Unraveling the Mechanism of Water Oxidation by Ruthenium-Oxo Complexes
|
|
|
- Victoria Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unraveling the Mechanism of Water xidation by thenium-xo Complexes Casseday Richers Literature Seminar ovember 20, 2007 The oxidation of water to dioxygen and protons represents one half the watersplitting reaction: This reaction is important in photosynthesis, and as a possible non-hydrocarbon-based source of hydrogen gas. 1 Although a few catalysts are known for this reaction, relatively little is understood about the mechanism. 2-4 The discovery of a molecular catalyst, cis,cis- [(bpy) 2 ( 2 ) III III ( 2 )(bpy) 2 ] 4+ ([3,3]; bpy = 2,2 bipyridine) has provided a platform from which to carry out mechanistic investigations into the oxidation of water by ruthenium oxo complexes (the symbol [a,b] will refers only to the oxidation states of the two ruthenium and not to specific molecules which may vary in proton content and overall charge).. 5 Crystal structures for both [3,3] and [3,4] indicate very little interaction between the two cis-aqua ligands. The crystal structure for [3,3] is shown in Figure 1. 4 Figure 1: crystal structure for [(bpy) 2 ( 2 ) III III ( 2 )(bpy) 2 ] 4+ Bond distances of 1.87 and Å were observed for the -(µ-) and - 2 bonds, respectively. A bridging angle of 165º was observed for the -- group and a torsional angle of 66º was observed between the two cis-aqua ligands. The arrangement of atoms resulted in a distance of ~4.72 Å between the two cis-aqua oxygen atoms. The relatively short - distance for the µ-oxo ligand indicates multiple bonding. The crystal structure for [3,4] revealed -(µ-) bond distances of 1.83 and 1.85 Å. 4 The bridging angle was 170º and the torsion was 117º. The distance between cis-aqua oxygen atoms was ~5.55 Å. Cyclic voltammetry and pulse polarography experiments on [3,3] suggest that oxidation of the ruthenium dimer proceeds by successive one-, and two-electron
2 oxidations. 6 At p 5, oxidation of [3,3] produces [3,4], which subsequently oxidizes to [4,5], and eventually forms [5,5]. The oxidation states of the two ruthenium atoms were assigned based on similarities observed with more stable osmium analogues and are supported by later studies. 7 Direct determinations of the oxidation states by coulometry could not be carried over because the higher oxidation states are unstable, presumably due to water oxidation. The [4,4] oxidation state is never observed and is predicted to be unstable at all p values. A plot of redox potentials versus p is given in Figure 2. [3,3] -e - [3,4] -2e - [4,5] -e - [5,5] Figure 2: Redox Potential vs p; xidation Scheme at p = 5. In general, the redox potentials increase with decreasing p. At p values less than 2.2, [4,5] becomes unstable with respect to disproportionation and the oxidation of [3,4] becomes a three-electron process. An alternative mechanism for the oxidation of [3,3] to [5,5] is shown in Figure 3. 8 [3,3] -e - [3,4] e - [4,4] -2e - [5,5] Figure 3: xidation Scheme proposed by urst and co-workers. Evidence for the [4,4] and [5,5] oxidation state is obtained from titrations the moreoxidized dimers, with s(bpy) Additional support for the [4,4] state comes from mixing experiments which show that only one product is formed upon mixing [3,3] and [5,5] in equal amounts (two products, [3,4] and [4,5], would be expected if [4,5] was the intermediate), and Resonance Raman spectroscopy which indicates that only one species in solution contains a = bond (both [4,5] and [5,5] are expected to contain = bonds). Discrepancies between this second oxidation pathway and the original oxidation pathway obtained by cyclic voltammetry may result from differences in reaction conditions (1M Cl 4 vs. 0.5M CF 3 S 3 ).
