THE power transfer capability is one of the most fundamental
|
|
|
- Terence Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4172 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 27, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2012 Letters Power Characterization of Isolated Bidirectional Dual-Active-Bridge DC DC Converter With Dual-Phase-Shift Control Biao Zhao, Qiang Song, and Wenhua Liu Abstract Compared to the traditional single-phase-shift control, dual-phase-shift (DPS) control can greatly improve the performance of the isolated bidirectional dual-active-bridge dc dc converter (IBDC). This letter points out some wrong knowledge about transmission power of IBDC under DPS control in the earlier studies. On this basis, this letter gives the detailed theoretical and experimental analyses of the transmission power of IBDC under DPS control. And the experimental results showed agreement with theoretical analysis. Index Terms Bidirectional converter, dc dc converter, dual active bridge, phase-shift control, transmission power. I. INTRODUCTION THE power transfer capability is one of the most fundamental and significant evaluating factors of isolated bidirectional dual-active-bridge dc dc converter (IBDC) [1] [4]. In order to improve the performance of IBDC, various control algorithms are explored. Single-phase-shift (SPS) control is the most widely used algorithm in IBDC, but it is essentially an active-power-centered control algorithm. It not only lacks flexibility in power regulation, but also brings additional stress to the devices used in the converter during steady-state operation [1] [5]. In order to improve the performance of SPS control, Bai and coworkers proposed a dual-phase-shift (DPS) control algorithm aiming at eliminating reactive power and increasing system power capability [5], [6]. Compared to the traditional SPS control, the DPS control has many significant advantages, which can decrease peak current, limit inrush current, eliminate reactive power, increase system efficiency, and minimize the output capacitance. The DPS control also has generality, which extended out a family of improved phase-shift control methods of IBDC, such as an improved modulation strategy that allows operating IBDC under soft switching in the whole operating range [7], [8], and a composite modulation strategy Manuscript received November 25, 2011; revised February 3, 2012; accepted February 24, Date of current version May 15, This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Recommended for publication by Associate Editor C. C. Mi. The authors are with the Department of Electrical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing , China ( b-zhao09@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn; songqiang@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn; liuwenh@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn). Color versions of one or more of the figures in this paper are available online at Digital Object Identifier /TPEL Fig. 1. Equivalent circuit of IBDC with phase-shift control. to extend the soft-switching range down to zero-load condition, reduces rms and peak currents, and results in significant size reduction of the transformer [9]. Krismer and Kolar studied the application performance improvement of IBDC with DPS control [10], [11]. These studies are mainly focused on the solutions to decrease power losses and optimize efficiency of IBDC and are conducted for an existing hardware prototype of an IBDC for an automotive application. They are of important significance to the actual engineering of IBDC. However, the studies in [5] are based on simulation and theoretical analysis, and there are some errors in the theoretical derive formulas about transmission power, which results in the wrong conclusion obtained in [5] that the maximum output power is 4/3 times of the SPS control. In subsequent research papers [6] [11], the detailed analysis of the transmission power under DPS control is still not involved, and the further experiments are also not conducted to validate the earlier theoretical analysis. In this letter, the detailed theoretical and experimental analyses of the transmission power of IBDC under DPS control will be conducted to make the right conclusion. II. OPERATION PRINCIPLE OF DUAL-PHASE-SHIFT CONTROL The equivalent circuit of IBDC with phase-shift control is shown in Fig. 1 [6] [8], where V 1 and V 2 are input and output voltage, respectively, n is transformer voltage ratio, L is the sum of the transformer leakage inductance and auxiliary inductor, v h1 and v h2 are the equivalent ac output voltages of H 1 and H 2 in V 1 side, respectively, v L and i L are the voltage and current of inductor L, respectively. The main waveforms of IBDC under DPS control with the conditions of 0 D 1 D 2 1 and 0 D 2 < D 1 1 are shown in Fig. 2, where T hs is a half switching period, D 1 and D 2 are the inner and outer phase-shift ratio, respectively, where 0 D 1 1, 0 D 2 1 and 0 D 1 + D 2 1. Different from the SPS control, the DPS control adds another degree of freedom to the /$ IEEE
2 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 27, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER Fig. 2. (a) Waveforms of IBDC under DPS control in the condition of 0 D 1 D 2 1. (b) Waveforms of IBDC under DPS control in the condition of 0 D 2 < D 1 1. TABLE I TIMETABLE OF DPS CONTROL IN HALF SWITCHING CYCLE Based on these expressions, the average transmission power of the IBDC with DPS and SPS control can be derived in Table III, where D is the phase-shift ratio of the SPS control. converter by adjusting the time sequence between the driving signals of diagonal semiconductor switches of bridges H 1 and H 2 in Fig. 1. III. TRANSMISSION POWER OF IBDC WITH DPS CONTROL From the equivalent circuit in Fig. 1, the expressions of i L for each interval defined in Fig. 2 yields can be expressed as follows: di L (t) = v h1(t) v h2 (t). (1) dt L Assuming that the initial time of one switching cycle is zero, the timetable can be shown in Table I. Considering the average current of the inductors over one switching period 2T hs should be zero in the steady state, combining (1) and Table I, the peak currents of half switching cycle can be derived in Table II, where f s = 1/(2T hs ) is the switching frequency, and k = V 1 /nv 2 is the voltage conversion ratio. From Fig. 2, the average transmission power of the IBDC converter with DPS control can be expressed as follows: P = 1 T hs v h1 i L (t)dt. (2) T hs 0 IV. COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF POWER CHARACTERIZATION For the convenience of analysis, the unified transmission power of the IBDC under DPS and SPS control are defined as follows: p = P 4D 2 (1 D 2 ) 2D1 2 0 D 1 D 2 1 = P N 4D 2 (1 D 1 1 ) 2 D 2 0 D 2 <D 1 1 p T = P T =4D(1 D) 0 D 1 P N (3) where P N is the maximum power of the IBDC with SPS control, that is P N = nv 1V 2 8f s L. (4) When taking the outer phase-shift ratio D 2 in DPS control is equal to the phase-shift ratio D in SPS control, the 3-D curves of the unified transmission power p and p T varied with D 1 and D 2 can be shown in Fig. 3(a). As can be seen from Fig. 3(a), when D 1 = 0, then p = p T, and with different D 1, p will be different with p T. In fact, taking the derivative value of (3), we can derive dp 4D1 0 D 1 D 2 1 = (5) dd 1 4D 2 0 D 2 <D 1 1.
