CFG PSA Algorithm. Sequence Alignment Guided By Common Motifs Described By Context Free Grammars
|
|
|
- Polly Watkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FG PS lgorithm Sequence lignment Guided By ommon Motifs Described By ontext Free Grammars
2 motivation Find motifs- conserved regions that indicate a biological function or signature. Other algorithm do not always align motif regions together. Incorporate knowledge about common structures into the alignment process. Forcing the alignments align such common motifs. Internal Loop External Base Hairpin Loop Multi-loop Bulge Hairpin Loop
3 The goal To align sequences in a way to include all or some of the motif-matches in an order to optimize the resulting score. Example k+1 max z i, wi + max β(g) i=1 y,x G, G (,)+(G,G)+(UU,U)+(G,G)+ β(g 1 )+β(g 2 )+β(g 3 )
4 Problem definition Let (u, v) denote the maximum ordinary alignment score for strings u and v that can be computed using the lignment algorithm. Given: two sequences S1 and S2 set of context-free grammars = {G 1,..., G f } each of which represents a motif with all its possible variations. weight function β(g) ompute: k+1 max i=1 Z i, wi + max X,Y G, G β(g) over all possible X 1, X 2,...,X k, Y 1, Y 2,..., Y k S1 = z 1 x 1 z 2 x 2... z k x k z k+1 S2 = w 1 y 1 w 2 y 2...w k y k w k+1 Each Z j or w j, 1 <= j <= k + 1, can be an empty string For all I 1<= i<= k, there exists a G such that y i, x i L G, where L(G) is the language generated by FG G. motif-matching region
5 ={G 1, G 2, G 3, G } G 1 =(V,T,P,V 0 ) context free grammar Set of variables V = {V 0, V 1, V 2 } V 0 is a start variable Terminal symbols T = {,U,,G} Set of rules: V0 --> V 1 G GV 1 V1 --> GV 2 V2 --> G G 2 ={ {V 0, V 1, V 2 }, {,U,,G}, p, V 0 } Set of rules: V0 --> V 1 U UV 1 V1 --> V 2 G V2 --> GG G 3 ={ {V 0, V 1, V 2, V 3 }, {,U,,G}, p, V 0 } Set of rules: V0 --> V 1 U GV 1 V 1 G V1 --> V 2 U V2 --> V 3 U UV 3 V3-->
6 Reminder YK lgorithm YK is an algorithm that receives a NF, G, and a string S, and determines if S can be produced from G, and how. Parsell Parsell is a modification of YK that receives a NF, G, and a string S, and finds all of the substrings of S that can be produced from G. NF homsky normal form NF is a FG in which all of the production rules are of one of the forms: V TS V a S ε Every FG is easily convertible to NF by following a simple algorithm.
7 Running Example: NF G V0 B you 1 No 2 one B B2 can B2 understand DP it. D Dynamic P Programming String S = Poor fool, do you think you can understand Dynamic Programming? No one can understand it.
8 you can understand Running Example: T[,]={} T[,]={} T[,]={} T[,]={} D Dynamic T[,]={D} P Programming T[,]={P} 1 No T[,]={1} 2 one T[,]={2} can T[,]={} understand T[,]={} it T[1,1]={} String S = Poor fool, do you think you can understand Dynamic Programming? No one can understand it.
9 Running Example: 1 D P 1 2 1
10 Running Example: DP B2 1 D P 1 2 B2 1
11 Running Example: B2 B B2 1 B2 D P 1 2 B B2 1
12 Running Example: B B2 1 B B2 D P 1 2 B B2 1
13 Running Example: V0 B V0 B 1 V0 B B2 D P 1 V0 2 B B2 1
14 Running Example: S1 = [,] S2=[,1] 1 V0 B B2 D P 1 V0 2 B B2 1
15 lgorithm Parsell (input string S, length n, FG G) Step 1. Find the substrings derived by the rules of the form X a: for i =1 to n do set T[i, i]= ϕ for each variable X if X S[i] is a rule then add X to T[i, i] Step 2. Find the substrings derived by the rules of the form X YZ: for l =2 to n do for i =1 to n - l +1 do set j = i + l 1 for k = i to j - 1 do for each rule X YZ if Y T[i, k] and Z T[k +1,j] Then add X to T[i, j] Step 3. Return the set of all substrings generated by G: P = ϕ for i =1 to n do for j = i to n do if V0 T[i, j] then add (i, j) to P return P Runtime = O( G N 3 )
16 -1-1 _ G G G U _ G G G G U
17 Preprocessing For all G k in do: X k parsell(s 1,n 1,G k) Y k parsell(s 2,n 2,G k) Move every (i',i) X k to list X as (i,j,k) Move every (i',i) Y k to list Y as (i,j,k) Sort X & Y in ascending order of the end points i'. Y (1,2,) (2,, 1) (3,, ) (,, 1) (3,, 2) (,, ) (,, 1) (,1, 3) X (1,, 2) (2,, ) (,, 3) (3,, 2) (,, 1) (2,, ) (,, 3) i= j=
18 Time omplexity of Where N=max{N 1,N 2 } Running Parsell for nd creating X, Y: Sorting X, Y: O( N 3 ) O( X log X + Y log Y ) omputing the maxterms: O( X Y + N 2 ) Because of the usual N 2 table checking, and the new maxterm: max{h(i,j ) +β(g k1 )} (i,i,k 1,j,j,k 2 ) X i *Y j,g k1 =G k2 Which passes every NF in X and Y and check for matching NFs. Total time complexity: O( N 3 + X Y )
19 Possible Modifications ffine gap penalties local alignment computations more advanced algorithms used in the alignment of non-motif-matching regions. Same or better complexity. Solve the general problem of optimally aligning multiple sequences guided by a given set of motifs described by FGs.
