BNG/ECE 487 FINAL (W16)
|
|
|
- Mildred Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BNG/ECE 487 FINAL (W16) NAME: 4 Problems for 100 pts This exam is closed-everything (no notes, books, etc.). Calculators are permitted. Possibly useful formulas and tables are provided on this page. Fourier Transform Pairs and Properties cos2 Ultrasound equations: Bandwidth for Gaussian Pulse Envelope: Depth resolution: Near-field Region: Focal width: Depth of focus: 0.5 # # MRI equations: 0 1 / BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
2 Problem #1: General Knowledge (25 pts) (a) Ultrasound: Choose true or false for each of the following statements. If you choose false, then provide the correct statement. (i) A large fractional bandwidth means more cycles within the ultrasound pulse envelope. (ii) Imaging with higher ultrasound frequencies is always desirable, since this maximizes spatial resolution. (iii) A common transducer material is Led Zeppelin Tarantino (LZT). (b) Ultrasound: Suppose you want to image renal (kidney) blood flow, where the velocities are much lower than in cardiac imaging. Would you use continuous-wave Doppler, power Doppler, or pulsed-wave Doppler? Choose one and briefly explain why. (c) Ultrasound: Suppose an ultrasound pulse has a rect-shaped envelope (rather than Gaussian). The pulse is given by: p(t) = rect(t/)cos(2f 0 t), where = 0.8 s and f 0 = 5 MHz. Sketch p(t) and its spectrum P(f), making sure to label important features. Possibly helpful formulas are on the front page of this exam. BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
3 (d) MRI: Suppose an MRI brain scan uses a spin echo time of TE = 70 ms and a pulse repetition time of TR = 4000 ms. What type of weighting is performed in this scan? Briefly explain why. Tissue Type Relative PD T2 (ms) T1 (ms) White matter Gray matter Cerebrospinal fluid (e) MRI: Suppose an MRI brain scan uses TE = 10 ms and TR = 800 ms. Which tissue type (from the above table) gives the strongest signal and weakest signal? Explain why. (f) MRI: Suppose an MRI pulse sequence first applies a 180 pulse (diagram a ) followed by a 90 pulse (diagram b ). On each diagram, sketch the behavior of the magnetization vector M (e.g. before and after). z z y y B180 x B90 x (a) (b) (g) Nuclear Imaging: Explain the difference in gamma ray emission by a radiotracer in planar scintigraphy (e.g. Tc-99m) compared to positron emission tomography (e.g. Fluorine-18). BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
4 Problem #2: Ultrasound Imaging (25 pts) You are asked to design a linear array scanner to image the kidney. The desired field of view is 100 mm across and 150 mm deep. The ADC electronics operate at a 40 MHz sampling rate. The TGC electronics can produce a maximum gain of 100 db. Assume a wave speed c = 1.5 mm/s and attenuation coefficient a = 1 db/cm/mhz. (a) You must choose between transducer probes with f 0 = 1.5, 3, 5, and 7 MHz. Assuming you only need to compensate for tissue attenuation, which frequency is the best choice? Array T/R TGC A/D (b) If the desired lateral resolution is w = 1.2 mm at a depth z = 75 mm, would you use a sub-array size of 16, 32, or 64 elements? Assume the element spacing is d = 0. Show all work. (c) In order to achieve a depth resolution of 0.75 mm, what is the minimum required fractional bandwidth? Assume the ultrasound pulse has a Gaussian waveform. Hint: The front page of this exam has some useful formulas. (d) What is the total number of elements in the array? (e) What is the approximate frame rate of your imaging system? Express your answer in Hz. BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
5 (extra sheet for work) BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
6 Problem #3: Fast MRI with Spiral Scanning (25 pts) One way to achieve fast MRI acquisition is to use a single 90-pulse followed by a spiral trajectory that starts at the origin and ends at the outer edge. No spin echoes are used in this sequence. v The following assumptions can be made: B 0 = 1.5 Tesla and /2 = MHz/Tesla for all tissue. The spiral trajectory consists of segments that trace out a spiral path. For example, the sketch to the right shows 13 segments. Segment #1 starts at the origin, while segment #13 is at the very bottom. Both G x and G y are T PULSE = 50 s in duration during each segment of the spiral trajectory. Output images are 128 x 128 pixels with a pixel spacing of x = y = 1 mm. u (a) Compute G x and G y during the first segment (e.g. starting from the origin and moving to the right). Express your answer in Gauss/cm. Hint: The front page of this exam has some useful formulas. (b) Each successive segment of the spiral trajectory requires incrementing the magnitude of G x by dg x and the magnitude of G y by dg y. Compute the increments dg x and dg y (units = Gauss/cm). (c) Sketch the RF, G x, G y, and G z fields for the first 13 segments of the spiral trajectory (e.g. as shown in the above sketch). You can assume the readout starts immediately after slice selection. (d) What is the approximate total imaging time of your pulse sequence? Express your answer in ms. BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
7 (extra sheet for work) BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
8 Problem #4: MRI of Rotator Cuff Injury (25 pts) The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons connecting the upper arm to the shoulder blade. A torn tendon typically results in the accumulation of fluid. Design a MRI spin echo pulse sequence that performs 2D Fourier imaging of a rotator cuff injury. MRI properties of relevant tissue types are shown in the table below. Tissue Type Relative PD T2 (ms) T1 (ms) Tendon Bone Fluid The following assumptions can be made: B 0 = 3 Tesla and /2 = MHz/Tesla for all tissue. Gx = G/cm during encode. The encode and readout times T ENCODE and T READ are the SAME. Output images are 256 x 256 pixels with a pixel spacing of 0.5 mm. (a) Suppose you want your final image to maximize the ratio of the fluid signal to the other two tissue types (bone and tendons). You must choose between spin echo times of TE = 5 and 100 ms and pulse repetition intervals of TR = 500 and 5000 ms. Which is the best combination of TE and TR? You must also explain why the other combinations are not good choices. (b) Assuming the RF pulses are 0.3 ms in duration, compute the magnitude of B 90 and B 180. Express your answer in Gauss. (c) Compute T ENCODE and dg y during phase encode. Express T ENCODE in ms and dg y in G/cm. (d) Sketch the RF, G x, G y, and G z fields for your pulse sequence. Clearly label when the 180 pulse and spin echo occurs, as well as the duration and amplitude of encode and readout gradients. What is the total imaging time for your pulse sequence? BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
9 (extra sheet for work) BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
10 (extra sheet for work) BNG/ECE 487: Medical Imaging Systems Final Exam Mar 17,
EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam
 EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam (closed book, 1 sheets of notes double sided allowed, no calculator or other electronic devices allowed) 1. Ultrasound Physics (15 pt) A) (9
EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam (closed book, 1 sheets of notes double sided allowed, no calculator or other electronic devices allowed) 1. Ultrasound Physics (15 pt) A) (9
Take-Home Final Exam Last Possible Due Date: Dec. 21, 2004, 5 p.m.
