Prof. Shayla Sawyer CP08 solution
|
|
|
- Anis Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What does the time constant represent in an exponential function? How do you define a sinusoid? What is impedance? How is a capacitor affected by an input signal that changes over time? How is an inductor affected by an input signal that changes over time? How do you derive the equation for an integrator and differentiator? Why does a capacitor or inductor in the op amp circuit cause integration or differentiation? Sinusoidal waveform Draw sinusoid with VA is the amplitude in volts and definies minimum and maximum values To is the period in seconds) which is the time required to complete once cylce Can be expressed with either sine or cosine function, the choice between the two depends where we choose to define t0. If we chose t0, v(t)0 v( t) V A sin If we choose t0, v(t)+va v( t) V A cos V V typically use cosine version (still call it a sinusoid) General expression for the sinusoid replaces t with (t-ts) to signify a shift in time (Ts is the time shift parameter) Peak nearest the origin occurs at tts Shift can also be definied as a phase angle or phase shift. Changing the phase angle moves the waveform to the left or right, revealing different phases of the oscillating waveform. Based on the circular interpretation of the cosine function. A period is divided into 2πradians or 360 degrees. T s T s QFi6s4RXXY ϕ 2π com/unitcircle/unit_circle _applet.html The phase angle is often given in degrees but must be converted to radians so units of the 2πt/T0 terms match of
2 Fourier coefficients An alternative form of the general sinusoid equation is obtained using the identity cos( x + y) cos( x) cos( y) sin( x) sin( y) v( t) ( V A cosϕ)cos 2π t a also sin( x + y) sinx cosy + ( V A sinφ) sin 2π t V A cosϕ Fourier coefficients-constants b V A sinϕ v( t) a cos T 0 ϕ tan b a + b sin V Cyclic frequency f0 is defined as the number of periods per unit time. f 0 units Hz Angular frequency ω0 is in radians per second and related by ω 0 2π f 0 2π Primary parameters. Amplitude: either VA or the Fourier coefficients a and b 2. Time shift: either Ts or the phase angle ϕ 3. Time/frequency: either T0, f0, or ω0 V + cosx siny Three equivalent ways to represent a sinusoid t T s v( t) V A cos 2π V T A cos + ϕ 0 T a cos 0 v( t) V A cos 2π f 0 t T s V A cos 2π f 0 t + ϕ a cos 2π f 0 t v( t) V A cos ω 0 t T s V A cos ω 0 t + ϕ a cos ω 0 t + bsin + b sin ω 0 t V V + b sin 2π f 0 t V 2 of
3 ) (Example 5-9 in the text book) The diagram below is an oscilloscope display of a sinusoid. The vertical axis (amplitude) is calibrated at 5V per division, and the horizontal axis (time) is calibrated at 0. ms per division. Derive an expression for the sinusoid (IF t0 is in the center of the oscilloscope). a. Find the amplitude VA Note: the waveform is centered on the x-axis V A ( 4div) 5 V 20V div b. Find T0 Need cycle: Can find by taking /2 cycle and multiplying times 2 ( 4div 2) 0. ms div 0.8ms c. Find f0 and ω0 f 0 : f 0.8ms 0.25 khz ω 0 : rad s 2π f 0 3 of
4 d. Determine Ts T s : T s 0.05 T.s is positive and positive peak is delayed e. Calculate ϕ0, Fourier coefficients t 0.05 T s T s ϕ 2π 360 ϕ : 2 π ϕ 22.5 deg ϕ rad a : 20 cos( ϕ) a b : 20 sin( ϕ) b f. Write equations v( t) V A cos ( ωt) T s v( t) 20 cos 7854t V v( t) V A cos( ωt + ϕ) V v( t) 20 cos( 7854t 22.5deg) V v( t) a cos( ωt) + b sin( ωt) V v( t) 8.48 cos( 7854ωt) sin( 7854ωt) 4 of
5 2.) Sketch the waveform described by v( t) 0 cos( 2000π t 60deg) V v( t) V A cos 2π f 0 t + ϕ V A 0 f 02 : 2000Hz Hz 2 : f 02 2 ms T s ϕ ms ms T s.67ms 5 of
6 3.) Characterize the composite waveform generated by subtracting an exponential from a step function with the same amplitude t v( t) V A u( t) TC V A e u( t) V t TC V A e u( t) V For t<0, the waveform is 0 because the step function is 0 before that time. At t 0 the waveform is still zero because the step and exponential cancel: v( 0) V A e 0 0 For t>>>tc, the waveform approaches a constant value VA because the exponential term decays to zero. For practical purposes v(t) is within less than % of its final value VA when t 5 Tc At ttc v( t) V A e 0.632V A e The waveform rises to about 63% of its value in one time constant e of
7 4.) Find an expression for the equivalent impedance A C 4E-9 L 4E-6 C3 8E-9 B L2 E-6 C2 8E-9 C4 8E-9 C C 4 : 8nF : 4nF C 2 : 8nF C 3 : 8nF L : 4μH L 2 : μh C3 and C4 are in series C 34 : + C 3 C 4 C 34 4 nf C 4E-9 L 4E-6 C2 8E-9 CEQ 4E-9 L2 E-6 7 of
8 C2 and C34 in parallel C 234 : C 2 + C 34 C nf C 4E-9 L 4E-6 CEQ2 2E-9 L2 E-6 C and C234 in series C 234 : + C 234 C C nf CEQ3 3E-9 L 4E-6 L2 E-6 8 of
9 L and L2 in series L 2 : L + L 2 CEQ3 3E-9 L 5E-6 L 2 5μH No more reduction is possible 9 of
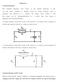
10 Determine the relationship between the input voltage and the output voltage for the circuits below Vin R k 0 U V+ OS2 OUT 2-4 OS ua74 V- 5 6 Vout ( a) C n Vin C2 n 0 U V+ OS2 OUT 2-4 OS ua74 V- 5 6 Vout ( b) R2 k ( a) KCL at node V0 ir + ic 0 0 V in d 0 V out + C R 0 dt V in Vout + C R d 0 dt dv out V in C dt R V out R C V in dt 0 of
