Lecture VIII Protistans Dr. Kopeny
|
|
|
- Linda Price
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture VIII Protistans Dr. Kopeny Delivered 2/8, 2/11 Lecture VIII Protistans Lecture Themes structure and function; recurring evolutionary themes and unifying features the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts Impact of Protists on Human Health and Welfare The key to understanding the protists is to recognize that a series of important innovations occurred, often repeatedly, as eukaryoites diversified. (Freeman 2002)
2 Source: Freeman (2002) surface waters teem with microscopic protists In some near-shore areas, gigantic protists from underwater forests Protists are particularly abundant in tidal habitats Morphologies and lifestyles found among protists. Protists are abundant in a wide variety of aquatic habitats. In marine environments, they are found in open ocean as well as in near-shore intertidal habitats (Freeman 2002) Euglena Eugleazoa includes both photosynthetic and heterotrophic flagellates. Most are autotrophic, but the lineage includes Trypanosoma
3 Ciliates dinoflagellates Alvoelata are unicellular, and bear a cavity called and alveoli. Diverse in body form. Apicompla water molds diatoms brown algae Stramenopilan are a diverse lineage of heterotrophs and phothynthetic forms (algae). The name refers to fine hairs on the flagella of members of this lineage
4 Rhodophyta are red algae unlike other eukaryotic algae, they lack flagella at any stage in their life history. They are the most abundant algae in tropical coastal areas Dulce, a large, edible red algae Volvox colonies Sea lettuce Green Algae and Plants evolved from a common photoautotrophic ancestor. Over 7000 species, mostly fresh water. Desmid
5 Choanoflagellida Flagellate protists. