GRaBS Assessment Tool User Guidance
|
|
|
- Florence Ryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GRaBS Assessment Tool User Guidance Richard Kingston & Gina Cavan Centre for Urban and Regional Ecology School of Environment & Development University of Manchester August The latest version of the user guidance can be found on-line.
2 Table of Contents List of Figures 2 List of Tables 2 1. Introduction 3 2. What does the GRaBS Tool do? 6 3. How can it be used? Exploring the Assessment Tool: European Level Basic functions European themes Adding your own data to the Assessment Tool Risk of flooding in the London Borough of Sutton Critical infrastructure protection in Styria Risk of high temperatures in Catania Summary References 35 1
3 List of Figures Figure 1: Collaborative Tool Development... 5 Figure 2: The Menu System List of Tables Table 1: Data types... 6 Document Control: Version no. Prepared/ Updated By Date 1.0 Richard Kingston (richard.kingston@manchester.ac.uk) 12 th August
4 1. Introduction Building on research originally carried out in the Centre for Urban and Regional Ecology at The University of Manchester (UoM) a major aim of the GRaBS project was to develop an innovative, cost effective and user friendly risk and vulnerability assessment tool, to aid the strategic planning of climate change adaptation responses in towns, cities and regions across Europe. The main aim of this document is to provide guidance on how to use the GRaBS Assessment Tool (the Tool) and is divided in to five sections. We firstly introduce the GRaBS project and the rationale for developing the Tool, which is followed by an explanation of what the Tool can do (and what it cannot do) in section 2. We then explain how it can be used to support the development of Climate Change Adaptation Action Plans (AAPs) through the concept of a storyline. The main aim of the GRaBS Assessment Tool was to assess current vulnerability of urban areas to climate change impacts, with an additional assessment of relative spatial patterns of risk where suitable data is available. The Tool is based on a Geographical Information System (GIS) and was built on top of the Google Maps interface using a range of spatial data for the whole of Europe, together with specific spatial data from project partners in total over 325 different map layers. From the start of the project there was a desire to develop a Tool which would be easily accessible to a wide range of stakeholders involved in climate change adaptation, including the general public. With eleven partners responsible for developing Adaptation Action Plans, developing a tool which would meet the needs of all project partners was quite a challenge. At the heart of the GRaBS project is the understanding that climate change is a problem that impacts on urban in different ways according to their specific exposure to climate and weather hazards. Urban areas also have varying characteristics (e.g. population structures, development patterns etc) that influence how they will be affected by climate change. Improving understanding of these issues in an urban context can support adaptation planning, and this is what the Assessment Tool aims to do. GRaBS also recognises that within a European context, being able to understand that Europe s climate is changing is important in order to take a broader perspective of how climate change will influence its urban areas. Associated climate impacts, such as flooding and heat waves have been experienced across Europe over recent decades, and future projections highlight the magnitude of change likely to be experienced over the coming decades. The GRaBS project looked in detail at the potential impacts of climate change across Europe. This understanding helped to provide a context for the Assessment Tool from the perspective of assessing vulnerability to climate change in the partner cities and regions. Two key issues are: Temperatures are projected to increase over Europe at levels higher than the global average. Increases of between 2-6 C are expected depending on the greenhouse gas emissions scenario considered. The north is projected to warm at a slightly faster pace than the south. Precipitation patterns are expected to change significantly. Recent seasonal and geographic changes in rainfall are projected to intensify. Northern Europe has become wetter over the last century, a trend that is likely to continue particularly over the winter. However, Southern Europe has become drier with further reductions in summer precipitation expected. Increases in precipitation extremes are also likely. 3
5 These changes in temperature and precipitation will generate impacts including: Flooding events are expected to increase in frequency and magnitude, especially over northern and western Europe during the winter months where river discharges are projected to increase. Extreme rainfall events will increase the threat of flash floods across most of Europe. Lower rainfall and associated river discharge/aquifer recharge will increase drought risk, particularly over southern and eastern Europe. The threat of longer dry spells is lower in northern Europe. Central and eastern Europe in particular are likely to experience summer heat waves of increasing intensity and duration. By 2050, the Mediterranean could have an extra month with days over 25 C. During the 1990 s, the number of extreme weather events (floods, storms, droughts) doubled. This increase in frequency has continued into the early 21 st Century and is projected to continue to do so. It is extreme events, not gradual changes in climate, which cause the most significant impacts on human and natural systems. Sea level rise is a key threat to coastal communities and ecosystems. Globally, increases of 18-59cm are projected, with regional variations also likely. The prospect of more significant increases cannot be ruled out, for example relating to the melting of the polar ice caps. Climate change is expected to bring with it changes in wind speeds, with significant regional variation. Increases of 10-15% in average and extreme wind speeds are possible over northern Europe, with a 10-15% decline in speeds in southern Europe. An increase in storminess over Western Europe during the winter months is also possible. Source: EEA, The most up to date information on recent and projected future change to Europe s climate can be found in the European Environment Agency publication Impacts of Europe s changing climate indicator-based assessment (EAA, 2008). With this overview setting the context for the project and feeding into the requirements of the Tool, individual partners set about assessing their own climate impact priorities and deciding what their own priorities were within their own municipalities. In the first 6 months of the project, a literature review was undertaken to explore the stateof-the-art on climate change adaptation and existing vulnerability/risk assessment tools, with a particular emphasis on their relationship with the findings from the ASCCUE project (Lindley, 2009). The literature review formed part of an overall strategy to develop the Tool in collaboration with all GRaBS partners as outlined in Figure 1 below. This began by undertaking a User Needs and Requirements Analysis (UNRA), which asked all partners about the key climate change issues in their municipalities, what the important aspects that the Tool should address were and extensive questions about data availability and copyright. The combination of the literature review, the most appropriate available technology, which could be used by twelve partners in eight countries, and the UNRA, led to the development of an initial functional specification. Together with the GRaBS partners, the University developed the specification for the planning and design of the Assessment Tool. An interactive start up workshop at the first Thematic Seminar, organised by UoM, increased understanding of the Assessment Tool amongst GRaBS partners and was used to review partner roles and needs in the process of developing the Tool and to provide initial guidance 4
6 for the specification of the Tool. Its development follows the principles of an on-line Public Participation GIS (Kingston et al, 2000; Kingston, 2007). Here, the main aim is to develop web-based Geographical Information Systems (GIS) to enhance public involvement and participation in environmental planning and decision making. These systems are referred to as PPGIS and are a form of Planning Support System. The main objective is based on the belief that by providing all stakeholders, including citizens, with access to information and data in the form of maps and visualisations, they can make better informed decisions about the natural and built environment around them. The nature of the GRaBS project with a pan-european user-base meant that the Tool had to be built using a common map base for all partners. Using Google Map s API (Application Programming Interface) which is a free, generic, highly customisable, and probably, most important from a user perspective, very simple to use and navigate, meant that we were able to build a single generic tool for all partners. Figure 1: Collaborative Tool Development 5
7 2. What does the GRaBS Tool do? The main aim of the GRaBS Assessment Tool was to assess current vulnerability of urban areas to climate change impacts, with an additional assessment of relative patterns of spatial risk where suitable data is available. This helps to build the evidence base available to decision makers and other stakeholders when developing adaptation plans and strategies. Vulnerability relates to the susceptibility of elements at risk (e.g. people, buildings, greenspace) to climate hazards such as heat stress or flooding. Vulnerability to climate change impacts can be high where certain elements at risk, such as elderly people, zones of high density development, or critical infrastructure, are exposed to climate hazards. Identifying locations where vulnerability is high is central to the development of climate change adaptation strategies. Adaptation strategies act to reduce vulnerability by lowering exposure and increasing resilience of elements at risk from climate hazards. Where vulnerability is lowered, the impacts of climate hazards can be significantly reduced. The GRaBS Assessment Tool therefore focuses on highlighting vulnerability to climate change impacts within the partner s case study locations. In order to do so, we needed to obtain spatial data on the location of a range of receptors that are potentially vulnerable to climate hazards. At the start of the project it was difficult to anticipate the amount and complexity of the data layers which would be used in the Tool. Indeed we involved all partners in assessing what were the key climate impact factors and climate-related issues in their areas so that the tool was fit for purpose in each of the municipalities and regions across Europe. Thus the project team embarked on a collaborative process of tool development with all the partners, in order to shape the exact form and function of the final tool (see Figure 1). Through the use of the UNRA, partners were asked to identify the types of functionality and their anticipated requirements of the Tool; what their climate change impact priorities were; a series of questions on the availability of data to input into the Assessment Tool; and the origin and source of the spatial data and report any copyright issues on the data provided. There are currently over 325 different spatial layers in the Tool, with partner level data ranging from 7 to 50 layers (see table 1). This reflects the extent to which different municipalities have been collecting relevant data and their ability to work across departmental boundaries to obtain necessary data. In addition, at the EU level there are 32 spatial layers available. Table 1: Data types Partner Level No. of layers Social Infrastructure (schools, hospitals, emergency services, care homes, prisons etc.) 52 Civil Infrastructure (utility services, railway stations, roads at risk of flooding, waste disposal 49 facilities etc.) Population Structure (population density, areas of deprivation) 14 Green & Blue space (parks, trees, playgrounds, sports fields, water bodies, cemeteries etc.) 54 Vulnerability (population ages over 75 and under 4, people with poor health, people on low income, people vulnerable to high temperatures & to flooding, properties vulnerable to flooding, population living on ground floor or basement and living on third floor or higher) 60 6
8 Hazards (flood zones, historic flooding events, surface water flooding, groundwater flooding, sewer flood risk) Urban Development (current and proposed residential and industrial development, historic and cultural buildings) European Level 39 7 Climate (including the 2080s IPCC A2 emissions scenarios mean temperature & 15 precipitation from PRUDENCE) Climate hazards (drought, extreme temperature, river flooding, forest fires, storm surge, 5 storm events) from ESPON Civil Infrastructure (airports, mayor roads and railway lines) 3 Population Structure (density, growth, 0-14 and 60+ years) 4 Urban Development (degree of urbanisation, urban areas) 2 Green & Blue space (urban green space, blue space, protected areas) 3 To complement the UNRA a review of climate change vulnerability, risk and adaptation assessment tools was undertaken (Lindley, 2009). This review concluded that a wide range of on-line tools are available for risk assessment and risk management but that there was debate surrounding what comprises such a tool in relation to climate adaptation. The review also identified that there was no existing tool specifically for vulnerability assessment, and there was a scarcity of tools specifically focused on cities and urban areas. This was further enhanced by a review of the available technology, and at the time of development, only the Google Maps platform provided what is called an API (Application Programming Interface), allowing software developers to customise and build other tools on top of a common map base. Given the popularity and familiarity of the Google Maps interface, this was deemed a suitable platform to build the tool on. The combination of the above aspects of the Tool s development revealed that the Tool needed to: allow map overlay to enable identification of priority areas for adaptation actions; map vulnerability and risk (where data was available) to climate change hazards and show spatial distributions; to consider the possibility of a data upload element in the tool; to house the GRaBS tool within a website which acts as a data/tool portal; to place the tool within a clear risk management and adaptation assessment framework/process; generate a list of climate hazards and receptors; identify relative patterns of risk in urban environments; show the severity of the impacts; inform preparation of planning documents to enable accounting of climate change impacts on people, property, assets and infrastructure; to be fully accessible to all stakeholders online, including residents, developers, local business, utilities and councils; to ensure that terminology is clear and full documentation is provided for users. It is also important to stress that the Tool in its current form can only deal with current vulnerability to climate change and not future vulnerability to climate. Future research will 7