 Take-Home Final Exam Last Possible Due Date: Dec 1, 004, 5 pm Your solutions to the exam should be handed in to the instructor (BIRB 1088) or to Eve Gochis, the MRI lab administrator (BIRB 107) no later
Take-Home Final Exam Last Possible Due Date: Dec 1, 004, 5 pm Your solutions to the exam should be handed in to the instructor (BIRB 1088) or to Eve Gochis, the MRI lab administrator (BIRB 107) no later
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 10 pages Written test, 12 December 2012 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: None. Pocket calculator not allowed "Weighting":
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 10 pages Written test, 12 December 2012 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: None. Pocket calculator not allowed "Weighting":
Field trip: Tuesday, Feb 5th
 Pulse Sequences Field trip: Tuesday, Feb 5th Hardware tour of VUIIIS Philips 3T Meet here at regular class time (11.15) Complete MRI screening form! Chuck Nockowski Philips Service Engineer Reminder: Project/Presentation
Pulse Sequences Field trip: Tuesday, Feb 5th Hardware tour of VUIIIS Philips 3T Meet here at regular class time (11.15) Complete MRI screening form! Chuck Nockowski Philips Service Engineer Reminder: Project/Presentation
Structure of Biological Materials
 ELEC ENG 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Notes for Lecture #19 Monday, November 22, 2010 6.5 Nuclear medicine imaging Nuclear imaging produces images of the distribution of radiopharmaceuticals
ELEC ENG 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Notes for Lecture #19 Monday, November 22, 2010 6.5 Nuclear medicine imaging Nuclear imaging produces images of the distribution of radiopharmaceuticals
K-space. Spin-Warp Pulse Sequence. At each point in time, the received signal is the Fourier transform of the object s(t) = M( k x
 Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2015 MRI Lecture 4 k (t) = γ 2π k y (t) = γ 2π K-space At each point in time, the received signal is the Fourier transform of the object
Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2015 MRI Lecture 4 k (t) = γ 2π k y (t) = γ 2π K-space At each point in time, the received signal is the Fourier transform of the object
NMR/MRI examination (8N080 / 3F240)
 NMR/MRI examination (8N080 / 3F240) Remarks: 1. This test consists of 3 problems with at total of 26 sub-questions. 2. Questions are in English. You are allowed to answer them in English or Dutch. 3. Please
NMR/MRI examination (8N080 / 3F240) Remarks: 1. This test consists of 3 problems with at total of 26 sub-questions. 2. Questions are in English. You are allowed to answer them in English or Dutch. 3. Please
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jeffrey A. Fessler EECS Department The University of Michigan NSS-MIC: Fundamentals of Medical Imaging Oct. 20, 2003 NMR-0 Background Basic physics 4 magnetic fields
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jeffrey A. Fessler EECS Department The University of Michigan NSS-MIC: Fundamentals of Medical Imaging Oct. 20, 2003 NMR-0 Background Basic physics 4 magnetic fields
Introduction to Biomedical Imaging
 Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu MRI advantages Superior soft-tissue contrast Depends on among
Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu MRI advantages Superior soft-tissue contrast Depends on among
Procesamiento de Imágenes y Bioseñales
 Procesamiento de Imágenes y Bioseñales Dr. Víctor Castañeda Agenda Physical basis of X-ray- CT, NMR, Ultrasound, Nuclear Medicine Sensors (cameras, gamma probes, microphone) Computational Tomography (CT)
Procesamiento de Imágenes y Bioseñales Dr. Víctor Castañeda Agenda Physical basis of X-ray- CT, NMR, Ultrasound, Nuclear Medicine Sensors (cameras, gamma probes, microphone) Computational Tomography (CT)
Exam 8N080 - Introduction to MRI
 Exam 8N080 - Introduction to MRI Friday April 10 2015, 18.00-21.00 h For this exam you may use an ordinary calculator (not a graphical one). In total there are 5 assignments and a total of 50 points can
Exam 8N080 - Introduction to MRI Friday April 10 2015, 18.00-21.00 h For this exam you may use an ordinary calculator (not a graphical one). In total there are 5 assignments and a total of 50 points can
Part III Minor Option in Medical Physics 2018 Examples Sheet
 Part III Minor Option in Medical Physics 2018 Examples Sheet Any errors or comments should be addressed sent to: seb53@cam.ac.uk URLs that may be useful: Stanford Event Generation Simulator: http://tinyurl.com/pkg476r
Part III Minor Option in Medical Physics 2018 Examples Sheet Any errors or comments should be addressed sent to: seb53@cam.ac.uk URLs that may be useful: Stanford Event Generation Simulator: http://tinyurl.com/pkg476r
HW6: MRI Imaging Pulse Sequences (7 Problems for 100 pts)
 HW6: MRI Imaging Pulse Sequences (7 Problems for 100 ps) GOAL The overall goal of HW6 is o beer undersand pulse sequences for MRI image reconsrucion. OBJECTIVES 1) Design a spin echo pulse sequence o image
HW6: MRI Imaging Pulse Sequences (7 Problems for 100 ps) GOAL The overall goal of HW6 is o beer undersand pulse sequences for MRI image reconsrucion. OBJECTIVES 1) Design a spin echo pulse sequence o image
Introduction to MRI. Spin & Magnetic Moments. Relaxation (T1, T2) Spin Echoes. 2DFT Imaging. K-space & Spatial Resolution.
 Introduction to MRI Spin & Magnetic Moments Relaxation (T1, T2) Spin Echoes 2DFT Imaging Selective excitation, phase & frequency encoding K-space & Spatial Resolution Contrast (T1, T2) Acknowledgement:
Introduction to MRI Spin & Magnetic Moments Relaxation (T1, T2) Spin Echoes 2DFT Imaging Selective excitation, phase & frequency encoding K-space & Spatial Resolution Contrast (T1, T2) Acknowledgement:
Physics of MR Image Acquisition
 Physics of MR Image Acquisition HST-583, Fall 2002 Review: -MRI: Overview - MRI: Spatial Encoding MRI Contrast: Basic sequences - Gradient Echo - Spin Echo - Inversion Recovery : Functional Magnetic Resonance
Physics of MR Image Acquisition HST-583, Fall 2002 Review: -MRI: Overview - MRI: Spatial Encoding MRI Contrast: Basic sequences - Gradient Echo - Spin Echo - Inversion Recovery : Functional Magnetic Resonance
Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Doppler echocardiography. History: - Langevin developed sonar.