3 Global analysis of the spectroscopic data obtained by Meyer points to a complex mechanism involving rapid conversion of [3,3] to [3,4], slow conversion of [3,4] to [4,5], rapid conversion of [4,5] to [5,5] and rapid decomposition of [5,5], but does not provide additional information regarding water oxidation. 9 Rate data taken by urst on the decay of [5,5] indicate it is an immediate precursor to water oxidation, but does not point to a specific mechanism. The immediate product of [5,5] decay is [4,4], suggesting that hydrogen peroxide may be formed in the reaction. The decay of [5,5] is first order with respect to [5,5]. 12 Pseudo-zero-order kinetics observed for 2 production in studies by Meyer may result from annation of the catalyst during catalytic turnover Labeling studies performed on [3,3] suggest that more than one mechanism is responsible for 2 production In the studies, unlabeled [3,3] was incubated in 18 2 for extended periods to effect substitution of the unlabeled aquo ligands with labeled aquo ligands. Subsequent oxidation of the labeled [3,3] with one equivalent of Ce(IV) produced labeled [3,4] which was then treated with unlabeled 2 in the presence of a slight stoichiometric excess of oxidant to produce dioxygen. Product distributions obtained by Meyer indicate that roughly 13% of the 2 produced received both oxygen atoms from the ruthenium dimer ( 36 2 ), whereas 64% of the 2 received one oxygen atom from the ruthenium dimer and one oxygen atom from the solvent ( 34 2 ), and 23% of the 2 received both oxygen atoms from the solvent ( 32 2 ). 10 In comparison the product distribution obtained by urst was roughly 50: : 32 2 with little if any ,12 General pathways for the production of 2 from [5,5] are presented in Figure 4. A (bpy) 2 2 (bpy) 2 B 2 (bpy) 2 (bpy) 2 (bpy) 2 C (bpy) 2 (bpy) 2 D (bpy) (bpy) 2 E (bpy) 2 2 (bpy) (bpy) 2 2 F (bpy) 2 2 (bpy) 2 2 (bpy) 2 Figure 4: General Pathways for the production of 2 from [5,5]
4 The small amount of 36 2 produced in the labeling studies implies that coupling of two terminal oxo groups is negligible (Pathways B-D). ther mechanisms are more difficult to exclude. ucleophilic attack by water on a = group could account for the formation of 34 2 (Pathway A). Likewise nucleophilic attack by water on a bound peroxide or ozonide, formed by prior nucleophilc attack by water on a = group, could account for the formation of 32 2 (Pathway E). An alternative mechanism for the formation of 32 is nucleophilic attack by water on the bipyridine ring of the catalyst, followed by ligand-to-metal charge transfer and nucleophilic attack by a second water to form a bis-hydroxo species, which could eliminate hydrogen peroxide and eventually generate water (Figure 5). Evidence for nucleophilic attack by water on coordinated bipyridine rings is supplied by Dutta and co-workers who report water oxidation by zeolite-encaged (bpy) EPR data taken for [5,5] is suggestive of a ligand-based radical. In the absence of a zeolite cage, (bpy) 3+ 3 oxidizes bipyridine to carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas. 12 Mechanisms involving the formation of free radicals are energetically prohibited. L 2 L 2 L 2 L 2 L 2 L L 2 L Figure 5: ucleophilic Attack on coordinated bipyridine and elimination of 2 2 Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations on the addition of water to = support a mechanism in which initial ligand-to-metal charge transfer from the oxo ligands to the ruthenium atoms produces a pair of oxyl radicals, which then cleave the - bond in water. 14 Proton transfer, metal-to-metal charge transfer, and ligand-to-metal charge transfer eventually lead to a bound superoxo intermediate which undergoes intersystem crossing and ligand-to-metal charge transfer to produce triplet 2 and triplet [3,3]. Intersystem crossing and oxidation of [3,3] to [5,5] complete the catalytic cycle. Redox potentials predicted by these calculations are in fairly good agreement with experimentally determined values and lend weight to these studies. ther mechanisms were not investigated. The ground state of [5,5] is predicted to be low-spin with weakly coupled antiferromagnetic electrons on each of the ruthenium centers. Conversion to a high-spin antiferromagnetic state by rotation around -- bonds is expected to be facile and to immediately precede ligand-to-metal charge transfer from the oxo ligands to the ruthenium atoms. Recent reports, however, have called into question the validity of these calculations. 15 ther catalysts for the oxidation of water are shown in Figure ,3 Although these catalysts may follow mechanisms similar to [3,3], mechanistic studies on them have not been performed. Additional studies are required on these and on [3,3] before a clear picture of water oxidation by ruthenium-oxo complexes emerges.
