Residual dipolar coupling constants: An elementary derivation of key equations
|
|
|
- Maximilian Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Conceps in Magneic Resonance 1A, Residual dipola coupling consans: An elemena deivaion of ke equaions F. Kame, M. V. Deshmukh, H. Kessle and S. J. Glase* Insiu fü Oganische Chemie und Biochemie, Technische Univesiä München, Lichenegsaße 4, 85747, Gaching, Geman * Coespondence o: Pof. D. Seffen Glase Phone: Fa: , Glase@ch.um.de
2 ABSTRACT Residual dipola couplings RDC have ecenl found a wide ange of applicaions in high esoluion NMR of iomolecules in he liquid sae. A non-isoopic oienaional disiuion of a molecule of inees esuls in non-eo aveage dipola coupling consans. Hee, we pesen an inuiive inoducion o he alignmen enso and an elemena deivaion of ke equaions. KEYWORDS alignmen enso, coupling consan, dipola coupling, dipola Hamilonian, ode mai, poaili mai, esidual dipola coupling, Saupe mai.
3 INTRODUCTION While dipola couplings ae he dominan ineacions in solid sae NMR of spin 1/ nuclei, he ae aveaged o eo fo isoopicall eoiening molecules in he liquid sae. This makes i possile o achieve high-esoluion speca wih elaive ease in liquid sae NMR. On he ohe hand, a wealh of sucual infomaion is los if dipola couplings vanish. Howeve, even in liquid sae NMR, molecules can e paiall aligned, e. g. eenal fields magneic o elecic o anisoopic solvens 1-8. Fo eample in liquid csalline solvens, he dissolved molecules ae paiall aligned hough seic and anisoopic ineacions wih he solven molecules, and dipola couplings can e oseved 9, 10. The ecen success and wide use of such esidual dipola couplings is due o he developmen and chaaceiaion of seveal new alignmen media such as icelles 5, filamenous phage Pf1 11, and polaclamide gels 1, 1, which make i possile o ceae a elaivel small, unale degee of alignmen. This allows he specoscopis o adjus he alignmen in such a wa, ha he sie of he aveage dipola coupling is in he ode of he J couplings. In his case, he esuling speca ae sill simple, and dipola coupling consans can e measued elaivel eas compaing line spliings in isoopic and in aligned samples. Techniques o measue esidual dipola couplings and a wide ange of applicaions have een discussed in a nume of aicles and eviews -8. Hee, we evisi he fundamenal quesion of how o calculae he epeced esidual dipola coupling consan fo a homonuclea e.g. 1 H- 1 H o heeonuclea e.g. 15 N- 1 H spin pai. This uns ou o e a supisingl simple calculaion if we know he oienaion and he hee pincipal componens of he so-called alignmen enso. This alignmen enso is a ke concep, ha is cucial o undesand esidual dipola couplings. Howeve, in ou epeience, man sudens and even seasoned paciiones in he field of NMR have concepual 1
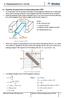
4 difficulies o full undesand he phsical meaning of he alignmen enso which someimes lead o seious misconcepions vide infa. This ma esul in pa fom he common pacice in lieaue, o deive he alignmen enso using mahemaicall elegan, u no ve inuiive appoaches ased on spheical hamonics, hei addiion heoems, Legende polnomials, Wigne oaion maices and a confusing nume of angles eween vaious aes. In conas, we hee use a seamlined geomeic appoach simila o he oiginal deivaion Saupe 9, 10, which is ased on he Caesian epesenaion of vecos. Ecep fo he mos asic ules of mai and veco muliplicaion, onl elemena mahemaics is needed o deive he alignmen enso. As a didacical aid on he wa o undesanding he alignmen enso, we discuss he elaed poaili enso. Numeical eamples and illusaing figues ae used o conve he phsical meaning of hese ensos. In he Appendi, vaious epessions fo he esidual dipola coupling consans commonl found in lieaue ae deived fom he pesened ke esuls. STATIC DIPOLAR COUPLING HAMILTONIAN We conside wo spins I and S wih an inenuclea veco R v see Fig. 1. This veco can e epessed in he fom v v R R, [1] whee R is he disance eween he wo nuclei and v is a uni veco poining in he diecion of R v. Similal, he veco epesening he eenal magneic field B v can e epessed in he fom
5 v v B B, [] whee B is he magniude of he saic magneic field, and v is a uni veco poining in he L diecion of he magneic field. In he la fame, L, L, whee convenion he magneic field poins along he L ais, he uncaed dipola coupling Hamilonian has he fom H D D% I L S L ' I L S L ' I L S L. [] If he spins I and S ae heeonuclea, he second and hid em in he acke can e negleced, esuling in he simple weak dipola coupling Hamilonian H [4] D DI L S L which has he same fom as he weak heeonuclea J coupling Hamilonian. In oh cases, he dipola coupling consan which in he weak coupling limi coesponds diecl o he epeimenall oseved line spliings in unis of H is given 14: 1 cos D, ' [5] R % whee is he angle eween he inenuclea veco and he magneic field see Fig. 1. The em
6 µ I 0h [6] 8 S onl depends on phsical consans 14: he gomagneic aios I and S of spin I and S especivel, he Planck consan h h / and he pemeaili of vacuum µ 0. Fo eample, fo 1 H- 1 H, 1 C- 1 H and 15 N- 1 H spin pais, kh Å, kh Å and 6.5 kh Å, especivel. The maimum possile value of cos is 1 fo 0 o, and hence, accoding o Eq. [5], he maimum possile dipola coupling consan is D ma / R 1 1/ / / R, [7] which coesponds e. g. o 1.7 kh fo a 15 N- 1 H spin pai wih disance R 1.04 Å. Rememe ha he scala poduc eween wo uni vecos is idenical o he cosine of he angle eween he wo vecos. Hence, he em cos in Eq. [5] can alwas e epessed in he fom v cos T v. [8] Hee, T v is a ow veco he anspose of he column veco v which allows us o wie he scala poduc of he wo vecos as a usual mai poduc eween he 1 mai v T and he 1 mai v vide infa. 4
7 TIME-DEPENDENT AND AVERAGE DIPOLAR COUPLING HAMILTONIAN Now we conside he wo spins I and S o e pa of a molecule in soluion. In he la fame, he magneic field veco B v is consan poining along he L ais, u he inenuclea veco R v is now ime-dependen see Fig. A. Fo simplici, we assume ha he molecule is igid no inenal dnamics and consan disance R, such ha he imedependence of R v is solel due o he oaional umling moion of he molecule. Hence, he em cos and as a esul also he dipola coupling consan D and he dipola coupling Hamilonian is ime-dependen. Fo poeins, he oaional coelaion ime is in he ode of nanoseconds and on he ime-scale of he NMR epeimen, onl he imeaveaged dipola Hamilonian H D gives ise o spliings in he specum elaaion effecs caused he flucuaions of he dipola Hamilonian will no e consideed hee. The ime-aveaged dipola coupling consan 1 D cos ' [9] R % epesens he so-called esidual dipola coupling consan, which depends on he aveage alignmen of he molecule. OUTLINE AND KEY RESULTS The goal of his manuscip is o deive a geneal appoach fo he calculaion of D fo an pai of spins if he alignmen popeies of he molecule ae known. Befoe we go ino he fomal deivaion, we give a ief ouline of he seps and sae he final esul. Fis, we L move fom he la fame, L, L c.f. Fig. A o a fame of efeence,, ha is 5
