LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
|
|
|
- Susanna Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections finish Ch.4, start Ch.5 (1) 4.7 Addition of halogens: halogenation NET RESULT: Add X-X across the C=C bond vicinal dihalide product MECHANISM: polarizable X X acts as δ + X Xδ - 1.) C=C bond attacks X+ cyclic halonium ion intermediate 2.) nucleophile (X ) attacks halonium ion X ends up bonded to the more highly substituted C does not actually exist Br shares lone pair with C Bromonium ion reacts with first Nu it encounters vicinal = on adjacent C s Imagine it as if C+ forms 1 st (but not true!) & then C+ shares adjacent X s lone pair Result: no atoms have open valence! much more stable than a C+! Thus: NO carbocation intermediate rearrangements do NOT occur. (2)
2 Some details about halogenation of alkenes Can we use all the halogens to prepare vicinal dihalides from alkenes? NO: Cl 2 & Br 2 are the only synthetically useful halogens F 2 is too reactive (explosive reaction too dangerous) I 2 rxn thermo. unfavourable (diiodide products unstable) Halonium ions are reactive intermediates (even though more stable than C+) react with whichever Nu they encounter first THUS: be sure Nu of interest is most concentrated Nu present THIS AFFECTS OUR CHOICE OF SOLVENT: If want a vicinal dihalide: use non-nucleophilic solvent e.g., CH 2 Cl 2 only Nu the halonium ion sees is the X anion If we use a nucleophilic solvent: e.g., water solvent will be the nucleophile present in highest concentration! solvent reacts with the halonium ion intermediate useful route to vicinally heterodisubstituted compounds, such as halohydrins (next slide) (3) Addition of Halogens in the Presence of Water: Halohydrin formation (cmpd with vicinal X & OH) Why does the Nu attack the more substituted C? Regiochemistry: the OH ends up on the more highly substituted C (as usual: electrophile bonds to the C with more H s on it) Resembles the more stable carbocation (but true C+ isn t formed ) (4)
3 What products would these reaction conditions yield? Ask yourself: 1) What is the electrophile? 2) Does a carbocation result? 3) What is the nucleophile? (of highest concentration) π-bond attacks E s δ + atom & E ends up on least substituted C If yes: form most stable cation possible 1 st : via regiochemistry of E addition 2 nd : via rearrangement(s) Nu reacts with electrophilic carbon (be sure to check if solvent is nucleophilic!) H 2 SO 4 CH 3 OH CH 3 OMe + CH 3 OMe E =? H + from H 2 SO 4 C+? yes on 3 sp 2 C (no rearrangement) Nu =? CH 3 OH Br 2 CH 2 Cl 2 Br Br Br Br + E =? Br + from Br 2 C+? No bromonium ion (anti addition!) Nu =? Br (CH 2 Cl 2 not a Nu) (5) 4.9 Addition of borane: hydroboration-oxidation anti-markovnikov addition of water NET RESULT: Add H-OH across the C=C bond anti-markovnikov! Follows a different mechanism: different electrophile! Anti-Markovnikov addition Syn addition! (6) Markovnikov addition: H goes where more H s are
4 Mechanism of hydroboration: B is the electrophile Boron has lower electronegativity than hydrogen BUT more importantly: in trivalent boron compounds: B has open valence shell! H δ THUS: the BORON is the electrophilic part of BH δ 3 H B highly reactive towards lone pairs & π-electrons!! δ + H δ MECHANISM OF HYDROBORATION: 1.) C=C bond attacks boron (δ + ) at same time as δ H attacks sp 2 C a concerted (1-step) process thus: H & B on same side of C=C syn addition Follows usual rule: electrophile adds to the less highly-sub d C WHY? Steric demand of borane group! H BH 2 δ δ + 2.) & subsequent steps: oxidation by H 2 O 2, OH, H 2 O removes boron group & replaces with OH (you are not responsible for the details here) (7) Stereochemistry of Hydroboration Oxidation i.e., relative orientation of groups in the products (see more in Ch.5) Always syn addition In 1 st step: H-B can add to either side of C=C initially, so get both possible syn products subsequent steps: do not change the orientation of the groups thus: stereochemistry dictated by 1 st step (8)
