Dept. of Biomed. Eng. BME302: Biomedical Instrumentation Kyung Hee Univ. Chapter 11 Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation
|
|
|
- Joanna Stephens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 11 Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Analysis of patient specimens: to aid in the diagnosis and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy Clinical phathology or clinical laboratory department Chemistry: blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and other fluids Hematology: RBC, WBC, platelets, function of physiological systems in blood (clotting) Microbiology: pathological microorganisms in body tissues and fluids Blood bank: ABO grouping, blood bank Accuracy and precision are extremely important Fast response is required Automation using computer technology 11.1 Spectrophotometry A general term for a class of instruments including photometers and colorimeters Enough accuracy and precision, suitable for automation widely used Substances of clinical interests selectively absorb or emit electromagnetic energy at different wavelengths: ultraviolet (200 ~ 400 nm), visible (400 ~ 700 nm), and near infrared (700 ~ 800 nm) alc Beer's law: P P 10 where 0 R S T P 0 P 100P Percent transmittance, %T P Absorbance, A 0 radiant power arriving at the cuvette radiant power leaving the cuvette a absorptivity of the sample L length of the path through the sample C concentration of the absorbing substance alc P0 100 log log 2 log(% T) P % T F H G I K J F H G I K J Keep a and L constant and calibrate to get the absorbance, A s of the same substance with a known concentration, C s. Then, the unknown sample concentration, alc 1 Eung Je Woo
2 F H G u C C A u s A s I KJ Block diagram in Fig Power sources: Wavelength selectors Cuvette Sample Photometric system 2 Eung Je Woo
3 Flame Photometers Power source and sample-holder function are combined in the flame as in Fig In most cases, measure the sample's emission of light Only for determining the concentrations of pure metals Atomic Emission Flame Photometry Limited use for only Na +, K +, and Li + (with complicated optical system, Ca 2+ ) Only 1% of the atoms are raised to an excited level Only a few elements produce enough power at a single wavelength as they move back to lower-energy orbits Fig. 11.2(a): sample combined with a solvent nebulizer flame Fuel: propane or natural gas mixed with compressed air Solvent evaporates and particles disintegrate to yield atoms Atoms emit light as they move back to lower-energy orbits Parallel determinations of Na +, K +, and Li + Li + is used as the internal standard to correct the errors due to variations in the rate of solution uptake, aerosol production, and flame characteristics Good for small variations Cannot be used for patients receiving Li + to treat a psychotic disorder Atomic Absorption Flame Photometry Very accurate concentration determination for calcium, lead, copper, zinc, iron, magnesium Majority of atoms in a flame absorb energy at a characteristic wavelength Block diagram (Fig. 11.2(b)) Power source: placed in an atmosphere of an inert gas, hollow cathode lamp constructed from the metal to be determined (or coating) Heat the cathode atoms leaves the cathode cathode cavity is filled with atomic vapor atoms are excited due to collisions with electrons and ions emit light when returning to the ground state this light is directed to the flame the amount of the light absorption is proportional to the concentration Monochromator Detector: PM tube Rotating-sector disk between the source and the flame pulse output from power source phase-sensitive demodulator to differentiate the light emitted 3 Eung Je Woo
4 by the atoms Fluorometry Molecules: absorption of radiant energy being raised to an excited state emit light in a characteristic spectrum Block diagram (Fig. 11.3) Power source: mercury arc lamp (365, 405, 436, and 546 nm) Wavelength selector Detector: PM tube, at the right angle to the power source to avoid direct light transmission Higher sensitivity (10 4 higher than spectrophotometry) and great specificity picogram can be detected Only a small number of substances have fluorescence property Sensitive to ph and temperature 11.2 Automatic Chemical Analyzers Spectrophotometric methods 4 Eung Je Woo
5 Specimen aspiration, dilution, combination of sample with reagents, movement of samples, computation, recording Enhanced productivity and reduced response time Synchron CX4 High-capacity specimen processing chemistry analyzer Microcomputer-controlled discrete random-access clinical analyzer Automated specimen handling Performance of a variety of analytical test techniques Extensive use of microcomputers Bar code identification technique End-point and rate assays at 30 and 37 C Automatic Clinical Analyzer (ACA) Flexibility rather than high-capacity Serial determination of any of 40 tests for each sample 5 Eung Je Woo
6 11.3 Chromatology A group of methods for separating a mixture of substances into component parts Differences in the rate of movement of components of the mixture in the mobile phase (gas or liquid) due to the interaction of these components with the stationary phase (liquid or solid) four possible combinations Liquid stationary phase: partition Solid stationary phase: adsorption Detection of complex substances such as drugs or hormones: gas-liquid chromatographs (GLC) and thin-layer chromatographs (TLC) Gas-Liquid Chromatographs (GLC) Block diagram (Fig. 11.7): fast response (15 min or 1 h), great sensitivity (1 ng), small amount of sample (a few ml) Injector 5 ml of sample in the solvent Temperature is set to flash-evaporate he sample and solvent Carrier gas: mobile phase N2 or He (inert gas) Sweeps the evaporated sample and solvent gas down the column Column: stationary phase 1 m long, less than 7 mm diameter 6 Eung Je Woo
7 Packed with solid support material (such as diatomaceous earth) Solid support is coated with the liquid phase, Enclosed in a temperature-controlled oven: temperature controller gradually increases the temperature of the column for the best separation Detector At the end of the column Output electrical signal proportional to the quantity of the compound in the effluent gas (Fig. 11.8) Ionization detector, thermal conductivity detector, electron capture detector Recorder X-axis (time) distinguishes the components Y-axis (detector output) determines the quantity of the components 11.4 Electrophoresis Measure proteins in plasma, urine, and CSF Separate enzymes into their component isoenzymes Identify antibodies 7 Eung Je Woo