5 R R Cl Cl Cl Figure 6: thenium-based catalysts for water oxdiation References 1 Lewis,.; ocera, D. G. Powering the Planet: Chemical Challenges in Solar Energy Utilization, Proc. at. Acad. Sci. 2006, 103, Rüttinger, W.; Dismukes, G. C. Synthetic Water-xidation Catalysts for Artificial Photosynthetic Water xidation, Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1. 3 Yagi, M.; Kaneko, M. Molecular Catalysts for Water xidation, Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, urst, J. K. Water xidation Catalyzed by Dimeric µ-xo Bridged thenium Diimine Complexes, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, Gersten, S. W.; Samuels, G. J.; Meyer, T. J. Catalytic xidation of Water by an xo Bridged thenium Dimer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, Gilbert, J. A.; Eggleston, D. S.; Murphy, W. R.; Geselowitz, D. A.; Gersten, S. W.; odgson, D. J.; Meyer, T. A. Structure and Redox Properties of the Water-xidation Catalyst [(bpy) 2 ( 2 )( 2 )(bpy) 2 ] 4+, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, Raven, S. J.; Meyer, T. J. Reactivity of the xo-bridged Ion [(bpy) 2 () IV IV ()(bpy) 2 ] 3+, Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, Yamada,.; urst, J. K. Resonance Raman, ptical Spectroscopic, and EPR Characterization of the igher xidation States of the Water xidation Catalyst, cis,cis-[(bpy) 2 ( 2 )] 2 4+, J. Am. Chem.. Soc. 2000, 122, Binstead, R. A.; Chronister, C. W.; i, J.; artshorn, C. M.; Meyer, T. J. Mechanism of Water xidation by the µ-xo Dimer [(bpy) 2 ( 2 ) III III ( 2 )(bpy) 2 ] 4+, J. Am. Chem.. Soc. 2000, 122, Geselowit, D.; Meyer, T. J. Water xidation by [(bpy) 2 () V V ()(bpy) 2 ] 4+. An xygen-labeling Study, Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, urst, J. K.; Zhou, J.; Lei, Y. Pathways for Water xidation Catalyzed by the [(bpy) 2 ( 2 )] 2 4+ Ion, Inorg. Chem. 1992, 31, Yamada,.; Siems, W. F.; Koike, T.; urst, J. K. Mechanisms of Water xidation Catalyzed by the cis,cis-[(bpy) 2 ( 2 )] 2 4+ Ion, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, Ledney, M.; Dutta, P. K. xidation of Water to Dioxygen by Intrazeolitic (bpy) 3+ 3, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, Yang, X.; Baik, M.. cis,cis-[(bpy) 2 V ] 2 4+ Catalyzes Water xidation Formally via in Situ Generation of Radicaloid IV-, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, Batista, E. R.; Martin, R. Electron Localization in the Ground State of the thenium Blume Dimer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, Sens, C.; Romero, I.; Rodríguez, M. Llobet, A.; Parella, T.; Benet-Buchholz, J. A ew Complex Capable of Catalytically xidizing Water to Molecular Dioxygen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, Wada, T.; Kiyoshi, T.; Tanaka, K. Electrochemical xidation of Water to Dioxygen Catalyzed by the xidized From of the Bis(ruthenium-hydroxo) Complex in 2, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, Zong, R.; Thummel, R. P.; A ew Family of Complexes for Water xidation, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127,
cis,cis-[(bpy) 2 Ru V O] 2 O 4+ Catalyzes Water Oxidation Formally via in Situ Generation of Radicaloid Ru IV -O
![cis,cis-[(bpy) 2 Ru V O] 2 O 4+ Catalyzes Water Oxidation Formally via in Situ Generation of Radicaloid Ru IV -O cis,cis-[(bpy) 2 Ru V O] 2 O 4+ Catalyzes Water Oxidation Formally via in Situ Generation of Radicaloid Ru IV -O](/thumbs/79/79100960.jpg) Published on Web 05/23/2006 cis,cis-[(bpy) 2 Ru V O] 2 O 4+ Catalyzes Water Oxidation Formally via in Situ Generation of Radicaloid Ru IV -O Xiaofan Yang and Mu-Hyun Baik* Contribution from the Department
Published on Web 05/23/2006 cis,cis-[(bpy) 2 Ru V O] 2 O 4+ Catalyzes Water Oxidation Formally via in Situ Generation of Radicaloid Ru IV -O Xiaofan Yang and Mu-Hyun Baik* Contribution from the Department
Direct-Coupling O Bond Forming Pathway in Cobalt Oxide Water Oxidation Catalysts
 Direct-Coupling Bond Forming Pathway in Cobalt xide Water xidation Catalysts The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Direct-Coupling Bond Forming Pathway in Cobalt xide Water xidation Catalysts The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Figure 1. Oxidation by iron-oxo complex. supported by porous solid
 Oxidation of Ethane to Ethanol by N 2 O in a Metal-Organic Framework with Coordinatively Unsaturated Iron(II) Sites Long, J.R, et al., Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 590. Mechanism of Oxidation of Ethane to Ethanol
Oxidation of Ethane to Ethanol by N 2 O in a Metal-Organic Framework with Coordinatively Unsaturated Iron(II) Sites Long, J.R, et al., Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 590. Mechanism of Oxidation of Ethane to Ethanol
Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis. Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat)
 Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat) Introduction Novel cross coupling was reported! Highly selective sp 3 C-H functionalization!
Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat) Introduction Novel cross coupling was reported! Highly selective sp 3 C-H functionalization!
Recommended Reading: 23, 29 (3rd edition); 22, 29 (4th edition) Ch 102 Problem Set 7 Due: Thursday, June 1 Before Class. Problem 1 (1 points) Part A
 Recommended Reading: 23, 29 (3rd edition); 22, 29 (4th edition) Ch 102 Problem Set 7 Due: Thursday, June 1 Before Class Problem 1 (1 points) Part A Kinetics experiments studying the above reaction determined
Recommended Reading: 23, 29 (3rd edition); 22, 29 (4th edition) Ch 102 Problem Set 7 Due: Thursday, June 1 Before Class Problem 1 (1 points) Part A Kinetics experiments studying the above reaction determined
Acceleration of Ligand Exchange by Coordinated Nitrate in Polypyridyl Ruthenium Complexes
 Acceleration of Ligand Exchange by Coordinated Nitrate in Polypyridyl Ruthenium Complexes By: Jerry L. Walsh and Cregg C. Yancey J. L. Walsh, C. Y. Yancey, "Acceleration of Ligand Exchange by Coordinated
Acceleration of Ligand Exchange by Coordinated Nitrate in Polypyridyl Ruthenium Complexes By: Jerry L. Walsh and Cregg C. Yancey J. L. Walsh, C. Y. Yancey, "Acceleration of Ligand Exchange by Coordinated
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation
 Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes
 1 Literature Seminar Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes 2016. 7. 23. Nagashima Nozomu 2 C-H functionalization by enzymes Enzymes enable aliphatic C-H functionalization 3 P450 oxidation
1 Literature Seminar Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes 2016. 7. 23. Nagashima Nozomu 2 C-H functionalization by enzymes Enzymes enable aliphatic C-H functionalization 3 P450 oxidation
ummary Manipulating Radicals
 Manipulating Radicals ummary Modern catalysis research tries to address issues such as material scarcity, sustainability or process costs. One solution is to replace expensive and scarce noble metal catalysts
Manipulating Radicals ummary Modern catalysis research tries to address issues such as material scarcity, sustainability or process costs. One solution is to replace expensive and scarce noble metal catalysts
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS. Model Complexes for Studying Heterometallic Effects Relevant to Fuel Cell Chemistry
 RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS From the Resnick Sustainability Institute Graduate Research Fellows at the California Institute of Technology Model Complexes for Studying Heterometallic Effects Relevant to Fuel Cell
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS From the Resnick Sustainability Institute Graduate Research Fellows at the California Institute of Technology Model Complexes for Studying Heterometallic Effects Relevant to Fuel Cell
Mechanistic Insides into Nickamine-Catalyzed Alkyl-Alkyl Cross-Coupling Reactions
 Mechanistic Insides into Nickamine-Catalyzed Alkyl-Alkyl Cross-Coupling Reactions Abstract Within the last decades the transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling of non-activated alkyl halides has significantly
Mechanistic Insides into Nickamine-Catalyzed Alkyl-Alkyl Cross-Coupling Reactions Abstract Within the last decades the transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling of non-activated alkyl halides has significantly
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Roles of Water Molecules in Modulating the Reactivity of Dioxygen-bound - ZSM-5 toward Methane: A Theoretical Prediction Takashi Yumura,,* Yuuki Hirose, Takashi Wakasugi, Yasushige
Supporting Information Roles of Water Molecules in Modulating the Reactivity of Dioxygen-bound - ZSM-5 toward Methane: A Theoretical Prediction Takashi Yumura,,* Yuuki Hirose, Takashi Wakasugi, Yasushige
On the Acid-Base Mechanism for Ruthenium Water Oxidation Catalysts
 n the Acid-Base Mechanism for Ruthenium Water xidation Catalysts The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
n the Acid-Base Mechanism for Ruthenium Water xidation Catalysts The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask M2 Takaya Togo
 C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask 2017.11.25 M2 Takaya Togo 1 Outline 1.Introduction 2.Free amines as DG Discovery of new activation mode Mechanistic studies Application of the
C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask 2017.11.25 M2 Takaya Togo 1 Outline 1.Introduction 2.Free amines as DG Discovery of new activation mode Mechanistic studies Application of the
Insertion Reactions. 1) 1,1 insertion in which the metal and the X ligand end up bound to the same (1,1) atom
 Insertion Reactions xidative addition and substitution allow us to assemble 1e and 2e ligands on the metal, respectively. With insertion, and its reverse reaction, elimination, we can now combine and transform
Insertion Reactions xidative addition and substitution allow us to assemble 1e and 2e ligands on the metal, respectively. With insertion, and its reverse reaction, elimination, we can now combine and transform
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Mechanistic Study of Alcohol Oxidation by the / /DMSO Catalyst System and Implications for the Development of Improved Aerobic Oxidation Catalysts Bradley A. Steinhoff, Shannon R.
Supporting Information Mechanistic Study of Alcohol Oxidation by the / /DMSO Catalyst System and Implications for the Development of Improved Aerobic Oxidation Catalysts Bradley A. Steinhoff, Shannon R.
Chem1B General Chemistry II Exam 1 Summer Read all questions carefully make sure that you answer the question that is being asked.
 ChemB General Chemistry II Exam Summer 20 Name: KEY GSI: Write your name on all pages of the exam. Read all questions carefully make sure that you answer the question that is being asked. Write neatly
ChemB General Chemistry II Exam Summer 20 Name: KEY GSI: Write your name on all pages of the exam. Read all questions carefully make sure that you answer the question that is being asked. Write neatly
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions
 Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Cambrian Explosion, Complex Eukaryotic Organism, Ozonosphere 3
 Reporter: Wang Yuefan Reporter: Wang Yuefan Supervisor: Prof. Yang Zhen Supervisor: Prof. Yang Zhen Prof. Chen Jiahua Prof. Chen Jiahua 1 2011-12-2727 2011-02 2012-03 02-25 03-23 25 Content Preface Nature
Reporter: Wang Yuefan Reporter: Wang Yuefan Supervisor: Prof. Yang Zhen Supervisor: Prof. Yang Zhen Prof. Chen Jiahua Prof. Chen Jiahua 1 2011-12-2727 2011-02 2012-03 02-25 03-23 25 Content Preface Nature
The Role of METAMORPhos Ligands in Transition Metal Complex Formation and Catalysis S. Oldenhof
 The Role of METAMORPhos Ligands in Transition Metal Complex Formation and Catalysis S. Oldenhof Summary Catalysis plays a key role in the prosperity of our society, as catalysts are applied in the majority