5 MORE DETAILS ABOUT THE MECHANISM: 1 st steps: formation of alkyl boranes In hydroboration: 1 BH 3 actually reacts with 3 alkene molecules First: Second: H BH 2 δ δ + Third: You are not responsible for reproducing this but seeing the full mechanism will help you understand the reaction (9) & then: subsequent oxidation steps ( bonds to O): OH replaces boron to yield alcohol You are not responsible for reproducing this but it might help you understand how we end up with an alcohol! Still open-valence, so still a strong Lewis acid a 1,2-alkyl shift (C-O bond is stronger) displaces OH (ok here: rxn in basic solution) alcohol! (10)
6 Key synthetically useful features of hydroboration: 1.) adds H-OH with anti-markovnikov regiochemistry 2.) avoids rearrangements of molecule (no carbocation int.) predictable, clean regiochemistry (good product control!) Acid-catalyzed hydration would involve 2 carbocation would rearrange THUS: major product would be 2-methyl-2-butanol 3-methyl-2-butanol as a minor product Hydroboration product no rearrangement anti-markovnikov syn addition of H & OH (syn not noticeable here since rxn did not generate stereochemistry) (11) What products would these reaction conditions yield? aromatic ring will remain H 2 SO 4 H 2 O OH major product (from resonancestabilized cation) + OH trace? likely none... (from non-resonancestabilized 2 o cation) E =? H + from H 2 SO 4 C+? yes on 2 sp 2 C (benzylic preferred!) Nu=?H 2 O 1.) BH 3 / THF 2.) H 2 O 2 / OH - / H 2 O H CH 3 + OH H H CH 3 OH H E =?B from BH 3 C+? No - hydroboration syn addition of H 2 O anti-markovnikov Nu=?In 1 st step: H (12)
7 What conditions would we use to prepare this compound?? H 3 O + Specific conditions? e.g., H 2 SO 4 / H 2 O OH no rearrangement (1 st C+ already 3 ) Addition of? H-OH (hydration) Regiochemistry? Markovnikov Conditions? Acid-catalyzed (13) 4.10 Addition of Radicals to Alkenes: Anti-Markovnikov addition of H-Br So far: Hydrohalogenation = route to alkyl halides Markovnikov addition product RADICAL HYDROBROMINATION: opposite regiochemistry hν or Anti- Markovnikov addition! Choose reaction conditions that yield desired regiochemistry! a) HBr at RT in the dark Markovnikov addition b) HBr with heat or light anti-markovnikov addition (+peroxide) (14)
8 Mechanism: Addition of Radicals to Alkenes hν or Form the 1 st reactant radicals Good radical initiators = organic peroxides (ROOR) weak O-O bond homolytically cleaves under heat or light Desired product More stable of 2 possible Form radical intermediates that propagate radical chain rxn (15) Relative Stabilities of Alkyl Radicals: similar trend as for carbocations, for same reason Hydrobromination with peroxide: via a radical intermediate! stability: 3 > 2 > 1 >> methyl C centre is sp 2 -hybridized (like C+) methyl radical CH 3 IMPLICATIONS: 1. regiochemistry: radical centre (& then H) will be on the more substituted C 2. stereochemistry: racemization (if chiral) see this in Ch.5 (16)
9 Mechanism: Addition of Radicals to Alkenes Side product: dihalide Radical-coupling rxns do not generate new radicals Summary: Radical hydrobromination anti-markovnikov HBr addition (via more stable radical intermediate) use dilute solution (to minimize dimerization of radical intermediates) use an inert solvent (usually CCl 4 or benzene; never a protic solvent!) And after Ch.5 (ignore for now), you ll see racemized alkyl halide product (if chiral centre created ) (17) Side product: dimer (i.e., 2 units coupled) Use of peroxide only changes the regiochemistry of HBr addition, not HCl or HI addition A radical process will occur instead of the non-radical mechanism ONLY if both of the propagation steps are exothermic: propagation steps: (a) are sometimes exothermic, but not always (b) use radicals AND produce radicals termination steps (consuming only radicals) are always exothermic & fast they compete with desired propagation steps & can use up the radicals before endothermic propagation occurs (18)
10 ASSIGNED READINGS BEFORE NEXT LECTURE: Read: Practice: rest of Ch.4 writing mechanisms & predicting products (19)
LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008
 CEM 221 section 52 LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6-3.8 Introduction to organic rxn mechanisms 4.1-4.5 Alkene reactions electrophilic addition mechanism carbocation
CEM 221 section 52 LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6-3.8 Introduction to organic rxn mechanisms 4.1-4.5 Alkene reactions electrophilic addition mechanism carbocation