8 fied o he molecule. In his fame of efeence, he em cos can e convenienl epessed wih he help of a poaili enso P, which is a second ode appoimaion of he oienaional poaili disiuion of he diecion of he eenal magneic field in he molecula fied fame of efeence 6, 15. This poaili enso P can e epesened an ellipsoid c.f. Fig. A wih a fied oienaion in he chosen molecula fame,,. The pincipal values P~, P~ and P~ of he poaili enso i.e. he lenghs of he half aes of he poaili ellipsoid ae he poailiies o find he magneic field along he coesponding pincipal aes of he poaili ellipsoid, and hence P~ P~ P~ 1. Fo eample, fo an isoopicall eoiening molecule, P~ P~ P~ 1/, and he poaili ellipsoid is educed o a sphee see Fig. 4 C. On he ohe hand, if a molecule is full aligned, P~ P~ 0 and P~ 1 convenion, he pincipal elemens ae odeed wih inceasing magniude, i.e. he poaili enso is educed o a single line in he diecion of he magneic field. In geneal, he pincipal aes of he poaili ellipsoid define a special molecula fied ais ssem ~, ~, ~, in which he calculaion of esidual dipola coupling consans is especiall simple see Fig. B: If we know he hee Caesian componens ~, ~ and ~ of an given inenuclea uni veco v in his pincipal ais ssem, he em cos in Eq. [8] is simpl given cos ~ ~ ~ ~ P P P. [10] ~ ~ 6
9 If his simple equaion deived elow is inseed ino Eq. [9], he esidual coupling consan can e pediced fo an aia spin pai in a molecule, as long as he oienaion and pincipal values of he poaili enso ae known. Wih his ke esul, we can calculae evehing, and we could sop hee, ecep ha esidual dipola coupling consans ae commonl no epessed in ems of he inoduced poaili enso P coesponding in geneal o a eal smmeic mai wih ace 1 u in ems of is aceless pa is esolven P 1/ 1, which is called he alignmen enso A 5: 1 A P 1. [11] The hee pincipal componens A~, A~ and A~ of he alignmen enso A ae simpl given 1 A ~ P~, 1 A ~ P~, 1 A ~ P~, [1] and he pincipal aes of A and P ae idenical. Noe ha in conas o he poaili enso P see Figs. and 4, he alignmen enso A canno e epesened as an ellipsoid, ecause one o wo of he pincipal componens A~, A~, and A~ of he alignmen enso ae negaive if an of he hee componens is noneo due o A ~ A~ A~ 0. Alenaive gaphical epesenaions of he effecs of he alignmen enso ae shown in Figs. 5 and 6 vide infa. 7
10 In ems of he pincipal componens of he alignmen enso, he em cos 1/ in he equaion fo he esidual dipola coupling consan Eq. [9] can e epessed as 1 cos ' A ~ ~ A~ ~ A~ ~. [1] % If his equaion is inseed ino Eq. [9], i is again possile o pedic he esidual coupling consan fo an aia spin pai in a molecule, povided ha he oienaion and pincipal values of he alignmen enso ae known. Convesel, he alignmen enso A o he poaili enso P can e deemined if a sufficien nume of epeimenal dipola coupling consans ae measued fo a given molecule 16. As will e shown elow, he alignmen enso A and he poaili enso P is chaaceied five independen paamees. Theefoe, a leas five dipola coupling consans need o e measued in ode o deemine he five unknown paamees 16. In man cases, i is also possile o accuael pedic he alignmen enso A 17 o he poaili enso P fo a given molecule in a given liquid csalline solven, and hence o pedic he epeced dipola coupling consans fo a poposed molecula sucue fom fis pinciples. 8
11 9 DERIVATION OF THE PROBABILITY AND ALIGNMENT TENSORS In an aiail chosen molecula fame wih aes,, see Fig. B, a given inenuclea veco R v is consan sill assuming a igid molecule wihou inenal dnamics:. R % R R v v [14] Howeve, in his fame of efeence, he diecion of he magneic field veco B v is imedependen if he molecule umles in soluion:. B % B B v v [15] The definiion of cos via he scala poduc of he uni vecos v and v c.f. Eq. [8] is valid in an fame of efeence. Hence, we can epess cos in he molecula fame as a funcion of he componens of he uni vecos v and v, which poin in he vaing diecion of he magneic field B v and of he consan inenuclea veco R v, especivel: % ' cos v T v [16], and
12 10. cos [17] Noe ha Eq. [17] can also e epessed in he fom % % cos '. [18] Hence, he ime aveage of cos is given. cos T v P v % % ' [19] We call he mai % P [0] he poaili mai. Fo a known poaili mai P, he esidual dipola coupling consan Eq. [9] is given
13 v 1 T v D ' P. [1] R % The mai P is eal, smmeic, and has a ace of 1 ecause { } P P P 1 P [] since definiion, v is a uni veco, and hence, 1 fo all imes. Theefoe, P is full specified onl five independen paamees. The mai P can e epesened gaphicall as an ellipsoid see Fig. and 4. The hee pincipal aes ~, ~ and ~ of his ellipsoid ae defined he hee eigenvecos of he mai P and he lenghs of he hee half aes ae defined he eigenvalues P~, P~ and P~ see Fig. A. In he special fame of efeence defined his pincipal ais ssem see Fig. B, he mai P is diagonal: P~ 0 0 P 0 P~ 0. [] % 0 0 P~ In his case he eigenvalues pincipal values P, ~ ~ ~ ~ P and P ~ ~ ae he poailiies o find he magneic field along he pincipal aes ~, ~ and ~, especivel. Theefoe we call P simpl he poaili enso. Rigoousl, P coesponds o he sum of he eo and second ode em of a spheical hamonics epansion of he poaili 11
14 1 disiuion funcion desciing he oienaion of a efeence veco elaive o a igid od 4, 15. In he pincipal ais ssem, Eq. [1] fo he calculaion of he esidual dipola coupling educes simpl o % ' 1 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ P P P R D. [4] Fo eample, in he saic case, % v is consan, and hence,. % P [5] The mai has a much simple fom in he pincipal ais fame ~, ~, ~ whee he ~ ais is paallel o he veco v. In his efeence fame, % % ~ ~ ~ v and % P [6] In his case, he poaili ellipsoid is educed o a line along he ~ ais and he dipola coupling consan is
15 D D ~ R % 1 '. [7] Fo a compleel isoopicall eoiening molecule, he aveages, ae eo, and P ~ P~ P~ 1/, i. e. he poaili mai, P 0 0 [8] % is diagonal in an molecula fied fame of efeence. Hence, hee is an equal poaili of 1/ fo he magneic field diecion o poin along all hee aes of efeence. The coesponding poaili ellipsoid is a sphee wih adius 1/ see Fig. 4 C, and he esidual dipola coupling consan is D R % 1 ~ ~ ~ ' 0. 1 [9] Fig. 4 A shows an eample of an aiall smmeic poaili ellipsoid wih he pincipal values P ~ P~ 0. 5 and P ~ Fig. 4 B shows an eample wihou aial smme whee P ~ 0., P ~ 0. and P ~ Noe ha he lack of aial smme simpl means ha hee ae wo diffeen poailiies P P~ ~ fo he magneic field o poin along he pincipal aes ~ and ~ of he molecula-fied poaili enso. Howeve, his does no means impl ha in he la fame hee ae diffeen poailiies fo he molecule o e 1
