Repetitive control : Power Electronics. Applications
|
|
|
- Primrose Molly Park
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Repetitive control : Power Electronics Applications Ramon Costa Castelló Advanced Control of Energy Systems (ACES) Instituto de Organización y Control (IOC) Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) Barcelona, Spain
2 Contents Repetitive Control Basics Introduction Periodic Signals Performance Discrete Time The Odd-Harmonic case Control Scheme Cascade Approach Plug-in Approach The active filter application Introduction Basic Concept Architecture Control Problem Experimental Setup Experimental Results
3 Introduction A key topic in classical control theory is the Internal Model Principle (IMP). B. Francis and W. Wonham, Internal Model Principle in control theory, Automatica, vol. 12, pp , This principle states that if a certain signal must be tracked or rejected without steady-state error, the generator must be inside the control loop, in the controller, or in the plant itself.
4 Introduction : Type Concept Standard classical control subjects include the IMP concept implicitly when they introduce the system-type concept. The type concept can only be applied to polynomial signals (step, ramp, and parabola) whose generator has the form in the Laplace domain.
5 Introduction : Type Concept (II)
6 Introduction : Systems with periodical disturbances or references In practice, many real systems have to handle tracking and rejecting periodic signals. Magnet power supply for a proton synchrotron (Nakano and others)
7 Introduction : Systems with periodical disturbances or references (II) Demonstration of the Internal Model Principle by Digital Repetitive Control of an Educational Laboratory Plant. Ramon Costa- Castelló and Jordi Nebot and Robert Griñó.IEEE Transactions on Education. Vol. 48, No.1, Pages (February 2005). ISSN :
8 Introduction : Power Electronics Inverter : Generating a 50/60 Hz signal from dc one (Tracking a reference signal) Active filter : Compensation of harmonic signals (Rejecting periodic signals)
9 Periodical Signals Any periodical signal can be written as: The control loop should include:
10 Periodical Signals : Generator Yamamoto, Y. (1993). Learning control and related problems in infinitedimensional systems. In: Proceedings of the 1993 European Control Conference. pp
11 Periodical Signals : Generator I
12 Periodical Signals : Generator II T p +
13 Periodical Signals : Generator III
14 Performance C(s) P(s) Open Loop Transfer Function Sensitivity Function Complementary Sensitivity Function
15 Digital Case
16 Digital Case II ( ) R z T p = z + N 1 T p 1 z N = N T s 2π j i N 2π z = e ω = i i i N T p
17 Odd-Harmonic Case Digital repetitive plug-in controller for odd-harmonic periodic references and disturbances Robert Griñó and Ramon Costa- Castelló. Automatica. Volume 41, Issue 1,Pages (January 2005)
18 Odd-Harmonic Case II N=3 traditional N=3 odd harmonic Imaginary Axis Pole-Zero Map Real Axis
19 Control Scheme Cascade form Plug-in Form
20 Control Scheme : Cascade form P(z)
21 Control Scheme : Plug-in Approach Repetitive Controller z N F( z) Gx ( z) Gc ( z) Gp ( z)
22 Control Scheme : Plug-in Approach II
23 Control Scheme : Plug-in Approach III
24 Plug-in Approach : Stability Conditions 1. First stability Condition : The System without the Repetitive Controller must be stable. 2. Second stability Condition 3. Third stability Condition : Gx ( z) Gc F( z) < 1 ( z)
25 Plug-in Approach : Filter F(z) should fulfill the second stability condition. Usually, a low-pass null-phase FIR filter is used. To assure unitary gain a DC frequency the parameters must fulfill : No causality problems exist because that the filter is in cascade with a N periods delay. The filter reduces the open-loop gain at those frequencies at which uncertainty exists (robustness). Unfortunately it slightly moves the open-loop pole positions in z-plane (precision loose).
26 Plug-in Approach : G x (z) A common approach to design G x (z) is Unfortunately, this approach cannot be applied to nonminimum-phase plants. Another approach is to cancel minimum-phase zeros and compensate the phase for the non minimum-phase ones: k r is fixed by a trade-off between robustness and transient response.
27 Contents Repetitive Control Basics Introduction Periodic Signals Performance Discrete Time The Odd-Harmonic case Control Scheme Cascade Approach Plug-in Approach The active filter application Introduction Basic Concept Architecture Control Problem Experimental Setup Experimental Results
28 Introduction Proliferation of nonlinear loads ->This fact has deteriorated the power quality of electrical power systems. More stringent requirements proposals IEC {2,4} and IEEE-519.
29 Basic Concepts v s i s Linear Load Active Filter Nonlinear Load
30 Architecture : Complete Picture Full Bridge Boost Converter
31 Control Problem: Control Goals Current in phase with the voltage waveform: ( ) * sin s d r i = I ω t Constant average value of the voltage at the DC bus capacitor: * x = V 2 0 d
32 Architecture : Boost Converter u r L r L & = 1 C x& = x 1 x 1 Vs x2 L x1+ x2 + r x1 = v s x C 2 1 & = 1 C x& = x L x1 x2 + r x1 = v s 2 1 u Vs x2 C
33 Architecture : Boost u & + + = = 1 C x& 2 = x1 Converter II L x1 x2 r x1 v s & L x1 = ux2 r x1+ v s C x& = ux & 2 1 L x1 = u x2 r x1+ v s C x& = u x 2 1 & u = 1 C x& = x L x1 x2 + r x1 = v s 2 1 u = { 1,1} The averaged model u = [ 1,1]
34 Control Problem: Current L x& = u x r x + v Control loop s x = V 2 d L x& = u V r x + V 1 d 1 V x ( ) 1 s = r = G ( ) ( ) p s u s L d s + 1 r s G () ( 1 ( ) 1 ) p s Gp z = z Z s ZOH, T
35 Control Problem: Voltage Loop C x y = x 2 C y& = u x x & = u x ( ) 2 2 x1 () t = Id sin ( ωrt) al cos( l ωrt) + blsin ( l ωrt) l= Iload Current loop in steady state k+ 1 T k 2 2 ET k 2 ( d 1) ( l l ) ( d 1) C y = r kt I b + a + b + I b l 2 r=0 ( k+ 1) T ET k C y = I b kt 2 ( ) d 1
36 Control Problem: Voltage Loop 2 V d 2 PI E T z 2 1 y b 1
37 Control Problem: Proposed Two control loops : Scheme Current loop : Digital Repetitive Control Voltage loop : Classical PI Control I d sin ( ωr t) Repetitive Controller PI Controller Boost Converter Odd-Harmonic Digital Repetitive Control of a Single-Phase Current Active Filter. Ramon Costa-Castelló, Robert Griñó & Enric Fossas IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics. Volume: 19, Issue: 4, Year: July E.Page(s): x 2 x 1 V d * I s I l
38 Experimental Setup Active filter parameters: Capacitor: 6600 uf, 450 V DC Inductor: 0.8 mh parasitic resistance: 0.04 Ohm IGBT: 1200 V, 100 A Feedback paths (sensors): Network voltage: voltage transformer (220V/15V) Network current: Hall-effect sensor (TECSA-HA ) (50A) DC bus voltage: AD-215BY isolation amplifier Control hardware: ADSP floating-point DSP ADMC-200 coprocessor: A/D channels and PWM generation
39 Experimental Setup : General view
40 Experimental setup : IGBT drivers
41 Experimental setup : Control hardware
42 Experimental Results: Nonlinear Load
43 Experimental Results: No-Load
44 Experimental Results: Full NL load
45 Experimental Results: Full NL load
46 Experimental Results: Full load to No-load
47 Experimental Results: No-load to full load
Non-uniform sampling in digital repetitive control systems: an LMI stability analysis Germán A. Ramos, Josep M. Olm, Ramon Costa-Castelló.
