Tracking down protein-protein interaction via FRET-system using site-specific thiol-labeling
|
|
|
- Anna Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Tracking down protein-protein interaction via FRET-system using site-specific thiol-labeling B. Söveges, a T. Imre, b Á. L. Póti, c P. Sok, c Zs. Kele, a A. Alexa, c P. Kele a and K. Németh* a a. Research Centre for Natural Sciences of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chemical Biology Research Group, H-1117 Budapest, Magyar tudósok krt. 2, Hungary. nemeth.krisztina@ttk.mta.hu; Tel: b. Research Centre for Natural Sciences of Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Instrumentation Center, MS Metabolomics Research Group; H-1117 Budapest, Magyar tudósok krt. 2., Hungary. c. Research Centre for Natural Sciences of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Enzymology, Protein Research Group, H-1117 Budapest, Magyar tudósok krt. 2, Hungary. Supporting information Content S1. Mass spectra of the intact protein... 2 S2. Identification of labeling site... 9 S3. LC-MS analysis of Cy3-labeled pepmk S3. Accessible surface area calculations S4. Evaluation of non-specific labeling S5. Identification of the FRET-pair dyes S6. Evaluation of K d values S7. K d of p38 C162S and pepmk S8. Protein-protein FRET measurements S9. Characterization of the compounds S10. References
2 S1. Mass spectra of the intact protein The molecular weights of the intact unmodified and labeled p38 C162S and MK2 were identified using a Triple TOF hybrid Quadrupole-TOF LC/MS/MS system (Sciex, Singapore, Woodlands) equipped with a DuoSpray IonSource coupled with a Perkin Elmer Series 200 micro-lc system (Massachusetts, USA) consisting of binary pump and an autosampler. Data acquisition and processing were performed using Analyst TF software version (AB Sciex Instruments, CA, USA). Chromatographic separation was achieved by Phenomenex Aeris Widepore XB-C8 (50 mm 2.1 mm, 3.6 µm, 200 Å) HPLC column. Sample was eluted in gradient elution mode using solvent A (0.1% formic acid in water) and solvent B (0.1% formic acid in CH 3 CN). The initial condition was 20% B, followed by a linear gradient reaching 90% B within 5 min, from 5 to 6 min 90% B was retained; and from 6 to 6.5 min back to initial condition with 20% eluent B and kept from 6.5 to 9.5 min. Flow rate was set to 0.25 ml/min. The column temperature was set at room temperature and the injection volume was 5 µl. Nitrogen was used as the nebulizer gas (GS1), heater gas (GS2), and curtain gas with the optimum values set at 30, 30 and 35 (arbitrary units), respectively. Data were acquired in positive electrospray mode in the mass range of m/z=500 to 2500, with 1 s accumulation time. The source temperature was 350 C and the spray voltage was set to 5500 V. Declustering potential value was set to 80 V. Peak View Software TM V.2.2 (version 2.2, Sciex, Redwood City, CA, USA) was used for deconvoluting the raw electrospray data to obtain the neutral molecular masses. In order to demonstrate thiol selectivity of our heterobifunctional linker GSH linker 10 conjugate was studied in MS-MS mode, with mass range of m/z=100 to 1500 and 1 s accumulation time. Declustering potential value was set to 80 V, and collision energy to 35 ev. The presence of ions m/z=458 and m/z=558 proves that the linker binds to sulfur not to amino nitrogen (Fig. S1). (These fragments can only be formed when the linker binds to the sulfur atom of cysteine.) The high-resolution data support the elemental composition of these fragment ions. 2
3 Fig. S1. ESI MS-MS spectra of GSH linker 10 conjugate. Efficiency of fluorescent labeling process was verified by intact protein MS. After deconvolution of protein spectra, the measured protein mass for sample p38 C162S was Da (Fig. S2). The spectrum contained several adduct peaks as well, which gave additional peaks in automated deconvolution. After incubation (10 min at room temperature) of the intact protein (60 µm) with the heterobifunctional linker 10 (120 µm) the peak of the untreated protein disappeared and the mono-conjugated species at Da appeared (Fig. S3). 100% conversion was detected after 10 minutes of addition of dye 11 (240 µm). This peak at Da corresponds to the mono-derivatized form of p38 C162S (Fig. S4). In case of dyes the same efficiency was observed (Fig. S5 8) however, a negligible amount of double-conjugated variant could also be detected (<10%). In case of MK2 protein the untreated form was detected at Da molecular mass (Fig. S9). Upon addition of the linker 10 in two-fold molar excess, the peak of the original protein diminished and two new peaks evolved corresponding to the mono- and double-derivatized species of MK2 protein (Fig. S10). Fluorescent labeling with dye 12 showed similar results as demonstrated for p38 C162S. 3
4 Fig. S2. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the intact and unmodified p38 C162S. Fig. S3. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the linker 10 conjugated p38 C162S. 4
5 Fig. S4. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the linker 10 conjugated and the dye 11 modified p38 C162S. Fig. S5. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the linker 10 conjugated and the dye 12 modified p38 C162S. 5
6 Fig. S6. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the linker 10 conjugated and the dye 13 modified p38 C162S. Fig. S7. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the linker 10 conjugated and the dye 14 modified p38 C162S. 6
7 Fig. S8. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the linker 10 conjugated and the dye 15 modified p38 C162S. 7
8 Fig. S9. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the intact and unmodified MK2 protein. Fig. S10. Deconvoluted ESI-MS spectrum of the linker 10 conjugated MK2 protein. 8
9 S2. Identification of labeling site In order to identify the labeling site of p38 C162S and MK2 protein the Cys containing peptide fragments obtained by tryptic digestion of the proteins were investigated by LC-MS/MS. Untreated and derivatized samples were compared. In p38 C162S the Cys 119 was labeled by compound 9 (Fig. S11). The possible labeling site of MK2 could be the Cys 98, 140, and 224 according to the ASA values (Table S1). The decrease of the amount of the peptide fragments in the conjugated samples given in the percentage of the referring untreated ones was significant in the case of Cys 224 (96%) and Cys 98 (69%) (Table S2). Sample preparation for the tryptic digestion. The method for proteolysis was adapted from that developed previously for AGP. 1 Briefly, 50 µl of MK2 and p38 (2 mg/ml, 50 µm, 2.5 nmol) with or without pretreatment and 10 μl 0.2% (w/v) RapiGest SF solution buffered with 50 mm NH 4 HCO 3 were mixed. 2 µl of 45 mm DTT in 100 mm NH 4 HCO 3 were added and kept at 37.5 C for 30 min. After cooling the sample to room temperature, 2.5 μl of 100 mm iodoacetamide in 100 mm NH 4 HCO 3 were added and placed in the dark for 30 min. The reduced and alkylated protein was then digested by 5 μl (2 mg/ml) trypsin (the enzyme to protein ratio was 1/10). The sample was incubated overnight at 37 C. Sample preparation for mass spectrometry. To degrade the surfactant, 7 μl of formic acid (500 mm) solution was added to the digested protein sample to have the final concentration between 30 and 50 mm (ph 2) and was incubated at 37 C for 45 min. For LC-MS analysis the acid treated sample was centrifuged for 10 min at rpm. LC-MS/MS measurements of tryptic digest of p38 and MK2. QTRAP 6500 triple quadruple linear ion trap mass spectrometer, equipped with a Turbo V source in electrospray mode (AB Sciex, CA, USA) and a Perkin Elmer Series 200 micro LC system (Massachusetts, USA) was used for LC-MS/MS analysis. Data acquisition and processing were performed using Analyst software version (AB Sciex Instruments, CA, USA). Chromatographic separation was achieved by using the Vydac 218 TP52 Protein & Peptide C 18 column (250 mm 2.1 mm, 5 μm). The sample was eluted with a gradient of solvent A (0.1% formic acid in water) and solvent B (0.1% formic acid in CH 3 CN). The flow rate was set to 0.2 ml min 1. The initial conditions for separation were 5% B for 3 min, followed by a linear gradient to 25% B by 27 min (from 3 to 30 min) and from 30 to 40 min to 90%. Then from 40 to 45 min 90% B is retained; from 45 to 50 min back to the initial conditions with 5% eluent B retained to 53 min. The injection volume was 10 μl (300 pmol on the column). Information Dependent Acquisiton (IDA) LC-MS/MS experiment was carried out to identify the modified tryptic MK2 and p38 peptide fragments. Enhanced MS scan (EMS) was applied as survey scan and enhanced product ion (EPI) was the dependent scan. The collision energy in EPI experiments was set to rolling collision energy mode, where the actual value was set on the basis of the mass and charge state of the selected ion. Further IDA criteria: ions greater than m/z, which exceeds 106 counts, exclude former target ions for 30 seconds after 2 occurrence(s). In EMS and in EPI mode the scan rate was 1000 Da/s as well. Nitrogen was used as the nebulizer gas (GS1), heater gas (GS2), and curtain gas with the optimum values set at 50, 40 and 40 (arbitrary units). The source temperature was 350 C and the ion spray 9