9 investigate possibilities for adding What if? capabilities to the Tool to allow modelling of different scenarios over 5-, 10-, 15- and 20-year time horizons. This is a difficult task when dealing with fine grain data at the neighbourhood scale and its relationship with climate modelling outputs. The availability of data across Europe was a limiting factor, since the availability of relevant datasets is key in framing the issues, and therefore, the better the data available, the better the story to be told. The experience of developing the Tool has highlighted the need for a common approach throughout Europe on identifying and collecting datasets to enable a more harmonised approach to spatial planning for adaptation to climate change. This would also have cost benefits, after initial upfront costs invested in collecting the correct data, to inform the evidence base for adapting to climate change a key consideration in the current financial climate. The use of the Tool is therefore only as good as the data it contains, and therefore, at the partner level, it is dependent on the spatial data that each of the partners provided. In addition to the main Assessment Tool, further work was undertaken with one GRaBS partners case study area to develop more tools to assist in climate change adaptation planning, specifically, for assessing the potential of green infrastructure in adapting urban areas to climate change. The STaR (Surface Temperature and Runoff) tools were developed by The Mersey Forest, in collaboration with the University of Manchester, for Northwest England. The STAR models are web-based, intuitive, and user friendly models that have been developed to allow users to assess the potential of green infrastructure in adapting their areas to climate change. In these tools, users can determine how surface temperatures and runoff varies as they increase or decrease the proportion of green infrastructure, under different climate scenarios. The STAR tools were a late addition to the GRaBS Assessment Tool programme of work, and are currently being finalised, due for release in late August They will be available to use from the GRaBS Assessment Tool website and are explained in more detail in a forthcoming document. 8
10 3. How can it be used? This section is divided into five parts and uses the concept of a storyline to guide the user through the application of the GRaBS Assessment Tool. In doing so, it introduces the Tool and demonstrates its functionality, datasets and information available. Each storyline starts with the same introduction exploring the Tool at the European Level. This is outlined in section 3.1 below. Three storylines 1 have been developed and offer typical examples of how an individual or organisation might use the GRaBS web-based Tool to support climate change adaptation policy and decision-making within their organisation. The first storyline is based on the risk of river flooding to people in the London Borough of Sutton as follows: The Flood Group wants to develop an emergency plan for areas exposed to fluvial (riverine) flooding within their neighbourhoods. They need to know where help is the most needed in cases of both emergency and recovery. Also, they would like to look specifically at the current provision of social infrastructure and where it could be enhanced. The second storyline helps to assess social infrastructure in the region of Styria, Austria as follows: The Regional Authority are attempting to assess the vulnerability of key critical infrastructure in the event of future incidences of flooding. They use the Tool to map out where current social and civil infrastructure is located such as power plants, sewerage treatment works, electricity transformer stations and hospitals, and develop an action plan to inform decisions about where current facilities need to be adapted and where new facilities should be sited in the future in relationship to vulnerable locations across the region. The third storyline helps assess the risk of high temperatures to people in Catania as follows: The Regional Authority are attempting to coordinate a joint response to dealing with heat waves and high temperatures, by investigating which parts of the city are most susceptible to high temperatures. They use the Tool to map out were the most vulnerable people live (old and young) and the relationships between these locations, land cover characteristics, and social infrastructure such as schools, hospitals, and community centres, and develop an action plan to put in place appropriate facilities at key locations. We recommend that before exploring the Tool, users upgrade their web browser to the latest version and have JavaScript turned on. This is usually on by default on most web browsers, but if required, instructions can be found here The spatial data sets used in the Tool are predominantly in ESRI s ( shp format for vector data although some of the EU scale data is in raster format. The Tool uses the open source web mapping platform called MapServer and converts proprietary spatial GIS 1 Individual storylines are on the GRaBS 9
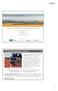
11 data in to an image format (in this case png) which speeds up the map rendering process for the user. This also means that the user of the Tool does not have access to the source GIS data overcoming data access restrictions which might apply to some of the datasets depending upon their source of origin. Figure 2: The Menu System This system is designed to be intuitive, easy to use and can be updated fairly easily. Navigation of the data layers is done using an expanding menu system which is familiar to users of the Windows operating system as can be seen here in Figure 2. Spatial layers are turned on or off using a checkbox. The menu system has been designed in such a way that it is relatively straightforward for a GIS/web developer to add new layers of data in the future. This is key to the future use and adaptability of the Assessment Tool. It is possible for a user to overlay their own spatial data (using the kml/kmz file format) on the website to advance their knowledge. A partner wishing to add their own spatial layers which are not necessarily in the Tool can export their own ESRI shp or any other spatial data files into the kml format. This is particularly useful for partners with sensitive or restricted information that they do not want in the public domain. See section 3.2 below Exploring the Assessment Tool: European Level Please open a web browser such as FireFox or Internet Explorer, and navigate to the GRaBS Assessment Tool portal: Click on Assessment Tool. The introductory page sets out the three stages involved in working through the Tool. Click on START THE TOOL to navigate to the Assessment Tool. The Assessment tool opens at the European level. The Terrain map of Europe is displayed as a default. This background map shows major roads, cities and country borders Basic functions Changing the display: You can change the display to show a normal map, aerial photography or a combination of a map and aerial photography by clicking on Map Satellite or Hybrid in the top left hand corner. The Map option shows the administrative boundaries, cities, roads and railway lines. Navigating around the map: To move around the map, either use the pan tools, or using the mouse: click in the map, 10
12 hold down the button and move the mouse. To reset the map to the default European view at any time, click on the hand icon in the centre of the pan tool. Zooming in and out: You can zoom in or out by clicking in the map and moving the wheel on your mouse, or by using the scroll bar on the left of the display. Again, click on the hand icon to re-set the map to the default European view at any time. Use pan tools to move around or re-set map Drag scroll bar to zoom in or out Click here to change map display The European level of the Assessment Tool provides important contextual information for the user regarding climate hazards at the European level. This provides users with some useful information, including details of their baseline and projected future climate, climate hazards, and population structure. It also allows them to put their area in a European context, and to compare the characteristics of their city or region with the rest of Europe European themes The menu is open at the European tab as a default. The information available at the European level in the Tool is shown on the European menu. The first type of information relates to the climate. Displaying a theme on the map The Baseline climate ( ) can be displayed by clicking on the symbol to expand the menu. This indicates that the data for the baseline climate includes maximum temperature, minimum temperature and precipitation. Click on the symbol again, next to Precipitation to expand the menu as overleaf. Turn on the Precipitation, Winter theme by clicking in the check box. The mean winter precipitation for across Europe will be displayed in the map. 11
13 Click on the + to expand Baseline climate menu Menu expands Query the map layer To query the map layer, click the mouse inside the white legend box. QUERY ENABLED is then displayed above the legend box, and you then can click a location inside the map. This provides the value of the indicator currently displayed on the map. This only works on vector layers! If the legend covers the area that you are interested in, please move the map or zoom out. If the query returns undefined, there is no information to display. Setting the transparency of data Click in box to turn theme on The transparency of the data can be altered by sliding the bar in the legend window (above). This can be set anywhere between 0 to 100% (completely transparent to solid colour). It is most effective to use this function when overlaying data i.e. when displaying more than one theme. Slide the bar to set transparency Click anywhere in the white box to enable the query option. Click on the Source button to display Data source 12
14 Looking up the map details and source A short description of the map display is provided in a Data note which you can view by clicking on the INFO button next to the theme name on the menu. A pop-out box then appears, and displays the Data note. It can also be opened by click on the INFO button in the legend as shown above. This pop-out box is moveable and collapsible. If it obscures the data display, please move it around the screen by hovering over the corner and reducing it with the arrow, or by grabbing it with the mouse curser to move it. Tip: You can also view the Data note before displaying the theme. Note: If you click in anywhere in the map, the Data note minimises to the tray. Please click the INFO button to display it again and close it. Further information about the theme, including links to obtain the actual data displayed on the Assessment Tool platform, is provided in the Data Source. This is located on the legend. Click on the Source button to view the Data source in a pop-out box. To close the pop-out box, click on the the top right-hand corner. in Click on the Info button to display Data note Data note is displayed in a moveable and collapsible popout box Displaying the GRaBS partner s administrative boundaries You can display the GRaBS partner s administrative boundaries from the GRaBS partners menu item. Click on the check box next to GRaBS partners boundaries to display these. Navigating to a region/city/town: Enter your location into the search box in the bottom left corner of the map and then click on Search. Alternatively, navigate to a place using the mouse and zooming in. To go back to the default European view at any time, click on the hand icon in the centre of the pan tool. Click on centre of pan tool to re-set Enter location here Next, you can have a look at data showing what the future climate could be like in your area. First, close the current theme. Click in the Baseline climate Precipitation Winter box to uncheck the tick. This will close the current theme from the map display. Please note that this theme can be left on (i.e. ticked ) but the data display is clearer if each theme is viewed separately. Please also re-set the map using the button. 13
15 Then, click on the symbol to expand the menu under the Climate Projections 2080s Medhigh title. Click on the INFO button next to the menu item to read more about the climate projections data. You can then repeat the stages above to view the themes for winter precipitation, including the data note and data source information. Note that two future projections are provided, the IPCC Med-high (A2) and Med-low (B2) emissions scenarios. These projections offer two differing views of how the climate of Europe could change by the end of this century based on different levels of greenhouse gas emissions. NOTE: In order to find out more about the future climate projections data, please look at the INFO of each menu item and data source of each theme for detailed information. Climate hazards - flooding In the example here we are interested in the issue of flood hazard. The European level of the Assessment Tool has a river flood hazard theme. Please close any open themes. Find the river flood hazard theme in the menu under Climate hazards and turn it on to explore the data. If we compare the Sutton to this data, as we do in the first storyline, this indicates that compared to the rest of Europe, Sutton has a moderate river flood hazard potential. The Data source explains that this map is based on historical floods, recorded from 1987 to 2002, and mapped at NUTS3 level (areas with a population of 150, ,000 2 ). Tip: If you are unsure of where Sutton is, type this into the Location search box at the top of the menu. The map will then zoom to Sutton. Click in the centre of the pan tool to re-set map to the view of Europe. Un-check the River flood hazard box to close the theme. London Borough of Sutton Check box to turn theme on/off River flood hazard potential map indicates Sutton has moderate risk 2 For more information on NUTS levels, see 14
16 Population structure The population structure themes provide an overview of the characteristics of the population on a European scale, including population density, growth and vulnerable populations (those aged under 14 and over 60 3 ). Again comparing this data to Sutton these themes provide an overview of the vulnerability of people to flood hazard in Sutton, compared to the rest of Europe. Turn on the Population density theme. This indicates the relationship between levels of population density compared to the rest of Europe. Un-check the Population density box to close the theme. Please also explore the other population structure themes and read the Data notes accessible from the INFO buttons for more information. Check box to turn theme on/off Population density map indicates Sutton has a very high population density Please use the functions above to explore the rest of the themes in the European level of the Assessment Tool. For example, you may wish to look at different future climate change scenarios, different climate change hazards (e.g. droughts and extreme temperature events) and issues related to the location of critical infrastructure. Please note that it is best to uncheck each box before displaying the next theme so that the data display is clearer. 3 At the GRaBS Partner level, vulnerable populations are defined as those aged between 0-4 years and 75+ years. Ideally, these age ranges would also be shown at the European level, but such data was not available so broader age groups had to be used. 15
