snc.edu.w Absrc n hs er we roose fs lgorh for seedng u he rocess
Fs Algorh for Robus Tele Mchng wh M-esors Jun-Hung Chen Chu-Song Chen nd Yong-Sheng Chen nsue of nforon Scence Acde Snc Te Twn e-l: song@s.snc.edu.w Absrc n hs er we roose fs lgorh for seedng u he rocess
Physics 201 Lecture 15
 Phscs 0 Lecue 5 l Goals Lecue 5 v Elo consevaon of oenu n D & D v Inouce oenu an Iulse Coens on oenu Consevaon l oe geneal han consevaon of echancal eneg l oenu Consevaon occus n sses wh no ne eenal foces
Phscs 0 Lecue 5 l Goals Lecue 5 v Elo consevaon of oenu n D & D v Inouce oenu an Iulse Coens on oenu Consevaon l oe geneal han consevaon of echancal eneg l oenu Consevaon occus n sses wh no ne eenal foces
September 20 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
Main questions Motivation: Recognition
 Tod Algnen & Wrpng Thursd, Oc 9 Algnen & wrpng d rnsforons Forwrd nd nverse ge wrpng Consrucng oscs Hoogrphes Rous fng wh RANSAC Krsen Grun UT-Ausn Mn quesons Movon: Recognon T Wrpng: Gven source ge nd
Tod Algnen & Wrpng Thursd, Oc 9 Algnen & wrpng d rnsforons Forwrd nd nverse ge wrpng Consrucng oscs Hoogrphes Rous fng wh RANSAC Krsen Grun UT-Ausn Mn quesons Movon: Recognon T Wrpng: Gven source ge nd
r = cos θ + 1. dt ) dt. (1)
 MTHE 7 Proble Set 5 Solutions (A Crdioid). Let C be the closed curve in R whose polr coordintes (r, θ) stisfy () Sketch the curve C. r = cos θ +. (b) Find pretriztion t (r(t), θ(t)), t [, b], of C in polr
MTHE 7 Proble Set 5 Solutions (A Crdioid). Let C be the closed curve in R whose polr coordintes (r, θ) stisfy () Sketch the curve C. r = cos θ +. (b) Find pretriztion t (r(t), θ(t)), t [, b], of C in polr
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture #4
 PHYSICS 5 Noe for Online Lecure #4 Acceleraion The ga pedal in a car i alo called an acceleraor becaue preing i allow you o change your elociy. Acceleraion i how fa he elociy change. So if you ar fro re
PHYSICS 5 Noe for Online Lecure #4 Acceleraion The ga pedal in a car i alo called an acceleraor becaue preing i allow you o change your elociy. Acceleraion i how fa he elociy change. So if you ar fro re
Speech, NLP and the Web
 peech NL ad he Web uhpak Bhaacharyya CE Dep. IIT Bombay Lecure 38: Uuperved learg HMM CFG; Baum Welch lecure 37 wa o cogve NL by Abh Mhra Baum Welch uhpak Bhaacharyya roblem HMM arg emac ar of peech Taggg
peech NL ad he Web uhpak Bhaacharyya CE Dep. IIT Bombay Lecure 38: Uuperved learg HMM CFG; Baum Welch lecure 37 wa o cogve NL by Abh Mhra Baum Welch uhpak Bhaacharyya roblem HMM arg emac ar of peech Taggg
A Group Key Management Scheme Based on Random Transmission for VANET Liang PANG1, b, Da WEI1, 2, Qi ZHAO3, Jianqi ZHU1, 2, a
 6h Inernonl Conference on Mchnery, Merl, Envronmen, Boechnology nd Compuer (MMEBC 06) A Group ey Mngemen cheme Bed on Rndom rnmon for ANE ng PANG, b, D WEI,, Q ZHAO3, Jn ZHU,, College of Compuer cence
6h Inernonl Conference on Mchnery, Merl, Envronmen, Boechnology nd Compuer (MMEBC 06) A Group ey Mngemen cheme Bed on Rndom rnmon for ANE ng PANG, b, D WEI,, Q ZHAO3, Jn ZHU,, College of Compuer cence
CHAPTER II AC POWER CALCULATIONS
 CHAE AC OWE CACUAON Conens nroducon nsananeous and Aerage ower Effece or M alue Apparen ower Coplex ower Conseraon of AC ower ower Facor and ower Facor Correcon Maxu Aerage ower ransfer Applcaons 3 nroducon
CHAE AC OWE CACUAON Conens nroducon nsananeous and Aerage ower Effece or M alue Apparen ower Coplex ower Conseraon of AC ower ower Facor and ower Facor Correcon Maxu Aerage ower ransfer Applcaons 3 nroducon