10 voltage was set to 5000 V. Declustering potential value was set to 150 V. GPMAW 4.2. software and ProteinProspector ( was used to analyse the large number of MS-MS spectra and identify the modified tryptic MK2 and p38 peptides. Fig. S11. a) Selected ion chromatogram (XIC) of m/z p38 C162S [ ] peptide fragment conjugated with compound 9; b) MS/MS mass spectrum of p38 C162S [ ] peptide fragment conjugated with compound 9. 10
11 S3. LC-MS analysis of Cy3-labeled pepmk2 A Sciex 6500 QTRAP triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometer, equipped with a Turbo V Source in electrospray mode (Sciex, CA, USA) and a Perkin Elmer Series 200 micro LC system (Massachusetts, USA) consisting of binary pump and an autosampler was used for LC MS analysis. Data acquisition and processing were performed using Analyst software version (AB Sciex Instruments, CA, USA). Chromatographic separation was achieved by Purospher STAR RP-18 endcapped (55 mm 2.1mm, 3µm) LiChocart 55-2 HPLC Cartridge. Sample was eluted with gradient elution using solvent A (0.1% formic acid in water) and solvent B (0.1% formic acid in CH 3 CN). Flow rate was set to 0.5 ml/min. The initial condition was 5% B for 2 min, followed by a linear gradient to 95% B by 4 min, from 6 to 8 min 95% B was retained; and from 8 to 8.5 min back to initial condition with 5% eluent B and retained to 14 min. The column temperature was kept at room temperature and the injection volume was 10 µl. Nitrogen was used as the nebulizer gas (GS1), heater gas (GS2), and curtain gas with the optimum values set at 35, 45 and 45 (arbitrary units). Data were acquired in positive ionization mode from m/z=100 to 2000 in 1.7 sec. The source temperature was 450 C and the spray voltage was set at 5000 V. Declustering potential value was set to 150 V. Figure S12. a) Selected ion chromatogram (XIC) of m/z 602 [M+6H] 6+ ion of Cy3-labeled pepmk2; b) ESI mass spectrum of Cy3-labeled pepmk2 (MW=3602). 11
12 S3. Accessible surface area calculations Table S1. The solvent accessible surface area of the cysteines of p38 C162S and MK2 based on the calculations of the online prediction toolkit ( The most accessible cysteines are highlighted. Protein PDB ID Cys ASA RSA p38 C162S 2Y8O MK2 2OZA Table S2. Site specific labeling of linker 10 on MK2 protein. Peptide fragment Cys position Untreated Cy3-conjugated MK2 MK2 Normalized intensity Remaining nonderivatized form (%) ;
13 S4. Evaluation of non-specific labeling p38 protein was incubated with four-fold excess of the fluorescent dyes with or without the pretreatment of the heterobifunctional linker 10. After purification the fluorescent intensities of the samples were measured. The ratios of the non-specific (non-covalent) association of the fluorescent dyes given in the percentage of the specific ones was negligible since did not exceeded 7% (Table S3). Table S3. Ratio of the aspecific labeling of p38 C162S with linker 10 and the fluorescent dyes. The fluorescence intensity of the different dyes was measured at the following wavelengths ( exc / em in nm 11: 434/482; 12: 580/600; 13: 515/602; 14: 530/630; 15: 670/692). Dye Fluorescence intensity (RFU) with 10 without 10 %
14 S5. Identification of the FRET-pair dyes Fig. S13. The excitation and emission spectra of the possible FRET-pair dyes. S6. Evaluation of K d values K d was calculated in Originlab sofware (ver.9) using non-linear regression according to the following equation: where I = I min + (I max I min ) (T 0 + K 0 + K d (T 0 + K 0 + K d ) 2 4T 0 K 0 ) 2K 0 I min the FRET efficiency at the minimum point, I max the FRET efficiency at the maximum point, T 0 the concentration of the MK2 / pepmk2 at the given point, K 0 the constant concentration of the p38, K d the dissociation constant of the two interacting partners. 14
15 S7. K d of p38 C162S and pepmk2 A slight difference was recorded between literature data (50 nm for p38 wt and CF-pepMK2 wt in FP buffer) and our K d value obtained by FRET (240 nm in PBS) for Cy1-labeled p38 C162S and Cy3-conjugated pepmk2. The difference between those values is attributed to several alterations between the conditions of the two measurements: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) the method: fluorescence polarization vs. FRET efficiency the buffer composition including ph and ionic strength: FP buffer [20 mm Tris (ph 8.0), 100 mm NaCl, 0.05% Brij35P, and 2 mm DTT] vs. PBS [ 10 mm Na 2 HPO 4, 1.8 mm KH 2 PO 4, 137 mm NaCl, 2.7 mm KCl, (ph7.4)] the labeling fluorophore: fluorescein at N-terminal amino group vs. Cy3 on thiol group at N-terminal Cys the AA composition of the protein at position 162 (in docking site) wild type: Cys vs. mutant: Ser the peptide sequence: IKIKKIEDASNPLLLKRRKK vs CQIKIKKIEDASNPLLLKRRKK. In order to assess the background of the differences between K d values we measured several combinations of wild type and mutant protein with the peptide in different buffers with an orthogonal method. While the changes in fluorescent intensity of Cy3-pepMK2 were proportional to the concentration of the protein we estimated dissociation constants based on this titration. The K d value for unlabeled p38 wt with Cy3-conjugated pepmk2 in FP and PBS buffer was 175 nm (not shown) and 314 nm, respectively (Fig. S14a). Accordingly, not only the buffer composition can alter the affinity but the additional CQ amino acids at the N-terminal of the peptide increased the dissociation constant compared to the literature data (50 nm). K d for unlabeled mutant p38 C162S and Cy3-conjugated pepmk2 in PBS was 96 nm (Fig. S14b) and after labeling p38 C162S with Cy1 the same constant was 49 nm (Fig. S14c). In summary, the association of p38 and MK2 peptide could slightly differ if we changed the composition, the ionic strength and ph of the buffer as well as it depended on the measuring method, the peptide sequence and the labeling fluorophore and moreover the type of protein residue at 162 position. 15
16 a) Fluorescence intensity (AU) p38 wt concentration ( M) b) Fluorescence intensity (AU) p38 C162S concentration ( M) c) 700 Fluorescence intensity (AU) p38 C162S concentration ( M) Fig. S14. Binding of unlabeled p38 wt (a) or unlabeled (b) and Cy1-conjugated (c) p38 C162S to Cy3- pepmk2. 16
17 S8. Protein-protein FRET measurements 1.0 Fluorescence intensity (RFU) Wavelength (nm) Fig S15. Fluorescence intensity of the Cy1-labeled p38 C162S in the presence of unlabeled MK2 at the respective concentrations. 17
18 S9. Characterization of the compounds Fig S16. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra of tert-butyl (2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl)carbamate (2). 18
19 Fig S17. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra 2-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)ethoxy)ethyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate (3). 19
20 Fig S18. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra of ethyl 4-(2-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)-amino)ethoxy)ethoxy)benzoate (4). 20
21 Fig S19. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra of tert-butyl (2-(2-(4-(hydrazinecarbonyl)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethyl)carbamate (5). 21
22 Fig S20. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra of tert-butyl (2-(2-(4-(5-mercapto-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2- yl)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethyl)carbamate (6). 22
23 Fig S21. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra of tert-butyl (2-(2-(4-(5-(methylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2- yl)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethyl)carbamate (7). 23
24 Fig S22. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra of tert-butyl (2-(2-(4-(5-(methylsulfonyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2- yl)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethyl)carbamate (8). 24
25 Fig S23. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra of 2-(2-(4-(5-(methylsulfonyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethan-1- aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (9). 25
26 Fig S24. 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra of bicyclo[6.1.0]non-4-yn-9-ylmethyl (2-(2-(4-(5-(methylsulfonyl)-1,3,4- oxadiazol-2-yl)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethyl)carbamate (10). 26