17 3.2. Adding your own data to the Assessment Tool You can add your own data to the Tool via the Add kml function. This is particularly useful if you have sensitive data that you do not want to be in the public domain as this function only allows the individual user to view the uploaded kml layer. This can be done by typing the web address of where your kml file has been published online or by pasting it in to the kml window. This can be done at the European scale or at the Partner level. Enter the kml web address and click Add KML. You can then clear the KML when finished KML data can be created by converting ESRI shp files and other GIS file formats to the KML format using freely available software or functions within proprietary software such as ArcGIS or MapInfo. It is a file format used by Google Earth and Google Maps for displaying geo-referenced data and stands for Keyhole Mark-up Language. See here for a list of programmes that can do this: If you are unfamiliar with kml files, this documentation will help: 16
18 3.3. Risk of flooding in the London Borough of Sutton Summary The Flood Group wants to develop an emergency plan for areas exposed to fluvial (riverine) flooding within their neighbourhoods. They need to know where help is the most needed in cases of both emergency and recovery. Also, they would like to look specifically at the current provision of social infrastructure and where it could be enhanced. The Flood Group firstly explored the European level of the Assessment Tool (as in Section 3.2) and found that the future climate projections data indicates that precipitation in winter is likely to increase. The current impact of flooding from rivers in Sutton is significant on a European scale, and the population density is very high compared to other regions across Europe. Therefore, with more rainfall in winter, the risk of flooding is likely to increase further, and the potential number of people exposed is high. Crucially, where population density and flood risk are high, this presents a significant issue for organisations involved in developing emergency responses to flood events to consider. The Flood Group now explore the London Borough of Sutton in more detail at the GRaBS partner level of the Assessment Tool. Exploring the Assessment Tool at the Partner level The partner level of the Tool can be reached by clicking on the GRaBS Partners tab at the top of the Tool menu. This changes the menu from the European level to the GRaBS Partner areas. To choose a partner, click on the name. For this storyline, we will select Sutton. A pop-out box opens with details of a Climate Impacts Assessment for the London Borough of Sutton. This provides the Flood Group with an introduction to the characteristics of their area, the GRaBS partner, and climate impacts in their area. This indicates that the GRaBS partner consider the probability and severity of flooding from rivers in Sutton to be of moderate significance (a score of 3). The elements identified to be at risk from flooding from rivers include people, residential property and community infrastructure. Click on the Close button in the pop-out box to close it and reveal the Terrain map of Sutton. 17
19 Click on tab to go to GRaBS partner area Click to close Click on Sutton, UK to display Climate Impacts Assessment Climate Impacts Assessment popout box Click the symbol to expand the Sutton menu to reveal the themes available to view. The themes available include social infrastructure, civil infrastructure, population structure, green and blue space, vulnerability and hazards. We are interested in the vulnerability of people to flooding, and will therefore explore the vulnerability theme first. Click the INFO button next to the Vulnerability menu item to read a definition of vulnerability. Close the Data note when you have read this. Click the symbols to expand the Sutton Vulnerability menu. The list of vulnerability indices available will be displayed. Check the Vulnerability of people to flooding box to turn on the theme. Click on + to navigate to vulnerability of people to flooding Check the box to turn on the Vulnerability of people to flooding theme Use the scroll bar to view the whole menu 18
20 Vulnerability index People and Flooding This displays the Vulnerability index of people to flooding in Sutton, mapped at the UK Census Lower Super Output Area (an area with a population of around 1500 smaller than the LAU2 level 4 ). Click on the INFO button to read about vulnerability, impacts of flooding on human health, and a description of the map. The Vulnerability index incorporates a number of different indicators, e.g. population aged 75 years old and over, and population aged 0-4 years old. Click on the Data source for full details about how the Vulnerability index is calculated. Data note Vulnerability of people to flooding in Sutton This highlights the areas where people are particularly vulnerable to flooding due to their personal or situational circumstances. However, these people may not necessarily be exposed to a flood hazard. To establish this, we must look at the Exposure indicators and Hazards. Before doing so, un-check the Vulnerability of people to flooding box to close the theme. Note: Up to 6 themes can be viewed at one time, but it may be clearer to first view them separately before overlaying them. Tip: Use the transparency bars on the legend of each theme to enable better viewing when overlaying maps. Next, turn on the Exposure indicators to find out if the populations vulnerable to flooding are exposed to flooding hazard. The relevant indicator here is the percentage of population living on ground and lower-ground floors. Turn this theme on. 4 For more information on LAU levels, see 19
21 To find out if these populations live within a flood hazard zone, please explore the hazard theme. Click the symbol to expand the Sutton Hazards menu. Click the symbol to expand the Flooding menu, click the again to reach the Riverine flooding menu, and turn on the first three themes. View the Data notes to find out more about these themes. This highlights the extent of the flood zones or flood risk areas in Sutton, and the populations that are exposed to flooding. You can also explore where past flooding events have occurred by turning on the Historic flooding events theme. Turn on the exposure indicator and hazard themes Hazard and Exposure indicators for vulnerability of people to flooding Please also explore the separate vulnerability indicators. The vulnerability indicators are mapped as separate themes in the menu and can be viewed independently of the Vulnerability index. Viewing the separate vulnerability indicators is useful to distinguish between the areas which may need help in an emergency i.e. those with high percentages of populations aged 0-4 years old and over 75 years old; and, those areas which may need financial help to recover after a flood event i.e. those with high percentages of populations living on low incomes. By looking at vulnerability to flooding in this way, the Flood Group can help to determine what strategies would be appropriate to employ in different areas. Please turn off all themes before moving onto the next section. Critical Social Infrastructure Critical social infrastructure includes: health facilities, community centres and other centres such as schools, that can be set up to support the community when a flood event occurs. This critical infrastructure data can be overlaid on top of the vulnerability of people to flooding index. Tip: Read the social infrastructure Data note for more information. Turn on the Vulnerability of people to flooding index, from the Vulnerability menu. Set the transparency to about 40%. 20
22 Click the symbols to expand the Sutton Social infrastructure menu. Check all of the boxes to turn on all of the themes. Set the transparency of these themes to 100%. This shows which areas within the London Borough of Sutton are well-covered by social facilities, and areas which are less well covered. The south-west of the borough is particularly sparse of social facilities. If a flood event was to occur in this area, additional emergency social facilities may need to be provided, or the Flood Group could begin to develop these as a precautionary measure. Adjust map transparency Turn on all the social infrastructure layers Querying the data You can query or view the actual data values within the map. This may be helpful to view the name of social infrastructure, such as a hospital, or the exact data value e.g. pensioners living alone in an area. To do this, click the mouse on the legend, and QUERY ENABLED will be displayed above the legend box. Then, click on the map at the place you are interested in, zooming in first if necessary. A pop-out box displays the value for the area you selected. To close the pop-out box, click on the in the top right-hand corner. 21
23 Click on the legend until QUERY ENABLED displays above Information is provided in a pop-out when area of interest is selected Summary: The Flood Group has explored the GRaBS Partner level of the Tool using the London Borough of Sutton as a case study. They have investigated the location of populations that are particularly vulnerable to flooding due to their personal or situational circumstances. They have then looked at the hazard layers to investigate if the vulnerable populations have the potential to be exposed to the flood hazard. Also, they have looked at the separate vulnerability indices to highlight the populations who require assistance during and after a flood event. Finally, they looked at the distribution of critical social infrastructure across the LB Sutton and established where these should be enhanced. 22
24 3.4. Critical infrastructure protection in Styria Summary The Regional Authority are attempting to assess the vulnerability of key critical infrastructure in the event of future incidences of flooding. They use the Tool to map out where current social and civil infrastructure is located such as power plants, sewerage treatment works, electricity transformer stations and hospitals, and develop an action plan to inform decisions about where current facilities need to be adapted and where new facilities should be sited in the future in relationship to vulnerable locations across the region. The Regional Authority has explored the European level of the Assessment Tool (in section 3.2) and has found that the future climate projections data indicates that precipitation in winter is likely to increase. The current impact of flooding from rivers in Styria is less significant on a European scale than in other partner areas e.g. Sutton, and the population density is low to medium compared to other regions across Europe. Whilst this may be the case on a Europe-wide scale the Regional Authority are aware of anecdotal evidence that indicates that this is not always the case and feel that flood risk is significant in their region. They now explore the Region of Styria in more detail at the GRaBS partner level of the Assessment Tool. Exploring the Assessment Tool at the Partner level The partner level of the Tool can be reached by clicking on the GRaBS Partners tab at the top of the Tool menu. This changes the menu from the European level to the GRaBS Partner areas. To choose a partner, click on the name. For this storyline, we will select Styria, Austria. A pop-out box opens with details of a Climate Impacts Assessment for Styria. This provides the Regional Authority with an introduction to the characteristics of their area, the GRaBS partner, and climate impacts in their area. This indicates that the GRaBS partner consider the probability and severity of flooding from rivers and urban flooding in Styria to be of high significance (a score of 4.5). The elements identified to be at risk from flooding from rivers and urban flooding includes people, residential property and social, community, industrial, commercial and transport infrastructure. Click on the Close button Styria. in the pop-out box to close it and reveal the Terrain map of 23
25 Click on tab to go to GRaBS partner area Click the view. symbol to expand the Styria menu to reveal the themes available to Click to close Click on Styria, Austria to display Climate Impacts Climate Impacts Assessment popout box The themes available include social infrastructure, civil infrastructure, population structure, green and blue space, hazards and vulnerability. We are interested in the risk of certain types of infrastructure to flooding, and will therefore explore the civil infrastructure theme first. Click the INFO button next to the Civil Infrastructure menu item to read a definition of elements at risk. Close the Data note when you have read this. Check the Power plant and Electricity transformer station boxes to turn on these two map layers. Next click the symbols to expand the Styria Hazards menu. Two hazards are listed: flood risk areas and flood control basins. Check the Flood risk areas box to turn on the theme. Check the box to turn on the Flood risk areas theme Click on + to navigate to civil infrastructure layers 24
26 Risk to Critical Infrastructure Power Supplies and Flooding The Tool should now display three map layers: power plants, electricity transformer stations and flood risk areas. This highlights the areas where these types of critical infrastructure could be vulnerable to flood hazards. At the current map scale it s a bit difficult to see if any infrastructure is at risk. Zoom in to the area south of Graz, following the A9 through the flood risk area until you come to a town called Lebring. The Tool will now show several power plants within the flood risk areas. Reduce the transparency of the flood risk areas theme to 30 % and increase the two infrastructure layers to 100%. It is now possible to see the spatial relationship between the infrastructure and the flood risk areas highlighting a number of power plants in flood risk areas. Set map transparency Data note Note: Up to 6 themes can be viewed at one time, but it may be clearer to first view them separately before overlaying them. Tip: Use the transparency bars on the legend of each theme to enable better viewing when overlaying maps. Please turn off all the map layers before moving onto the next section. Critical Social Infrastructure Critical social infrastructure includes: health facilities, community centres and other centres such as schools, that can be set up to support the community when a flood event occurs. This critical infrastructure data can be overlaid on top of the flood risk areas and the Vulnerability index. Tip: Read the social infrastructure Data note for more information. 25