The Role of METAMORPhos Ligands in Transition Metal Complex Formation and Catalysis S. Oldenhof Summary Catalysis plays a key role in the prosperity of our society, as catalysts are applied in the majority
Coordination and Special Materials Chemistry. Elective I/II: WS 2005/6 (Lecture) H.J. Deiseroth. Part 2
 Coordination and Special Materials Chemistry Elective I/II: WS 2005/6 (Lecture) H.J. Deiseroth Part 2 Coordination Chemistry: Spectroscopy -microstates and spectroscopic symbols (RS and jj coupling), see
Coordination and Special Materials Chemistry Elective I/II: WS 2005/6 (Lecture) H.J. Deiseroth Part 2 Coordination Chemistry: Spectroscopy -microstates and spectroscopic symbols (RS and jj coupling), see
Supplementary Figure 1 Morpholigical properties of TiO 2-x SCs. The statistical particle size distribution (a) of the defective {001}-TiO 2-x SCs and
 Supplementary Figure 1 Morpholigical properties of TiO 2-x s. The statistical particle size distribution (a) of the defective {1}-TiO 2-x s and their typical TEM images (b, c). Quantity Adsorbed (cm 3
Supplementary Figure 1 Morpholigical properties of TiO 2-x s. The statistical particle size distribution (a) of the defective {1}-TiO 2-x s and their typical TEM images (b, c). Quantity Adsorbed (cm 3
Theoretical studies on the chemical activation of carbon dioxide
 Theoretical studies on the chemical activation of carbon dioxide h. D. theses Gábor Schubert Supervisor Dr. Imre ápai Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Faculty of Chemical Engineering Chemical
Theoretical studies on the chemical activation of carbon dioxide h. D. theses Gábor Schubert Supervisor Dr. Imre ápai Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Faculty of Chemical Engineering Chemical
FINAL REPORT For Japan-Korea Joint Research Project
 (Form4-2) FINAL REPRT For Japan-Korea Joint Research Project AREA 1. Mathematics & Physics 2. Chemistry & Material Science 3. Biology 4. Informatics & Mechatronics 5. Geo-Science & Space Science 6. Medical
(Form4-2) FINAL REPRT For Japan-Korea Joint Research Project AREA 1. Mathematics & Physics 2. Chemistry & Material Science 3. Biology 4. Informatics & Mechatronics 5. Geo-Science & Space Science 6. Medical
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July
 344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July 30 2013 Summary of Grignard lecture Organometallic chemistry - the chemistry of compounds
344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July 30 2013 Summary of Grignard lecture Organometallic chemistry - the chemistry of compounds
2.2.7 Research Area Oxidative Coupling Reactions Methods and Mechanisms (M. Klußmann)
 2.2.7 Research Area Oxidative Coupling Reactions Methods and Mechanisms (M. Klußmann) Involved: E. Böß, P. Karier, K. M. Jones, T. Hillringhaus, C. Schmitz, J. Demaerel, B. Schweitzer-Chaput, N. Gulzar,
2.2.7 Research Area Oxidative Coupling Reactions Methods and Mechanisms (M. Klußmann) Involved: E. Böß, P. Karier, K. M. Jones, T. Hillringhaus, C. Schmitz, J. Demaerel, B. Schweitzer-Chaput, N. Gulzar,
Laboratory for Analytical Chemistry: Molecular Electrochemistry, Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Chemistry
 Laboratory for Analytical Chemistry: Molecular Electrochemistry, Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Chemistry http://www.sci.osaka-cu.ac.jp/chem/analy/analy.html Current Research and Principal
Laboratory for Analytical Chemistry: Molecular Electrochemistry, Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Chemistry http://www.sci.osaka-cu.ac.jp/chem/analy/analy.html Current Research and Principal
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
Formal Charge. Formal Charge. Formal Charge. Formal Charge. Most Lewis structures do not require any formal charges.
 : a charge assigned to each atom in a structure by assuming that the shared electrons are divided equally between the bonded atoms. Most Lewis structures do not require any formal charges. tructures that
: a charge assigned to each atom in a structure by assuming that the shared electrons are divided equally between the bonded atoms. Most Lewis structures do not require any formal charges. tructures that
Lecture 12. Metalloproteins - II
 Lecture 12 Metalloproteins - II Metalloenzymes Metalloproteins with one labile coordination site around the metal centre are known as metalloenzyme. As with all enzymes, the shape of the active site is
Lecture 12 Metalloproteins - II Metalloenzymes Metalloproteins with one labile coordination site around the metal centre are known as metalloenzyme. As with all enzymes, the shape of the active site is
1. Addition of HBr to alkenes
 eactions of Alkenes I eading: Wade chapter 8, sections 8-1- 8-8 tudy Problems: 8-47, 8-48, 8-55, 8-66, 8-67, 8-70 Key Concepts and kills: Predict the products of additions to alkenes, including regiochemistry
eactions of Alkenes I eading: Wade chapter 8, sections 8-1- 8-8 tudy Problems: 8-47, 8-48, 8-55, 8-66, 8-67, 8-70 Key Concepts and kills: Predict the products of additions to alkenes, including regiochemistry
CHEM Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kinetics Catalysts A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of the reaction but is neither created nor destroyed in the process. Catalysts can be divided into two broad categories. Homogeneous
Chemical Kinetics Catalysts A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of the reaction but is neither created nor destroyed in the process. Catalysts can be divided into two broad categories. Homogeneous
Catalytic Solar Water Splitting Inspired by Photosynthesis. Homogeneous Catalysts with a Mechanical ( Machine-Like ) Action.