3 4174 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 27, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2012 TABLE II PEAK CURRENT OF DPS CONTROL IN HALF SWITCHING CYCLE TABLE III TRANSMISSION POWER OF DPS AND SPS CONTROL This is not the conclusion obtained in [5] that the maximum output power is 4/3 times of the SPS control. Combining (4) and considering the constraint 0 D 1 + D 2 1, we can derive 4D2 (1 D 2 ) D 1 =0 p max = (6) 2D 2 (2 3D 2 ) D 1 = D 2 2D2 (2 3D 2 ) D 1 = D 2 p min = (7) 2D2 2 D 1 =1 D 2 where 0 D 2 < D2 (1 D 2 ) D 1 =0 p max = (8) 2(1 D2 )(3D 2 1) D 1 =1 D 2 p min = (9) where 0.5 D 2 1. From (6) to (9), Fig. 3(a) can be converted to the 2-D picture, as shown in Fig. 3(b). The thickened line is the regulating curve of transmission power in SPS control, and the dark-shaded area is the regulating area of transmission power in DPS control. From Fig. 3(b), due to the addition of D 1, the regulating range of transmission power is changed from the single curve to the 2-D area. And with the same outer phase-shift ratio (D 2 = D), the DPS control offers wider power transmission range than the SPS control does, which will also enhance regulating flexibility. But the two control methods have the same global maximum power. V. EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS In order to verify the aforementioned theoretical analysis, a laboratory prototype is constructed based on TMS320F2812 DSP. And the main parameters of converter are as follows: auxiliary inductor L 1 = 0.2 mh, dc capacitors C 1 = C 2 = 2200 μf, transformer voltage ratio n = 2, and switching frequency f s = 10 khz. Fig. 4 shows the steady-state experimental waveforms of v h 1, v h 2, and i L under SPS (D 1 = 0) and DPS (D 1 = 0.4) control for the same transmission power 380 W, where the output voltage is in closed-loop control for 48 V. From Fig. 4, the current stress is different in SPS and DPS control for the same transmission power, and the DPS control generates less current stress than the SPS control does. In other words, with the same current stress, the DPS control can transfer more power than the SPS control does. Fig. 5 shows the curves of the transmission power varied with D 1 and D 2. The input voltage and the output load are specified as 220 V and 6 Ω, respectively. It can be seen that the transmission power of IBDC can be regulated both by D 1 and D 2 under DPS control. From Fig. 5(a), with the specified D 1 D 2, the IBDC obtains the similar transmission power at D 2 and 1 D 2, which coincides with the theoretical analysis in (4). From Fig. 5(b), the maximum and minimum values of transmission power in the condition of 0 D 1 D 2 1are obtained about at D 1 = 0 and D 1 = D 2, in the condition of 0 D 2 < D 1 1 are obtained about at D 1 = D 2 and D 1 = 1 D 2, and in the whole range are obtained about at D 1 = 0 and D 1 = 1 D 2, respectively. And with the same outer phase-shift ratio D 2, the DPS control (D 1 0) can offer wider power transmission range than the SPS control (D 1 = 0) does that will also enhance regulating flexibility. But the two control methods have the approximately same global maximum power, which agrees with the aforementioned theoretical analysis in Section IV. Fig. 6 shows the comparative 3-D curves of experimental and theoretical results of the transmission power varied with D 1
4 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 27, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER Fig. 3. Relation curves of the unified transmission power p (p T ) with D 1 and D 2. (a) 3-D curves. (b) 2-D curves. Fig. 4. Experimental waveforms of v h 1, v h 2,andi L under SPS and DPS control for the same transmission. (a) SPS control with V 1 = 300 V, and V 2 = 48 V. (b) DPS control with V 1 = 300 V, V 2 = 48 V, and D 1 = 0.4. Fig. 5. Curves of the transmission power varied with D 1 and D 2. (a) Curves of the transmission power varied with D 1 when D 2 is specified. (b) Curves of the transmission power varied with D 2 when D 1 is specified.
5 4176 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 27, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2012 methods have the same global maximum power, which is not the conclusion obtained in [5] that the maximum output power is 4/3 times of the SPS control. REFERENCES Fig. 6. Comparative 3-D curves of experimental and theoretical results of the transmission power varied with D 1 and D 2. and D 2. As can be seen from Fig. 6, the experimental results basically coincide with the theoretical analysis across the whole range. VI. CONCLUSION In this letter, the detailed theoretical and experimental analyses of the transmission power of IBDC under DPS control have been conducted. And the experimental results showed agreement with theoretical analysis. Some conclusions can be found from the study: with the same outer phase-shift ratio D 2,the DPS control can offer wider power transmission range than the SPS control does that will also enhance regulating flexibility, and with the same current stress, the DPS control can transfer more power than the SPS control does; however, the two control [1] I. Shigenori and A. Hirofumi, A bidirectional isolated DC-DC converter as a core circuit of the next-generation medium-voltage power conversion system, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 22, no. 2, pp , Mar [2] J. Shi, W. Gou, H. Yuan, T. Zhao, and A. Q. Huang, Research on voltage and power balance control for cascaded modular solid-state transformer, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 26, no. 4, pp , Apr [3] Y. H. Xie, J. Sun, and S. F. James, Power flow characterization of a bidirectional galvanically isolated high-power DC/DC converter over a wide operating range, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 25, no. 1, pp , Jan [4] H. Bai, C. Mi, and S. Gargies, The short-time-scale transient processes in high-voltage and high-power isolated bidirectional dc-dc converters, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 23, no. 6, pp , Nov [5] H. Bai and C. Mi, Eliminate reactive power and increase system efficiency of isolated bidirectional dual-active-bridge DC-DC converters using novel dual-phase-shift control, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 23, no. 6, pp , Nov [6] H. Bai, Z. Nie, and C. Mi, Experimental comparision of traditional phaseshift, dual-phase-shift, and model-based control of isolated bidirectional dc-dc converters, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 25,no.6, pp , Jun [7] G. G. Oggier, G. O. García, and A. R. Oliva, Modulation strategy to operate the dual active bridge dc-dc converter under soft switching in the whole operating range, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 26, no. 4, pp , Apr [8] G.G.Oggier,G.O.García, and A. R. Oliva, Switching control strategy to minimize dual active bridge converter losses, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 24, no. 7, pp , Jul [9] A. K. Jain and R. Ayyanar, PWM control of dual active bridge: Comprehensive analysis and experimental verification, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 26, no. 4, pp , Apr [10] F. Krismer and J. W. Kolar, Efficiency-optimized high current dual active bridge converter for automotive applications, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 59, no. 7, pp , Jul [11] F. Krismer and J. W. Kolar, Closed form solution for minimum conduction loss modulation of DAB converters, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 27, no. 1, pp , Jan
THE bidirectional galvanically isolated dual active bridge
 54 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 5, NO. 1, JANUARY 010 Power Flow Characterization of a Bidirectional Galvanically Isolated High-Power DC/DC Converter Over a Wide Operating Range Yanhui
54 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 5, NO. 1, JANUARY 010 Power Flow Characterization of a Bidirectional Galvanically Isolated High-Power DC/DC Converter Over a Wide Operating Range Yanhui
Implementation Possibilities of SMD Capacitors for High Power Applications
 doi: 10.2478/v10314-012-0003-2 2012 / 1 Implementation Possibilities of MD Capacitors for High Power Applications Janis Zakis (enior Research Fellow, Tallinn University of Technology), Dmitri Vinnikov
doi: 10.2478/v10314-012-0003-2 2012 / 1 Implementation Possibilities of MD Capacitors for High Power Applications Janis Zakis (enior Research Fellow, Tallinn University of Technology), Dmitri Vinnikov
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity. Copyright IEEE.