8 Basic Principles Movement of a solid phase with respect to a liquid (buffer solution) Buffer solution Carry current Keep the ph of the solution constant during migration Supported by a solid substance (medium) Zone Electrophoresis Sample is applied to the medium under electric field particles with similar size, charge, and shape migrate at similar rate separation of particles into zones Magnitude of charge: mobility (distance a particle moves in unit time per unit field strength, cm 2 /V s) of a particle is directly related with its net charge Ionic strength of buffer: higher buffer concentration slower migration Buffer ions themselves carry current Interaction between buffer ions and particles Temperature: mobility is directly related with temperature Current flow heat production temperature of medium increases resistance decreases increased migration rate Heat water evaporation increased particle concentration increased 8 Eung Je Woo
9 migration rate For gel type medium, constant-current source is used to minimize the heat production Time: distance of migration is directly related to the time Types of support media: paper, cellulose acetate, starch gel, agar gel, acrylamide gel, sucrose Cellulose acetate (Fig ) is widely used Constant voltage of 250 V for 15 ~ 20 min, initial current of 4 ~ 6 ma Use fixative to fix the migrated protein bands to the buffer Use dye to stain the bands Dried for densitometry Densitometer (Fig ): light source, filter, holder, detector (photodiode), recorder X-axis: migration distance Y-axis: membrane density (the amount of the component) Integrator Other factors: electroendosmosis, chromatography, particle shape, "barrier" effect, "wick flow", streaming potential 11.5 Hematology Basic Concepts Blood: formed elements (RBC, WBC, and platelet), substances in solution, and water Red blood cell (RBC) 9 Eung Je Woo
10 Carry oxygen and carbon dioxide RBC count: 4.6 ~ / L (normal adult male), 4.2 ~ / L (normal adult female), White blood cell (WBC) Defend the body against infection Five types (decreasing order): neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils WBC count: ~ / L (normal adult male and female) Platelet Plug small breaks in the walls of the blood vessels Participate in the clotting mechanism Platelet count: ~ / L (normal adult male and female) Hematocrit (HCT): % of the volume of all formed elements to the total volume of blood sample 40 ~ 54 % (normal adult men), 35 ~ 47 % (normal adult female) Hemoglobin (Hb) Conjugated protein in RBC Transports most of O2 and a portion of CO ~ 18 g/dl (normal adult men), 12 ~ 16 g/dl (normal adult female) RBC indices: characterization of RBC volume and Hb concentration MCV (mean corpuscular volume): 82 ~ 98 m 3 10HCT MCV RBC count MCH (mean corpuscular hemoglobin): 27 ~ 31 pg 10Hb MCH RBC count MCHC (mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration): 32 ~ 35 % MCHC 100Hb HCT RDW (volume distribution width): measure of the spread of the RBC volume distribution Electronic Devices for Measuring Blood Characteristics Detection of changes in electric resistance of a solution when a formed blood element is passed through an aperture: Coulter, Clay Adams, Lors & Lundberg, Baker Detection of deflection of light beam caused by the passage of formed blood elements: 10 Eung Je Woo
11 Technicon Coulter STKS (Fig ) Blood sample is anticoagulated with EDTA Accurate automatic aspiration Dilution (1:224) with a solution similar to plasma (Diluter I) Path 1 for Hb and WBC Mixing and lysing chamber Drabkin's solution converts hemoglobin to cyanmethemoglobin and lysing agent ruptures RBC Hb and WBC count Aperture bath (Fig ): constant-current source WBC or RBC voltage pulse Counts from three channels are within a range (common WBC-counting-bath electrode and individual aperture tube electrodes) average them to produce the result correction for coincidence using statistical signal processing Calibration using a specimen with a known WBC count threshold for pulse detection Path 2 for RBC Diluter II: further dilution of 1:224 due to greater RBC concentration RBC counter is identical to WBC counter (Fig ) Cells with volumes greater than 35.9 fl are classified as RBCs 256 channel RBC size histogram MCV and RDW Cells with volumes in the 2 ~ 20 fl range are classified as platelets 64 channel platelet size histogram MPV, PDW used for quality control Path 3 for WBC differential count WBC differential mixing and lysing chamber: RBC removal and WBC stabilization Flow cytometry: low frequency impedance, high frequency conductivity, and light scatter (laser illumination) Three-dimensional scatter plot (two-dimensional view in Fig ) Reticulocytes count RBCs are dyed with New Methylene Blue Separate run of the instrument RBC, Hb, MCV computer HCT, MCH, MCHC 11 Eung Je Woo
12 Diluter I Diluting fluid WBC stabilizing agent Lysing agent Diluter II Figure A block diagram of a Coulter Model STKS. (Modified from J. Davidsohn and J. B. Henry, Todd Sanford Clinical Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods, 15 ed. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co.) Lysing and mixing Triple transducer module WBC bath Lysing and mixing Hemoglobinometer Hgb C C C C C C RBC bath Analyzer computer Laboratory computer system Data management system Printer Vacuum (6"Hg) Aperture current Internal electrode External electrode + 75 m 100 m Sample beaker - Blood cell suspension Detail of aperture (WBC) Aperture Aperture tube Figure Coulter STKS aperture bath 12 Eung Je Woo
13 Automatic Differential Counts Pattern recognition technique Hematrak (Geometric Data Co.): Fig Used in cytology lab for automatic screening of pap smears for abnormal cells detection of early cervical carcinoma Color video scanner with microscope optics image memory morphological analyzer 13 Eung Je Woo
14 14 Eung Je Woo
(Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation)
 (Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation) Analysis of patient specimens: to aid in the diagnosis and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy Clinical phathology or clinical laboratory department Chemistry: blood,
(Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation) Analysis of patient specimens: to aid in the diagnosis and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy Clinical phathology or clinical laboratory department Chemistry: blood,
