Grunntækni og rafmagn í riðstraums (AC) raforkukerfi
|
|
|
- Cory Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 1 Grunntækni og rafmagn í riðstraums (AC) raforkukerfi Haust 2016
2 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 2 Samræmi vélrænna og rafrænna stærða Afl = straumur * spenna U U V = Ex = gx = q m U = qe x U = F x = mg x du dq du dx p = = Ex = I V p = = F = F v dt dt dt dt dm = gx dt V = spenna, q= hleðsla, g = þyngdarhröðun, x = fjarlægð m= massi, U = orka, p = afl, t = tími, v = hraði, F = kraftur I = rafstraumur E = rafsvið, V = rafspenna
3 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 3 Power and Energy concepts Mechanical Energy Rotational Energy Electrical Energy Power Electrical Power
4 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 4 Instantaneous Sinusoidal Current/Voltage in Power Systems Einkennandi stærðir: (A) STÆRÐ sveiflunnar enna, i = 2I eða v = 2V (A) FASI eða fasahorn sveiflunnar v max i max φ Spenna 1/50 sek Straumur δ vt ( ) = v sinωt max it () = i sin( ωt φ) max tìmi max [%] ω = 2 π f = 49,86-49,90 49,90-49,94 49,94-49,98 49,98-50,02 max f tíðni í Hz Frequency Range (Hz) 50,02-50,06 50,06-50,10 50,10-50,14 Tíðni/Frequency: 50Hz in Europe (60 Hz in North America)
5 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 5 Power in AC Circuits Consider a simple AC circuit with voltage and current: i( t) = i sin( ) max ωt φ vt ( ) = v sinωt max it ( ) = i sin( ωt φ) max Ix Ir φ Ir I Ix V = I = V e I e V j 0! j φ v( t) = vmax sin ωt Use the trigonometric identity: 1 sin xsin y = cos( x y) cos( x+ y) 2 [ ] Instantaneous power will be current times voltage: pt () = vtit ()() = v i sinωtsin( ωt φ) max max vmax imax pt () = cosφ cos( 2ωt φ) 2
6 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 6 Current, Voltage and Power vmax imax pt () = cosφ cos( 2ωt φ) 2 Voltage, current or power Voltage v(t) Current i(t) Instantaneous power p(t) f time Real average power
7 Phasors and Instantaneous VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 7 Power Define: V I = = i v max 2 max 2 Then from the previous eq.: pt ( ) = V Icosφ V Icos(2 ωt φ) Using a trigonometric identity: cos( x y) = cos xcos y + sin xsin y pt ( ) = V Icosφ 1 cos 2ωt V I sinφ sin 2ωt we get: ( )
8 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 8 Real Power - Reactive Power Defining the following quantities P = V I cosφ (P is called Real Power) Q = V I sinφ (Q is called Reactive Power) We get: ( ) pt () = P1 cos2ωt Qsin2ωt
9 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 9 Real Power - Reactive Power From the last equation the instantaneous power is made up of 2 components: The first component is always positive with an average value P. Power is always transferred in the same direction and can do useful work The second component swings back and forth. The average = 0, while the amplitude is Q power swings back and forth and does NOT do useful work
10 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 10 Real and Reactive Power current voltage Average power or real power, P Instantaneous power, p(t) P(1-cos(2ω t)) Qsin(2 ω t))
11 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 11 The Power Triangle S = V I P = V I cosφ 2 2 S = P + Q Q = V I sinφ S f P Q
12 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 12 Apparent Power Apparent power is defined as the product of the RMS Voltage and RMS current: S = V I The unit of measurement is watt. However the power industry tradition is to use the unit VA (= volt - amperes), or kva or MVA
13 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 13 Definition of Power Concepts Power concept Units Formula Real power W, kw,mw P = V I cosφ Reactive power Apparent power Var, kvar,mvar VA, kva,mva Q= V S = I V I sinφ
14 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 14 Real Power The instantaneous power in an AC circuit oscillates, with a frequency double that of the voltage and current, around a certain average value. (In a 50 Hz system the frequencey of the power oscillation is thus 100 Hz) The real power is a measure of this average value (~ is this average value)
15 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 15 Reactive power The instantaneous power in an AC circuit oscillates, with a frequency double that of the voltage and current, around a certain average value. The reactive power is a measure of the amplitude of this oscillation (or a measure of the deviation of the instantaneous power from this average value)
16 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 16 The Apparent Power In an AC circuit of a specified voltage the apparent power is a measure of the magnitude (amplitude) of the alternating current (AC)
17 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 17 3 phase power systems (line to line/phase voltages/currents, 3 phase power, star/delta connections, 3 phase 3 wire/4 wire)
18 Advantages of three VÉL102M phase. - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Why Hreinsson 18 3 phases systems? Smooth flow of power (instantaneous power is a constant). Constant torque (reduced vibrations) The power delivery capacity is tripled (increased by 200%!) by increasing the number of conductors from 2 to 3 (increase by 50%) Reduced cost (same power less wire or more power same wire) Greater "power per kg" in motors, generators, and transformers.