 Title Loss analysis of permanent magnet hybrid brushless machines with and without HTS field windings Author(s) Liu, C; Chau, KT; Li, W Citation The 21st International Conference on Magnet Technology,
Title Loss analysis of permanent magnet hybrid brushless machines with and without HTS field windings Author(s) Liu, C; Chau, KT; Li, W Citation The 21st International Conference on Magnet Technology,
Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency
 Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency 3.1. The dc transformer model 3.2. Inclusion of inductor copper loss 3.3. Construction of equivalent circuit model 3.4. How to
Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency 3.1. The dc transformer model 3.2. Inclusion of inductor copper loss 3.3. Construction of equivalent circuit model 3.4. How to
Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode
 Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode Introduction 11.1. DCM Averaged Switch Model 11.2. Small-Signal AC Modeling of the DCM Switch Network 11.3. High-Frequency
Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode Introduction 11.1. DCM Averaged Switch Model 11.2. Small-Signal AC Modeling of the DCM Switch Network 11.3. High-Frequency
Circuit Analysis-II. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 5 Monday 23 rd April, 18
 Circuit Analysis-II Capacitors in AC Circuits Introduction ü The instantaneous capacitor current is equal to the capacitance times the instantaneous rate of change of the voltage across the capacitor.
Circuit Analysis-II Capacitors in AC Circuits Introduction ü The instantaneous capacitor current is equal to the capacitance times the instantaneous rate of change of the voltage across the capacitor.
AC Circuits Homework Set
 Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Modeling, Analysis and Control of an Isolated Boost Converter for System Level Studies
 1 Modeling, Analysis and Control of an Isolated Boost Converter for System Level Studies Bijan Zahedi, Student Member, IEEE, and Lars E. Norum, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract-- This paper performs a modeling
1 Modeling, Analysis and Control of an Isolated Boost Converter for System Level Studies Bijan Zahedi, Student Member, IEEE, and Lars E. Norum, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract-- This paper performs a modeling
Modelling and Teaching of Magnetic Circuits
 Asian Power Electronics Journal, Vol. 1, No. 1, Aug 2007 Modelling and Teaching of Magnetic Circuits Yim-Shu Lee 1 and Martin H.L. Chow 2 Abstract In the analysis of magnetic circuits, reluctances are
Asian Power Electronics Journal, Vol. 1, No. 1, Aug 2007 Modelling and Teaching of Magnetic Circuits Yim-Shu Lee 1 and Martin H.L. Chow 2 Abstract In the analysis of magnetic circuits, reluctances are
Reactive power control strategies for UNIFLEX-PM Converter
 Reactive power control strategies for UNIFLEX-PM Converter S. Pipolo, S. Bifaretti, V. Bonaiuto Dept. of Industrial Engineering University of Rome Tor Vergata Rome, Italy Abstract- The paper presents various
Reactive power control strategies for UNIFLEX-PM Converter S. Pipolo, S. Bifaretti, V. Bonaiuto Dept. of Industrial Engineering University of Rome Tor Vergata Rome, Italy Abstract- The paper presents various
Novel DC-AC Converter Topology for Multilevel Battery Energy Storage Systems. Mario Gommeringer, Felix Kammerer, Johannes Kolb, Michael Braun
 Elektrotechnisches Institut (ETI) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Michael Braun Prof. Dr.-Ing. Martin Doppelbauer Prof. Dr.-Ing. Marc Hiller Kaiserstr.12. 76131 Karlsruhe 13. Sept. 216 Title: Novel DC-C Converter Topology
Elektrotechnisches Institut (ETI) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Michael Braun Prof. Dr.-Ing. Martin Doppelbauer Prof. Dr.-Ing. Marc Hiller Kaiserstr.12. 76131 Karlsruhe 13. Sept. 216 Title: Novel DC-C Converter Topology
Basic RL and RC Circuits R-L TRANSIENTS: STORAGE CYCLE. Engineering Collage Electrical Engineering Dep. Dr. Ibrahim Aljubouri
 st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 . W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 2.4 Cuk converter example L 1 C 1 L 2 Cuk converter, with ideal switch i 1 i v 1 2 1 2 C 2 v 2 Cuk
. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 2.4 Cuk converter example L 1 C 1 L 2 Cuk converter, with ideal switch i 1 i v 1 2 1 2 C 2 v 2 Cuk
Computationally efficient models for simulation of non-ideal DC DC converters operating in continuous and discontinuous conduction modes
 Sādhanā Vol. 40, Part 7, October 2015, pp. 2045 2072. c Indian Academy of Sciences Computationally efficient models for simulation of non-ideal DC DC converters operating in continuous and discontinuous
Sādhanā Vol. 40, Part 7, October 2015, pp. 2045 2072. c Indian Academy of Sciences Computationally efficient models for simulation of non-ideal DC DC converters operating in continuous and discontinuous
Dynamic phasor based stability analysis of an inverter connected to grid
 Dynamic phasor based stability analysis of an inverter connected to grid A. Sawant, P. Jagtap, J. Aute, U. Mumbaikar Department of Electrical Engineering VJTI, Mumbai Email: savant.apurva@yahoo.com Abstract
Dynamic phasor based stability analysis of an inverter connected to grid A. Sawant, P. Jagtap, J. Aute, U. Mumbaikar Department of Electrical Engineering VJTI, Mumbai Email: savant.apurva@yahoo.com Abstract
6.3. Transformer isolation
 6.3. Transformer isolation Objectives: Isolation of input and output ground connections, to meet safety requirements eduction of transformer size by incorporating high frequency isolation transformer inside
6.3. Transformer isolation Objectives: Isolation of input and output ground connections, to meet safety requirements eduction of transformer size by incorporating high frequency isolation transformer inside
Reactive Power Flow Control of a Dual Unified Power Quality Conditioner
 Reactive Power Flow Control of a Dual Unified Power uality Conditioner aimon M. Fagundes anta Catarina tate University UDEC Electric Power Processing Group - npee 89.19-71, Joinville - C, Brazil saimon.m.f.@gmail.com
Reactive Power Flow Control of a Dual Unified Power uality Conditioner aimon M. Fagundes anta Catarina tate University UDEC Electric Power Processing Group - npee 89.19-71, Joinville - C, Brazil saimon.m.f.@gmail.com
Nonlinear dynamic simulation model of switched reluctance linear machine
 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1320 1324 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology Nonlinear
Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1320 1324 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology Nonlinear
Lecture 17 Push-Pull and Bridge DC-DC converters Push-Pull Converter (Buck Derived) Centre-tapped primary and secondary windings
 ecture 17 Push-Pull and Bridge DC-DC converters Push-Pull Converter (Buck Derived) Centre-tapped primary and secondary windings 1 2 D 1 i v 1 v 1s + v C o R v 2 v 2s d 1 2 T 1 T 2 D 2 Figure 17.1 v c (
ecture 17 Push-Pull and Bridge DC-DC converters Push-Pull Converter (Buck Derived) Centre-tapped primary and secondary windings 1 2 D 1 i v 1 v 1s + v C o R v 2 v 2s d 1 2 T 1 T 2 D 2 Figure 17.1 v c (
Tackling the Little Box Challenge - New circuit architectures to achieve a 216 W/in 3 power density 2 kw inverter
 Tackling the Little Box Challenge - New circuit architectures to achieve a 6 W/in 3 power density kw inverter Robert Pilawa-Podgurski, Yutian Lei, Shibin Qin, Chris Barth, Wen-Chuen Liu, Andrew Stillwell,
Tackling the Little Box Challenge - New circuit architectures to achieve a 6 W/in 3 power density kw inverter Robert Pilawa-Podgurski, Yutian Lei, Shibin Qin, Chris Barth, Wen-Chuen Liu, Andrew Stillwell,
MICROGRID is a future trend of integrating renewable
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 64, NO. 7, JULY 2017 5741 New Perspectives on Droop Control in AC Microgrid Yao Sun, Xiaochao Hou, Jian Yang, Hua Han, Mei Su, and Josep M. Guerrero Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 64, NO. 7, JULY 2017 5741 New Perspectives on Droop Control in AC Microgrid Yao Sun, Xiaochao Hou, Jian Yang, Hua Han, Mei Su, and Josep M. Guerrero Abstract
HighpowerfactorforwardAC-DC converter with low storage capacitor voltage stress
 HAIT Journal of Science and Engineering B, Volume 2, Issues 3-4, pp. 305-326 Copyright C 2005 Holon Academic Institute of Technology HighpowerfactorforwardAC-DC converter with low storage capacitor voltage
HAIT Journal of Science and Engineering B, Volume 2, Issues 3-4, pp. 305-326 Copyright C 2005 Holon Academic Institute of Technology HighpowerfactorforwardAC-DC converter with low storage capacitor voltage
The output voltage is given by,
 71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
Repetitive control : Power Electronics. Applications
 Repetitive control : Power Electronics Applications Ramon Costa Castelló Advanced Control of Energy Systems (ACES) Instituto de Organización y Control (IOC) Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) Barcelona,
Repetitive control : Power Electronics Applications Ramon Costa Castelló Advanced Control of Energy Systems (ACES) Instituto de Organización y Control (IOC) Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) Barcelona,
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012
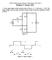 ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas
 Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module
Refresher course on Electrical fundamentals (Basics of A.C. Circuits) by B.M.Vyas A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module
Stability analysis of digitally controlled dual active bridge converters
 J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy (201) 6(2):375 33 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40565-017-0317-9 Stability analysis of digitally controlled dual active bridge converters Ling SHI 1, Wanjun LEI 1, Zhuoqiang
J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy (201) 6(2):375 33 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40565-017-0317-9 Stability analysis of digitally controlled dual active bridge converters Ling SHI 1, Wanjun LEI 1, Zhuoqiang
Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System Simulation *
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com AASRI Procedia 3 (2012 ) 262 269 2012 AASRI Conference on Modeling, Identification and Control Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com AASRI Procedia 3 (2012 ) 262 269 2012 AASRI Conference on Modeling, Identification and Control Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Synergetic Synthesis Of Dc-Dc Boost Converter Controllers: Theory And Experimental Analysis
 Synergetic Synthesis Of Dc-Dc Boost Converter Controllers: Theory And Experimental Analysis A. Kolesnikov ( + ), G. Veselov ( + ), A. Kolesnikov ( + ), A. Monti ( ++ ), F. Ponci ( ++ ), E. Santi ( ++ ),
Synergetic Synthesis Of Dc-Dc Boost Converter Controllers: Theory And Experimental Analysis A. Kolesnikov ( + ), G. Veselov ( + ), A. Kolesnikov ( + ), A. Monti ( ++ ), F. Ponci ( ++ ), E. Santi ( ++ ),
A simple model based control of self excited induction generators over a wide speed range
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 10 (2014) No. 3, pp. 206-213 A simple model based control of self excited induction generators over a wide speed range Krishna
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 10 (2014) No. 3, pp. 206-213 A simple model based control of self excited induction generators over a wide speed range Krishna
Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink
 Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink A powerful environment for system modeling and simulation MATLAB: programming and scripting environment Simulink: block diagram modeling environment that runs
Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink A powerful environment for system modeling and simulation MATLAB: programming and scripting environment Simulink: block diagram modeling environment that runs
Centralized Supplementary Controller to Stabilize an Islanded AC Microgrid
 Centralized Supplementary Controller to Stabilize an Islanded AC Microgrid ESNRajuP Research Scholar, Electrical Engineering IIT Indore Indore, India Email:pesnraju88@gmail.com Trapti Jain Assistant Professor,
Centralized Supplementary Controller to Stabilize an Islanded AC Microgrid ESNRajuP Research Scholar, Electrical Engineering IIT Indore Indore, India Email:pesnraju88@gmail.com Trapti Jain Assistant Professor,
Regulated DC-DC Converter
 Regulated DC-DC Converter Zabir Ahmed Lecturer, BUET Jewel Mohajan Lecturer, BUET M A Awal Graduate Research Assistant NSF FREEDM Systems Center NC State University Former Lecturer, BUET 1 Problem Statement
Regulated DC-DC Converter Zabir Ahmed Lecturer, BUET Jewel Mohajan Lecturer, BUET M A Awal Graduate Research Assistant NSF FREEDM Systems Center NC State University Former Lecturer, BUET 1 Problem Statement
A Novel of Bidirectional DC-DC converter drive
 Vol.2, Issue.2, Mar-Apr 2012 pp-186-196 ISSN: 2249-6645 A Novel of Bidirectional DC-DC converter drive N.MAHESH M-Tech Scholar, Power Electronics and Drives, Department Of Electrical And Electrical Engineering,