 Non-uniform sampling in digital repetitive control systems: an LMI stability analysis Germán A. Ramos, Josep M. Olm, Ramon Costa-Castelló. ACES - Control Avançat de sistemes d'energia IOC-DT-P-2009-01
Non-uniform sampling in digital repetitive control systems: an LMI stability analysis Germán A. Ramos, Josep M. Olm, Ramon Costa-Castelló. ACES - Control Avançat de sistemes d'energia IOC-DT-P-2009-01
Lecture 13: Internal Model Principle and Repetitive Control
 ME 233, UC Berkeley, Spring 2014 Xu Chen Lecture 13: Internal Model Principle and Repetitive Control Big picture review of integral control in PID design example: 0 Es) C s) Ds) + + P s) Y s) where P s)
ME 233, UC Berkeley, Spring 2014 Xu Chen Lecture 13: Internal Model Principle and Repetitive Control Big picture review of integral control in PID design example: 0 Es) C s) Ds) + + P s) Y s) where P s)
Control System Design
 ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #36 Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room: CRL-229 Phone ext.: 26984 Email: ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Friday, April 4, 2003 3. Cascade Control Next we turn to an
ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #36 Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room: CRL-229 Phone ext.: 26984 Email: ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Friday, April 4, 2003 3. Cascade Control Next we turn to an
The output voltage is given by,
 71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
Compensator Design for Closed Loop Hall-Effect Current Sensors
 Compensator Design for Closed Loop HallEffect Current Sensors Ashish Kumar and Vinod John Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 5600, India. Email: ashishk@ee.iisc.ernet.in,
Compensator Design for Closed Loop HallEffect Current Sensors Ashish Kumar and Vinod John Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 5600, India. Email: ashishk@ee.iisc.ernet.in,
Contents. PART I METHODS AND CONCEPTS 2. Transfer Function Approach Frequency Domain Representations... 42
 Contents Preface.............................................. xiii 1. Introduction......................................... 1 1.1 Continuous and Discrete Control Systems................. 4 1.2 Open-Loop
Contents Preface.............................................. xiii 1. Introduction......................................... 1 1.1 Continuous and Discrete Control Systems................. 4 1.2 Open-Loop
DESIGN OF GRID CONNECTED PV INVERTER THROUGH FEEDBACK LINEARIZATION
 TJPRC: International Journal of Power Systems & Microelectronics (TJPRC: IJPSM) Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jun 2016, 83-94 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. DESIGN OF GRID CONNECTED PV INVERTER THROUGH FEEDBACK LINEARIZATION G.KUSUMA
TJPRC: International Journal of Power Systems & Microelectronics (TJPRC: IJPSM) Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jun 2016, 83-94 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. DESIGN OF GRID CONNECTED PV INVERTER THROUGH FEEDBACK LINEARIZATION G.KUSUMA
Chapter 13 Digital Control
 Chapter 13 Digital Control Chapter 12 was concerned with building models for systems acting under digital control. We next turn to the question of control itself. Topics to be covered include: why one
Chapter 13 Digital Control Chapter 12 was concerned with building models for systems acting under digital control. We next turn to the question of control itself. Topics to be covered include: why one
CDS 101/110a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design
 CDS 11/11a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design Richard M. Murray 17 November 28 Goals: Describe canonical control design problem and standard performance measures Show how to use loop shaping to achieve
CDS 11/11a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design Richard M. Murray 17 November 28 Goals: Describe canonical control design problem and standard performance measures Show how to use loop shaping to achieve
Averaged dynamics of a coupled-inductor boost converter under sliding mode control using a piecewise linear complementarity model
 IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics (5) Page of doi:.93/imamat/dri7 Averaged dynamics of a coupledinductor boost converter under sliding mode control using a piecewise linear complementarity model NILIANA
IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics (5) Page of doi:.93/imamat/dri7 Averaged dynamics of a coupledinductor boost converter under sliding mode control using a piecewise linear complementarity model NILIANA
GEOPLEX: Back-to-back converter for an electrical machine application. C. Batlle, A. Dòria, E. Fossas, C. Gaviria, R. Griñó
 GEOPLEX: Back-to-back converter for an electrical machine application C. Batlle, A. Dòria, E. Fossas, C. Gaviria, R. Griñó IOC-DT-P-2004-22 Octubre 2004 A back-to-back converter for an electrical machine
GEOPLEX: Back-to-back converter for an electrical machine application C. Batlle, A. Dòria, E. Fossas, C. Gaviria, R. Griñó IOC-DT-P-2004-22 Octubre 2004 A back-to-back converter for an electrical machine
Chapter 2. Classical Control System Design. Dutch Institute of Systems and Control
 Chapter 2 Classical Control System Design Overview Ch. 2. 2. Classical control system design Introduction Introduction Steady-state Steady-state errors errors Type Type k k systems systems Integral Integral
Chapter 2 Classical Control System Design Overview Ch. 2. 2. Classical control system design Introduction Introduction Steady-state Steady-state errors errors Type Type k k systems systems Integral Integral
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
Output high order sliding mode control of unity-power-factor in three-phase AC/DC Boost Converter
 Output high order sliding mode control of unity-power-factor in three-phase AC/DC Boost Converter JianXing Liu, Salah Laghrouche, Maxim Wack Laboratoire Systèmes Et Transports (SET) Laboratoire SeT Contents