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Pattern Matching (Exact Matching) Overview
 CSI/BINF 5330 Pattern Matching (Exact Matching) Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University Overview Pattern Matching Exhaustive Search DFA Algorithm KMP Algorithm
CSI/BINF 5330 Pattern Matching (Exact Matching) Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University Overview Pattern Matching Exhaustive Search DFA Algorithm KMP Algorithm
Computability Theory
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7
 Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about
Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Chapter 6. Properties of Regular Languages
 Chapter 6 Properties of Regular Languages Regular Sets and Languages Claim(1). The family of languages accepted by FSAs consists of precisely the regular sets over a given alphabet. Every regular set is
Chapter 6 Properties of Regular Languages Regular Sets and Languages Claim(1). The family of languages accepted by FSAs consists of precisely the regular sets over a given alphabet. Every regular set is
Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y.
 CSE2001, Fall 2006 1 Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y. S 00S1 A - xay, where x = 2 y.
CSE2001, Fall 2006 1 Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y. S 00S1 A - xay, where x = 2 y.
Efficient Divide-and-Conquer Parsing of Practical Context-Free Languages
 Efficient Divide-and-onquer Parsing of Practical ontext-free Languages Jean-Philippe ernardy Koen laessen LASP Seminar, Nov 14, 2016 FP workhorse: lists : 1 : 2 : 3 : 4 [] FP workhorse: lists : 1 : 2 :
Efficient Divide-and-onquer Parsing of Practical ontext-free Languages Jean-Philippe ernardy Koen laessen LASP Seminar, Nov 14, 2016 FP workhorse: lists : 1 : 2 : 3 : 4 [] FP workhorse: lists : 1 : 2 :
CSE182-L7. Protein Sequence Analysis Patterns (regular expressions) Profiles HMM Gene Finding CSE182
 CSE182-L7 Protein Sequence Analysis Patterns (regular expressions) Profiles HMM Gene Finding 10-07 CSE182 Bell Labs Honors Pattern matching 10-07 CSE182 Just the Facts Consider the set of all substrings
CSE182-L7 Protein Sequence Analysis Patterns (regular expressions) Profiles HMM Gene Finding 10-07 CSE182 Bell Labs Honors Pattern matching 10-07 CSE182 Just the Facts Consider the set of all substrings
V Honors Theory of Computation
 V22.0453-001 Honors Theory of Computation Problem Set 3 Solutions Problem 1 Solution: The class of languages recognized by these machines is the exactly the class of regular languages, thus this TM variant
V22.0453-001 Honors Theory of Computation Problem Set 3 Solutions Problem 1 Solution: The class of languages recognized by these machines is the exactly the class of regular languages, thus this TM variant
Solutions to Problem Set 3
 V22.0453-001 Theory of Computation October 8, 2003 TA: Nelly Fazio Solutions to Problem Set 3 Problem 1 We have seen that a grammar where all productions are of the form: A ab, A c (where A, B non-terminals,
V22.0453-001 Theory of Computation October 8, 2003 TA: Nelly Fazio Solutions to Problem Set 3 Problem 1 We have seen that a grammar where all productions are of the form: A ab, A c (where A, B non-terminals,
Sequence Bioinformatics. Multiple Sequence Alignment Waqas Nasir
 Sequence Bioinformatics Multiple Sequence Alignment Waqas Nasir 2010-11-12 Multiple Sequence Alignment One amino acid plays coy; a pair of homologous sequences whisper; many aligned sequences shout out
Sequence Bioinformatics Multiple Sequence Alignment Waqas Nasir 2010-11-12 Multiple Sequence Alignment One amino acid plays coy; a pair of homologous sequences whisper; many aligned sequences shout out
Homework 4. Chapter 7. CS A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science. By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz
 CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 4 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 7 Problem: Chap 7.1 part a This PDA accepts the language
CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 4 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 7 Problem: Chap 7.1 part a This PDA accepts the language
Multiple Alignment. Slides revised and adapted to Bioinformática IST Ana Teresa Freitas
 n Introduction to Bioinformatics lgorithms Multiple lignment Slides revised and adapted to Bioinformática IS 2005 na eresa Freitas n Introduction to Bioinformatics lgorithms Outline Dynamic Programming
n Introduction to Bioinformatics lgorithms Multiple lignment Slides revised and adapted to Bioinformática IS 2005 na eresa Freitas n Introduction to Bioinformatics lgorithms Outline Dynamic Programming
Multiple Sequence Alignment (MAS)
 Multiple Sequence lignment (MS) Group-to-group alignments Steven driaensen & Ken Tanaka References Osamu Goto Optimal lignment between groups of sequences and its application to multiple sequence alignment
Multiple Sequence lignment (MS) Group-to-group alignments Steven driaensen & Ken Tanaka References Osamu Goto Optimal lignment between groups of sequences and its application to multiple sequence alignment
Dynamic Programming. Weighted Interval Scheduling. Algorithmic Paradigms. Dynamic Programming
 lgorithmic Paradigms Dynamic Programming reed Build up a solution incrementally, myopically optimizing some local criterion Divide-and-conquer Break up a problem into two sub-problems, solve each sub-problem