Vol.2, Issue.2, Mar-Apr 2012 pp-186-196 ISSN: 2249-6645 A Novel of Bidirectional DC-DC converter drive N.MAHESH M-Tech Scholar, Power Electronics and Drives, Department Of Electrical And Electrical Engineering,
AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm
 7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
Modeling Buck Converter by Using Fourier Analysis
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 8, 2010 705 Modeling Buck Converter by Using Fourier Analysis Mao Zhang 1, Weiping Zhang 2, and Zheng Zhang 2 1 School of Computing, Engineering and Physical Sciences, University
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 8, 2010 705 Modeling Buck Converter by Using Fourier Analysis Mao Zhang 1, Weiping Zhang 2, and Zheng Zhang 2 1 School of Computing, Engineering and Physical Sciences, University
Shanming Wang, Ziguo Huang, Shujun Mu, and Xiangheng Wang. 1. Introduction
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 215, Article ID 467856, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/467856 Research Article A Straightforward Convergence Method for ICCG Simulation of Multiloop and
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 215, Article ID 467856, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/467856 Research Article A Straightforward Convergence Method for ICCG Simulation of Multiloop and
Sliding Mode Control for Stabilizing of Boost Converter in a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
 BUGARAN ACADEMY OF SCENCES CYBERNETCS AND NFORMATON TECHNOOGES Volume 13, No 4 Sofia 013 Print SSN: 1311-970; Online SSN: 1314-4081 DO: 10.478/cait-013-0060 Sliding Mode Control for Stabilizing of Boost
BUGARAN ACADEMY OF SCENCES CYBERNETCS AND NFORMATON TECHNOOGES Volume 13, No 4 Sofia 013 Print SSN: 1311-970; Online SSN: 1314-4081 DO: 10.478/cait-013-0060 Sliding Mode Control for Stabilizing of Boost
A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 88, 121 134, 2008 A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER Y. Wu, Y. Liu, and S. Li School of Electronic Engineering Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 88, 121 134, 2008 A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER Y. Wu, Y. Liu, and S. Li School of Electronic Engineering Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Pre-charging of module capacitors of MMC when the module switches are driven by a source derived from the module capacitor
 Sādhanā Vol. 42, No. 8, August 2017, pp. 1251 1262 DOI 10.1007/s12046-017-0655-3 Ó Indian Academy of Sciences Pre-charging of module capacitors of MMC when the module switches are driven by a source derived
Sādhanā Vol. 42, No. 8, August 2017, pp. 1251 1262 DOI 10.1007/s12046-017-0655-3 Ó Indian Academy of Sciences Pre-charging of module capacitors of MMC when the module switches are driven by a source derived
Schedule. ECEN 301 Discussion #20 Exam 2 Review 1. Lab Due date. Title Chapters HW Due date. Date Day Class No. 10 Nov Mon 20 Exam Review.
 Schedule Date Day lass No. 0 Nov Mon 0 Exam Review Nov Tue Title hapters HW Due date Nov Wed Boolean Algebra 3. 3.3 ab Due date AB 7 Exam EXAM 3 Nov Thu 4 Nov Fri Recitation 5 Nov Sat 6 Nov Sun 7 Nov Mon
Schedule Date Day lass No. 0 Nov Mon 0 Exam Review Nov Tue Title hapters HW Due date Nov Wed Boolean Algebra 3. 3.3 ab Due date AB 7 Exam EXAM 3 Nov Thu 4 Nov Fri Recitation 5 Nov Sat 6 Nov Sun 7 Nov Mon
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Inertia Identification and Auto-Tuning. of Induction Motor Using MRAS
 Inertia Identification and Auto-Tuning of Induction Motor Using MRAS Yujie GUO *, Lipei HUANG *, Yang QIU *, Masaharu MURAMATSU ** * Department of Electrical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing,
Inertia Identification and Auto-Tuning of Induction Motor Using MRAS Yujie GUO *, Lipei HUANG *, Yang QIU *, Masaharu MURAMATSU ** * Department of Electrical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing,
Cahier Technique N 13 Principe de réduction des courants d enclenchement des transformateurs
 Cahier Technique N 13 Principe de réduction des courants d enclenchement des transformateurs Numerical transformer inrush current minimizer Principle of the operation Rev 1.0 Document version information
Cahier Technique N 13 Principe de réduction des courants d enclenchement des transformateurs Numerical transformer inrush current minimizer Principle of the operation Rev 1.0 Document version information
The Study of a Digital Equivalent Capacitor Circuit
 Vol.7, No. (0), pp. http://dx.doi.org/0.7/ijhit.0.7..0 The Study of a Digital Equivalent Capacitor Circuit QingHua Shang, Wenjie Cao, hen Huang and Xiaoqing hang School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Vol.7, No. (0), pp. http://dx.doi.org/0.7/ijhit.0.7..0 The Study of a Digital Equivalent Capacitor Circuit QingHua Shang, Wenjie Cao, hen Huang and Xiaoqing hang School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Conduction Modes of a Peak Limiting Current Mode Controlled Buck Converter
 Conduction Modes of a Peak Limiting Current Mode Controlled Buck Converter Predrag Pejović and Marija Glišić Abstract In this paper, analysis of a buck converter operated applying a peak limiting current
Conduction Modes of a Peak Limiting Current Mode Controlled Buck Converter Predrag Pejović and Marija Glišić Abstract In this paper, analysis of a buck converter operated applying a peak limiting current
Designing an LLC Resonant Half-Bridge Power Converter
 Topic 3 Designing an LLC Resonant Half-Bridge Power Converter Hong Huang Agenda. Introduction Brief review Advantages 2. Design Prerequisites Configuration Operation Modeling Voltage gain function 3. Design
Topic 3 Designing an LLC Resonant Half-Bridge Power Converter Hong Huang Agenda. Introduction Brief review Advantages 2. Design Prerequisites Configuration Operation Modeling Voltage gain function 3. Design
Magnetic vibration analysis of a new DC-excited multitoothed switched reluctance machine. Liu, C; Chau, KT; Lee, CHT; Lin, F; Li, F; Ching, TW
 Title Magnetic vibration analysis of a new DC-excited multitoothed switched reluctance machine Author(s) Liu, C; Chau, KT; Lee, CHT; Lin, F; Li, F; Ching, TW Citation The 2014 IEEE International Magnetics
Title Magnetic vibration analysis of a new DC-excited multitoothed switched reluctance machine Author(s) Liu, C; Chau, KT; Lee, CHT; Lin, F; Li, F; Ching, TW Citation The 2014 IEEE International Magnetics
A Novel Simulation Method for Power Electronics: Discrete State Event Driven Method