11 ( b) KCL at node V0 ic 2 + ir 2 0 d 0 V in C 2 dt 0 V out + 0 R 2 dv in C 2 dt V out R 2 dv in Vout R 2 C 2 dt of
Circuit Analysis-III. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 3 Friday 06 th April, 18
 Circuit Analysis-III Sinusoids Example #1 ü Find the amplitude, phase, period and frequency of the sinusoid: v (t ) =12cos(50t +10 ) Signal Conversion ü From sine to cosine and vice versa. ü sin (A ± B)
Circuit Analysis-III Sinusoids Example #1 ü Find the amplitude, phase, period and frequency of the sinusoid: v (t ) =12cos(50t +10 ) Signal Conversion ü From sine to cosine and vice versa. ü sin (A ± B)
ECE 201 Fall 2009 Final Exam
 ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
Handout 11: AC circuit. AC generator
 Handout : AC circuit AC generator Figure compares the voltage across the directcurrent (DC) generator and that across the alternatingcurrent (AC) generator For DC generator, the voltage is constant For
Handout : AC circuit AC generator Figure compares the voltage across the directcurrent (DC) generator and that across the alternatingcurrent (AC) generator For DC generator, the voltage is constant For
Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors
 Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors 1. Motivation 2. Sinusoid Features 3. Phasors 4. Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements 5. Impedance and Admittance 6. Kirchhoff s Laws in the Frequency Domain 7. Impedance
Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors 1. Motivation 2. Sinusoid Features 3. Phasors 4. Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements 5. Impedance and Admittance 6. Kirchhoff s Laws in the Frequency Domain 7. Impedance
Sinusoids and Phasors
 CHAPTER 9 Sinusoids and Phasors We now begins the analysis of circuits in which the voltage or current sources are time-varying. In this chapter, we are particularly interested in sinusoidally time-varying
CHAPTER 9 Sinusoids and Phasors We now begins the analysis of circuits in which the voltage or current sources are time-varying. In this chapter, we are particularly interested in sinusoidally time-varying
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE
 EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 18 121025 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review RMS Values Complex Numbers Phasors Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 18 121025 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review RMS Values Complex Numbers Phasors Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8. θ (radians) θ (degrees) cos θ sin θ π/ /2 1/2 π/4 45 2/2 2/2 π/3 60 1/2 3/2 π/
 Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8 Trigonometric Identities ( cos(θ) = cos(θ) sin(θ) = sin(θ) sin(θ) = cos θ π ) 2 Cosines and Sines of common angles Euler s Formula θ (radians) θ (degrees)
Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8 Trigonometric Identities ( cos(θ) = cos(θ) sin(θ) = sin(θ) sin(θ) = cos θ π ) 2 Cosines and Sines of common angles Euler s Formula θ (radians) θ (degrees)
Frequency Response. Re ve jφ e jωt ( ) where v is the amplitude and φ is the phase of the sinusoidal signal v(t). ve jφ
 27 Frequency Response Before starting, review phasor analysis, Bode plots... Key concept: small-signal models for amplifiers are linear and therefore, cosines and sines are solutions of the linear differential
27 Frequency Response Before starting, review phasor analysis, Bode plots... Key concept: small-signal models for amplifiers are linear and therefore, cosines and sines are solutions of the linear differential
Revision of Basic A.C. Theory
 Revision of Basic A.C. Theory 1 Revision of Basic AC Theory (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Electricity is generated in power stations
Revision of Basic A.C. Theory 1 Revision of Basic AC Theory (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Electricity is generated in power stations
2.3 Oscillation. The harmonic oscillator equation is the differential equation. d 2 y dt 2 r y (r > 0). Its solutions have the form
 2. Oscillation So far, we have used differential equations to describe functions that grow or decay over time. The next most common behavior for a function is to oscillate, meaning that it increases and
2. Oscillation So far, we have used differential equations to describe functions that grow or decay over time. The next most common behavior for a function is to oscillate, meaning that it increases and
Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas
 Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module
Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module
ENGR 2405 Chapter 8. Second Order Circuits
 ENGR 2405 Chapter 8 Second Order Circuits Overview The previous chapter introduced the concept of first order circuits. This chapter will expand on that with second order circuits: those that need a second
ENGR 2405 Chapter 8 Second Order Circuits Overview The previous chapter introduced the concept of first order circuits. This chapter will expand on that with second order circuits: those that need a second