lgorithmic Paradigms Dynamic Programming reed Build up a solution incrementally, myopically optimizing some local criterion Divide-and-conquer Break up a problem into two sub-problems, solve each sub-problem
Sequence Alignment (chapter 6)
 Sequence lignment (chapter 6) he biological problem lobal alignment Local alignment Multiple alignment Introduction to bioinformatics, utumn 6 Background: comparative genomics Basic question in biology:
Sequence lignment (chapter 6) he biological problem lobal alignment Local alignment Multiple alignment Introduction to bioinformatics, utumn 6 Background: comparative genomics Basic question in biology:
The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars
 The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) is a simple and useful form of a CFG Every rule of a CNF grammar is in the form A BC A a Where a is any terminal
The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) is a simple and useful form of a CFG Every rule of a CNF grammar is in the form A BC A a Where a is any terminal
L bor y nnd Union One nnd Inseparable. LOW I'LL, MICHIGAN. WLDNHSDA Y. JULY ), I8T. liuwkll NATIdiNAI, liank
 G k y $5 y / >/ k «««# ) /% < # «/» Y»««««?# «< >«>» y k»» «k F 5 8 Y Y F G k F >«y y
G k y $5 y / >/ k «««# ) /% < # «/» Y»««««?# «< >«>» y k»» «k F 5 8 Y Y F G k F >«y y
Top-Down Parsing and Intro to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Predictive Parsers op-down Parsing and Intro to Bottom-Up Parsing Lecture 7 Like recursive-descent but parser can predict which production to use By looking at the next few tokens No backtracking Predictive
Predictive Parsers op-down Parsing and Intro to Bottom-Up Parsing Lecture 7 Like recursive-descent but parser can predict which production to use By looking at the next few tokens No backtracking Predictive
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG:
![Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG: Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG:](/thumbs/87/95229917.jpg) Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] S X T#X X#T T#X#T X axa bxb #T# # T at bt #T ε Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG: R XRX S S atb bta T XTX X ε X a b q start ε, ε $ ε, R X ε, ε R ε, ε X ε, R S ε, T X ε, T ε ε, X a
Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] S X T#X X#T T#X#T X axa bxb #T# # T at bt #T ε Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG: R XRX S S atb bta T XTX X ε X a b q start ε, ε $ ε, R X ε, ε R ε, ε X ε, R S ε, T X ε, T ε ε, X a
Flexible RNA design under structure and sequence constraints using a language theoretic approach
 Flexible RN design under structure and sequence constraints using a language theoretic approach Yu Zhou,, Yann Ponty Stéphane Vialette Jérôme Waldispühl Yi Zhang lain Denise LRI, niv. Paris-Sud, Orsay
Flexible RN design under structure and sequence constraints using a language theoretic approach Yu Zhou,, Yann Ponty Stéphane Vialette Jérôme Waldispühl Yi Zhang lain Denise LRI, niv. Paris-Sud, Orsay
CS 301. Lecture 18 Decidable languages. Stephen Checkoway. April 2, 2018
 CS 301 Lecture 18 Decidable languages Stephen Checkoway April 2, 2018 1 / 26 Decidable language Recall, a language A is decidable if there is some TM M that 1 recognizes A (i.e., L(M) = A), and 2 halts
CS 301 Lecture 18 Decidable languages Stephen Checkoway April 2, 2018 1 / 26 Decidable language Recall, a language A is decidable if there is some TM M that 1 recognizes A (i.e., L(M) = A), and 2 halts
1. Induction on Strings
 CS/ECE 374: Algorithms & Models of Computation Version: 1.0 Fall 2017 This is a core dump of potential questions for Midterm 1. This should give you a good idea of the types of questions that we will ask
CS/ECE 374: Algorithms & Models of Computation Version: 1.0 Fall 2017 This is a core dump of potential questions for Midterm 1. This should give you a good idea of the types of questions that we will ask
HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review. Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed
 HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed For the most part, all about strings! String induction (to some extent) Regular languages Regular expressions (regexps) Deterministic finite
HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed For the most part, all about strings! String induction (to some extent) Regular languages Regular expressions (regexps) Deterministic finite
Theory of Computation (IX) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IX) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review The Definition of Algorithm Polynomials and their roots A polynomial is a sum of terms, where each term is a product of certain variables and
Theory of Computation (IX) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review The Definition of Algorithm Polynomials and their roots A polynomial is a sum of terms, where each term is a product of certain variables and
Background: comparative genomics. Sequence similarity. Homologs. Similarity vs homology (2) Similarity vs homology. Sequence Alignment (chapter 6)
 Sequence lignment (chapter ) he biological problem lobal alignment Local alignment Multiple alignment Background: comparative genomics Basic question in biology: what properties are shared among organisms?
