Biogeography. Lecture 19
|
|
|
- Molly Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biogeography. Lecture 19 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University March 23, 2018 Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
2 Outline Biogeography of the World Distribution: the basic concept Floristic kingdoms and faunistic provinces Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
3 Distribution: the basic concept Biogeography of the World Distribution: the basic concept Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
4 Distribution: the basic concept Species distribution Range Restricted with climate, history and natural barriers Disjunction Examples: East Asia/East Coast; Pacific (West Washington/North Idaho) Endemics Every species is endemic to some region. What is important, is the size of region. There also species endemic only to Earth: cosmopolitan species like braken fern (Pteridium). Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
5 Floristic kingdoms and faunistic provinces Biogeography of the World Floristic kingdoms and faunistic provinces Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
6 Floristic kingdoms and faunistic provinces Contemporary look on plant biogeography: five kingdoms (Cox, 2001) Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
7 Floristic kingdoms and faunistic provinces Contemporary look on animal biogeography: 10 provinces (Holt et al., 2013) Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
8 Floristic kingdoms and faunistic provinces Classification of tropical forests (Silk et al., 2018) Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
9 Floristic kingdoms and faunistic provinces Our approach: 5 regions Holarctic (I and II) Neotropical African and Madagascan Indo-Pacific Australian Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
10 Biogeography of the World Holarctic region I: Nearctic North America Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
11 Climate/temperatures: hardiness zones Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
12 Climate/precipitation Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
13 Ecoregions Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
14 Glaciation Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
15 Plant distribution (McLaughin, 2007) Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
16 Biogeographical regions Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
17 North America: 21 region 1. Arctic Islands and Greenland 2. Labrador, Sr. Lawrence Valley 3. Canadian Northwest 4. Alaska 5. Yukon and British Columbia 6. Great Lakes and Central Lowlands 7. Appalachians 8. East Coast 9. Coastal Lowlands 10. Central Pacific Coast Ranges 11. Great Plains 12. Mississippi delta 13. South Florida 14. South Texas 15. South Montane region 16. North Montane region 17. Great Basin 18. Southern California 19. Sonora 20. Chihuahua 21. Mexican Sierras Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
18 Region 1. Tundra Very similar to Eurasia, almost all species are same Few mammals (reindeer, musk ox, lemmings), only migratory birds, no reptiles and amphibians Forest border is supported mostly by lowest temperatures and permafrost Lichens and mosses are more competitive than flowering plants Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
19 Regions 2 and 3. Taiga: boreal conifer forests Again, very similar to Eurasia Typical trees: deciduous Larix (larch) and evergreen Picea (spruce); North American boreal forests are richer thank Eurasian. Forest interleaves with muskegs, swampy areas shaped mostly by peatmoss (Sphagnum spp.) Food chains are based on large herbivores (deers, moose, elks). Many warm-blood vertebrates will follow the Bergman rule: representative of northern species are bigger, and representatives of tropical species are smaller. Plus fact which is still unexplained: for some reason, American species of many genera are bigger in size than Eurasian (moose, bears, beavers and many others including plants) Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
20 Regions 4 and 5: wet northwest Anomalous high temperatures and precipitation rates. However: almost no rain in July-September so broadleaved trees are not surviving there. Flora and fauna have many connections with Siberia and Eurasian East due to Beringian landbridge. However, some elements (like porcupines) are clearly Neotropical. Rich coastal life: salmon, seabirds, bears, walruses, sea otters (the only species of marine weasels) Vast amount of conifer species, e.g. different cedars like Pseudotsuga; and ferns Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
21 Sea otter (Enhydra lutris) Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
22 Some Alaskan photos Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
23 For Further Reading I. Sanderson. The Continent We Live On Mode of access: http: // North America. A. Shipunov. Biogeography [Electronic resource] onwards. Mode of access: A. Shipunov. Introduction to Biogegraphy and Tropical Biology [Electronic resource] onwards. Mode of access: intr_biogeogr_trop_biol/intr_biogeogr_trop_biol.pdf Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 19 March 23, / 23
Biomes of the World What is a Biome?
 Biomes of the World What is a Biome? A large, relatively distinct terrestrial region with characteristic Climate Soil Plants Animals Interacting landscapes 1 Terrestrial Biomes Using Precipitation And
Biomes of the World What is a Biome? A large, relatively distinct terrestrial region with characteristic Climate Soil Plants Animals Interacting landscapes 1 Terrestrial Biomes Using Precipitation And
Tropical Moist Rainforest
 Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Chapter 6, Part Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great.
 Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
community. A biome can be defined as a major biological community of plants and animals with similar life forms and
 Science & Math Earth's Systems: What is a biome? The major recognizable life zones of the continents are called biomes. Because vegetation is usually the dominant and most apparent feature of the landscape,
Science & Math Earth's Systems: What is a biome? The major recognizable life zones of the continents are called biomes. Because vegetation is usually the dominant and most apparent feature of the landscape,
Spheres of Life. Ecology. Chapter 52. Impact of Ecology as a Science. Ecology. Biotic Factors Competitors Predators / Parasites Food sources
 "Look again at that dot... That's here. That's home. That's us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives. Ecology Chapter
"Look again at that dot... That's here. That's home. That's us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives. Ecology Chapter
The United States & Canada. A Regional Study of Anglo America
 A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
In 1749 Linneaus sent a colleague to North America to collect plants
 In 1749 Linneaus sent a colleague to North America to collect plants Desired for use in decorative gardens Climate similar to Eastern NA and China but very different vegetation Why were these introduction
In 1749 Linneaus sent a colleague to North America to collect plants Desired for use in decorative gardens Climate similar to Eastern NA and China but very different vegetation Why were these introduction
Landform Regions of Canada
 Landform Regions of Canada The movement of the earth s plates, and the resulting folding, faulting, and volcanic activity, have combined with the forces of erosion and weathering to create a variety of
Landform Regions of Canada The movement of the earth s plates, and the resulting folding, faulting, and volcanic activity, have combined with the forces of erosion and weathering to create a variety of
Lesson 2: Terrestrial Ecosystems
 Lesson 2: Terrestrial Ecosystems A terrestrial ecosystem is a land ecosystem. Terrestrial ecosystems include tundra, forests, grasslands, deserts, and rainforests. 1 The arctic tundra is earth s coldest
Lesson 2: Terrestrial Ecosystems A terrestrial ecosystem is a land ecosystem. Terrestrial ecosystems include tundra, forests, grasslands, deserts, and rainforests. 1 The arctic tundra is earth s coldest
Chapter 8: Biogeography. Biotic Provinces. Biotic Provinces. Biotic Provinces 10/4/2012
 Chapter 8: Biogeography Why were introductions of new species into Europe so popular long ago? In 1749 Linneaus sent a colleague to NA to collect plants Desired for use in decorative gardens Climate similar
Chapter 8: Biogeography Why were introductions of new species into Europe so popular long ago? In 1749 Linneaus sent a colleague to NA to collect plants Desired for use in decorative gardens Climate similar
Bright blue marble floating in space. Biomes & Ecology
 Bright blue marble floating in space Biomes & Ecology Chapter 50 Spheres of life Molecules Cells (Tissues Organ Organ systems) Organisms Populations Community all the organisms of all the species that
Bright blue marble floating in space Biomes & Ecology Chapter 50 Spheres of life Molecules Cells (Tissues Organ Organ systems) Organisms Populations Community all the organisms of all the species that
Markville. CGC 1DL/PL Geography. Geography of Canada. Natural Environment Unit Test
 Markville CGC 1DL/PL Geography Geography of Canada Natural Environment Unit Test Name: Thinking /10 Knowledge /10 Application /10 Communication /10 Part A: Blanks (1 mark each) Thinking Choose the correct
Markville CGC 1DL/PL Geography Geography of Canada Natural Environment Unit Test Name: Thinking /10 Knowledge /10 Application /10 Communication /10 Part A: Blanks (1 mark each) Thinking Choose the correct
Weather and Climate in Canada. October 2 nd, 2017
 Weather and Climate in Canada October 2 nd, 2017 Big Ideas How are climate and weather in Canada influenced by geography? How do weather and climate affect the lives of Canadians? Weather and Climate
Weather and Climate in Canada October 2 nd, 2017 Big Ideas How are climate and weather in Canada influenced by geography? How do weather and climate affect the lives of Canadians? Weather and Climate
Unit 2. United States Physical Geography
 Unit 2 United States Physical Geography Physical Geography U.S. extends from the Atlantic to Pacific U.S. is the 3rd largest country U.S. has fertile soils, vast forests, and variety of minerals All major
Unit 2 United States Physical Geography Physical Geography U.S. extends from the Atlantic to Pacific U.S. is the 3rd largest country U.S. has fertile soils, vast forests, and variety of minerals All major
Biosphere Organization
 Biosphere Organization What is a biome? Biomes refer to a large region or area characterized by the following: 1. A particular climate pattern of the annual temperature and precipitation distribution,
Biosphere Organization What is a biome? Biomes refer to a large region or area characterized by the following: 1. A particular climate pattern of the annual temperature and precipitation distribution,
Biomes. What is a Biome?