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Chapter 4. Reactions of alkenes. Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions
 Chapter 4 Reactions of alkenes Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions Prob 47 p192. Give the reagents that would be required (including catalyst). Ch 4 #2 Electrophilic addition Ch 4
Chapter 4 Reactions of alkenes Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions Prob 47 p192. Give the reagents that would be required (including catalyst). Ch 4 #2 Electrophilic addition Ch 4
Double and Triple Bonds. The addition of an electrophile and a
 Chapter 11 Additions to Carbon-Carbon Double and Triple Bonds The addition of an electrophile and a nucleophile to a C-C C double or triple bonds 11.1 The General Mechanism Pi electrons of the double bond
Chapter 11 Additions to Carbon-Carbon Double and Triple Bonds The addition of an electrophile and a nucleophile to a C-C C double or triple bonds 11.1 The General Mechanism Pi electrons of the double bond
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
2/26/18. Practice Questions. Practice Questions B F. How many steps are there in this reaction?
 Practice Questions Practice Questions D B F C E A G How many steps are there in this reaction? 1 Practice Questions D B F C E A G What is the highest-energy transitions state? Practice Questions D B F
Practice Questions Practice Questions D B F C E A G How many steps are there in this reaction? 1 Practice Questions D B F C E A G What is the highest-energy transitions state? Practice Questions D B F
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2,
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6 How alkenes react: curved arrows to show
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6 How alkenes react: curved arrows to show
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2018
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
Organic Chemistry Lecture 2 - Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Substitutions
 ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem reaction what is added to the C=C what kind of molecule results addition of HX HX only
 I. Addition Reactions of Alkenes Introduction Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem 2310 An addition reaction always involves changing a double bond to a single bond and adding a new bond
I. Addition Reactions of Alkenes Introduction Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem 2310 An addition reaction always involves changing a double bond to a single bond and adding a new bond
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition. Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i. Chapter 10 Alkenes
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry. Alkenes (2)
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkenes (2) by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkenes (2) by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions "
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Alkenes are prepared by the reverse of the electrophilic reactions in the last chapter. That is, they are prepared by elimination reactions.
 Ch 8 Alkene Reactions and Syntheses Alkenes are prepared by the reverse of the electrophilic reactions in the last chapter. That is, they are prepared by elimination reactions. Dehydrohalogenation - Mechanism
Ch 8 Alkene Reactions and Syntheses Alkenes are prepared by the reverse of the electrophilic reactions in the last chapter. That is, they are prepared by elimination reactions. Dehydrohalogenation - Mechanism
Chapter 8 - Alkenes and Alkynes II Addition Reactions of Alkenes - Electrons in the π bond of alkenes react with electrophiles
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 8 - Alkenes and Alkynes II 8.1 - Addition Reactions of Alkenes - Electrons in the π bond of alkenes react with electrophiles 8.2 - Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes:
Andrew Rosen Chapter 8 - Alkenes and Alkynes II 8.1 - Addition Reactions of Alkenes - Electrons in the π bond of alkenes react with electrophiles 8.2 - Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes:
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2015
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
What is the major product of the following reaction?