16 aligned along he L o P, L diecion. Fo eample in he case shown in Fig. 4 B, ~ 0. P ~ 0. and P ~ 0. 5 ae he poailiies ha he ~, ~ and ~ aes ae aligned paallel o B 0. In he NMR lieaue, i is no cusoma o conside he poaili enso P which can e nicel depiced as an ellipsoid, u o use is aceless pa which is called he alignmen enso 1 A P 1. [0] If we mulipl A fom he lef wih he uni ow veco vt and fom he igh wih he column veco v and using Eq. [19] and Eq. [0], we ge v T v vt' 1 v A % P- 1 vt v 1 v P - 1 cos, T v [1] which can also e used o calculae he esidual dipola coupling consan in Eq. [1]: v T v A D. [] R 14
17 P and A have he same pincipal ais ssem ~, ~, ~ ecep fo a possile eodeing of he ais laels if he convenion is used ha P ~ P~ P~ and A ~ A~ A~, and he pincipal values ae elaed 1 A ~ P~, 1 A ~ P~, and 1 A ~ P~, [] wih A ~ A~ A~ 0. In he pincipal ais ssem 1 cos ' A ~ ~ A~ ~ A~ ~, [4] % and hence, he esidual dipola coupling consan is given A~ ~ ~ ~ A ~ A ~ D. [5] R The alignmen enso canno e epesened as an ellipsoid, ecause a leas one of he pincipal values is alwas negaive if A 0. 15
18 In Fig. 5, we show a gaphical epesenaion of he A ensos which coespond o he P v T v A ensos shown in Fig. 4. The plos show he sufaces whee he em is consan. R Hence, if spin I is assumed o e locaed in he oigin, he plos show he possile locaions of spin S fo which he esidual dipola coupling consan has he same magniude. Fo he case of an isoopicall eoiening molecule spheical poaili enso, he esidual dipola coupling is alwas eo, and no such suface eiss. The dependence of he scaling faco cos 1/ on he oienaion of he inenuclea veco is someimes shown he colo of a uni sphee. Fo he hee cases shown in Fig. 4 and 5, he coesponding gascale coded suface epesenaions of he alignmen ensos ae shown in Fig. 6. The gascale inensi epesens he scaling faco of a esidual dipola coupling consan if spin I is locaed a he oigin and spin S is moved ove he suface, i. e. assuming a consan inenuclea disance. Fo eample, in he aiall smmeic case shown in Fig. 6 A wih A ~ A~ 1/ 1 and A ~ 1/ 6, he scaling faco cos 1/ is eo if he ~ -componen of he inenuclea veco is ~ 1/, which is saighfowad o see if Eq. [4] is se o eo and using. This coesponds o an angle of accos 1/ he magic ~ ~ 1 ~ angle eween he inenuclea veco and he ~ -ais. Fo he case shown in Fig. 6 B wih A ~ / 15, A ~ 1/ 0 and A ~ 1/ 6, he pola angle, when he scaling faco is eo, depends also on he aimuhal angle eween he ~ -ais and he pojecion of v on he ~ / ~ plane. Fo eample, in he ~ / ~ plane, he scaling faco is eo if ~ / 16
19 coesponding o accos / , and in he ~ / ~ plane, he scaling faco is eo if ~ 1/ 6 accos 1/ In he isoopic case shown in Fig. 6 C, he scaling faco cos 1/ is eo fo all oienaions of he inenuclea veco R v. APPENDIX In he appendi, he ke equaions Eq. [4] and Eq. [5] fo he calculaion of he esidual dipola coupling consan D ae eepessed in vaious foms found in lieaue. If he uni veco v is defined in ems of he pola coodinaes and in he pincipal ais ssem of he alignmen enso A, hen v % ~ ~ ~ sin' cos sin' sin % cos' [6] and hence accoding o Eq. [4]: ' cos 1 * A ~ sin cos A~ sin sin A~ cos. [7] % This can e simplified noing ha cos 1 cos / and sin 1 cos / : * cos 1 ' % A~ ~ A~ A sin sin cos sin A ~ A ~ A sin ~ A ~ A~ sin sin cos A cos ~ cos A cos ~ [8] 17
20 Since A is a aceless mai, A ~ A~ A~, and we can ewie Eq. [8] as * 1 ' * sin ' A~ A~ cos % A~ cos sin cos. % [9] The pe-faco of A % can e fuhe simplified using he elaion sin 1 cos : cos 1 cos sin cos 1 cos 1. [40] Thus, we aive a * 1 ' A ~ A~ A~ cos % cos 1 sin cos. [41] Eq. [41] can alenaivel e epessed in ems of he pincipal values S %, S % and S % of he Saupe mai o ode mai S, which is simpl he alignmen mai A scaled a faco of /, if he opical ais of he liquid csal is collinea wih he diecion of he magneic field 9, 10: S / A. [4] Hence, 18
21 * cos { S ~ cos 1 S~ S~ sin cos }. 1 ' 1 % [4] Ofen, he aial componen A a of he alignmen enso is defined as 5 A a A~ S~, [44] and he homic componen A of he alignmen enso is defined as A A ~ ~ A S~ S~. [45] Wih hese definiions, we can epess Eqs. [41] and [4] as - cos, cos / ' 1 A sin / cos, 1 * 1 ' % A a. [46] 0 which in un is ofen wien as 1 / cos 0 1. Aa %, * - Aa cos % 1 Rsin cos ' { cos % 1 sin cos } [47] whee 19
22 A A R [48] a is called he homici of he alignmen enso and A~ A~ S~ S~ R [49] A~ S~ is called he asmme paamee which descies he deviaion fom aiall smmeic odeing 6. So fa, we have assumed a igid molecule ha umles in soluion. In he pesence of inenal moions he deivaion of esidual dipola couplings ecomes moe complicaed 6, 18, 19. Povided he alignmen pocess is no affeced inamolecula moion, he analsis is elaivel saighfowad. If he inenal moion of he inenuclea veco v is aiall v smmeic wih espec o he aveage oienaion av, he dipola coupling epeced fo his aveage oienaion is scaled a faco, which is idenical o a genealied ode paamee S 0 S The lae coesponds mahemaicall o he spin elaaion ode paamee 19, 0, u ehiis a sensiivi o moions eending o he millisecond ime scale 6, 18. This leads o he following equaion of he esidual dipola coupling consan: { cos % 1 sin cos }. Aa D S [50] R 0
23 This epession is ofen ewien using he maimum dipola coupling D R ma / / c. f. Eq. [7] o he so called magniude of he esidual dipola coupling enso D D A / 7: a ma a D S D D S SD a ma { cos ' 1 * sin cos } A { cos ' 1 * sin cos } ma a Aa % P * cos sin cos, [51] whee P cos 1 / is he second-ode Legende polnomial. Finall, we use he esuls deived in his manuscip o inoduce he conceps of he genealied degee of ode GDO of a given alignmen enso A and he genealied angle eween wo diffeen alignmen ensos 1 A and A. In complee analog o he scala poduc eween wo eal vecos, he scala poduc e- 1 ween wo eal maices e. g. wo alignmen maices A and A is defined as 1 1 A A A ij A ij [5] i, j and he nom A of he eal mai A is given A A A. [5] i, j A ij 1
24 The maimum ode is found fo he saic case, whee he poaili enso P ma is given Eq. [6] in he pincipal ais ssem. The coesponding maimum alignmen enso A P 1/ 1 has he fom ma ma ' 1/ 0 0 A ma 0 ' 1/ 0. [54] 0 0 / % The nom of A ma is given A ma. [55] The genealied degee of ode GDO of a given ode mai A can e defined as A GDO A. [56] A ma In ems of he Saupe mai S / A c. f. Eq. [4], his can e wien as 6, GDO S. [57] In lieaue, he smol is ofen used fo he GDO u we do no use he smol hee in ode o avoid confusion wih he pola angle defined in Eq. [6].