 Biomes What is a Biome? Ecosystems can be grouped into larger categories called biomes Biome A collection of ecosystems that are related to each other, usually based on the type of places they support
Biomes What is a Biome? Ecosystems can be grouped into larger categories called biomes Biome A collection of ecosystems that are related to each other, usually based on the type of places they support
Ecology 312 SI STEVEN F. Last Session: Aquatic Biomes, Review This Session: Plate Tectonics, Lecture Quiz 2
 Ecology 312 SI STEVEN F. Last Session: Aquatic Biomes, Review This Session: Plate Tectonics, Lecture Quiz 2 Questions? Warm up: KWL KNOW: On a piece of paper, write down things that you know well enough
Ecology 312 SI STEVEN F. Last Session: Aquatic Biomes, Review This Session: Plate Tectonics, Lecture Quiz 2 Questions? Warm up: KWL KNOW: On a piece of paper, write down things that you know well enough
Lecture 7. Our Sun. Ecology. Mushroom. Introduction. Food Chain. Food Chain. Circle of Life
 Introduction Mushroom George Wong, mycologist Office Hour: TBA Office: St. John 612B Telephone: X63940 Email: biol101@hawaii hawaii.edu Lecture 7 Our Sun Ecology How organisms interact with each other
Introduction Mushroom George Wong, mycologist Office Hour: TBA Office: St. John 612B Telephone: X63940 Email: biol101@hawaii hawaii.edu Lecture 7 Our Sun Ecology How organisms interact with each other
3 Temperate and Polar Zones
 CHAPTER 3 3 Temperate and Polar Zones SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What biomes are found in the temperate zone? What biomes
CHAPTER 3 3 Temperate and Polar Zones SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What biomes are found in the temperate zone? What biomes
discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms and bodies of
 Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
How does the physical environment influence communities and ecosystems? Hoodoos in Cappadocia, Turkey
 Biomes of the World How does the physical environment influence communities and ecosystems? Hoodoos in Cappadocia, Turkey ecosystems are shaped by: abiotic factors climate/weather space Rainfall Soil air
Biomes of the World How does the physical environment influence communities and ecosystems? Hoodoos in Cappadocia, Turkey ecosystems are shaped by: abiotic factors climate/weather space Rainfall Soil air
Boreal Forests. Boreal, Canadian Rockies, Alberta. Taiga, Siberia
 Coniferous forests are mainly found in broad circumpolar belt across the northern hemisphere and on mountain ranges where low temperatures limit the growing season to a few months each year - thus too
Coniferous forests are mainly found in broad circumpolar belt across the northern hemisphere and on mountain ranges where low temperatures limit the growing season to a few months each year - thus too
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles.
 EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
Biome. Biome - A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms When we talk about biomes, we typically mean LARGE areas.
 Biome Biome - A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms When we talk about biomes, we typically mean LARGE areas. Living or Nonliving? Biomes are determined by two factors:
Biome Biome - A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms When we talk about biomes, we typically mean LARGE areas. Living or Nonliving? Biomes are determined by two factors:
Pages 63 Monday May 01, 2017
 Pages 6 Notebook check: Biome basics and A Modern Desert Biome Warm up: Copy the graph below, title it Defining factor a biome: temperature and precipitation Pages 6 an based on regarding Learning scale:
Pages 6 Notebook check: Biome basics and A Modern Desert Biome Warm up: Copy the graph below, title it Defining factor a biome: temperature and precipitation Pages 6 an based on regarding Learning scale:
Through their research, geographers gather a great deal of data about Canada.
 Ecozones What is an Ecozone? Through their research, geographers gather a great deal of data about Canada. To make sense of this information, they often organize and group areas with similar features.
Ecozones What is an Ecozone? Through their research, geographers gather a great deal of data about Canada. To make sense of this information, they often organize and group areas with similar features.
The area on and near the Earth s surface where living things exist. The biosphere:
 The area on and near the Earth s surface where living things exist The biosphere: The Biosphere If you use an apple to model the world, which part of the apple would represent the biosphere? Today define:
The area on and near the Earth s surface where living things exist The biosphere: The Biosphere If you use an apple to model the world, which part of the apple would represent the biosphere? Today define:
ENVIRONMENTS and LIFE
 ENVIRONMENTS and LIFE part III The Terrestrial Realm Notes from (Stanley and Luczaj, 2015) Earth System History, Chapter 4 Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. A lynx, or bobcat, in the suburban Los Angeles chaparral
ENVIRONMENTS and LIFE part III The Terrestrial Realm Notes from (Stanley and Luczaj, 2015) Earth System History, Chapter 4 Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. A lynx, or bobcat, in the suburban Los Angeles chaparral
Define Ecology. study of the interactions that take place among organisms and their environment
 Ecology Define Ecology Define Ecology study of the interactions that take place among organisms and their environment Describe each of the following terms: Biosphere Biotic Abiotic Describe each of the
Ecology Define Ecology Define Ecology study of the interactions that take place among organisms and their environment Describe each of the following terms: Biosphere Biotic Abiotic Describe each of the
Ecological Levels of Organization
 Ecological Levels of Organization Foldable (outside): Map of Biomes Earth s Biomes Temperate Deciduous Forest Taiga/Coniferous Forest Tropical Rain Forest Grassland (Savanna) Desert Tundra Water Biomes
Ecological Levels of Organization Foldable (outside): Map of Biomes Earth s Biomes Temperate Deciduous Forest Taiga/Coniferous Forest Tropical Rain Forest Grassland (Savanna) Desert Tundra Water Biomes
Unit 1: Geography. For additional information, refer to this website: 1 G e o g r a p h y
 Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Name Hour. Chapter 4 Review
 Name Hour Chapter 4 Review 1. The average, year-after-year conditions of temperature and precipitation within a particular region are its weather. climate. greenhouse effect. d. biotic factors. 2. The
Name Hour Chapter 4 Review 1. The average, year-after-year conditions of temperature and precipitation within a particular region are its weather. climate. greenhouse effect. d. biotic factors. 2. The
Zoogeographic Regions. Reflective of the general distribution of energy and richness of food chemistry
 Terrestrial Flora & Fauna Part II In short, the animal and vegetable lines, diverging widely above, join below in a loop. 1 Asa Gray Zoogeographic Regions Reflective of the general distribution of energy
Terrestrial Flora & Fauna Part II In short, the animal and vegetable lines, diverging widely above, join below in a loop. 1 Asa Gray Zoogeographic Regions Reflective of the general distribution of energy
Abiotic Dominant Dominant Factors Plants Animals
 TERRESTRIAL BIOMES Abiotic Dominant Dominant Factors Plants Animals Tropical Rain Forest Hot & wet year round Ferns Woody vines Broad leaved evergreen trees Sloths Jaguars Monkeys Toucans Tropical Dry
TERRESTRIAL BIOMES Abiotic Dominant Dominant Factors Plants Animals Tropical Rain Forest Hot & wet year round Ferns Woody vines Broad leaved evergreen trees Sloths Jaguars Monkeys Toucans Tropical Dry
Biomes There are 2 types: Terrestrial Biomes (on land) Aquatic Biomes (in the water)
 Biomes There are 2 types: Terrestrial Biomes (on land) Aquatic Biomes (in the water) Terrestrial Biomes Grassland, Desert, and Tundra Biomes: Savanna Temperate grassland Chaparral Desert Tundra Chapter
Biomes There are 2 types: Terrestrial Biomes (on land) Aquatic Biomes (in the water) Terrestrial Biomes Grassland, Desert, and Tundra Biomes: Savanna Temperate grassland Chaparral Desert Tundra Chapter
Terms. divide headwaters tributary fall line fishery
 Chapter 5 Preview Section 1 The Land Objectives Identify some key similarities and differences in the physical geography of the United States and Canada. Explain why rivers have played such an important
Chapter 5 Preview Section 1 The Land Objectives Identify some key similarities and differences in the physical geography of the United States and Canada. Explain why rivers have played such an important
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 3 Content: Climate Zones Notes
 Introduction Latitude is such an important climate factor that you can make generalizations about a location's climate based on its latitude. Areas near the equator or the low latitudes are generally hot
Introduction Latitude is such an important climate factor that you can make generalizations about a location's climate based on its latitude. Areas near the equator or the low latitudes are generally hot
BIOMES. Definition of a Biome. Terrestrial referring to land. Climatically controlled sets of ecosystems. Characterized by distinct vegetation
 BIOMES An Introduction to the Biomes of the World Definition of a Biome Terrestrial referring to land Climatically controlled sets of ecosystems Characterized by distinct vegetation 1 In a Biome There
BIOMES An Introduction to the Biomes of the World Definition of a Biome Terrestrial referring to land Climatically controlled sets of ecosystems Characterized by distinct vegetation 1 In a Biome There
Biomes of the World. Plant and Animal Adaptations
 Biomes of the World Plant and Animal Adaptations Biomes and Adaptations Biome- A large geographic area with similar climate and a distinctive community of organisms. Adaptation- an anatomical, physiological,
Biomes of the World Plant and Animal Adaptations Biomes and Adaptations Biome- A large geographic area with similar climate and a distinctive community of organisms. Adaptation- an anatomical, physiological,
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS
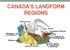 CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
BIO B.4 Ecology You should be able to: Keystone Vocabulary:
 Name Period BIO B.4 Ecology You should be able to: 1. Describe ecological levels of organization in the biosphere 2. Describe interactions and relationships in an ecosystem.. Keystone Vocabulary: Ecology:
Name Period BIO B.4 Ecology You should be able to: 1. Describe ecological levels of organization in the biosphere 2. Describe interactions and relationships in an ecosystem.. Keystone Vocabulary: Ecology:
Climax Vegetation is the natural vegetation in the last possible stage of vegetation development. Climax vegetation is stable and in balance with the
 Climax Vegetation is the natural vegetation in the last possible stage of vegetation development. Climax vegetation is stable and in balance with the climatic conditions. It should change very little if
Climax Vegetation is the natural vegetation in the last possible stage of vegetation development. Climax vegetation is stable and in balance with the climatic conditions. It should change very little if
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University February 7, 2017 What a difference from last year at this time. Temperatures in January and February
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University February 7, 2017 What a difference from last year at this time. Temperatures in January and February
Biomes. Chapter 4.4. Chapter 4.4
 Biomes Chapter 4.4 Chapter 4.4 What is a biome? Biomes are described in terms of abiotic factors and biotic factors. Each biome is associated with seasonal patterns of temperature and precipitation. Major
Biomes Chapter 4.4 Chapter 4.4 What is a biome? Biomes are described in terms of abiotic factors and biotic factors. Each biome is associated with seasonal patterns of temperature and precipitation. Major
forest tropical jungle swamp marsh prairie savanna pampas Different Ecosystems (rainforest)
 Different Ecosystems forest A region of land that is covered with many trees and shrubs. tropical jungle (rainforest) swamp A region with dense trees and a variety of plant life. It has a tropical climate.
Different Ecosystems forest A region of land that is covered with many trees and shrubs. tropical jungle (rainforest) swamp A region with dense trees and a variety of plant life. It has a tropical climate.