Sequence lignment (chapter ) he biological problem lobal alignment Local alignment Multiple alignment Background: comparative genomics Basic question in biology: what properties are shared among organisms?
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Even More on Dynamic Programming
 Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Even More on Dynamic Programming Lecture 15 Thursday, October 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 26 Part I Longest Common Subsequence
Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Even More on Dynamic Programming Lecture 15 Thursday, October 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 26 Part I Longest Common Subsequence
A graph kernel approach to the identification and characterisation of structured non-coding RNAs using multiple sequence alignment information
 graph kernel approach to the identification and characterisation of structured noncoding RNs using multiple sequence alignment information Mariam lshaikh lbert Ludwigs niversity Freiburg, Department of
graph kernel approach to the identification and characterisation of structured noncoding RNs using multiple sequence alignment information Mariam lshaikh lbert Ludwigs niversity Freiburg, Department of
Part 4 out of 5 DFA NFA REX. Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 4 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 12 2017 Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 4 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 12 2017 Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
3130CIT Theory of Computation
 GRIFFITH UNIVERSITY School of Computing and Information Technology 3130CIT Theory of Computation Final Examination, Semester 2, 2006 Details Total marks: 120 (40% of the total marks for this subject) Perusal:
GRIFFITH UNIVERSITY School of Computing and Information Technology 3130CIT Theory of Computation Final Examination, Semester 2, 2006 Details Total marks: 120 (40% of the total marks for this subject) Perusal:
Computational Models - Lecture 4
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs
 CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
Combinatorial approaches to RNA folding Part II: Energy minimization via dynamic programming
 ombinatorial approaches to RNA folding Part II: Energy minimization via dynamic programming Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences lemson niversity http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math
ombinatorial approaches to RNA folding Part II: Energy minimization via dynamic programming Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences lemson niversity http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing expands a parse tree
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing expands a parse tree
Fooling Sets and. Lecture 5
 Fooling Sets and Introduction to Nondeterministic Finite Automata Lecture 5 Proving that a language is not regular Given a language, we saw how to prove it is regular (union, intersection, concatenation,
Fooling Sets and Introduction to Nondeterministic Finite Automata Lecture 5 Proving that a language is not regular Given a language, we saw how to prove it is regular (union, intersection, concatenation,
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing
Searching Sear ( Sub- (Sub )Strings Ulf Leser
 Searching (Sub-)Strings Ulf Leser This Lecture Exact substring search Naïve Boyer-Moore Searching with profiles Sequence profiles Ungapped approximate search Statistical evaluation of search results Ulf
Searching (Sub-)Strings Ulf Leser This Lecture Exact substring search Naïve Boyer-Moore Searching with profiles Sequence profiles Ungapped approximate search Statistical evaluation of search results Ulf
Conflict Removal. Less Than, Equals ( <= ) Conflict
 Conflict Removal As you have observed in a recent example, not all context free grammars are simple precedence grammars. You have also seen that a context free grammar that is not a simple precedence grammar
Conflict Removal As you have observed in a recent example, not all context free grammars are simple precedence grammars. You have also seen that a context free grammar that is not a simple precedence grammar
The Real Story on Synchronous Rewriting Systems. Daniel Gildea Computer Science Department University of Rochester
 The Real Story on Synchronous Rewriting Systems Daniel Gildea omputer Science Department University of Rochester Overview Factorization Tree Decomposition Factorization of LFRS YK Parsing w 2 : [, x 1,
The Real Story on Synchronous Rewriting Systems Daniel Gildea omputer Science Department University of Rochester Overview Factorization Tree Decomposition Factorization of LFRS YK Parsing w 2 : [, x 1,
Intro to Theory of Computation
 Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
98 Algorithms in Bioinformatics I, WS 06, ZBIT, D. Huson, December 6, 2006
 98 Algorithms in Bioinformatics I, WS 06, ZBIT, D. Huson, December 6, 2006 8.3.1 Simple energy minimization Maximizing the number of base pairs as described above does not lead to good structure predictions.