27 Click the symbols to expand the Styria Social infrastructure menu. Check the boxes to turn on the Hospitals theme. Set the transparency of this theme to 100%. This shows which areas within the region of Styria that are well-covered by hospital facilities, and areas which are less well covered. The area around Graz is well covered, but to the south along the A9 this is less so. Certain types of climate impacts such as a flood event or high temperature could put pressure on facilities in some areas of the region. Additional emergency social facilities may need to be provided, or the Regional Authority could begin to develop these as a precautionary measure. Turn on the Elements at risk: people -> Vulnerability index index, from the Vulnerability menu. Set the transparency to about 40%. Turn on the hospitals in the social infrastructure layers Data note Now add the Flood risk areas theme again and look at the relationship between the locations of hospitals and these areas. Experiment further with other social infrastructure themes to see if any other types of social infrastructure are at risk from flooding. Querying the data You can query or view the actual data values within the map. This may be helpful to view the name of social infrastructure, such as a hospital, or the exact data value e.g. the vulnerability index value for a specific location. To do this, click on the Vulnerability index legend, and QUERY ENABLED will be displayed above the legend. Then, click on the map at the place you are interested in, zooming in first if necessary. A pop-out box displays the value for the area you selected. To close the pop-out box, click on the in the top right-hand corner. Over the page there is a screenshot so you can see how this works. 26
28 Click on the legend until QUERY ENABLED displays above Information is provided in pop-out when area of interest is selected Summary: The Regional Authority of Styria has explored the GRaBS Partner level of the Tool using their region as a case study. They have investigated the location of civil infrastructure that is particularly vulnerable to flooding due to their proximity to flood risk areas. The Tool highlighted in particular where power plants were potentially vulnerable to flooding. They then looked at various social infrastructure layers to investigate the relationship between social infrastructure provision and vulnerable populations. Some parts of the region, particularly south of Graz along the A9 appeared to lack access to hospital facilities and also showed high levels of people vulnerable to climate hazards. This analysis allowed the Regional Authority to establish where their critical infrastructure should be enhanced. 27
29 3.5. Risk of high temperatures in Catania Summary The Regional Authority are attempting to coordinate a joint response to dealing with heat waves and high temperatures, by investigating which parts of the city are most susceptible to high temperatures. They use the Tool to map out were the most vulnerable people live (old and young) and the relationships between these locations, land cover characteristics, and social infrastructure such as schools, hospitals, and community centres, and develop an action plan to put in place appropriate facilities at key locations. The Regional Authority has explored the European level of the Assessment Tool and has found that the future climate projections data indicates that high temperatures in summer during both day and night-time are likely to increase. Catania s population density is relatively high compared to other regions across Europe. Therefore, with higher summer temperatures, the risk of heat stress is likely to increase further, and the potential number of people exposed is high. Crucially, where population density and risk of high temperatures and heat waves are high, this presents a significant issue for organisations involved in developing emergency responses to heat wave and high temperature events to consider. The Regional Authority now explores the Catania Metropolitan area in more detail using the GRaBS partner level of the Assessment Tool. Exploring the Assessment Tool at the Partner level The partner level of the Tool can be reached by clicking on the GRaBS Partners tab at the top of the Tool menu. This changes the menu from the European level to the GRaBS Partner areas. To choose a partner, click on the name. For this storyline, we will select Catania, Sicily. A pop-out box opens with details of a Climate Impacts Assessment for Catania. This provides the Regional Authority with an introduction to the characteristics of their area, the GRaBS partner, and climate impacts in their area. This indicates that the GRaBS partner consider the probability and severity of heat waves and high temperatures in Catania to be of very high significance (a score of 5). The elements identified to be at risk from heat waves and high temperatures include people, flora and fauna and transport infrastructure. Click on the Close button in the pop-out box to close it and reveal the Terrain map of Catania. 28
30 Click on tab to go to GRaBS partner area Click to close Click on Catania, Sicily to display Climate Impacts Assessment Climate Impacts Assessment popout box Click the symbol to expand the Catania menu to reveal the themes available to view. The themes available include social infrastructure, civil infrastructure, population structure, green and blue space, vulnerability and risk. Click on + to navigate to Vulnerability index Check the box to turn on the Vulnerability index: people theme We are interested in the vulnerability of people to high temperatures, and will therefore explore the vulnerability theme first. Click the INFO button next to the Vulnerability menu item to read a definition of vulnerability. Close the Data note when you have read this. Click the symbols to expand the Catania Vulnerability menu. Check the Vulnerability index: people box to turn on the theme. Use the scroll bar to view the whole menu 29
31 Vulnerability index People and high temperatures This displays the Vulnerability index for people to climate hazards in Catania, mapped at the Commune level (an area equivalent to the LAU2 level 5 ). Click on the INFO button to read about vulnerability, impacts of climate hazards on people, and a description of the map. The Vulnerability index incorporates a number of different indicators, e.g. population aged 75 years and over, and population aged 0-4 years. Click on the Data source for details about how the Vulnerability index is calculated. Data note Vulnerability of people to climate hazards in Catania This highlights the areas where people are particularly vulnerable to hazards such as high temperatures due to their personal circumstances. However, these people may not necessarily be exposed to high temperatures. To establish this, we must look at the Hazards. Before doing so, un-check the Vulnerability index box to close the theme. Note: Up to 6 themes can be viewed at one time, but it may be clearer to first view them separately before overlaying them. Tip: Use the transparency bars on the legend of each theme to enable better viewing when overlaying maps. Next, click the symbol to expand the Catania Hazard menu. Turn on the High temperature hazard. This shows the high temperature hazard theme for three municipalities of Catania. View the data note and source information to find out more about this theme. Risk index People and High temperatures 5 For more information on LAU levels, see 30
32 To view the Risk index of high temperature to people, click on the Risk index: people theme from the Risk menu item. This shows the risk index for three municipalities of Catania. This index is a combined index of vulnerability, hazard and exposure. Click on the INFO button to read about Risk and the Risk index. Turn on the Risk index: people Risk of high temperatures to people in 3 municipalities of Catania Please also explore the separate vulnerability indicators. The separate vulnerability indicators are mapped as separate themes in the menu and can be viewed independently of the Vulnerability index. Viewing the separate vulnerability indicators is useful to distinguish between the areas which may need particular types of help in an emergency e.g. areas with high percentages of populations aged 0-4 years may require different emergency facilities to areas with high percentages of people over 75 years. By looking at vulnerability to climate hazards in this way, the Regional Authority can help to determine what strategies would be appropriate to employ in different areas. Please turn off all themes before moving onto the next section. Critical Social Infrastructure Critical social infrastructure includes: health facilities, community centres and other centres such as schools, that can be set up to support the community when a flood event occurs. This critical infrastructure data can be overlaid on top of the Risk index. Tip: Read the social infrastructure data note for more information. Turn on the Risk index: people theme, from the Vulnerability menu. Set the transparency to about 40%. Click the symbols to expand the Catania Social infrastructure menu. Check all of the boxes to turn on all of the themes. Set the transparency of these themes to 100%. This shows the social infrastructure for three municipalities in Catania. Within these municipalities, it shows areas which are well-covered by social facilities, and areas which are 31
33 less well covered. Areas sparse of facilities may need additional emergency social facilities to be provided, or the Regional Authority could begin to develop these as a precautionary measure. Adjust map transparency Turn on all the social infrastructure layers Querying the data You can query or view the actual data values within the map. This may be helpful to view the exact data value e.g. percentage of population over 75 years old in a particular area. To do this, click on the legend, and QUERY ENABLED will be displayed. Then, click on the map at the place you are interested in, zooming in first if necessary. A pop-out box displays the value for the area you selected. To close the pop-out box, click on the in the top righthand corner. Click on the legend until QUERY ENABLED displays above Information is provided in pop-out when area of interest is selected 32
Child Opportunity Index Mapping
 Child Opportunity Index Mapping A partnership project of How to Use and Interpret the Child Opportunity Index Maps How to Use the Child Opportunity Index Maps Getting Started: How to Find and Open a Child
Child Opportunity Index Mapping A partnership project of How to Use and Interpret the Child Opportunity Index Maps How to Use the Child Opportunity Index Maps Getting Started: How to Find and Open a Child
GIS in Weather and Society
 GIS in Weather and Society Olga Wilhelmi Institute for the Study of Society and Environment National Center for Atmospheric Research WAS*IS November 8, 2005 Boulder, Colorado Presentation Outline GIS basic
GIS in Weather and Society Olga Wilhelmi Institute for the Study of Society and Environment National Center for Atmospheric Research WAS*IS November 8, 2005 Boulder, Colorado Presentation Outline GIS basic
The ESPON Programme. Goals Main Results Future
 The ESPON Programme Goals Main Results Future Structure 1. Goals Objectives and expectations Participation, organisation and networking Themes addressed in the applied research undertaken in ESPON projects
The ESPON Programme Goals Main Results Future Structure 1. Goals Objectives and expectations Participation, organisation and networking Themes addressed in the applied research undertaken in ESPON projects
OneStop Map Viewer Navigation
 OneStop Map Viewer Navigation» Intended User: Industry Map Viewer users Overview The OneStop Map Viewer is an interactive map tool that helps you find and view information associated with energy development,
OneStop Map Viewer Navigation» Intended User: Industry Map Viewer users Overview The OneStop Map Viewer is an interactive map tool that helps you find and view information associated with energy development,
Write a report (6-7 pages, double space) on some examples of Internet Applications. You can choose only ONE of the following application areas:
 UPR 6905 Internet GIS Homework 1 Yong Hong Guo September 9, 2008 Write a report (6-7 pages, double space) on some examples of Internet Applications. You can choose only ONE of the following application
UPR 6905 Internet GIS Homework 1 Yong Hong Guo September 9, 2008 Write a report (6-7 pages, double space) on some examples of Internet Applications. You can choose only ONE of the following application
Water Information Portal User Guide. Updated July 2014
 Water Information Portal User Guide Updated July 2014 1. ENTER THE WATER INFORMATION PORTAL Launch the Water Information Portal in your internet browser via http://www.bcogc.ca/public-zone/water-information
Water Information Portal User Guide Updated July 2014 1. ENTER THE WATER INFORMATION PORTAL Launch the Water Information Portal in your internet browser via http://www.bcogc.ca/public-zone/water-information
Guide to Hydrologic Information on the Web
 NOAA s National Weather Service Guide to Hydrologic Information on the Web Colorado River at Lees Ferry Photo: courtesy Tim Helble Your gateway to web resources provided through NOAA s Advanced Hydrologic
NOAA s National Weather Service Guide to Hydrologic Information on the Web Colorado River at Lees Ferry Photo: courtesy Tim Helble Your gateway to web resources provided through NOAA s Advanced Hydrologic
Poland, European Territory, ESPON Programme Warsaw, 2 July 2007 STRATEGY OF THE ESPON 2013 PROGRAMME
 Poland, European Territory, ESPON Programme 2007-2013 Warsaw, 2 July 2007 STRATEGY OF THE ESPON 2013 PROGRAMME Territory matters Regional diversity as asset Territorial potentials increasing in importance
Poland, European Territory, ESPON Programme 2007-2013 Warsaw, 2 July 2007 STRATEGY OF THE ESPON 2013 PROGRAMME Territory matters Regional diversity as asset Territorial potentials increasing in importance
Module 10 Summative Assessment
 Module 10 Summative Assessment Activity In this activity you will use the three dimensions of vulnerability that you learned about in this module exposure, sensitivity, and adaptive capacity to assess
Module 10 Summative Assessment Activity In this activity you will use the three dimensions of vulnerability that you learned about in this module exposure, sensitivity, and adaptive capacity to assess
Compact guides GISCO. Geographic information system of the Commission
 Compact guides GISCO Geographic information system of the Commission What is GISCO? GISCO, the Geographic Information System of the COmmission, is a permanent service of Eurostat that fulfils the requirements
Compact guides GISCO Geographic information system of the Commission What is GISCO? GISCO, the Geographic Information System of the COmmission, is a permanent service of Eurostat that fulfils the requirements
An Instructional Module. FieldScope Unit 1. Introduction to National Geographic Society s FieldScope Program.