19 3 separate identical VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 19 and simple 1 phase systems + V a I a V b + V c I b I c - 6 conductors can be reduced to 3! Generation Transmission Load
20 Waveforms: b- Phase VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 20 Different representation of 3 phase quantities : Voltage or current time v ( t) = 2 V sin( ωt) a v ( t) = 2 V sin ( ωt 120 ) b v ( t) = 2 V sin ( ωt+ 120 ) c Formulas: a- Phase c- Phase i ( t) = 2 I sin( ωt φ) a i ( t) = 2 I sin( ωt 120 φ) b i ( t) = 2 I sin( ωt+ 120 φ) c i () t + i () t + i () t = a b c [ 2 I sin( ωt ϕ) + sin( ωt 120 ϕ) + sin( ωt ϕ) = 0 The 3 return conductors can be thrown away!! ]
21 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 21 A 3 phase 3 wire system + V a I a V b + V c I b I c - Both neutrals may or may not be grounded
22 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 22 A mechanical analogy with a 3 phase hydraulic generator The total power delivery in a three phase system is smooth!
23 A mechanical analogy VÉL102M - Orkufrek with framleiðsluferli - Egill a Benedikt 1 Hreinsson 23 phase hydraulic generator Rafali Flutningur Stefna aflflæ is Álag Fyllt og loku vökvarás The power delivery in a one phase system is bumpy!
24 A 3 phase 4 wire VÉL102M system - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 24 (with ground wire) + V a I a V b + V c I b I c - Ground wire Both neutrals may or may not be grounded
25 A 2 phase 3 wire VÉL102M system - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill with Benedikt Hreinsson 25 ground wire) - + v a + v b i a i b - Ground wire v ( t) = 2 V cos( ωt) i ( t) = 2 I cos( ωt φ) a π π vb( t) = 2 V cos( ωt ) ib( t) = 2 I cos( ωt φ ) 2 2 a
26 A 1 phase system VÉL102M with - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli 2 - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 26 wires i a v () t = 2V cos( ωt) 1 1 z= r+ jωl V 2 + L /2 L /2 -i a z= r+ jωl 25 km The system is balanced against the earth
27 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 27 How are the 3 phases labelled? North America: a, b, c Europe: (old) R,S,T Europe: (new) L1, L2, L3
28 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 28 Instantaneous power in a 3 phase system v ( t) = 2 V sin( ωt) a v ( t) = 2 V sin ( ωt 120 ) b v ( t) = 2 V sin ( ωt+ 120 ) c 3 phase voltage: i ( t) = 2 I sin( ωt φ) a i ( t) = 2 I sin( ωt 120 φ) b i ( t) = 2 I sin( ωt+ 120 φ) c 3-phase current: From the above formulas, we get the total instantaneous power: p () t = v () t i () t + v () t i () t + v () t i () t 3 phase a a b b c c
29 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 29 Instantaneous power in a 3 phase system(2) p () t = v () t i () t + v () t i () t + v () t i () t 3 phase a a b b c c By inserting the formulas, we get: [ = 2 I V sin( ωt)sin( ωt φ) + sin( ωt 120 )sin( ωt 120 φ) + sin( ωt+ 120 )sin( ωt+ 120 φ) ]
30 Instantaneous power VÉL102M in - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli a 3 - Egill phase Benedikt Hreinsson 30 system (3) Use the following trigonometric identities to simplify: 1 sin xsin y = cos( x y) cos( x+ y) 2 [ ] cos( x) + cos( x 120 ) + cos( x+ 120 ) = 0 And we get finally the following formula p () t = 3I V cosφ = 3 P 3phase 1phase P = I V 1phase cos φ
31 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 31 Total 3 phase power Therefore, the total instantaneous power in all 3 phases is constant - or - 3 times the real power in each phase The power oscillates in each phase (although the sum of power in the phases is constant) No reactive power appears in the formula!! Reactive power is, however, very much present in each individual phase Remember: 200% increase in power with only 50% more wires
32 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 32 Y - Delta Connections in 3 Phase Systems
33 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 33 A 3 phase system - drawn like phasors - Star (Y) configuration V cf Neutral grounding I c V af I a V bf I b Neutral grounding
34 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson A 3 phase system with neutral 34 return V cf + I c + V bf + n V 1 af I a n 2 I b The neutrals are labelled n 1 and n 2 respectively n I
35 VÉL102M - Orkufrek framleiðsluferli - Egill Benedikt Hreinsson 35 A 3 phase system - drawn like phasors - Delta (D) connection V cf Neutral grounding I c V af I a V bf I b The Delta connection has never any neutral!