 1 Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging History: - Langevin developed sonar. - 1940s development of pulse-echo. - 1950s development of mode A and B. - 1957 development of continuous wave
1 Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging History: - Langevin developed sonar. - 1940s development of pulse-echo. - 1950s development of mode A and B. - 1957 development of continuous wave
NMR and MRI : an introduction
 Intensive Programme 2011 Design, Synthesis and Validation of Imaging Probes NMR and MRI : an introduction Walter Dastrù Università di Torino walter.dastru@unito.it \ Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Intensive Programme 2011 Design, Synthesis and Validation of Imaging Probes NMR and MRI : an introduction Walter Dastrù Università di Torino walter.dastru@unito.it \ Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Medical Imaging Signals and Systems Jerry L. Prince and Jonathan M. Links Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006
 i Medical Imaging Signals and Systems Jerry L. Prince and Jonathan M. Links Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006 Errata, Version 1.02, August 8, 2006 This errata applies to the first printing
i Medical Imaging Signals and Systems Jerry L. Prince and Jonathan M. Links Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006 Errata, Version 1.02, August 8, 2006 This errata applies to the first printing
The physics US and MRI. Prof. Peter Bogner
 The physics US and MRI Prof. Peter Bogner Sound waves mechanical disturbance, a pressure wave moves along longitudinal wave compression rarefaction zones c = nl, (c: velocity, n: frequency, l: wavelength
The physics US and MRI Prof. Peter Bogner Sound waves mechanical disturbance, a pressure wave moves along longitudinal wave compression rarefaction zones c = nl, (c: velocity, n: frequency, l: wavelength
Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging. Fall Quarter 2006 Ultrasound Lecture 1
 Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2006 Ultrasound Lecture 1 From Suetens 2002 1 Basic System Echo occurs at t=2z/c where c is approximately 1500 m/s or 1.5 mm/µs Macovski
Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2006 Ultrasound Lecture 1 From Suetens 2002 1 Basic System Echo occurs at t=2z/c where c is approximately 1500 m/s or 1.5 mm/µs Macovski
Introduction to Medical Imaging. Medical Imaging
 Introduction to Medical Imaging BME/EECS 516 Douglas C. Noll Medical Imaging Non-invasive visualization of internal organs, tissue, etc. I typically don t include endoscopy as an imaging modality Image
Introduction to Medical Imaging BME/EECS 516 Douglas C. Noll Medical Imaging Non-invasive visualization of internal organs, tissue, etc. I typically don t include endoscopy as an imaging modality Image
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging. Outline
 A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI. Assignment 9 Solutions. Due April 29th, 2013
 EE5E/BIOE65 Spring 013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig This is the last homework in class. Enjoy it. Assignment 9 Solutions Due April 9th, 013 1) In class when we presented the spin-echo saturation recovery
EE5E/BIOE65 Spring 013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig This is the last homework in class. Enjoy it. Assignment 9 Solutions Due April 9th, 013 1) In class when we presented the spin-echo saturation recovery
3. Which of the following statements is (are) TRUE about detector crystals in Anger cameras?
 BioE 1330 - Exam 2 11/13/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. Unlike CT, in nuclear medicine A. Bremsstrahlung is not used to produce high-energy photons. B. signal can be increased
BioE 1330 - Exam 2 11/13/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. Unlike CT, in nuclear medicine A. Bremsstrahlung is not used to produce high-energy photons. B. signal can be increased
FREQUENCY SELECTIVE EXCITATION
 PULSE SEQUENCES FREQUENCY SELECTIVE EXCITATION RF Grad 0 Sir Peter Mansfield A 1D IMAGE Field Strength / Frequency Position FOURIER PROJECTIONS MR Image Raw Data FFT of Raw Data BACK PROJECTION Image Domain
PULSE SEQUENCES FREQUENCY SELECTIVE EXCITATION RF Grad 0 Sir Peter Mansfield A 1D IMAGE Field Strength / Frequency Position FOURIER PROJECTIONS MR Image Raw Data FFT of Raw Data BACK PROJECTION Image Domain
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2016 Principles of MRI. Assignment 4. Due Friday Feb 19st, 2016, Self Grading Due Monday Feb 22nd, 2016
 EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2016 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 4 Due Friday Feb 19st, 2016, Self Grading Due Monday Feb 22nd, 2016 1. Finish reading Nishimura Ch.4 and Ch. 5. 2. The following pulse
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2016 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 4 Due Friday Feb 19st, 2016, Self Grading Due Monday Feb 22nd, 2016 1. Finish reading Nishimura Ch.4 and Ch. 5. 2. The following pulse
M R I Physics Course. Jerry Allison Ph.D., Chris Wright B.S., Tom Lavin B.S., Nathan Yanasak Ph.D. Department of Radiology Medical College of Georgia
 M R I Physics Course Jerry Allison Ph.D., Chris Wright B.S., Tom Lavin B.S., Nathan Yanasak Ph.D. Department of Radiology Medical College of Georgia M R I Physics Course Spin Echo Imaging Hahn Spin Echo
M R I Physics Course Jerry Allison Ph.D., Chris Wright B.S., Tom Lavin B.S., Nathan Yanasak Ph.D. Department of Radiology Medical College of Georgia M R I Physics Course Spin Echo Imaging Hahn Spin Echo
Contrast Mechanisms in MRI. Michael Jay Schillaci
 Contrast Mechanisms in MRI Michael Jay Schillaci Overview Image Acquisition Basic Pulse Sequences Unwrapping K-Space Image Optimization Contrast Mechanisms Static and Motion Contrasts T1 & T2 Weighting,
Contrast Mechanisms in MRI Michael Jay Schillaci Overview Image Acquisition Basic Pulse Sequences Unwrapping K-Space Image Optimization Contrast Mechanisms Static and Motion Contrasts T1 & T2 Weighting,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Pål Erik Goa Associate Professor in Medical Imaging Dept. of Physics
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Pål Erik Goa Associate Professor in Medical Imaging Dept. of Physics pal.e.goa@ntnu.no 1 Why MRI? X-ray/CT: Great for bone structures and high spatial resolution Not so great