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
I. Impedance of an R-L circuit.
 I. Impedance of an R-L circuit. [For inductor in an AC Circuit, see Chapter 31, pg. 1024] Consider the R-L circuit shown in Figure: 1. A current i(t) = I cos(ωt) is driven across the circuit using an AC
I. Impedance of an R-L circuit. [For inductor in an AC Circuit, see Chapter 31, pg. 1024] Consider the R-L circuit shown in Figure: 1. A current i(t) = I cos(ωt) is driven across the circuit using an AC
SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
 SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1. Introduction A sinusoidal current has the following form: where I m is the amplitude value; ω=2 πf is the angular frequency; φ is the phase shift. i (t )=I m.sin
SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1. Introduction A sinusoidal current has the following form: where I m is the amplitude value; ω=2 πf is the angular frequency; φ is the phase shift. i (t )=I m.sin
Electric Circuit Theory
 Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 11 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 11.1
Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 11 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 11.1
y 2 Well it is a cos graph with amplitude of 3 and only half a waveform between 0 and 2π because the cos argument is x /2: y =3cos π 2
 Complete Solutions Eamination Questions Complete Solutions to Eamination Questions 4. (a) How do we sketch the graph of y 3? Well it is a graph with amplitude of 3 and only half a waveform between 0 and
Complete Solutions Eamination Questions Complete Solutions to Eamination Questions 4. (a) How do we sketch the graph of y 3? Well it is a graph with amplitude of 3 and only half a waveform between 0 and
04-Electric Power. ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems
 04-Electric Power ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems Overview Review of Electric Circuits Phasor Representation Electrical Power Power Factor Dr. Louie 2 Introduction Majority of the electrical energy
04-Electric Power ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems Overview Review of Electric Circuits Phasor Representation Electrical Power Power Factor Dr. Louie 2 Introduction Majority of the electrical energy
ELEC 202 Electric Circuit Analysis II Lecture 10(a) Complex Arithmetic and Rectangular/Polar Forms
 Dr. Gregory J. Mazzaro Spring 2016 ELEC 202 Electric Circuit Analysis II Lecture 10(a) Complex Arithmetic and Rectangular/Polar Forms THE CITADEL, THE MILITARY COLLEGE OF SOUTH CAROLINA 171 Moultrie Street,
Dr. Gregory J. Mazzaro Spring 2016 ELEC 202 Electric Circuit Analysis II Lecture 10(a) Complex Arithmetic and Rectangular/Polar Forms THE CITADEL, THE MILITARY COLLEGE OF SOUTH CAROLINA 171 Moultrie Street,
ENGR-4300 Spring 2009 Test 2. Name: SOLUTION. Section: 1(MR 8:00) 2(TF 2:00) 3(MR 6:00) (circle one) Question I (20 points): Question II (20 points):
 ENGR43 Test 2 Spring 29 ENGR43 Spring 29 Test 2 Name: SOLUTION Section: 1(MR 8:) 2(TF 2:) 3(MR 6:) (circle one) Question I (2 points): Question II (2 points): Question III (17 points): Question IV (2 points):
ENGR43 Test 2 Spring 29 ENGR43 Spring 29 Test 2 Name: SOLUTION Section: 1(MR 8:) 2(TF 2:) 3(MR 6:) (circle one) Question I (2 points): Question II (2 points): Question III (17 points): Question IV (2 points):
f = 1 T 6 a.c. (Alternating Current) Circuits Most signals of interest in electronics are periodic : they repeat regularly as a function of time.
 Analogue Electronics (Aero).66 66 Analogue Electronics (Aero) 6.66 6 a.c. (Alternating Current) Circuits Most signals of interest in electronics are periodic : they repeat regularly as a function of time.
Analogue Electronics (Aero).66 66 Analogue Electronics (Aero) 6.66 6 a.c. (Alternating Current) Circuits Most signals of interest in electronics are periodic : they repeat regularly as a function of time.