27 S10. References 1. T. Imre, G. Schlosser, G. Pocsfalvi, R. Siciliano, É. Molnár-Szöllősi, T. Kremmer, A. Malorni, K. Vékey, J. Mass Spectrom., 2005, 40,
Profiling of Diferulates (Plant Cell Wall Cross- Linkers) Using Ultrahigh-performance Liquid. Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Supporting Information for: Profiling of Diferulates (Plant Cell Wall Cross- Linkers) Using Ultrahigh-performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Ramin Vismeh a,b, Fachuang Lu c,d, Shishir
Supporting Information for: Profiling of Diferulates (Plant Cell Wall Cross- Linkers) Using Ultrahigh-performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Ramin Vismeh a,b, Fachuang Lu c,d, Shishir
Improved 6- Plex TMT Quantification Throughput Using a Linear Ion Trap HCD MS 3 Scan Jane M. Liu, 1,2 * Michael J. Sweredoski, 2 Sonja Hess 2 *
 Improved 6- Plex TMT Quantification Throughput Using a Linear Ion Trap HCD MS 3 Scan Jane M. Liu, 1,2 * Michael J. Sweredoski, 2 Sonja Hess 2 * 1 Department of Chemistry, Pomona College, Claremont, California
Improved 6- Plex TMT Quantification Throughput Using a Linear Ion Trap HCD MS 3 Scan Jane M. Liu, 1,2 * Michael J. Sweredoski, 2 Sonja Hess 2 * 1 Department of Chemistry, Pomona College, Claremont, California
Information Dependent Acquisition (IDA) 1
 Information Dependent Acquisition (IDA) Information Dependent Acquisition (IDA) enables on the fly acquisition of MS/MS spectra during a chromatographic run. Analyst Software IDA is optimized to generate
Information Dependent Acquisition (IDA) Information Dependent Acquisition (IDA) enables on the fly acquisition of MS/MS spectra during a chromatographic run. Analyst Software IDA is optimized to generate
Quantitation of a target protein in crude samples using targeted peptide quantification by Mass Spectrometry
 Quantitation of a target protein in crude samples using targeted peptide quantification by Mass Spectrometry Jon Hao, Rong Ye, and Mason Tao Poochon Scientific, Frederick, Maryland 21701 Abstract Background:
Quantitation of a target protein in crude samples using targeted peptide quantification by Mass Spectrometry Jon Hao, Rong Ye, and Mason Tao Poochon Scientific, Frederick, Maryland 21701 Abstract Background:
Application Note LCMS-112 A Fully Automated Two-Step Procedure for Quality Control of Synthetic Peptides
 Application Note LCMS-112 A Fully Automated Two-Step Procedure for Quality Control of Synthetic Peptides Abstract Here we describe a two-step QC procedure for synthetic peptides. In the first step, the
Application Note LCMS-112 A Fully Automated Two-Step Procedure for Quality Control of Synthetic Peptides Abstract Here we describe a two-step QC procedure for synthetic peptides. In the first step, the
LC-MS Based Metabolomics
 LC-MS Based Metabolomics Analysing the METABOLOME 1. Metabolite Extraction 2. Metabolite detection (with or without separation) 3. Data analysis Metabolite Detection GC-MS: Naturally volatile or made volatile
LC-MS Based Metabolomics Analysing the METABOLOME 1. Metabolite Extraction 2. Metabolite detection (with or without separation) 3. Data analysis Metabolite Detection GC-MS: Naturally volatile or made volatile
Technical Note. Introduction
 Technical Note Analysis and Characterization of Psilocybin and Psilocin Using Liquid Chromatography - Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS) with Collision-Induced-Dissociation (CID) and
Technical Note Analysis and Characterization of Psilocybin and Psilocin Using Liquid Chromatography - Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS) with Collision-Induced-Dissociation (CID) and
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37 Most analytes separated by HPLC are thermally stable and non-volatile (liquids) (unlike in GC) so not ionized easily by EI or CI techniques. MS must be at
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37 Most analytes separated by HPLC are thermally stable and non-volatile (liquids) (unlike in GC) so not ionized easily by EI or CI techniques. MS must be at
Tandem mass spectra were extracted from the Xcalibur data system format. (.RAW) and charge state assignment was performed using in house software
 Supplementary Methods Software Interpretation of Tandem mass spectra Tandem mass spectra were extracted from the Xcalibur data system format (.RAW) and charge state assignment was performed using in house
Supplementary Methods Software Interpretation of Tandem mass spectra Tandem mass spectra were extracted from the Xcalibur data system format (.RAW) and charge state assignment was performed using in house
Accurate Mass Measurement for Intact Proteins using ESI-oa-TOF. Application Note. Donghui Yi and Christine Miller Agilent Technologies
 Accurate Mass Measurement for Intact Proteins using ESI-oa-TOF Application Note Donghui Yi and Christine Miller Jon D. Williams, GlaxoSmithKline Introduction Mass spectrometry (MS) has become a core technology
Accurate Mass Measurement for Intact Proteins using ESI-oa-TOF Application Note Donghui Yi and Christine Miller Jon D. Williams, GlaxoSmithKline Introduction Mass spectrometry (MS) has become a core technology
Confirmation of In Vitro Nefazodone Metabolites using the Superior Fragmentation of the QTRAP 5500 LC/MS/MS System
 Confirmation of In Vitro Nefazodone Metabolites using the Superior Fragmentation of the QTRAP 5500 LC/MS/MS System Claire Bramwell-German, Elliott Jones and Daniel Lebre AB SCIEX, Foster City, California
Confirmation of In Vitro Nefazodone Metabolites using the Superior Fragmentation of the QTRAP 5500 LC/MS/MS System Claire Bramwell-German, Elliott Jones and Daniel Lebre AB SCIEX, Foster City, California
Methods for proteome analysis of obesity (Adipose tissue)
 Methods for proteome analysis of obesity (Adipose tissue) I. Sample preparation and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric analysis Instruments, softwares, and materials AB SCIEX Triple TOF 5600
Methods for proteome analysis of obesity (Adipose tissue) I. Sample preparation and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric analysis Instruments, softwares, and materials AB SCIEX Triple TOF 5600
AB SCIEX SelexION Technology Used to Improve Mass Spectral Library Searching Scores by Removal of Isobaric Interferences
 AB SCIEX SelexION Technology Used to Improve Mass Spectral Library Searching s by Removal of Isobaric Interferences Differential Mobility Used as a Tool to Address Selectivity Challenges Adrian M. Taylor
AB SCIEX SelexION Technology Used to Improve Mass Spectral Library Searching s by Removal of Isobaric Interferences Differential Mobility Used as a Tool to Address Selectivity Challenges Adrian M. Taylor
Rapid Distinction of Leucine and Isoleucine in Monoclonal Antibodies Using Nanoflow. LCMS n. Discovery Attribute Sciences
 Rapid Distinction of Leucine and Isoleucine in Monoclonal Antibodies Using Nanoflow LCMS n Dhanashri Bagal *, Eddie Kast, Ping Cao Discovery Attribute Sciences Amgen, South San Francisco, California, United
Rapid Distinction of Leucine and Isoleucine in Monoclonal Antibodies Using Nanoflow LCMS n Dhanashri Bagal *, Eddie Kast, Ping Cao Discovery Attribute Sciences Amgen, South San Francisco, California, United
Analyst Software. Peptide and Protein Quantitation Tutorial
 This document is provided to customers who have purchased AB Sciex equipment to use in the operation of such AB Sciex equipment. This document is copyright protected and any reproduction of this document
This document is provided to customers who have purchased AB Sciex equipment to use in the operation of such AB Sciex equipment. This document is copyright protected and any reproduction of this document
Application Note. Edgar Naegele. Abstract
 Fast identification of main drug metabolites by quadrupole time-of-flight LC/MS Measuring accurate MS and MS/MS data with the Agilent 651 Q-TOF LC/MS and identification of main meta-bolites by comparison
Fast identification of main drug metabolites by quadrupole time-of-flight LC/MS Measuring accurate MS and MS/MS data with the Agilent 651 Q-TOF LC/MS and identification of main meta-bolites by comparison
Quantitative Analysis and Identification of Migrants in Food Packaging Using LC-MS/MS
 Quantitative Analysis and Identification of Migrants in Food Packaging Using LC-MS/MS Cécile Busset 1 and Stephen J. Lock 2 1 AB SCIEX, Paris (France); 2 AB SCIEX, Warrington, Cheshire (U.K.) Introduction
Quantitative Analysis and Identification of Migrants in Food Packaging Using LC-MS/MS Cécile Busset 1 and Stephen J. Lock 2 1 AB SCIEX, Paris (France); 2 AB SCIEX, Warrington, Cheshire (U.K.) Introduction
Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4.
 Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4. Field Desorption 5. MS MS techniques Matrix assisted
Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4. Field Desorption 5. MS MS techniques Matrix assisted
MS-based proteomics to investigate proteins and their modifications
 MS-based proteomics to investigate proteins and their modifications Francis Impens VIB Proteomics Core October th 217 Overview Mass spectrometry-based proteomics: general workflow Identification of protein
MS-based proteomics to investigate proteins and their modifications Francis Impens VIB Proteomics Core October th 217 Overview Mass spectrometry-based proteomics: general workflow Identification of protein
EPA Method 535: Detection of Degradates of Chloroacetanilides and other Acetamide Herbicides in Water by LC/MS/MS
 EPA Method 535: Detection of Degradates of Chloroacetanilides and other Acetamide Herbicides in Water by LC/MS/MS Christopher Borton AB SCIEX Golden, Colorado verview Described here is the analysis of
EPA Method 535: Detection of Degradates of Chloroacetanilides and other Acetamide Herbicides in Water by LC/MS/MS Christopher Borton AB SCIEX Golden, Colorado verview Described here is the analysis of
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Discovery of Hydrocarbon-Stapled Short α-helical Peptides as Promising Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Fusion Inhibitors Chao Wang,, Shuai Xia,, Peiyu Zhang,
Supporting Information Discovery of Hydrocarbon-Stapled Short α-helical Peptides as Promising Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Fusion Inhibitors Chao Wang,, Shuai Xia,, Peiyu Zhang,
Quantitative analysis of mitragynine in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
 Quantitative analysis of mitragynine in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry Shijun Lua, Buu N. Trana, Jamie L. Nelsenb, Kenneth M. Aldousa. Journal of Chromatography
Quantitative analysis of mitragynine in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry Shijun Lua, Buu N. Trana, Jamie L. Nelsenb, Kenneth M. Aldousa. Journal of Chromatography
Overview. Introduction. André Schreiber AB SCIEX Concord, Ontario (Canada)
 Quantitation and Identification of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCP) in Environmental Samples using Advanced TripleTOF MS/MS Technology André Schreiber AB SCIEX Concord, Ontario (Canada)
Quantitation and Identification of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCP) in Environmental Samples using Advanced TripleTOF MS/MS Technology André Schreiber AB SCIEX Concord, Ontario (Canada)
Accurate, High-Throughput Protein Identification Using the Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System and Pro ID Software
 www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +1.847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment ABI Q Trap Pro LC/MS/MS Accurate, High-Throughput Protein Identification
www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +1.847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment ABI Q Trap Pro LC/MS/MS Accurate, High-Throughput Protein Identification
Supporting Information. Labeled Ligand Displacement: Extending NMR-based Screening of Protein Targets
 Supporting Information Labeled Ligand Displacement: Extending NMR-based Screening of Protein Targets Steven L. Swann, Danying Song, Chaohong Sun, Philip J. Hajduk, and Andrew M. Petros Global Pharmaceutical
Supporting Information Labeled Ligand Displacement: Extending NMR-based Screening of Protein Targets Steven L. Swann, Danying Song, Chaohong Sun, Philip J. Hajduk, and Andrew M. Petros Global Pharmaceutical
Toxicity, Teratogenic and Estrogenic Effects of Bisphenol A and its Alternative. Replacements Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F and Bisphenol AF in Zebrafish.
 1 Supporting Information 2 3 Toxicity, Teratogenic and Estrogenic Effects of Bisphenol A and its Alternative Replacements Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F and Bisphenol AF in Zebrafish. 4 5 John Moreman, Okhyun
1 Supporting Information 2 3 Toxicity, Teratogenic and Estrogenic Effects of Bisphenol A and its Alternative Replacements Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F and Bisphenol AF in Zebrafish. 4 5 John Moreman, Okhyun
Supporting Information. Time-Resolved Botulinum Neurotoxin A Activity Monitored using. Peptide-Functionalized Au Nanoparticle Energy Transfer Sensors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Time-Resolved Botulinum Neurotoxin A Activity Monitored using Peptide-Functionalized
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Time-Resolved Botulinum Neurotoxin A Activity Monitored using Peptide-Functionalized
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Performance comparison of two cascade reaction models in fluorescence
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Performance comparison of two cascade reaction models in fluorescence
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION. Michael O Leary, Jennifer Gough, Tanya Tollifson Waters Corporation, Milford, MA USA
 Use of High Speed/High Resolution Size-Based Chromatographic Separation of Surfactants and Oligomeric Materials with Single Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Michael O Leary, Jennifer Gough, Tanya Tollifson
Use of High Speed/High Resolution Size-Based Chromatographic Separation of Surfactants and Oligomeric Materials with Single Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Michael O Leary, Jennifer Gough, Tanya Tollifson
Identification of Human Hemoglobin Protein Variants Using Electrospray Ionization-Electron Transfer Dissociation Mass Spectrometry
 Identification of Human Hemoglobin Protein Variants Using Electrospray Ionization-Electron Transfer Dissociation Mass Spectrometry Jonathan Williams Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA A P P L I C AT
Identification of Human Hemoglobin Protein Variants Using Electrospray Ionization-Electron Transfer Dissociation Mass Spectrometry Jonathan Williams Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA A P P L I C AT
Reagents. Affinity Tag (Biotin) Acid Cleavage Site. Figure 1. Cleavable ICAT Reagent Structure.