Biogeography. An ecological and evolutionary approach SEVENTH EDITION. C. Barry Cox MA, PhD, DSc and Peter D. Moore PhD
 Biogeography An ecological and evolutionary approach C. Barry Cox MA, PhD, DSc and Peter D. Moore PhD Division of Life Sciences, King's College London, Fmnklin-Wilkins Building, Stamford Street, London
Biogeography An ecological and evolutionary approach C. Barry Cox MA, PhD, DSc and Peter D. Moore PhD Division of Life Sciences, King's College London, Fmnklin-Wilkins Building, Stamford Street, London
The Big Break-Down of Biomes
 Let s Start at the Top! The Big Break-Down of Biomes Another fantabulous presentation by Mrs. Battistone This biome is found just south of the North Pole northern Canada, Northern Europe and Asia. - less
Let s Start at the Top! The Big Break-Down of Biomes Another fantabulous presentation by Mrs. Battistone This biome is found just south of the North Pole northern Canada, Northern Europe and Asia. - less
Biome- complex of terrestrial communities that cover a large area; characterized by soil, climate, plants, and animals Plants and animals vary by
 Major Land Biomes Biome- complex of terrestrial communities that cover a large area; characterized by soil, climate, plants, and animals Plants and animals vary by tolerance to temperature and precipitation
Major Land Biomes Biome- complex of terrestrial communities that cover a large area; characterized by soil, climate, plants, and animals Plants and animals vary by tolerance to temperature and precipitation
KEY UNDERSTANDING...In each biome, the unique characteristics of that biome s environment supports specific varieties of organisms!!
 Name Period Date Biomes of the World KEY UNDERSTANDING...In each biome, the unique characteristics of that biome s environment supports specific varieties of organisms!! Rain Forest Rainforests are generally
Name Period Date Biomes of the World KEY UNDERSTANDING...In each biome, the unique characteristics of that biome s environment supports specific varieties of organisms!! Rain Forest Rainforests are generally
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Land Biomes. Biome- geographic areas that have similar climates and ecosystems
 Land Biomes Land Biomes Biome- geographic areas that have similar climates and ecosystems Land Biomes The 6 most common biomes are: Tundra Taiga Temperate Deciduous Forest Tropical Rain Forest Grassland
Land Biomes Land Biomes Biome- geographic areas that have similar climates and ecosystems Land Biomes The 6 most common biomes are: Tundra Taiga Temperate Deciduous Forest Tropical Rain Forest Grassland
Biomes. Land. What are land biomes? Lesson. p 6.LS2.4, 6.ESS3.3 ESSENTIAL QUESTION
 Lesson 1 Land Biomes ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are land biomes? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the characteristics of different biomes that exist on land. The North American prairie
Lesson 1 Land Biomes ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are land biomes? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the characteristics of different biomes that exist on land. The North American prairie
Unit 2: Ecology. 3.1 What is Ecology?
 Unit 2: Ecology 3.1 What is Ecology? Ecologists study environments at different. - Ecology is the study of the interactions among, and between and their. An is an individual living thing, such as an alligator.
Unit 2: Ecology 3.1 What is Ecology? Ecologists study environments at different. - Ecology is the study of the interactions among, and between and their. An is an individual living thing, such as an alligator.
1.3 What are the needs of Organisms? *Autotrophs: organisms that can (i.e. plants) *Heterotrophs: organisms that (i.e. humans)
 1.3 What are the needs of Organisms? 5 Things Living Organisms Need 1- -Organisms get energy from in order to. *Autotrophs: organisms that can (i.e. plants) *Heterotrophs: organisms that (i.e. humans)
1.3 What are the needs of Organisms? 5 Things Living Organisms Need 1- -Organisms get energy from in order to. *Autotrophs: organisms that can (i.e. plants) *Heterotrophs: organisms that (i.e. humans)
Environmental Science: Biomes Test
 Name: Date: Pd. VERSION 1 Environmental Science: Biomes Test 1. Eland are large herbivores with loose skin under the throat and neck. This patch of skin aids in lowering the body temperature when temperatures
Name: Date: Pd. VERSION 1 Environmental Science: Biomes Test 1. Eland are large herbivores with loose skin under the throat and neck. This patch of skin aids in lowering the body temperature when temperatures
Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS
 Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS 1. aquatic biomes photic zone aphotic zone 2. 9 terrestrial (land) biomes tropical rain forest savannah (tropical
Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS 1. aquatic biomes photic zone aphotic zone 2. 9 terrestrial (land) biomes tropical rain forest savannah (tropical
UNIT 3. World Ecosystems
 UNIT 3 World Ecosystems Description and Review World Geography 3202 World Ecosystems Climax Vegetation Climax Vegetation is the natural vegetation in the last possible stage of vegetation development.
UNIT 3 World Ecosystems Description and Review World Geography 3202 World Ecosystems Climax Vegetation Climax Vegetation is the natural vegetation in the last possible stage of vegetation development.