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 28 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 3 TUTORIAL 1 - TRIGONOMETRICAL GRAPHS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 28 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 3 TUTORIAL 1 - TRIGONOMETRICAL GRAPHS CONTENTS 3 Be able to understand how to manipulate trigonometric expressions and apply
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 28 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 3 TUTORIAL 1 - TRIGONOMETRICAL GRAPHS CONTENTS 3 Be able to understand how to manipulate trigonometric expressions and apply
EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3. Name:
 EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed Scientific calculators are allowed Complete
EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed Scientific calculators are allowed Complete
Chapter 9 Objectives
 Chapter 9 Engr8 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 9 Objectives Understand the concept of a phasor; Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the frequency domain using phasor
Chapter 9 Engr8 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 9 Objectives Understand the concept of a phasor; Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the frequency domain using phasor
REACTANCE. By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013
 REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
LINEAR CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (EED) U.E.T. TAXILA 09
 LINEAR CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (EED) U.E.T. TAXILA 09 ENGR. M. MANSOOR ASHRAF INTRODUCTION Thus far our analysis has been restricted for the most part to dc circuits: those circuits excited by constant or time-invariant
LINEAR CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (EED) U.E.T. TAXILA 09 ENGR. M. MANSOOR ASHRAF INTRODUCTION Thus far our analysis has been restricted for the most part to dc circuits: those circuits excited by constant or time-invariant
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
L L, R, C. Kirchhoff s rules applied to AC circuits. C Examples: Resonant circuits: series and parallel LRC. Filters: narrowband,
 Today in Physics 1: A circuits Solving circuit problems one frequency at a time. omplex impedance of,,. Kirchhoff s rules applied to A circuits. it V in Examples: esonant circuits: i series and parallel.
Today in Physics 1: A circuits Solving circuit problems one frequency at a time. omplex impedance of,,. Kirchhoff s rules applied to A circuits. it V in Examples: esonant circuits: i series and parallel.
Lectures 16 & 17 Sinusoidal Signals, Complex Numbers, Phasors, Impedance & AC Circuits. Nov. 7 & 9, 2011
 Lectures 16 & 17 Sinusoidal Signals, Complex Numbers, Phasors, Impedance & AC Circuits Nov. 7 & 9, 2011 Material from Textbook by Alexander & Sadiku and Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications,
Lectures 16 & 17 Sinusoidal Signals, Complex Numbers, Phasors, Impedance & AC Circuits Nov. 7 & 9, 2011 Material from Textbook by Alexander & Sadiku and Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications,
EE100Su08 Lecture #11 (July 21 st 2008)
 EE100Su08 Lecture #11 (July 21 st 2008) Bureaucratic Stuff Lecture videos should be up by tonight HW #2: Pick up from office hours today, will leave them in lab. REGRADE DEADLINE: Monday, July 28 th 2008,
EE100Su08 Lecture #11 (July 21 st 2008) Bureaucratic Stuff Lecture videos should be up by tonight HW #2: Pick up from office hours today, will leave them in lab. REGRADE DEADLINE: Monday, July 28 th 2008,
EE40 Homework #6. Due Oct 15 (Thursday), 12:00 noon in Cory 240
 Fall 2009 EE40 Homework #6 Due Oct 15 (Thursday), 12:00 noon in Cory 240 Reading Assignments Chapter 5 of Hambley textbook. Section 5.7 on Three-Phase circuit is optional Sections 6.1-6.5 of Hambley textbook
Fall 2009 EE40 Homework #6 Due Oct 15 (Thursday), 12:00 noon in Cory 240 Reading Assignments Chapter 5 of Hambley textbook. Section 5.7 on Three-Phase circuit is optional Sections 6.1-6.5 of Hambley textbook
Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis. Phasors
 Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis Lecture 6, 0/07/05 OUTLINE Phasor ReCap Capacitor/Inductor Example Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis with Complex Impedance Phasor
Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis Lecture 6, 0/07/05 OUTLINE Phasor ReCap Capacitor/Inductor Example Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis with Complex Impedance Phasor
EXP. NO. 3 Power on (resistive inductive & capacitive) load Series connection
 OBJECT: To examine the power distribution on (R, L, C) series circuit. APPARATUS 1-signal function generator 2- Oscilloscope, A.V.O meter 3- Resisters & inductor &capacitor THEORY the following form for
OBJECT: To examine the power distribution on (R, L, C) series circuit. APPARATUS 1-signal function generator 2- Oscilloscope, A.V.O meter 3- Resisters & inductor &capacitor THEORY the following form for
AC analysis. EE 201 AC analysis 1
 AC analysis Now we turn to circuits with sinusoidal sources. Earlier, we had a brief look at sinusoids, but now we will add in capacitors and inductors, making the story much more interesting. What are
AC analysis Now we turn to circuits with sinusoidal sources. Earlier, we had a brief look at sinusoids, but now we will add in capacitors and inductors, making the story much more interesting. What are
Response of Second-Order Systems
 Unit 3 Response of SecondOrder Systems In this unit, we consider the natural and step responses of simple series and parallel circuits containing inductors, capacitors and resistors. The equations which
Unit 3 Response of SecondOrder Systems In this unit, we consider the natural and step responses of simple series and parallel circuits containing inductors, capacitors and resistors. The equations which
a + b Time Domain i(τ)dτ.
 R, C, and L Elements and their v and i relationships We deal with three essential elements in circuit analysis: Resistance R Capacitance C Inductance L Their v and i relationships are summarized below.
R, C, and L Elements and their v and i relationships We deal with three essential elements in circuit analysis: Resistance R Capacitance C Inductance L Their v and i relationships are summarized below.
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY TUTORIAL 3 PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY TUTORIAL 3 PERIODIC FUNCTIONS This is the one of a series of basic tutorials in mathematics aimed at beginners or anyone wanting to refresh themselves on fundamentals.
