LawsoftheElectroElectricalInduction
|
|
|
- Martin Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing: F Elecical and Eleconics Engineeing Volume 15 Issue 9 Vesion 1. Yea 15 Type: Double Blind Pee Reviewed Inenaional Reseach Jounal Publishe: Global Jounals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: Pin ISSN: By F. F. Mende & A. S. Dubovin Absac- The concep of scala-veco poenial, he assuming dependence of he scala poenial of chage and i pou on fom he speed i made possible o explain a whole seies of he phenomena, conneced wih he moion of chage, which ealie in he classical elecodynamics an explanaion did no have. Such phenomena include he phase abeaion of elecomagneic waves, he ansvese Dopple effec, he phenomenon of Loenz foce. In his aicle he new law of eleco-elecical inducion, which explains naue of dipole emission, will be examined on he basis of he concep of scala- veco poenial. Keywods: maxwell equaion, scala-veco poenial, dipole momen, dipole emission, ampee law, helmholz heoem. GJRE-F Classificaion: FOR Code: 991 LawsofheElecoElecicalInducion Sicly as pe he compliance and egulaions of: 15. F. F. Mende & A. S. Dubovin. This is a eseach/eview pape, disibued unde he ems of he Ceaive Commons Aibuion-Noncommecial 3. Unpoed License hp://ceaivecommons.og/licenses/by-nc/3./), pemiing all non-commecial use, disibuion, and epoducion in any medium, povided he oiginal wok is popely cied.
2 F F. F. Mende α & A. S. Dubovin σ Absac- The concep of scala-veco poenial, he assuming dependence of he scala poenial of chage and i pou on fom he speed i made possible o explain a whole seies of he phenomena, conneced wih he moion of chage, which ealie in he classical elecodynamics an explanaion did no have. Such phenomena include he phase abeaion of elecomagneic waves, he ansvese Dopple effec, he phenomenon of Loenz foce. In his aicle he new law of eleco-elecical inducion, which explains naue of dipole emission, will be examined on he basis of he concep of scala- veco poenial. Keywods: maxwell equaion, scala-veco poenial, dipole momen, dipole emission, ampee law, helmholz heoem. I. Inoducion Maxwell equaions aes o he fac ha in he fee space he ansvese elecomagneic waves can exis [1, ]. Togehe wih he bounday condiions hese equaions give he possibiliy o solve he poblems of eflecion and popagaion of such waves in he locked and limied sucues. Wih he aid of Maxwell equaions i is possible o solve he poblems of emission. Bu since he equaions indicaed ae phenomenological, physics of such pocesses hus fa emains no clea. Simila poblems can be solved, also, wih he use of poenials. This appoach opens geae possibiliies, bu physics of he veco poenial of magneic field also up o now emained no clea. The developmen of he concep of scala- veco poenial, which dedicaed a numbe of woks [3-1], i made i possible o open he physical essence of a numbe of he fundamenal laws of elecodynamics, chages conneced wih he moion. This concep assumes he dependence of he scala poenial of chage on is elaive speed. I is obained by he way of he symmeizaion of he laws of inducion wih he use by he subsanional deivaive. This appoach made possible o explain such phenomena as he phase abeaion of elecomagneic waves, ansvese Dopple effec, powe ineacion of he cuen caying sysems and naue of Loenz foce. In his aicle he new law of eleco-elecical inducion, which explains naue of dipole emission, will be examined on he basis of he concep of scala-veco poenial. Auho α: mende_fedo@mail.u II. Law of he Eleco-Elecical Inducion In he woks [3-1] is developed he concep of scala veco poenial, fom which i follows ha he scala poenial depends on speed. This dependence is deemined by elaionship. ϕ(,) v g ch c, wheev is componen of he chage ae g, nomal o o veco, connecing chage wih he obsevaion poin. Since pou on any pocess of he popagaion of elecical and poenials i is always conneced wih he delay, le us inoduce he being lae scala- veco poenial, by consideing ha he field of his poenial is exended in his medium wih a speed of ligh [1, ]: v g ch ϕ(,) c (.1) whee is componen of he chage ae of v g, nomal o o he veco a he momen of he ime c, is disance beween he chage and he poin, a which is deemined he field, a he momen of he ime. Using a elaionship of E gad ϕ(,), le us find field a poin 1 (Fig. 1) The gadien of he numeical value of a adius of he veco of is a scala funcion of wo poins: he iniial poin of a adius of veco and is end poin (in his case his poin 1 on he axis of x and poin a he oigin of coodinaes). Poin 1 is he poin of souce, while poin - by obsevaion poin. Wih he deeminaion of gadien fom he funcion, which conains a adius depending on he condiions of ask i is necessay o disinguish wo cases: 1) he poin of souce is fixed and is consideed as he funcion of he posiion of obsevaion poin. ) obsevaion poin is fixed and is consideed as he funcion of he posiion of he poin of souce. Yea Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing ( ) Volume XV Issue IX Vesion I 15 Global Jounals Inc. (US)
3 y v ( ) y Yea Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing ( F ) Volum e XV Issue IX Vesion I We will conside ha he chage of e accomplishes flucuaing moion along he axis of y, in he envionmen of poin, which is obsevaion poin, E y g x (1) ( ) Fig. 1 : Diagam of shaping of he induced elecic field. x and fixed poin 1 is he poin of souce and is consideed as he funcion of he posiion of chage. Then we wie down he value of elecic field a poin 1: ( y,) vy ϕ (,) e c (1) ch y y4 πε ( y,) c When he ampliude of he flucuaions of chage is consideably less han disance o he x x vy vy obsevaion poin, i is possible o conside a adius e (,) x sh veco consan. We obain wih his condiion: cx y c whee x is some fixed poin on he axis x. Taking ino accoun ha we obain fom (.) x x x vy vy vy 1 y y vy x x vy vy e 1 (,) x sh cx x c (.3) vy This is a complee emission law of he moving chage. If we ake only fis em of he expansion of vy sh, hen we will obain fom (.3): c (.) x x vy eay e (,) x cx cx (.4) whee is being lae acceleaion of chage. This ay elaionship is wave equaion and defines boh he ampliude and phase esponses of he wave of he elecic field, adiaed by he moving chage. If we as he diecion of emission ake he veco, which lies a he plane xy, and which 15 Global Jounals Inc. (US)
4 F consiues wih he axis y he angleα, hen elaionship (.4) akes he fom: eay sin α ( x,, α) (.5) cx The elaionship (.5) deemines he adiaion paen. Since in his case hee is axial symmey elaive o he axis y, i is possible o calculae he complee adiaion paen of his emission. This diagam coesponds o he adiaion paen of dipole emission. evz Since is being lae veco A x poenial, elaionship (.5) i is possible o ewie x x eay sin A α 1 ( x,, α) cx ε c A µ Is again obained complee ageemen wih he equaions of he being lae veco poenial, bu veco poenial is inoduced hee no by phenomenological mehod, bu wih he use of a concep of he being lae scala- veco poenial. I is necessay o noe one impoan cicumsance: in Maxwell's equaions he elecic fields, which pesen wave, voex. In his case he elecic fields bea gadien naue. Le us demonsae he sill one possibiliy, which opens elaionship (.5). Is known ha in he elecodynamics hee is his concep, as he elecic dipole and he dipole emission, when he chages, which ae vaied in he elecic dipole, emi elecomagneic waves. Two chages wih he opposie signs have he dipole momen: p ed, (.6) whee he vecod is dieced fom he negaive chage owad he posiive chage. Theefoe cuen can be expessed hough he deivaive of dipole momen on he ime Consequenly and d p ev e 1 p v, e v 1 p a e Subsiuing his elaionship ino expession (.5), we obain he emission law of he being vaied dipole.. 1 p ( ) E c c. (.7) This is also vey well known elaionship [1]. In he pocess of flucuaing he elecic dipole ae ceaed he elecic fields of wo foms. Fis, hese ae he elecical inducion fields of emission, epesened by equaions (.4), (.5) and (.6), conneced wih he acceleaion of chage. In addiion o his, aound he being vaied dipole ae fomed he elecic fields of saic dipole, which change in he ime in connecion wih he fac ha he disance beween he chages i depends on ime. Specifically, enegy of hese pou on he feely being vaied dipole and i is expended on he emission. oweve, he summay value of field aound his dipole a any momen of ime defines as supeposiion pou on saic dipole pou on emissions. The laws (.4), (.5), (.7) ae he laws of he diec acion, in which aleady hee is neihe magneic pou on no veco poenials. I.e. hose sucues, by which hee wee he magneic field and magneic veco poenial, ae aleady aken and hey no longe wee necessay o us. Using elaionship (.5) i is possible o obain he laws of eflecion and scaeing boh fo he single chages and, fo any quaniy of hem. If any chage o goup of chages undego he acion of exenal (sange) elecic field, hen such chages begin o accomplish a foced moion, and each of hem emis elecic fields in accodance wih elaionship (.5). The supeposiion of elecical pou on, adiaed by all chages, i is elecical wave. If on he chage acs he elecic field of, hen he acceleaion of chage is deemined by he equaion: Yea Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing ( ) Volume XV Issue IX Vesion I 15 Global Jounals Inc. (US)
5 e a E sin y ω. m Taking ino accoun his elaionship (.5) assumes he fom e sinα x K x y α y ω y ω c x c c mx E ( x,, ) E sin ( ) E sin ( ) (.8) Yea Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing ( F ) Volum e XV Issue IX Vesion I whee he coefficien e sinα K can be named he cm coefficien of scaeing (e-emission) single chage in he assigned diecion, since i deemines he abiliy of chage o e-emi he acing on i exenal elecic field. The cuen wave of he displacemen accompanies he wave of elecic field: vy esinα jy (,) x ε cx If chage accomplishes is moion unde he acion of he elecic field of, hen bias cuen in he disan zone will be wien down as e ω x jy( x, ) E y cosω c mx.. (.9) The sum wave, which pesens he popagaion of elecical pou on (.8) and bias cuens (.9), can be named he elecocuen wave. In his cuen wave of displacemen lags behind he wave of elecic field o π he angle equal. Fo he fis ime his em and definiion of his wave was used in he woks [3, 4]. In paallel wih he elecical waves i is possible o inoduce magneic waves, if we assume ha E j ε o div. (.1), Inoduced hus magneic field is voex. Compaing (.9) and (.1) we obain: ( x, ) e z ω sinα E y cosω x x c mx. Inegaing his elaionship on he coodinae, we find he value of he magneic field e sinα z( x, ) E y sinω cmx. (.11) Thus, elaionship (.8), (.9) and (.11) can be named he laws of elecical-elecical inducion, since. They give he diec coupling beween he elecic fields, applied o he chage, and by fields and by cuens induced by his chage in is envionmen. Chage iself comes ou in he ole of he ansfome, which ensues his pozess. The magneic field, which can be calculaed wih he aid of elaionship (.11), is dieced nomally boh owad he elecic field and owad he diecion of popagaion, and hei elaion a each poin of he space is equal: (,) x 1 (,) x ε c z µ ε, whee Z is wave dag of fee space Wave dag deemines he acive powe of losses on he single aea, locaed nomal o he diecion of popagaion of he wave: 1 P ZE. y Theefoe elecocuen wave, cossing his aea, ansfes hough i he powe, deemined by he daa by elaionship, which is locaed in accodance wih Poyning heoem abou he powe flux of elecomagneic wave. Theefoe, fo finding all paamees, which chaaceize wave pocess, i is sufficien examinaion only of elecocuen wave and knowledge of he wave dag of space. In his case i is in no way compulsoy o inoduce his concep as magneic field and is veco poenial, alhough hee is nohing illegal in his. In his seing of he elaionships, obained fo he elecical and magneic field, hey compleely saisfy elmholz's heoem. This heoem says, ha any single-valued and coninuous vecoial F, which uns ino zeo a infiniy, can be field epesened uniquely as he sum of he gadien of a ceain scala funcion ϕ and oo of a ceain veco funcion C, whose divegence is equal o zeo: F gadϕ + oc, divc. Z 15 Global Jounals Inc. (US)