25 The GDO is independen of he molecula-fied fame, in which he alignmen enso A is epessed. In he pincipal ais ssem onl he diagonal elemens of A ae noneo and Eq. [56] simplifies o GDO A ~ ~. ~ A A [58] Fo aiall smmeic alignmen ensos A A~ A~ / his simplifies fuhe o : ~ GDO 1 A % 4 A ~ ~ S ~. 1 4 A ~ A ~ A ~ [59] Wih he help of he scala poduc, we can also define he genealied angle eween wo alignmen ensos 1 A and A which coespond e. g. o wo diffeen alignmen media. If he mai epesenaions of 1 A and A ae given in a common molecula fame of efeence, he cosine of he genealied angle eween hese alignmen ensos can e defined as he nomalied scala poduc eween hem : 1 A A cos. [60] 1 A A
26 REFERENCES 1. Basiaan EW, Maclean C, Van Zijl PCM, Bohne-B AA. High-esoluion NMR of liquids and gases: effecs of magneic-field-induced molecula alignmen. Annual Repos on NMR Specoscop 1987; 19: Tolman JR, Flanagan J, Kenned MA, Pesegad JH. Nuclea magneic dipole ineacions in field-oiened poeins: infomaion fo sucue deeminaion in soluion. Poc Nal Acad Sci 1995; 9: Bohne-B AA. Magneic Field Induced Alignmen of Molecules. In Encclopedia of Nuclea Magneic Resonance, Gan DM and Hais RK, edios. Wile: London; p Emsle JW. Liquid Csals: Geneal Consideaions. In Encclopedia of Nuclea Magneic Resonance, Gan DM and Hais RK, edios. Wile: London; p Tjanda N and Ba A. Diec measuemen of disances and angles in iomolecules NMR in a dilue liquid csalline medium. Science 1997; 78: Pesegad JH, Al-Hashimi HM, Tolman JR. NMR sucues of iomolecules using field oiened media and esidual dipola couplings. Qua Rev Biophs 000; : Ba A, Konais G, Tjanda N. Dipola Couplings in macomolecula sucue deeminaion. Meh in Enm 001; 9: Bunne E. The use of esidual dipola couplings in poein NMR. Conceps Magn Reson 001; 1: Saupe A and Engle G. High-esoluion nuclea magneic esonance speca of oiened molecules. Phs Rev Le 196; 11:
27 10. Engle E, Saupe A. Kenesonanen in kisallinen Flüssigkeien und in kisallinflüssigen Lösungen. Teil I. Zeischif fü Naufoschung 1964; 19A: Hansen MR, Muelle L, Padi A. Tunale alignmen of macomolecules filamenous phage ields dipola coupling ineacions. Na Suc Biol 1998; 5: Tcko R, Blanco FJ, Ishii Y. Alignmen of iopolmes in sained gels: A new wa o ceae deecale dipole-dipole couplings in high-esoluion iomolecula NMR. J Am Chem Soc 000; 1: Sass HJ, Musco G, Sahl SJ, Wingfield PT, Gesiek S. Soluion NMR of poeins wihin polaclamide gels: Diffusional popeies and esidual alignmen mechanical sess o emedding of oiened puple memanes. J Biomol NMR 000; 18: Ens RR, Bodenhausen G, Wokaun A. Pinciples of Nuclea Magneic Resonance in one and wo dimensions, Ofod Univesi Pess, New Yok: Snde LC. Analsis of molecula magneic esonance speca of molecules in liquid-csal solvens. J Chem Phs 1965; 4: Losonci JA, Andec M, Fische MWF, Pesegad JH. Ode mai analsis of esidual dipola couplings using singula value decomposiion. J Magn Reson 1999; 18: Zwecksee M and Ba A. Pedicion of Seicall Induced Alignmen in a Dilue Liquid Csalline Phase: Aid o Poein Sucue Deeminaion NMR. J Am Chem Soc 000; 1: Tolman JR, Flanagan JM, Kenned MA and Pesegad JH. NMR evidence fo slow collecive moions in canomemogloin. Naue Suc Biol 1997; 4: Lipai G and Sao A. Model-fee appoach o he inepeaion of Nuclea Magneic Resonance Relaaion in Macomolecules. 1. Theo and ange of validi. J Am Chem Soc 198; 104:
28 0. Lipai G and Sao A. Model-fee appoach o he inepeaion of Nuclea Magneic Resonance Relaaion in Macomolecules.. Analsis of Epeimenal Resuls. J Am Chem Soc 198; 104: Meile J, Pompes JJ, Pei W, Giesinge C, Büschweile R. Model-fee Appoach o he Dnamic Inepeaion of Residual Dipola Couplings in Gloula Poeins. J Am Chem Soc 001; 1: Tolman JR, Al-Hashimi HM, Ka LE, Pesegad JH. Sucual and Dnamic Analsis of Residual Dipola Coupling Daa fo Poeins. J Am Chem Soc 001; 1: Sass J, Codie F, Hoffmann A, Rogowski M, Cousin A, Omichinski JG, Löwen H, Gesiek S. Puple Memane Induced Alignmen of Biological Macomolecules in he Magneic Field. J Am Chem Soc 1999; 11:
29 FIGURE CAPTIONS Figue 1: Definiion of he angle eween he inenuclea veco R v connecing spins I Figue : Figue : Figue 4: and S and he magneic field veco B v. The uni vecos v and v poin in he diecion of R v and B v, especivel. Effec of molecula umling of a igid molecule as seen Panel A fom he la fame of efeence wih aes L, L, L and Panel B fom an aia molecula fame of efeence wih aes,,. In he la fame Panel A, he magneic field B v is consan and poins definiion along he L ais, wheeas he inenuclea veco R v keeps changing is diecion. In a molecula fame Panel B, he siuaion is evesed: hee, an given inenuclea veco is consan, wheeas he oienaion of he magneic field is ime-dependen. The molecule, a given inenuclea veco R v and he poaili ellipsoid a gaphical epesenaion of he poaili enso P, c.f. Eq. [5] ae shown Panel A in an aiail chosen molecula fame c.f. Fig. B and Panel B in he special coodinae ssem wih aes ~, ~, ~ defined he pincipal aes of he poaili ellipsoid. Eamples of hee chaaceisic poaili ellipsoids gaphical epesenaions of he poaili enso P, c.f. Eq. [5] as seen fom he pincipal ais ssem wih aes ~, ~, ~ c.f. Fig. B. Panel A shows an aiall smmeic poaili ellipsoid wih P % P % 0.5 and P % 0.5 Panel A. Panel B depics a homic po- 7
30 aili ellipsoid wih P % 0., P % 0. and P % 0.5. Panel C shows an isoopic poaili ellipsoid wih P % P % P % 1/. Figue 5: Gaphical epesenaions of he alignmen ensos Panel A which coespond o he hee poaili ensos shown in Fig. 4 A-C. The pincipal componens of he alignmen enso ae A A ~ A~ 0.5 1/ 1/ 1, A ~ 0.5 1/ 1/ 6, B A ~ 0. 1/ /15, A ~ 0. 1/ 1/ 0, A ~ 0.5 1/ 1/ 6 and C vt v - A ~ A~ A~ 1/ 1/ 0. The plos show he sufaces whee A / R 1Å ligh ga o -1 Å - dak ga if he ~, ~ and ~ aes ae laelled in unis of Å. Figue 6: Fo he hee cases shown in Fig. 4 and 5 wih A A ~ A~ 1/ 1, A ~ 1/ 6, B A ~ / 15, A ~ 1/ 0, A ~ 1/ 6 and C A ~ A~ A~ 0 he magniude of he scaling faco cos 1/ is coded on a uni sphee as a funcion of he oienaion of he inenuclea veco R v whie: vanishing scaling faco. Posiive and negaive scaling facos ae denoed he especive sign. 8
31 Figue 1
32 Figue
33 Figue