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits
 Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas
 Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module
Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module
Three Phase Circuits
 Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
ECE 421/521 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I 2 Basic Principles. Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2013
 ECE 41/51 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I Basic Principles Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 013 1 Outline Power in a 1-phase AC circuit Complex power Balanced 3-phase circuit Single Phase AC System
ECE 41/51 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I Basic Principles Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 013 1 Outline Power in a 1-phase AC circuit Complex power Balanced 3-phase circuit Single Phase AC System
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Basics of Electric Circuits
 António Dente Célia de Jesus February 2014 1 Alternating Current Circuits 1.1 Using Phasors There are practical and economic reasons justifying that electrical generators produce emf with alternating and
António Dente Célia de Jesus February 2014 1 Alternating Current Circuits 1.1 Using Phasors There are practical and economic reasons justifying that electrical generators produce emf with alternating and
LO 1: Three Phase Circuits
 Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Analysis of AC Power RMS and Phasors Power Factor. Power Factor. Eduardo Campero Littlewood
 Power Factor Eduardo Campero Littlewood Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Azcapotzalco Campus Energy Department Content 1 Analysis of AC Power 2 RMS and Phasors 3 Power Factor Recommended Bibliography
Power Factor Eduardo Campero Littlewood Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Azcapotzalco Campus Energy Department Content 1 Analysis of AC Power 2 RMS and Phasors 3 Power Factor Recommended Bibliography
BASIC PRINCIPLES. Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit
 BASIC PRINCIPLES Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit Let instantaneous voltage be v(t)=v m cos(ωt+θ v ) Let instantaneous current be i(t)=i m cos(ωt+θ i ) The instantaneous p(t) delivered to the load is p(t)=v(t)i(t)=v
BASIC PRINCIPLES Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit Let instantaneous voltage be v(t)=v m cos(ωt+θ v ) Let instantaneous current be i(t)=i m cos(ωt+θ i ) The instantaneous p(t) delivered to the load is p(t)=v(t)i(t)=v
Circuit Analysis-III. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 3 Friday 06 th April, 18
 Circuit Analysis-III Sinusoids Example #1 ü Find the amplitude, phase, period and frequency of the sinusoid: v (t ) =12cos(50t +10 ) Signal Conversion ü From sine to cosine and vice versa. ü sin (A ± B)
Circuit Analysis-III Sinusoids Example #1 ü Find the amplitude, phase, period and frequency of the sinusoid: v (t ) =12cos(50t +10 ) Signal Conversion ü From sine to cosine and vice versa. ü sin (A ± B)
11. AC Circuit Power Analysis
 . AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
. AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
6. Three-Phase Systems. Department of Electrical, Electronic, and Information Engineering (DEI) - University of Bologna
 6. Three-Phase Systems J B G Three-Phase Systems v v v i i i The generation and the distribution of electrical energy is usually done by three- phase systems. There are three wire system connected to a
6. Three-Phase Systems J B G Three-Phase Systems v v v i i i The generation and the distribution of electrical energy is usually done by three- phase systems. There are three wire system connected to a
Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit
 CA2627 Building Science Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit Instructor: Jiayu Chen Ph.D. Announcement 1. Makeup Midterm 2. Midterm grade Grade 25 20 15 10 5 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Grade Jiayu Chen, Ph.D. 2
CA2627 Building Science Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit Instructor: Jiayu Chen Ph.D. Announcement 1. Makeup Midterm 2. Midterm grade Grade 25 20 15 10 5 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Grade Jiayu Chen, Ph.D. 2
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON:
 VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON: 10EE35 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION BY DR. M.S. RAVIPRAKASHA PROFESSOR & HEAD DEPT. OF E&E ENGG. MALNAD COLLEGE OF ENGG. HASSAN 573 201. SUBJECT CODE
VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON: 10EE35 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION BY DR. M.S. RAVIPRAKASHA PROFESSOR & HEAD DEPT. OF E&E ENGG. MALNAD COLLEGE OF ENGG. HASSAN 573 201. SUBJECT CODE
12. Introduction and Chapter Objectives
 Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 1: Steady-State Sinusoidal Power 1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives In this chapter we will address the issue of power transmission via sinusoidal or AC) signals. This
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 1: Steady-State Sinusoidal Power 1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives In this chapter we will address the issue of power transmission via sinusoidal or AC) signals. This
ECE 420. Review of Three Phase Circuits. Copyright by Chanan Singh, Panida Jirutitijaroen, and Hangtian Lei, For educational use only-not for sale.
 ECE 40 Review of Three Phase Circuits Outline Phasor Complex power Power factor Balanced 3Ф circuit Read Appendix A Phasors and in steady state are sinusoidal functions with constant frequency 5 0 15 10
ECE 40 Review of Three Phase Circuits Outline Phasor Complex power Power factor Balanced 3Ф circuit Read Appendix A Phasors and in steady state are sinusoidal functions with constant frequency 5 0 15 10
Electronic Power Conversion
 Electronic Power Conversion Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts Challenge the future 3. Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts Notation Electric circuits Steady state
Electronic Power Conversion Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts Challenge the future 3. Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts Notation Electric circuits Steady state
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement ENE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement Class 11, February 4, 2009 werapon.chi@kmutt.ac.th 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction
Power and Energy Measurement ENE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement Class 11, February 4, 2009 werapon.chi@kmutt.ac.th 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction
Lecture 11 - AC Power
 - AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
- AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
Balanced three-phase systems and operation
 ELEC0014 - Introduction to power and energy systems Balanced three-phase systems and operation Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2017 1 / 17 system used for
ELEC0014 - Introduction to power and energy systems Balanced three-phase systems and operation Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2017 1 / 17 system used for
Three-phase AC Circuits. Measurement of Power in a Three-phase Circuit
 Three-phase AC Circuits Lesson Measurement of Power in a Three-phase Circuit In the previous lesson, the phase and line currents for balanced delta-connected load fed from a three-phase supply, along with
Three-phase AC Circuits Lesson Measurement of Power in a Three-phase Circuit In the previous lesson, the phase and line currents for balanced delta-connected load fed from a three-phase supply, along with
Chapter 2-3 Transformers
 Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics Chapter 2-3 Transformers Third Edition P. C. Sen Auto transformer Per unit system S b = S rate V b1 = V rate1 V b2 = V rate2 S b I b1 = = S rate =
Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics Chapter 2-3 Transformers Third Edition P. C. Sen Auto transformer Per unit system S b = S rate V b1 = V rate1 V b2 = V rate2 S b I b1 = = S rate =
ECE 476 Power System Analysis Fall 2014 Exam #1, Thursday, October 2, :30AM - 10:50AM
 ECE 476 Power System Analysis Fall 4 Exam #, Thursday, October, 4. 9:3AM - :5AM Name: Problem (5 p) Two balanced 3-phase loads are connected in parallel. One is Y-connected and draws 75 kw (3-phase) at.8
ECE 476 Power System Analysis Fall 4 Exam #, Thursday, October, 4. 9:3AM - :5AM Name: Problem (5 p) Two balanced 3-phase loads are connected in parallel. One is Y-connected and draws 75 kw (3-phase) at.8
Revision of Basic A.C. Theory
 Revision of Basic A.C. Theory 1 Revision of Basic AC Theory (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Electricity is generated in power stations
Revision of Basic A.C. Theory 1 Revision of Basic AC Theory (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Electricity is generated in power stations
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
Chapter 15 Power And Harmonics in Nonsinusoidal Systems
 Chapter 15 Power And Harmonics in Nonsinusoidal Systems 15.1. Average power in terms of Fourier series 15.2. RMS value of a waveform 15.3. Power factor THD Distortion and Displacement factors 15.4. Power
Chapter 15 Power And Harmonics in Nonsinusoidal Systems 15.1. Average power in terms of Fourier series 15.2. RMS value of a waveform 15.3. Power factor THD Distortion and Displacement factors 15.4. Power
Calculations of Capacitance for Transposed Bundled Conductor Transmission Lines
 Calculations of Capacitance for Transposed Bundled Conductor Transmission Lines Multi-conductor Lines. An example with a conductor bundle r: conductor radius, d: distance between conductors of the same
Calculations of Capacitance for Transposed Bundled Conductor Transmission Lines Multi-conductor Lines. An example with a conductor bundle r: conductor radius, d: distance between conductors of the same
Consider a simple RC circuit. We might like to know how much power is being supplied by the source. We probably need to find the current.
 AC power Consider a simple RC circuit We might like to know how much power is being supplied by the source We probably need to find the current R 10! R 10! is VS Vmcosωt Vm 10 V f 60 Hz V m 10 V C 150
AC power Consider a simple RC circuit We might like to know how much power is being supplied by the source We probably need to find the current R 10! R 10! is VS Vmcosωt Vm 10 V f 60 Hz V m 10 V C 150
Lecture 3: Three-phase power circuits
 1/24/28 Lecture : Three-phase power circuits 1 nstructor: Dr. Gleb. Tcheslavski Contact: gleb@ee.lamar.edu Office Hours: TBD; Room 2 Class web site: MyLamar ntroduction 2 Almost all electric power generation
1/24/28 Lecture : Three-phase power circuits 1 nstructor: Dr. Gleb. Tcheslavski Contact: gleb@ee.lamar.edu Office Hours: TBD; Room 2 Class web site: MyLamar ntroduction 2 Almost all electric power generation
Revised October 6, EEL , Henry Zmuda. 2. Three-Phase Circuits 1
 Three Phase Circuitsit Revised October 6, 008. Three-Phase Circuits 1 Preliminary Comments and a quick review of phasors. We live in the time domain. We also assume a causal (nonpredictive) world. Real-world
Three Phase Circuitsit Revised October 6, 008. Three-Phase Circuits 1 Preliminary Comments and a quick review of phasors. We live in the time domain. We also assume a causal (nonpredictive) world. Real-world
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
ECE 421/521 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I 2 Basic Principles. Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2014
 ECE 41/51 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I Basic Princiles Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 014 1 Outline Power in a 1-hase AC circuit Comlex ower Balanced 3-hase circuit Single Phase AC System
ECE 41/51 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I Basic Princiles Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 014 1 Outline Power in a 1-hase AC circuit Comlex ower Balanced 3-hase circuit Single Phase AC System
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis 9 Assessment Problems AP 9. [a] V = 70/ 40 V [b] 0 sin(000t +20 ) = 0 cos(000t 70 ).. I = 0/ 70 A [c] I =5/36.87 + 0/ 53.3 =4+j3+6 j8 =0 j5 =.8/ 26.57 A [d] sin(20,000πt
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis 9 Assessment Problems AP 9. [a] V = 70/ 40 V [b] 0 sin(000t +20 ) = 0 cos(000t 70 ).. I = 0/ 70 A [c] I =5/36.87 + 0/ 53.3 =4+j3+6 j8 =0 j5 =.8/ 26.57 A [d] sin(20,000πt
Lecture 9 Time Domain vs. Frequency Domain
 . Topics covered Lecture 9 Time Domain vs. Frequency Domain (a) AC power in the time domain (b) AC power in the frequency domain (c) Reactive power (d) Maximum power transfer in AC circuits (e) Frequency
. Topics covered Lecture 9 Time Domain vs. Frequency Domain (a) AC power in the time domain (b) AC power in the frequency domain (c) Reactive power (d) Maximum power transfer in AC circuits (e) Frequency
15-884/484 Electric Power Systems 1: DC and AC Circuits