6 F Consequenly, mus exis clea sepaaion pou on o he gadien and he voex. I is eviden ha in he expessions, obained fo hose induced pou on, his sepaaion is locaed. Elecic fields bea gadien naue, and magneic is voex. Thus, he consucion of elecodynamics should have been begun fom he acknowledgemen of he dependence of scala poenial on he speed. Bu naue vey deeply hides is seces, and in ode o come o his simple conclusion, i was necessay o pass way by lengh almos ino wo cenuies. The gi, which so hamoniously wee eeced aound he magne poles, in a saigh manne indicaed he pesence of some powe pou on poenial naue, bu o his hey did no un aenion; heefoe i uned ou ha all examined only ip of he icebeg, whose subsanial pa emained invisible of almos wo hunded yeas. Taking ino accoun enie afoesaid one should assume ha a he basis of he ovewhelming majoiy of saic and dynamic phenomena a he elecodynamics only one fomula (.1), which assumes he dependence of he scala poenial of chage on he speed, lies. Fom his fomula i follows and saic ineacion of chages, and laws of powe ineacion in he case of hei muual moion, and emission laws and scaeing. This appoach made i possible o explain fom he posiions of classical elecodynamics such phenomena as phase abeaion and he ansvese Dopple effec, which wihin he famewok he classical elecodynamics of explanaion did no find. Afe enie afoesaid i is possible o emove consucion foess, such as magneic field and magneic veco poenial, which do no allow hee aleady almos wo hunded yeas o see he building of elecodynamics in enie is sublimiy and beauy. Le us poin ou ha one of he fundamenal equaions of inducion (.4) could be obained diecly fom he Ampee law, sill long befoe appeaed Maxwell equaions. The Ampee law, expessed in he veco fom, deemines magneic field a he poin xyz,, 1 Idl 3 whee I is cuen in he elemendl, dieced fom dl o he poin xyz.,, I is possible o show ha and, besides he fac ha [ dl ] 1 gad dl 3 is veco, 1 dl 1 gad dl o o dl. bu he oodl is equal o zeo and heefoe is final whee dl o I o A π A 4 dl I (.1) he emakable popey of his expession is ha ha he veco poenial depends fom he disance o he obsevaion poin as 1. Specifically, his popey makes i possible o obain emission laws. A gv dl Fo he single chage of e his elaionship akes he fom: and since ha Since I gv, whee g he quaniy of chages, which falls pe uni of he lengh of conduco, fom (.1) we obain: A ev A E µ v g dl ga dl E µ µ, (.13) whee a is acceleaion of chage. This elaionship appeas as follows fo he single chage: µ ea E,,. (.14) If we in elaionships (.13) and (.14) conside ha he poenials ae exended wih he final speed and o conside he delay of, and assuming 1, hese elaionships will ake he fom: µ ε c ga( ) dl ga( ) dl E µ c c, (.15) c ea( ) E c c. (.16) Yea Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing ( ) Volume XV Issue IX Vesion I 15 Global Jounals Inc. (US)
7 Yea Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing ( F ) Volum e XV Issue IX Vesion I The elaionship (.15) and (.16) epesen, i is as shown highe (see (.4)), wave equaions. Le us noe ha hese equaions - his soluion of Maxwell's equaions, bu in his case hey ae obained diecly fom he Ampee law, no a all coming unning o Maxwell equaions. To hee emains only pesen he quesion, why elecodynamics in is ime is no banal by his mehod. Given examples show, as elecodynamics in he ime of is exisence lile moved. The phenomenon of elecomagneic inducion Faaday opened ino 1831 and aleady almos yeas is sudy undewen pacically no changes, and he physical causes fo he mos elemenay elecodynamic phenomena, unil now, wee misundesood. Ceainly, fo his ime Faaday was genius, bu ha hey did make physics afe i? Thee wee sill such billian figues as Maxwell and ez, bu even hey did no undesand ha he dependence of he scala poenial of chage on is elaive speed is he basis of enie classical elecodynamics, and ha his is ha basic law, fom which follow he fundamenal laws of elecodynamics. III. Conclusion Maxwell equaions aes o he fac ha in he fee space he ansvese elecomagneic waves can exis. Togehe wih he bounday condiions hese equaions give he possibiliy o solve he poblems of eflecion and popagaion of such waves in he locked and limied sucues. Wih he aid of Maxwell equaions i is possible o solve he poblems of emission. Bu since he equaions indicaed ae phenomenological, physics of such pocesses hus fa emains no clea. Simila poblems can be solved, also, wih he use of poenials. This appoach opens geae possibiliies, bu physics of he veco poenial of magneic field also up o now emained no clea. The developmen of he concep of scala-veco poenial, which dedicaed a numbe of woks [3-1], i made i possible o open he physical essence of a numbe of he fundamenal laws of elecodynamics, chages conneced wih he moion. This concep assumes he dependence of he scala poenial of chage on is elaive speed. I is obained by he way of he symmeizaion of he laws of inducion wih he use by he subsanional deivaive. This appoach made possible o explain such phenomena as he phase abeaion of elecomagneic waves, ansvese Dopple effec, powe ineacion of he cuen caying sysems and naue of Loenz foce. In his aicle he new law of eleco-elecical inducion, which explains naue of dipole emission, will be examined on he basis of he concep of scala-veco poenial. Refeences Réféences Refeencias 1. S. Ramo, John. Winne. Fieldsand Waves in moden eleconics.ogiz: V. V. Nicolsky, T.I. Nicolskaya, Elecodynamics and popagaion of adio waves, Moscow, Nauka, F. F. Mende, On efinemen of equaions of elecomagneic inducion, Khakov, deposied in VINITI, No 774 B88 Dep., F. F. Mende. On efinemen of ceain laws of classical elecodynamics, axiv, physics/ F. F. Mende. Concepion of he scala-veco poenial in conempoay elecodynamics, axiv. og/abs/physics/ F. F. Mende New elecodynamics. Revoluion in he moden physics. Khakov, NTMT, F. F. Mende, On efinemen of ceain laws of classical elecodynamics, LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing F. F. Mende. The Classical Convesions of Elecomagneic Fields on Thei Consequences AASCIT Jounal of PhysicsVol.1, No. 1, Publicaion Dae: Mach 8, 15, Page: F. F. Mende. On hephysical basis ofunipola inducion.a new ype of unipola geneao. EngineeingPhysics, 6, 13, p F. F. Mende, Concep of Scala-Veco Poenial in he Conempoay Elecodynamic, Poblem of omopola Inducion and Is Soluion, Inenaional Jounal of Physics, 14, Vol., No. 6, R. Feynman, R. Leighon, M. Sends, Feynman lecues on physics, М..Mi, Vol. 6, Global Jounals Inc. (US)