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Pål Erik Goa Associate Professor in Medical Imaging Dept. of Physics pal.e.goa@ntnu.no 1 Why MRI? X-ray/CT: Great for bone structures and high spatial resolution Not so great
Part III: Sequences and Contrast
 Part III: Sequences and Contrast Contents T1 and T2/T2* Relaxation Contrast of Imaging Sequences T1 weighting T2/T2* weighting Contrast Agents Saturation Inversion Recovery JUST WATER? (i.e., proton density
Part III: Sequences and Contrast Contents T1 and T2/T2* Relaxation Contrast of Imaging Sequences T1 weighting T2/T2* weighting Contrast Agents Saturation Inversion Recovery JUST WATER? (i.e., proton density
MRI in Review: Simple Steps to Cutting Edge Part I
 MRI in Review: Simple Steps to Cutting Edge Part I DWI is now 2 years old... Mike Moseley Radiology Stanford DWI, b = 1413 T2wt, 28/16 ASN 21 San Francisco + Disclosures: Funding NINDS, NCRR, NCI 45 minutes
MRI in Review: Simple Steps to Cutting Edge Part I DWI is now 2 years old... Mike Moseley Radiology Stanford DWI, b = 1413 T2wt, 28/16 ASN 21 San Francisco + Disclosures: Funding NINDS, NCRR, NCI 45 minutes
(INCLUDING THIS FRONT PAGE)
 I'IFIITIIBIFI UNIVERSITY OF SCIEI'ICE RITD TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (MAJOR AND MINOR) QUALIFICATION
I'IFIITIIBIFI UNIVERSITY OF SCIEI'ICE RITD TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (MAJOR AND MINOR) QUALIFICATION
Pixel-based Beamforming for Ultrasound Imaging
 Pixel-based Beamforming for Ultrasound Imaging Richard W. Prager and Nghia Q. Nguyen Department of Engineering Outline v Introduction of Ultrasound Imaging v Image Formation and Beamforming v New Time-delay
Pixel-based Beamforming for Ultrasound Imaging Richard W. Prager and Nghia Q. Nguyen Department of Engineering Outline v Introduction of Ultrasound Imaging v Image Formation and Beamforming v New Time-delay
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
RAD229: Final Exam 2014/ SOLUTIONS You will have 3 hours to complete this Exam
 RAD229: Final Exam 2014/2015 - SOLUTIONS You will have 3 hours to complete this Exam Solutions are given in Blue. In some cases, different interpretations may have led to different, but reasonable answers,
RAD229: Final Exam 2014/2015 - SOLUTIONS You will have 3 hours to complete this Exam Solutions are given in Blue. In some cases, different interpretations may have led to different, but reasonable answers,
Electrical Engineering 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials
 Electrical Engineering 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Day Class Instructor: Dr. I. C. BRUCE Duration of Examination: 3 Hours McMaster University Final Examination December, 2004 This examination
Electrical Engineering 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Day Class Instructor: Dr. I. C. BRUCE Duration of Examination: 3 Hours McMaster University Final Examination December, 2004 This examination
MRI Physics I: Spins, Excitation, Relaxation
 MRI Physics I: Spins, Excitation, Relaxation Douglas C. Noll Biomedical Engineering University of Michigan Michigan Functional MRI Laboratory Outline Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI Physics I: Spins, Excitation, Relaxation Douglas C. Noll Biomedical Engineering University of Michigan Michigan Functional MRI Laboratory Outline Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Introductory MRI Physics
 C HAPR 18 Introductory MRI Physics Aaron Sodickson EXRNAL MAGNETIC FIELD, PROTONS AND EQUILIBRIUM MAGNETIZATION Much of the bulk of the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner apparatus is dedicated to
C HAPR 18 Introductory MRI Physics Aaron Sodickson EXRNAL MAGNETIC FIELD, PROTONS AND EQUILIBRIUM MAGNETIZATION Much of the bulk of the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner apparatus is dedicated to
Basic System. Basic System. Sonosite 180. Acuson Sequoia. Echo occurs at t=2z/c where c is approximately 1500 m/s or 1.5 mm/µs
 Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2007 Ultrasound Lecture Sonosite 80 From Suetens 2002 Acuson Sequoia Basic System Basic System Echo occurs at t=2/c where c is approximately
Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2007 Ultrasound Lecture Sonosite 80 From Suetens 2002 Acuson Sequoia Basic System Basic System Echo occurs at t=2/c where c is approximately
BASIC MRI PHYSICS SPIN GYMNASTICS Don Plewes PhD, Walter Kucharczyk MD
 BASIC MRI PHYSICS SPIN GYMNASTICS Don Plewes PhD, Walter Kucharczyk MD Introduction To understand MRI, it is first necessary to understand the physics of proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR). The most
BASIC MRI PHYSICS SPIN GYMNASTICS Don Plewes PhD, Walter Kucharczyk MD Introduction To understand MRI, it is first necessary to understand the physics of proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR). The most
The physics of medical imaging US, CT, MRI. Prof. Peter Bogner
 The physics of medical imaging US, CT, MRI Prof. Peter Bogner Clinical radiology curriculum blocks of lectures and clinical practice (7x2) Physics of medical imaging Neuroradiology Head and neck I. Head
The physics of medical imaging US, CT, MRI Prof. Peter Bogner Clinical radiology curriculum blocks of lectures and clinical practice (7x2) Physics of medical imaging Neuroradiology Head and neck I. Head
22.56J Noninvasive Imaging in Biology and Medicine Instructor: Prof. Alan Jasanoff Fall 2005, TTh 1-2:30
 22.56J Noninvasive Imaging in Biology and Medicine Instructor: Prof. Alan Jasanoff Fall 2005, TTh 1-2:30 Sample problems HW1 1. Look up (e.g. in the CRC Manual of Chemistry and Physics www.hbcpnetbase.com)
22.56J Noninvasive Imaging in Biology and Medicine Instructor: Prof. Alan Jasanoff Fall 2005, TTh 1-2:30 Sample problems HW1 1. Look up (e.g. in the CRC Manual of Chemistry and Physics www.hbcpnetbase.com)
Part II: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
 Part II: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Contents Magnetic Field Gradients Selective Excitation Spatially Resolved Reception k-space Gradient Echo Sequence Spin Echo Sequence Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Part II: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Contents Magnetic Field Gradients Selective Excitation Spatially Resolved Reception k-space Gradient Echo Sequence Spin Echo Sequence Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Background II. Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Pulse Sequences Sampling and Trajectories Parallel Imaging. B.Hargreaves - RAD 229.