Output high order sliding mode control of unity-power-factor in three-phase AC/DC Boost Converter JianXing Liu, Salah Laghrouche, Maxim Wack Laboratoire Systèmes Et Transports (SET) Laboratoire SeT Contents
Analysis and control design of two cascaded boost converter
 MAT EC Web of Conferences 16, 64 (214) DOI: 1.151/ matecconf/ 21416 64 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 214 Analysis and control design of two cascaded boost converter A. Moutabir 1,
MAT EC Web of Conferences 16, 64 (214) DOI: 1.151/ matecconf/ 21416 64 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 214 Analysis and control design of two cascaded boost converter A. Moutabir 1,
Experimental results on an IDA-PBC controller for a full-bridge boost converter Carles Batlle, Arnau Dòria Cerezo, Enric Fossas
 Experimental results on an IDA-PBC controller for a full-bridge boost converter Carles Batlle, Arnau Dòria Cerezo, Enric Fossas ACES: Control Avançat de Sistemes d Energia IOC-DT-P-6-13 Abril 6 Experimental
Experimental results on an IDA-PBC controller for a full-bridge boost converter Carles Batlle, Arnau Dòria Cerezo, Enric Fossas ACES: Control Avançat de Sistemes d Energia IOC-DT-P-6-13 Abril 6 Experimental
Performance of an Adaptive Algorithm for Sinusoidal Disturbance Rejection in High Noise
 Performance of an Adaptive Algorithm for Sinusoidal Disturbance Rejection in High Noise MarcBodson Department of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 842, U.S.A. (8) 58 859 bodson@ee.utah.edu
Performance of an Adaptive Algorithm for Sinusoidal Disturbance Rejection in High Noise MarcBodson Department of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 842, U.S.A. (8) 58 859 bodson@ee.utah.edu
Ultimate State. MEM 355 Performance Enhancement of Dynamical Systems
 Ultimate State MEM 355 Performance Enhancement of Dnamical Sstems Harr G. Kwatn Department of Mechanical Engineering & Mechanics Drexel Universit Outline Design Criteria two step process Ultimate state
Ultimate State MEM 355 Performance Enhancement of Dnamical Sstems Harr G. Kwatn Department of Mechanical Engineering & Mechanics Drexel Universit Outline Design Criteria two step process Ultimate state
Digital Signal Processing
 COMP ENG 4TL4: Digital Signal Processing Notes for Lecture #21 Friday, October 24, 2003 Types of causal FIR (generalized) linear-phase filters: Type I: Symmetric impulse response: with order M an even
COMP ENG 4TL4: Digital Signal Processing Notes for Lecture #21 Friday, October 24, 2003 Types of causal FIR (generalized) linear-phase filters: Type I: Symmetric impulse response: with order M an even
THE power transfer capability is one of the most fundamental
 4172 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 27, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2012 Letters Power Characterization of Isolated Bidirectional Dual-Active-Bridge DC DC Converter With Dual-Phase-Shift Control Biao
4172 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 27, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2012 Letters Power Characterization of Isolated Bidirectional Dual-Active-Bridge DC DC Converter With Dual-Phase-Shift Control Biao
Robust QFT-based PI controller for a feedforward control scheme
 Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, May 9-11, 218 ThAT4.4 Robust QFT-based PI controller for a feedforward control scheme Ángeles Hoyo José Carlos Moreno José Luis Guzmán Tore Hägglund Dep. of
Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, May 9-11, 218 ThAT4.4 Robust QFT-based PI controller for a feedforward control scheme Ángeles Hoyo José Carlos Moreno José Luis Guzmán Tore Hägglund Dep. of
Robust Internal Model Control for Impulse Elimination of Singular Systems
 International Journal of Control Science and Engineering ; (): -7 DOI:.59/j.control.. Robust Internal Model Control for Impulse Elimination of Singular Systems M. M. Share Pasandand *, H. D. Taghirad Department
International Journal of Control Science and Engineering ; (): -7 DOI:.59/j.control.. Robust Internal Model Control for Impulse Elimination of Singular Systems M. M. Share Pasandand *, H. D. Taghirad Department
Speaker: Arthur Williams Chief Scientist Telebyte Inc. Thursday November 20 th 2008 INTRODUCTION TO ACTIVE AND PASSIVE ANALOG
 INTRODUCTION TO ACTIVE AND PASSIVE ANALOG FILTER DESIGN INCLUDING SOME INTERESTING AND UNIQUE CONFIGURATIONS Speaker: Arthur Williams Chief Scientist Telebyte Inc. Thursday November 20 th 2008 TOPICS Introduction
INTRODUCTION TO ACTIVE AND PASSIVE ANALOG FILTER DESIGN INCLUDING SOME INTERESTING AND UNIQUE CONFIGURATIONS Speaker: Arthur Williams Chief Scientist Telebyte Inc. Thursday November 20 th 2008 TOPICS Introduction
Unit 11 - Week 7: Quantitative feedback theory (Part 1/2)
 X reviewer3@nptel.iitm.ac.in Courses» Control System Design Announcements Course Ask a Question Progress Mentor FAQ Unit 11 - Week 7: Quantitative feedback theory (Part 1/2) Course outline How to access
X reviewer3@nptel.iitm.ac.in Courses» Control System Design Announcements Course Ask a Question Progress Mentor FAQ Unit 11 - Week 7: Quantitative feedback theory (Part 1/2) Course outline How to access
Power Factor Compensation is Equivalent to Cyclodissipassivation
 Proceedings of the 007 American Control Conference Marriott Marquis Hotel at Times Square New York City, USA, July 11-13, 007 FrC16.3 Power Factor Compensation is Equivalent to Cyclodissipassivation Eloísa
Proceedings of the 007 American Control Conference Marriott Marquis Hotel at Times Square New York City, USA, July 11-13, 007 FrC16.3 Power Factor Compensation is Equivalent to Cyclodissipassivation Eloísa
Raktim Bhattacharya. . AERO 422: Active Controls for Aerospace Vehicles. Basic Feedback Analysis & Design
 AERO 422: Active Controls for Aerospace Vehicles Basic Feedback Analysis & Design Raktim Bhattacharya Laboratory For Uncertainty Quantification Aerospace Engineering, Texas A&M University Routh s Stability