8 Global Jounals Inc. (US) Guidelines andbook 15
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
On Control Problem Described by Infinite System of First-Order Differential Equations
 Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
Combinatorial Approach to M/M/1 Queues. Using Hypergeometric Functions
 Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH
 Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Two-dimensional Effects on the CSR Interaction Forces for an Energy-Chirped Bunch. Rui Li, J. Bisognano, R. Legg, and R. Bosch
 Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
r r r r r EE334 Electromagnetic Theory I Todd Kaiser
 334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
7 Wave Equation in Higher Dimensions
 7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
MEEN 617 Handout #11 MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Systems with VISCOUS DAMPING
 MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
The sudden release of a large amount of energy E into a background fluid of density
 10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Monochromatic Wave over One and Two Bars
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Electrical and current self-induction
 Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
Lecture-V Stochastic Processes and the Basic Term-Structure Equation 1 Stochastic Processes Any variable whose value changes over time in an uncertain
 Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba
![( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba ( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba](/thumbs/83/87856399.jpg) THE INTEACTION OF ADIATION AND MATTE: SEMICLASSICAL THEOY PAGE 26 III. EVIEW OF BASIC QUANTUM MECHANICS : TWO -LEVEL QUANTUM SYSTEMS : The lieaue of quanum opics and lase specoscop abounds wih discussions
THE INTEACTION OF ADIATION AND MATTE: SEMICLASSICAL THEOY PAGE 26 III. EVIEW OF BASIC QUANTUM MECHANICS : TWO -LEVEL QUANTUM SYSTEMS : The lieaue of quanum opics and lase specoscop abounds wih discussions
Orthotropic Materials
 Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
2. v = 3 4 c. 3. v = 4c. 5. v = 2 3 c. 6. v = 9. v = 4 3 c
 Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
An Automatic Door Sensor Using Image Processing
 An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
ÖRNEK 1: THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MOMENTUM RELATION Calculate the linear momentum of a particle of mass m=10 kg which has a. kg m s
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
Relative and Circular Motion
 Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION
 Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL METHOD FOR THE COMPUTATION OF THE BODIES MOTION IN ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
 AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL METHOD FOR THE COMPUTATION OF THE BODIES MOTION IN ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD GEORGE-MARIAN VASILESCU, MIHAI MARICARU, BOGDAN DUMITRU VĂRĂTICEANU, MARIUS AUREL COSTEA Key wods: Eddy cuen
AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL METHOD FOR THE COMPUTATION OF THE BODIES MOTION IN ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD GEORGE-MARIAN VASILESCU, MIHAI MARICARU, BOGDAN DUMITRU VĂRĂTICEANU, MARIUS AUREL COSTEA Key wods: Eddy cuen
Risk tolerance and optimal portfolio choice
 Risk oleance and opimal pofolio choice Maek Musiela BNP Paibas London Copoae and Invesmen Join wok wih T. Zaiphopoulou (UT usin) Invesmens and fowad uiliies Pepin 6 Backwad and fowad dynamic uiliies and
Risk oleance and opimal pofolio choice Maek Musiela BNP Paibas London Copoae and Invesmen Join wok wih T. Zaiphopoulou (UT usin) Invesmens and fowad uiliies Pepin 6 Backwad and fowad dynamic uiliies and
r P + '% 2 r v(r) End pressures P 1 (high) and P 2 (low) P 1 , which must be independent of z, so # dz dz = P 2 " P 1 = " #P L L,
 Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
P h y s i c s F a c t s h e e t
 P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS
 Mem. Fac. Inegaed As and Sci., Hioshima Univ., Se. IV, Vol. 8 9-33, Dec. 00 ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS YOSHIO AGAOKA *, BYUNG HAK KIM ** AND JIN HYUK CHOI ** *Depamen of Mahemaics, Faculy
Mem. Fac. Inegaed As and Sci., Hioshima Univ., Se. IV, Vol. 8 9-33, Dec. 00 ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS YOSHIO AGAOKA *, BYUNG HAK KIM ** AND JIN HYUK CHOI ** *Depamen of Mahemaics, Faculy
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Probabilistic Models
 CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
General Non-Arbitrage Model. I. Partial Differential Equation for Pricing A. Traded Underlying Security
 1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
PHYS GENERAL RELATIVITY AND COSMOLOGY PROBLEM SET 7 - SOLUTIONS
 PHYS 54 - GENERAL RELATIVITY AND COSMOLOGY - 07 - PROBLEM SET 7 - SOLUTIONS TA: Jeome Quinin Mach, 07 Noe ha houghou hee oluion, we wok in uni whee c, and we chooe he meic ignaue (,,, ) a ou convenion..