 CES TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 1, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2017 273 A Novel Simulation Method for Power Electronics: Discrete State Event Driven Method Boyang Li, Zhengming Zhao, Yi
CES TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 1, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2017 273 A Novel Simulation Method for Power Electronics: Discrete State Event Driven Method Boyang Li, Zhengming Zhao, Yi
SWITCHED reluctance motor (SRM) drives have been
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 45, NO. 5, OCTOBER 1998 815 A Novel Power Converter with Voltage-Boosting Capacitors for a Four-Phase SRM Drive Yasser G. Dessouky, Barry W. Williams,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 45, NO. 5, OCTOBER 1998 815 A Novel Power Converter with Voltage-Boosting Capacitors for a Four-Phase SRM Drive Yasser G. Dessouky, Barry W. Williams,
Dynamic Phasors in Modeling, Analysis and Control of Energy Processing Systems
 Dynamic Phasors in Modeling, Analysis and Control of Energy Processing Systems 6/20/02 Alex M. Stanković Northeastern University, Boston, MA 1 Research Program Overview My research program focuses on the
Dynamic Phasors in Modeling, Analysis and Control of Energy Processing Systems 6/20/02 Alex M. Stanković Northeastern University, Boston, MA 1 Research Program Overview My research program focuses on the
Simple Time Domain Analysis of a 4-Level H-bridge Flying Capacitor Converter Voltage Balancing
 Simple Time Domain Analysis of a 4-evel H-bridge Flying Capacitor Converter Voltage Balancing Steven Thielemans Alex uderman Boris eznikov and Jan Melkebeek Electrical Energy Systems and Automation Department
Simple Time Domain Analysis of a 4-evel H-bridge Flying Capacitor Converter Voltage Balancing Steven Thielemans Alex uderman Boris eznikov and Jan Melkebeek Electrical Energy Systems and Automation Department
AC Source and RLC Circuits
 X X L C = 2π fl = 1/2π fc 2 AC Source and RLC Circuits ( ) 2 Inductive reactance Capacitive reactance Z = R + X X Total impedance L C εmax Imax = Z XL XC tanφ = R Maximum current Phase angle PHY2054: Chapter
X X L C = 2π fl = 1/2π fc 2 AC Source and RLC Circuits ( ) 2 Inductive reactance Capacitive reactance Z = R + X X Total impedance L C εmax Imax = Z XL XC tanφ = R Maximum current Phase angle PHY2054: Chapter
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Power Electronics
 Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
LED lamp driving technology using variable series-parallel charge pump
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.10, No.13, 1 7 LED lamp driving technology using variable series-parallel charge pump Jeongduk Ryeom a) Department of Electrical Engineering, Soongsil University,
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.10, No.13, 1 7 LED lamp driving technology using variable series-parallel charge pump Jeongduk Ryeom a) Department of Electrical Engineering, Soongsil University,
Study of Chaos and Dynamics of DC-DC Converters BY SAI RAKSHIT VINNAKOTA ANUROOP KAKKIRALA VIVEK PRAYAKARAO
 Study of Chaos and Dynamics of DC-DC Converters BY SAI RAKSHIT VINNAKOTA ANUROOP KAKKIRALA VIVEK PRAYAKARAO What are DC-DC Converters?? A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit which converts a source
Study of Chaos and Dynamics of DC-DC Converters BY SAI RAKSHIT VINNAKOTA ANUROOP KAKKIRALA VIVEK PRAYAKARAO What are DC-DC Converters?? A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit which converts a source
Chapter 2 Voltage-, Current-, and Z-source Converters
 Chapter 2 Voltage-, Current-, and Z-source Converters Some fundamental concepts are to be introduced in this chapter, such as voltage sources, current sources, impedance networks, Z-source, two-port network,
Chapter 2 Voltage-, Current-, and Z-source Converters Some fundamental concepts are to be introduced in this chapter, such as voltage sources, current sources, impedance networks, Z-source, two-port network,
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
REACTANCE. By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013
 REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
A Review and Modeling of Different Droop Control Based Methods for Battery State of the Charge Balancing in DC Microgrids
 A Review and Modeling of Different Droop Control Based Methods for Battery State of the Charge Balancing in DC Microgrids Niloofar Ghanbari, M. Mobarrez 2, and S. Bhattacharya Department of Electrical
A Review and Modeling of Different Droop Control Based Methods for Battery State of the Charge Balancing in DC Microgrids Niloofar Ghanbari, M. Mobarrez 2, and S. Bhattacharya Department of Electrical
Power efficiency and optimum load formulas on RF rectifiers featuring flow-angle equations
 This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Power efficiency and optimum load formulas on
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Power efficiency and optimum load formulas on
ISSN: (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies
 ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Paper / Case Study Available online at:
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Paper / Case Study Available online at:
Design and Control of a Buck Boost Charger-Discharger for DC-Bus Regulation in Microgrids
 energies Article Design and Control of a Buck Boost Charger-Discharger for DC-Bus Regulation in Microgrids Carlos Andrés Ramos-Paja 1, *, ID, Juan David Bastidas-Rodríguez 2 ID, Daniel González 3 ID, Santiago
energies Article Design and Control of a Buck Boost Charger-Discharger for DC-Bus Regulation in Microgrids Carlos Andrés Ramos-Paja 1, *, ID, Juan David Bastidas-Rodríguez 2 ID, Daniel González 3 ID, Santiago
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors)
 Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 6 CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 5.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase SEIG has been discussed in the previous chapters. In this chapter,
6 CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 5.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase SEIG has been discussed in the previous chapters. In this chapter,
COMPARISION BETWEEN TWO LEVEL AND THREE LEVEL INVERTER FOR DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 COMPARISION BETWEEN TWO LEVEL AND THREE LEVEL INVERTER FOR DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE Shailesh B. Kadu 1, Prof. J.G. Choudhari 2 Research Scholar (Department of Electrical Engineering,