 An Instructional Module FieldScope Unit 1 www.budburst.org/fieldscope Introduction to National Geographic Society s FieldScope Program Unit Contents Overview 3 Learning Objectives Time Commitment Technical
An Instructional Module FieldScope Unit 1 www.budburst.org/fieldscope Introduction to National Geographic Society s FieldScope Program Unit Contents Overview 3 Learning Objectives Time Commitment Technical
Background and History
 p1 Background and History What is the Indian Ocean Climate Initiative? The Indian Ocean Climate Initiative (IOCI) is a strategic program of research and information transfer to support government decision-making.
p1 Background and History What is the Indian Ocean Climate Initiative? The Indian Ocean Climate Initiative (IOCI) is a strategic program of research and information transfer to support government decision-making.
The Church Demographic Specialists
 The Church Demographic Specialists Easy-to-Use Features Map-driven, Web-based Software An Integrated Suite of Information and Query Tools Providing An Insightful Window into the Communities You Serve Key
The Church Demographic Specialists Easy-to-Use Features Map-driven, Web-based Software An Integrated Suite of Information and Query Tools Providing An Insightful Window into the Communities You Serve Key
BOUNDARY MAP USER GUIDE
 BOUNDARY MAP USER GUIDE Get Exploring. Boundaries. The Northern Ontario Boundary Map provides users with the ability to explore the many community, administrative and service provider boundaries in the
BOUNDARY MAP USER GUIDE Get Exploring. Boundaries. The Northern Ontario Boundary Map provides users with the ability to explore the many community, administrative and service provider boundaries in the
CREATING A REPORT ON FIRE (April 2011)
 CREATING A REPORT ON FIRE (April 2011) The Fire Report feature on the NAFI website lets you create simple summaries of fire activity for areas of land in far northern Australia (north of 20 degrees where
CREATING A REPORT ON FIRE (April 2011) The Fire Report feature on the NAFI website lets you create simple summaries of fire activity for areas of land in far northern Australia (north of 20 degrees where
The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth
 The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth CSC Threads The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth 1 Table of Contents The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth - CSC Introduction How to access CSC data with
The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth CSC Threads The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth 1 Table of Contents The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth - CSC Introduction How to access CSC data with
Jim Fox. copyright UNC Asheville's NEMAC
 Decisions and System Thinking Jim Fox November, 2012 1 UNC Asheville s s NEMAC National Environmental Modeling and Analysis Center Applied Research and technology development on integration of environmental
Decisions and System Thinking Jim Fox November, 2012 1 UNC Asheville s s NEMAC National Environmental Modeling and Analysis Center Applied Research and technology development on integration of environmental
Applying Hazard Maps to Urban Planning
 Applying Hazard Maps to Urban Planning September 10th, 2014 SAKAI Yuko Disaster Management Expert JICA Study Team for the Metro Cebu Roadmap Study on the Sustainable Urban Development 1 Contents 1. Outline
Applying Hazard Maps to Urban Planning September 10th, 2014 SAKAI Yuko Disaster Management Expert JICA Study Team for the Metro Cebu Roadmap Study on the Sustainable Urban Development 1 Contents 1. Outline
Pegaso map viewer workshop
 PEGASO / 05 Deliverable Plan 2010-12-23 Pegaso Project People for Ecosystem based Governance in Assessing Sustainable development of Ocean and coast Funded by the European Union under FP7 ENV.2009.2.2.1.4
PEGASO / 05 Deliverable Plan 2010-12-23 Pegaso Project People for Ecosystem based Governance in Assessing Sustainable development of Ocean and coast Funded by the European Union under FP7 ENV.2009.2.2.1.4
Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE)
 Introduction Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE) Lesson: Using ArcGIS Explorer to Analyze the Connection between Topography, Tectonics, and Rainfall GIS-intensive Lesson This
Introduction Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE) Lesson: Using ArcGIS Explorer to Analyze the Connection between Topography, Tectonics, and Rainfall GIS-intensive Lesson This
Table-Top Exercise for Emergency Preparedness Evaluation: Little Anse, Isle Madame
 Table-Top Exercise for Emergency Preparedness Evaluation: Little Anse, Isle Madame Alexander Chung, M.Sc. Candidate C-Change Student Research Associate May 2013 The Community of Little Anse Coastal community
Table-Top Exercise for Emergency Preparedness Evaluation: Little Anse, Isle Madame Alexander Chung, M.Sc. Candidate C-Change Student Research Associate May 2013 The Community of Little Anse Coastal community
Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other?
 Tectonics Investigation 5: Teacher Guide Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other? Plates move sideways past each other at transform boundaries. At these boundaries, the
Tectonics Investigation 5: Teacher Guide Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other? Plates move sideways past each other at transform boundaries. At these boundaries, the
Urban Spatial Scenario Design Modelling (USSDM) in Dar es Salaam: Background Information
 Urban Spatial Scenario Design Modelling (USSDM) in Dar es Salaam: Background Information Modelling urban settlement dynamics in Dar es Salaam Revision: 2 (July 2013) Prepared by: Katja Buchta TUM team
Urban Spatial Scenario Design Modelling (USSDM) in Dar es Salaam: Background Information Modelling urban settlement dynamics in Dar es Salaam Revision: 2 (July 2013) Prepared by: Katja Buchta TUM team
Use of climate reanalysis for EEA climate change assessment. Blaz Kurnik. European Environment Agency (EEA)
 Use of climate reanalysis for EEA climate change assessment Blaz Kurnik European Environment Agency (EEA) 2016: EEA content priorities Circular economy Climate and Energy Sustainable Development Goals
Use of climate reanalysis for EEA climate change assessment Blaz Kurnik European Environment Agency (EEA) 2016: EEA content priorities Circular economy Climate and Energy Sustainable Development Goals
CentropeSTATISTICS Working Interactively with Cross-Border Statistic Data Clemens Beyer, Walter Pozarek, Manfred Schrenk
 Clemens Beyer, Walter Pozarek, Manfred Schrenk (Dipl.-Ing. Clemens Beyer, CEIT ALANOVA, Concorde Business Park 2/F, 2320 Schwechat, Austria, c.beyer@ceit.at) (Dipl.-Ing. Walter Pozarek, PGO Planungsgemeinschaft
Clemens Beyer, Walter Pozarek, Manfred Schrenk (Dipl.-Ing. Clemens Beyer, CEIT ALANOVA, Concorde Business Park 2/F, 2320 Schwechat, Austria, c.beyer@ceit.at) (Dipl.-Ing. Walter Pozarek, PGO Planungsgemeinschaft
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 2 July 2012 E/C.20/2012/10/Add.1 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Second session New York, 13-15
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 2 July 2012 E/C.20/2012/10/Add.1 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Second session New York, 13-15
Coastal Emergency Risks Assessment - CERA Real-Time Storm Surge and Wave Visualization Tool
 Coastal Emergency Risks Assessment - CERA Real-Time Storm Surge and Wave Visualization Tool Introduction This document provides guidance for using the Coastal Emergency Risks Assessment (CERA) visualization
Coastal Emergency Risks Assessment - CERA Real-Time Storm Surge and Wave Visualization Tool Introduction This document provides guidance for using the Coastal Emergency Risks Assessment (CERA) visualization
Climate Risk Visualization for Adaptation Planning and Emergency Response
 Climate Risk Visualization for Adaptation Planning and Emergency Response NCR Flood Fact Finding Workshop Ricardo Saavedra ricardo@vizonomy.com Social Media, Mobile, and Big Data St. Peter s Basilica,
Climate Risk Visualization for Adaptation Planning and Emergency Response NCR Flood Fact Finding Workshop Ricardo Saavedra ricardo@vizonomy.com Social Media, Mobile, and Big Data St. Peter s Basilica,
Grant Agreement No. EIE/07/595/SI BEn
 Biomass energy register for sustainable site development for European regions Grant Agreement No. EIE/07/595/SI2.499697 BEn Biomass energy register for sustainable site development for European regions
Biomass energy register for sustainable site development for European regions Grant Agreement No. EIE/07/595/SI2.499697 BEn Biomass energy register for sustainable site development for European regions
Noise Maps, Report & Statistics, Dublin City Council Noise Mapping Project Roads and Traffic Department
 Noise Maps, Report & Statistics, Dublin City Council Noise Mapping Project Roads and Traffic Department Produced by Traffic Noise & Air Quality Unit November 2007 Contact: brian.mcmanus@dublincity.ie Ph;
Noise Maps, Report & Statistics, Dublin City Council Noise Mapping Project Roads and Traffic Department Produced by Traffic Noise & Air Quality Unit November 2007 Contact: brian.mcmanus@dublincity.ie Ph;
Flood Map. National Dataset User Guide
 Flood Map National Dataset User Guide Version 1.1.5 20 th April 2006 Copyright Environment Agency 1 Contents 1.0 Record of amendment... 3 2.0 Introduction... 4 2.1 Description of the Flood Map datasets...4
Flood Map National Dataset User Guide Version 1.1.5 20 th April 2006 Copyright Environment Agency 1 Contents 1.0 Record of amendment... 3 2.0 Introduction... 4 2.1 Description of the Flood Map datasets...4
The Governance of Land Use
 The planning system The Governance of Land Use United Kingdom Levels of government and their responsibilities The United Kingdom is a unitary state with three devolved governments in Northern Ireland,
The planning system The Governance of Land Use United Kingdom Levels of government and their responsibilities The United Kingdom is a unitary state with three devolved governments in Northern Ireland,
Sea Level Affecting Marshes Model (SLAMM) for Coastal Long Island Sound:
 2100 DATA VIEWER MANUAL Sea Level Affecting Marshes Model (SLAMM) for Coastal Long Island Sound: Using a Web Mapping Application Data Viewer to Examine Predicted Land Cover Change for 2100 AUTHOR: KEVIN
2100 DATA VIEWER MANUAL Sea Level Affecting Marshes Model (SLAMM) for Coastal Long Island Sound: Using a Web Mapping Application Data Viewer to Examine Predicted Land Cover Change for 2100 AUTHOR: KEVIN
Understanding Weather and Climate Risk. Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017
 Understanding Weather and Climate Risk Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017 What is risk in a weather and climate context? Hazard: something with the
Understanding Weather and Climate Risk Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017 What is risk in a weather and climate context? Hazard: something with the
User Guide. Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing Data and Mapping Tool. U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development
 User Guide Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing Data and Mapping Tool U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development December, 2015 1 Table of Contents 1. Getting Started... 5 1.1 Software Version...