AERO 422: Active Controls for Aerospace Vehicles Basic Feedback Analysis & Design Raktim Bhattacharya Laboratory For Uncertainty Quantification Aerospace Engineering, Texas A&M University Routh s Stability
Video 5.1 Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh
 Video 5.1 Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.1 1 The Purpose of Control Input/Stimulus/ Disturbance System or Plant Output/ Response Understand the Black Box Evaluate the Performance Change the Behavior
Video 5.1 Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.1 1 The Purpose of Control Input/Stimulus/ Disturbance System or Plant Output/ Response Understand the Black Box Evaluate the Performance Change the Behavior
FEEDBACK CONTROL SYSTEMS
 FEEDBAC CONTROL SYSTEMS. Control System Design. Open and Closed-Loop Control Systems 3. Why Closed-Loop Control? 4. Case Study --- Speed Control of a DC Motor 5. Steady-State Errors in Unity Feedback Control
FEEDBAC CONTROL SYSTEMS. Control System Design. Open and Closed-Loop Control Systems 3. Why Closed-Loop Control? 4. Case Study --- Speed Control of a DC Motor 5. Steady-State Errors in Unity Feedback Control
Application of Simple Adaptive Control to a DC/DC Boost Converter with Load Variation
 Application of Simple Adaptive Control to a DC/DC Boost Converter with oad Variation Goo-Jong Jeong 1, In-Hyuk Kim 1 and Young-Ik Son 1 1 NPTC, Department of Electrical Engineering, Myongji University,
Application of Simple Adaptive Control to a DC/DC Boost Converter with oad Variation Goo-Jong Jeong 1, In-Hyuk Kim 1 and Young-Ik Son 1 1 NPTC, Department of Electrical Engineering, Myongji University,
A DESIGN METHOD FOR SIMPLE REPETITIVE CONTROLLERS WITH SPECIFIED INPUT-OUTPUT CHARACTERISTIC
 International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information Control ICIC International c 202 ISSN 349-498 Volume 8, Number 7(A), July 202 pp. 4883 4899 A DESIGN METHOD FOR SIMPLE REPETITIVE CONTROLLERS
International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information Control ICIC International c 202 ISSN 349-498 Volume 8, Number 7(A), July 202 pp. 4883 4899 A DESIGN METHOD FOR SIMPLE REPETITIVE CONTROLLERS
DESIGN USING TRANSFORMATION TECHNIQUE CLASSICAL METHOD
 206 Spring Semester ELEC733 Digital Control System LECTURE 7: DESIGN USING TRANSFORMATION TECHNIQUE CLASSICAL METHOD For a unit ramp input Tz Ez ( ) 2 ( z ) D( z) G( z) Tz e( ) lim( z) z 2 ( z ) D( z)
206 Spring Semester ELEC733 Digital Control System LECTURE 7: DESIGN USING TRANSFORMATION TECHNIQUE CLASSICAL METHOD For a unit ramp input Tz Ez ( ) 2 ( z ) D( z) G( z) Tz e( ) lim( z) z 2 ( z ) D( z)
Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives
 1 / 22 Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 22 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises
1 / 22 Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 22 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises
Index. Index. More information. in this web service Cambridge University Press
 A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
Essence of the Root Locus Technique
 Essence of the Root Locus Technique In this chapter we study a method for finding locations of system poles. The method is presented for a very general set-up, namely for the case when the closed-loop
Essence of the Root Locus Technique In this chapter we study a method for finding locations of system poles. The method is presented for a very general set-up, namely for the case when the closed-loop
the machine makes analytic calculation of rotor position impossible for a given flux linkage and current value.
 COMPARISON OF FLUX LINKAGE ESTIMATORS IN POSITION SENSORLESS SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTOR DRIVES Erkan Mese Kocaeli University / Technical Education Faculty zmit/kocaeli-turkey email: emese@kou.edu.tr ABSTRACT
COMPARISON OF FLUX LINKAGE ESTIMATORS IN POSITION SENSORLESS SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTOR DRIVES Erkan Mese Kocaeli University / Technical Education Faculty zmit/kocaeli-turkey email: emese@kou.edu.tr ABSTRACT
Frequency Adaptive Control Technique for Periodic Runout and Wobble Cancellation in Optical Disk Drives
 Frequency Adaptive Control Technique for Periodic Runout and Wobble Cancellation in Optical Disk Drives Yee-Pien YANG and Jieng-Jang LIU Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Taiwan University,
Frequency Adaptive Control Technique for Periodic Runout and Wobble Cancellation in Optical Disk Drives Yee-Pien YANG and Jieng-Jang LIU Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Taiwan University,
An Analysis and Synthesis of Internal Model Principle Type Controllers
 29 American Control Conference Hyatt Regency Riverfront, St. Louis, MO, USA June -2, 29 WeA5.6 An Analysis and Synthesis of Internal Model Principle Type Controllers Yigang Wang, Kevin C. Chu and Tsu-Chin
29 American Control Conference Hyatt Regency Riverfront, St. Louis, MO, USA June -2, 29 WeA5.6 An Analysis and Synthesis of Internal Model Principle Type Controllers Yigang Wang, Kevin C. Chu and Tsu-Chin
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012
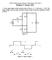 ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
Lecture 12. Upcoming labs: Final Exam on 12/21/2015 (Monday)10:30-12:30
 289 Upcoming labs: Lecture 12 Lab 20: Internal model control (finish up) Lab 22: Force or Torque control experiments [Integrative] (2-3 sessions) Final Exam on 12/21/2015 (Monday)10:30-12:30 Today: Recap
289 Upcoming labs: Lecture 12 Lab 20: Internal model control (finish up) Lab 22: Force or Torque control experiments [Integrative] (2-3 sessions) Final Exam on 12/21/2015 (Monday)10:30-12:30 Today: Recap
Prüfung Regelungstechnik I (Control Systems I) Übersetzungshilfe / Translation aid (English) To be returned at the end of the exam!