PHYS 54 - GENERAL RELATIVITY AND COSMOLOGY - 07 - PROBLEM SET 7 - SOLUTIONS TA: Jeome Quinin Mach, 07 Noe ha houghou hee oluion, we wok in uni whee c, and we chooe he meic ignaue (,,, ) a ou convenion..
Chapter 7. Interference
 Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
Ferent equation of the Universe
 Feen equaion of he Univese I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize - Discoveies Feen equaion of he Univese: i + ia = = (... N... N M m i= i ) i a M m j=
Feen equaion of he Univese I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize - Discoveies Feen equaion of he Univese: i + ia = = (... N... N M m i= i ) i a M m j=
New method to explain and calculate the gyroscopic torque and its possible relation to the spin of electron
 Laes Tends in Applied and Theoeical Mechanics New mehod o explain and calculae he gyoscopic oque and is possible elaion o he o elecon BOJIDAR DJORDJEV Independen Reseache 968 4- Dobudja see, Ezeovo, Vana
Laes Tends in Applied and Theoeical Mechanics New mehod o explain and calculae he gyoscopic oque and is possible elaion o he o elecon BOJIDAR DJORDJEV Independen Reseache 968 4- Dobudja see, Ezeovo, Vana
Fig. 1S. The antenna construction: (a) main geometrical parameters, (b) the wire support pillar and (c) the console link between wire and coaxial
 a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY
 Mahemaics Today Vol7(Dec-)54-6 ISSN 976-38 EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY K Punachanda Rao Depamen of Mahemaics Chiala Engineeing College Chiala 53 57 Andha Padesh, INDIA E-mail: dkpaocecc@yahoocoin ABSTRACT
Mahemaics Today Vol7(Dec-)54-6 ISSN 976-38 EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY K Punachanda Rao Depamen of Mahemaics Chiala Engineeing College Chiala 53 57 Andha Padesh, INDIA E-mail: dkpaocecc@yahoocoin ABSTRACT
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Properties of Logarithms. Properties. Properties. log. Exponential. Logarithmic.
 Eponenial and Logaihmic Equaions and Popeies of Logaihms Popeies Eponenial a a s = a +s a /a s = a -s (a ) s = a s a b = (ab) Logaihmic log s = log + logs log/s = log - logs log s = s log log a b = loga
Eponenial and Logaihmic Equaions and Popeies of Logaihms Popeies Eponenial a a s = a +s a /a s = a -s (a ) s = a s a b = (ab) Logaihmic log s = log + logs log/s = log - logs log s = s log log a b = loga
156 There are 9 books stacked on a shelf. The thickness of each book is either 1 inch or 2
 156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
4. Fundamental of A.C. Circuit
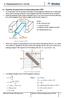 4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
The shortest path between two truths in the real domain passes through the complex domain. J. Hadamard
 Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Energy dispersion relation for negative refraction (NR) materials
 Enegy dispesion elaion fo negaive efacion (NR) maeials Y.Ben-Ayeh Physics Depamen, Technion Isael of Technology, Haifa 3, Isael E-mail addess: ph65yb@physics.echnion,ac.il; Fax:97 4 895755 Keywods: Negaive-efacion,
Enegy dispesion elaion fo negaive efacion (NR) maeials Y.Ben-Ayeh Physics Depamen, Technion Isael of Technology, Haifa 3, Isael E-mail addess: ph65yb@physics.echnion,ac.il; Fax:97 4 895755 Keywods: Negaive-efacion,
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chapter 2 Wave Motion
 Lecue 4 Chape Wae Moion Plane waes 3D Diffeenial wae equaion Spheical waes Clindical waes 3-D waes: plane waes (simples 3-D waes) ll he sufaces of consan phase of disubance fom paallel planes ha ae pependicula
Lecue 4 Chape Wae Moion Plane waes 3D Diffeenial wae equaion Spheical waes Clindical waes 3-D waes: plane waes (simples 3-D waes) ll he sufaces of consan phase of disubance fom paallel planes ha ae pependicula
Physics 2001/2051 Moments of Inertia Experiment 1
 Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
Representing Knowledge. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Properties of BNs. Independence? Reachability (the Bayes Ball) Example
 C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
The Method of Images in Velocity-Dependent Systems
 >1< The Mehod of Images in Velociy-Dependen Sysems Dan Censo Ben Guion Univesiy of he Negev Depamen of Elecical and Compue Engineeing Bee Sheva, Isael 8415 censo@ee.bgu.ac.il Absac This sudy invesigaes
>1< The Mehod of Images in Velociy-Dependen Sysems Dan Censo Ben Guion Univesiy of he Negev Depamen of Elecical and Compue Engineeing Bee Sheva, Isael 8415 censo@ee.bgu.ac.il Absac This sudy invesigaes
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Gauge invariance and the vacuum state. Dan Solomon Rauland-Borg Corporation 3450 W. Oakton Skokie, IL Please send all correspondence to:
 Gauge invaiance and he vacuum sae 1 Gauge invaiance and he vacuum sae by Dan Solomon Rauland-Bog Copoaion 345 W. Oakon Skokie, IL 676 Please send all coespondence o: Dan Solomon 164 Bummel Evanson, IL
Gauge invaiance and he vacuum sae 1 Gauge invaiance and he vacuum sae by Dan Solomon Rauland-Bog Copoaion 345 W. Oakon Skokie, IL 676 Please send all coespondence o: Dan Solomon 164 Bummel Evanson, IL
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION
 1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
Section 7.4 Modeling Changing Amplitude and Midline
 488 Chaper 7 Secion 7.4 Modeling Changing Ampliude and Midline While sinusoidal funcions can model a variey of behaviors, i is ofen necessary o combine sinusoidal funcions wih linear and exponenial curves
488 Chaper 7 Secion 7.4 Modeling Changing Ampliude and Midline While sinusoidal funcions can model a variey of behaviors, i is ofen necessary o combine sinusoidal funcions wih linear and exponenial curves
Low-complexity Algorithms for MIMO Multiplexing Systems
 Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
THERMAL PHYSICS. E nc T. W PdV. degrees of freedom. 32 m N V. P mv. Q c. AeT (emitted energy rate) E Ae T Tsurroundings. Q nc p
 HRMA PHYSICS PHY 8 Final es: Compehensie Concep and Fomula Shee NB: Do no add anyhing o he fomula shee excep in he space specially assigned. hemodynamic Paamees: Volume V of mass m wih densiy ρ: V m empeaue
HRMA PHYSICS PHY 8 Final es: Compehensie Concep and Fomula Shee NB: Do no add anyhing o he fomula shee excep in he space specially assigned. hemodynamic Paamees: Volume V of mass m wih densiy ρ: V m empeaue
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) , PART A PHYSICS
 Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
Heat Conduction Problem in a Thick Circular Plate and its Thermal Stresses due to Ramp Type Heating
 ISSN(Online): 319-8753 ISSN (Pin): 347-671 Inenaional Jounal of Innovaive Reseac in Science, Engineeing and Tecnology (An ISO 397: 7 Ceified Oganiaion) Vol 4, Issue 1, Decembe 15 Hea Concion Poblem in
ISSN(Online): 319-8753 ISSN (Pin): 347-671 Inenaional Jounal of Innovaive Reseac in Science, Engineeing and Tecnology (An ISO 397: 7 Ceified Oganiaion) Vol 4, Issue 1, Decembe 15 Hea Concion Poblem in
Traveling Waves. Chapter Introduction
 Chaper 4 Traveling Waves 4.1 Inroducion To dae, we have considered oscillaions, i.e., periodic, ofen harmonic, variaions of a physical characerisic of a sysem. The sysem a one ime is indisinguishable from
Chaper 4 Traveling Waves 4.1 Inroducion To dae, we have considered oscillaions, i.e., periodic, ofen harmonic, variaions of a physical characerisic of a sysem. The sysem a one ime is indisinguishable from
Research on the Algorithm of Evaluating and Analyzing Stationary Operational Availability Based on Mission Requirement
 Reseach on he Algoihm of Evaluaing and Analyzing Saionay Opeaional Availabiliy Based on ission Requiemen Wang Naichao, Jia Zhiyu, Wang Yan, ao Yilan, Depamen of Sysem Engineeing of Engineeing Technology,
Reseach on he Algoihm of Evaluaing and Analyzing Saionay Opeaional Availabiliy Based on ission Requiemen Wang Naichao, Jia Zhiyu, Wang Yan, ao Yilan, Depamen of Sysem Engineeing of Engineeing Technology,
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
Electromagnetic Stealth with Parallel electric and magnetic Fields
 DMO / ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΜΑΓΝΗΤΙΚΗ ΑΟΡΑΤΟΤΗΤΑ ΜΕ ΠΑΡΑΛΛΗΛΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΑ Κ ΜΑΓΝΗΤΙΚΑ ΠΕ ΙΑ Θ.. ΡΑΠΤΗΣ lecomagneic Sealh wih Paallel elecic and magneic Fields T.. RAPTΙS ΕΚΕΦΕ «ΗΜΟΚΡΙΤΟΣ» Τ. Θ. 68, 53 ΑΓΙΑ ΠΑΡΑΣΚΕΥΗ (Αθήνα)
DMO / ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΜΑΓΝΗΤΙΚΗ ΑΟΡΑΤΟΤΗΤΑ ΜΕ ΠΑΡΑΛΛΗΛΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΑ Κ ΜΑΓΝΗΤΙΚΑ ΠΕ ΙΑ Θ.. ΡΑΠΤΗΣ lecomagneic Sealh wih Paallel elecic and magneic Fields T.. RAPTΙS ΕΚΕΦΕ «ΗΜΟΚΡΙΤΟΣ» Τ. Θ. 68, 53 ΑΓΙΑ ΠΑΡΑΣΚΕΥΗ (Αθήνα)
Wall. x(t) f(t) x(t = 0) = x 0, t=0. which describes the motion of the mass in absence of any external forcing.
 MECHANICS APPLICATIONS OF SECOND-ORDER ODES 7 Mechanics applicaions of second-order ODEs Second-order linear ODEs wih consan coefficiens arise in many physical applicaions. One physical sysems whose behaviour
MECHANICS APPLICATIONS OF SECOND-ORDER ODES 7 Mechanics applicaions of second-order ODEs Second-order linear ODEs wih consan coefficiens arise in many physical applicaions. One physical sysems whose behaviour
Circuits 24/08/2010. Question. Question. Practice Questions QV CV. Review Formula s RC R R R V IR ... Charging P IV I R ... E Pt.