 DATA SHEET Protein Expression Analysis Reagents Background The ultimate goal of proteomics is to identify and quantify proteins that are relevant to a given biological state; and to unearth networks of
DATA SHEET Protein Expression Analysis Reagents Background The ultimate goal of proteomics is to identify and quantify proteins that are relevant to a given biological state; and to unearth networks of
EPA Method 535: Detection of Degradates of Chloroacetanilides and other Acetamide Herbicides in Water by LC/MS/MS
 Application Note EPA Method 535 EPA Method 535: Detection of Degradates of Chloroacetanilides and other Acetamide Herbicides in Water by LC/MS/MS API 3200 LC/MS/MS System Overview Described here is the
Application Note EPA Method 535 EPA Method 535: Detection of Degradates of Chloroacetanilides and other Acetamide Herbicides in Water by LC/MS/MS API 3200 LC/MS/MS System Overview Described here is the
Supplementary information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary information 1. Composition of the nanoparticles 2. Dynamic light scattering 3. Scanning
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary information 1. Composition of the nanoparticles 2. Dynamic light scattering 3. Scanning
Analysis of Polar Metabolites using Mass Spectrometry
 Analysis of Polar Metabolites using Mass Spectrometry TransMed Course: Basics in Clinical Proteomics and Metabolomics. Oct 10-19, 2012 dd.mm.yyyy Vidya Velagapudi, Ph.D, Adjunct Professor Head of the Metabolomics
Analysis of Polar Metabolites using Mass Spectrometry TransMed Course: Basics in Clinical Proteomics and Metabolomics. Oct 10-19, 2012 dd.mm.yyyy Vidya Velagapudi, Ph.D, Adjunct Professor Head of the Metabolomics
Protein and antibody functionalization using continuous flow microreactor technology. Table of Contents
 1 Protein and antibody functionalization using continuous flow microreactor technology Meaghan M. Sebeika, Nicholas G. Gedeon, Sara Sadler, Nicholas L. Kern, Devan J. Wilkins, David E. Bell and Graham
1 Protein and antibody functionalization using continuous flow microreactor technology Meaghan M. Sebeika, Nicholas G. Gedeon, Sara Sadler, Nicholas L. Kern, Devan J. Wilkins, David E. Bell and Graham
Linear Dependence of Water Proton Transverse Relaxation Rate on Shear Modulus in Hydrogels
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 ESI (Electronic Support Information) Linear Dependence of Water Proton Transverse Relaxation Rate
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 ESI (Electronic Support Information) Linear Dependence of Water Proton Transverse Relaxation Rate
Self-assembling covalent organic frameworks functionalized. magnetic graphene hydrophilic biocomposite as an ultrasensitive
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supporting Information for: Self-assembling covalent organic frameworks functionalized
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supporting Information for: Self-assembling covalent organic frameworks functionalized
Powerful Scan Modes of QTRAP System Technology
 Powerful Scan Modes of QTRAP System Technology Unique Hybrid Triple Quadrupole Linear Ion Trap Technology Provides Powerful Workflows to Answer Complex Questions with No Compromises While there are many
Powerful Scan Modes of QTRAP System Technology Unique Hybrid Triple Quadrupole Linear Ion Trap Technology Provides Powerful Workflows to Answer Complex Questions with No Compromises While there are many
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Antimicrobial activity of chlorinated amino acids and peptides
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Antimicrobial activity of chlorinated amino acids and peptides Melanie S. A. Coker*, Wan-Ping Hu, Senti T Senthilmohan and Anthony J. Kettle Free Radical Research Group, University
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Antimicrobial activity of chlorinated amino acids and peptides Melanie S. A. Coker*, Wan-Ping Hu, Senti T Senthilmohan and Anthony J. Kettle Free Radical Research Group, University
The Quantitation and Identification of Coccidiostats in Food by LC-MS/MS using the AB SCIEX 4000 Q TRAP System
 The Quantitation and Identification of Coccidiostats in Food by LC-MS/MS using the AB SCIEX 4000 Q TRAP System Bertram ieland 1 and Stephen Lock 2 1 AB SCIEX ieuwerkerk aan den Ijssel, The etherlands;
The Quantitation and Identification of Coccidiostats in Food by LC-MS/MS using the AB SCIEX 4000 Q TRAP System Bertram ieland 1 and Stephen Lock 2 1 AB SCIEX ieuwerkerk aan den Ijssel, The etherlands;
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a
 Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
High-Throughput Protein Quantitation Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring
 High-Throughput Protein Quantitation Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring Application Note Authors Ning Tang, Christine Miller, Joe Roark, Norton Kitagawa and Keith Waddell Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa
High-Throughput Protein Quantitation Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring Application Note Authors Ning Tang, Christine Miller, Joe Roark, Norton Kitagawa and Keith Waddell Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa
LC MS analysis of metabolites. Basis of Chromatography
 GBS 724 LC MS analysis of metabolites Stephen Barnes, PhD 4 7117; sbarnes@uab.edu Basis of Chromatography A moving (mobile) phase passes over an inert, stationary phase The compounds differentially interact
GBS 724 LC MS analysis of metabolites Stephen Barnes, PhD 4 7117; sbarnes@uab.edu Basis of Chromatography A moving (mobile) phase passes over an inert, stationary phase The compounds differentially interact
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Rapid and sensitive detection of acrylic acid using a novel fluorescence
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Rapid and sensitive detection of acrylic acid using a novel fluorescence
Introduction to the Q Trap LC/MS/MS System
 www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +1.847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment ABI Q Trap LC/MS/MS Introduction to the Q Trap LC/MS/MS System The Q Trap
www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +1.847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment ABI Q Trap LC/MS/MS Introduction to the Q Trap LC/MS/MS System The Q Trap
PosterREPRINT COMPARISON OF PEAK PARKING VERSUS AUTOMATED FRACTION ANALYSIS OF A COMPLEX PROTEIN MIXTURE. Introduction
 Introduction The study of protein expression allows a greater understanding of biological function and can now routinely be performed using mass spectrometry. However, analysis of the post-translational
Introduction The study of protein expression allows a greater understanding of biological function and can now routinely be performed using mass spectrometry. However, analysis of the post-translational
Translational Biomarker Core
 Translational Biomarker Core Instrumentation Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantum Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometers. There are two TSQ Quantum Ultra AM instruments available in the TBC. The TSQ Quantum Ultra
Translational Biomarker Core Instrumentation Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantum Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometers. There are two TSQ Quantum Ultra AM instruments available in the TBC. The TSQ Quantum Ultra
Supplementary Materials: Localization and Spectroscopic Analysis of the Cu(I) Binding Site in Wheat Metallothionein Ec-1
 S1 of S8 Supplementary Materials: Localization and Spectroscopic Analysis of the Cu(I) Binding Site in Wheat Metallothionein Ec-1 Katsiaryna Tarasava, Jens Loebus and Eva Freisinger Figure S1. Deconvoluted
S1 of S8 Supplementary Materials: Localization and Spectroscopic Analysis of the Cu(I) Binding Site in Wheat Metallothionein Ec-1 Katsiaryna Tarasava, Jens Loebus and Eva Freisinger Figure S1. Deconvoluted
Analysis of Illegal Dyes in Food Matrices using Automated Online Sample Preparation with LC/MS
 Application Note: 56 Analysis of Illegal Dyes in Food Matrices using Automated Online Sample Preparation with LC/MS Yang Shi, Catherine Lafontaine, Matthew Berube, John Fink, François Espourteille Thermo
Application Note: 56 Analysis of Illegal Dyes in Food Matrices using Automated Online Sample Preparation with LC/MS Yang Shi, Catherine Lafontaine, Matthew Berube, John Fink, François Espourteille Thermo
Strategies for the Analysis of Therapeutic Peptides in Biofluids by LC-MS/MS. Lee Goodwin
 Strategies for the Analysis of Therapeutic Peptides in Biofluids by LC-MS/MS Lee Goodwin Sample Preparation Chromatography Detection General Strategies Examples New Approaches Summary Outline ABUNDANCE
Strategies for the Analysis of Therapeutic Peptides in Biofluids by LC-MS/MS Lee Goodwin Sample Preparation Chromatography Detection General Strategies Examples New Approaches Summary Outline ABUNDANCE
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry Supporting information for:
 Supporting information for: Preparation of 1-D Nanoparticle Superstructures with Tailorable Thicknesses using Gold-Binding Peptide Conjugates: New Insights into Fabrication Process and Mechanism Leekyoung
Supporting information for: Preparation of 1-D Nanoparticle Superstructures with Tailorable Thicknesses using Gold-Binding Peptide Conjugates: New Insights into Fabrication Process and Mechanism Leekyoung
A mitochondria-targeting fluorescent probe for detection of mitochondrial labile Fe(II) ion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Metallomics. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 A mitochondria-targeting fluorescent probe for detection of mitochondrial labile Fe(II) ion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Metallomics. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 A mitochondria-targeting fluorescent probe for detection of mitochondrial labile Fe(II) ion
Plasma Metanephrines and 3-Methoxytyramine by LC/MS/MS Using Agilent SimpliQ WCX SPE, 1290 Infi nity LC, and 6460 Triple Quadrupole LC/MS
 Plasma Metanephrines and 3-Methoxytyramine by LC/MS/MS Using Agilent SimpliQ WCX SPE, 129 Infi nity LC, and 646 Triple Quadrupole LC/MS Application Note Clinical Research Authors Linda Côté and Christophe
Plasma Metanephrines and 3-Methoxytyramine by LC/MS/MS Using Agilent SimpliQ WCX SPE, 129 Infi nity LC, and 646 Triple Quadrupole LC/MS Application Note Clinical Research Authors Linda Côté and Christophe
New Approaches in the Analysis of Amadori Compounds
 7 TH Wartburg Symposium on Flavor Chemistry and Biology Eisenach, April 21 st - April 23 rd, 2004 New Approaches in the Analysis of Amadori Compounds T. Davidek, I. Blank, K. Kraehenhuehl, J. Hau and S.