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 17 Clinical Systems Today Week in PBS&D Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Spectrophotometry Autoanalyzers Chromatology - Gas Chromatgraphs (Mass) Spectroscopy
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 17 Clinical Systems Today Week in PBS&D Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Spectrophotometry Autoanalyzers Chromatology - Gas Chromatgraphs (Mass) Spectroscopy
Clinical performance of Swelab Lumi 5-part hematology analyzer
 Clinical performance of Swelab Lumi -part hematology analyzer A complete blood count (CBC) is frequently requested by physicians to obtain information about a patient s blood status, and tests are routinely
Clinical performance of Swelab Lumi -part hematology analyzer A complete blood count (CBC) is frequently requested by physicians to obtain information about a patient s blood status, and tests are routinely
Spectrophotometry. Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology
 Spectrophotometry Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology Content Introduction Beer-Lambert law Instrument Applications Introduction 3 Body fluids such as blood, csf and urine contain organic and
Spectrophotometry Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology Content Introduction Beer-Lambert law Instrument Applications Introduction 3 Body fluids such as blood, csf and urine contain organic and
2101 Atomic Spectroscopy
 2101 Atomic Spectroscopy Atomic identification Atomic spectroscopy refers to the absorption and emission of ultraviolet to visible light by atoms and monoatomic ions. It is best used to analyze metals.
2101 Atomic Spectroscopy Atomic identification Atomic spectroscopy refers to the absorption and emission of ultraviolet to visible light by atoms and monoatomic ions. It is best used to analyze metals.
Spectrophotometry. Introduction
 Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
10/2/2008. hc λ. νλ =c. proportional to frequency. Energy is inversely proportional to wavelength And is directly proportional to wavenumber
 CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis
 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION
 FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION Atomic spectroscopy is based on the absorption, emission or fluorescence process of light by atoms or elementary ions. Information for atomic scale is obtained in two
FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION Atomic spectroscopy is based on the absorption, emission or fluorescence process of light by atoms or elementary ions. Information for atomic scale is obtained in two
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry
 Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
Atomization. In Flame Emission
 FLAME SPECTROSCOPY The concentration of an element in a solution is determined by measuring the absorption, emission or fluorescence of electromagnetic by its monatomic particles in gaseous state in the
FLAME SPECTROSCOPY The concentration of an element in a solution is determined by measuring the absorption, emission or fluorescence of electromagnetic by its monatomic particles in gaseous state in the
By Mohsin Al-Saleh Clinical Biochemistry Department (SQUH)
 Laboratory Automation By Mohsin Al-Saleh Clinical Biochemistry Department (SQUH) Objectives: Define automation and lab automation Advantages of laboratory automation History of laboratory automation Fluidic
Laboratory Automation By Mohsin Al-Saleh Clinical Biochemistry Department (SQUH) Objectives: Define automation and lab automation Advantages of laboratory automation History of laboratory automation Fluidic
Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis
 Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis 1. Which one of the following techniques can be used for the detection in a liquid chromatograph? a. Ultraviolet absorbance or refractive index measurement.
Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis 1. Which one of the following techniques can be used for the detection in a liquid chromatograph? a. Ultraviolet absorbance or refractive index measurement.
Emission spectrum of H
 Atomic Spectroscopy Atomic spectroscopy measures the spectra of elements in their atomic/ionized states. Atomic spectrometry, exploits quantized electronic transitions characteristic of each individual
Atomic Spectroscopy Atomic spectroscopy measures the spectra of elements in their atomic/ionized states. Atomic spectrometry, exploits quantized electronic transitions characteristic of each individual
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon
 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon Defination In analytical chemistry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon Defination In analytical chemistry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a
Chem 321 Name Answer Key D. Miller
 1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION. Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: _1/13
 Page 1 SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17544 Model Answer Page No: _1/13 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
Page 1 SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17544 Model Answer Page No: _1/13 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
UNIT: Basic Designs in Automation
 UNIT: Basic Designs in Automation 6basic.wpd Instrumentation IV Task To introduce basic designs and procedures in automation. Objectives Upon completion of this exercise, the student will: 1. Discuss common
UNIT: Basic Designs in Automation 6basic.wpd Instrumentation IV Task To introduce basic designs and procedures in automation. Objectives Upon completion of this exercise, the student will: 1. Discuss common
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
Chapter 18. Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry. Properties of Light
 Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY (AAS) is an analytical technique that measures the concentrations of elements. It makes use of the absorption of light
 ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY (AAS) is an analytical technique that measures the concentrations of elements. It makes use of the absorption of light by these elements in order to measure their concentration.
ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY (AAS) is an analytical technique that measures the concentrations of elements. It makes use of the absorption of light by these elements in order to measure their concentration.
AN INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY
 AN INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY Atomic spectroscopy deals with the absorption, emission, or fluorescence by atom or elementary ions. Two regions of the spectrum yield atomic information- the UV-visible
AN INTRODUCTION TO ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY Atomic spectroscopy deals with the absorption, emission, or fluorescence by atom or elementary ions. Two regions of the spectrum yield atomic information- the UV-visible
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
 Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy A. Evaluation of Analytical Parameters in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Objective The single feature that contributes most to making atomic
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy A. Evaluation of Analytical Parameters in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Objective The single feature that contributes most to making atomic
CHROMATOGRAPHY. The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments.
 CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS.
 School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 100 Internal Examiners: Professor A Kindness Dr T Msagati
School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 100 Internal Examiners: Professor A Kindness Dr T Msagati
Sub-category: Physics and Principles of Measurement Topic: Monitoring anesthetic gases and vapours Date: January 15-17, 2016 Language: English
 Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Physics and Principles of Measurement Topic: Monitoring anesthetic gases
Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Physics and Principles of Measurement Topic: Monitoring anesthetic gases
1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY?
 1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY? 1.1 The Nature Of Electromagnetic Radiation Anyone who has been sunburnt will know that light packs a punch: in scientific terms, it contains considerable amounts of energy. All
1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY? 1.1 The Nature Of Electromagnetic Radiation Anyone who has been sunburnt will know that light packs a punch: in scientific terms, it contains considerable amounts of energy. All
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
JAPAN QUALITY. Automated Clinical Analyzer
 JAPAN QUALITY Automated Clinical Analyzer Higher test performance and operability with new functions The clinical analyzer in the next stage 1 The best to the requirements for functionality and usability
JAPAN QUALITY Automated Clinical Analyzer Higher test performance and operability with new functions The clinical analyzer in the next stage 1 The best to the requirements for functionality and usability
Course Details. Analytical Techniques Based on Optical Spectroscopy. Course Details. Textbook. SCCH 211: Analytical Chemistry I
 SCCH 211: Analytical Chemistry I Analytical Techniques Based on Optical Spectroscopy Course Details September 22 October 10 September 22 November 7 November 17 December 1 Topic Period Introduction to Spectrometric
SCCH 211: Analytical Chemistry I Analytical Techniques Based on Optical Spectroscopy Course Details September 22 October 10 September 22 November 7 November 17 December 1 Topic Period Introduction to Spectrometric
Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry. Flexible. Reliable. Personal.
 L A B O R A T O R Y C O M P E T E N C E Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry Flexible. Reliable. Personal. The interaction of light with molecules is an essential and well accepted technique
L A B O R A T O R Y C O M P E T E N C E Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry Flexible. Reliable. Personal. The interaction of light with molecules is an essential and well accepted technique
COLORIMETER AND LAMBERT S-BEER S LAW. Shingala vaishali Sandha prafulla Tiwari Kuldeep
 COLORIMETER AND LAMBERT S-BEER S LAW Shingala vaishali Sandha prafulla Tiwari Kuldeep TOPIC What is colorimeter? Use of colorimeter. Component & It s function. Function of colorimeter. The principle of
COLORIMETER AND LAMBERT S-BEER S LAW Shingala vaishali Sandha prafulla Tiwari Kuldeep TOPIC What is colorimeter? Use of colorimeter. Component & It s function. Function of colorimeter. The principle of
PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY. Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC
 PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC CHROMATOGRAPHY Laboratory technique for the Separation of mixtures Chroma -"color" and graphein
PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC CHROMATOGRAPHY Laboratory technique for the Separation of mixtures Chroma -"color" and graphein
Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells
 Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells The Coulter counter Each cell that passes through the aperture reduces the current gives a spike. Cell behaves like an insulating sphere.
Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells The Coulter counter Each cell that passes through the aperture reduces the current gives a spike. Cell behaves like an insulating sphere.