 Background II Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Pulse Sequences Sampling and Trajectories Parallel Imaging 1 SNR: Signal-to-Noise Ratio Signal: Desired voltage in coil Noise: Thermal, electronic Noise Thermal
Background II Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Pulse Sequences Sampling and Trajectories Parallel Imaging 1 SNR: Signal-to-Noise Ratio Signal: Desired voltage in coil Noise: Thermal, electronic Noise Thermal
Outlines: (June 11, 1996) Instructor:
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (June 11, 1996) Instructor: Tai-huang Huang Institute of Biomedical Sciences Academia Sinica Tel. (02) 2652-3036; Fax. (02) 2788-7641 E. mail: bmthh@ibms.sinica.edu.tw Reference:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (June 11, 1996) Instructor: Tai-huang Huang Institute of Biomedical Sciences Academia Sinica Tel. (02) 2652-3036; Fax. (02) 2788-7641 E. mail: bmthh@ibms.sinica.edu.tw Reference:
A. I, II, and III B. I C. I and II D. II and III E. I and III
 BioE 1330 - Review Chapters 7, 8, and 9 (Nuclear Medicine) 9/27/2018 Instructions: On the Answer Sheet, enter your 2-digit ID number (with a leading 0 if needed) in the boxes of the ID section. Fill in
BioE 1330 - Review Chapters 7, 8, and 9 (Nuclear Medicine) 9/27/2018 Instructions: On the Answer Sheet, enter your 2-digit ID number (with a leading 0 if needed) in the boxes of the ID section. Fill in
Sequence Overview. Gradient Echo Spin Echo Magnetization Preparation Sampling and Trajectories Parallel Imaging. B.Hargreaves - RAD 229
 Sequence Overview Gradient Echo Spin Echo Magnetization Preparation Sampling and Trajectories Parallel Imaging 75 Pulse Sequences and k-space RF k y G z k x G x 3D k-space G y k y k z Acq. k x 76 Gradient
Sequence Overview Gradient Echo Spin Echo Magnetization Preparation Sampling and Trajectories Parallel Imaging 75 Pulse Sequences and k-space RF k y G z k x G x 3D k-space G y k y k z Acq. k x 76 Gradient
Medical Biophysics II. Final exam theoretical questions 2013.
 Medical Biophysics II. Final exam theoretical questions 2013. 1. Early atomic models. Rutherford-experiment. Franck-Hertz experiment. Bohr model of atom. 2. Quantum mechanical atomic model. Quantum numbers.
Medical Biophysics II. Final exam theoretical questions 2013. 1. Early atomic models. Rutherford-experiment. Franck-Hertz experiment. Bohr model of atom. 2. Quantum mechanical atomic model. Quantum numbers.
On Signal to Noise Ratio Tradeoffs in fmri
 On Signal to Noise Ratio Tradeoffs in fmri G. H. Glover April 11, 1999 This monograph addresses the question of signal to noise ratio (SNR) in fmri scanning, when parameters are changed under conditions
On Signal to Noise Ratio Tradeoffs in fmri G. H. Glover April 11, 1999 This monograph addresses the question of signal to noise ratio (SNR) in fmri scanning, when parameters are changed under conditions
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging History Nuclear magnetic resonance was first described by Isidor Rabi in 1938 - Columbia University, New York City, (Nobel Prize Nobel Prize in Physics 1944) 1946 - Edward Mills
Magnetic Resonance Imaging History Nuclear magnetic resonance was first described by Isidor Rabi in 1938 - Columbia University, New York City, (Nobel Prize Nobel Prize in Physics 1944) 1946 - Edward Mills
Elec Eng 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials
 Elec Eng 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Page 1 of 12 Day Class Instructor: Dr. I. C. BRUCE Duration of Examination: 3 Hours McMaster University Final Examination December 5, 2008 This examination
Elec Eng 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Page 1 of 12 Day Class Instructor: Dr. I. C. BRUCE Duration of Examination: 3 Hours McMaster University Final Examination December 5, 2008 This examination
Navigator Echoes. BioE 594 Advanced Topics in MRI Mauli. M. Modi. BioE /18/ What are Navigator Echoes?
 Navigator Echoes BioE 594 Advanced Topics in MRI Mauli. M. Modi. 1 What are Navigator Echoes? In order to correct the motional artifacts in Diffusion weighted MR images, a modified pulse sequence is proposed
Navigator Echoes BioE 594 Advanced Topics in MRI Mauli. M. Modi. 1 What are Navigator Echoes? In order to correct the motional artifacts in Diffusion weighted MR images, a modified pulse sequence is proposed
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI
 Magnetic resonance imaging MRI Introduction What is MRI MRI is an imaging technique used primarily in medical settings that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce very clear and detailed
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI Introduction What is MRI MRI is an imaging technique used primarily in medical settings that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce very clear and detailed
MRI Homework. i. (0.5 pt each) Consider the following arrangements of bar magnets in a strong magnetic field.
 MRI Homework 1. While x-rays are used to image bones, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to examine tissues within the body by detecting where hydrogen atoms (H atoms) are and their environment (e.g.
MRI Homework 1. While x-rays are used to image bones, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to examine tissues within the body by detecting where hydrogen atoms (H atoms) are and their environment (e.g.