7 TH Wartburg Symposium on Flavor Chemistry and Biology Eisenach, April 21 st - April 23 rd, 2004 New Approaches in the Analysis of Amadori Compounds T. Davidek, I. Blank, K. Kraehenhuehl, J. Hau and S.
Measuring Drug-to-Antibody Ratio (DAR) for Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) with UHPLC/Q-TOF
 Measuring Drug-to-Antibody Ratio (DAR) for Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) with UHPLC/Q-TOF Application Note Biopharma Author Shuai Zuo Tao Bo Suresh Babu C.V. Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract In this
Measuring Drug-to-Antibody Ratio (DAR) for Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) with UHPLC/Q-TOF Application Note Biopharma Author Shuai Zuo Tao Bo Suresh Babu C.V. Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract In this
Mass Spectrometry. Hyphenated Techniques GC-MS LC-MS and MS-MS
 Mass Spectrometry Hyphenated Techniques GC-MS LC-MS and MS-MS Reasons for Using Chromatography with MS Mixture analysis by MS alone is difficult Fragmentation from ionization (EI or CI) Fragments from
Mass Spectrometry Hyphenated Techniques GC-MS LC-MS and MS-MS Reasons for Using Chromatography with MS Mixture analysis by MS alone is difficult Fragmentation from ionization (EI or CI) Fragments from
Bicyclic helical peptides as dual inhibitors selective. for Bcl2A1 and Mcl-1 proteins
 Supporting Inormation Bicyclic helical peptides as dual inhibitors selective or Bcl2A1 and Mcl-1 proteins de Araujo A.D.; Lim, J.; Wu, K-C.; Xiang, Y.; Good, A. C.; Skerlj, R.; Fairlie, D. P.* Contents
Supporting Inormation Bicyclic helical peptides as dual inhibitors selective or Bcl2A1 and Mcl-1 proteins de Araujo A.D.; Lim, J.; Wu, K-C.; Xiang, Y.; Good, A. C.; Skerlj, R.; Fairlie, D. P.* Contents
Maximizing Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Productivity with the Agilent StreamSelect LC/MS System
 Maximizing Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Productivity with the Agilent StreamSelect LC/MS System Application Note Authors Kevin McCann, Sameer Nene, Doug McIntyre, Edmond Neo, Dennis Nagtalon, and
Maximizing Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Productivity with the Agilent StreamSelect LC/MS System Application Note Authors Kevin McCann, Sameer Nene, Doug McIntyre, Edmond Neo, Dennis Nagtalon, and
Metal-catalyzed oxidation of Aβ and the resulting reorganization of the Cu binding sites promote ROS production. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Metallomics. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Metal-catalyzed oxidation of Aβ and the resulting reorganization of the Cu binding sites promote
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Metallomics. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Metal-catalyzed oxidation of Aβ and the resulting reorganization of the Cu binding sites promote
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing 0.1% SDS without boiling. The gel was analyzed by a fluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing 0.1% SDS without boiling. The gel was analyzed by a fluorescent
Application Note. Edgar Naegele. Abstract
 Agilent MassHunter Fast computer aided analysis of LC/ESI-TF data from complex natural product extracts Part 1: Analysis of Agilent 6210 TF data with the Molecular Feature Extractor in MassHunter Workstation
Agilent MassHunter Fast computer aided analysis of LC/ESI-TF data from complex natural product extracts Part 1: Analysis of Agilent 6210 TF data with the Molecular Feature Extractor in MassHunter Workstation
Bioanalytical Chem: 4590: LC-MSMS of analgesics LC-MS Experiment Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS)
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS) Prelab Questions: Questions to be answered before doing the experiment. The answers are due at the beginning of each experiment without exception (the questions
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS) Prelab Questions: Questions to be answered before doing the experiment. The answers are due at the beginning of each experiment without exception (the questions
Simplified Approaches to Impurity Identification using Accurate Mass UPLC/MS
 Simplified Approaches to Impurity Identification using Accurate Mass UPLC/MS Marian Twohig, Michael D. Jones, Dominic Moore, Peter Lee, and Robert Plumb Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION
Simplified Approaches to Impurity Identification using Accurate Mass UPLC/MS Marian Twohig, Michael D. Jones, Dominic Moore, Peter Lee, and Robert Plumb Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Synthesis of a new class of ribose functionalized dinucleotide cap analogues for biophysical studies on interaction of cap-binding proteins with the 5 end of mrna. Karolina Piecyk,
Supporting Information Synthesis of a new class of ribose functionalized dinucleotide cap analogues for biophysical studies on interaction of cap-binding proteins with the 5 end of mrna. Karolina Piecyk,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Ionization of Phosphopeptides at Low ph by Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Ning Pan, a, b Pengyuan Liu, b Weidong Cui, c Bo Tang, a Jingmin
Supporting Information Highly Efficient Ionization of Phosphopeptides at Low ph by Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Ning Pan, a, b Pengyuan Liu, b Weidong Cui, c Bo Tang, a Jingmin
Supporting Information for. PNA FRET Pair Miniprobes for Quantitative. Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization to Telomeric DNA in Cells and Tissue
 Supporting Information for PNA FRET Pair Miniprobes for Quantitative Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization to Telomeric DNA in Cells and Tissue Orenstein, et al Page S2... PNA synthesis procedure Page S3...
Supporting Information for PNA FRET Pair Miniprobes for Quantitative Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization to Telomeric DNA in Cells and Tissue Orenstein, et al Page S2... PNA synthesis procedure Page S3...