 15-884/484 Electric Power Systems 1: DC and AC Circuits J. Zico Kolter October 8, 2013 1 Hydro Estimated U.S. Energy Use in 2010: ~98.0 Quads Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Solar 0.11 0.01 8.44
15-884/484 Electric Power Systems 1: DC and AC Circuits J. Zico Kolter October 8, 2013 1 Hydro Estimated U.S. Energy Use in 2010: ~98.0 Quads Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Solar 0.11 0.01 8.44
2 Signal Frequency and Impedances First Order Filter Circuits Resonant and Second Order Filter Circuits... 13
 Lecture Notes: 3454 Physics and Electronics Lecture ( nd Half), Year: 7 Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University //7 Contents Power in Ac Circuits Signal Frequency and Impedances
Lecture Notes: 3454 Physics and Electronics Lecture ( nd Half), Year: 7 Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University //7 Contents Power in Ac Circuits Signal Frequency and Impedances
ELECTRIC POWER CIRCUITS BASIC CONCEPTS AND ANALYSIS
 Contents ELEC46 Power ystem Analysis Lecture ELECTRC POWER CRCUT BAC CONCEPT AND ANALY. Circuit analysis. Phasors. Power in single phase circuits 4. Three phase () circuits 5. Power in circuits 6. ingle
Contents ELEC46 Power ystem Analysis Lecture ELECTRC POWER CRCUT BAC CONCEPT AND ANALY. Circuit analysis. Phasors. Power in single phase circuits 4. Three phase () circuits 5. Power in circuits 6. ingle
EM Oscillations. David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 212
 I ve got an oscillating fan at my house. The fan goes back and forth. It looks like the fan is saying No. So I like to ask it questions that a fan would say no to. Do you keep my hair in place? Do you
I ve got an oscillating fan at my house. The fan goes back and forth. It looks like the fan is saying No. So I like to ask it questions that a fan would say no to. Do you keep my hair in place? Do you
Power Systems - Basic Concepts and Applications - Part I
 PDHonline Course E104 (1 PDH) Power ystems Basic Concepts and Applications Part I Instructor: hihmin Hsu PhD PE 01 PDH Online PDH Center 57 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax A 006658 Phone & Fax: 709880088
PDHonline Course E104 (1 PDH) Power ystems Basic Concepts and Applications Part I Instructor: hihmin Hsu PhD PE 01 PDH Online PDH Center 57 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax A 006658 Phone & Fax: 709880088
REACTANCE. By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013
 REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
Chapter 31: AC Circuits
 hapter 31: A ircuits A urrents and Voltages In this chapter, we discuss the behior of circuits driven by a source of A. Recall that A means, literally, alternating current. An alternating current is a
hapter 31: A ircuits A urrents and Voltages In this chapter, we discuss the behior of circuits driven by a source of A. Recall that A means, literally, alternating current. An alternating current is a
Power system conductor volume calculation
 Power system conductor volume calculation Dr Audih alfaoury T&D power systems 2017-1018 Electrical Energy Engineering Department Dr Audih alfaoury 1 The transmission of electric power is carried at high
Power system conductor volume calculation Dr Audih alfaoury T&D power systems 2017-1018 Electrical Energy Engineering Department Dr Audih alfaoury 1 The transmission of electric power is carried at high
Course Updates. Reminders: 1) Assignment #10 due Today. 2) Quiz # 5 Friday (Chap 29, 30) 3) Start AC Circuits
 ourse Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr10/physics272.html eminders: 1) Assignment #10 due Today 2) Quiz # 5 Friday (hap 29, 30) 3) Start A ircuits Alternating urrents (hap 31) In this
ourse Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr10/physics272.html eminders: 1) Assignment #10 due Today 2) Quiz # 5 Friday (hap 29, 30) 3) Start A ircuits Alternating urrents (hap 31) In this
Toolbox: Electrical Systems Dynamics
 Toolbox: Electrical Systems Dynamics Dr. John C. Wright MIT - PSFC 05 OCT 2010 Introduction Outline Outline AC and DC power transmission Basic electric circuits Electricity and the grid Image removed due
Toolbox: Electrical Systems Dynamics Dr. John C. Wright MIT - PSFC 05 OCT 2010 Introduction Outline Outline AC and DC power transmission Basic electric circuits Electricity and the grid Image removed due
a + b Time Domain i(τ)dτ.
 R, C, and L Elements and their v and i relationships We deal with three essential elements in circuit analysis: Resistance R Capacitance C Inductance L Their v and i relationships are summarized below.
R, C, and L Elements and their v and i relationships We deal with three essential elements in circuit analysis: Resistance R Capacitance C Inductance L Their v and i relationships are summarized below.
ALTERNATING CURRENT. with X C = 0.34 A. SET UP: The specified value is the root-mean-square current; I. EXECUTE: (a) V = (0.34 A) = 0.12 A.
 ATENATING UENT 3 3 IDENTIFY: i Icosωt and I I/ SET UP: The specified value is the root-mean-square current; I 34 A EXEUTE: (a) I 34 A (b) I I (34 A) 48 A (c) Since the current is positive half of the time
ATENATING UENT 3 3 IDENTIFY: i Icosωt and I I/ SET UP: The specified value is the root-mean-square current; I 34 A EXEUTE: (a) I 34 A (b) I I (34 A) 48 A (c) Since the current is positive half of the time
Work, Energy and Power
 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
Pre-Lab. Introduction
 Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Chapter 32A AC Circuits. A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University
 Chapter 32A AC Circuits A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University 2007 Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Describe
Chapter 32A AC Circuits A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University 2007 Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Describe
2.3 Oscillation. The harmonic oscillator equation is the differential equation. d 2 y dt 2 r y (r > 0). Its solutions have the form
 2. Oscillation So far, we have used differential equations to describe functions that grow or decay over time. The next most common behavior for a function is to oscillate, meaning that it increases and
2. Oscillation So far, we have used differential equations to describe functions that grow or decay over time. The next most common behavior for a function is to oscillate, meaning that it increases and
BASIC NETWORK ANALYSIS
 SECTION 1 BASIC NETWORK ANALYSIS A. Wayne Galli, Ph.D. Project Engineer Newport News Shipbuilding Series-Parallel dc Network Analysis......................... 1.1 Branch-Current Analysis of a dc Network......................