Fundamental MRI Principles Module Two
 Fundamental MRI Principles Module Two 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance There are three main subatomic particles: protons neutrons electrons positively charged no significant charge negatively charged Protons
Fundamental MRI Principles Module Two 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance There are three main subatomic particles: protons neutrons electrons positively charged no significant charge negatively charged Protons
Advanced Topics and Diffusion MRI
 Advanced Topics and Diffusion MRI Slides originally by Karla Miller, FMRIB Centre Modified by Mark Chiew (mark.chiew@ndcn.ox.ac.uk) Slides available at: http://users.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/~mchiew/teaching/ MRI
Advanced Topics and Diffusion MRI Slides originally by Karla Miller, FMRIB Centre Modified by Mark Chiew (mark.chiew@ndcn.ox.ac.uk) Slides available at: http://users.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/~mchiew/teaching/ MRI
Lab 2: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Developed by: Galen Reed and Miki Lustig Lab 2: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction In this lab, we will get some hands-on experience with an
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Developed by: Galen Reed and Miki Lustig Lab 2: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction In this lab, we will get some hands-on experience with an
AQA Physics /7408
 AQA Physics - 7407/7408 Module 10: Medical physics You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 10.1 Physics of the eye 10.1.1 Physics of vision The eye as an optical refracting system,
AQA Physics - 7407/7408 Module 10: Medical physics You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 10.1 Physics of the eye 10.1.1 Physics of vision The eye as an optical refracting system,
Principles of MRI EE225E / BIO265. Instructor: Miki Lustig UC Berkeley, EECS
 Principles of MRI EE225E / BIO265 Instructor: Miki Lustig UC Berkeley, EECS Today... Administration http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee225e/sp16/ Intro to Medical Imaging and MRI Medical Imaging (Before
Principles of MRI EE225E / BIO265 Instructor: Miki Lustig UC Berkeley, EECS Today... Administration http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee225e/sp16/ Intro to Medical Imaging and MRI Medical Imaging (Before
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A journey of a thousand miles must begin with a single step. LaoZi Tomography is an important area in the ever-growing field of imaging science. The term tomos (rofio
Chapter 1 Introduction A journey of a thousand miles must begin with a single step. LaoZi Tomography is an important area in the ever-growing field of imaging science. The term tomos (rofio
Nuclear Medicine Intro & Physics from Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, Chapter 7, by Prince and Links
 Nuclear Medicine Intro & Physics from Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, Chapter 7, by Prince and Links NM - introduction Relies on EMISSION of photons from body (versus transmission of photons through
Nuclear Medicine Intro & Physics from Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, Chapter 7, by Prince and Links NM - introduction Relies on EMISSION of photons from body (versus transmission of photons through
Index. p, lip, 78 8 function, 107 v, 7-8 w, 7-8 i,7-8 sine, 43 Bo,94-96
 p, lip, 78 8 function, 107 v, 7-8 w, 7-8 i,7-8 sine, 43 Bo,94-96 B 1,94-96 M,94-96 B oro!' 94-96 BIro!' 94-96 I/r, 79 2D linear system, 56 2D FFT, 119 2D Fourier transform, 1, 12, 18,91 2D sinc, 107, 112
p, lip, 78 8 function, 107 v, 7-8 w, 7-8 i,7-8 sine, 43 Bo,94-96 B 1,94-96 M,94-96 B oro!' 94-96 BIro!' 94-96 I/r, 79 2D linear system, 56 2D FFT, 119 2D Fourier transform, 1, 12, 18,91 2D sinc, 107, 112
31545 Medical Imaging systems
 31545 Medical Imaging systems Lecture 2: Ultrasound physics Jørgen Arendt Jensen Department of Electrical Engineering (DTU Elektro) Biomedical Engineering Group Technical University of Denmark September
31545 Medical Imaging systems Lecture 2: Ultrasound physics Jørgen Arendt Jensen Department of Electrical Engineering (DTU Elektro) Biomedical Engineering Group Technical University of Denmark September
Outline of today Medical Imaging systems. Wave types. 1. Discussion assignment on B-mode imaging
 Outline of today 3545 Medical Imaging systems. Discussion assignment on B-mode imaging Lecture : Ultrasound physics. Derivation of wave equation and role of speed of sound Jørgen Arendt Jensen Department
Outline of today 3545 Medical Imaging systems. Discussion assignment on B-mode imaging Lecture : Ultrasound physics. Derivation of wave equation and role of speed of sound Jørgen Arendt Jensen Department
Sound wave bends as it hits an interface at an oblique angle. 4. Reflection. Sound wave bounces back to probe
 : Ultrasound imaging and x-rays 1. How does ultrasound imaging work?. What is ionizing electromagnetic radiation? Definition of ionizing radiation 3. How are x-rays produced? Bremsstrahlung Auger electron
: Ultrasound imaging and x-rays 1. How does ultrasound imaging work?. What is ionizing electromagnetic radiation? Definition of ionizing radiation 3. How are x-rays produced? Bremsstrahlung Auger electron
Cambridge University Press MRI from A to Z: A Definitive Guide for Medical Professionals Gary Liney Excerpt More information
 Main glossary Aa AB systems Referring to molecules exhibiting multiply split MRS peaks due to spin-spin interactions. In an AB system, the chemical shift between the spins is of similar magnitude to the
Main glossary Aa AB systems Referring to molecules exhibiting multiply split MRS peaks due to spin-spin interactions. In an AB system, the chemical shift between the spins is of similar magnitude to the
MEDICAL IMAGING. METHODS OF MODERN IMAGING, BASED ON ELECTRO-MAGNETIC RADIATION (radiowaves, infrared radiation, X-rays, γ-rays ) AND ULTRASOUND
 MEDICAL IMAGING MEDICAL IMAGING METHODS OF MODERN IMAGING, BASED ON ELECTRO-MAGNETIC RADIATION (radiowaves, infrared radiation, X-rays, γ-rays ) AND ULTRASOUND MEDICAL IMAGING RADIOLOGY NUCLEAR MEDICINE
MEDICAL IMAGING MEDICAL IMAGING METHODS OF MODERN IMAGING, BASED ON ELECTRO-MAGNETIC RADIATION (radiowaves, infrared radiation, X-rays, γ-rays ) AND ULTRASOUND MEDICAL IMAGING RADIOLOGY NUCLEAR MEDICINE
Tissue Parametric Mapping:
 Tissue Parametric Mapping: Contrast Mechanisms Using SSFP Sequences Jongho Lee Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Tissue Parametric Mapping: Contrast Mechanisms Using bssfp Sequences Jongho
Tissue Parametric Mapping: Contrast Mechanisms Using SSFP Sequences Jongho Lee Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Tissue Parametric Mapping: Contrast Mechanisms Using bssfp Sequences Jongho
Apodization. Gibbs Artifact. Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging. Fall Quarter 2013 MRI Lecture 5. rect(k x )
 Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2013 MRI Lecture 5 GE Medical Systems 2003 Gibbs Artifact Apodization rect(k ) Hanning Window h(k )=1/2(1+cos(2πk ) 256256 image 256128
Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2013 MRI Lecture 5 GE Medical Systems 2003 Gibbs Artifact Apodization rect(k ) Hanning Window h(k )=1/2(1+cos(2πk ) 256256 image 256128
31545 Medical Imaging systems
 Simulation of ultrasound systems and non-linear imaging 545 Medical Imaging systems Lecture 9: Simulation of ultrasound systems and non-linear imaging Jørgen Arendt Jensen Department of Electrical Engineering
Simulation of ultrasound systems and non-linear imaging 545 Medical Imaging systems Lecture 9: Simulation of ultrasound systems and non-linear imaging Jørgen Arendt Jensen Department of Electrical Engineering
RAD229: Midterm Exam 2015/2016 October 19, Minutes. Please do not proceed to the next page until the exam begins.