COMPARISION BETWEEN TWO LEVEL AND THREE LEVEL INVERTER FOR DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE Shailesh B. Kadu 1, Prof. J.G. Choudhari 2 Research Scholar (Department of Electrical Engineering,
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development SIMULATION OF FIELD ORIENTED CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 SIMULATION
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 SIMULATION
ENGR 2405 Chapter 8. Second Order Circuits
 ENGR 2405 Chapter 8 Second Order Circuits Overview The previous chapter introduced the concept of first order circuits. This chapter will expand on that with second order circuits: those that need a second
ENGR 2405 Chapter 8 Second Order Circuits Overview The previous chapter introduced the concept of first order circuits. This chapter will expand on that with second order circuits: those that need a second
Compensator Design for Closed Loop Hall-Effect Current Sensors
 Compensator Design for Closed Loop HallEffect Current Sensors Ashish Kumar and Vinod John Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 5600, India. Email: ashishk@ee.iisc.ernet.in,
Compensator Design for Closed Loop HallEffect Current Sensors Ashish Kumar and Vinod John Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 5600, India. Email: ashishk@ee.iisc.ernet.in,
Sliding-Mode Control of the DC-DC Ćuk Converter in Discontinuous Conduction Mode
 Sliding-Mode Control of the DC-DC Ćuk Converter in Discontinuous Conduction Mode Vadood Hajbani, Mahdi Salimi 2 Department of Electrical Engineering, Ahar Branch, Islamic Azad University, Ahar, Iran. Email:
Sliding-Mode Control of the DC-DC Ćuk Converter in Discontinuous Conduction Mode Vadood Hajbani, Mahdi Salimi 2 Department of Electrical Engineering, Ahar Branch, Islamic Azad University, Ahar, Iran. Email:
Direct Matrix Synthesis for In-Line Diplexers with Transmission Zeros Generated by Frequency Variant Couplings
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 78, 45 52, 2018 Direct Matrix Synthesis for In-Line Diplexers with Transmission Zeros Generated by Frequency Variant Couplings Yong-Liang Zhang1, 2,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 78, 45 52, 2018 Direct Matrix Synthesis for In-Line Diplexers with Transmission Zeros Generated by Frequency Variant Couplings Yong-Liang Zhang1, 2,
MCE603: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems. Chapter 1: Impedance Analysis for Electromechanical Interfacing
 MCE63: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems Chapter 1: Impedance Analysis for Electromechanical Interfacing Part B: Input and Output Impedance Cleveland State University Mechanical Engineering
MCE63: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems Chapter 1: Impedance Analysis for Electromechanical Interfacing Part B: Input and Output Impedance Cleveland State University Mechanical Engineering
P4C164 ULTRA HIGH SPEED 8K X 8 STATIC CMOS RAMS FEATURES DESCRIPTION. Full CMOS, 6T Cell. Common Data I/O
 FEATURES Full CMOS, 6T Cell High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle Times) 8/10/12/15/20/25/35/70/100 ns (Commercial) 10/12/15/20/25/35/70/100 ns(industrial) 12/15/20/25/35/45/70/100 ns (Military) Low Power
FEATURES Full CMOS, 6T Cell High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle Times) 8/10/12/15/20/25/35/70/100 ns (Commercial) 10/12/15/20/25/35/70/100 ns(industrial) 12/15/20/25/35/45/70/100 ns (Military) Low Power
DC and AC Impedance of Reactive Elements
 3/6/20 D and A Impedance of Reactive Elements /6 D and A Impedance of Reactive Elements Now, recall from EES 2 the complex impedances of our basic circuit elements: ZR = R Z = jω ZL = jωl For a D signal
3/6/20 D and A Impedance of Reactive Elements /6 D and A Impedance of Reactive Elements Now, recall from EES 2 the complex impedances of our basic circuit elements: ZR = R Z = jω ZL = jωl For a D signal
Single-Phase Synchronverter for DC Microgrid Interface with AC Grid
 The First Power Electronics and Renewable Energy Workshop (PEREW 2017) March 1-2, 2017- Aswan Faculty of Engineering, Aswan Egypt Single-Phase Synchronverter for Microgrid Interface with AC Grid Presenter:
The First Power Electronics and Renewable Energy Workshop (PEREW 2017) March 1-2, 2017- Aswan Faculty of Engineering, Aswan Egypt Single-Phase Synchronverter for Microgrid Interface with AC Grid Presenter:
Shunt Hybrid Power Filter combined with Thyristor- Controlled Reactor for Power Quality Improvement.
 Shunt Hybrid Power Filter combined with Thyristor- Controlled Reactor for Power Quality Improvement. 1 Pallavi P, Pooja P S, Chethan H R, 4 Nandish B M 1, Student,,4 ssistant professor Electrical and Electronics
Shunt Hybrid Power Filter combined with Thyristor- Controlled Reactor for Power Quality Improvement. 1 Pallavi P, Pooja P S, Chethan H R, 4 Nandish B M 1, Student,,4 ssistant professor Electrical and Electronics
CASCADED DUAL MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL OF AN ACTIVE FRONT-END RECTIFIER
 CASCADED DUAL MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL OF AN ACTIVE FRONT-END RECTIFIER 1 PENTA SRAVANTHI, 2 RAVULA SWATHI 1 M.Tech, BALAJI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE 2 Assistant professor, BALAJI INSTITUTE OF
CASCADED DUAL MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL OF AN ACTIVE FRONT-END RECTIFIER 1 PENTA SRAVANTHI, 2 RAVULA SWATHI 1 M.Tech, BALAJI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE 2 Assistant professor, BALAJI INSTITUTE OF
DATA SHEET SURFACE MOUNT MULTILAYER CERAMIC CAPACITORS General purpose & High capacitance Class 2, X5R
 DATA SHEET SURFACE MOUNT MULTILAYER CERAMIC CAPACITORS General purpose & High capacitance Class 2, 4 V TO 50 V 100 pf to 100 µf RoHS compliant & Halogen free Product Specification Product specification
DATA SHEET SURFACE MOUNT MULTILAYER CERAMIC CAPACITORS General purpose & High capacitance Class 2, 4 V TO 50 V 100 pf to 100 µf RoHS compliant & Halogen free Product Specification Product specification
A Novel Three-phase Matrix Converter Based Induction Motor Drive Using Power Factor Control
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 8(4) Special 214, Pages: 49-417 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com A Novel
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 8(4) Special 214, Pages: 49-417 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com A Novel
AN019. A Better Approach of Dealing with Ripple Noise of LDO. Introduction. The influence of inductor effect over LDO
 Better pproach of Dealing with ipple Noise of Introduction It has been a trend that cellular phones, audio systems, cordless phones and portable appliances have a requirement for low noise power supplies.