Macrolides in Honey Using Agilent Bond Elut Plexa SPE, Poroshell 120, and LC/MS/MS
 Macrolides in Honey Using Agilent Bond Elut Plexa SPE, Poroshell 120, and LC/MS/MS Application Note Food Testing and Agriculture Author Chen-Hao (Andy) Zhai and Rong-jie Fu Agilent Technologies (Shanghai)
Macrolides in Honey Using Agilent Bond Elut Plexa SPE, Poroshell 120, and LC/MS/MS Application Note Food Testing and Agriculture Author Chen-Hao (Andy) Zhai and Rong-jie Fu Agilent Technologies (Shanghai)
Rapid method development to study plasma stability of diverse pharmaceutical compounds using Rapid Resolution LC and triple quadrupole MS
 Rapid method development to study plasma stability of diverse pharmaceutical compounds using Rapid Resolution LC and triple quadrupole MS Application Note Drug Discovery Authors Srividya Kailasam Agilent
Rapid method development to study plasma stability of diverse pharmaceutical compounds using Rapid Resolution LC and triple quadrupole MS Application Note Drug Discovery Authors Srividya Kailasam Agilent
Agilent 1290 Infinity Quaternary LC Stepwise Transfer to Methods with MS-Compatible Mobile Phases
 Agilent 129 Infinity Quaternary LC Stepwise Transfer to Methods with MS-Compatible Mobile Phases Technical Overview Author A.G.Huesgen Agilent Technologies, Inc. Waldbronn, Germany Abstract The Agilent
Agilent 129 Infinity Quaternary LC Stepwise Transfer to Methods with MS-Compatible Mobile Phases Technical Overview Author A.G.Huesgen Agilent Technologies, Inc. Waldbronn, Germany Abstract The Agilent
Overview. Introduction. André Schreiber 1 and Yun Yun Zou 1 1 AB SCIEX, Concord, Ontario, Canada
 LC-MS/MS Based Strategy for the Non-Targeted Screening of an Unlimited Number of Contaminants in Food Using the AB SCIEX TripleTOF 5600 System and Advanced Software Tools André Schreiber 1 and Yun Yun
LC-MS/MS Based Strategy for the Non-Targeted Screening of an Unlimited Number of Contaminants in Food Using the AB SCIEX TripleTOF 5600 System and Advanced Software Tools André Schreiber 1 and Yun Yun
Supporting Information. Experimental details
 Electronic Supporting Information Experimental details Chemicals and reagents Pseudoboehmite (78.4 wt% Al 2 O 3 ), phosphoric acid (85 wt%), triethylamine (TEA, 99%), tetrabutyl titanate (IV) (99%) and
Electronic Supporting Information Experimental details Chemicals and reagents Pseudoboehmite (78.4 wt% Al 2 O 3 ), phosphoric acid (85 wt%), triethylamine (TEA, 99%), tetrabutyl titanate (IV) (99%) and
4000 Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System. Advanced Linear Ion Trap technology at the highest level of sensitivity 4000 QTRAP. LC/MS/MS System
 4000 Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System Advanced Linear Ion Trap technology at the highest level of sensitivity 4000 QTRAP LC/MS/MS System The highest performance ion trap and the highest sensitivity triple quad.
4000 Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System Advanced Linear Ion Trap technology at the highest level of sensitivity 4000 QTRAP LC/MS/MS System The highest performance ion trap and the highest sensitivity triple quad.
A Sensitive and Reproducible Signature Peptide MRM Based Quantitation Method for Pegylated Interferon α-2b in Serum
 A Sensitive and Reproducible Signature Peptide MRM Based Quantitation Method for Pegylated Interferon α-2b in Serum SCIEX QTRAP 6500 LC-MS/MS System Faraz Rashid 1,Dipankar Malakar 1, Anoop Kumar 1,Manoj
A Sensitive and Reproducible Signature Peptide MRM Based Quantitation Method for Pegylated Interferon α-2b in Serum SCIEX QTRAP 6500 LC-MS/MS System Faraz Rashid 1,Dipankar Malakar 1, Anoop Kumar 1,Manoj
Disulfide Linkage Characterization of Disulfide Bond-Containing Proteins and Peptides by Reducing Electrochemistry and Mass Spectrometry
 Supporting Information to: Disulfide Linkage Characterization of Disulfide ond-containing roteins and eptides y Reducing Electrochemistry and Mass Spectrometry Christian N. Cramer 1,2, Kim F. Haselmann
Supporting Information to: Disulfide Linkage Characterization of Disulfide ond-containing roteins and eptides y Reducing Electrochemistry and Mass Spectrometry Christian N. Cramer 1,2, Kim F. Haselmann
Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry. Introduction
 Electrospray Ion Source Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry Introduction The key to using MS for solutions is the ability to transfer your analytes into the vacuum of the mass spectrometer as ionic
Electrospray Ion Source Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry Introduction The key to using MS for solutions is the ability to transfer your analytes into the vacuum of the mass spectrometer as ionic
Figure S1. Interaction of PcTS with αsyn. (a) 1 H- 15 N HSQC NMR spectra of 100 µm αsyn in the absence (0:1, black) and increasing equivalent
 Figure S1. Interaction of PcTS with αsyn. (a) 1 H- 15 N HSQC NMR spectra of 100 µm αsyn in the absence (0:1, black) and increasing equivalent concentrations of PcTS (100 µm, blue; 500 µm, green; 1.5 mm,
Figure S1. Interaction of PcTS with αsyn. (a) 1 H- 15 N HSQC NMR spectra of 100 µm αsyn in the absence (0:1, black) and increasing equivalent concentrations of PcTS (100 µm, blue; 500 µm, green; 1.5 mm,
Clinical Toxicology. Biomass Component Extraction: The uneaten cooked plant specimen was prepared for
 Clinical Toxicology Page of 0 Materials and Methods Biomass Component Extraction: The uneaten cooked plant specimen was prepared for chemical analysis as follows. The sample was frozen, diced, pulverized
Clinical Toxicology Page of 0 Materials and Methods Biomass Component Extraction: The uneaten cooked plant specimen was prepared for chemical analysis as follows. The sample was frozen, diced, pulverized
Novel fluorescent cationic benzothiazole dye response to G-quadruplex aptamer as a novel K + sensor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Novel fluorescent cationic benzothiazole dye response to G-quadruplex aptamer as a novel K + sensor
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Novel fluorescent cationic benzothiazole dye response to G-quadruplex aptamer as a novel K + sensor
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Photo-Induced Chemistry for the Design of ligonucleotide
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Photo-Induced Chemistry for the Design of ligonucleotide
Electron Transfer Dissociation of N-linked Glycopeptides from a Recombinant mab Using SYNAPT G2-S HDMS
 Electron Transfer Dissociation of N-linked Glycopeptides from a Recombinant mab Using SYNAPT G2-S HDMS Jonathan P. Williams, Jeffery M. Brown, Stephane Houel, Ying Qing Yu, and Weibin Chen Waters Corporation,
Electron Transfer Dissociation of N-linked Glycopeptides from a Recombinant mab Using SYNAPT G2-S HDMS Jonathan P. Williams, Jeffery M. Brown, Stephane Houel, Ying Qing Yu, and Weibin Chen Waters Corporation,
The photoluminescent graphene oxide serves as an acceptor rather. than a donor in the fluorescence resonance energy transfer pair of
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 20XX The photoluminescent graphene oxide serves as an acceptor rather than a donor in the fluorescence
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 20XX The photoluminescent graphene oxide serves as an acceptor rather than a donor in the fluorescence
Structure of the α-helix
 Structure of the α-helix Structure of the β Sheet Protein Dynamics Basics of Quenching HDX Hydrogen exchange of amide protons is catalyzed by H 2 O, OH -, and H 3 O +, but it s most dominated by base
Structure of the α-helix Structure of the β Sheet Protein Dynamics Basics of Quenching HDX Hydrogen exchange of amide protons is catalyzed by H 2 O, OH -, and H 3 O +, but it s most dominated by base
Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist Ross W. Cheloha, Tomoyuki Watanabe, Thomas Dean, Samuel H. Gellman*, Thomas J. Gardella* *Corresponding
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist Ross W. Cheloha, Tomoyuki Watanabe, Thomas Dean, Samuel H. Gellman*, Thomas J. Gardella* *Corresponding
+ butanal + 2-picolineborane. + acetic acid. + butanal + 2-picolineborane. + acetic acid
 PO-CON1751E Quantitation of plasma metanephrine and normetanephrine by derivatization using an integrated LC-MS/MS analyzer equipped with fully-automated sample preparation device ASMS 2017 ThP-099 Atsuhiko
PO-CON1751E Quantitation of plasma metanephrine and normetanephrine by derivatization using an integrated LC-MS/MS analyzer equipped with fully-automated sample preparation device ASMS 2017 ThP-099 Atsuhiko
Bis sulfone Reagents. Figure 1.