98 Algorithms in Bioinformatics I, WS 06, ZBIT, D. Huson, December 6, 2006 8.3.1 Simple energy minimization Maximizing the number of base pairs as described above does not lead to good structure predictions.
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing expands a parse tree from
Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing expands a parse tree from
CISC4090: Theory of Computation
 CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules).
 Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 /9/ lgorithmic Paradigms hapter Dynamic Programming reed. Build up a solution incrementally, myopically optimizing some local criterion. Divide-and-conquer. Break up a problem into two sub-problems, solve
/9/ lgorithmic Paradigms hapter Dynamic Programming reed. Build up a solution incrementally, myopically optimizing some local criterion. Divide-and-conquer. Break up a problem into two sub-problems, solve
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing
Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing
How to write proofs - II
 How to write proofs - II Problem (Ullman and Hopcroft, Page 104, Exercise 4.8). Let G be the grammar Prove that S ab ba A a as baa B b bs abb L(G) = { x {a, b} x contains equal number of a s and b s }.
How to write proofs - II Problem (Ullman and Hopcroft, Page 104, Exercise 4.8). Let G be the grammar Prove that S ab ba A a as baa B b bs abb L(G) = { x {a, b} x contains equal number of a s and b s }.
October 6, Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Gramm
 Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Chapter 0 Introduction. Fourth Academic Year/ Elective Course Electrical Engineering Department College of Engineering University of Salahaddin
 Chapter 0 Introduction Fourth Academic Year/ Elective Course Electrical Engineering Department College of Engineering University of Salahaddin October 2014 Automata Theory 2 of 22 Automata theory deals
Chapter 0 Introduction Fourth Academic Year/ Elective Course Electrical Engineering Department College of Engineering University of Salahaddin October 2014 Automata Theory 2 of 22 Automata theory deals
Fall 1999 Formal Language Theory Dr. R. Boyer. 1. There are other methods of nding a regular expression equivalent to a nite automaton in
 Fall 1999 Formal Language Theory Dr. R. Boyer Week Four: Regular Languages; Pumping Lemma 1. There are other methods of nding a regular expression equivalent to a nite automaton in addition to the ones
Fall 1999 Formal Language Theory Dr. R. Boyer Week Four: Regular Languages; Pumping Lemma 1. There are other methods of nding a regular expression equivalent to a nite automaton in addition to the ones
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
RNA Basics. RNA bases A,C,G,U Canonical Base Pairs A-U G-C G-U. Bases can only pair with one other base. wobble pairing. 23 Hydrogen Bonds more stable
 RNA STRUCTURE RNA Basics RNA bases A,C,G,U Canonical Base Pairs A-U G-C G-U wobble pairing Bases can only pair with one other base. 23 Hydrogen Bonds more stable RNA Basics transfer RNA (trna) messenger
RNA STRUCTURE RNA Basics RNA bases A,C,G,U Canonical Base Pairs A-U G-C G-U wobble pairing Bases can only pair with one other base. 23 Hydrogen Bonds more stable RNA Basics transfer RNA (trna) messenger
Context-free grammars and languages
 Context-free grammars and languages The next class of languages we will study in the course is the class of context-free languages. They are defined by the notion of a context-free grammar, or a CFG for
Context-free grammars and languages The next class of languages we will study in the course is the class of context-free languages. They are defined by the notion of a context-free grammar, or a CFG for
Context Free Languages. Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6. Languages That Are Not Regular. Non-Regular Languages
 Context Free Languages Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6 Context Free Languages Last Time Decision procedures for FAs Minimum-state DFAs Today The Myhill-Nerode Theorem The Pumping Lemma Context-free
Context Free Languages Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6 Context Free Languages Last Time Decision procedures for FAs Minimum-state DFAs Today The Myhill-Nerode Theorem The Pumping Lemma Context-free
Areas. ! Bioinformatics. ! Control theory. ! Information theory. ! Operations research. ! Computer science: theory, graphics, AI, systems,.
 lgorithmic Paradigms hapter Dynamic Programming reed Build up a solution incrementally, myopically optimizing some local criterion Divide-and-conquer Break up a problem into two sub-problems, solve each
lgorithmic Paradigms hapter Dynamic Programming reed Build up a solution incrementally, myopically optimizing some local criterion Divide-and-conquer Break up a problem into two sub-problems, solve each
Turing Machines (TM) Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM) Nondeterministic Turing Machine (NDTM)
 Turing Machines (TM) Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM) Nondeterministic Turing Machine (NDTM) 1 Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM).. B B 0 1 1 0 0 B B.. Finite Control Two-way, infinite tape, broken into
Turing Machines (TM) Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM) Nondeterministic Turing Machine (NDTM) 1 Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM).. B B 0 1 1 0 0 B B.. Finite Control Two-way, infinite tape, broken into
What we have done so far
 What we have done so far DFAs and regular languages NFAs and their equivalence to DFAs Regular expressions. Regular expressions capture exactly regular languages: Construct a NFA from a regular expression.
What we have done so far DFAs and regular languages NFAs and their equivalence to DFAs Regular expressions. Regular expressions capture exactly regular languages: Construct a NFA from a regular expression.
Lecture 4: September 19
 CSCI1810: Computational Molecular Biology Fall 2017 Lecture 4: September 19 Lecturer: Sorin Istrail Scribe: Cyrus Cousins Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes
CSCI1810: Computational Molecular Biology Fall 2017 Lecture 4: September 19 Lecturer: Sorin Istrail Scribe: Cyrus Cousins Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes
RNA Abstract Shape Analysis
 ourse: iegerich RN bstract nalysis omplete shape iegerich enter of Biotechnology Bielefeld niversity robert@techfak.ni-bielefeld.de ourse on omputational RN Biology, Tübingen, March 2006 iegerich ourse:
ourse: iegerich RN bstract nalysis omplete shape iegerich enter of Biotechnology Bielefeld niversity robert@techfak.ni-bielefeld.de ourse on omputational RN Biology, Tübingen, March 2006 iegerich ourse:
Multiple Sequence Alignment
 Multiple equence lignment Four ami Khuri Dept of omputer cience an José tate University Multiple equence lignment v Progressive lignment v Guide Tree v lustalw v Toffee v Muscle v MFFT * 20 * 0 * 60 *
Multiple equence lignment Four ami Khuri Dept of omputer cience an José tate University Multiple equence lignment v Progressive lignment v Guide Tree v lustalw v Toffee v Muscle v MFFT * 20 * 0 * 60 *
Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Algorithms in Bioinformatics Sami Khuri Department of omputer Science San José State University San José, alifornia, USA khuri@cs.sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Pairwise Sequence Alignment Homology
Algorithms in Bioinformatics Sami Khuri Department of omputer Science San José State University San José, alifornia, USA khuri@cs.sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Pairwise Sequence Alignment Homology
Crew of25 Men Start Monday On Showboat. Many Permanent Improvements To Be Made;Project Under WPA
 U G G G U 2 93 YX Y q 25 3 < : z? 0 (? 8 0 G 936 x z x z? \ 9 7500 00? 5 q 938 27? 60 & 69? 937 q? G x? 937 69 58 } x? 88 G # x 8 > x G 0 G 0 x 8 x 0 U 93 6 ( 2 x : X 7 8 G G G q x U> x 0 > x < x G U 5
U G G G U 2 93 YX Y q 25 3 < : z? 0 (? 8 0 G 936 x z x z? \ 9 7500 00? 5 q 938 27? 60 & 69? 937 q? G x? 937 69 58 } x? 88 G # x 8 > x G 0 G 0 x 8 x 0 U 93 6 ( 2 x : X 7 8 G G G q x U> x 0 > x < x G U 5
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory Course Notes Part II: The Recognition Problem (II) Chapter II.4.: Properties of Regular Languages (13) Anton Setzer (Based on a book draft by J. V. Tucker and
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory Course Notes Part II: The Recognition Problem (II) Chapter II.4.: Properties of Regular Languages (13) Anton Setzer (Based on a book draft by J. V. Tucker and
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
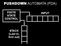 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
Homework 5 - Solution
 DCP3122 Introduction to Formal Languages, Spring 2015 Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 5 - Solution 5-May-2015 Due: 18-May-2015 1. Given Σ = {a, b, c}, find an NPDA that accepts L = {a n b n+m
DCP3122 Introduction to Formal Languages, Spring 2015 Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 5 - Solution 5-May-2015 Due: 18-May-2015 1. Given Σ = {a, b, c}, find an NPDA that accepts L = {a n b n+m
10. The GNFA method is used to show that
 CSE 355 Midterm Examination 27 February 27 Last Name Sample ASU ID First Name(s) Ima Exam # Sample Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been recorded correctly, return the entire
CSE 355 Midterm Examination 27 February 27 Last Name Sample ASU ID First Name(s) Ima Exam # Sample Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been recorded correctly, return the entire
Local Alignment of RNA Sequences with Arbitrary Scoring Schemes
 Local Alignment of RNA Sequences with Arbitrary Scoring Schemes Rolf Backofen 1, Danny Hermelin 2, ad M. Landau 2,3, and Oren Weimann 4 1 Institute of omputer Science, Albert-Ludwigs niversität Freiburg,
Local Alignment of RNA Sequences with Arbitrary Scoring Schemes Rolf Backofen 1, Danny Hermelin 2, ad M. Landau 2,3, and Oren Weimann 4 1 Institute of omputer Science, Albert-Ludwigs niversität Freiburg,
ECS 120 Lesson 20 The Post Correspondence Problem