 4/08/00 eview Fomul s icuis cice s BL B A B I I I I E...... s n n hging Q Q 0 e... n... Q Q n 0 e Q I I0e Dischging Q U Q A wie mde of bss nd nohe wie mde of silve hve he sme lengh, bu he dimee of he bss
4/08/00 eview Fomul s icuis cice s BL B A B I I I I E...... s n n hging Q Q 0 e... n... Q Q n 0 e Q I I0e Dischging Q U Q A wie mde of bss nd nohe wie mde of silve hve he sme lengh, bu he dimee of he bss
Authors name Giuliano Bettini* Alberto Bicci** Title Equivalent waveguide representation for Dirac plane waves
 Auhos name Giuliano Beini* Albeo Bicci** Tile Equivalen waveguide epesenaion fo Diac plane waves Absac Ideas abou he elecon as a so of a bound elecomagneic wave and/o he elecon as elecomagneic field apped
Auhos name Giuliano Beini* Albeo Bicci** Tile Equivalen waveguide epesenaion fo Diac plane waves Absac Ideas abou he elecon as a so of a bound elecomagneic wave and/o he elecon as elecomagneic field apped
Variance and Covariance Processes
 Vaiance and Covaiance Pocesses Pakash Balachandan Depamen of Mahemaics Duke Univesiy May 26, 2008 These noes ae based on Due s Sochasic Calculus, Revuz and Yo s Coninuous Maingales and Bownian Moion, Kaazas
Vaiance and Covaiance Pocesses Pakash Balachandan Depamen of Mahemaics Duke Univesiy May 26, 2008 These noes ae based on Due s Sochasic Calculus, Revuz and Yo s Coninuous Maingales and Bownian Moion, Kaazas
[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u
![[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u [ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u](/thumbs/89/100187624.jpg) Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Kinematics. Position. Lectures 3 and 4 Motion in One Dimension. A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan
 Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
ME 304 FLUID MECHANICS II
 ME 304 LUID MECHNICS II Pof. D. Haşme Tükoğlu Çankaya Uniesiy aculy of Engineeing Mechanical Engineeing Depamen Sping, 07 y du dy y n du k dy y du k dy n du du dy dy ME304 The undamenal Laws Epeience hae
ME 304 LUID MECHNICS II Pof. D. Haşme Tükoğlu Çankaya Uniesiy aculy of Engineeing Mechanical Engineeing Depamen Sping, 07 y du dy y n du k dy y du k dy n du du dy dy ME304 The undamenal Laws Epeience hae
Antennas & Propagation
 Antennas & Popagation 1 Oveview of Lectue II -Wave Equation -Example -Antenna Radiation -Retaded potential THE KEY TO ANY OPERATING ANTENNA ot H = J +... Suppose: 1. Thee does exist an electic medium,
Antennas & Popagation 1 Oveview of Lectue II -Wave Equation -Example -Antenna Radiation -Retaded potential THE KEY TO ANY OPERATING ANTENNA ot H = J +... Suppose: 1. Thee does exist an electic medium,
15. Vector Valued Functions
 1. Vecor Valued Funcions Up o his poin, we have presened vecors wih consan componens, for example, 1, and,,4. However, we can allow he componens of a vecor o be funcions of a common variable. For example,
1. Vecor Valued Funcions Up o his poin, we have presened vecors wih consan componens, for example, 1, and,,4. However, we can allow he componens of a vecor o be funcions of a common variable. For example,
The k-filtering Applied to Wave Electric and Magnetic Field Measurements from Cluster
 The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
A Weighted Moving Average Process for Forecasting. Shou Hsing Shih Chris P. Tsokos
 A Weighed Moving Aveage Pocess fo Foecasing Shou Hsing Shih Chis P. Tsokos Depamen of Mahemaics and Saisics Univesiy of Souh Floida, USA Absac The objec of he pesen sudy is o popose a foecasing model fo
A Weighed Moving Aveage Pocess fo Foecasing Shou Hsing Shih Chis P. Tsokos Depamen of Mahemaics and Saisics Univesiy of Souh Floida, USA Absac The objec of he pesen sudy is o popose a foecasing model fo
Chapter Q1. We need to understand Classical wave first. 3/28/2004 H133 Spring
 Chaper Q1 Inroducion o Quanum Mechanics End of 19 h Cenury only a few loose ends o wrap up. Led o Relaiviy which you learned abou las quarer Led o Quanum Mechanics (1920 s-30 s and beyond) Behavior of
Chaper Q1 Inroducion o Quanum Mechanics End of 19 h Cenury only a few loose ends o wrap up. Led o Relaiviy which you learned abou las quarer Led o Quanum Mechanics (1920 s-30 s and beyond) Behavior of
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
336 ERIDANI kfk Lp = sup jf(y) ; f () jj j p p whee he supemum is aken ove all open balls = (a ) inr n, jj is he Lebesgue measue of in R n, () =(), f
 TAMKANG JOURNAL OF MATHEMATIS Volume 33, Numbe 4, Wine 2002 ON THE OUNDEDNESS OF A GENERALIED FRATIONAL INTEGRAL ON GENERALIED MORREY SPAES ERIDANI Absac. In his pape we exend Nakai's esul on he boundedness
TAMKANG JOURNAL OF MATHEMATIS Volume 33, Numbe 4, Wine 2002 ON THE OUNDEDNESS OF A GENERALIED FRATIONAL INTEGRAL ON GENERALIED MORREY SPAES ERIDANI Absac. In his pape we exend Nakai's esul on he boundedness
Electromagnetic interaction in dipole grids and prospective high-impedance surfaces
 ADIO SCIENCE, VOL.,, doi:.29/2s36, 25 Elecomagneic ineacion in dipole gids and pospecive high-impedance sufaces C.. Simovsi Depamen of Physics, S. Peesbug Insiue of Fine Mechanics and Opics, S. Peesbug,
ADIO SCIENCE, VOL.,, doi:.29/2s36, 25 Elecomagneic ineacion in dipole gids and pospecive high-impedance sufaces C.. Simovsi Depamen of Physics, S. Peesbug Insiue of Fine Mechanics and Opics, S. Peesbug,
An Electrostatic Analogue for the Novel Temporary Magnetic Remanence Thermodynamic Cycles
 -1- An Elecosaic Analogue fo he Novel Tempoay Magneic emanence Themodynamic Cycles Absac emi Conwall Fuue Enegy eseach Goup Queen May, Univesiy of London, Mile End oad, London E1 4NS hp://webspace.qmul.ac.uk/oconwall
-1- An Elecosaic Analogue fo he Novel Tempoay Magneic emanence Themodynamic Cycles Absac emi Conwall Fuue Enegy eseach Goup Queen May, Univesiy of London, Mile End oad, London E1 4NS hp://webspace.qmul.ac.uk/oconwall
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 In. J. Pue Appl. Sci. Technol., 4 (211, pp. 23-29 Inenaional Jounal of Pue and Applied Sciences and Technology ISS 2229-617 Available online a www.ijopaasa.in eseach Pape Opizaion of he Uiliy of a Sucual
In. J. Pue Appl. Sci. Technol., 4 (211, pp. 23-29 Inenaional Jounal of Pue and Applied Sciences and Technology ISS 2229-617 Available online a www.ijopaasa.in eseach Pape Opizaion of he Uiliy of a Sucual
Q & Particle-Gas Multiphase Flow. Particle-Gas Interaction. Particle-Particle Interaction. Two-way coupling fluid particle. Mass. Momentum.