GLOBAL CLIMATES FOCUS
 which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
Land Biomes. Biome- geographic areas that have similar climates and ecosystems
 Land Biomes Land Biomes Biome- geographic areas that have similar climates and ecosystems Land Biomes The 6 most common biomes are: Tundra Taiga Temperate Deciduous Forest Tropical Rain Forest Grassland
Land Biomes Land Biomes Biome- geographic areas that have similar climates and ecosystems Land Biomes The 6 most common biomes are: Tundra Taiga Temperate Deciduous Forest Tropical Rain Forest Grassland
AP Biology. Environmental factors. Earth s biomes. Marine. Tropical rainforest. Savanna. Desert. Abiotic factors. Biotic factors
 Earth s biomes Environmental factors Abiotic factors non-living chemical & physical factors temperature light water nutrients Biotic factors living components animals plants Marine Tropical rainforest
Earth s biomes Environmental factors Abiotic factors non-living chemical & physical factors temperature light water nutrients Biotic factors living components animals plants Marine Tropical rainforest
Terrestrial Flora and Fauna
 Terrestrial Flora & Fauna Part I In short, the animal and vegetable lines, diverging widely above, join below in a loop. 1 Asa Gray Terrestrial Flora and Fauna Ecosystems and Biomes Terrestrial Flora Terrestrial
Terrestrial Flora & Fauna Part I In short, the animal and vegetable lines, diverging widely above, join below in a loop. 1 Asa Gray Terrestrial Flora and Fauna Ecosystems and Biomes Terrestrial Flora Terrestrial
PHYTOG~EOGRAPHICAL REGIONS OF LABRADOR
 I of PHYTOG~EOGRAPHICAL REGIONS OF LABRADOR By I. Hustich" A s LONG ago as 1913 the great American botanist L. M. Fernald pointed out the necessity of dividing the Labrador peninsula into smaller phytogeographical
I of PHYTOG~EOGRAPHICAL REGIONS OF LABRADOR By I. Hustich" A s LONG ago as 1913 the great American botanist L. M. Fernald pointed out the necessity of dividing the Labrador peninsula into smaller phytogeographical
Environmental Science
 Environmental Science A Study of Interrelationships Cui Jiansheng Hebei University of Science and Technology CH06 Kinds of Ecosystems and Communities Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you
Environmental Science A Study of Interrelationships Cui Jiansheng Hebei University of Science and Technology CH06 Kinds of Ecosystems and Communities Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Climate Change in Canada
 1 Climate Change in Canada Climate change is an urgent, global concern. The implications of climate change are significant and far reaching, with the potential of impacting future generations throughout
1 Climate Change in Canada Climate change is an urgent, global concern. The implications of climate change are significant and far reaching, with the potential of impacting future generations throughout
soils E) the Coriolis effect causes the moisture to be carried sideways towards the earth's oceans, leaving behind dry land masses
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A biome is characterized primarily by A) flora and fauna. B) soil structure and flora. C) temperature
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A biome is characterized primarily by A) flora and fauna. B) soil structure and flora. C) temperature
Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 13 Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13) The definition of the term Physiography Physiography (n.) The science which treats of the earth's exterior physical features,
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 13 Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13) The definition of the term Physiography Physiography (n.) The science which treats of the earth's exterior physical features,
By Dava Swafford. Saturday, December 6, 14
 By Dava Swafford By Dava Swafford What is a Biome? Scientists have developed the term Biome to describe areas on the earth with similar climate, plants, and animals. The plants and animals that live in
By Dava Swafford By Dava Swafford What is a Biome? Scientists have developed the term Biome to describe areas on the earth with similar climate, plants, and animals. The plants and animals that live in
Name ECOLOGY TEST #1 Fall, 2014
 Name ECOLOGY TEST #1 Fall, 2014 Answer the following questions in the spaces provided. The value of each question is given in parentheses. Devote more explanation to questions of higher point value. 1.
Name ECOLOGY TEST #1 Fall, 2014 Answer the following questions in the spaces provided. The value of each question is given in parentheses. Devote more explanation to questions of higher point value. 1.
Chapter 6 Test: Species Interactions and Community Ecology
 ! Chapter 6 Test: Species Interactions and Community Ecology Graph and Figure Interpretation Questions Use the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 1) What does the diagram illustrate?
! Chapter 6 Test: Species Interactions and Community Ecology Graph and Figure Interpretation Questions Use the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 1) What does the diagram illustrate?
Biodiversity: Facts and figures (tables from the report)
 Vascular plant * Country Number Australia 15,638 Brazil 56,215 China 8,200 Colombia 32,200 Congo, Democratic Republic 11,007 Costa Rica 12,119 Ecuador 19,362 India 18,664 Indonesia 29,375 Madagascar 9,505
Vascular plant * Country Number Australia 15,638 Brazil 56,215 China 8,200 Colombia 32,200 Congo, Democratic Republic 11,007 Costa Rica 12,119 Ecuador 19,362 India 18,664 Indonesia 29,375 Madagascar 9,505
Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate
 Climate Global Climates Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate Keys to Climate Climate the average
Climate Global Climates Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate Keys to Climate Climate the average
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences
 Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Taxonomic diversity of skeletonized marine animal families during the Phanerozoic Spindle diagram of family diversification/extinction PNAS 1994. 91:6758-6763. Background