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY TUTORIAL 3 PERIODIC FUNCTIONS This is the one of a series of basic tutorials in mathematics aimed at beginners or anyone wanting to refresh themselves on fundamentals.
Experiment Guide for RC Circuits
 Guide-P1 Experiment Guide for RC Circuits I. Introduction 1. Capacitors A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field. The unit of capacitance is
Guide-P1 Experiment Guide for RC Circuits I. Introduction 1. Capacitors A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field. The unit of capacitance is
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Laboratory I: Impedance
 Physics 331, Fall 2008 Lab I - Handout 1 Laboratory I: Impedance Reading: Simpson Chapter 1 (if necessary) & Chapter 2 (particularly 2.9-2.13) 1 Introduction In this first lab we review the properties
Physics 331, Fall 2008 Lab I - Handout 1 Laboratory I: Impedance Reading: Simpson Chapter 1 (if necessary) & Chapter 2 (particularly 2.9-2.13) 1 Introduction In this first lab we review the properties
Solutions to these tests are available online in some places (but not all explanations are good)...
 The Physics GRE Sample test put out by ETS https://www.ets.org/s/gre/pdf/practice_book_physics.pdf OSU physics website has lots of tips, and 4 additional tests http://www.physics.ohiostate.edu/undergrad/ugs_gre.php
The Physics GRE Sample test put out by ETS https://www.ets.org/s/gre/pdf/practice_book_physics.pdf OSU physics website has lots of tips, and 4 additional tests http://www.physics.ohiostate.edu/undergrad/ugs_gre.php
In Chapter 15, you learned how to analyze a few simple ac circuits in the time
 In Chapter 15, you learned how to analyze a few simple ac circuits in the time domain using voltages and currents expressed as functions of time. However, this is not a very practical approach. A more
In Chapter 15, you learned how to analyze a few simple ac circuits in the time domain using voltages and currents expressed as functions of time. However, this is not a very practical approach. A more
MODULE I. Transient Response:
 Transient Response: MODULE I The Transient Response (also known as the Natural Response) is the way the circuit responds to energies stored in storage elements, such as capacitors and inductors. If a capacitor
Transient Response: MODULE I The Transient Response (also known as the Natural Response) is the way the circuit responds to energies stored in storage elements, such as capacitors and inductors. If a capacitor
C R. Consider from point of view of energy! Consider the RC and LC series circuits shown:
 ircuits onsider the R and series circuits shown: ++++ ---- R ++++ ---- Suppose that the circuits are formed at t with the capacitor charged to value. There is a qualitative difference in the time development
ircuits onsider the R and series circuits shown: ++++ ---- R ++++ ---- Suppose that the circuits are formed at t with the capacitor charged to value. There is a qualitative difference in the time development
Print Name : ID : ECE Test #1 9/22/2016
 Print Name : Email ID : ECE 2660 Test #1 9/22/2016 All answers must be recorded on the answer page (page 2). You must do all questions on the exam. For Part 4 you must show all your work and write your
Print Name : Email ID : ECE 2660 Test #1 9/22/2016 All answers must be recorded on the answer page (page 2). You must do all questions on the exam. For Part 4 you must show all your work and write your
ECE Spring 2017 Final Exam
 ECE 20100 Spring 2017 Final Exam May 2, 2017 Section (circle below) Qi (12:30) 0001 Tan (10:30) 0004 Hosseini (7:30) 0005 Cui (1:30) 0006 Jung (11:30) 0007 Lin (9:30) 0008 Peleato-Inarrea (2:30) 0009 Name
ECE 20100 Spring 2017 Final Exam May 2, 2017 Section (circle below) Qi (12:30) 0001 Tan (10:30) 0004 Hosseini (7:30) 0005 Cui (1:30) 0006 Jung (11:30) 0007 Lin (9:30) 0008 Peleato-Inarrea (2:30) 0009 Name
09/29/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapter 5 and Appendix A
 EE40 Lec 10 Complex Numbers and Phasors Prof. Nathan Cheung 09/29/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapter 5 and Appendix A Slide 1 OUTLINE Phasors as notation for Sinusoids Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex
EE40 Lec 10 Complex Numbers and Phasors Prof. Nathan Cheung 09/29/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapter 5 and Appendix A Slide 1 OUTLINE Phasors as notation for Sinusoids Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Almost all electrical systems, whether signal or power, operate with alternating currents and voltages. We have seen that when any circuit is disturbed (switched on or
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Almost all electrical systems, whether signal or power, operate with alternating currents and voltages. We have seen that when any circuit is disturbed (switched on or
E40M. Op Amps. M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1
 E40M Op Amps M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1 Reading A&L: Chapter 15, pp. 863-866. Reader, Chapter 8 Noninverting Amp http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/opamp/opamp_3.html Inverting Amp http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/opamp/opamp_2.html
E40M Op Amps M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1 Reading A&L: Chapter 15, pp. 863-866. Reader, Chapter 8 Noninverting Amp http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/opamp/opamp_3.html Inverting Amp http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/opamp/opamp_2.html