34 Figue 4 Figue 5 Figue 6
35 Figue 4 Figue 5 colo - - Figue 6 colo
( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba
![( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba ( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba](/thumbs/83/87856399.jpg) THE INTEACTION OF ADIATION AND MATTE: SEMICLASSICAL THEOY PAGE 26 III. EVIEW OF BASIC QUANTUM MECHANICS : TWO -LEVEL QUANTUM SYSTEMS : The lieaue of quanum opics and lase specoscop abounds wih discussions
THE INTEACTION OF ADIATION AND MATTE: SEMICLASSICAL THEOY PAGE 26 III. EVIEW OF BASIC QUANTUM MECHANICS : TWO -LEVEL QUANTUM SYSTEMS : The lieaue of quanum opics and lase specoscop abounds wih discussions
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Poisson s Ratio
 Fouh diion MCHANICS OF MATRIALS Poisson s Raio Bee Johnson DeWolf Fo a slende ba subjeced o aial loading: 0 The elongaion in he -diecion is accompanied b a conacion in he ohe diecions. Assuming ha he maeial
Fouh diion MCHANICS OF MATRIALS Poisson s Raio Bee Johnson DeWolf Fo a slende ba subjeced o aial loading: 0 The elongaion in he -diecion is accompanied b a conacion in he ohe diecions. Assuming ha he maeial
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Orthotropic Materials
 Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Pressure Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Stress Analysis
 Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
MEEN 617 Handout #11 MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Systems with VISCOUS DAMPING
 MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
Projection of geometric models
 ojecion of geomeic moels Copigh@, YZU Opimal Design Laboao. All ighs eseve. Las upae: Yeh-Liang Hsu (-9-). Noe: his is he couse maeial fo ME55 Geomeic moeling an compue gaphics, Yuan Ze Univesi. a of his
ojecion of geomeic moels Copigh@, YZU Opimal Design Laboao. All ighs eseve. Las upae: Yeh-Liang Hsu (-9-). Noe: his is he couse maeial fo ME55 Geomeic moeling an compue gaphics, Yuan Ze Univesi. a of his
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH
 Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Lecture-V Stochastic Processes and the Basic Term-Structure Equation 1 Stochastic Processes Any variable whose value changes over time in an uncertain
 Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
Projection of geometric models
 ojecion of geomeic moels Eie: Yeh-Liang Hsu (998-9-2); ecommene: Yeh-Liang Hsu (2-9-26); las upae: Yeh-Liang Hsu (29--3). Noe: This is he couse maeial fo ME55 Geomeic moeling an compue gaphics, Yuan Ze
ojecion of geomeic moels Eie: Yeh-Liang Hsu (998-9-2); ecommene: Yeh-Liang Hsu (2-9-26); las upae: Yeh-Liang Hsu (29--3). Noe: This is he couse maeial fo ME55 Geomeic moeling an compue gaphics, Yuan Ze
7 Wave Equation in Higher Dimensions
 7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
Low-complexity Algorithms for MIMO Multiplexing Systems
 Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Combinatorial Approach to M/M/1 Queues. Using Hypergeometric Functions
 Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
The sudden release of a large amount of energy E into a background fluid of density
 10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Chapter 2 Wave Motion
 Lecue 4 Chape Wae Moion Plane waes 3D Diffeenial wae equaion Spheical waes Clindical waes 3-D waes: plane waes (simples 3-D waes) ll he sufaces of consan phase of disubance fom paallel planes ha ae pependicula
Lecue 4 Chape Wae Moion Plane waes 3D Diffeenial wae equaion Spheical waes Clindical waes 3-D waes: plane waes (simples 3-D waes) ll he sufaces of consan phase of disubance fom paallel planes ha ae pependicula
CAMERA GEOMETRY. Ajit Rajwade, CS 763, Winter 2017, IITB, CSE department
 CAMERA GEOMETRY Aji Rajwade, CS 763, Wine 7, IITB, CSE depamen Conens Tansfomaions of poins/vecos in D Tansfomaions of poins/vecos in 3D Image Fomaion: geome of pojecion of 3D poins ono D image plane Vanishing
CAMERA GEOMETRY Aji Rajwade, CS 763, Wine 7, IITB, CSE depamen Conens Tansfomaions of poins/vecos in D Tansfomaions of poins/vecos in 3D Image Fomaion: geome of pojecion of 3D poins ono D image plane Vanishing
Fig. 1S. The antenna construction: (a) main geometrical parameters, (b) the wire support pillar and (c) the console link between wire and coaxial
 a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
P h y s i c s F a c t s h e e t
 P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
2-d Motion: Constant Acceleration
 -d Moion: Consan Acceleaion Kinemaic Equaions o Moion (eco Fom Acceleaion eco (consan eloci eco (uncion o Posiion eco (uncion o The eloci eco and posiion eco ae a uncion o he ime. eloci eco a ime. Posiion
-d Moion: Consan Acceleaion Kinemaic Equaions o Moion (eco Fom Acceleaion eco (consan eloci eco (uncion o Posiion eco (uncion o The eloci eco and posiion eco ae a uncion o he ime. eloci eco a ime. Posiion
Authors name Giuliano Bettini* Alberto Bicci** Title Equivalent waveguide representation for Dirac plane waves
 Auhos name Giuliano Beini* Albeo Bicci** Tile Equivalen waveguide epesenaion fo Diac plane waves Absac Ideas abou he elecon as a so of a bound elecomagneic wave and/o he elecon as elecomagneic field apped
Auhos name Giuliano Beini* Albeo Bicci** Tile Equivalen waveguide epesenaion fo Diac plane waves Absac Ideas abou he elecon as a so of a bound elecomagneic wave and/o he elecon as elecomagneic field apped
The k-filtering Applied to Wave Electric and Magnetic Field Measurements from Cluster
 The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
On The Estimation of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complete Block Designs
 Mahemaical Theoy and Modeling ISSN 45804 (Pape ISSN 505 (Online Vol.6, No.7, 06 www.iise.og On The Esimaion of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complee Bloc Designs EFFANGA, EFFANGA OKON AND BASSE, E.
Mahemaical Theoy and Modeling ISSN 45804 (Pape ISSN 505 (Online Vol.6, No.7, 06 www.iise.og On The Esimaion of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complee Bloc Designs EFFANGA, EFFANGA OKON AND BASSE, E.