 Catalytic Solar Water Splitting Inspired by Photosynthesis. Homogeneous Catalysts with a Mechanical ( Machine-Like ) Action Gerry Swiegers Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Electromaterials
Catalytic Solar Water Splitting Inspired by Photosynthesis. Homogeneous Catalysts with a Mechanical ( Machine-Like ) Action Gerry Swiegers Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Electromaterials
Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones
 Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
Chiral Ru/PNNP complexes in catalytic and stoichiometric electrophilic O- and F-atom transfer to 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 78, No. 2, pp. 391 396, 2006. doi:10.1351/pac200678020391 2006 IUPAC Chiral Ru/PNNP complexes in catalytic and stoichiometric electrophilic O- and F-atom transfer to 1,3-dicarbonyl
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 78, No. 2, pp. 391 396, 2006. doi:10.1351/pac200678020391 2006 IUPAC Chiral Ru/PNNP complexes in catalytic and stoichiometric electrophilic O- and F-atom transfer to 1,3-dicarbonyl
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds
 hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ADDITION REACTIONS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENERAL MECHANISM Addition reactions are ones in which 1 bond is broken and 2 new bonds are formed. They are the inverse of reactions EXAMPLE: Provide the mechanism for the
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENERAL MECHANISM Addition reactions are ones in which 1 bond is broken and 2 new bonds are formed. They are the inverse of reactions EXAMPLE: Provide the mechanism for the
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Formation of Ruthenium Carbenes by gem-hydrogen Transfer to Internal Alkynes: Implications for Alkyne trans-hydrogenation Markus Leutzsch, Larry M. Wolf, Puneet Gupta, Michael Fuchs,
Supporting Information Formation of Ruthenium Carbenes by gem-hydrogen Transfer to Internal Alkynes: Implications for Alkyne trans-hydrogenation Markus Leutzsch, Larry M. Wolf, Puneet Gupta, Michael Fuchs,
LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
Course Goals for CHEM 202
 Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito
 1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
CHEM 303 Organic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers
 CEM 303 rganic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers 1) Explain the reason for the different chemical reactivity of cyclopentadiene and cycloheptatriene toward bromine. 2 + 2 + oth no doubt start
CEM 303 rganic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers 1) Explain the reason for the different chemical reactivity of cyclopentadiene and cycloheptatriene toward bromine. 2 + 2 + oth no doubt start
An Introduction to Chemical Kinetics
 An Introduction to Chemical Kinetics Michel Soustelle WWILEY Table of Contents Preface xvii PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMICAL KINETICS 1 Chapter 1. Chemical Reaction and Kinetic Quantities 3 1.1. The
An Introduction to Chemical Kinetics Michel Soustelle WWILEY Table of Contents Preface xvii PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMICAL KINETICS 1 Chapter 1. Chemical Reaction and Kinetic Quantities 3 1.1. The
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hem A225 Notes Page 67 I. Introduction hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (=) with no other heteroatoms attached. An aldehyde has at least one hydrogen attached;
hem A225 Notes Page 67 I. Introduction hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (=) with no other heteroatoms attached. An aldehyde has at least one hydrogen attached;
Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics
 Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics Thus far we have calculated rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, etc. based on observations of macroscopic properties, but what is happening at the molecular
Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics Thus far we have calculated rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, etc. based on observations of macroscopic properties, but what is happening at the molecular
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides
 Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex. CHM 5.33 Fall 2005
 Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex CHM 5.33 Fall 2005 Introduction The experiment is based on research performed in the laboratory of Professor Cummins during the early 90 s.
Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex CHM 5.33 Fall 2005 Introduction The experiment is based on research performed in the laboratory of Professor Cummins during the early 90 s.
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of benzyl alcohol by Oxone catalyzed by Keggin type 12-tungstocobaltate(II)
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2014, 6 (3):133-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Kinetics
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2014, 6 (3):133-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Kinetics
N-Heterocyclic Carbenes
 N-Heterocyclic Carbenes References 1. "N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Organocatalysts." Marion, N.; Diez- Gonzalez, S.; Nolan, S.P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 26, 2988. (general review) 2. "Stable Carbenes."
N-Heterocyclic Carbenes References 1. "N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Organocatalysts." Marion, N.; Diez- Gonzalez, S.; Nolan, S.P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 26, 2988. (general review) 2. "Stable Carbenes."
Computer Modeling (Physical Chemistry) of Enzyme Catalysis, Metalloenzymes
 Computer Modeling (Physical Chemistry) of Enzyme Catalysis, Metalloenzymes Lubomír Rulíšek, Martin Srnec Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry AS CR J. Heyrovský Institute of Physical Chemistry
Computer Modeling (Physical Chemistry) of Enzyme Catalysis, Metalloenzymes Lubomír Rulíšek, Martin Srnec Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry AS CR J. Heyrovský Institute of Physical Chemistry
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Description
 CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
Additions to Metal-Alkene and -Alkyne Complexes
 Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Mechanism of Selective Oxidation and Ammoxidation of Propene on Bismuth Molybdates from DFT Calculations on Model Clusters
 J. Phys. Chem. B 00, 106, 5997-601 5997 Mechanism of Selective Oxidation and Ammoxidation of Propene on Bismuth Molybdates from DFT Calculations on Model Clusters Yun Hee Jang and William A. Goddard III*
J. Phys. Chem. B 00, 106, 5997-601 5997 Mechanism of Selective Oxidation and Ammoxidation of Propene on Bismuth Molybdates from DFT Calculations on Model Clusters Yun Hee Jang and William A. Goddard III*
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
Lecture 11 Organic Chemistry 1
 EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
FIVE MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES
 FIVE MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES 63 Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of five membered aromatic heterocycles X = O, S or NH a-substitution b-substitution The Substitution is regioselective
FIVE MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES 63 Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of five membered aromatic heterocycles X = O, S or NH a-substitution b-substitution The Substitution is regioselective
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms
 Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms 6.1 Enthalpy Enthalpy (ΔH or q) is the heat energy exchange between the reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure Breaking a bond requires the system
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms 6.1 Enthalpy Enthalpy (ΔH or q) is the heat energy exchange between the reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure Breaking a bond requires the system
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
KINETICS AND MECHANISM OF KEGGIN TYPE 12-TUNGSTOCOBALTATE (II) CATALYZED POTASSIUM IODIDE OXIDATION BY PERBORATE
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 12(1), 2014, 145-154 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com KINETICS AND MECHANISM OF KEGGIN TYPE 12-TUNGSTOCOBALTATE (II) CATALYZED POTASSIUM IODIDE OXIDATION BY PERBORATE D. S.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 12(1), 2014, 145-154 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com KINETICS AND MECHANISM OF KEGGIN TYPE 12-TUNGSTOCOBALTATE (II) CATALYZED POTASSIUM IODIDE OXIDATION BY PERBORATE D. S.
Theophylline (TH), the structure of which is presented below, is a bronchial-dilator used for the treatment of asthma.
 1 EXAM SCIETIIC CULTURE CEMISTRY PRBLEM 1: Theophylline (T), the structure of which is presented below, is a bronchial-dilator used for the treatment of asthma. 3 C 7 1 3 9 1.1 Structural study and acid-base
1 EXAM SCIETIIC CULTURE CEMISTRY PRBLEM 1: Theophylline (T), the structure of which is presented below, is a bronchial-dilator used for the treatment of asthma. 3 C 7 1 3 9 1.1 Structural study and acid-base
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
THE RATE EQUATION. might have a rate equation like this r = k [A] [B] 2
![THE RATE EQUATION. might have a rate equation like this r = k [A] [B] 2 THE RATE EQUATION. might have a rate equation like this r = k [A] [B] 2](/thumbs/85/91943336.jpg) Kinetics 2813 2816 9 THE RATE EQUATION Format is an equation that links the rate of reaction to the concentration of reactants can only be found by doing actual experiments cannot be found by just looking
Kinetics 2813 2816 9 THE RATE EQUATION Format is an equation that links the rate of reaction to the concentration of reactants can only be found by doing actual experiments cannot be found by just looking
D. X. Hu Towards Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation of Alkenes Burns Group
 D. X. Hu Towards Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation of Alkenes Burns Group Literature Review Organic Synthesis 10, 20, 50 Years from Now? Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation October 6 th, 2012
D. X. Hu Towards Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation of Alkenes Burns Group Literature Review Organic Synthesis 10, 20, 50 Years from Now? Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation October 6 th, 2012
Organometallic Catalysis
 Organometallic Catalysis The catalysts we will study are termed homogeneous catalysts as they are dissolved in th e same solvent as the substrate. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysts, such as palladium
Organometallic Catalysis The catalysts we will study are termed homogeneous catalysts as they are dissolved in th e same solvent as the substrate. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysts, such as palladium
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
CHEMISTRY Topic #8: Oxidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
a. Why do the amides coordinate to Zr and the phosphines to Co?
 Reactivity and Bonding of mplexes with Metal-Metal Bonds Goals: Determine electron counts and oxidation states of complexes with M-M bonds using CBC method of electron counting Draw molecular orbital diagrams
Reactivity and Bonding of mplexes with Metal-Metal Bonds Goals: Determine electron counts and oxidation states of complexes with M-M bonds using CBC method of electron counting Draw molecular orbital diagrams
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles
 Oxidative Couplings of Hydrocarbons Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles Oxidants involved: O 2 H 2 O 2 high h valent metals(copper salts) halides(iodine(Ⅲ) oxidants) Lei, A. W. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111,
Oxidative Couplings of Hydrocarbons Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles Oxidants involved: O 2 H 2 O 2 high h valent metals(copper salts) halides(iodine(Ⅲ) oxidants) Lei, A. W. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111,
Lecture 22 February 25, 2011 Metal Oxide Catalysis
 Lecture 22 February 25, 2011 Metal xide Catalysis ature of the Chemical Bond with applications to catalysis, materials science, nanotechnology, surface science, bioinorganic chemistry, and energy William
Lecture 22 February 25, 2011 Metal xide Catalysis ature of the Chemical Bond with applications to catalysis, materials science, nanotechnology, surface science, bioinorganic chemistry, and energy William
Ch120 Lecture: The BiMoO x Story
 Ch120 Lecture: The Bi x Story Heterogeneous selective (amm)oxidation of propene. Kimberly Chenoweth November 28, 2007 What do these processes have in common? Late 1800s Early 1900s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s
Ch120 Lecture: The Bi x Story Heterogeneous selective (amm)oxidation of propene. Kimberly Chenoweth November 28, 2007 What do these processes have in common? Late 1800s Early 1900s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, April 20, 2001, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, April 20, 2001, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the textbook and lab manual. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution notes
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the textbook and lab manual. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution notes History and Application: The rate of a reaction directly impacts the commercial
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the textbook and lab manual. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution notes History and Application: The rate of a reaction directly impacts the commercial
Investigation of the Role and Form. Formation. Michael Enright
 Investigation of the Role and Form of Silver Catalysts in C N Bond Formation Michael Enright Ripon College Importance Carbon Nitrogen Bonds Medicine Biological compounds Make C N bonds whenever we want
Investigation of the Role and Form of Silver Catalysts in C N Bond Formation Michael Enright Ripon College Importance Carbon Nitrogen Bonds Medicine Biological compounds Make C N bonds whenever we want
Catalysts in Petroleum Refining & Petrochemicals
 Iridium homogeneous catalysts following outer-sphere mechanisms Luis A. Oro Departamento de Química Inorgánica, Instituto de Síntesis Química y Catálisis Homogénea, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, 50010-Zaragoza,
Iridium homogeneous catalysts following outer-sphere mechanisms Luis A. Oro Departamento de Química Inorgánica, Instituto de Síntesis Química y Catálisis Homogénea, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, 50010-Zaragoza,
Oxidation of Phenolic Wastewater by Fenton's Reagent
 Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Vol.0 No. ( June 009) 35-4 ISSN: 997-4884 University of Baghdad College of Engineering xidation of
Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Vol.0 No. ( June 009) 35-4 ISSN: 997-4884 University of Baghdad College of Engineering xidation of
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Non-Heme Diiron Model Complexes Can Mediate Direct NO Reduction: Mechanistic Insight Into Flavodiiron NO Reductases Hai T. Dong, a Corey J. White, a Bo Zhang, b Carsten Krebs, b
Supporting Information Non-Heme Diiron Model Complexes Can Mediate Direct NO Reduction: Mechanistic Insight Into Flavodiiron NO Reductases Hai T. Dong, a Corey J. White, a Bo Zhang, b Carsten Krebs, b
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
5.03, Inorganic Chemistry Prof. Daniel G. Nocera Lecture 15 Apr 11: Substitution Reactions and the Trans Effect
 5.03, Inorganic Chemistry Prof. Daniel G. ocera Lecture 15 Apr 11: Substitution Reactions and the Trans Effect A substitution reaction is one in which an existing ligand on a metal center is replaced by
5.03, Inorganic Chemistry Prof. Daniel G. ocera Lecture 15 Apr 11: Substitution Reactions and the Trans Effect A substitution reaction is one in which an existing ligand on a metal center is replaced by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMETARY IFORMATIO DOI: 10.1038/CHEM.1874 Time-Resolved Observations of Water Oxidation Intermediates on a Cobalt Oxide anoparticle Catalyst Miao Zhang, Moreno de Respinis, and Heinz Frei * Physical
SUPPLEMETARY IFORMATIO DOI: 10.1038/CHEM.1874 Time-Resolved Observations of Water Oxidation Intermediates on a Cobalt Oxide anoparticle Catalyst Miao Zhang, Moreno de Respinis, and Heinz Frei * Physical
Lecture (3) 1. Reaction Rates. 2 NO 2 (g) 2 NO(g) + O 2 (g) Summary:
 Summary: Lecture (3) The expressions of rate of reaction and types of rates; Stoichiometric relationships between the rates of appearance or disappearance of components in a given reaction; Determination
Summary: Lecture (3) The expressions of rate of reaction and types of rates; Stoichiometric relationships between the rates of appearance or disappearance of components in a given reaction; Determination
Quanjuan Zhang, Na Zhang, Yi-Tao Long, Xuhong Qian, and Youjun Yang,, *
 Quanjuan Zhang, Na Zhang, Yi-Tao Long, Xuhong Qian, and Youjun Yang,, * State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Chemical Biology, School of Pharmacy, Department of Chemistry,
Quanjuan Zhang, Na Zhang, Yi-Tao Long, Xuhong Qian, and Youjun Yang,, * State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Chemical Biology, School of Pharmacy, Department of Chemistry,
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
CHEM Core Chemistry 3. Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms
 CHEM3012 - Core Chemistry 3 Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms 5. Mechanisms of electron transfer between metal ions This section of the course is concerned with the mechanisms of electron transfer reactions,
CHEM3012 - Core Chemistry 3 Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms 5. Mechanisms of electron transfer between metal ions This section of the course is concerned with the mechanisms of electron transfer reactions,
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation and Reduction Section 1 Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions involve transfer of electrons Oxidation loss of electrons Reduction gain of electrons Both half-reactions
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation and Reduction Section 1 Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions involve transfer of electrons Oxidation loss of electrons Reduction gain of electrons Both half-reactions
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker Oxidation. Tyler W. Wilson SED Group Meeting
 The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker xidation Tyler W. Wilson SE Group Meeting 11.27.2007 Introduction xidation of ethene by (II) chloride solutions (Phillips, 1894) -First used as a test for alkenes
The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker xidation Tyler W. Wilson SE Group Meeting 11.27.2007 Introduction xidation of ethene by (II) chloride solutions (Phillips, 1894) -First used as a test for alkenes
Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework
 Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework Major points: 1) Why reactions have barriers, and how catalysts
Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework Major points: 1) Why reactions have barriers, and how catalysts
Chemical Kinetics. Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions:
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions: reactant concentration temperature action of catalysts surface
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions: reactant concentration temperature action of catalysts surface
σ Bonded ligands: Transition Metal Alkyls and Hydrides
 σ Bonded ligands: Transition Metal Alkyls and Hydrides Simplest of organo-transitionmetal species Rare until and understanding of their stability in the 60 s and 70 s Metal alkyls can be considered as
σ Bonded ligands: Transition Metal Alkyls and Hydrides Simplest of organo-transitionmetal species Rare until and understanding of their stability in the 60 s and 70 s Metal alkyls can be considered as
What is the major product of the following reaction?
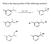 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