SECTION 1 BASIC NETWORK ANALYSIS A. Wayne Galli, Ph.D. Project Engineer Newport News Shipbuilding Series-Parallel dc Network Analysis......................... 1.1 Branch-Current Analysis of a dc Network......................
THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS
 THR-HAS CIRCUITS 4.1 Introduction Generation, Transmission and distribution of electricity via the National Grid system is accomplished by three-phase alternating currents. The voltage induced by a single
THR-HAS CIRCUITS 4.1 Introduction Generation, Transmission and distribution of electricity via the National Grid system is accomplished by three-phase alternating currents. The voltage induced by a single
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Review of DC Electric Circuit. DC Electric Circuits Examples (source:
 Review of DC Electric Circuit DC Electric Circuits Examples (source: http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dcex.html) 1 Review - DC Electric Circuit Multisim Circuit Simulation DC Circuit
Review of DC Electric Circuit DC Electric Circuits Examples (source: http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dcex.html) 1 Review - DC Electric Circuit Multisim Circuit Simulation DC Circuit
Chapter 21: RLC Circuits. PHY2054: Chapter 21 1
 Chapter 21: RC Circuits PHY2054: Chapter 21 1 Voltage and Current in RC Circuits AC emf source: driving frequency f ε = ε sinωt ω = 2π f m If circuit contains only R + emf source, current is simple ε ε
Chapter 21: RC Circuits PHY2054: Chapter 21 1 Voltage and Current in RC Circuits AC emf source: driving frequency f ε = ε sinωt ω = 2π f m If circuit contains only R + emf source, current is simple ε ε
Driven RLC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions
 Driven LC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions Problem : Using the same circuit as in problem 6, only this time leaving the function generator on and driving below resonance, which in the following pairs
Driven LC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions Problem : Using the same circuit as in problem 6, only this time leaving the function generator on and driving below resonance, which in the following pairs
Power Electronics
 Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
AC Electric Machines. Objectives. Introduction. 1. To understand what the meant by the term ac circuit. 2. To understand how to analyze ac circuits.
 AC Electric Machines Objectives 1. To understand what the meant by the term ac circuit.. To understand how to analyze ac circuits. 3. To understand the basic construction and operation of an ac machine.
AC Electric Machines Objectives 1. To understand what the meant by the term ac circuit.. To understand how to analyze ac circuits. 3. To understand the basic construction and operation of an ac machine.
UNIT- I Phase Sequence:
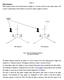 UNIT- I Phase Sequence: Phase sequence refers to the relation between voltages (or currents, as well) in a three-phase system. The common representation of this relation is in terms of a phasor diagram,
UNIT- I Phase Sequence: Phase sequence refers to the relation between voltages (or currents, as well) in a three-phase system. The common representation of this relation is in terms of a phasor diagram,
12 Chapter Driven RLC Circuits
 hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis
 Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis 1. Identify the frequency, angular frequency, peak value, rms value, and phase of a sinusoidal signal. 2. Solve steady-state
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis 1. Identify the frequency, angular frequency, peak value, rms value, and phase of a sinusoidal signal. 2. Solve steady-state
EXP. NO. 3 Power on (resistive inductive & capacitive) load Series connection
 OBJECT: To examine the power distribution on (R, L, C) series circuit. APPARATUS 1-signal function generator 2- Oscilloscope, A.V.O meter 3- Resisters & inductor &capacitor THEORY the following form for
OBJECT: To examine the power distribution on (R, L, C) series circuit. APPARATUS 1-signal function generator 2- Oscilloscope, A.V.O meter 3- Resisters & inductor &capacitor THEORY the following form for
Power Transfer Across a Power System Component as a Single Impedance
 1 Power Transfer Across a Power System Component as a Single Impedance Bus 1 S 1 =P 1 +jq 1 S =P +jq Z=jX + I + Bus V 1 - - V V j 1 V1 e δ j V e δ 1 = V = Power Transfer Across a Single Impedance Power
1 Power Transfer Across a Power System Component as a Single Impedance Bus 1 S 1 =P 1 +jq 1 S =P +jq Z=jX + I + Bus V 1 - - V V j 1 V1 e δ j V e δ 1 = V = Power Transfer Across a Single Impedance Power
Prof. Shayla Sawyer CP08 solution
 What does the time constant represent in an exponential function? How do you define a sinusoid? What is impedance? How is a capacitor affected by an input signal that changes over time? How is an inductor
What does the time constant represent in an exponential function? How do you define a sinusoid? What is impedance? How is a capacitor affected by an input signal that changes over time? How is an inductor
AC Power Analysis. Chapter Objectives:
 AC Power Analysis Chapter Objectives: Know the difference between instantaneous power and average power Learn the AC version of maximum power transfer theorem Learn about the concepts of effective or value
AC Power Analysis Chapter Objectives: Know the difference between instantaneous power and average power Learn the AC version of maximum power transfer theorem Learn about the concepts of effective or value
1 Phasors and Alternating Currents
 Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Lecture 35: FRI 17 APR Electrical Oscillations, LC Circuits, Alternating Current I
 Physics 3 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 35: FRI 7 APR Electrical Oscillations, LC Circuits, Alternating Current I Nikolai Tesla What are we going to learn? A road map Electric charge è Electric force on other
Physics 3 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 35: FRI 7 APR Electrical Oscillations, LC Circuits, Alternating Current I Nikolai Tesla What are we going to learn? A road map Electric charge è Electric force on other
Chapter 28: Alternating Current
 hapter 8: Alternating urrent Phasors and Alternating urrents Alternating current (A current) urrent which varies sinusoidally in tie is called alternating current (A) as opposed to direct current (D).
