Biology Chapter 8 Reading Guide Interphase obtains nutrients duplicates (copies) its chromatids the nucleus molecule DNA centromere
|
|
|
- Victor Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology Chapter 8 Reading Guide v Cell cycle Ø Cell reproduction Cell division the reproduction of cell through duplication of the genome and division of the cytoplasm Ø Chromosomes a threadlike gene found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and most visible during mitosis and meiosis also the main gene carrying structure of a prokaryotic cell consists of a very long piece of chromatin a commination of DNA and protein Ø Asexual reproduction the creation of genetically identical offspring by a single parent without the participation of sperm or egg Sea stars new individuals from fragmented pieces Ø Sexual reproduction the creation of genetically unique offspring bu the fusion of 2 haploid sex cells (gametes) forming a diploid zygote v Binary fission a means of asexual reproduction in which a parent organism often a single cell divides into two genetically identical individuals of about equal size Ø Prokaryotes v The cell cycle or the cell division cycle is the series of events that takes place in the eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These events can be divided into two parts interphase (in between divisions phases grouping G1 phase S phase and G2 phase) during which the cell is forming and carries on with its normal metabolic functions. The mitotic phase (M mitosis) during which the cell is replicating itself. Thus cell division cycle is and essential process by which a single cell fertilized egg develops into a mature organism and the process by which hair skin and blood cells and some internal organs are formed v Interphase is a phase of the cell cycle, defined only by the absence of cell division. During interphase, the cell obtains nutrients, and duplicates (copies) its chromatids (genetic material). The genetic material or chromatids are located in the nucleus of the cell and are made of the molecule DNA. v Chromatids are connected by the centromere and have a LONG AND SHORT ARM. v Most eukaryotic cells spend most of their time in interphase. For example, human skin cells, which divide about once a day, spend roughly 22 hours in interphase. About 90 percent of cells are in interphase. Some cells, such as nerve cells, can stay in interphase for decades. There are 3 parts of interphase: G 1 (growth 1 in which the cell creates organelles and begins
2 metabolism), S phase (DNA synthesis in which the chromosomes of the cell are copied) and G 2 (growth 2 in which the cell grows in preparation for cell division). v Sometimes the cells exit the cell cycle (usually from G 1 phase) and enter the G 0 phase. In the G 0 phase, cells are alive and metabolically active, but do not divide. In this phase cells do not copy their DNA and do not prepare for cell division. Many cells in the human body, including those in heart muscle, eyes, and brain are in the G 0 phase. If these cells are damaged they cannot be replaced. v The G 1 phase is a period in the cell cycle during interphase, after cytokinesis (process whereby a single cell is divided into two identical daughter cells whenever the cytoplasm is divided) and before the S phase. For many cells, this phase is the major period of cell growth during its lifespan. During this stage new organelles are being synthesized (made), so the cell requires both structural proteins and enzymes, resulting in great amount of protein synthesis. v The S phase, short for synthesis phase, is a period in the cell cycle during interphase, between G1 phase and the G2 phase. Following G1, the cell enters the S stage, when DNA synthesis or replication occurs. At the beginning of the S stage, each chromosome is composed of one coiled DNA double helix molecule, which is called a chromatid. At the end of this stage, each chromosome has two identical DNA double helix molecules, and therefore is composed of two sister chromatids. During S phase, the centrosome is also duplicated. v G 2 phase is the third, final, and usually the shortest subphase during interphase within the cell cycle in which the cell undergoes a period of rapid growth to prepare for mitosis. It follows successful completion of DNA synthesis and chromosomal replication during the S phase, and occurs during a period of often four to five hours. Although chromosomes have been replicated they cannot yet be distinguished individually because
3 they are still in the form of loosely packed chromatin fibers. The G 2 phase continues growth of the cell and prepares the cell for mitosis (M phase) by producing all of the enzymes that the cell will need in order to divide v After the G 2 phase of interphase, the cell is ready to start dividing. The nucleus and nuclear material (chromosomes made of DNA) divide first during stage known as MITOSIS. Mitosis is also called KARYOKINESIS (karyon means nucleus) because only the nucleus is dividing. v Mitosis is the process in which a eukaryotic cell (cell containing a nucleus) separates its already duplicated chromosomes (copied during the S phase) into two sets of chromosomes so there will be two identical nuclei. It is generally followed by cytokinesis which divides the cytoplasm and cell membrane. This results in two identical cells (both have an identical set of chromosomes) with an equal distribution of organelles and other cellular components. The mitotic (M) phase and cytokinesis (C phase) together are called cell division, the division of the parent cell (original) into two daughter cells (new cells), each with the same genetic information (chromosomes) as the parent cell. Mitosis does NOT occur in prokaryotic cells that do NOT have a nucleus. In multicellular organisms, the somatic cells (body cells) undergo mitosis, while germ cells cells destined to become sperm in males or ova (eggs) in females divide by a related process called meiosis. Prokaryotic cells (bacteria), which lack a nucleus, divide by a process called binary fission.