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits
 Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
12 Chapter Driven RLC Circuits
 hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA
 EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis 9 Assessment Problems AP 9. [a] V = 70/ 40 V [b] 0 sin(000t +20 ) = 0 cos(000t 70 ).. I = 0/ 70 A [c] I =5/36.87 + 0/ 53.3 =4+j3+6 j8 =0 j5 =.8/ 26.57 A [d] sin(20,000πt
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis 9 Assessment Problems AP 9. [a] V = 70/ 40 V [b] 0 sin(000t +20 ) = 0 cos(000t 70 ).. I = 0/ 70 A [c] I =5/36.87 + 0/ 53.3 =4+j3+6 j8 =0 j5 =.8/ 26.57 A [d] sin(20,000πt
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 12
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 12 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 12 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
Driven RLC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions
 Driven LC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions Problem : Using the same circuit as in problem 6, only this time leaving the function generator on and driving below resonance, which in the following pairs
Driven LC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions Problem : Using the same circuit as in problem 6, only this time leaving the function generator on and driving below resonance, which in the following pairs
1. (10 points) Find the general solution to the following second-order differential equation:
 Math 307A, Winter 014 Midterm Solutions Page 1 of 8 1. (10 points) Find the general solution to the following second-order differential equation: 4y 1y + 9y = 9t. To find the general solution to this nonhomogeneous
Math 307A, Winter 014 Midterm Solutions Page 1 of 8 1. (10 points) Find the general solution to the following second-order differential equation: 4y 1y + 9y = 9t. To find the general solution to this nonhomogeneous
Time Varying Circuit Analysis
 MAS.836 Sensor Systems for Interactive Environments th Distributed: Tuesday February 16, 2010 Due: Tuesday February 23, 2010 Problem Set # 2 Time Varying Circuit Analysis The purpose of this problem set
MAS.836 Sensor Systems for Interactive Environments th Distributed: Tuesday February 16, 2010 Due: Tuesday February 23, 2010 Problem Set # 2 Time Varying Circuit Analysis The purpose of this problem set
Chapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance
 hapter 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplex Impedance In this chapter we introduce the concept of complex resistance, or impedance, by studying two reactive circuit elements, the capacitor and the inductor.
hapter 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplex Impedance In this chapter we introduce the concept of complex resistance, or impedance, by studying two reactive circuit elements, the capacitor and the inductor.
Physics 4B Chapter 31: Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current
 Physics 4B Chapter 31: Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current People of mediocre ability sometimes achieve outstanding success because they don't know when to quit. Most men succeed because
Physics 4B Chapter 31: Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current People of mediocre ability sometimes achieve outstanding success because they don't know when to quit. Most men succeed because
AC Circuits Homework Set
 Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam
 ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam December 12, 2013 Circle your division: Division 0101: Furgason (8:30 am) Division 0201: Bermel (9:30 am) Name (Last, First) Purdue ID # There are 18 multiple choice problems
ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam December 12, 2013 Circle your division: Division 0101: Furgason (8:30 am) Division 0201: Bermel (9:30 am) Name (Last, First) Purdue ID # There are 18 multiple choice problems
ECE 241L Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering. Experiment 6 AC Circuits
 ECE 241L Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Experiment 6 AC Circuits A. Objectives: Objectives: I. Calculate amplitude and phase angles of a-c voltages and impedances II. Calculate the reactance and
ECE 241L Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Experiment 6 AC Circuits A. Objectives: Objectives: I. Calculate amplitude and phase angles of a-c voltages and impedances II. Calculate the reactance and
 Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE
 EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 20 121101 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Chapters 1-3 Circuit Analysis Techniques Chapter 10 Diodes Ideal Model
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 20 121101 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Chapters 1-3 Circuit Analysis Techniques Chapter 10 Diodes Ideal Model
Learnabout Electronics - AC Theory
 Learnabout Electronics - AC Theory Facts & Formulae for AC Theory www.learnabout-electronics.org Contents AC Wave Values... 2 Capacitance... 2 Charge on a Capacitor... 2 Total Capacitance... 2 Inductance...
Learnabout Electronics - AC Theory Facts & Formulae for AC Theory www.learnabout-electronics.org Contents AC Wave Values... 2 Capacitance... 2 Charge on a Capacitor... 2 Total Capacitance... 2 Inductance...