ANALYSIS OF ZINC IN HAIR USING FLAME ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY
 ANALYSIS OF ZINC IN HAIR USING FLAME ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to determine the concentration of zinc in a sample of hair. You will use both the calibration
ANALYSIS OF ZINC IN HAIR USING FLAME ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to determine the concentration of zinc in a sample of hair. You will use both the calibration
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section 2: Planar Chromatography. Prof. Tarek A. Fayed
 Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section 2: Planar Chromatography Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Planar chromatography includes two types: 1- Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC). 2- Paper Chromatography (PC). Thin
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section 2: Planar Chromatography Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Planar chromatography includes two types: 1- Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC). 2- Paper Chromatography (PC). Thin
PRINCIPLE OF ICP- AES
 INTRODUCTION Non- flame atomic emission techniques, which use electrothermal means to atomize and excite the analyte, include inductively coupled plasma and arc spark. It has been 30 years since Inductively
INTRODUCTION Non- flame atomic emission techniques, which use electrothermal means to atomize and excite the analyte, include inductively coupled plasma and arc spark. It has been 30 years since Inductively
Spectroscopy Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT Spectroscopy
 Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT.00.009 Spectroscopy 04.09.12 http://tera.chem.ut.ee/~koit/arstpr/spe_en.pdf 1 ntroduction Spectroscopy is a general term for methods that investigate interactions
Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT.00.009 Spectroscopy 04.09.12 http://tera.chem.ut.ee/~koit/arstpr/spe_en.pdf 1 ntroduction Spectroscopy is a general term for methods that investigate interactions
Cork Institute of Technology. Summer 2005 Instrumental Analysis (Time: 3 Hours) Section A
 Cork Institute of Technology Higher Certificate in Science in Applied Biology Award (National Certificate in Science in Applied Biology Award) Answer FIVE questions; answer Section A, TWO questions from
Cork Institute of Technology Higher Certificate in Science in Applied Biology Award (National Certificate in Science in Applied Biology Award) Answer FIVE questions; answer Section A, TWO questions from
An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13)
 An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13) Beer s Law: A = -log T = -logp 0 / P = e x b x C See Table 13-1 for terms. In measuring absorbance or transmittance, one should
An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13) Beer s Law: A = -log T = -logp 0 / P = e x b x C See Table 13-1 for terms. In measuring absorbance or transmittance, one should
TURBIDIMETRY & NEPHELOMETRY. Mohsin Al-Saleh, Senior Biomedical Scientist (BSc. MLS-2004/MSc Clini. Chem. 2013) ID#6837
 TURBIDIMETRY & NEPHELOMETRY Mohsin Al-Saleh, Senior Biomedical Scientist (BSc. MLS-2004/MSc Clini. Chem. 2013) ID#6837 Lecture Objectives: Introduction (An Overview about laboratory techniques) Definition
TURBIDIMETRY & NEPHELOMETRY Mohsin Al-Saleh, Senior Biomedical Scientist (BSc. MLS-2004/MSc Clini. Chem. 2013) ID#6837 Lecture Objectives: Introduction (An Overview about laboratory techniques) Definition
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry
 1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
high temp ( K) Chapter 20: Atomic Spectroscopy
 high temp (2000-6000K) Chapter 20: Atomic Spectroscopy 20-1. An Overview Most compounds Atoms in gas phase high temp (2000-6000K) (AES) (AAS) (AFS) sample Mass-to-charge (ICP-MS) Atomic Absorption experiment
high temp (2000-6000K) Chapter 20: Atomic Spectroscopy 20-1. An Overview Most compounds Atoms in gas phase high temp (2000-6000K) (AES) (AAS) (AFS) sample Mass-to-charge (ICP-MS) Atomic Absorption experiment
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 17. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 17 Introduction to Optical Atomic Spectrometry From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 17 Introduction to Optical Atomic Spectrometry From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry
Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy
 Electronic Supplementary Material Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy Minhuan Lan 1,, Shaojing Zhao 1,, Zhenyu
Electronic Supplementary Material Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy Minhuan Lan 1,, Shaojing Zhao 1,, Zhenyu
JAPAN QUALITY. Automated Clinical Analyzer
 JAPAN QUALITY Automated Clinical Analyzer Higher test performance and operability with new functions The clinical analyzer in the next stage 1 The best to the requirements for functionality and usability
JAPAN QUALITY Automated Clinical Analyzer Higher test performance and operability with new functions The clinical analyzer in the next stage 1 The best to the requirements for functionality and usability
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law.
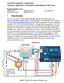 The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
2001 Spectrometers. Instrument Machinery. Movies from this presentation can be access at
 2001 Spectrometers Instrument Machinery Movies from this presentation can be access at http://www.shsu.edu/~chm_tgc/sounds/sound.html Chp20: 1 Optical Instruments Instrument Components Components of various
2001 Spectrometers Instrument Machinery Movies from this presentation can be access at http://www.shsu.edu/~chm_tgc/sounds/sound.html Chp20: 1 Optical Instruments Instrument Components Components of various
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1. Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry. Accuracy vs Precision
 Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1 Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry 3 Accuracy vs Precision Precision is the consistency of a measurement made
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1 Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry 3 Accuracy vs Precision Precision is the consistency of a measurement made
Thin Layer Chromatography
 Thin Layer Chromatography Thin-layer chromatography involves the same principles as column chromatography, it also is a form of solid-liquid adsorption chromatography. In this case, however, the solid
Thin Layer Chromatography Thin-layer chromatography involves the same principles as column chromatography, it also is a form of solid-liquid adsorption chromatography. In this case, however, the solid
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
 Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) Alex Miller ABC s of Electrochemistry 3/8/2012 Contents What is Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy? Basic Anatomy of an AAS system Theory of Operation Practical Operation
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) Alex Miller ABC s of Electrochemistry 3/8/2012 Contents What is Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy? Basic Anatomy of an AAS system Theory of Operation Practical Operation
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed
 Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Gas Chromatography (GC) In gas chromatography, the sample is vaporized and injected onto the head of a chromatographic
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Gas Chromatography (GC) In gas chromatography, the sample is vaporized and injected onto the head of a chromatographic
x Contents 3 The Stationary Phase in Thin-Layer Chromatography Activating and Deactivating Stationary Phases Snyder s Adsorption M
 Contents 1 History of Planar Chromatography... 1 1.1 History of Paper Chromatography (PC)... 1 1.2 History of Thin-Layer Chromatography... 7 1.3 The History of Quantitative Planar Chromatography... 8 References.....