4 v The process of mitosis (division of the nucleus) is divided into four stages (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase). Immediately following nuclear division (mitosis), the cell membrane must also divide (cytokinesis). Animal cells divide the cytoplasm by constricting the cell membrane in the middle to form a cleavage furrow. Plant cells form a cell plate in the center to divide the cytoplasm. At Interphase, there is only one cell, but after cytokinesis there are two identical cells. v During interphase, the genetic material is called chromatin and can NOT be clearly seen because it isn t tightly coiled. When prophase begins, the DNA molecules are progressively shortened and condensed by coiling, to form visible chromosomes. Enzymes during prophase break down the nuclear membrane and nucleolus so they are no longer visible. Spindle fibers also form in
5 prophase which will attach to the chromosomes. At metaphase, the spindle fibers attach themselves to the centromeres of the chromosomes and align the chromosomes at the equator (middle of the cell). Anaphase is the next stage. The spindle fibers shorten and the centromere splits separating the two sister chromatids. During telophase, the chromosomes pairs (chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope and nucleolus reform before the chromosomes uncoil. The spindle fibers disintegrate. v Growth factor a protein secreted by certain body cells that stimulates other cells to divide v Density dependent inhibition the ceasing of cell division that occurs when cells touch one another v Anchorage dependence the requirement that to divide a cell must be attached to a solid surface v Cell cycle control cynically operating set of molecules in the cell that both triggers and coordinates key events in the cell cycle Ø Default stage checkpoint in animal cells Halt of the cell cycle of these checkpoints unless overridden by specific go- ahead signals
6 Ø Major checkpoints cell cycle Dividing the G1 and G2 sub- phases of interphase and in the metaphase v The growth factor binds to the cells receptor protein embedded in the plasma membrane then the receptor protein passes on the signal to a relay protein in the cytoplasm to signal another relay protein that is in the nucleus which signals the checkpoint in the cell cycle to go v Biochemical reactions that cause relay proteins to take signal to the nucleus = transduction pathway v Cancer Ø Tumor an abnormal mass of rapidly growing cells that forms within otherwise normal tissue Ø Benign tumor an abnormal mass of cells that remains as its original site in the body Ø Malignant tumor an abnormal tumor tissue mass that can spread to neighboring tissue and to other pairs of the body a cancerous tumor Ø Metastasis the spread of cancer cells beyond their original site Ø Carcinoma cancer that originates in the coverings of the body such as skin or the lining of the intestinal tract Ø Sarcoma cancer o the supportive tissues such as bone cartilidge and the muscle Ø Lymphoma cancer of the tissues that form white blood cells Ø Researchers have discovered that cancer cells respond to growth factors and checkpoints in the cell cycle as follows: not need normal dignals that regulate
7 the cell cycle many have defective cell cycle control systems, proceed past checkpoints in absence of growth factors Ø Immortal because they can go on dividing indefinitely as long as they have a supply of nutrients normal cells divide only times Ø Ways that cancer is treated Removed surgically High energy radiation Chemotherapy Drugs Ø Side effects of radiation Ovaries/testes causes sterility Ø Side effects of chemotherapy Nausea from effects intestinal cells hair loss effects immune cell production v Meiosis Ø Somatic cell any cell in a multicellular organism except a sperm or egg cell that develops into a sperm or egg Ø Homologous chromosome the two chromosomes that make up a matened pair staining pattern and possessed genes for the same characteristics t corresponding loci one is inherited from organisms father and the other from the mother Ø Locus the particular site where a gene is found on a chromosome homologues chromosomes have corresponding gene loci Ø Sex chromosomes a chromosome that determines whether an individual is male or female Ø Life cycle the entire sequence of stages in the life of an organism from the adults of one generation to the adults of the next Ø Diploid in an organism that reproduces sexually a cell containing two homologous