hapter 8: Alternating urrent Phasors and Alternating urrents Alternating current (A current) urrent which varies sinusoidally in tie is called alternating current (A) as opposed to direct current (D).
Generation, transmission and distribution, as well as power supplied to industrial and commercial customers uses a 3 phase system.
 Three-phase Circuits Generation, transmission and distribution, as well as power supplied to industrial and commercial customers uses a 3 phase system. Where 3 voltages are supplied of equal magnitude,
Three-phase Circuits Generation, transmission and distribution, as well as power supplied to industrial and commercial customers uses a 3 phase system. Where 3 voltages are supplied of equal magnitude,
Current and Resistance
 Current and Resistance 1 Define the current. Understand the microscopic description of current. Discuss the rat at which the power transfer to a device in an electric current. 2 2-1 Electric current 2-2
Current and Resistance 1 Define the current. Understand the microscopic description of current. Discuss the rat at which the power transfer to a device in an electric current. 2 2-1 Electric current 2-2
EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain.
![EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain. EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain.](/thumbs/95/123488230.jpg) Name If you have any questions ask them. Remember to include all units on your answers (V, A, etc). Clearly indicate your answers. All angles must be in the range 0 to +180 or 0 to 180 degrees. 1) [6 pts]
Name If you have any questions ask them. Remember to include all units on your answers (V, A, etc). Clearly indicate your answers. All angles must be in the range 0 to +180 or 0 to 180 degrees. 1) [6 pts]
THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS. Historical Profiles
 C H A P T E R THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS 1 2 Society is never prepared to receive any invention. Every new thing is resisted, and it takes years for the inventor to get people to listen to him and years more
C H A P T E R THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS 1 2 Society is never prepared to receive any invention. Every new thing is resisted, and it takes years for the inventor to get people to listen to him and years more
Chapter 9 Objectives
 Chapter 9 Engr8 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 9 Objectives Understand the concept of a phasor; Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the frequency domain using phasor
Chapter 9 Engr8 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 9 Objectives Understand the concept of a phasor; Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the frequency domain using phasor
04-Electric Power. ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems
 04-Electric Power ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems Overview Review of Electric Circuits Phasor Representation Electrical Power Power Factor Dr. Louie 2 Introduction Majority of the electrical energy
04-Electric Power ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems Overview Review of Electric Circuits Phasor Representation Electrical Power Power Factor Dr. Louie 2 Introduction Majority of the electrical energy
Power Systems - Basic Concepts and Applications - Part I
 PDHonline Course E104A (1 PDH) Power Systems - Basic Concepts and Applications - Part I Instructor: Shih-Min Hsu, Ph.D., P.E. 01 PDH Online PDH Center 57 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 030-6658 Phone
PDHonline Course E104A (1 PDH) Power Systems - Basic Concepts and Applications - Part I Instructor: Shih-Min Hsu, Ph.D., P.E. 01 PDH Online PDH Center 57 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 030-6658 Phone
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
Work, Energy and Power
 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
Electric Circuits II Power Measurement. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Circuits II Power Measurement Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Single-Phase Power Measurement 2 Three-Phase Power Measurement 2 Single-Phase Power Measurement The wattmeter is the instrument
Electric Circuits II Power Measurement Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Single-Phase Power Measurement 2 Three-Phase Power Measurement 2 Single-Phase Power Measurement The wattmeter is the instrument
CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation
 CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 26, 2005 1 Sinusoids Sinusoids
CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 26, 2005 1 Sinusoids Sinusoids
Laboratory I: Impedance
 Physics 331, Fall 2008 Lab I - Handout 1 Laboratory I: Impedance Reading: Simpson Chapter 1 (if necessary) & Chapter 2 (particularly 2.9-2.13) 1 Introduction In this first lab we review the properties
Physics 331, Fall 2008 Lab I - Handout 1 Laboratory I: Impedance Reading: Simpson Chapter 1 (if necessary) & Chapter 2 (particularly 2.9-2.13) 1 Introduction In this first lab we review the properties
10.1 COMPLEX POWER IN CIRCUITS WITH AC SIGNALS
 HAPER 10 Power in A ircuits HAPER OUINE 10.1 omplex Power in ircuits with A ignals 10. How to alculate omplex Power 10.3 omplex Power alculations in eries Parallel ircuits 10.4 Power Factor and pf orrection
HAPER 10 Power in A ircuits HAPER OUINE 10.1 omplex Power in ircuits with A ignals 10. How to alculate omplex Power 10.3 omplex Power alculations in eries Parallel ircuits 10.4 Power Factor and pf orrection
Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations
 Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations 5-1 Repeating the Example on Power Factor Correction (Given last Class) P? Q? S? Light Motor From source 1000 volts @ 60 Htz 10kW
Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations 5-1 Repeating the Example on Power Factor Correction (Given last Class) P? Q? S? Light Motor From source 1000 volts @ 60 Htz 10kW
EEE3405 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 2 - TEST
 ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis. Phasors
 Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis Lecture 6, 0/07/05 OUTLINE Phasor ReCap Capacitor/Inductor Example Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis with Complex Impedance Phasor
Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis Lecture 6, 0/07/05 OUTLINE Phasor ReCap Capacitor/Inductor Example Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis with Complex Impedance Phasor