Chapter Finite Difference Method for Ordinary Differential Equations
 Chape 8.7 Finie Diffeence Mehod fo Odinay Diffeenial Eqaions Afe eading his chape, yo shold be able o. Undesand wha he finie diffeence mehod is and how o se i o solve poblems. Wha is he finie diffeence
Chape 8.7 Finie Diffeence Mehod fo Odinay Diffeenial Eqaions Afe eading his chape, yo shold be able o. Undesand wha he finie diffeence mehod is and how o se i o solve poblems. Wha is he finie diffeence
On Control Problem Described by Infinite System of First-Order Differential Equations
 Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
Energy dispersion relation for negative refraction (NR) materials
 Enegy dispesion elaion fo negaive efacion (NR) maeials Y.Ben-Ayeh Physics Depamen, Technion Isael of Technology, Haifa 3, Isael E-mail addess: ph65yb@physics.echnion,ac.il; Fax:97 4 895755 Keywods: Negaive-efacion,
Enegy dispesion elaion fo negaive efacion (NR) maeials Y.Ben-Ayeh Physics Depamen, Technion Isael of Technology, Haifa 3, Isael E-mail addess: ph65yb@physics.echnion,ac.il; Fax:97 4 895755 Keywods: Negaive-efacion,
STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION
 Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
Risk tolerance and optimal portfolio choice
 Risk oleance and opimal pofolio choice Maek Musiela BNP Paibas London Copoae and Invesmen Join wok wih T. Zaiphopoulou (UT usin) Invesmens and fowad uiliies Pepin 6 Backwad and fowad dynamic uiliies and
Risk oleance and opimal pofolio choice Maek Musiela BNP Paibas London Copoae and Invesmen Join wok wih T. Zaiphopoulou (UT usin) Invesmens and fowad uiliies Pepin 6 Backwad and fowad dynamic uiliies and
Two-dimensional Effects on the CSR Interaction Forces for an Energy-Chirped Bunch. Rui Li, J. Bisognano, R. Legg, and R. Bosch
 Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
General Non-Arbitrage Model. I. Partial Differential Equation for Pricing A. Traded Underlying Security
 1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
ÖRNEK 1: THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MOMENTUM RELATION Calculate the linear momentum of a particle of mass m=10 kg which has a. kg m s
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
Application of Bernoulli wavelet method for numerical solution of fuzzy linear Volterra-Fredholm integral equations Abstract Keywords
 Applicaion o enoulli wavele mehod o numeical soluion o uzz linea Volea-edholm inegal equaions Mohamed A. Ramadan a and Mohamed R. Ali b a Depamen o Mahemaics acul o Science Menouia Univesi Egp mamadan@eun.eg;
Applicaion o enoulli wavele mehod o numeical soluion o uzz linea Volea-edholm inegal equaions Mohamed A. Ramadan a and Mohamed R. Ali b a Depamen o Mahemaics acul o Science Menouia Univesi Egp mamadan@eun.eg;
EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY
 Mahemaics Today Vol7(Dec-)54-6 ISSN 976-38 EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY K Punachanda Rao Depamen of Mahemaics Chiala Engineeing College Chiala 53 57 Andha Padesh, INDIA E-mail: dkpaocecc@yahoocoin ABSTRACT
Mahemaics Today Vol7(Dec-)54-6 ISSN 976-38 EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY K Punachanda Rao Depamen of Mahemaics Chiala Engineeing College Chiala 53 57 Andha Padesh, INDIA E-mail: dkpaocecc@yahoocoin ABSTRACT
IMPROVED DESIGN EQUATIONS FOR ASYMMETRIC COPLANAR STRIP FOLDED DIPOLES ON A DIELECTRIC SLAB
 IMPROVED DESIGN EQUATIONS FOR ASYMMETRIC COPLANAR STRIP FOLDED DIPOLES ON A DIELECTRIC SLAB H.J. Visse* * Hols Cene TNO P.O. Bo 855 565 N Eindhoven, The Nehelands E-mail: hui.j.visse@no.nl eywods: Coupled
IMPROVED DESIGN EQUATIONS FOR ASYMMETRIC COPLANAR STRIP FOLDED DIPOLES ON A DIELECTRIC SLAB H.J. Visse* * Hols Cene TNO P.O. Bo 855 565 N Eindhoven, The Nehelands E-mail: hui.j.visse@no.nl eywods: Coupled
The shortest path between two truths in the real domain passes through the complex domain. J. Hadamard
 Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Kalman Filter: an instance of Bayes Filter. Kalman Filter: an instance of Bayes Filter. Kalman Filter. Linear dynamics with Gaussian noise
 COM47 Inoducion o Roboics and Inelligen ysems he alman File alman File: an insance of Bayes File alman File: an insance of Bayes File Linea dynamics wih Gaussian noise alman File Linea dynamics wih Gaussian
COM47 Inoducion o Roboics and Inelligen ysems he alman File alman File: an insance of Bayes File alman File: an insance of Bayes File Linea dynamics wih Gaussian noise alman File Linea dynamics wih Gaussian
Research Article A Note on Multiplication and Composition Operators in Lorentz Spaces
 Hindawi Publishing Copoaion Jounal of Funcion Spaces and Applicaions Volume 22, Aicle ID 29363, pages doi:.55/22/29363 Reseach Aicle A Noe on Muliplicaion and Composiion Opeaos in Loenz Spaces Eddy Kwessi,
Hindawi Publishing Copoaion Jounal of Funcion Spaces and Applicaions Volume 22, Aicle ID 29363, pages doi:.55/22/29363 Reseach Aicle A Noe on Muliplicaion and Composiion Opeaos in Loenz Spaces Eddy Kwessi,
Chapter 7. Interference
 Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Monochromatic Wave over One and Two Bars
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
Relative and Circular Motion
 Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Department of Chemical Engineering University of Tennessee Prof. David Keffer. Course Lecture Notes SIXTEEN
 D. Keffe - ChE 40: Hea Tansfe and Fluid Flow Deamen of Chemical Enee Uniesi of Tennessee Pof. Daid Keffe Couse Lecue Noes SIXTEEN SECTION.6 DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS OF CONTINUITY SECTION.7 DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS
D. Keffe - ChE 40: Hea Tansfe and Fluid Flow Deamen of Chemical Enee Uniesi of Tennessee Pof. Daid Keffe Couse Lecue Noes SIXTEEN SECTION.6 DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS OF CONTINUITY SECTION.7 DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS
r r r r r EE334 Electromagnetic Theory I Todd Kaiser
 334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
OPTIMIZATION OF TOW-PLACED, TAILORED COMPOSITE LAMINATES
 6 H INERNAIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSIE MAERIALS OPIMIZAION OF OW-PLACED AILORED COMPOSIE LAMINAES Adiana W. Blom* Mosafa M. Abdalla* Zafe Güdal* *Delf Univesi of echnolog he Nehelands Kewods: vaiable siffness
6 H INERNAIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSIE MAERIALS OPIMIZAION OF OW-PLACED AILORED COMPOSIE LAMINAES Adiana W. Blom* Mosafa M. Abdalla* Zafe Güdal* *Delf Univesi of echnolog he Nehelands Kewods: vaiable siffness
Engineering Accreditation. Heat Transfer Basics. Assessment Results II. Assessment Results. Review Definitions. Outline
 Hea ansfe asis Febua 7, 7 Hea ansfe asis a Caeo Mehanial Engineeing 375 Hea ansfe Febua 7, 7 Engineeing ediaion CSUN has aedied pogams in Civil, Eleial, Manufauing and Mehanial Engineeing Naional aediing
Hea ansfe asis Febua 7, 7 Hea ansfe asis a Caeo Mehanial Engineeing 375 Hea ansfe Febua 7, 7 Engineeing ediaion CSUN has aedied pogams in Civil, Eleial, Manufauing and Mehanial Engineeing Naional aediing
An Automatic Door Sensor Using Image Processing
 An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications. Nagarajan Murali 1D - Methods Lecture 5
 NMR pecroscop: Principles and Applicaions Nagarajan Murali D - Mehods Lecure 5 D-NMR To full appreciae he workings of D NMR eperimens we need o a leas consider wo coupled spins. omeimes we need o go up
NMR pecroscop: Principles and Applicaions Nagarajan Murali D - Mehods Lecure 5 D-NMR To full appreciae he workings of D NMR eperimens we need o a leas consider wo coupled spins. omeimes we need o go up
EN221 - Fall HW # 7 Solutions
 EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
ME 210 Applied Mathematics for Mechanical Engineers
 Tangent and Ac Length of a Cuve The tangent to a cuve C at a point A on it is defined as the limiting position of the staight line L though A and B, as B appoaches A along the cuve as illustated in the
Tangent and Ac Length of a Cuve The tangent to a cuve C at a point A on it is defined as the limiting position of the staight line L though A and B, as B appoaches A along the cuve as illustated in the
336 ERIDANI kfk Lp = sup jf(y) ; f () jj j p p whee he supemum is aken ove all open balls = (a ) inr n, jj is he Lebesgue measue of in R n, () =(), f