 RAD229: Midterm Exam 2015/2016 October 19, 2015 ---- 75 Minutes Name: Student ID: General Instructions: 1. Write your name legibly on this page. 2. You may use notes including lectures, homework, solutions
RAD229: Midterm Exam 2015/2016 October 19, 2015 ---- 75 Minutes Name: Student ID: General Instructions: 1. Write your name legibly on this page. 2. You may use notes including lectures, homework, solutions
EE 5345 Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 6: slides
 EE 5345 Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 6: slides 129-147 Carlos E. Davila, Electrical Engineering Dept. Southern Methodist University slides can be viewed at: http:// www.seas.smu.edu/~cd/ee5345.html
EE 5345 Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 6: slides 129-147 Carlos E. Davila, Electrical Engineering Dept. Southern Methodist University slides can be viewed at: http:// www.seas.smu.edu/~cd/ee5345.html
BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging
 BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture 9 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (imaging) Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu Blackboard: http://cityonline.ccny.cuny.edu/ 1 Schedule 1. Introduction, Spatial Resolution,
BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture 9 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (imaging) Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu Blackboard: http://cityonline.ccny.cuny.edu/ 1 Schedule 1. Introduction, Spatial Resolution,
RF Pulse Design. Multi-dimensional Excitation I. M229 Advanced Topics in MRI Kyung Sung, Ph.D Class Business
 RF Pulse Design Multi-dimensional Excitation I M229 Advanced Topics in MRI Kyung Sung, Ph.D. 2018.04.10 Class Business Office hours - Instructors: Fri 10-12pm TAs: Xinran Zhong and Zhaohuan Zhang (time:
RF Pulse Design Multi-dimensional Excitation I M229 Advanced Topics in MRI Kyung Sung, Ph.D. 2018.04.10 Class Business Office hours - Instructors: Fri 10-12pm TAs: Xinran Zhong and Zhaohuan Zhang (time:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction The Components The Technology (MRI) Physics behind MR Most slides taken from http:// www.slideworld.org/ viewslides.aspx/magnetic- Resonance-Imaging- %28MRI%29-MR-Imaging-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction The Components The Technology (MRI) Physics behind MR Most slides taken from http:// www.slideworld.org/ viewslides.aspx/magnetic- Resonance-Imaging- %28MRI%29-MR-Imaging-
Application of Nuclear Physics
 Application of Nuclear Physics Frontier of gamma-ray spectroscopy 0.1 IR visible light UV soft X-ray X-ray hard X-ray gamma-ray 1 10 100 1e3 1e4 1e5 1e6 energy [ev] Photoelectric effect e - Compton scattering
Application of Nuclear Physics Frontier of gamma-ray spectroscopy 0.1 IR visible light UV soft X-ray X-ray hard X-ray gamma-ray 1 10 100 1e3 1e4 1e5 1e6 energy [ev] Photoelectric effect e - Compton scattering
The NMR Inverse Imaging Problem
 The NMR Inverse Imaging Problem Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Protons and Neutrons have intrinsic angular momentum Atoms with an odd number of proton and/or odd number of neutrons have a net magnetic moment=>
The NMR Inverse Imaging Problem Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Protons and Neutrons have intrinsic angular momentum Atoms with an odd number of proton and/or odd number of neutrons have a net magnetic moment=>
Lecture k-space. k-space illustrations. Zeugmatography 3/7/2011. Use of gradients to make an image echo. K-space Intro to k-space sampling
 Lecture 21-3-16 K-space Intro to k-space sampling (chap 3) Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling (chap 2) Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling principles (chap 3) Basic Contrast
Lecture 21-3-16 K-space Intro to k-space sampling (chap 3) Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling (chap 2) Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling principles (chap 3) Basic Contrast
Professor Stuart Bunt 217
 Professor Stuart Bunt 217 Traditional Anatomy Phrenology, the study of bumps on the skull. Measuring brain weights and size (still being done..see the fuss about Einstein s brain). Little link between
Professor Stuart Bunt 217 Traditional Anatomy Phrenology, the study of bumps on the skull. Measuring brain weights and size (still being done..see the fuss about Einstein s brain). Little link between
Basic Pulse Sequences I Saturation & Inversion Recovery UCLA. Radiology
 Basic Pulse Sequences I Saturation & Inversion Recovery Lecture #5 Learning Objectives Explain what the most important equations of motion are for describing spin systems for MRI. Understand the assumptions
Basic Pulse Sequences I Saturation & Inversion Recovery Lecture #5 Learning Objectives Explain what the most important equations of motion are for describing spin systems for MRI. Understand the assumptions
ELG7173 Topics in signal Processing II Computational Techniques in Medical Imaging
 ELG7173 Topics in signal Processing II Computational Techniques in Medical Imaging Topic #1: Intro to medical imaging Medical Imaging Classifications n Measurement physics Send Energy into body Send stuff
ELG7173 Topics in signal Processing II Computational Techniques in Medical Imaging Topic #1: Intro to medical imaging Medical Imaging Classifications n Measurement physics Send Energy into body Send stuff
Midterm Review. EE369B Concepts Simulations with Bloch Matrices, EPG Gradient-Echo Methods. B.Hargreaves - RAD 229
 Midterm Review EE369B Concepts Simulations with Bloch Matrices, EPG Gradient-Echo Methods 292 Fourier Encoding and Reconstruction Encoding k y x Sum over image k x Reconstruction k y Gradient-induced Phase
Midterm Review EE369B Concepts Simulations with Bloch Matrices, EPG Gradient-Echo Methods 292 Fourier Encoding and Reconstruction Encoding k y x Sum over image k x Reconstruction k y Gradient-induced Phase
Chapter 26 Sequence Design, Artifacts and Nomenclature. Yongquan Ye, Ph.D. Assist. Prof. Radiology, SOM Wayne State University
 Chapter 26 Sequence Design, Artifacts and Nomenclature Yongquan Ye, Ph.D. Assist. Prof. Radiology, SOM Wayne State University Previous classes: RF pulse, Gradient, Signal Readout Gradient echo, spin echo,
Chapter 26 Sequence Design, Artifacts and Nomenclature Yongquan Ye, Ph.D. Assist. Prof. Radiology, SOM Wayne State University Previous classes: RF pulse, Gradient, Signal Readout Gradient echo, spin echo,
Nuclear Radiation. Natural Radioactivity. A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield.