User Guide Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing Data and Mapping Tool U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development December, 2015 1 Table of Contents 1. Getting Started... 5 1.1 Software Version...
SEISMIC RISK ASSESSMENT IN ARMENIA
 SEISMIC RISK ASSESSMENT IN ARMENIA Hovhannes Khangeldyan Head of National Crisis Management Center Rescue Service Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Armenia Tokyo, 2016 ARMENIA: GEOGRAPHICAL
SEISMIC RISK ASSESSMENT IN ARMENIA Hovhannes Khangeldyan Head of National Crisis Management Center Rescue Service Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Armenia Tokyo, 2016 ARMENIA: GEOGRAPHICAL
Norwegian spatial data infrastructure supporting disaster risk management Norwegian Mapping Authority
 Norwegian spatial data infrastructure supporting disaster risk management Norwegian Mapping Authority Arvid Lillethun, Norwegian Mapping Authority Land and Poverty 2018 Conference, World Bank 19.-23. March
Norwegian spatial data infrastructure supporting disaster risk management Norwegian Mapping Authority Arvid Lillethun, Norwegian Mapping Authority Land and Poverty 2018 Conference, World Bank 19.-23. March
Population 24/7 Download: User Guide. Purpose
 Population 24/7 Download: User Guide Purpose The Population 24/7 Download application is designed to enable a user to navigate around a map of England and Wales; select an area of interest represented
Population 24/7 Download: User Guide Purpose The Population 24/7 Download application is designed to enable a user to navigate around a map of England and Wales; select an area of interest represented
Appendix 1: UK climate projections
 Appendix 1: UK climate projections The UK Climate Projections 2009 provide the most up-to-date estimates of how the climate may change over the next 100 years. They are an invaluable source of information
Appendix 1: UK climate projections The UK Climate Projections 2009 provide the most up-to-date estimates of how the climate may change over the next 100 years. They are an invaluable source of information
UCL Institute for Environmental Design and Engineering
 Heat Risk in London Group Meeting Monday 5 th February 2018, TfL, The International Quarter, London ONGOING AND FUTURE WORK Mapping heat vulnerability in London Dr Anna Mavrogianni Senior Lecturer in Sustainable
Heat Risk in London Group Meeting Monday 5 th February 2018, TfL, The International Quarter, London ONGOING AND FUTURE WORK Mapping heat vulnerability in London Dr Anna Mavrogianni Senior Lecturer in Sustainable
Static risk mapping using a Geographic Information System
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Static risk mapping using a Geographic Information System This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author.
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Static risk mapping using a Geographic Information System This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author.
Residents Emergency Response Checklist
 COMMUNITY RESILIENCE PLAN Residents Emergency Response Checklist A helpful guide in the event of extreme weather or bushfire events. < PREVIOUS I NEXT > 02 Purchasing an existing property or building a
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE PLAN Residents Emergency Response Checklist A helpful guide in the event of extreme weather or bushfire events. < PREVIOUS I NEXT > 02 Purchasing an existing property or building a
Copernicus Overview. Major Emergency Management Conference Athlone 2017
 Copernicus Overview Major Emergency Management Conference Athlone 2017 Copernicus is a European programme implemented by the European Commission. The services address six thematic areas: land, marine,
Copernicus Overview Major Emergency Management Conference Athlone 2017 Copernicus is a European programme implemented by the European Commission. The services address six thematic areas: land, marine,
UTAH S STATEWIDE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION DATABASE
 UTAH S STATEWIDE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION DATABASE Data Information and Knowledge Management NASCIO Awards 2009 STATE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION DATABASE B. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Utah has developed one of the most
UTAH S STATEWIDE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION DATABASE Data Information and Knowledge Management NASCIO Awards 2009 STATE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION DATABASE B. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Utah has developed one of the most
How advances in atmospheric modelling are used for improved flood forecasting. Dr Michaela Bray Cardiff University
 How advances in atmospheric modelling are used for improved flood forecasting Dr Michaela Bray Cardiff University Overview of current short term rainfall forecasting Advancements and on going research
How advances in atmospheric modelling are used for improved flood forecasting Dr Michaela Bray Cardiff University Overview of current short term rainfall forecasting Advancements and on going research
Outdoor Recreation Valuation (ORVal) User Guide
 Outdoor Recreation Valuation (ORVal) User Guide Version 1.0 June 2016 Land, Environment, Economics and Policy (LEEP) Institute College of Social Sciences and International Studies University of Exeter
Outdoor Recreation Valuation (ORVal) User Guide Version 1.0 June 2016 Land, Environment, Economics and Policy (LEEP) Institute College of Social Sciences and International Studies University of Exeter
Community Inclusion in Colorado
 A Mapping Project for Emergency Preparedness and Response Aimee Voth Siebert, MA Julia Beems, MA Rachel Coles, MA Devon Williford, MPH Adam Anderson, MURP, MPH March 2015 understanding that HUMAN ENERGY
A Mapping Project for Emergency Preparedness and Response Aimee Voth Siebert, MA Julia Beems, MA Rachel Coles, MA Devon Williford, MPH Adam Anderson, MURP, MPH March 2015 understanding that HUMAN ENERGY
ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS. Week 1: What is GIS?
 ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 1: What is GIS? 1 WHAT IS GIS? A GIS integrates hardware, software, and data for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information.
ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 1: What is GIS? 1 WHAT IS GIS? A GIS integrates hardware, software, and data for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information.
GIS: Introductory Guide to MapPlace. Workshop Agenda. How the Maps Work. Geographic Information Systems. -The MapPlace is a web GIS application
 1 Introductory Guide to MapPlace Workshop 2007 Larry Jones MapPlace & Geoscience Databases Pat Desjardins Corporate GIS Gib McArthur Manager, Resource Information Kirk Hancock MINFILE Geologist Ward Kilby
1 Introductory Guide to MapPlace Workshop 2007 Larry Jones MapPlace & Geoscience Databases Pat Desjardins Corporate GIS Gib McArthur Manager, Resource Information Kirk Hancock MINFILE Geologist Ward Kilby
European spatial policy and regionalised approaches
 Findings of the ESPON 2006 Programme COMMIN Final Conference 26-27 April 2007 European spatial policy and regionalised approaches by Dr. Kai BöhmeB ! Territory matters Structure of presentation! Territorial
Findings of the ESPON 2006 Programme COMMIN Final Conference 26-27 April 2007 European spatial policy and regionalised approaches by Dr. Kai BöhmeB ! Territory matters Structure of presentation! Territorial
Long Term Plan What is planned for Murchison?