 ECS 120 Lesson 20 The Post Correspondence Problem Oliver Kreylos Wednesday, May 16th, 2001 Today we will continue yesterday s discussion of reduction techniques by looking at another common strategy, reduction
ECS 120 Lesson 20 The Post Correspondence Problem Oliver Kreylos Wednesday, May 16th, 2001 Today we will continue yesterday s discussion of reduction techniques by looking at another common strategy, reduction
X-MA2C01-1: Partial Worked Solutions
 X-MAC01-1: Partial Worked Solutions David R. Wilkins May 013 1. (a) Let A, B and C be sets. Prove that (A \ (B C)) (B \ C) = (A B) \ C. [Venn Diagrams, by themselves without an accompanying logical argument,
X-MAC01-1: Partial Worked Solutions David R. Wilkins May 013 1. (a) Let A, B and C be sets. Prove that (A \ (B C)) (B \ C) = (A B) \ C. [Venn Diagrams, by themselves without an accompanying logical argument,
Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Laurent Vanbever. ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October,
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 5 2017 Part 3 out of 5 Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 5 2017 Part 3 out of 5 Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular
Part 3 out of 5. Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular languages
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 3 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 5 2017 Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 3 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 5 2017 Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular
Context Free Grammars: Introduction. Context Free Grammars: Simplifying CFGs
 Context Free Grammars: Introduction CFGs are more powerful than RGs because of the following 2 properties: 1. Recursion Rule is recursive if it is of the form X w 1 Y w 2, where Y w 3 Xw 4 and w 1, w 2,
Context Free Grammars: Introduction CFGs are more powerful than RGs because of the following 2 properties: 1. Recursion Rule is recursive if it is of the form X w 1 Y w 2, where Y w 3 Xw 4 and w 1, w 2,
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture)
 Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Computational Models: Class 3
 Computational Models: Class 3 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University November 2, 2015 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Computational Models: Class 3 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University November 2, 2015 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs
 Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
NODIA AND COMPANY. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer Science Engineering Theory of Computation. Copyright By NODIA & COMPANY
 No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer
No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer
Chapter 6. Weighted Interval Scheduling. Dynamic Programming. Algorithmic Paradigms. Dynamic Programming Applications
 lgorithmic Paradigms hapter Dynamic Programming reedy. Build up a solution incrementally, myopically optimizing some local criterion. Divide-and-conquer. Break up a problem into sub-problems, solve each
lgorithmic Paradigms hapter Dynamic Programming reedy. Build up a solution incrementally, myopically optimizing some local criterion. Divide-and-conquer. Break up a problem into sub-problems, solve each
Turing Machines Part III
 Turing Machines Part III Announcements Problem Set 6 due now. Problem Set 7 out, due Monday, March 4. Play around with Turing machines, their powers, and their limits. Some problems require Wednesday's
Turing Machines Part III Announcements Problem Set 6 due now. Problem Set 7 out, due Monday, March 4. Play around with Turing machines, their powers, and their limits. Some problems require Wednesday's
LOWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y G y G Y 87 y Y 8 Y - $ X ; ; y y q 8 y $8 $ $ $ G 8 q < 8 6 4 y 8 7 4 8 8 < < y 6 $ q - - y G y G - Y y y 8 y y y Y Y 7-7- G - y y y ) y - y y y y - - y - y 87 7-7- G G < G y G y y 6 X y G y y y 87 G
Y G y G Y 87 y Y 8 Y - $ X ; ; y y q 8 y $8 $ $ $ G 8 q < 8 6 4 y 8 7 4 8 8 < < y 6 $ q - - y G y G - Y y y 8 y y y Y Y 7-7- G - y y y ) y - y y y y - - y - y 87 7-7- G G < G y G y y 6 X y G y y y 87 G
Dynamic Programming. Shuang Zhao. Microsoft Research Asia September 5, Dynamic Programming. Shuang Zhao. Outline. Introduction.