Contents 1 History of Planar Chromatography... 1 1.1 History of Paper Chromatography (PC)... 1 1.2 History of Thin-Layer Chromatography... 7 1.3 The History of Quantitative Planar Chromatography... 8 References.....
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 7. Endpoint vs Kinetic Techniques. Instrumentation and Assay techniques
 Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 7 Instrumentation and Assay techniques Endpoint vs Kinetic Techniques two different approaches to analyzing for a substance Endpoint methods use all the
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 7 Instrumentation and Assay techniques Endpoint vs Kinetic Techniques two different approaches to analyzing for a substance Endpoint methods use all the
3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
 3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Introduction Atomic-absorption (AA) spectroscopy uses the absorption of light to measure the concentration of gas-phase atoms. Since samples are usually liquids or solids,
3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Introduction Atomic-absorption (AA) spectroscopy uses the absorption of light to measure the concentration of gas-phase atoms. Since samples are usually liquids or solids,
Reference literature. (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters )
 September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
II. Spectrophotometry (Chapters 17, 19, 20)
 II. Spectrophotometry (Chapters 17, 19, 20) FUNDAMENTALS (Chapter 17) Spectrophotometry: any technique that uses light to measure concentrations (here: U and visible - ~190 800 nm) c = 2.99792 x 10 8 m/s
II. Spectrophotometry (Chapters 17, 19, 20) FUNDAMENTALS (Chapter 17) Spectrophotometry: any technique that uses light to measure concentrations (here: U and visible - ~190 800 nm) c = 2.99792 x 10 8 m/s
Volumetric Analysis. Quantitative analysis answers the second question
 Volumetric Analysis Volumetric analysis is a form of quantitative analysis involving the measuring of volumes of reacting solutions, it involves the use of titrations. When buying food we often have two
Volumetric Analysis Volumetric analysis is a form of quantitative analysis involving the measuring of volumes of reacting solutions, it involves the use of titrations. When buying food we often have two
SPECTROPHOTOMETRY AND SPECTROMETRY - CONCEPT AND APPLICATIONS
 SPECTROPHOTOMETRY AND SPECTROMETRY - CONCEPT AND APPLICATIONS Renjini A 1, Dani Dileep 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Rajadhani Institute of Engineering and Technology, Kerala, India 2 PG
SPECTROPHOTOMETRY AND SPECTROMETRY - CONCEPT AND APPLICATIONS Renjini A 1, Dani Dileep 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Rajadhani Institute of Engineering and Technology, Kerala, India 2 PG
Chromatography. Mrs. D. MEENA MPharm PA & QA KTPC
 Chromatography Mrs. D. MEENA MPharm PA & QA KTPC INTRODUCTION ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Analytical chemistry involves separating, identifying and determining the relative amount of the components in a sample
Chromatography Mrs. D. MEENA MPharm PA & QA KTPC INTRODUCTION ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Analytical chemistry involves separating, identifying and determining the relative amount of the components in a sample
2014 학년도 1 학기 분석화학실험. 담당교수 : 이원용 ( 연구실 : 과 443-C, 전화 : , 전자우편 : 분광분석 / / 분리분석 / 전기분석화학
 2014 학년도 1 학기 분석화학실험 담당교수 : 이원용 ( 연구실 : 과 443-C, 전화 : 2123-2649, 전자우편 : wylee@yonsei.ac.kr) 분광분석 / / 분리분석 / 전기분석화학 Instrumental Analysis General concept Spectrophotometric experiment I A Lamp Monochromator
2014 학년도 1 학기 분석화학실험 담당교수 : 이원용 ( 연구실 : 과 443-C, 전화 : 2123-2649, 전자우편 : wylee@yonsei.ac.kr) 분광분석 / / 분리분석 / 전기분석화학 Instrumental Analysis General concept Spectrophotometric experiment I A Lamp Monochromator
Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy. Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy
 Topic 1: Atomic Spectroscopy Text: Chapter 12,13 & 14 Rouessac (~2 weeks) 1.0 Review basic concepts in Spectroscopy 2.0 Atomic Absorption and Graphite Furnace Instruments 3.0 Inductively Coupled Plasmas
Topic 1: Atomic Spectroscopy Text: Chapter 12,13 & 14 Rouessac (~2 weeks) 1.0 Review basic concepts in Spectroscopy 2.0 Atomic Absorption and Graphite Furnace Instruments 3.0 Inductively Coupled Plasmas
Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy. Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy
 Topic 2b: X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Text: Chapter 12 Rouessac (1 week) 4.0 X-ray Fluorescence Download, read and understand EPA method 6010C ICP-OES Winter 2009 Page 1 Atomic X-ray Spectrometry Fundamental
Topic 2b: X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Text: Chapter 12 Rouessac (1 week) 4.0 X-ray Fluorescence Download, read and understand EPA method 6010C ICP-OES Winter 2009 Page 1 Atomic X-ray Spectrometry Fundamental
Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY
 Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY The emission and absorption of light energy of particular wavelengths by atoms and molecules is a common phenomenon. The emissions/absorptions are characteristic for each
Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY The emission and absorption of light energy of particular wavelengths by atoms and molecules is a common phenomenon. The emissions/absorptions are characteristic for each
Chromatography. Gas Chromatography
 Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR-603203 EI 2302 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS QUESTION BANK UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. State Lambert
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR-603203 EI 2302 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS QUESTION BANK UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. State Lambert
BRIEFING. Pharmacopeial Discussion Group Sign Off Document Attributes EP JP USP Definition Loss on drying Readily carbonizable substances
 BRIEFING Saccharin, NF 22 page 2825 and page 1711 of PF 29(5) [Sept. Oct. 2003]. The United States Pharmacopeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards
BRIEFING Saccharin, NF 22 page 2825 and page 1711 of PF 29(5) [Sept. Oct. 2003]. The United States Pharmacopeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
 Atomic Emission Spectroscopy Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451 Saudi Arabia Building:
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451 Saudi Arabia Building:
 HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
Protein separation and characterization
 Address:800 S Wineville Avenue, Ontario, CA 91761,USA Website:www.aladdin-e.com Email USA: tech@aladdin-e.com Email EU: eutech@aladdin-e.com Email Asia Pacific: cntech@aladdin-e.com Protein separation
Address:800 S Wineville Avenue, Ontario, CA 91761,USA Website:www.aladdin-e.com Email USA: tech@aladdin-e.com Email EU: eutech@aladdin-e.com Email Asia Pacific: cntech@aladdin-e.com Protein separation
Spectroscopy and Chromatography
 Spectroscopy and Chromatography Introduction Visible light is one very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The different properties of the various types of radiation depend upon their wavelength.