 Long Term Plan 2018-2028 What is planned for Murchison? 1.0 Introduction The following information provides an overview of significant projects Council has planned for the Murchison settlement in the Long
Long Term Plan 2018-2028 What is planned for Murchison? 1.0 Introduction The following information provides an overview of significant projects Council has planned for the Murchison settlement in the Long
Lesson Plan 3 Google Earth Tutorial on Land Use for Middle and High School
 An Introduction to Land Use and Land Cover This lesson plan builds on the lesson plan on Understanding Land Use and Land Cover Using Google Earth. Please refer to it in terms of definitions on land use
An Introduction to Land Use and Land Cover This lesson plan builds on the lesson plan on Understanding Land Use and Land Cover Using Google Earth. Please refer to it in terms of definitions on land use
Create Satellite Image, Draw Maps
 Create Satellite Image, Draw Maps 1. The goal Using Google Earth, we want to create and import a background file into our Adviser program. From there, we will be creating paddock boundaries. The accuracy
Create Satellite Image, Draw Maps 1. The goal Using Google Earth, we want to create and import a background file into our Adviser program. From there, we will be creating paddock boundaries. The accuracy
Launch of the ESPON 2013 Programme. European observation network on territorial development and cohesion
 Launch of the ESPON 2013 Programme European observation network on territorial development and cohesion Framework conditions for the ESPON 2013 Programme Policy development in use of territorial evidence
Launch of the ESPON 2013 Programme European observation network on territorial development and cohesion Framework conditions for the ESPON 2013 Programme Policy development in use of territorial evidence
A Web-GIS Based Integrated Climate Adaptation Model (ICAM): Exemplification from the City of Melbourne, Australia
 A Web-GIS Based Integrated Climate Adaptation Model (ICAM): Exemplification from the City of Melbourne, Australia JOSHPHAR KUNAPO 1,2, MATTHEW J. BURNS 1, TIM D. FLETCHER 1, ANTHONY R. LADSON 3, LUKE CUNNINGHAM
A Web-GIS Based Integrated Climate Adaptation Model (ICAM): Exemplification from the City of Melbourne, Australia JOSHPHAR KUNAPO 1,2, MATTHEW J. BURNS 1, TIM D. FLETCHER 1, ANTHONY R. LADSON 3, LUKE CUNNINGHAM
Spatial Data Availability Energizes Florida s Citizens
 NASCIO 2016 Recognition Awards Nomination Spatial Data Availability Energizes Florida s Citizens State of Florida Agency for State Technology & Department of Environmental Protection Category: ICT Innovations
NASCIO 2016 Recognition Awards Nomination Spatial Data Availability Energizes Florida s Citizens State of Florida Agency for State Technology & Department of Environmental Protection Category: ICT Innovations
LONDON & TE December 2009
 LONDON & TE2100 10 December 2009 Tim Reeder Environment Agency How is London vulnerable to CC? Flooding Overheating Water resources Air Quality Subsidence and heave Wind storms Global climate events What
LONDON & TE2100 10 December 2009 Tim Reeder Environment Agency How is London vulnerable to CC? Flooding Overheating Water resources Air Quality Subsidence and heave Wind storms Global climate events What
GIS Workshop UCLS_Fall Forum 2014 Sowmya Selvarajan, PhD TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS TITLE PAGE NO. 1. ArcGIS Basics I 2 a. Open and Save a Map Document 2 b. Work with Map Layers 2 c. Navigate in a Map Document 4 d. Measure Distances 4 2. ArcGIS Basics II 5 a. Work with
TABLE OF CONTENTS TITLE PAGE NO. 1. ArcGIS Basics I 2 a. Open and Save a Map Document 2 b. Work with Map Layers 2 c. Navigate in a Map Document 4 d. Measure Distances 4 2. ArcGIS Basics II 5 a. Work with
The UN-GGIM: Europe core data initiative to encourage Geographic information supporting Sustainable Development Goals Dominique Laurent, France
 INSPIRE conference Strasbourg 6 September 2017 The UN-GGIM: Europe core data initiative to encourage Geographic information supporting Sustainable Development Goals Dominique Laurent, France Introduction
INSPIRE conference Strasbourg 6 September 2017 The UN-GGIM: Europe core data initiative to encourage Geographic information supporting Sustainable Development Goals Dominique Laurent, France Introduction
GIS Geographical Information Systems. GIS Management
 GIS Geographical Information Systems GIS Management Difficulties on establishing a GIS Funding GIS Determining Project Standards Data Gathering Map Development Recruiting GIS Professionals Educating Staff
GIS Geographical Information Systems GIS Management Difficulties on establishing a GIS Funding GIS Determining Project Standards Data Gathering Map Development Recruiting GIS Professionals Educating Staff
Geological information for Europe : Towards a pan-european Geological Data Infrastructure
 Geological information for Europe : Towards a pan-european Geological Data Infrastructure Integrating geoscientific information for EU competitiveness Co-funded by the European Union European societal
Geological information for Europe : Towards a pan-european Geological Data Infrastructure Integrating geoscientific information for EU competitiveness Co-funded by the European Union European societal
Seamless weather and climate for security planning
 Seamless weather and climate for security planning Kirsty Lewis, Principal Climate Change Consultant, Met Office Hadley Centre 28 June 2010 Global Climate Models Mitigation timescale changes could be avoided
Seamless weather and climate for security planning Kirsty Lewis, Principal Climate Change Consultant, Met Office Hadley Centre 28 June 2010 Global Climate Models Mitigation timescale changes could be avoided
RETA 6422: Mainstreaming Environment for Poverty Reduction Category 2 Subproject
 RETA 6422: Mainstreaming Environment for Poverty Reduction Category 2 Subproject A. Basic Data 1. Subproject Title: Poverty-Environment Mapping to Support Decision Making 2. Country Director: Adrian Ruthenberg
RETA 6422: Mainstreaming Environment for Poverty Reduction Category 2 Subproject A. Basic Data 1. Subproject Title: Poverty-Environment Mapping to Support Decision Making 2. Country Director: Adrian Ruthenberg
User Guide for Source-Pathway-Receptor Modelling Tool for Estimating Flood Impact of Upland Land Use and Management Change
 User Guide for Source-Pathway-Receptor Modelling Tool for Estimating Flood Impact of Upland Land Use and Management Change Dr Greg O Donnell Professor John Ewen Professor Enda O Connell Newcastle University
User Guide for Source-Pathway-Receptor Modelling Tool for Estimating Flood Impact of Upland Land Use and Management Change Dr Greg O Donnell Professor John Ewen Professor Enda O Connell Newcastle University
Local Area Key Issues Paper No. 13: Southern Hinterland townships growth opportunities
 Draft Sunshine Coast Planning Scheme Review of Submissions Local Area Key Issues Paper No. 13: Southern Hinterland townships growth opportunities Key Issue: Growth opportunities for Southern Hinterland
Draft Sunshine Coast Planning Scheme Review of Submissions Local Area Key Issues Paper No. 13: Southern Hinterland townships growth opportunities Key Issue: Growth opportunities for Southern Hinterland
Integrated Geodatabase Model for effective planning of District -Hamirpur
 Integrated Geodatabase Model for effective planning of District -Hamirpur Developed by District Administration,Hamirpur in collaboration with Centre for Geoinformatics Research and Training, CSK HPAU,Palampur
Integrated Geodatabase Model for effective planning of District -Hamirpur Developed by District Administration,Hamirpur in collaboration with Centre for Geoinformatics Research and Training, CSK HPAU,Palampur
The European territory: Strategic developmentd
 The European territory: Strategic developmentd Peter Mehlbye Workshop Strategic Development Catalonia 11 June 2002 THE LECTURE Structure I. Territorial trends II. Strategy for European spatial development
The European territory: Strategic developmentd Peter Mehlbye Workshop Strategic Development Catalonia 11 June 2002 THE LECTURE Structure I. Territorial trends II. Strategy for European spatial development
Expanding Canada s Rail Network to Meet the Challenges of the Future
 Expanding Canada s Rail Network to Meet the Challenges of the Future Lesson Overview Rail may become a more popular mode of transportation in the future due to increased population, higher energy costs,
Expanding Canada s Rail Network to Meet the Challenges of the Future Lesson Overview Rail may become a more popular mode of transportation in the future due to increased population, higher energy costs,
2 nd Semester. Core Courses. C 2.1 City and Metropolitan Planning. Module 1: Urban Structure and Growth Implications
 2 nd Semester Core Courses C 2.1 City and Metropolitan Planning Module 1: Urban Structure and Growth Implications Growth of cities; cities as engine of growth; urban sprawl; land value, economic attributes
2 nd Semester Core Courses C 2.1 City and Metropolitan Planning Module 1: Urban Structure and Growth Implications Growth of cities; cities as engine of growth; urban sprawl; land value, economic attributes
Current and future climate of the Cook Islands. Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program
 Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Penrhyn Pukapuka Nassau Suwarrow Rakahanga Manihiki N o r t h e r n C o o k I s l a nds S o u t h e Palmerston r n C o o k I s l
Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Penrhyn Pukapuka Nassau Suwarrow Rakahanga Manihiki N o r t h e r n C o o k I s l a nds S o u t h e Palmerston r n C o o k I s l
Use of Geospatial data for disaster managements
 Use of Geospatial data for disaster managements Source: http://alertsystemsgroup.com Instructor : Professor Dr. Yuji Murayama Teaching Assistant : Manjula Ranagalage What is GIS? A powerful set of tools
Use of Geospatial data for disaster managements Source: http://alertsystemsgroup.com Instructor : Professor Dr. Yuji Murayama Teaching Assistant : Manjula Ranagalage What is GIS? A powerful set of tools
Climate change in the U.S. Northeast
 Climate change in the U.S. Northeast By U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.10.17 Word Count 1,109 Killington Ski Resort is located in Vermont. As temperatures increase
Climate change in the U.S. Northeast By U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.10.17 Word Count 1,109 Killington Ski Resort is located in Vermont. As temperatures increase
Roles of NGII in successful disaster management
 The Second UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting Roles of NGII in successful disaster management Republic of Korea Teheran Iran 28 October 2013 Sanghoon Lee, Ph.D. NGII Outline Type of Disasters Occur in Korea Practical
The Second UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting Roles of NGII in successful disaster management Republic of Korea Teheran Iran 28 October 2013 Sanghoon Lee, Ph.D. NGII Outline Type of Disasters Occur in Korea Practical
Consents Resource Consents Map
 Consents Resource Consents Map Select the map from the Maps introduction page http://www.waikatoregion.govt.nz/maps/ If you have the map browser open the Resource Consents map will also display when selected
Consents Resource Consents Map Select the map from the Maps introduction page http://www.waikatoregion.govt.nz/maps/ If you have the map browser open the Resource Consents map will also display when selected
Lesson Plan 2 - Middle and High School Land Use and Land Cover Introduction. Understanding Land Use and Land Cover using Google Earth
 Understanding Land Use and Land Cover using Google Earth Image an image is a representation of reality. It can be a sketch, a painting, a photograph, or some other graphic representation such as satellite
Understanding Land Use and Land Cover using Google Earth Image an image is a representation of reality. It can be a sketch, a painting, a photograph, or some other graphic representation such as satellite