sets of chromosomes one set inherited from each parent a 2n cell Ø Gametes a sex cell haploid egg or sperm the union of two gametes of opposite sex (fertile action) produces a zygote Ø Haploid in the life cycle of an organism that reproduces sexually a cell containing a single set of chromosomes, n cell Ø Fertilization the union of the nucleus of the sperm cell with the nucleus of an egg cell producing a zygote Ø Zygote the diploid fertilized egg which results from the union of sperm cell nucleus and an egg cell nucleus Ø Meiosis in a sexually reproducing organism the division of a single diploid nucleus into 4 haploid daughter nuclei Meiosis and cytokinesis produce haploid gametes from diploid cells in the reproductive organs of the parents Ø Phases Interphase Meiosis I Prophase I
8 Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I and cytokinesis Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II and cytokinesis v Genetic variability Ø Formation random combination chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to the laws of probability of one of each diploid pair of homologous chromosomes into each gamete independently of each other pair Ø Crossing over homologous chromosomes during synapis in prophase I of meiosis also exchange of segments between DNA molecules in prokaryotes Ø Genetic recombination the production by crossing over/independent assortment combination different from those in the parents more specifically mean the production by crossing over of eukaryotic/prokaryotic chromosomes with gene combinations different from original chromosomes Ø Karyotype display of which graphs of the metaphase chromosomes of a cell changed by size and centromere position may be used identify chromosomal abnormalities Ø Homologous chromosomes contribute to the genetic variability of gametes Can bear two different kinds of genetic information for the same characteristic Ø Crossing over contributing to genetic variability of genes Produces hybrid chromosomes with new combinations maternal/parental genes 4 types not 2 Ø How does independent orientation contribute to genetic variability of gametes Placement chromosomes results in different (completely) from original parental cell Daughter cell combinations make different cells based on locations at metaphase plate Ø Trisomy 21 down syndrome Ø Down syndrome a human genetic disorder resulting from the presence of an extra chromosome 21 Ø Nondisjunction an accident of meiosis/mitosis in which a pair of homologous chromosomes or pair system chromatids fail to separate at anaphase Ø Klinefelter s syndrome (males) have male sex organs normal intelligence testes abnormally small, sterile, often larger breasts and other female (secondary) characteristics, has more than 3 sex chromosomes Ø Turner syndrome lacks X chromosome
9 Ø Polyploidy an organism that has more than two complete sets of chromosomes as a result of an accident of cell division Ø Effects child with down syndrome Found face fold inner corner of the eye flattened nose bridge small irregular teeth short stature heart defects susceptibility respiratory infections leukemia Alzheimer s disease Ø What is the genetic combination of sex chromosomes in Klinefelter s and Turner syndrome and characteristics Klinefelter s: XXYY, XXXY, XXXXY means more likely disabilities (developmental) Characteristic: small testes, mini breasts, female characteristics Turner: X0 Characteristic: short stature webbed skin neck and shoulders sterile sex organ not fully mature Poor development of breasts and other secondary sex characteristics with normal intelligence Ø In what animal/plant species have scientists observed polyploidy Wheat Potatoes Apples Cotton Fishes Amphibians Rat
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Roles of Cell Division. Reproduction - Like begets like, more or less. Examples of Cell Numbers. Outline Cell Reproduction
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Cell cycle, mitosis & meiosis. Chapter 6
 Cell cycle, mitosis & meiosis Chapter 6 Why do cells divide? Asexual reproduction Growth Replacement / repair Cell division: The big picture Two steps Before cells can divide, DNA needs to replicate DNA
Cell cycle, mitosis & meiosis Chapter 6 Why do cells divide? Asexual reproduction Growth Replacement / repair Cell division: The big picture Two steps Before cells can divide, DNA needs to replicate DNA
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS. Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent.
 THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring
 In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES
 CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
Chapter 8. Introduction. Introduction. The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance. Cancer cells. In a healthy body, cell division allows for
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
8.8 Growth factors signal the cell cycle control system
 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance : part II PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Biology 1408 Dr. Chris Doumen
The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance : part II PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Biology 1408 Dr. Chris Doumen
Key Concepts. n Cell Cycle. n Interphase. n Mitosis. n Cytokinesis
 The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cell Reproduction. Objectives
 Cell Reproduction Lecture 10 Objectives At the end of this series of lectures you should be able to: Define terms. Describe the functions of cellular reproduction. Compare the parent offspring relationship
Cell Reproduction Lecture 10 Objectives At the end of this series of lectures you should be able to: Define terms. Describe the functions of cellular reproduction. Compare the parent offspring relationship
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome
 Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Sexual Cell Reproduction Chapter 17
 Sexual Cell Reproduction Chapter 17 1 The Importance of Meiosis Meiosis is a two stage cell division in which the chromosome number of the parental cell is reduced by half. Meiosis is the process by which
Sexual Cell Reproduction Chapter 17 1 The Importance of Meiosis Meiosis is a two stage cell division in which the chromosome number of the parental cell is reduced by half. Meiosis is the process by which
The Cellular Basis of Inheritance
 CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders
 Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders 1. Clearly explain the difference between the following: a) chromosomes and chromatin
Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders 1. Clearly explain the difference between the following: a) chromosomes and chromatin
Cell Reproduction Review
 Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
 Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction
Biology. Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction. I. Chromosomes
 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction I. Chromosomes Long thin molecules that store genetic information. A. Chromosome Structure 1. Rod shaped structure composed of DNA and protein. 2. DNA is wrapped around
Biology Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction I. Chromosomes Long thin molecules that store genetic information. A. Chromosome Structure 1. Rod shaped structure composed of DNA and protein. 2. DNA is wrapped around
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Anaphase, Telophase. Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Cleavage furrow. Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by...
 The 4 phases of mitosis Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by... Cell which after division is identical to the original is called a Prophase, Metaphase,
The 4 phases of mitosis Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by... Cell which after division is identical to the original is called a Prophase, Metaphase,
Reading Assignments. A. Systems of Cell Division. Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis No matter the type of cell, all cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division. The cell may be the
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis No matter the type of cell, all cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division. The cell may be the
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
Human biology Laboratory. Cell division. Lecturer Maysam A Mezher
 Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
Biology: Life on Earth
 Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Sexual reproduction & Meiosis
 Sexual reproduction & Meiosis Sexual Reproduction When two parents contribute DNA to the offspring The offspring are the result of fertilization the unification of two gametes (sperm & egg) Results in
Sexual reproduction & Meiosis Sexual Reproduction When two parents contribute DNA to the offspring The offspring are the result of fertilization the unification of two gametes (sperm & egg) Results in
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11. Reproduction Section 1
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Learning Objectives Chapter 8
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 Brief overview of prokaryotic cell replication The three main phases of eukaryotic cell division: Interphase, M phase, C phase Interphase is broken down into three sub-phases
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 Brief overview of prokaryotic cell replication The three main phases of eukaryotic cell division: Interphase, M phase, C phase Interphase is broken down into three sub-phases
Name 8 Cell Cycle and Meiosis Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of the replicated chromosome. The stages of mitosis.
 Name 8 Cell Cycle and Meiosis Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of the replicated chromosome. The stages of mitosis. The role of kinases and cyclin in the regulation of the cell cycle.
Name 8 Cell Cycle and Meiosis Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of the replicated chromosome. The stages of mitosis. The role of kinases and cyclin in the regulation of the cell cycle.
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis. PPT Questions. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete copy of the original cell s DNA?
 1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time?
 Chapter 5 Cell Reproduction Mitosis Think about this Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time? EQ: Why is cell division necessary for the growth & development of living organisms? Section
Chapter 5 Cell Reproduction Mitosis Think about this Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time? EQ: Why is cell division necessary for the growth & development of living organisms? Section
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into 2.
 1. Cell division functions in 3 things : reproduction, growth, and repair The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into
1. Cell division functions in 3 things : reproduction, growth, and repair The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into
Meiosis. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words)
 CELL REPRODUCTION- CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words) 1. Chromosome 2. histone 3. chromatid 4. Centromere 5. chromatin 6. autosome 7. Sex chromosome 8. homologous chromosome 9.
CELL REPRODUCTION- CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words) 1. Chromosome 2. histone 3. chromatid 4. Centromere 5. chromatin 6. autosome 7. Sex chromosome 8. homologous chromosome 9.