 Prüfung Regelungstechnik I (Control Systems I) Prof. Dr. Lino Guzzella 29. 8. 2 Übersetzungshilfe / Translation aid (English) To be returned at the end of the exam! Do not mark up this translation aid
Prüfung Regelungstechnik I (Control Systems I) Prof. Dr. Lino Guzzella 29. 8. 2 Übersetzungshilfe / Translation aid (English) To be returned at the end of the exam! Do not mark up this translation aid
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
Robust Repetitive Control with an Application to a Linear Actuator
 Robust Repetitive Control with an Application to a Linear Actuator Submitted for the completion of the degree Doctor of Philosophy Maria Mitrevska 2018 Faculty of Science, Engineering and Technology Swinburne
Robust Repetitive Control with an Application to a Linear Actuator Submitted for the completion of the degree Doctor of Philosophy Maria Mitrevska 2018 Faculty of Science, Engineering and Technology Swinburne
GATE EE Topic wise Questions SIGNALS & SYSTEMS
 www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
LAPLACE TRANSFORMATION AND APPLICATIONS. Laplace transformation It s a transformation method used for solving differential equation.
 LAPLACE TRANSFORMATION AND APPLICATIONS Laplace transformation It s a transformation method used for solving differential equation. Advantages The solution of differential equation using LT, progresses
LAPLACE TRANSFORMATION AND APPLICATIONS Laplace transformation It s a transformation method used for solving differential equation. Advantages The solution of differential equation using LT, progresses
IDA-PBC controller for a bidirectional power flow full-bridge rectifier*
 IDA-PBC controller for a bidirectional power flow full-bridge rectifier* Carles Batlle MAIV, EPSEVG and IOC, 88 Vilanova i la G., Spain carles.batlle@upc.edu Arnau Dòria-Cerezo Dept. of Electrical Eng.,
IDA-PBC controller for a bidirectional power flow full-bridge rectifier* Carles Batlle MAIV, EPSEVG and IOC, 88 Vilanova i la G., Spain carles.batlle@upc.edu Arnau Dòria-Cerezo Dept. of Electrical Eng.,
Pipelined multi step A/D converters
 Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Chennai, 600036, India 04 Nov 2006 Motivation for multi step A/D conversion Flash converters: Area and power consumption increase
Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Chennai, 600036, India 04 Nov 2006 Motivation for multi step A/D conversion Flash converters: Area and power consumption increase
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
RELAY CONTROL WITH PARALLEL COMPENSATOR FOR NONMINIMUM PHASE PLANTS. Ryszard Gessing
 RELAY CONTROL WITH PARALLEL COMPENSATOR FOR NONMINIMUM PHASE PLANTS Ryszard Gessing Politechnika Śl aska Instytut Automatyki, ul. Akademicka 16, 44-101 Gliwice, Poland, fax: +4832 372127, email: gessing@ia.gliwice.edu.pl
RELAY CONTROL WITH PARALLEL COMPENSATOR FOR NONMINIMUM PHASE PLANTS Ryszard Gessing Politechnika Śl aska Instytut Automatyki, ul. Akademicka 16, 44-101 Gliwice, Poland, fax: +4832 372127, email: gessing@ia.gliwice.edu.pl
Transient Response of Transmission Lines and TDR/TDT
 Transient Response of Transmission Lines and TDR/TDT Tzong-Lin Wu, Ph.D. EMC Lab. Department of Electrical Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Outlines Why do we learn the transient response of
Transient Response of Transmission Lines and TDR/TDT Tzong-Lin Wu, Ph.D. EMC Lab. Department of Electrical Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Outlines Why do we learn the transient response of
IMPROVE THE PERFORMANCE OF SHUNT ACTIVE POWER FILTERS WITH CONTROL STRATEGY OF ROBUST DC-LINK VOLTAGE
 IMPROVE THE PERFORMANCE OF SHUNT ACTIVE POWER FILTERS WITH CONTROL STRATEGY OF ROBUST DC-LINK VOLTAGE 1 K S R VENKATARAMANA, 2 G SESHADRI 1 M.Tech, SIDDARTHA INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (SIETK)
IMPROVE THE PERFORMANCE OF SHUNT ACTIVE POWER FILTERS WITH CONTROL STRATEGY OF ROBUST DC-LINK VOLTAGE 1 K S R VENKATARAMANA, 2 G SESHADRI 1 M.Tech, SIDDARTHA INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (SIETK)
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 . W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder Part II" Converter Dynamics and Control! 7.!AC equivalent circuit modeling! 8.!Converter transfer
. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder Part II" Converter Dynamics and Control! 7.!AC equivalent circuit modeling! 8.!Converter transfer
EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS IN A MODIFIED CLOSED LOOP V/F INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 31, No. 3, November, 2012, pp. 365 369. Copyright 2012 Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria. ISSN 1115-8443 EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS
Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 31, No. 3, November, 2012, pp. 365 369. Copyright 2012 Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria. ISSN 1115-8443 EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS
CONVENTIONAL stability analyses of switching power
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MAY 2008 1449 Multiple Lyapunov Function Based Reaching Condition for Orbital Existence of Switching Power Converters Sudip K. Mazumder, Senior Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MAY 2008 1449 Multiple Lyapunov Function Based Reaching Condition for Orbital Existence of Switching Power Converters Sudip K. Mazumder, Senior Member,
Model Predictive Controller of Boost Converter with RLE Load
 Model Predictive Controller of Boost Converter with RLE Load N. Murali K.V.Shriram S.Muthukumar Nizwa College of Vellore Institute of Nizwa College of Technology Technology University Technology Ministry
Model Predictive Controller of Boost Converter with RLE Load N. Murali K.V.Shriram S.Muthukumar Nizwa College of Vellore Institute of Nizwa College of Technology Technology University Technology Ministry
Modeling, Analysis and Control of an Isolated Boost Converter for System Level Studies
 1 Modeling, Analysis and Control of an Isolated Boost Converter for System Level Studies Bijan Zahedi, Student Member, IEEE, and Lars E. Norum, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract-- This paper performs a modeling
1 Modeling, Analysis and Control of an Isolated Boost Converter for System Level Studies Bijan Zahedi, Student Member, IEEE, and Lars E. Norum, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract-- This paper performs a modeling
EE155/255 Green Electronics