 TAMKANG JOURNAL OF MATHEMATIS Volume 33, Numbe 4, Wine 2002 ON THE OUNDEDNESS OF A GENERALIED FRATIONAL INTEGRAL ON GENERALIED MORREY SPAES ERIDANI Absac. In his pape we exend Nakai's esul on he boundedness
TAMKANG JOURNAL OF MATHEMATIS Volume 33, Numbe 4, Wine 2002 ON THE OUNDEDNESS OF A GENERALIED FRATIONAL INTEGRAL ON GENERALIED MORREY SPAES ERIDANI Absac. In his pape we exend Nakai's esul on he boundedness
r P + '% 2 r v(r) End pressures P 1 (high) and P 2 (low) P 1 , which must be independent of z, so # dz dz = P 2 " P 1 = " #P L L,
 Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
ME 304 FLUID MECHANICS II
 ME 304 LUID MECHNICS II Pof. D. Haşme Tükoğlu Çankaya Uniesiy aculy of Engineeing Mechanical Engineeing Depamen Sping, 07 y du dy y n du k dy y du k dy n du du dy dy ME304 The undamenal Laws Epeience hae
ME 304 LUID MECHNICS II Pof. D. Haşme Tükoğlu Çankaya Uniesiy aculy of Engineeing Mechanical Engineeing Depamen Sping, 07 y du dy y n du k dy y du k dy n du du dy dy ME304 The undamenal Laws Epeience hae
A Weighted Moving Average Process for Forecasting. Shou Hsing Shih Chris P. Tsokos
 A Weighed Moving Aveage Pocess fo Foecasing Shou Hsing Shih Chis P. Tsokos Depamen of Mahemaics and Saisics Univesiy of Souh Floida, USA Absac The objec of he pesen sudy is o popose a foecasing model fo
A Weighed Moving Aveage Pocess fo Foecasing Shou Hsing Shih Chis P. Tsokos Depamen of Mahemaics and Saisics Univesiy of Souh Floida, USA Absac The objec of he pesen sudy is o popose a foecasing model fo
Representing Knowledge. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Properties of BNs. Independence? Reachability (the Bayes Ball) Example
 C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
Educational Software Bundle for Studying Magnetotelluric Theory and Specific Geoelectric Structure Models
 ducaional Sofwae Bundle fo Suding Magneoelluic Theo and Specific Geoelecic Sucue Models DSPINA KALISPRI ), GORG LOUPIS ), JON P. MAKRIS 1), DRK RUST 3), FILIPPOS VALLIANATOS ), VASSILIOS SALTAS ), PANTLIS
ducaional Sofwae Bundle fo Suding Magneoelluic Theo and Specific Geoelecic Sucue Models DSPINA KALISPRI ), GORG LOUPIS ), JON P. MAKRIS 1), DRK RUST 3), FILIPPOS VALLIANATOS ), VASSILIOS SALTAS ), PANTLIS
Electromagnetic interaction in dipole grids and prospective high-impedance surfaces
 ADIO SCIENCE, VOL.,, doi:.29/2s36, 25 Elecomagneic ineacion in dipole gids and pospecive high-impedance sufaces C.. Simovsi Depamen of Physics, S. Peesbug Insiue of Fine Mechanics and Opics, S. Peesbug,
ADIO SCIENCE, VOL.,, doi:.29/2s36, 25 Elecomagneic ineacion in dipole gids and pospecive high-impedance sufaces C.. Simovsi Depamen of Physics, S. Peesbug Insiue of Fine Mechanics and Opics, S. Peesbug,
ME 3560 Fluid Mechanics
 ME3560 Flid Mechanics Fall 08 ME 3560 Flid Mechanics Analsis of Flid Flo Analsis of Flid Flo ME3560 Flid Mechanics Fall 08 6. Flid Elemen Kinemaics In geneal a flid paicle can ndego anslaion, linea defomaion
ME3560 Flid Mechanics Fall 08 ME 3560 Flid Mechanics Analsis of Flid Flo Analsis of Flid Flo ME3560 Flid Mechanics Fall 08 6. Flid Elemen Kinemaics In geneal a flid paicle can ndego anslaion, linea defomaion
Online Completion of Ill-conditioned Low-Rank Matrices
 Online Compleion of Ill-condiioned Low-Rank Maices Ryan Kennedy and Camillo J. Taylo Compue and Infomaion Science Univesiy of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA, USA keny, cjaylo}@cis.upenn.edu Laua Balzano
Online Compleion of Ill-condiioned Low-Rank Maices Ryan Kennedy and Camillo J. Taylo Compue and Infomaion Science Univesiy of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA, USA keny, cjaylo}@cis.upenn.edu Laua Balzano
Kinematics Vocabulary. Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion. Position. Coordinate System in One Dimension. Kinema means movement 8.
 Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
New sufficient conditions of robust recovery for low-rank matrices
 New sufficien condiions of ous ecovey fo low-an maices Jianwen Huang a, Jianjun Wang a,, Feng Zhang a, Wendong Wang a a School of Mahemaics and Saisics, Souhwes Univesiy, Chongqing, 400715, China Reseach
New sufficien condiions of ous ecovey fo low-an maices Jianwen Huang a, Jianjun Wang a,, Feng Zhang a, Wendong Wang a a School of Mahemaics and Saisics, Souhwes Univesiy, Chongqing, 400715, China Reseach
ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS
 Mem. Fac. Inegaed As and Sci., Hioshima Univ., Se. IV, Vol. 8 9-33, Dec. 00 ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS YOSHIO AGAOKA *, BYUNG HAK KIM ** AND JIN HYUK CHOI ** *Depamen of Mahemaics, Faculy
Mem. Fac. Inegaed As and Sci., Hioshima Univ., Se. IV, Vol. 8 9-33, Dec. 00 ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS YOSHIO AGAOKA *, BYUNG HAK KIM ** AND JIN HYUK CHOI ** *Depamen of Mahemaics, Faculy
[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u
![[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u [ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u](/thumbs/89/100187624.jpg) Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
156 There are 9 books stacked on a shelf. The thickness of each book is either 1 inch or 2
 156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
Pseudosteady-State Flow Relations for a Radial System from Department of Petroleum Engineering Course Notes (1997)
 Pseudoseady-Sae Flow Relaions fo a Radial Sysem fom Deamen of Peoleum Engineeing Couse Noes (1997) (Deivaion of he Pseudoseady-Sae Flow Relaions fo a Radial Sysem) (Deivaion of he Pseudoseady-Sae Flow
Pseudoseady-Sae Flow Relaions fo a Radial Sysem fom Deamen of Peoleum Engineeing Couse Noes (1997) (Deivaion of he Pseudoseady-Sae Flow Relaions fo a Radial Sysem) (Deivaion of he Pseudoseady-Sae Flow
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Probabilistic Models
 CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
4. Fundamental of A.C. Circuit
 4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
The Method of Images in Velocity-Dependent Systems
 >1< The Mehod of Images in Velociy-Dependen Sysems Dan Censo Ben Guion Univesiy of he Negev Depamen of Elecical and Compue Engineeing Bee Sheva, Isael 8415 censo@ee.bgu.ac.il Absac This sudy invesigaes
>1< The Mehod of Images in Velociy-Dependen Sysems Dan Censo Ben Guion Univesiy of he Negev Depamen of Elecical and Compue Engineeing Bee Sheva, Isael 8415 censo@ee.bgu.ac.il Absac This sudy invesigaes
Design Guideline for Buried Hume Pipe Subject to Coupling Forces
 Design Guideline fo Buied Hume Pipe Sujec o Coupling Foces Won Pyo Hong 1), *Seongwon Hong 2), and Thomas Kang 3) 1) Depamen of Civil, nvionmenal and Plan ngineeing, Chang-Ang Univesiy, Seoul 06974, Koea
Design Guideline fo Buied Hume Pipe Sujec o Coupling Foces Won Pyo Hong 1), *Seongwon Hong 2), and Thomas Kang 3) 1) Depamen of Civil, nvionmenal and Plan ngineeing, Chang-Ang Univesiy, Seoul 06974, Koea
Chapter 2: The Derivation of Maxwell Equations and the form of the boundary value problem
 Chape : The eiaion of Mawell quaions and he fom of he bounda alue poblem In moden ime, phsics, including geophsics, soles eal-wold poblems b appling fis pinciples of phsics wih a much highe capabili han
Chape : The eiaion of Mawell quaions and he fom of he bounda alue poblem In moden ime, phsics, including geophsics, soles eal-wold poblems b appling fis pinciples of phsics wih a much highe capabili han
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Kinematics in two dimensions
 Lecure 5 Phsics I 9.18.13 Kinemaics in wo dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teaching/phsicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo36.uml.edu/danlo13/phsics1fall.hml 95.141, Fall 13, Lecure 5
Lecure 5 Phsics I 9.18.13 Kinemaics in wo dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teaching/phsicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo36.uml.edu/danlo13/phsics1fall.hml 95.141, Fall 13, Lecure 5
Section 4.4 Logarithmic Properties
 Secion. Logarihmic Properies 5 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Secion. Logarihmic Properies 5 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
b g [2] M N QP L N M
![b g [2] M N QP L N M b g [2] M N QP L N M](/thumbs/87/95232007.jpg) Econ. 5 Spin 998 C. Sims inea Raional Expecaions odel Execise Answes (i) - (iii): The FC s in he eneal case ae C: C = A: λ = βe λ + + µ + λ [] [] wih µ = when (3) is no indin, and λ = when () is no indin.