Spectroscopy and Chromatography Introduction Visible light is one very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The different properties of the various types of radiation depend upon their wavelength.
1. SETTING UP A PRACTICE LABORATORY. General Clinical Pathology LECTURE 3. EQUIPMENT FOR VETERINARY PRACTICE LABORATORIES OVERVIEW
 Undergraduate Course in Veterinary Clinical Pathology Socrates - Erasmus programme General Clinical Pathology LECTURE 3. EQUIPMENT FOR VETERINARY PRACTICE LABORATORIES 3-1 OVERVIEW 1. Setting up a practice
Undergraduate Course in Veterinary Clinical Pathology Socrates - Erasmus programme General Clinical Pathology LECTURE 3. EQUIPMENT FOR VETERINARY PRACTICE LABORATORIES 3-1 OVERVIEW 1. Setting up a practice
2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography
 2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography Chromatography Scheme Gas chromatography - specifically gas-liquid chromatography - involves a sample being vaporized and injected onto the head of the chromatographic
2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography Chromatography Scheme Gas chromatography - specifically gas-liquid chromatography - involves a sample being vaporized and injected onto the head of the chromatographic
PAPER AND THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY (TLC)
 PAPER AND THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY (TLC) Objectives Understand the principle of Paper and Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC). Diagnose two samples of urine for Phenylketonuria and Cystinuria, using paper
PAPER AND THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY (TLC) Objectives Understand the principle of Paper and Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC). Diagnose two samples of urine for Phenylketonuria and Cystinuria, using paper
Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant
 Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
Lecture 7: Atomic Spectroscopy
 Lecture 7: Atomic Spectroscopy 1 Atomic spectroscopy The wavelengths of absorbance and emission from atoms in the gas phase are characteristic of atomic orbitals. 2 In the lowest energy transition, the
Lecture 7: Atomic Spectroscopy 1 Atomic spectroscopy The wavelengths of absorbance and emission from atoms in the gas phase are characteristic of atomic orbitals. 2 In the lowest energy transition, the
Absorption photometry
 The light Absorption photometry Szilvia Barkó University of Pécs, Faculty of Medicines, Dept. Biophysics February 2011 Transversal wave E Electromagnetic wave electric gradient vector wavelength The dual
The light Absorption photometry Szilvia Barkó University of Pécs, Faculty of Medicines, Dept. Biophysics February 2011 Transversal wave E Electromagnetic wave electric gradient vector wavelength The dual
MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer
 Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Luminescence transitions. Fluorescence spectroscopy
 Luminescence transitions Fluorescence spectroscopy Advantages: High sensitivity (single molecule detection!) Measuring increment in signal against a dark (zero) background Emission is proportional to excitation
Luminescence transitions Fluorescence spectroscopy Advantages: High sensitivity (single molecule detection!) Measuring increment in signal against a dark (zero) background Emission is proportional to excitation
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 18. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 18 Instrumentation Radiation sources Hollow cathode lamp Most common source Consist of W anode and a cathode sealed in a glass tube filled with Ne or Ar. Hollow
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 18 Instrumentation Radiation sources Hollow cathode lamp Most common source Consist of W anode and a cathode sealed in a glass tube filled with Ne or Ar. Hollow
CHIRAL SEPARATION USING THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
 CHIRAL SEPARATION USING THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Chiral Chromatography Chiral - adjective: not superimposable on its mirror image: used to describe a molecule whose arrangement of atoms is such that it
CHIRAL SEPARATION USING THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Chiral Chromatography Chiral - adjective: not superimposable on its mirror image: used to describe a molecule whose arrangement of atoms is such that it
Chapter 9. Atomic emission and Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry Emission spectrophotometric Techniques
 Chapter 9 Atomic emission and Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry Emission spectrophotometric Techniques Emission Spectroscopy Flame and Plasma Emission Spectroscopy are based upon those particles that are
Chapter 9 Atomic emission and Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry Emission spectrophotometric Techniques Emission Spectroscopy Flame and Plasma Emission Spectroscopy are based upon those particles that are
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Atmospheric Analysis Gases. Sampling and analysis of gaseous compounds
 Atmospheric Analysis Gases Sampling and analysis of gaseous compounds Introduction - External environment (ambient air) ; global warming, acid rain, introduction of pollutants, etc - Internal environment
Atmospheric Analysis Gases Sampling and analysis of gaseous compounds Introduction - External environment (ambient air) ; global warming, acid rain, introduction of pollutants, etc - Internal environment