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction
 Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review
 Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Cell Division (Outline)
 Cell Division (Outline) 1. Overview of purpose and roles. Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes and relation between organelles and cell division. 2. Eukaryotic cell reproduction: asexual
Cell Division (Outline) 1. Overview of purpose and roles. Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes and relation between organelles and cell division. 2. Eukaryotic cell reproduction: asexual
Mitosis and. Meiosis. Presented by Kesler Science
 Mitosis and Meiosis Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are mitosis and meiosis? 2. What occurs at different phases in cell division? 3. How are mitosis and meiosis similar and different?
Mitosis and Meiosis Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are mitosis and meiosis? 2. What occurs at different phases in cell division? 3. How are mitosis and meiosis similar and different?
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
Mitosis. Meiosis MP3. Why do cells divide? Why Do Cells Need To Divide? Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11. What has to happen before a cell divides? divides?
 MP3 Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11 Mitosis Anaphase Mitosis Cell Cycle Telophase Cytokinesis Cell Division Metaphase 4 Daughter Cells Prophase Meiosis Diploid Somatic Cells Interphase Haploid Parent Cell Gametes
MP3 Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11 Mitosis Anaphase Mitosis Cell Cycle Telophase Cytokinesis Cell Division Metaphase 4 Daughter Cells Prophase Meiosis Diploid Somatic Cells Interphase Haploid Parent Cell Gametes
gametes Gametes somatic cells diploid (2n) haploid (n)
 Overview of Meiosis Meiosis is a form of cell division that leads to the production of gametes. Gametes: egg cells and sperm cells (reproductive) -contain half the number of chromosomes of an adult body
Overview of Meiosis Meiosis is a form of cell division that leads to the production of gametes. Gametes: egg cells and sperm cells (reproductive) -contain half the number of chromosomes of an adult body
Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17
 Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17 Students will: Differentiate the process of meiosis and meiosis Describe the role of mitosis in asexual reproduction, and/or the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction,
Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17 Students will: Differentiate the process of meiosis and meiosis Describe the role of mitosis in asexual reproduction, and/or the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction,
Why mitosis?
 Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS
 CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS How do Organisms Reproduce? Option 1: Asexual Reproduction Can be done by a single organism without the involvement of gametes (sperm or egg) Offspring are clones of the parent,
CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS How do Organisms Reproduce? Option 1: Asexual Reproduction Can be done by a single organism without the involvement of gametes (sperm or egg) Offspring are clones of the parent,
You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the
 MEIOSIS You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the ovaries and testes. Gametes are sex cells: egg
MEIOSIS You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the ovaries and testes. Gametes are sex cells: egg
What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis?
 Sexual Reproduction What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fyfdfdrymq Somatic cells
Sexual Reproduction What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fyfdfdrymq Somatic cells
Meiosis. The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced.
 MEIOSIS Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced. diploid (2n) haploid (n) (complete set of chromosomes) (half the regular number of
MEIOSIS Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced. diploid (2n) haploid (n) (complete set of chromosomes) (half the regular number of
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
SCIENCE M E I O S I S
 SCIENCE 9 6. 1 - M E I O S I S OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the process of meiosis Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis Explain why meiosis is needed MEIOSIS
SCIENCE 9 6. 1 - M E I O S I S OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the process of meiosis Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis Explain why meiosis is needed MEIOSIS
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA)
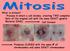 What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Why are cells small? As cells get bigger they don t work as well WHY? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient in moving nutrients/waste across its
The Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Why are cells small? As cells get bigger they don t work as well WHY? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient in moving nutrients/waste across its
Chapter 8. Cellular Reproduction: Cells from Cells. Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 8 Cellular Reproduction: Cells from Cells Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and
Chapter 8 Cellular Reproduction: Cells from Cells Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and
Concept 9.1: All Cells come from Cells Asexual Reproduction = Sexual Reproduction = Concept 9.2: The Cell Cycle multiplies Cells Chromatin =
 Honors Biology Chapter 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance p. 178-203 (How does 1 fertilized egg become the trillions of diff. types of cells in our bodies?) Concept 9.1: All Cells come from Cells (Char.
Honors Biology Chapter 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance p. 178-203 (How does 1 fertilized egg become the trillions of diff. types of cells in our bodies?) Concept 9.1: All Cells come from Cells (Char.