WMO Guide on Integrated Urban Weather, Environment and Climate Services for Cities (IUWECS) Hong Kong- an experience from a high-density city
 WMO Guide on Integrated Urban Weather, Environment and Climate Services for Cities (IUWECS) Hong Kong- an experience from a high-density city Dr. Chao REN Associate Professor School of Architecture The
WMO Guide on Integrated Urban Weather, Environment and Climate Services for Cities (IUWECS) Hong Kong- an experience from a high-density city Dr. Chao REN Associate Professor School of Architecture The
CENSUS MAPPING WITH GIS IN NAMIBIA. BY Mrs. Ottilie Mwazi Central Bureau of Statistics Tel: October 2007
 CENSUS MAPPING WITH GIS IN NAMIBIA BY Mrs. Ottilie Mwazi Central Bureau of Statistics E-mail: omwazi@npc.gov.na Tel: + 264 61 283 4060 October 2007 Content of Presentation HISTORICAL BACKGROUND OF CENSUS
CENSUS MAPPING WITH GIS IN NAMIBIA BY Mrs. Ottilie Mwazi Central Bureau of Statistics E-mail: omwazi@npc.gov.na Tel: + 264 61 283 4060 October 2007 Content of Presentation HISTORICAL BACKGROUND OF CENSUS
KENTUCKY HAZARD MITIGATION PLAN RISK ASSESSMENT
 KENTUCKY HAZARD MITIGATION PLAN RISK ASSESSMENT Presentation Outline Development of the 2013 State Hazard Mitigation Plan Risk Assessment Determining risk assessment scale Census Data Aggregation Levels
KENTUCKY HAZARD MITIGATION PLAN RISK ASSESSMENT Presentation Outline Development of the 2013 State Hazard Mitigation Plan Risk Assessment Determining risk assessment scale Census Data Aggregation Levels
EO Information Services. Assessing Vulnerability in the metropolitan area of Rio de Janeiro (Floods & Landslides) Project
 EO Information Services in support of Assessing Vulnerability in the metropolitan area of Rio de Janeiro (Floods & Landslides) Project Ricardo Armas, Critical Software SA Haris Kontoes, ISARS NOA World
EO Information Services in support of Assessing Vulnerability in the metropolitan area of Rio de Janeiro (Floods & Landslides) Project Ricardo Armas, Critical Software SA Haris Kontoes, ISARS NOA World
AFFH-T User Guide September 2017 AFFH-T User Guide U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development
 AFFH-T User Guide Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing Data and Mapping Tool v. 4.1 U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development September 2017 Version 4.1 ❿ September 2017 Page 1 Document History
AFFH-T User Guide Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing Data and Mapping Tool v. 4.1 U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development September 2017 Version 4.1 ❿ September 2017 Page 1 Document History
Geospatial natural disaster management
 Geospatial natural disaster management disasters happen. are you ready? Natural disasters can strike almost anywhere at any time, with no regard to a municipality s financial resources. These extraordinarily
Geospatial natural disaster management disasters happen. are you ready? Natural disasters can strike almost anywhere at any time, with no regard to a municipality s financial resources. These extraordinarily
Search for the Gulf of Carpentaria in the remap search bar:
 This tutorial is aimed at getting you started with making maps in Remap (). In this tutorial we are going to develop a simple classification of mangroves in northern Australia. Before getting started with
This tutorial is aimed at getting you started with making maps in Remap (). In this tutorial we are going to develop a simple classification of mangroves in northern Australia. Before getting started with
EuroGEOSS Protected Areas Pilot
 EuroGEOSS Protected Areas Pilot Max Craglia European Commission Joint Research Centre Part 1: the present MyNatura2000 Mobile app. Awareness raising & volunteered data collection. Natura2000 covers 18%
EuroGEOSS Protected Areas Pilot Max Craglia European Commission Joint Research Centre Part 1: the present MyNatura2000 Mobile app. Awareness raising & volunteered data collection. Natura2000 covers 18%
Great Lakes Online Watershed Interface W. Elliot, Research Engineer USDA Forest Service Rocky Mountain Research Station, Moscow, ID March, 2016
 Great Lakes Online Watershed Interface W. Elliot, Research Engineer USDA Forest Service Rocky Mountain Research Station, Moscow, ID March, 2016 Guidelines for using the Web WEPP Watershed Tool to Support
Great Lakes Online Watershed Interface W. Elliot, Research Engineer USDA Forest Service Rocky Mountain Research Station, Moscow, ID March, 2016 Guidelines for using the Web WEPP Watershed Tool to Support
West Carroll Parish Hazard Mitigation Plan Update Public Meeting. August 25, 2015 Oak Grove, LA
 West Carroll Parish Hazard Mitigation Plan Update Public Meeting August 25, 2015 Oak Grove, LA Agenda Hazard Mitigation Planning Process SDMI Staff Risk Assessment SDMI Staff Update on Previous/Current
West Carroll Parish Hazard Mitigation Plan Update Public Meeting August 25, 2015 Oak Grove, LA Agenda Hazard Mitigation Planning Process SDMI Staff Risk Assessment SDMI Staff Update on Previous/Current
Paul Bridge Meteorologist Vaisala/UKMO Work Groups/Committees: WMO/TRB/AMS
 Paul Bridge Meteorologist Vaisala/UKMO Work Groups/Committees: WMO/TRB/AMS Introduction (a) Identify and establish, if possible, inventories of transport networks in the ECE region which are vulnerable
Paul Bridge Meteorologist Vaisala/UKMO Work Groups/Committees: WMO/TRB/AMS Introduction (a) Identify and establish, if possible, inventories of transport networks in the ECE region which are vulnerable
Current and future climate of Vanuatu. Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program
 Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Hiu Torres Islands Vanua Lava Gaua Banks Islands Espiritu Santo Malekula Ambae Épi Maéwo Pentecost Ambrym Shepherd Islands Éfate
Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Hiu Torres Islands Vanua Lava Gaua Banks Islands Espiritu Santo Malekula Ambae Épi Maéwo Pentecost Ambrym Shepherd Islands Éfate
Implementation of the ESPON 2020 cooperation program. 16 January 2017 Anneloes van Noordt
 Implementation of the ESPON 2020 cooperation program 16 January 2017 Anneloes van Noordt Outline! ESPON Cooperation Program! Specific Objectives! Applied Research! Targeted Analysis! Database & Tools!
Implementation of the ESPON 2020 cooperation program 16 January 2017 Anneloes van Noordt Outline! ESPON Cooperation Program! Specific Objectives! Applied Research! Targeted Analysis! Database & Tools!
In this exercise we will learn how to use the analysis tools in ArcGIS with vector and raster data to further examine potential building sites.
 GIS Level 2 In the Introduction to GIS workshop we filtered data and visually examined it to determine where to potentially build a new mixed use facility. In order to get a low interest loan, the building
GIS Level 2 In the Introduction to GIS workshop we filtered data and visually examined it to determine where to potentially build a new mixed use facility. In order to get a low interest loan, the building
Introducing IMS. v) Select the Zoom to Full Extent tool. Did you return to the original view?
 Ocean/ENVIR 260, Winter 2006 Lab 1, Get to Know the Puget Sound Watershed Name Introducing IMS 1) Open your web browser and navigate to http://128.208.23.127/website/lab1. (This link can be found on the
Ocean/ENVIR 260, Winter 2006 Lab 1, Get to Know the Puget Sound Watershed Name Introducing IMS 1) Open your web browser and navigate to http://128.208.23.127/website/lab1. (This link can be found on the
Community Opportunity Map
 Community Opportunity Map User Guide and FAQs UPDATED FEBRUARY 2018 Contents User Guide... 2 Overview... 2 Choosing a location... 3 Search for a city or address... 4 Select a county or ZIP code... 4 Explore
Community Opportunity Map User Guide and FAQs UPDATED FEBRUARY 2018 Contents User Guide... 2 Overview... 2 Choosing a location... 3 Search for a city or address... 4 Select a county or ZIP code... 4 Explore
Disaster Risk Assessment: Opportunities for GIS and data management with Open DRI
 Disaster Risk Assessment: Opportunities for GIS and data management with Open DRI Jacob Opadeyi Department of Geomatics Engineering and Land Management, The University of the West Indies, St. Augustine,
Disaster Risk Assessment: Opportunities for GIS and data management with Open DRI Jacob Opadeyi Department of Geomatics Engineering and Land Management, The University of the West Indies, St. Augustine,
1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment
 1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment Although the variability of weather and associated shifts in the frequency and magnitude of climate events were not available from the
1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment Although the variability of weather and associated shifts in the frequency and magnitude of climate events were not available from the
Dar es Salaam - Reality Check Workshop
 Dar es Salaam - Reality Check Workshop hosted by GIZ and Dar es Salaam City Council Introduction: Key Urban Characteristics of Dar es Salaam Challenges and Opportunities for Resilient Development in the
Dar es Salaam - Reality Check Workshop hosted by GIZ and Dar es Salaam City Council Introduction: Key Urban Characteristics of Dar es Salaam Challenges and Opportunities for Resilient Development in the
Flooding on the Somerset Levels. ArcGIS Online
 Flooding on the Somerset Levels ArcGIS Online Using this resource This resource has been written to help teachers make use of the ArcGIS Online program. It provides; guidance on how to use the program
Flooding on the Somerset Levels ArcGIS Online Using this resource This resource has been written to help teachers make use of the ArcGIS Online program. It provides; guidance on how to use the program
The econ Planning Suite: CPD Maps and the Con Plan in IDIS for Consortia Grantees Session 1
 The econ Planning Suite: CPD Maps and the Con Plan in IDIS for Consortia Grantees Session 1 1 Training Objectives Use CPD Maps to analyze, assess, and compare levels of need in your community Use IDIS
The econ Planning Suite: CPD Maps and the Con Plan in IDIS for Consortia Grantees Session 1 1 Training Objectives Use CPD Maps to analyze, assess, and compare levels of need in your community Use IDIS
The Tyndall Cities Integrated Assessment Framework
 The Tyndall Cities Integrated Assessment Framework Alistair Ford 1, Stuart Barr 1, Richard Dawson 1, Jim Hall 2, Michael Batty 3 1 School of Civil Engineering & Geosciences and Centre for Earth Systems
The Tyndall Cities Integrated Assessment Framework Alistair Ford 1, Stuart Barr 1, Richard Dawson 1, Jim Hall 2, Michael Batty 3 1 School of Civil Engineering & Geosciences and Centre for Earth Systems
REPORT ON INVESTMENTS
 REPORT ON INVESTMENTS D.T2.3.3 Investments for technical equipment for the implementation of Web-GIS platform in Mantova 1 Local support group designing Mantova Web-GIS platform. Picture by Maria Giulia
REPORT ON INVESTMENTS D.T2.3.3 Investments for technical equipment for the implementation of Web-GIS platform in Mantova 1 Local support group designing Mantova Web-GIS platform. Picture by Maria Giulia
The GHG Reservoir Tool (G-res)
 UNESCO/IHA research project on the GHG status of freshwater reservoirs The GHG Reservoir Tool (G-res) User guidelines for the Earth Engine functionality United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural
UNESCO/IHA research project on the GHG status of freshwater reservoirs The GHG Reservoir Tool (G-res) User guidelines for the Earth Engine functionality United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural
NEW HOLLAND IH AUSTRALIA. Machinery Market Information and Forecasting Portal *** Dealer User Guide Released August 2013 ***
 NEW HOLLAND IH AUSTRALIA Machinery Market Information and Forecasting Portal *** Dealer User Guide Released August 2013 *** www.cnhportal.agriview.com.au Contents INTRODUCTION... 5 REQUIREMENTS... 6 NAVIGATION...
NEW HOLLAND IH AUSTRALIA Machinery Market Information and Forecasting Portal *** Dealer User Guide Released August 2013 *** www.cnhportal.agriview.com.au Contents INTRODUCTION... 5 REQUIREMENTS... 6 NAVIGATION...