 Nuclear Radiation Natural Radioactivity A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield. 1 Radioactive Isotopes A radioactive isotope has an unstable
Nuclear Radiation Natural Radioactivity A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield. 1 Radioactive Isotopes A radioactive isotope has an unstable
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: NUCLEAR MEDICINE. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: NUCLEAR MEDICINE Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook Introduction to Medical Imaging: Physics, Engineering and Clinical Applications, by Nadine Barrie Smith
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: NUCLEAR MEDICINE Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook Introduction to Medical Imaging: Physics, Engineering and Clinical Applications, by Nadine Barrie Smith
Chapter 2. Interaction with Soft Tissue
 Chapter 2 Interaction with Soft Tissue Ultrasound interacts with human soft tissue in several predictable ways that allow engineers to design instruments that provide diagnostic information that forms
Chapter 2 Interaction with Soft Tissue Ultrasound interacts with human soft tissue in several predictable ways that allow engineers to design instruments that provide diagnostic information that forms
Welcome to MR! CT PET (with FDG) MRI (T2 w.) MR Image types: T2 weighted T1 weighted Sequence parameters FLAIR Diffusion
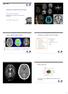 Phsics Images Welcome to R! Introduction to agnetic Resonance Imaging Adam Espe Hansen, PET/R-phsicist Department of Clinical Phsiolog, Nuclear medicine & PET Rigshospitalet Basic Kinetic odeling in olecular
Phsics Images Welcome to R! Introduction to agnetic Resonance Imaging Adam Espe Hansen, PET/R-phsicist Department of Clinical Phsiolog, Nuclear medicine & PET Rigshospitalet Basic Kinetic odeling in olecular
The Basics of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 The Basics of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Nathalie JUST, PhD nathalie.just@epfl.ch CIBM-AIT, EPFL Course 2013-2014-Chemistry 1 Course 2013-2014-Chemistry 2 MRI: Many different contrasts Proton density T1
The Basics of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Nathalie JUST, PhD nathalie.just@epfl.ch CIBM-AIT, EPFL Course 2013-2014-Chemistry 1 Course 2013-2014-Chemistry 2 MRI: Many different contrasts Proton density T1
Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI of the brain, ca. 1978. ca. 1993 ca. 2006 2014 Modality Characteristics and Comparison Radiography CT scanning Nuclear medicine MRI transmission modalities
Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI of the brain, ca. 1978. ca. 1993 ca. 2006 2014 Modality Characteristics and Comparison Radiography CT scanning Nuclear medicine MRI transmission modalities
A small object is placed a distance 2.0 cm from a thin convex lens. The focal length of the lens is 5.0 cm.
 TC [66 marks] This question is about a converging (convex) lens. A small object is placed a distance 2.0 cm from a thin convex lens. The focal length of the lens is 5.0 cm. (i) Deduce the magnification
TC [66 marks] This question is about a converging (convex) lens. A small object is placed a distance 2.0 cm from a thin convex lens. The focal length of the lens is 5.0 cm. (i) Deduce the magnification
Fundamental MRI Principles Module 2 N. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. X-ray. MRI Hydrogen Protons. Page 1. Electrons
 Fundamental MRI Principles Module 2 N S 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance There are three main subatomic particles: protons positively charged neutrons no significant charge electrons negatively charged Protons
Fundamental MRI Principles Module 2 N S 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance There are three main subatomic particles: protons positively charged neutrons no significant charge electrons negatively charged Protons
Spin Echo Imaging Sequence
 1 MRI In Stereotactic Procedures Edward F. Jackson, Ph.D. The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas 2 RF G slice G phase G freq Signal k-space Spin Echo Imaging Sequence TE 1st
1 MRI In Stereotactic Procedures Edward F. Jackson, Ph.D. The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas 2 RF G slice G phase G freq Signal k-space Spin Echo Imaging Sequence TE 1st
Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review. Outline of the Registry Exam: Certification Fees
 Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review Outline of the Registry Exam: Category: # of questions: A. Patient Care 30 B. Imaging Procedures 62 C. Data Acquisition and Processing 65 D. Physical Principles of Image
Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review Outline of the Registry Exam: Category: # of questions: A. Patient Care 30 B. Imaging Procedures 62 C. Data Acquisition and Processing 65 D. Physical Principles of Image
MR Advance Techniques. Flow Phenomena. Class I
 MR Advance Techniques Flow Phenomena Class I Flow Phenomena In this class we will explore different phenomenona produced from nuclei that move during the acquisition of data. Flowing nuclei exhibit different
MR Advance Techniques Flow Phenomena Class I Flow Phenomena In this class we will explore different phenomenona produced from nuclei that move during the acquisition of data. Flowing nuclei exhibit different
Spatial encoding in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Jean-Marie BONNY
 Spatial encoding in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jean-Marie BONNY What s Qu est an image ce qu une? image? «a reproduction of a material object by a camera or a related technique» Multi-dimensional signal
Spatial encoding in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jean-Marie BONNY What s Qu est an image ce qu une? image? «a reproduction of a material object by a camera or a related technique» Multi-dimensional signal
Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Pietro Gori
 Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Pietro Gori Enseignant-chercheur Equipe IMAGES - Télécom ParisTech pietro.gori@telecom-paristech.fr September 20, 2017 P. Gori BIOMED 20/09/2017 1 / 76
Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Pietro Gori Enseignant-chercheur Equipe IMAGES - Télécom ParisTech pietro.gori@telecom-paristech.fr September 20, 2017 P. Gori BIOMED 20/09/2017 1 / 76
Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions
 Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions 1 CHEMICAL Occurs when bonds are broken or formed. Atoms remained unchanged, though may be rearranged. Involves valence electrons Small energy
Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions 1 CHEMICAL Occurs when bonds are broken or formed. Atoms remained unchanged, though may be rearranged. Involves valence electrons Small energy
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics
 Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-302 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 24 Medical Imaging Effects of Radiation We now know what radiation is But what does it mean for our bodies? Radioactivity is quantified in
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-302 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 24 Medical Imaging Effects of Radiation We now know what radiation is But what does it mean for our bodies? Radioactivity is quantified in