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Taxonomic diversity of skeletonized marine animal families during the Phanerozoic Spindle diagram of family diversification/extinction PNAS 1994. 91:6758-6763. Background
BIOMES AND ECOSYSTEMS
 BIOMES AND ECOSYSTEMS What is a biome? A biome is a group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms There are 6 major land biomes and 2 major water ecosystems? LAND (6): RAINFORESTS, DESERTS,
BIOMES AND ECOSYSTEMS What is a biome? A biome is a group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms There are 6 major land biomes and 2 major water ecosystems? LAND (6): RAINFORESTS, DESERTS,
remain on the trees all year long) Example: Beaverlodge, Alberta, Canada
 Coniferous Forest Temperature: -40 C to 20 C, average summer temperature is 10 C Precipitation: 300 to 900 millimeters of rain per year Vegetation: Coniferous-evergreen trees (trees that produce cones
Coniferous Forest Temperature: -40 C to 20 C, average summer temperature is 10 C Precipitation: 300 to 900 millimeters of rain per year Vegetation: Coniferous-evergreen trees (trees that produce cones
Module 3. Basic Ecological Principles
 Module 3. Basic Ecological Principles Ecosystem Components Abiotic Biotic Species & Habitat The Biomes of North America Communities Energy & Matter Cycles in Ecosystems Primary Productivity Simple Ecosystem
Module 3. Basic Ecological Principles Ecosystem Components Abiotic Biotic Species & Habitat The Biomes of North America Communities Energy & Matter Cycles in Ecosystems Primary Productivity Simple Ecosystem
Landforms and Bodies of Water
 Chapter 5, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 115 120. The Land Terms to Know divide A high point or ridge that determines the direction that rivers flow (page 118) headwaters The source waters of a
Chapter 5, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 115 120. The Land Terms to Know divide A high point or ridge that determines the direction that rivers flow (page 118) headwaters The source waters of a
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 4, 2019 Summary: December was mild and dry over much of the west, while the east was much warmer than
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 4, 2019 Summary: December was mild and dry over much of the west, while the east was much warmer than
Science Unit 1: Diversity in Ecosystems
 Science 1206 Unit 1: Diversity in Ecosystems Paradigms and Paradigm Shifts Paradigm - a belief held by society, based on general beliefs, such as morals, values and evidence. Paradigm shift - rare and
Science 1206 Unit 1: Diversity in Ecosystems Paradigms and Paradigm Shifts Paradigm - a belief held by society, based on general beliefs, such as morals, values and evidence. Paradigm shift - rare and
Our climate system is based on the location of hot and cold air mass regions and the atmospheric circulation created by trade winds and westerlies.
 CLIMATE REGIONS Have you ever wondered why one area of the world is a desert, another a grassland, and another a rainforest? Or have you wondered why are there different types of forests and deserts with
CLIMATE REGIONS Have you ever wondered why one area of the world is a desert, another a grassland, and another a rainforest? Or have you wondered why are there different types of forests and deserts with
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Community Ecology. Section 2 Terrestrial Biomes & Aquatic Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Table of Contents Section 1 Community Ecology Section 2 Terrestrial Biomes & Section 1 Community Ecology Evolution in Communities Interactions Among Species Some interactions
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Table of Contents Section 1 Community Ecology Section 2 Terrestrial Biomes & Section 1 Community Ecology Evolution in Communities Interactions Among Species Some interactions
Chapter 7 Part III: Biomes
 Chapter 7 Part III: Biomes Biomes Biome: the major types of terrestrial ecosystems determined primarily by climate 2 main factors: Temperature and precipitation Depends on latitude or altitude; proximity
Chapter 7 Part III: Biomes Biomes Biome: the major types of terrestrial ecosystems determined primarily by climate 2 main factors: Temperature and precipitation Depends on latitude or altitude; proximity
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities Section Objectives: Identify some common limiting factors. Explain how limiting factors and ranges of tolerance affect distribution of organisms. Sequence the stages
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities Section Objectives: Identify some common limiting factors. Explain how limiting factors and ranges of tolerance affect distribution of organisms. Sequence the stages
Elements of weather and climate Temperature Range of temperature Seasonal temperature pattern Rainfall
 Climate Earth Science Chapter 20 Pages 560-573 Elements of weather and climate Temperature Range of temperature Seasonal temperature pattern Rainfall Overall rainfall Seasonal distribution of rainfall
Climate Earth Science Chapter 20 Pages 560-573 Elements of weather and climate Temperature Range of temperature Seasonal temperature pattern Rainfall Overall rainfall Seasonal distribution of rainfall
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
EKOLOGI BIOMA (BIOME) TEMA 10. Program Studi Tadris Biologi Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan Institut Agama Islam Negeri Jember
 EKOLOGI TEMA 10 BIOMA (BIOME) Program Studi Tadris Biologi Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan Institut Agama Islam Negeri Jember What is difference of this picture????? Why are they different????? Have
EKOLOGI TEMA 10 BIOMA (BIOME) Program Studi Tadris Biologi Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan Institut Agama Islam Negeri Jember What is difference of this picture????? Why are they different????? Have
Ecosystems. Section 4.2/pg.62. Life Beneath a Log 9/22/2014. What determines where an organism can live?