 Bis sulfone Reagents An intact IgG molecule has four accessible inter chain disulfide bonds that can be reduced to form eight free cysteine thiols, which can serve as sites for conjugation. The reaction
Bis sulfone Reagents An intact IgG molecule has four accessible inter chain disulfide bonds that can be reduced to form eight free cysteine thiols, which can serve as sites for conjugation. The reaction
In vivo monitoring of hydrogen sulfide using a cresyl violet-based ratiometric fluorescence probe
 Electronic Supplementary Information for: In vivo monitoring of hydrogen sulfide using a cresyl violet-based ratiometric fluorescence probe Qiongqiong Wan, Yanchao Song, Zhao Li, Xinghui Gao and Huimin
Electronic Supplementary Information for: In vivo monitoring of hydrogen sulfide using a cresyl violet-based ratiometric fluorescence probe Qiongqiong Wan, Yanchao Song, Zhao Li, Xinghui Gao and Huimin
PC235: 2008 Lecture 5: Quantitation. Arnold Falick
 PC235: 2008 Lecture 5: Quantitation Arnold Falick falickam@berkeley.edu Summary What you will learn from this lecture: There are many methods to perform quantitation using mass spectrometry (any method
PC235: 2008 Lecture 5: Quantitation Arnold Falick falickam@berkeley.edu Summary What you will learn from this lecture: There are many methods to perform quantitation using mass spectrometry (any method
Recommended Procedures for Labeling. Labeling Proteins with Amine-Reactive ATTO-Labels (NHS-Esters) Introduction
 Recommended Procedures for Labeling Introduction ATTO-TEC offers a large variety of high-quality dyes for labeling amino and thiol groups. ATTO reactive dyes cover the spectral region from 350 nm in the
Recommended Procedures for Labeling Introduction ATTO-TEC offers a large variety of high-quality dyes for labeling amino and thiol groups. ATTO reactive dyes cover the spectral region from 350 nm in the
Choosing the metabolomics platform
 GBS 748 Choosing the metabolomics platform Stephen Barnes, PhD 4 7117; sbarnes@uab.edu So, I have my samples what s next? You ve collected your samples and you may have extracted them Protein precipitation
GBS 748 Choosing the metabolomics platform Stephen Barnes, PhD 4 7117; sbarnes@uab.edu So, I have my samples what s next? You ve collected your samples and you may have extracted them Protein precipitation
Ultrafast Analysis of Buprenorphine and Norbuprenorphine in Urine Using the Agilent RapidFire High-Throughput Mass Spectrometry System
 Ultrafast Analysis of Buprenorphine and Norbuprenorphine in Urine Using the Agilent RapidFire High-Throughput Mass Spectrometry System Application Note Authors Mohamed Youssef and Vaughn P. Miller Agilent
Ultrafast Analysis of Buprenorphine and Norbuprenorphine in Urine Using the Agilent RapidFire High-Throughput Mass Spectrometry System Application Note Authors Mohamed Youssef and Vaughn P. Miller Agilent
Quantitative Proteomics
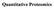 Quantitative Proteomics Quantitation AND Mass Spectrometry Condition A Condition B Identify and quantify differently expressed proteins resulting from a change in the environment (stimulus, disease) Lyse
Quantitative Proteomics Quantitation AND Mass Spectrometry Condition A Condition B Identify and quantify differently expressed proteins resulting from a change in the environment (stimulus, disease) Lyse
A High Sensitivity Dual Solid Phase Extraction LC-MS/MS Assay for the Determination of the Therapeutic Peptide Desmopressin in Human Plasma
 White Paper A High Sensitivity Dual Solid Phase Extraction LC-MS/MS Assay for the Determination of the Therapeutic Peptide Desmopressin in Human Plasma Lars Neudert, MSc, Senior Scientist Method Development
White Paper A High Sensitivity Dual Solid Phase Extraction LC-MS/MS Assay for the Determination of the Therapeutic Peptide Desmopressin in Human Plasma Lars Neudert, MSc, Senior Scientist Method Development
Chapter 5. Complexation of Tholins by 18-crown-6:
 5-1 Chapter 5. Complexation of Tholins by 18-crown-6: Identification of Primary Amines 5.1. Introduction Electrospray ionization (ESI) is an excellent technique for the ionization of complex mixtures,
5-1 Chapter 5. Complexation of Tholins by 18-crown-6: Identification of Primary Amines 5.1. Introduction Electrospray ionization (ESI) is an excellent technique for the ionization of complex mixtures,
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Bioconjugation of hydrogen-bonded organic semiconductors
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Bioconjugation of hydrogen-bonded organic semiconductors
Nontarget Analysis via LC-QTOF-MS to Assess the Release of Organic Substances from Polyurethane Coating
 Nontarget Analysis via LC-QTOF-MS to Assess the Release of Organic Substances from Polyurethane Coating Agnessa Luft, Kathrin Bröder, Uwe Kunkel,#, Manoj Schulz, Christian Dietrich, Roland Baier, Peter
Nontarget Analysis via LC-QTOF-MS to Assess the Release of Organic Substances from Polyurethane Coating Agnessa Luft, Kathrin Bröder, Uwe Kunkel,#, Manoj Schulz, Christian Dietrich, Roland Baier, Peter
Supplementary Materials. Synthesis of Reusable Silica Nanosphere-Supported Pt(IV) Complex for. Formation of Disulfide Bonds in Peptides
 Supplementary Materials Synthesis of Reusable Silica Nanosphere-Supported Pt(IV) Complex for Formation of Disulfide Bonds in Peptides Xiaonan Hou, Xiaowei Zhao, Yamei Zhang, Aiying Han, Shuying Huo*, and
Supplementary Materials Synthesis of Reusable Silica Nanosphere-Supported Pt(IV) Complex for Formation of Disulfide Bonds in Peptides Xiaonan Hou, Xiaowei Zhao, Yamei Zhang, Aiying Han, Shuying Huo*, and
Tutorial 1: Setting up your Skyline document
 Tutorial 1: Setting up your Skyline document Caution! For using Skyline the number formats of your computer have to be set to English (United States). Open the Control Panel Clock, Language, and Region
Tutorial 1: Setting up your Skyline document Caution! For using Skyline the number formats of your computer have to be set to English (United States). Open the Control Panel Clock, Language, and Region
At-a-Glance. Verapamil C 27 H 38 N 2 O 4 M+H + =
 Application ote #LC-MS 80 Simultaneous Quantitative and Qualitative Measurements in a Single Workflow to Increase Productivity in Primary Drug Metabolism Investigations At-a-Glance n Increased productivity
Application ote #LC-MS 80 Simultaneous Quantitative and Qualitative Measurements in a Single Workflow to Increase Productivity in Primary Drug Metabolism Investigations At-a-Glance n Increased productivity
Tandem MS = MS / MS. ESI-MS give information on the mass of a molecule but none on the structure
 Tandem MS = MS / MS ESI-MS give information on the mass of a molecule but none on the structure In tandem MS (MSMS) (pseudo-)molecular ions are selected in MS1 and fragmented by collision with gas. collision
Tandem MS = MS / MS ESI-MS give information on the mass of a molecule but none on the structure In tandem MS (MSMS) (pseudo-)molecular ions are selected in MS1 and fragmented by collision with gas. collision
A Fluorescence Turn-On Sensor for the Detection of Palladium Ions that Operates Through In-Situ Generation of Palladium Nanoparticles
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information for A Fluorescence Turn-On Sensor for the Detection of Palladium Ions that Operates Through In-Situ Generation of Palladium Nanoparticles
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information for A Fluorescence Turn-On Sensor for the Detection of Palladium Ions that Operates Through In-Situ Generation of Palladium Nanoparticles