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Spectrophotometry in the ultraviolet GPM.1.2.1.1.0003.15 and visible spectral regions Replaces the SPRF X GPM, SPRF XI GPM,
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Spectrophotometry in the ultraviolet GPM.1.2.1.1.0003.15 and visible spectral regions Replaces the SPRF X GPM, SPRF XI GPM,
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
 CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit IV Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering
CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit IV Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering
The solution for all of your
 The solution for all of your nanoparticle sizing and zeta potential needs. DelsaNano Series Blood Banking Capillary Electrophoresis Cell Analysis Centrifugation Genomics Lab Automation Lab Tools Particle
The solution for all of your nanoparticle sizing and zeta potential needs. DelsaNano Series Blood Banking Capillary Electrophoresis Cell Analysis Centrifugation Genomics Lab Automation Lab Tools Particle
Concepts, Techniques. Concepts, Techniques 9/11/2012. & Beer s Law. For a simple, transparent, COLORED material, e.g. ROYGBV
 9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
31. Applications of the chromatographic methods in drug analysis
 31. Applications of the chromatographic methods in drug analysis 31. 1. Depending on the processes that underlie the chromatographic separation, the following methods exist: A. adsorption chromatography
31. Applications of the chromatographic methods in drug analysis 31. 1. Depending on the processes that underlie the chromatographic separation, the following methods exist: A. adsorption chromatography
Analytical techniques: Environmental samples. Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve
 Analytical techniques: Environmental samples Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve Terms, definitions & applications Difference between technique and method: Analytical technique: Fundamental scientific application
Analytical techniques: Environmental samples Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve Terms, definitions & applications Difference between technique and method: Analytical technique: Fundamental scientific application
Complete the following. Clearly mark your answers. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT.
 CHEM 322 Name Exam 3 Spring 2013 Complete the following. Clearly mark your answers. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT. Warm-up (3 points each). 1. In Raman Spectroscopy, molecules are promoted
CHEM 322 Name Exam 3 Spring 2013 Complete the following. Clearly mark your answers. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT. Warm-up (3 points each). 1. In Raman Spectroscopy, molecules are promoted
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. 5.1 Light in Everyday Life. How do we experience light?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Fundamentals of Mass Spectrometry. Fundamentals of Mass Spectrometry. Learning Objective. Proteomics
 Mass spectrometry (MS) is the technique for protein identification and analysis by production of charged molecular species in vacuum, and their separation by magnetic and electric fields based on mass
Mass spectrometry (MS) is the technique for protein identification and analysis by production of charged molecular species in vacuum, and their separation by magnetic and electric fields based on mass
Ch 313 FINAL EXAM OUTLINE Spring 2010
 Ch 313 FINAL EXAM OUTLINE Spring 2010 NOTE: Use this outline at your own risk sometimes a topic is omitted that you are still responsible for. It is meant to be a study aid and is not meant to be a replacement
Ch 313 FINAL EXAM OUTLINE Spring 2010 NOTE: Use this outline at your own risk sometimes a topic is omitted that you are still responsible for. It is meant to be a study aid and is not meant to be a replacement
Far UV Absorbance Detector
 Far UV Absorbance Detector Theory Most organic and inorganic species absorb strongly in the far UV. Notable exceptions are the inert gases, helium and nitrogen which absorb very weakly in this region.
Far UV Absorbance Detector Theory Most organic and inorganic species absorb strongly in the far UV. Notable exceptions are the inert gases, helium and nitrogen which absorb very weakly in this region.
Chromatography. writing in color
 Chromatography writing in color Outlines of Lecture Chromatographic analysis» Principles and theory.» Definition.» Mechanism.» Types of chromatography.» Uses of Chromatography. In 1906 Mikhail Tswett used
Chromatography writing in color Outlines of Lecture Chromatographic analysis» Principles and theory.» Definition.» Mechanism.» Types of chromatography.» Uses of Chromatography. In 1906 Mikhail Tswett used
AIMALYTICAL CHEMISTRY
 Fundamentals of AIMALYTICAL CHEMISTRY Seventh Edition Douglas A. Skoog Stanford University Donald M. West San Jose State University F. James Holler University ;of Kentucky W r SAUNDERS COLLEGE PUBLISHING
Fundamentals of AIMALYTICAL CHEMISTRY Seventh Edition Douglas A. Skoog Stanford University Donald M. West San Jose State University F. James Holler University ;of Kentucky W r SAUNDERS COLLEGE PUBLISHING
The Biological Importance of Water
 The Biological Importance of Water Why is water important? Major component of all living systems and our planet. Occupies most of a cells volume. Has major properties that living systems require. Water
The Biological Importance of Water Why is water important? Major component of all living systems and our planet. Occupies most of a cells volume. Has major properties that living systems require. Water