Econ. 5 Spin 998 C. Sims inea Raional Expecaions odel Execise Answes (i) - (iii): The FC s in he eneal case ae C: C = A: λ = βe λ + + µ + λ [] [] wih µ = when (3) is no indin, and λ = when () is no indin.
Section 4.4 Logarithmic Properties
 Secion. Logarihmic Properies 59 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Secion. Logarihmic Properies 59 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 In. J. Pue Appl. Sci. Technol., 4 (211, pp. 23-29 Inenaional Jounal of Pue and Applied Sciences and Technology ISS 2229-617 Available online a www.ijopaasa.in eseach Pape Opizaion of he Uiliy of a Sucual
In. J. Pue Appl. Sci. Technol., 4 (211, pp. 23-29 Inenaional Jounal of Pue and Applied Sciences and Technology ISS 2229-617 Available online a www.ijopaasa.in eseach Pape Opizaion of he Uiliy of a Sucual
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
2. v = 3 4 c. 3. v = 4c. 5. v = 2 3 c. 6. v = 9. v = 4 3 c
 Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Support Vector Machines
 Suppo Veco Machine CSL 3 ARIFICIAL INELLIGENCE SPRING 4 Suppo Veco Machine O, Kenel Machine Diciminan-baed mehod olean cla boundaie Suppo veco coni of eample cloe o bounday Kenel compue imilaiy beeen eample
Suppo Veco Machine CSL 3 ARIFICIAL INELLIGENCE SPRING 4 Suppo Veco Machine O, Kenel Machine Diciminan-baed mehod olean cla boundaie Suppo veco coni of eample cloe o bounday Kenel compue imilaiy beeen eample
CHAPTER 2: Mathematics for Microeconomics
 CHAPTER : Mahemaics for Microeconomics The problems in his chaper are primarily mahemaical. They are inended o give sudens some pracice wih he conceps inroduced in Chaper, bu he problems in hemselves offer
CHAPTER : Mahemaics for Microeconomics The problems in his chaper are primarily mahemaical. They are inended o give sudens some pracice wih he conceps inroduced in Chaper, bu he problems in hemselves offer
Stress Analysis of Infinite Plate with Elliptical Hole
 Sess Analysis of Infinie Plae ih Ellipical Hole Mohansing R Padeshi*, D. P. K. Shaa* * ( P.G.Suden, Depaen of Mechanical Engg, NRI s Insiue of Infoaion Science & Technology, Bhopal, India) * ( Head of,
Sess Analysis of Infinie Plae ih Ellipical Hole Mohansing R Padeshi*, D. P. K. Shaa* * ( P.G.Suden, Depaen of Mechanical Engg, NRI s Insiue of Infoaion Science & Technology, Bhopal, India) * ( Head of,
Outline of Topics. Analysis of ODE models with MATLAB. What will we learn from this lecture. Aim of analysis: Why such analysis matters?
 of Topics wih MATLAB Shan He School for Compuaional Science Universi of Birmingham Module 6-3836: Compuaional Modelling wih MATLAB Wha will we learn from his lecure Aim of analsis: Aim of analsis. Some
of Topics wih MATLAB Shan He School for Compuaional Science Universi of Birmingham Module 6-3836: Compuaional Modelling wih MATLAB Wha will we learn from his lecure Aim of analsis: Aim of analsis. Some
Linear Dynamic Models
 Linear Dnamic Models and Forecasing Reference aricle: Ineracions beween he muliplier analsis and he principle of acceleraion Ouline. The sae space ssem as an approach o working wih ssems of difference
Linear Dnamic Models and Forecasing Reference aricle: Ineracions beween he muliplier analsis and he principle of acceleraion Ouline. The sae space ssem as an approach o working wih ssems of difference
A Numerical Hydration Model of Portland Cement
 A Numeical Hydaion Model of Poland Cemen Ippei Mauyama, Tesuo Masushia and Takafumi Noguchi ABSTRACT : A compue-based numeical model is pesened, wih which hydaion and micosucual developmen in Poland cemen-based
A Numeical Hydaion Model of Poland Cemen Ippei Mauyama, Tesuo Masushia and Takafumi Noguchi ABSTRACT : A compue-based numeical model is pesened, wih which hydaion and micosucual developmen in Poland cemen-based
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) , PART A PHYSICS
 Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
LawsoftheElectroElectricalInduction
 Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing: F Elecical and Eleconics Engineeing Volume 15 Issue 9 Vesion 1. Yea 15 Type: Double Blind Pee Reviewed Inenaional Reseach Jounal Publishe: Global Jounals Inc.
Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing: F Elecical and Eleconics Engineeing Volume 15 Issue 9 Vesion 1. Yea 15 Type: Double Blind Pee Reviewed Inenaional Reseach Jounal Publishe: Global Jounals Inc.
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chapter 5 Kinematics
 Chaper 5 Kinemaics In he firs place, wha do we mean b ime and space? I urns ou ha hese deep philosophical quesions have o be analzed ver carefull in phsics, and his is no eas o do. The heor of relaivi
Chaper 5 Kinemaics In he firs place, wha do we mean b ime and space? I urns ou ha hese deep philosophical quesions have o be analzed ver carefull in phsics, and his is no eas o do. The heor of relaivi
Fuzzy Hv-submodules in Γ-Hv-modules Arvind Kumar Sinha 1, Manoj Kumar Dewangan 2 Department of Mathematics NIT Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India
 Inenaional Jounal of Engineeing Reseach (IJOER) [Vol-1, Issue-1, Apil.- 2015] Fuzz v-submodules in Γ-v-modules Avind Kuma Sinha 1, Manoj Kuma Dewangan 2 Depamen of Mahemaics NIT Raipu, Chhaisgah, India
Inenaional Jounal of Engineeing Reseach (IJOER) [Vol-1, Issue-1, Apil.- 2015] Fuzz v-submodules in Γ-v-modules Avind Kuma Sinha 1, Manoj Kuma Dewangan 2 Depamen of Mahemaics NIT Raipu, Chhaisgah, India