I. Impedance of an R-L circuit.
 I. Impedance of an R-L circuit. [For inductor in an AC Circuit, see Chapter 31, pg. 1024] Consider the R-L circuit shown in Figure: 1. A current i(t) = I cos(ωt) is driven across the circuit using an AC
I. Impedance of an R-L circuit. [For inductor in an AC Circuit, see Chapter 31, pg. 1024] Consider the R-L circuit shown in Figure: 1. A current i(t) = I cos(ωt) is driven across the circuit using an AC
Lecture 9: Space-Vector Models
 1 / 30 Lecture 9: Space-Vector Models ELEC-E8405 Electric Drives (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Autumn 2017 2 / 30 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you will be able to: Include the number of
1 / 30 Lecture 9: Space-Vector Models ELEC-E8405 Electric Drives (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Autumn 2017 2 / 30 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you will be able to: Include the number of
PHYSICS NOTES ALTERNATING CURRENT
 LESSON 7 ALENAING CUEN Alternating current As we have seen earlier a rotating coil in a magnetic field, induces an alternating emf and hence an alternating current. Since the emf induced in the coil varies
LESSON 7 ALENAING CUEN Alternating current As we have seen earlier a rotating coil in a magnetic field, induces an alternating emf and hence an alternating current. Since the emf induced in the coil varies
Week No. 6 Chapter Six: Power Factor Improvement
 Week No. 6 Chapter Six: Power Factor Improvement The electrical energy is almost wholly generated, transmitted and distributed in the form of alternating current. Therefore, the question of power factor
Week No. 6 Chapter Six: Power Factor Improvement The electrical energy is almost wholly generated, transmitted and distributed in the form of alternating current. Therefore, the question of power factor
Three Phase Systems 295
 Three Phase Systems 95 9. MEASUEMENT OF POE Star-Connected Balanced Load with Neutral Point Power can be measured in this case by connecting a single wattmeter with its current coil in one line and the
Three Phase Systems 95 9. MEASUEMENT OF POE Star-Connected Balanced Load with Neutral Point Power can be measured in this case by connecting a single wattmeter with its current coil in one line and the
The Eects of Harmonics in Power Systems and Methods to Reduce or Eliminate Them
 The Eects of Harmonics in Power Systems and Methods to Reduce or Eliminate Them Wilbur N. Dale, Ph.D., P.E. wilburd@rstva.com March 15, 2012 Overview Introduction Analysis of Harmonics Sources of Harmonics
The Eects of Harmonics in Power Systems and Methods to Reduce or Eliminate Them Wilbur N. Dale, Ph.D., P.E. wilburd@rstva.com March 15, 2012 Overview Introduction Analysis of Harmonics Sources of Harmonics
Fault Analysis Power System Representation
 .1. Power System Representation Single Line Diagram: Almost all modern power systems are three phase systems with the phases of equal magnitude and equal phase difference (i.e., 10 o ). These three phase
.1. Power System Representation Single Line Diagram: Almost all modern power systems are three phase systems with the phases of equal magnitude and equal phase difference (i.e., 10 o ). These three phase
Electric Circuit Theory
 Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 11 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 11.1
Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 11 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 11.1
Sinusoidal steady-state analysis
 Sinusoidal steady-state analysis From our previous efforts with AC circuits, some patterns in the analysis started to appear. 1. In each case, the steady-state voltages or currents created in response
Sinusoidal steady-state analysis From our previous efforts with AC circuits, some patterns in the analysis started to appear. 1. In each case, the steady-state voltages or currents created in response
(Refer Slide Time: 00:55) Friends, today we shall continue to study about the modelling of synchronous machine. (Refer Slide Time: 01:09)
 (Refer Slide Time: 00:55) Power System Dynamics Prof. M. L. Kothari Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 09 Modelling of Synchronous Machine (Contd ) Friends,
(Refer Slide Time: 00:55) Power System Dynamics Prof. M. L. Kothari Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 09 Modelling of Synchronous Machine (Contd ) Friends,
K.K. Gan L3: R-L-C AC Circuits. amplitude. Volts. period. -Vo
 Lecture 3: R-L-C AC Circuits AC (Alternative Current): Most of the time, we are interested in the voltage at a point in the circuit will concentrate on voltages here rather than currents. We encounter
Lecture 3: R-L-C AC Circuits AC (Alternative Current): Most of the time, we are interested in the voltage at a point in the circuit will concentrate on voltages here rather than currents. We encounter