EIT Quick-Review Electrical Prof. Frank Merat
 CIRCUITS 4 The power supplied by the 0 volt source is (a) 2 watts (b) 0 watts (c) 2 watts (d) 6 watts (e) 6 watts 4Ω 2Ω 0V i i 2 2Ω 20V Call the clockwise loop currents i and i 2 as shown in the drawing
CIRCUITS 4 The power supplied by the 0 volt source is (a) 2 watts (b) 0 watts (c) 2 watts (d) 6 watts (e) 6 watts 4Ω 2Ω 0V i i 2 2Ω 20V Call the clockwise loop currents i and i 2 as shown in the drawing
Figure Circuit for Question 1. Figure Circuit for Question 2
 Exercises 10.7 Exercises Multiple Choice 1. For the circuit of Figure 10.44 the time constant is A. 0.5 ms 71.43 µs 2, 000 s D. 0.2 ms 4 Ω 2 Ω 12 Ω 1 mh 12u 0 () t V Figure 10.44. Circuit for Question
Exercises 10.7 Exercises Multiple Choice 1. For the circuit of Figure 10.44 the time constant is A. 0.5 ms 71.43 µs 2, 000 s D. 0.2 ms 4 Ω 2 Ω 12 Ω 1 mh 12u 0 () t V Figure 10.44. Circuit for Question
Experiment 3: Resonance in LRC Circuits Driven by Alternating Current
 Experiment 3: Resonance in LRC Circuits Driven by Alternating Current Introduction In last week s laboratory you examined the LRC circuit when constant voltage was applied to it. During this laboratory
Experiment 3: Resonance in LRC Circuits Driven by Alternating Current Introduction In last week s laboratory you examined the LRC circuit when constant voltage was applied to it. During this laboratory
1 Phasors and Alternating Currents
 Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
EE100Su08 Lecture #9 (July 16 th 2008)
 EE100Su08 Lecture #9 (July 16 th 2008) Outline HW #1s and Midterm #1 returned today Midterm #1 notes HW #1 and Midterm #1 regrade deadline: Wednesday, July 23 rd 2008, 5:00 pm PST. Procedure: HW #1: Bart
EE100Su08 Lecture #9 (July 16 th 2008) Outline HW #1s and Midterm #1 returned today Midterm #1 notes HW #1 and Midterm #1 regrade deadline: Wednesday, July 23 rd 2008, 5:00 pm PST. Procedure: HW #1: Bart
Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps
 Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps Frequency dependent feedback circuits The arguments that lead to expressions describing the circuit gain of inverting and non-inverting amplifier circuits with resistive
Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps Frequency dependent feedback circuits The arguments that lead to expressions describing the circuit gain of inverting and non-inverting amplifier circuits with resistive
Review of 1 st Order Circuit Analysis
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-7-07 P. Mathys Review of st Order Circuit Analysis First Order Differential Equation Consider the following circuit with input voltage v S (t) and output voltage
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-7-07 P. Mathys Review of st Order Circuit Analysis First Order Differential Equation Consider the following circuit with input voltage v S (t) and output voltage
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2003 Experiment 17: RLC Circuit (modified 4/15/2003) OBJECTIVES
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 7: R Circuit (modified 4/5/3) OBJECTIVES. To observe electrical oscillations, measure their frequencies, and verify energy
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 7: R Circuit (modified 4/5/3) OBJECTIVES. To observe electrical oscillations, measure their frequencies, and verify energy
EE40 Lecture 11 Josh Hug 7/19/2010
 EE40 Lecture Josh 7/9/200 Logistical Things Lab 4 tomorrow Lab 5 (active filter lab) on Wednesday Prototype for future lab for EE40 Prelab is very short, sorry. Please give us our feedback Google docs
EE40 Lecture Josh 7/9/200 Logistical Things Lab 4 tomorrow Lab 5 (active filter lab) on Wednesday Prototype for future lab for EE40 Prelab is very short, sorry. Please give us our feedback Google docs
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9 Name: Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9 Name: Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can
K.K. Gan L3: R-L-C AC Circuits. amplitude. Volts. period. -Vo
 Lecture 3: R-L-C AC Circuits AC (Alternative Current): Most of the time, we are interested in the voltage at a point in the circuit will concentrate on voltages here rather than currents. We encounter
Lecture 3: R-L-C AC Circuits AC (Alternative Current): Most of the time, we are interested in the voltage at a point in the circuit will concentrate on voltages here rather than currents. We encounter
CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation
 CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 26, 2005 1 Sinusoids Sinusoids
CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 26, 2005 1 Sinusoids Sinusoids
12. Introduction and Chapter Objectives
 Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 1: Steady-State Sinusoidal Power 1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives In this chapter we will address the issue of power transmission via sinusoidal or AC) signals. This
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 1: Steady-State Sinusoidal Power 1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives In this chapter we will address the issue of power transmission via sinusoidal or AC) signals. This
To find the step response of an RC circuit
 To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
CHAPTER 22 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 CHAPTER 22 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PROBLEMS 47. REASONING AND Using Equation 22.7, we find emf 2 M I or M ( emf 2 ) t ( 0.2 V) ( 0.4 s) t I (.6 A) ( 3.4 A) 9.3 0 3 H 49. SSM REASONING AND From the results
CHAPTER 22 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PROBLEMS 47. REASONING AND Using Equation 22.7, we find emf 2 M I or M ( emf 2 ) t ( 0.2 V) ( 0.4 s) t I (.6 A) ( 3.4 A) 9.3 0 3 H 49. SSM REASONING AND From the results
Impedance/Reactance Problems