 EE155/255 Green Electronics Electric Motors 10/19/16 Prof. William Dally Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University This week is flipped Course Logistics Discussion on 10/17, Motors on 10/19, Isolated
EE155/255 Green Electronics Electric Motors 10/19/16 Prof. William Dally Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University This week is flipped Course Logistics Discussion on 10/17, Motors on 10/19, Isolated
H-infinity Model Reference Controller Design for Magnetic Levitation System
 H.I. Ali Control and Systems Engineering Department, University of Technology Baghdad, Iraq 6043@uotechnology.edu.iq H-infinity Model Reference Controller Design for Magnetic Levitation System Abstract-
H.I. Ali Control and Systems Engineering Department, University of Technology Baghdad, Iraq 6043@uotechnology.edu.iq H-infinity Model Reference Controller Design for Magnetic Levitation System Abstract-
Novel DC-AC Converter Topology for Multilevel Battery Energy Storage Systems. Mario Gommeringer, Felix Kammerer, Johannes Kolb, Michael Braun
 Elektrotechnisches Institut (ETI) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Michael Braun Prof. Dr.-Ing. Martin Doppelbauer Prof. Dr.-Ing. Marc Hiller Kaiserstr.12. 76131 Karlsruhe 13. Sept. 216 Title: Novel DC-C Converter Topology
Elektrotechnisches Institut (ETI) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Michael Braun Prof. Dr.-Ing. Martin Doppelbauer Prof. Dr.-Ing. Marc Hiller Kaiserstr.12. 76131 Karlsruhe 13. Sept. 216 Title: Novel DC-C Converter Topology
EE451/551: Digital Control. Chapter 3: Modeling of Digital Control Systems
 EE451/551: Digital Control Chapter 3: Modeling of Digital Control Systems Common Digital Control Configurations AsnotedinCh1 commondigitalcontrolconfigurations As noted in Ch 1, common digital control
EE451/551: Digital Control Chapter 3: Modeling of Digital Control Systems Common Digital Control Configurations AsnotedinCh1 commondigitalcontrolconfigurations As noted in Ch 1, common digital control
The loop shaping paradigm. Lecture 7. Loop analysis of feedback systems (2) Essential specifications (2)
 Lecture 7. Loop analysis of feedback systems (2). Loop shaping 2. Performance limitations The loop shaping paradigm. Estimate performance and robustness of the feedback system from the loop transfer L(jω)
Lecture 7. Loop analysis of feedback systems (2). Loop shaping 2. Performance limitations The loop shaping paradigm. Estimate performance and robustness of the feedback system from the loop transfer L(jω)
EE 422G - Signals and Systems Laboratory
 EE 4G - Signals and Systems Laboratory Lab 9 PID Control Kevin D. Donohue Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 April, 04 Objectives: Identify the
EE 4G - Signals and Systems Laboratory Lab 9 PID Control Kevin D. Donohue Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 April, 04 Objectives: Identify the
On the passivity properties of a new family of repetitive (hyperbolic) controllers
 Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Cancun, Mexico, Dec. 9-11, 8 On the passivity properties of a new family of repetitive hyperbolic controllers P.G. Hernández-Briones, G.
Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Cancun, Mexico, Dec. 9-11, 8 On the passivity properties of a new family of repetitive hyperbolic controllers P.G. Hernández-Briones, G.
Hybrid Predictive and Input-output feedback linearization controllers design for Half Bridge Multicellular Inverter: Comparative study
 The nd International Conference on Power Electronics and their Applications (ICPEA 5), Djelfa on 9-3 March 5, Algeria Hybrid Predictive and Input-output feedback linearization controllers design for Half
The nd International Conference on Power Electronics and their Applications (ICPEA 5), Djelfa on 9-3 March 5, Algeria Hybrid Predictive and Input-output feedback linearization controllers design for Half
NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve
 D. SWATI et al., Nonlinear Control of ph System for Change Over Titration Curve, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 19 (4) 341 349 (2005) 341 NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve D. Swati, V. S. R.
D. SWATI et al., Nonlinear Control of ph System for Change Over Titration Curve, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 19 (4) 341 349 (2005) 341 NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve D. Swati, V. S. R.
AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm
 7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Passive RL and RC Filters
 NDSU Passive RL and RC Filters ECE 3 Passive RL and RC Filters A filter is a system whose gain changes with frequency. Essentially, all dynamic systems are filters. -Stage Low-Pass Filter For the following
NDSU Passive RL and RC Filters ECE 3 Passive RL and RC Filters A filter is a system whose gain changes with frequency. Essentially, all dynamic systems are filters. -Stage Low-Pass Filter For the following
CYBER EXPLORATION LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS
 CYBER EXPLORATION LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS 1 2 Cyber Exploration oratory Experiments Chapter 2 Experiment 1 Objectives To learn to use MATLAB to: (1) generate polynomial, (2) manipulate polynomials, (3)
CYBER EXPLORATION LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS 1 2 Cyber Exploration oratory Experiments Chapter 2 Experiment 1 Objectives To learn to use MATLAB to: (1) generate polynomial, (2) manipulate polynomials, (3)
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS 2.1 The Ideal Op Amp (Chapter 2.1) Amplifier Applications 2.2 The Inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.2) 2.3 The Non-inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.3) 2.4 Difference
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS 2.1 The Ideal Op Amp (Chapter 2.1) Amplifier Applications 2.2 The Inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.2) 2.3 The Non-inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.3) 2.4 Difference
Chapter 2 Voltage-, Current-, and Z-source Converters
 Chapter 2 Voltage-, Current-, and Z-source Converters Some fundamental concepts are to be introduced in this chapter, such as voltage sources, current sources, impedance networks, Z-source, two-port network,
Chapter 2 Voltage-, Current-, and Z-source Converters Some fundamental concepts are to be introduced in this chapter, such as voltage sources, current sources, impedance networks, Z-source, two-port network,