Better pproach of Dealing with ipple Noise of Introduction It has been a trend that cellular phones, audio systems, cordless phones and portable appliances have a requirement for low noise power supplies.
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique
 Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique S.Anuradha 1, N.Amarnadh Reddy 2 M.Tech (PE), Dept. of EEE, VNRVJIET, T.S, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.
Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique S.Anuradha 1, N.Amarnadh Reddy 2 M.Tech (PE), Dept. of EEE, VNRVJIET, T.S, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.
The Application of Anti-windup PI Controller, SIPIC on FOC of PMSM
 Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2016, 6(3): 39-48 DOI: 10.5923/j.eee.20160603.01 The Application of Anti-windup PI Controller, SIPIC on FOC of PMSM Hoo Choon Lih School of Engineering, Taylor s University,
Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2016, 6(3): 39-48 DOI: 10.5923/j.eee.20160603.01 The Application of Anti-windup PI Controller, SIPIC on FOC of PMSM Hoo Choon Lih School of Engineering, Taylor s University,
DATA SHEET. SURFACE MOUNT MULTILAYER CERAMIC CAPACITORS General purpose & High capacitance Class 2, X5R. 4 V TO 50 V 100 pf to 100 µf
 Product Specification March 31, 2014 V.17 DATA SHEET SURFACE MOUNT MULTILAYER CERAMIC CAPACITORS General purpose & High capacitance Class 2, 4 V TO 50 V 100 pf to 100 µf RoHS compliant & Halogen free Product
Product Specification March 31, 2014 V.17 DATA SHEET SURFACE MOUNT MULTILAYER CERAMIC CAPACITORS General purpose & High capacitance Class 2, 4 V TO 50 V 100 pf to 100 µf RoHS compliant & Halogen free Product
Estimation of Circuit Component Values in Buck Converter using Efficiency Curve
 ISPACS2017 Paper 2017 ID 21 Nov. 9 NQ-L5 Paper ID 21, Estimation of Circuit Component Values in Buck Converter using Efficiency Curve S. Sakurai, N. Tsukiji, Y. Kobori, H. Kobayashi Gunma University 1/36
ISPACS2017 Paper 2017 ID 21 Nov. 9 NQ-L5 Paper ID 21, Estimation of Circuit Component Values in Buck Converter using Efficiency Curve S. Sakurai, N. Tsukiji, Y. Kobori, H. Kobayashi Gunma University 1/36
Maria Carmela Di Piazza. Gianpaolo Vitale. Photovoltaic Sources. Modeling and Emulation. ^ Springer
 Maria Carmela Di Piazza Gianpaolo Vitale Photovoltaic Sources Modeling and Emulation ^ Springer Part I 1 From the Nuclear Fusion to the Radiated Energy on the Earth... 3 1.1 Inside the Universe 3 1.2 The
Maria Carmela Di Piazza Gianpaolo Vitale Photovoltaic Sources Modeling and Emulation ^ Springer Part I 1 From the Nuclear Fusion to the Radiated Energy on the Earth... 3 1.1 Inside the Universe 3 1.2 The
Chapter 14: Inductor design
 Chapter 14 Inductor Design 14.1 Filter inductor design constraints 14.2 A step-by-step design procedure 14.3 Multiple-winding magnetics design using the K g method 14.4 Examples 14.5 Summary of key points
Chapter 14 Inductor Design 14.1 Filter inductor design constraints 14.2 A step-by-step design procedure 14.3 Multiple-winding magnetics design using the K g method 14.4 Examples 14.5 Summary of key points
Postprint.
 http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper presented at 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE), SEP 05-09, 2016, GERMANY. Citation for the
http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper presented at 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE), SEP 05-09, 2016, GERMANY. Citation for the
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
1008 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 57, NO. 3, MARCH /$ IEEE
 1008 IEEE TANSACTIONS ON INDUSTIAL ELECTONICS, VOL. 57, NO. 3, MACH 010 Investigation on the ipple Voltage and the Stability of S Buck Converters With High Output Current and Low Output Voltage Masahito
1008 IEEE TANSACTIONS ON INDUSTIAL ELECTONICS, VOL. 57, NO. 3, MACH 010 Investigation on the ipple Voltage and the Stability of S Buck Converters With High Output Current and Low Output Voltage Masahito
ECE2262 Electric Circuits. Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
 ECE2262 Electric Circuits Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Capacitors Inductors Capacitor and Inductor Combinations Op-Amp Integrator and Op-Amp Differentiator 1 CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE Introduces
ECE2262 Electric Circuits Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Capacitors Inductors Capacitor and Inductor Combinations Op-Amp Integrator and Op-Amp Differentiator 1 CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE Introduces
Published in: Proceedings of the 39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, IECON 2013
 Aalborg Universitet Analysis, Modelling, and Simulation of Droop Control with Virtual Impedance Loop Applied to Parallel UPS Systems Lima, Francisco Kleber A.; Branco, Carlos Gustavo C.; Guerrero, Josep
Aalborg Universitet Analysis, Modelling, and Simulation of Droop Control with Virtual Impedance Loop Applied to Parallel UPS Systems Lima, Francisco Kleber A.; Branco, Carlos Gustavo C.; Guerrero, Josep
An improved deadbeat predictive current control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 22, June 2015, pp. 273-282 An improved deadbeat predictive current control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor Mingyi Wang, iyi i, Donghua
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 22, June 2015, pp. 273-282 An improved deadbeat predictive current control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor Mingyi Wang, iyi i, Donghua
Brief Steady of Power Factor Improvement
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 531-539 International Research PublicationHouse http://www.irphouse.com Brief Steady of Power Factor Improvement
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 531-539 International Research PublicationHouse http://www.irphouse.com Brief Steady of Power Factor Improvement
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
 Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Generalized Analysis for ZCS
 Generalized Analysis for ZCS The QRC cells (ZCS and ZS) analysis, including the switching waveforms, can be generalized, and then applies to each converter. nstead of analyzing each QRC cell (L-type ZCS,
Generalized Analysis for ZCS The QRC cells (ZCS and ZS) analysis, including the switching waveforms, can be generalized, and then applies to each converter. nstead of analyzing each QRC cell (L-type ZCS,
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