 Microsoft Research Asia September 5, 2005 1 2 3 4 Section I What is? Definition is a technique for efficiently recurrence computing by storing partial results. In this slides, I will NOT use too many formal
Microsoft Research Asia September 5, 2005 1 2 3 4 Section I What is? Definition is a technique for efficiently recurrence computing by storing partial results. In this slides, I will NOT use too many formal
Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review Forced handles Definition A handle h of a valid string v = xhy is a forced handle if h is the unique handle in every valid string xhŷ where
Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review Forced handles Definition A handle h of a valid string v = xhy is a forced handle if h is the unique handle in every valid string xhŷ where
ON MINIMAL CONTEXT-FREE INSERTION-DELETION SYSTEMS
 ON MINIMAL CONTEXT-FREE INSERTION-DELETION SYSTEMS Sergey Verlan LACL, University of Paris XII 61, av. Général de Gaulle, 94010, Créteil, France e-mail: verlan@univ-paris12.fr ABSTRACT We investigate the
ON MINIMAL CONTEXT-FREE INSERTION-DELETION SYSTEMS Sergey Verlan LACL, University of Paris XII 61, av. Général de Gaulle, 94010, Créteil, France e-mail: verlan@univ-paris12.fr ABSTRACT We investigate the
Pattern Matching. a b a c a a b. a b a c a b. a b a c a b. Pattern Matching Goodrich, Tamassia
 Pattern Matching a b a c a a b 1 4 3 2 Pattern Matching 1 Brute-Force Pattern Matching ( 11.2.1) The brute-force pattern matching algorithm compares the pattern P with the text T for each possible shift
Pattern Matching a b a c a a b 1 4 3 2 Pattern Matching 1 Brute-Force Pattern Matching ( 11.2.1) The brute-force pattern matching algorithm compares the pattern P with the text T for each possible shift
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES JUNE 2014
 Q.2 a. Show by using Mathematical Induction that n i= 1 i 2 n = ( n + 1) ( 2 n + 1) 6 b. Define language. Let = {0; 1} denote an alphabet. Enumerate five elements of the following languages: (i) Even binary
Q.2 a. Show by using Mathematical Induction that n i= 1 i 2 n = ( n + 1) ( 2 n + 1) 6 b. Define language. Let = {0; 1} denote an alphabet. Enumerate five elements of the following languages: (i) Even binary
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages
 Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
Ogden s Lemma. and Formal Languages. Automata Theory CS 573. The proof is similar but more fussy. than the proof of the PL4CFL.
 CS 573 Automata Theory and Formal Languages Professor Leslie Lander Lecture # 24 December 4, 2000 Ogden s Lemma (6.2) Let L be a CFL, then there is a constant n such that if z is a word in L with z > n
CS 573 Automata Theory and Formal Languages Professor Leslie Lander Lecture # 24 December 4, 2000 Ogden s Lemma (6.2) Let L be a CFL, then there is a constant n such that if z is a word in L with z > n
Some Inherently Ambiguous Context-Free Languages
 INFORMATION AND CONTROL 18, 355-363 (1971) Some Inherently Ambiguous Context-Free Languages ELIAHU SHAMIR Department of Mathematics, The Hebrew University, Jerusalem, Israel We prove the inherent ambiguity
INFORMATION AND CONTROL 18, 355-363 (1971) Some Inherently Ambiguous Context-Free Languages ELIAHU SHAMIR Department of Mathematics, The Hebrew University, Jerusalem, Israel We prove the inherent ambiguity
Solution Scoring: SD Reg exp.: a(a
 MA/CSSE 474 Exam 3 Winter 2013-14 Name Solution_with explanations Section: 02(3 rd ) 03(4 th ) 1. (28 points) For each of the following statements, circle T or F to indicate whether it is True or False.
MA/CSSE 474 Exam 3 Winter 2013-14 Name Solution_with explanations Section: 02(3 rd ) 03(4 th ) 1. (28 points) For each of the following statements, circle T or F to indicate whether it is True or False.
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove Tuesday 28 of May 2013 Total: 60 points TMV027/DIT321 registration VT13 TMV026/DIT321 registration before VT13 Exam
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove Tuesday 28 of May 2013 Total: 60 points TMV027/DIT321 registration VT13 TMV026/DIT321 registration before VT13 Exam
CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars
 CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars Why Parse General Grammars Can be difficult or impossible to make grammar unambiguous thus LL(k) and LR(k) methods cannot work, for such ambiguous
CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars Why Parse General Grammars Can be difficult or impossible to make grammar unambiguous thus LL(k) and LR(k) methods cannot work, for such ambiguous
Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x where
 Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Computational Models - Lecture 3
 Slides modified by Benny Chor, based on original slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University. p. 1 Computational Models - Lecture 3 Equivalence of regular expressions and regular languages (lukewarm leftover
Slides modified by Benny Chor, based on original slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University. p. 1 Computational Models - Lecture 3 Equivalence of regular expressions and regular languages (lukewarm leftover
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction) Objectives This lecture shows more undecidable languages Our proof is not based on diagonalization Instead, we reduce the problem
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction) Objectives This lecture shows more undecidable languages Our proof is not based on diagonalization Instead, we reduce the problem
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016
 CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL
 Theorem 14.1 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL Statement: Given a CFL L and string w, there is a decision procedure that determines whether w L. Proof: By construction. 1. Proof using a grammar
Theorem 14.1 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL Statement: Given a CFL L and string w, there is a decision procedure that determines whether w L. Proof: By construction. 1. Proof using a grammar