SECTION 4: STEADY STATE ERROR
 SECTION 4: STEADY STATE ERROR MAE 4421 Control of Aerospace & Mechanical Systems 2 Introduction Steady State Error Introduction 3 Consider a simple unity feedback system The error is the difference between
SECTION 4: STEADY STATE ERROR MAE 4421 Control of Aerospace & Mechanical Systems 2 Introduction Steady State Error Introduction 3 Consider a simple unity feedback system The error is the difference between
A Comparison between Integer Order and Non-integer Order Controllers Applied to a Water Levelling System
 AUTOMATYKA/AUTOMATICS 214 Vol. 18 No. 2 http://dx.doi.org/1.7494/automat.214.18.2.71 Bartosz Kania, Tomasz Dziwiński, Waldemar Bauer, Marta Zagórowska, Jerzy Baranowski A Comparison between Integer Order
AUTOMATYKA/AUTOMATICS 214 Vol. 18 No. 2 http://dx.doi.org/1.7494/automat.214.18.2.71 Bartosz Kania, Tomasz Dziwiński, Waldemar Bauer, Marta Zagórowska, Jerzy Baranowski A Comparison between Integer Order
Control Systems I. Lecture 2: Modeling. Suggested Readings: Åström & Murray Ch. 2-3, Guzzella Ch Emilio Frazzoli
 Control Systems I Lecture 2: Modeling Suggested Readings: Åström & Murray Ch. 2-3, Guzzella Ch. 2-3 Emilio Frazzoli Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control D-MAVT ETH Zürich September 29, 2017 E. Frazzoli
Control Systems I Lecture 2: Modeling Suggested Readings: Åström & Murray Ch. 2-3, Guzzella Ch. 2-3 Emilio Frazzoli Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control D-MAVT ETH Zürich September 29, 2017 E. Frazzoli
Acceleration Feedback
 Acceleration Feedback Mechanical Engineer Modeling & Simulation Electro- Mechanics Electrical- Electronics Engineer Sensors Actuators Computer Systems Engineer Embedded Control Controls Engineer Mechatronic
Acceleration Feedback Mechanical Engineer Modeling & Simulation Electro- Mechanics Electrical- Electronics Engineer Sensors Actuators Computer Systems Engineer Embedded Control Controls Engineer Mechatronic
Introduction to CMOS RF Integrated Circuits Design
 V. Voltage Controlled Oscillators Fall 2012, Prof. JianJun Zhou V-1 Outline Phase Noise and Spurs Ring VCO LC VCO Frequency Tuning (Varactor, SCA) Phase Noise Estimation Quadrature Phase Generator Fall
V. Voltage Controlled Oscillators Fall 2012, Prof. JianJun Zhou V-1 Outline Phase Noise and Spurs Ring VCO LC VCO Frequency Tuning (Varactor, SCA) Phase Noise Estimation Quadrature Phase Generator Fall
Disturbance Rejection in Parameter-varying Web-winding Systems
 Proceedings of the 17th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Disturbance Rejection in Parameter-varying Web-winding Systems Hua Zhong Lucy Y. Pao Electrical and Computer Engineering
Proceedings of the 17th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Disturbance Rejection in Parameter-varying Web-winding Systems Hua Zhong Lucy Y. Pao Electrical and Computer Engineering
EEE 188: Digital Control Systems
 EEE 88: Digital Control Systems Lecture summary # the controlled variable. Example: cruise control. In feedback control, sensors and measurements play an important role. In discrete time systems, the control
EEE 88: Digital Control Systems Lecture summary # the controlled variable. Example: cruise control. In feedback control, sensors and measurements play an important role. In discrete time systems, the control
1 An Overview and Brief History of Feedback Control 1. 2 Dynamic Models 23. Contents. Preface. xiii
 Contents 1 An Overview and Brief History of Feedback Control 1 A Perspective on Feedback Control 1 Chapter Overview 2 1.1 A Simple Feedback System 3 1.2 A First Analysis of Feedback 6 1.3 Feedback System
Contents 1 An Overview and Brief History of Feedback Control 1 A Perspective on Feedback Control 1 Chapter Overview 2 1.1 A Simple Feedback System 3 1.2 A First Analysis of Feedback 6 1.3 Feedback System
Dr Ian R. Manchester
 Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Inertia Identification and Auto-Tuning. of Induction Motor Using MRAS
 Inertia Identification and Auto-Tuning of Induction Motor Using MRAS Yujie GUO *, Lipei HUANG *, Yang QIU *, Masaharu MURAMATSU ** * Department of Electrical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing,
Inertia Identification and Auto-Tuning of Induction Motor Using MRAS Yujie GUO *, Lipei HUANG *, Yang QIU *, Masaharu MURAMATSU ** * Department of Electrical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing,
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2017/2018 ADVANCED BIOMECHATRONIC SYSTEMS
 ENG0016 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2017/2018 ADVANCED BIOMECHATRONIC SYSTEMS MODULE NO: BME6003 Date: Friday 19 January 2018
ENG0016 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2017/2018 ADVANCED BIOMECHATRONIC SYSTEMS MODULE NO: BME6003 Date: Friday 19 January 2018
Control Systems I Lecture 10: System Specifications
 Control Systems I Lecture 10: System Specifications Readings: Guzzella, Chapter 10 Emilio Frazzoli Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control D-MAVT ETH Zürich November 24, 2017 E. Frazzoli (ETH) Lecture
Control Systems I Lecture 10: System Specifications Readings: Guzzella, Chapter 10 Emilio Frazzoli Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control D-MAVT ETH Zürich November 24, 2017 E. Frazzoli (ETH) Lecture
AVOLTAGE SAG is a short-duration reduction in rms
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 20 NO. 2, APRIL 2005 1683 Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Voltage Sag Effects on Three-Phase Transformers Joaquín Pedra, Member, IEEE, Luis Sáinz, Felipe Córcoles,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 20 NO. 2, APRIL 2005 1683 Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Voltage Sag Effects on Three-Phase Transformers Joaquín Pedra, Member, IEEE, Luis Sáinz, Felipe Córcoles,
DIGITAL CONTROL OF POWER CONVERTERS. 3 Digital controller design
 DIGITAL CONTROL OF POWER CONVERTERS 3 Digital controller design Frequency response of discrete systems H(z) Properties: z e j T s 1 DC Gain z=1 H(1)=DC 2 Periodic nature j Ts z e jt e s cos( jt ) j sin(
DIGITAL CONTROL OF POWER CONVERTERS 3 Digital controller design Frequency response of discrete systems H(z) Properties: z e j T s 1 DC Gain z=1 H(1)=DC 2 Periodic nature j Ts z e jt e s cos( jt ) j sin(
Robust Control For Variable-Speed Two-Bladed Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines Via ChatteringControl