 Paicle-Gas Muliphase Flow Fluid Mass Momenum Enegy Paicles Q & m& F D Paicle-Gas Ineacion Concenaion highe dilue One-way coupling fluid paicle Two-way coupling fluid paicle Concenaion highe Paicle-Paicle
Paicle-Gas Muliphase Flow Fluid Mass Momenum Enegy Paicles Q & m& F D Paicle-Gas Ineacion Concenaion highe dilue One-way coupling fluid paicle Two-way coupling fluid paicle Concenaion highe Paicle-Paicle
On the Semi-Discrete Davey-Stewartson System with Self-Consistent Sources
 Jounal of Applied Mahemaics and Physics 25 3 478-487 Published Online May 25 in SciRes. hp://www.scip.og/jounal/jamp hp://dx.doi.og/.4236/jamp.25.356 On he Semi-Discee Davey-Sewason Sysem wih Self-Consisen
Jounal of Applied Mahemaics and Physics 25 3 478-487 Published Online May 25 in SciRes. hp://www.scip.og/jounal/jamp hp://dx.doi.og/.4236/jamp.25.356 On he Semi-Discee Davey-Sewason Sysem wih Self-Consisen
Research Article A Note on Multiplication and Composition Operators in Lorentz Spaces
 Hindawi Publishing Copoaion Jounal of Funcion Spaces and Applicaions Volume 22, Aicle ID 29363, pages doi:.55/22/29363 Reseach Aicle A Noe on Muliplicaion and Composiion Opeaos in Loenz Spaces Eddy Kwessi,
Hindawi Publishing Copoaion Jounal of Funcion Spaces and Applicaions Volume 22, Aicle ID 29363, pages doi:.55/22/29363 Reseach Aicle A Noe on Muliplicaion and Composiion Opeaos in Loenz Spaces Eddy Kwessi,
4.6 One Dimensional Kinematics and Integration
 4.6 One Dimensional Kinemaics and Inegraion When he acceleraion a( of an objec is a non-consan funcion of ime, we would like o deermine he ime dependence of he posiion funcion x( and he x -componen of
4.6 One Dimensional Kinemaics and Inegraion When he acceleraion a( of an objec is a non-consan funcion of ime, we would like o deermine he ime dependence of he posiion funcion x( and he x -componen of
The Maxwell Equations, the Lorentz Field and the Electromagnetic Nanofield with Regard to the Question of Relativity
 The Maxwell Equaions, he Lorenz Field and he Elecromagneic Nanofield wih Regard o he Quesion of Relaiviy Daniele Sasso * Absrac We discuss he Elecromagneic Theory in some main respecs and specifically
The Maxwell Equaions, he Lorenz Field and he Elecromagneic Nanofield wih Regard o he Quesion of Relaiviy Daniele Sasso * Absrac We discuss he Elecromagneic Theory in some main respecs and specifically
ME 141. Engineering Mechanics
 ME 141 Engineeing Mechnics Lecue 13: Kinemics of igid bodies hmd Shhedi Shkil Lecue, ep. of Mechnicl Engg, UET E-mil: sshkil@me.bue.c.bd, shkil6791@gmil.com Websie: eche.bue.c.bd/sshkil Couesy: Veco Mechnics
ME 141 Engineeing Mechnics Lecue 13: Kinemics of igid bodies hmd Shhedi Shkil Lecue, ep. of Mechnicl Engg, UET E-mil: sshkil@me.bue.c.bd, shkil6791@gmil.com Websie: eche.bue.c.bd/sshkil Couesy: Veco Mechnics
Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering
 Srucural Dynamics and Earhquae Engineering Course 1 Inroducion. Single degree of freedom sysems: Equaions of moion, problem saemen, soluion mehods. Course noes are available for download a hp://www.c.up.ro/users/aurelsraan/
Srucural Dynamics and Earhquae Engineering Course 1 Inroducion. Single degree of freedom sysems: Equaions of moion, problem saemen, soluion mehods. Course noes are available for download a hp://www.c.up.ro/users/aurelsraan/
LAB # 2 - Equilibrium (static)
 AB # - Equilibrium (saic) Inroducion Isaac Newon's conribuion o physics was o recognize ha despie he seeming compleiy of he Unierse, he moion of is pars is guided by surprisingly simple aws. Newon's inspiraion
AB # - Equilibrium (saic) Inroducion Isaac Newon's conribuion o physics was o recognize ha despie he seeming compleiy of he Unierse, he moion of is pars is guided by surprisingly simple aws. Newon's inspiraion
4.5 Constant Acceleration
 4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
- If one knows that a magnetic field has a symmetry, one may calculate the magnitude of B by use of Ampere s law: The integral of scalar product
 11.1 APPCATON OF AMPEE S AW N SYMMETC MAGNETC FEDS - f one knows ha a magneic field has a symmery, one may calculae he magniude of by use of Ampere s law: The inegral of scalar produc Closed _ pah * d
11.1 APPCATON OF AMPEE S AW N SYMMETC MAGNETC FEDS - f one knows ha a magneic field has a symmery, one may calculae he magniude of by use of Ampere s law: The inegral of scalar produc Closed _ pah * d
EN221 - Fall HW # 7 Solutions
 EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