 Ecosystems Section 4.2/pg.62 Biology 309 Chapter 4 What determines where an organism can live? Every species has its own range of tolerance ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental
Ecosystems Section 4.2/pg.62 Biology 309 Chapter 4 What determines where an organism can live? Every species has its own range of tolerance ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental
Chapter 4.3 Biomes. Slide 1 of 42. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Chapter 4.3 Biomes 1 of 42 2 of 42 Biomes A biome is a complex or group, of terrestrial or water communities that covers a large area characterized by certain soil and climate conditions is home to different
Chapter 4.3 Biomes 1 of 42 2 of 42 Biomes A biome is a complex or group, of terrestrial or water communities that covers a large area characterized by certain soil and climate conditions is home to different
10/6/ th Grade Ecology and the Environment. Chapter 2: Ecosystems and Biomes
 7 th Grade Ecology and the Environment Chapter 2: Ecosystems and Biomes Lesson 1 (Energy Flow in Ecosystems) Each organism in an ecosystem fills an energy role. Producer an organism that can make its own
7 th Grade Ecology and the Environment Chapter 2: Ecosystems and Biomes Lesson 1 (Energy Flow in Ecosystems) Each organism in an ecosystem fills an energy role. Producer an organism that can make its own
4-3 Biomes. biology. 4-3 Biomes. Biomes. Slide 1 of 54. Slide 2 of 54. Slide 3 of 54. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 54 2 of 54 Biomes A biome is a complex of terrestrial communities that covers a large area and is characterized by certain soil and climate conditions and particular assemblages of plants
biology 1 of 54 2 of 54 Biomes A biome is a complex of terrestrial communities that covers a large area and is characterized by certain soil and climate conditions and particular assemblages of plants
How does the greenhouse effect maintain the biosphere s temperature range? What are Earth s three main climate zones?
 Section 4 1 The Role of Climate (pages 87 89) Key Concepts How does the greenhouse effect maintain the biosphere s temperature range? What are Earth s three main climate zones? What Is Climate? (page 87)
Section 4 1 The Role of Climate (pages 87 89) Key Concepts How does the greenhouse effect maintain the biosphere s temperature range? What are Earth s three main climate zones? What Is Climate? (page 87)
Biomes Section 2. Chapter 6: Biomes Section 2: Forest Biomes DAY ONE
 Chapter 6: Biomes Section 2: Forest Biomes DAY ONE Of all the biomes in the world, forest biomes are the most widespread and the most diverse. The large trees of forests need a lot of water, so forests
Chapter 6: Biomes Section 2: Forest Biomes DAY ONE Of all the biomes in the world, forest biomes are the most widespread and the most diverse. The large trees of forests need a lot of water, so forests
Biomes of the World Roxanne Coffey Ms. Coffey
 Biomes of the World Roxanne Coffey Ms. Coffey DECIDUOUS FOREST DESCRIPTION The Deciduous Forest is a biome that is found throughout many parts of the world. It can be found on the Eastern side of North
Biomes of the World Roxanne Coffey Ms. Coffey DECIDUOUS FOREST DESCRIPTION The Deciduous Forest is a biome that is found throughout many parts of the world. It can be found on the Eastern side of North
Guided Reading Activity
 Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Physical Features Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? A Vast Land Directions: Read the lesson and use your text to decide whether each
Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Physical Features Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? A Vast Land Directions: Read the lesson and use your text to decide whether each
Section Objectives: The result is that conditions in one part of the world are suitable for supporting certain forms of life, but not others.
 Section Objectives: Identify some common limiting factors. Explain how limiting factors and ranges of tolerance affect distribution of organisms. Sequence the stages of ecological succession. Describe
Section Objectives: Identify some common limiting factors. Explain how limiting factors and ranges of tolerance affect distribution of organisms. Sequence the stages of ecological succession. Describe
Lecture 24 Plant Ecology
 Lecture 24 Plant Ecology Understanding the spatial pattern of plant diversity Ecology: interaction of organisms with their physical environment and with one another 1 Such interactions occur on multiple
Lecture 24 Plant Ecology Understanding the spatial pattern of plant diversity Ecology: interaction of organisms with their physical environment and with one another 1 Such interactions occur on multiple
Quizizz. Mean Green Science: Interdependency Date and: Life Science Quiz 2. Name : Class : What is a producer?
 Quizizz Name : Class : Mean Green Science: Interdependency Date and: Life Science Quiz 2 1. What is a producer? a) an organism that gets energy from eating other organisms c) an organism that gets energy
Quizizz Name : Class : Mean Green Science: Interdependency Date and: Life Science Quiz 2 1. What is a producer? a) an organism that gets energy from eating other organisms c) an organism that gets energy
The Great Ice Ages. Copyright abcteach.com 2001 Graphics from Art Today
 The Great Ice Ages The Great Ice Ages occurred during the Pleistocene epoch. The word epoch means time period. This period began about 2.5 million years ago and ended roughly 10,000 years ago. During the
The Great Ice Ages The Great Ice Ages occurred during the Pleistocene epoch. The word epoch means time period. This period began about 2.5 million years ago and ended roughly 10,000 years ago. During the
Unit 4: Terrestrial ecosystems and resources
 Unit 4: Terrestrial ecosystems and resources Chapter 5: Climate and terrestrial biodiversity > Climate > Terrestrial Ecosystems Chapter 10: Sustaining biodiversity (ecosystem approach) Chapter 11: Sustaining
Unit 4: Terrestrial ecosystems and resources Chapter 5: Climate and terrestrial biodiversity > Climate > Terrestrial Ecosystems Chapter 10: Sustaining biodiversity (ecosystem approach) Chapter 11: Sustaining
Chapter 1: America s Land Lesson 1: Land and Climate
 Chapter 1: America s Land Lesson 1: Land and Climate Geography: Describe landforms and other physical features of the United States. Geography: Explain how and why climate varies throughout the United
Chapter 1: America s Land Lesson 1: Land and Climate Geography: Describe landforms and other physical features of the United States. Geography: Explain how and why climate varies throughout the United