Learning Objectives. Self Organization Map. Hamming Distance(1/5) Introduction. Hamming Distance(3/5) Hamming Distance(2/5) 15/04/2015
 /4/ Learnng Objecves Self Organzaon Map Learnng whou Exaples. Inroducon. MAXNET 3. Cluserng 4. Feaure Map. Self-organzng Feaure Map 6. Concluson 38 Inroducon. Learnng whou exaples. Daa are npu o he syse
/4/ Learnng Objecves Self Organzaon Map Learnng whou Exaples. Inroducon. MAXNET 3. Cluserng 4. Feaure Map. Self-organzng Feaure Map 6. Concluson 38 Inroducon. Learnng whou exaples. Daa are npu o he syse
Lecture Slides for INTRODUCTION TO. Machine Learning. ETHEM ALPAYDIN The MIT Press,
 Lecure Sldes for INTRDUCTIN T Machne Learnng ETHEM ALAYDIN The MIT ress, 2004 alpaydn@boun.edu.r hp://www.cmpe.boun.edu.r/~ehem/2ml CHATER 3: Hdden Marov Models Inroducon Modelng dependences n npu; no
Lecure Sldes for INTRDUCTIN T Machne Learnng ETHEM ALAYDIN The MIT ress, 2004 alpaydn@boun.edu.r hp://www.cmpe.boun.edu.r/~ehem/2ml CHATER 3: Hdden Marov Models Inroducon Modelng dependences n npu; no
BEST PATTERN OF MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION
 ERI COADA GERMAY GEERAL M.R. SEFAIK AIR FORCE ACADEMY ARMED FORCES ACADEMY ROMAIA SLOVAK REPUBLIC IERAIOAL COFERECE of SCIEIFIC PAPER AFASES Brov 6-8 M BES PAER OF MULIPLE LIEAR REGRESSIO Corel GABER PEROLEUM-GAS
ERI COADA GERMAY GEERAL M.R. SEFAIK AIR FORCE ACADEMY ARMED FORCES ACADEMY ROMAIA SLOVAK REPUBLIC IERAIOAL COFERECE of SCIEIFIC PAPER AFASES Brov 6-8 M BES PAER OF MULIPLE LIEAR REGRESSIO Corel GABER PEROLEUM-GAS
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Optimality of Myopic Policy for a Class of Monotone Affine Restless Multi-Armed Bandit
 Univeriy of Souhern Cliforni Opimliy of Myopic Policy for Cl of Monoone Affine Rele Muli-Armed Bndi Pri Mnourifrd USC Tr Jvidi UCSD Bhkr Krihnmchri USC Dec 0, 202 Univeriy of Souhern Cliforni Inroducion
Univeriy of Souhern Cliforni Opimliy of Myopic Policy for Cl of Monoone Affine Rele Muli-Armed Bndi Pri Mnourifrd USC Tr Jvidi UCSD Bhkr Krihnmchri USC Dec 0, 202 Univeriy of Souhern Cliforni Inroducion
P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9
 P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 J A R T a l s o c o n c l u d e d t h a t a l t h o u g h t h e i n t e n t o f N e l s o n s r e h a b i l i t a t i o n p l a n i s t o e n h a n c e c o n n e
P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 J A R T a l s o c o n c l u d e d t h a t a l t h o u g h t h e i n t e n t o f N e l s o n s r e h a b i l i t a t i o n p l a n i s t o e n h a n c e c o n n e
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Physics 110. Spring Exam #1. April 23, 2008
 hyc Spng 8 E # pl 3, 8 Ne Soluon Mulple Choce / oble # / 8 oble # / oble #3 / 8 ol / In keepng wh he Unon College polcy on cdec honey, ued h you wll nehe ccep no pode unuhozed nce n he copleon o h wok.
hyc Spng 8 E # pl 3, 8 Ne Soluon Mulple Choce / oble # / 8 oble # / oble #3 / 8 ol / In keepng wh he Unon College polcy on cdec honey, ued h you wll nehe ccep no pode unuhozed nce n he copleon o h wok.
Reinforcement learning
 CS 75 Mchine Lening Lecue b einfocemen lening Milos Huskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Sque einfocemen lening We wn o len conol policy: : X A We see emples of bu oupus e no given Insed of we ge feedbck
CS 75 Mchine Lening Lecue b einfocemen lening Milos Huskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Sque einfocemen lening We wn o len conol policy: : X A We see emples of bu oupus e no given Insed of we ge feedbck