 Impedance/Reactance Problems. Consider the circuit below. An AC sinusoidal voltage of amplitude V and frequency ω is applied to the three capacitors, each of the same capacitance C. What is the total reactance
Impedance/Reactance Problems. Consider the circuit below. An AC sinusoidal voltage of amplitude V and frequency ω is applied to the three capacitors, each of the same capacitance C. What is the total reactance
Electrical Circuits Lab Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram
 Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
Lab #4 Capacitors and Inductors. Capacitor Transient and Steady State Response
 Capacitor Transient and Steady State Response Like resistors, capacitors are also basic circuit elements. Capacitors come in a seemingly endless variety of shapes and sizes, and they can all be represented
Capacitor Transient and Steady State Response Like resistors, capacitors are also basic circuit elements. Capacitors come in a seemingly endless variety of shapes and sizes, and they can all be represented
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Lab Fourier Analysis Do prelab before lab starts. PHSX 262 Spring 2011 Lecture 5 Page 1. Based with permission on lectures by John Getty
 Today /5/ Lecture 5 Fourier Series Time-Frequency Decomposition/Superposition Fourier Components (Ex. Square wave) Filtering Spectrum Analysis Windowing Fast Fourier Transform Sweep Frequency Analyzer
Today /5/ Lecture 5 Fourier Series Time-Frequency Decomposition/Superposition Fourier Components (Ex. Square wave) Filtering Spectrum Analysis Windowing Fast Fourier Transform Sweep Frequency Analyzer
Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
 Serial : ND_EE_NW_Analog Electronics_05088 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow ndore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: 0-4546 CLASS TEST 08-9 ELECTCAL ENGNEENG Subject
Serial : ND_EE_NW_Analog Electronics_05088 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow ndore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: 0-4546 CLASS TEST 08-9 ELECTCAL ENGNEENG Subject
Physics 4 Spring 1989 Lab 5 - AC Circuits
 Physics 4 Spring 1989 Lab 5 - AC Circuits Theory Consider the series inductor-resistor-capacitor circuit shown in figure 1. When an alternating voltage is applied to this circuit, the current and voltage
Physics 4 Spring 1989 Lab 5 - AC Circuits Theory Consider the series inductor-resistor-capacitor circuit shown in figure 1. When an alternating voltage is applied to this circuit, the current and voltage
Class #12: Experiment The Exponential Function in Circuits, Pt 1
 Class #12: Experiment The Exponential Function in Circuits, Pt 1 Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to begin to become familiar with the properties and uses of the exponential function in circuits
Class #12: Experiment The Exponential Function in Circuits, Pt 1 Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to begin to become familiar with the properties and uses of the exponential function in circuits
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Dynamic circuits: Frequency domain analysis
 Electronic Circuits 1 Dynamic circuits: Contents Free oscillation and natural frequency Transfer functions Frequency response Bode plots 1 System behaviour: overview 2 System behaviour : review solution
Electronic Circuits 1 Dynamic circuits: Contents Free oscillation and natural frequency Transfer functions Frequency response Bode plots 1 System behaviour: overview 2 System behaviour : review solution
8. Introduction and Chapter Objectives
 Real Analog - Circuits Chapter 8: Second Order Circuits 8. Introduction and Chapter Objectives Second order systems are, by definition, systems whose input-output relationship is a second order differential
Real Analog - Circuits Chapter 8: Second Order Circuits 8. Introduction and Chapter Objectives Second order systems are, by definition, systems whose input-output relationship is a second order differential
Basics of Electric Circuits
 António Dente Célia de Jesus February 2014 1 Alternating Current Circuits 1.1 Using Phasors There are practical and economic reasons justifying that electrical generators produce emf with alternating and
António Dente Célia de Jesus February 2014 1 Alternating Current Circuits 1.1 Using Phasors There are practical and economic reasons justifying that electrical generators produce emf with alternating and
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 28 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 2- ALGEBRAIC TECHNIQUES TUTORIAL 2 - COMPLEX NUMBERS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 8 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME - ALGEBRAIC TECHNIQUES TUTORIAL - COMPLEX NUMBERS CONTENTS Be able to apply algebraic techniques Arithmetic progression (AP):
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 8 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME - ALGEBRAIC TECHNIQUES TUTORIAL - COMPLEX NUMBERS CONTENTS Be able to apply algebraic techniques Arithmetic progression (AP):
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
EE 230. Lecture 4. Background Materials
 EE 230 Lecture 4 Background Materials Transfer Functions Test Equipment in the Laboratory Quiz 3 If the input to a system is a sinusoid at KHz and if the output is given by the following expression, what
EE 230 Lecture 4 Background Materials Transfer Functions Test Equipment in the Laboratory Quiz 3 If the input to a system is a sinusoid at KHz and if the output is given by the following expression, what
ECE Spring 2015 Final Exam
 ECE 20100 Spring 2015 Final Exam May 7, 2015 Section (circle below) Jung (1:30) 0001 Qi (12:30) 0002 Peleato (9:30) 0004 Allen (10:30) 0005 Zhu (4:30) 0006 Name PUID Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL
ECE 20100 Spring 2015 Final Exam May 7, 2015 Section (circle below) Jung (1:30) 0001 Qi (12:30) 0002 Peleato (9:30) 0004 Allen (10:30) 0005 Zhu (4:30) 0006 Name PUID Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL