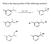 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
2. Hydrohalogenation: Propylene reacts with HBr to form 2-bromopropane.
 Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Organic Chemistry. Alkenes
 Organic Chemistry by Nurlin Abu Samah, Dr. Md. Shaheen & Dr. Nadeem Akhtar Faculty of Industrial Sciences & Technology nurlin@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims The students should understand the fundamental
Organic Chemistry by Nurlin Abu Samah, Dr. Md. Shaheen & Dr. Nadeem Akhtar Faculty of Industrial Sciences & Technology nurlin@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims The students should understand the fundamental
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
 Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis 1 Synthesis of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. loss of requires CH 2 CH 2 Cl Zaitsev s Rule: CH 2 C 2. Dehydration of
Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis 1 Synthesis of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. loss of requires CH 2 CH 2 Cl Zaitsev s Rule: CH 2 C 2. Dehydration of
Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7
 Sevada Chamras, Ph.D. Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7 Description: Examples: 3 Major Types of Organic Halides: 1. Alkyl Halides: Chapter 6 (Part 1/2) : Alkyl
Sevada Chamras, Ph.D. Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7 Description: Examples: 3 Major Types of Organic Halides: 1. Alkyl Halides: Chapter 6 (Part 1/2) : Alkyl
Ethers can be symmetrical or not:
 Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
6.10 Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes. Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes 6.10 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes O O reaction is acid catalyzed; typical hydration medium is 50% 2 SO 4-50% 2 O Follows Markovnikov's Rule Follows Markovnikov's
Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes 6.10 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes O O reaction is acid catalyzed; typical hydration medium is 50% 2 SO 4-50% 2 O Follows Markovnikov's Rule Follows Markovnikov's
Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes
 Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Electrophilic Additions o Regio vs stereoselectivity Regio where do the pieces add? Markovnikov s rule hydrogen will go to the side of the double bond with most hydrogens.
Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Electrophilic Additions o Regio vs stereoselectivity Regio where do the pieces add? Markovnikov s rule hydrogen will go to the side of the double bond with most hydrogens.
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Química Orgânica I. Organic Reactions
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
CHEMISTRY Topic #4: Electrophilic Addition Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay
 EMISTRY 2600 Topic #4: Electrophilic Addition Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay rganic Reactions (EM 2500 Review) Most reactions in organic chemistry fall into one (or more)
EMISTRY 2600 Topic #4: Electrophilic Addition Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay rganic Reactions (EM 2500 Review) Most reactions in organic chemistry fall into one (or more)
1. Addition of HBr to alkenes
 eactions of Alkenes I eading: Wade chapter 8, sections 8-1- 8-8 tudy Problems: 8-47, 8-48, 8-55, 8-66, 8-67, 8-70 Key Concepts and kills: Predict the products of additions to alkenes, including regiochemistry
eactions of Alkenes I eading: Wade chapter 8, sections 8-1- 8-8 tudy Problems: 8-47, 8-48, 8-55, 8-66, 8-67, 8-70 Key Concepts and kills: Predict the products of additions to alkenes, including regiochemistry
Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides
 Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides Ethers (R-O-R ) are compounds with two organic groups attached to an sp 3 oxygen. Epoxides are cyclic ethers where the sp 3 O is a part of a 3-membered ring. Thiols (R-S-H ) and
Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides Ethers (R-O-R ) are compounds with two organic groups attached to an sp 3 oxygen. Epoxides are cyclic ethers where the sp 3 O is a part of a 3-membered ring. Thiols (R-S-H ) and
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Study of Chemical Reactions
 Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
4. Alkenes are nucleophiles and like to attack electrophiles, like protons, with positive charges:
 Mechanism Steps: Answer Key 1. Alcohols are nucleophilic and like to grab protons,, to form water molecules: 2. 3. 4. Alkenes are nucleophiles and like to attack electrophiles, like protons, with positive
Mechanism Steps: Answer Key 1. Alcohols are nucleophilic and like to grab protons,, to form water molecules: 2. 3. 4. Alkenes are nucleophiles and like to attack electrophiles, like protons, with positive
Chapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups
 hapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups Preparation of alkenes: two common elimination reactions 1. Dehydration of alcohols Dehydration is a common biochemical reaction in carbohydrate
hapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups Preparation of alkenes: two common elimination reactions 1. Dehydration of alcohols Dehydration is a common biochemical reaction in carbohydrate
Essential Organic Chemistry. Chapter 9
 Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors
 1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors I, Cl, N 3, 3 P 4 pka 10 to 5 Super strong acids 3 + pka 1.7 RC 2 pka ~ 5 acids Ph pka ~ 10 get 2, R pka ~ 16 weaker RCC (alkynes) pka ~ 26 RN 2 pka
1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors I, Cl, N 3, 3 P 4 pka 10 to 5 Super strong acids 3 + pka 1.7 RC 2 pka ~ 5 acids Ph pka ~ 10 get 2, R pka ~ 16 weaker RCC (alkynes) pka ~ 26 RN 2 pka
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY. Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
CHEM 263 Oct 25, stronger base stronger acid weaker acid weaker base
 CEM 263 ct 25, 2016 Reactions and Synthesis (Preparation) of R- Breaking the - Bond of R- with Metals R + Li 0 or Na 0 or K 0 metal R Li + 1/2 2 alkoxide Breaking the - Bond of R- by Acid-Base Reaction
CEM 263 ct 25, 2016 Reactions and Synthesis (Preparation) of R- Breaking the - Bond of R- with Metals R + Li 0 or Na 0 or K 0 metal R Li + 1/2 2 alkoxide Breaking the - Bond of R- by Acid-Base Reaction
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ADDITION REACTIONS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENERAL MECHANISM Addition reactions are ones in which 1 bond is broken and 2 new bonds are formed. They are the inverse of reactions EXAMPLE: Provide the mechanism for the
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENERAL MECHANISM Addition reactions are ones in which 1 bond is broken and 2 new bonds are formed. They are the inverse of reactions EXAMPLE: Provide the mechanism for the
Learning Guide for Chapter 12 - Alkenes (II)
 Learning Guide for Chapter 12 - Alkenes (II) I. Addition reactions of alkenes Introduction to addition reactions Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes Hydroxylation of alkenes Epoxidation of alkenes Cyclopropanation
Learning Guide for Chapter 12 - Alkenes (II) I. Addition reactions of alkenes Introduction to addition reactions Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes Hydroxylation of alkenes Epoxidation of alkenes Cyclopropanation
p Bonds as Nucleophiles
 Chapter 8 p Bonds as Nucleophiles REACTIONS OF ALKENES, ALKYNES, DIENES, AND ENOLS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 8.2.1 Orbital structure of alkenes Geometry: Electrostatic potential: Electron-rich
Chapter 8 p Bonds as Nucleophiles REACTIONS OF ALKENES, ALKYNES, DIENES, AND ENOLS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 8.2.1 Orbital structure of alkenes Geometry: Electrostatic potential: Electron-rich
Chapter 8 Alkenes: Reactions
 Chamras Glendale Community College Organic Chemistry 105 Chapter 8 Alkenes: Reactions Name Type 1. alo-hydrogenation (Ionic & Radical) Electrophilic Addition 2. ydration (Acid-Catalyzed) Electrophilic
Chamras Glendale Community College Organic Chemistry 105 Chapter 8 Alkenes: Reactions Name Type 1. alo-hydrogenation (Ionic & Radical) Electrophilic Addition 2. ydration (Acid-Catalyzed) Electrophilic
Chem ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM 221 /4 02 Final Examination April 20, 2005 0900-1200 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x periodic table & pk a data table provided non-programmable calculators allowed molecular model kits allowed
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM 221 /4 02 Final Examination April 20, 2005 0900-1200 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x periodic table & pk a data table provided non-programmable calculators allowed molecular model kits allowed
ELECTROPHILIC ADDITIONS OF ALKENES AS THE COUNTERPART OF ELIMINATIONS
 ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
HONORS ORGANIC CHEM. HAHS MRS. RICHARDS
 NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds
 hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to:
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
What are radicals? H. Cl. Chapter 10 Radical Reactions. Production of radicals. Reactions of radicals. Electronic structure of methyl radical
 What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALKENES AND REACTIONS OF ALKENES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKENES and ALKYNES Alkenes/Alkynes are named by adding the suffix modifier (- /- ) to the end of the root. Alkenes/alkynes receive in numbering alkanes Location is assigned
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKENES and ALKYNES Alkenes/Alkynes are named by adding the suffix modifier (- /- ) to the end of the root. Alkenes/alkynes receive in numbering alkanes Location is assigned
C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes
 C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes. H C 2 H Biosynthesis of a prostaglandin from arachidonic acid: intermediate intramolecular radical addition CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts
C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes. H C 2 H Biosynthesis of a prostaglandin from arachidonic acid: intermediate intramolecular radical addition CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts
Alkenes - Addition Reactions
 Alkenes - Addition Reactions Alkenes- reactions. Addition Ionic Free radical Reduction Oxidation Substitution Reactions, alkenes: 1. Addition of hydrogen (reduction). 2. Addition of halogens. 3. Addition
Alkenes - Addition Reactions Alkenes- reactions. Addition Ionic Free radical Reduction Oxidation Substitution Reactions, alkenes: 1. Addition of hydrogen (reduction). 2. Addition of halogens. 3. Addition
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
Chapter 9. Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination
 Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides
 Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
5. Reactions of Alkenes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
Chapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides
 hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination
 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu,
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu,
Organic Chemistry CHM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl Halides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade)
 rganic Chemistry CM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl alides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade) Chapter utline I. Intro to RX (6-1 - 6-7) II. Substitution Reactions A) S N 2 (6-8,
rganic Chemistry CM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl alides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade) Chapter utline I. Intro to RX (6-1 - 6-7) II. Substitution Reactions A) S N 2 (6-8,
Loudon Chapter 14 Review: Reactions of Alkynes Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 1/16/2018
 An alkyne is any molecule with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds: the σ bond exists on a straight line between carbon atoms, while one π bond
An alkyne is any molecule with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds: the σ bond exists on a straight line between carbon atoms, while one π bond
Lecture 20 Organic Chemistry 1
 CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 20 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 18, 2010 1 Self-Test Question Capnellene (4) is a marine natural product that was isolated from coral
CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 20 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 18, 2010 1 Self-Test Question Capnellene (4) is a marine natural product that was isolated from coral
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) Complete the following reaction and provide a detailed, step-by-step mechanism for the process.
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) Complete the following reaction and provide a detailed, step-by-step mechanism for the process.
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles
 Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I 7.1 - Introduction - The simplest member of the alkenes has the common name of ethylene while the simplest member of the alkyne family has the common name
Andrew Rosen Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I 7.1 - Introduction - The simplest member of the alkenes has the common name of ethylene while the simplest member of the alkyne family has the common name
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides
 Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert:
 Substituent Effects There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert: RESONANCE effects are those that occur through the π system and can be represented by resonance structures. These
Substituent Effects There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert: RESONANCE effects are those that occur through the π system and can be represented by resonance structures. These
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview
 Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview Andrew Rosen Editor: Raghav Malik January 13, 2013 Contents I Library of Synthetic Reactions 3 II Organic Trends and Essentials 4 1 The Basics: Bonding and Molecular
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview Andrew Rosen Editor: Raghav Malik January 13, 2013 Contents I Library of Synthetic Reactions 3 II Organic Trends and Essentials 4 1 The Basics: Bonding and Molecular
10. Organohalides. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
PAPER No. 5: REACTION MECHANISM MODULE No. 2: Types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Ethers. Synthesis of Ethers. Chemical Properties of Ethers
 Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1 11.1 - Structure and Nomenclature - The common naming calls alcohols as alkyl alcohols (eg: methyl alcohol) - The common names of ethers have the groups
Andrew Rosen Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1 11.1 - Structure and Nomenclature - The common naming calls alcohols as alkyl alcohols (eg: methyl alcohol) - The common names of ethers have the groups
Chapter 8 Addition Reactions to Alkenes
 . 8 hapter 8 Addition eactions to Alkenes In this chapter will we study the addition reactions of alkenes. We will see that the π electrons of the double bond are loosely held and that their maximum electron
. 8 hapter 8 Addition eactions to Alkenes In this chapter will we study the addition reactions of alkenes. We will see that the π electrons of the double bond are loosely held and that their maximum electron
10: Alkenes and Alkynes. Electrophilic and Concerted Addition Reactions
 10: Alkenes and Alkynes. Electrophilic and Concerted Addition Reactions Addition Reactions Electrophilic Addition of H-X or X2 to Alkenes Addition of H-X and X2 to Alkynes Alkenes to Alcohols by Electrophilic
10: Alkenes and Alkynes. Electrophilic and Concerted Addition Reactions Addition Reactions Electrophilic Addition of H-X or X2 to Alkenes Addition of H-X and X2 to Alkynes Alkenes to Alcohols by Electrophilic
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
12AL Experiment 9: Markovnikov s Rule
 12AL Experiment 9: Markovnikov s Rule Safety: Proper lab goggles/glasses must be worn (even over prescription glasses). WEAR GLOVES this lab utilizes hydrogen peroxide which can burn your skin and multiple
12AL Experiment 9: Markovnikov s Rule Safety: Proper lab goggles/glasses must be worn (even over prescription glasses). WEAR GLOVES this lab utilizes hydrogen peroxide which can burn your skin and multiple
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
2. Which functional groups and structural features are present in the following molecule (strychnine)?
 Chapter 1-2: 1. Which of the following species has a negative charge but NO lone pair of valance shell nonbonding electrons? [all atoms have complete valance shell of electrons, but lone pairs are not
Chapter 1-2: 1. Which of the following species has a negative charge but NO lone pair of valance shell nonbonding electrons? [all atoms have complete valance shell of electrons, but lone pairs are not
Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions
 Grossman, CE 230 Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so
Grossman, CE 230 Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so
Organic Chemistry. Alkynes
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkynes by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkynes by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Substitution and Elimination reactions
 PART 3 Substitution and Elimination reactions Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of RX 9. Elimination reactions of RX 10. Substit n/elimin n of other comp ds 11. Organometallic comp ds 12. Radical reactions
PART 3 Substitution and Elimination reactions Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of RX 9. Elimination reactions of RX 10. Substit n/elimin n of other comp ds 11. Organometallic comp ds 12. Radical reactions
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Alkynes Nomenclature of Alkynes
 Chapter 7 Alkynes Alkynes - hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon triple bond (2 bonds) Acyclic alkanes = C n H 2n+2 Alkenes and cyclic alkanes = C n H 2n Alkynes (and cyclic alkenes) = C n H 2n-2 The
Chapter 7 Alkynes Alkynes - hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon triple bond (2 bonds) Acyclic alkanes = C n H 2n+2 Alkenes and cyclic alkanes = C n H 2n Alkynes (and cyclic alkenes) = C n H 2n-2 The
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides"
 Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides" t Introduction" The polarity of a carbon-halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge"
Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides" t Introduction" The polarity of a carbon-halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge"
Alkyl Halides. Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group.
 Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group. CHCl 3 (Chloroform: organic solvent) CF 2 Cl 2 (Freon-12: refrigerant
Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group. CHCl 3 (Chloroform: organic solvent) CF 2 Cl 2 (Freon-12: refrigerant
S N 1 Displacement Reactions
 S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat #
 Test 4 Name Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat # Part 1. Multiple Choice. Choose the one best answer, and clearly mark that answer
Test 4 Name Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat # Part 1. Multiple Choice. Choose the one best answer, and clearly mark that answer