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction. Chapter 11 Loulousis
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Loulousis Meiosis - Phenomena Parents can produce many types of offspring. Families will have resemblances, but no two are exactly alike Objectives Compare and
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Loulousis Meiosis - Phenomena Parents can produce many types of offspring. Families will have resemblances, but no two are exactly alike Objectives Compare and
Describe the process of cell division in prokaryotic cells. The Cell Cycle
 The Cell Cycle Objective # 1 In this topic we will examine the cell cycle, the series of changes that a cell goes through from one division to the next. We will pay particular attention to how the genetic
The Cell Cycle Objective # 1 In this topic we will examine the cell cycle, the series of changes that a cell goes through from one division to the next. We will pay particular attention to how the genetic
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology
 Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
The Process of Cell Division. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. 3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life.
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. 3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life.
Chapter 10.2 Notes. Genes don t exist free in the nucleus but lined up on a. In the body cells of animals and most plants, chromosomes occur in
 Chapter 10.2 Notes NAME Honors Biology Organisms have tens of thousands of genes that determine individual traits Genes don t exist free in the nucleus but lined up on a Diploid and Haploid Cells In the
Chapter 10.2 Notes NAME Honors Biology Organisms have tens of thousands of genes that determine individual traits Genes don t exist free in the nucleus but lined up on a Diploid and Haploid Cells In the
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR
 Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR meiosis plus fertilization Objective: You will be able
Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR meiosis plus fertilization Objective: You will be able
ACCELERATE ITS BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES WHICH WERE SLOWED DOWN BY MITOSIS. THE LENGTH OF THE G1 PHASE CREATES THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FAST DIVIDING
 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll
 Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Name: Date: Hour: Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis. Monomer Polymer Example Drawing Function in a cell DNA
 Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division. A. Definitions:
 Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division A. Definitions: In a human cell, a nucleus holds all the chromatin that condenses to form chromosomes when cells divide every cell in the body has the same set of chromosomes
Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division A. Definitions: In a human cell, a nucleus holds all the chromatin that condenses to form chromosomes when cells divide every cell in the body has the same set of chromosomes
CELL DIVISION MITOSIS & MEIOSIS
 CELL DIVISION MITOSIS & MEIOSIS Cell Cycle 2 distinct phases S Chromosome duplication Interphase G 2 Mitotic What's the most important event of interphase? What is significant about DNA in the S and G
CELL DIVISION MITOSIS & MEIOSIS Cell Cycle 2 distinct phases S Chromosome duplication Interphase G 2 Mitotic What's the most important event of interphase? What is significant about DNA in the S and G
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
The Cell Cycles Mitosis and Meiosis. Essential question: How do cells reproduce and why?
 The Cell Cycles Mitosis and Meiosis Essential question: How do cells reproduce and why? Objectives Section 10.1 Explain why cells divide in terms of growth and cell size Review - Types of Cell Division
The Cell Cycles Mitosis and Meiosis Essential question: How do cells reproduce and why? Objectives Section 10.1 Explain why cells divide in terms of growth and cell size Review - Types of Cell Division
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial cells have a single circular chromosome,
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial cells have a single circular chromosome,
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction. What is Cellular Reproduction?
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis
 Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis Outcomes 1. Describe mitosis in detail (460-465) interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis (the cell cycle) explain the importance of maintaining chromosome number through
Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis Outcomes 1. Describe mitosis in detail (460-465) interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis (the cell cycle) explain the importance of maintaining chromosome number through
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
Cell Division. Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 2/9/2016. Dr. Saud Alamri
 Cell Division Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 1 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by a type of cell division called binary fission 2 Prokaryotic chromosome Division into two daughter cells Plasma
Cell Division Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 1 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by a type of cell division called binary fission 2 Prokaryotic chromosome Division into two daughter cells Plasma
Name: Date: Period: Cell Cycles and DNA Study Guide
 Name: Date: Period: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the chemical inside the nucleus of cells that contains hereditary information. DNA is shaped like a double helix/twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder
Name: Date: Period: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the chemical inside the nucleus of cells that contains hereditary information. DNA is shaped like a double helix/twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder
5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis
 5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis Lesson Objectives Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Give an overview of sexual reproduction, and outline the phases of meiosis. Explain why sexual reproduction
5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis Lesson Objectives Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Give an overview of sexual reproduction, and outline the phases of meiosis. Explain why sexual reproduction
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Meiosis produces haploid gametes.
 Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 8 Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida
 Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