 Robust Control For Variable-Speed Two-Bladed Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines Via ChatteringControl Leonardo Acho, Yolanda Vidal, Francesc Pozo CoDAlab, Escola Universitària d'enginyeria Tècnica Industrial
Robust Control For Variable-Speed Two-Bladed Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines Via ChatteringControl Leonardo Acho, Yolanda Vidal, Francesc Pozo CoDAlab, Escola Universitària d'enginyeria Tècnica Industrial
QFT Framework for Robust Tuning of Power System Stabilizers
 45-E-PSS-75 QFT Framework for Robust Tuning of Power System Stabilizers Seyyed Mohammad Mahdi Alavi, Roozbeh Izadi-Zamanabadi Department of Control Engineering, Aalborg University, Denmark Correspondence
45-E-PSS-75 QFT Framework for Robust Tuning of Power System Stabilizers Seyyed Mohammad Mahdi Alavi, Roozbeh Izadi-Zamanabadi Department of Control Engineering, Aalborg University, Denmark Correspondence
Design of Nonlinear Control Systems with the Highest Derivative in Feedback
 SERIES ON STAB1UTY, VIBRATION AND CONTROL OF SYSTEMS SeriesA Volume 16 Founder & Editor: Ardeshir Guran Co-Editors: M. Cloud & W. B. Zimmerman Design of Nonlinear Control Systems with the Highest Derivative
SERIES ON STAB1UTY, VIBRATION AND CONTROL OF SYSTEMS SeriesA Volume 16 Founder & Editor: Ardeshir Guran Co-Editors: M. Cloud & W. B. Zimmerman Design of Nonlinear Control Systems with the Highest Derivative
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
Ch. 7: Z-transform Reading
 c J. Fessler, June 9, 3, 6:3 (student version) 7. Ch. 7: Z-transform Definition Properties linearity / superposition time shift convolution: y[n] =h[n] x[n] Y (z) =H(z) X(z) Inverse z-transform by coefficient
c J. Fessler, June 9, 3, 6:3 (student version) 7. Ch. 7: Z-transform Definition Properties linearity / superposition time shift convolution: y[n] =h[n] x[n] Y (z) =H(z) X(z) Inverse z-transform by coefficient
ECE1750, Spring Week 11 Power Electronics
 ECE1750, Spring 2017 Week 11 Power Electronics Control 1 Power Electronic Circuits Control In most power electronic applications we need to control some variable, such as the put voltage of a dc-dc converter,
ECE1750, Spring 2017 Week 11 Power Electronics Control 1 Power Electronic Circuits Control In most power electronic applications we need to control some variable, such as the put voltage of a dc-dc converter,
Observer Based Friction Cancellation in Mechanical Systems
 2014 14th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 2014) Oct. 22 25, 2014 in KINTEX, Gyeonggi-do, Korea Observer Based Friction Cancellation in Mechanical Systems Caner Odabaş
2014 14th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 2014) Oct. 22 25, 2014 in KINTEX, Gyeonggi-do, Korea Observer Based Friction Cancellation in Mechanical Systems Caner Odabaş
Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode
 Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode Introduction 11.1. DCM Averaged Switch Model 11.2. Small-Signal AC Modeling of the DCM Switch Network 11.3. High-Frequency
Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode Introduction 11.1. DCM Averaged Switch Model 11.2. Small-Signal AC Modeling of the DCM Switch Network 11.3. High-Frequency
Dr Ian R. Manchester Dr Ian R. Manchester AMME 3500 : Review
 Week Date Content Notes 1 6 Mar Introduction 2 13 Mar Frequency Domain Modelling 3 20 Mar Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 27 Mar Block Diagrams Assign 1 Due 5 3 Apr Feedback System Characteristics
Week Date Content Notes 1 6 Mar Introduction 2 13 Mar Frequency Domain Modelling 3 20 Mar Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 27 Mar Block Diagrams Assign 1 Due 5 3 Apr Feedback System Characteristics
Reactive Power Flow Control of a Dual Unified Power Quality Conditioner
 Reactive Power Flow Control of a Dual Unified Power uality Conditioner aimon M. Fagundes anta Catarina tate University UDEC Electric Power Processing Group - npee 89.19-71, Joinville - C, Brazil saimon.m.f.@gmail.com
Reactive Power Flow Control of a Dual Unified Power uality Conditioner aimon M. Fagundes anta Catarina tate University UDEC Electric Power Processing Group - npee 89.19-71, Joinville - C, Brazil saimon.m.f.@gmail.com
Grid-connected photovoltaic systems based on nonlinear control.
 University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2018 Grid-connected photovoltaic systems based on nonlinear control. Pablo
University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2018 Grid-connected photovoltaic systems based on nonlinear control. Pablo
ECEN 607 (ESS) Op-Amps Stability and Frequency Compensation Techniques. Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University
 ECEN 67 (ESS) Op-Amps Stability and Frequency Compensation Techniques Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Stability of Linear Systems Harold S. Black, 97 Negative feedback concept Negative
ECEN 67 (ESS) Op-Amps Stability and Frequency Compensation Techniques Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Stability of Linear Systems Harold S. Black, 97 Negative feedback concept Negative
AN ENERGY BASED MINIMUM-TIME OPTIMAL CONTROL OF DC-DC CONVERTERS
 Michigan Technological University Digital Commons @ Michigan Tech Dissertations, Master's Theses and Master's Reports - Open Dissertations, Master's Theses and Master's Reports 2015 AN ENERGY BASED MINIMUM-TIME
Michigan Technological University Digital Commons @ Michigan Tech Dissertations, Master's Theses and Master's Reports - Open Dissertations, Master's Theses and Master's Reports 2015 AN ENERGY BASED MINIMUM-TIME
ECE Branch GATE Paper The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2
 Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle
 Page 359 World Electric Vehicle Journal Vol. 3 - ISSN 232-6653 - 29 AVERE Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Tao Sun, Soon-O Kwon, Geun-Ho Lee, Jung-Pyo
Page 359 World Electric Vehicle Journal Vol. 3 - ISSN 232-6653 - 29 AVERE Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Tao Sun, Soon-O Kwon, Geun-Ho Lee, Jung-Pyo
Chapter 7 - Solved Problems
 Chapter 7 - Solved Problems Solved Problem 7.1. A continuous time system has transfer function G o (s) given by G o (s) = B o(s) A o (s) = 2 (s 1)(s + 2) = 2 s 2 + s 2 (1) Find a controller of minimal
Chapter 7 - Solved Problems Solved Problem 7.1. A continuous time system has transfer function G o (s) given by G o (s) = B o(s) A o (s) = 2 (s 1)(s + 2) = 2 s 2 + s 2 (1) Find a controller of minimal
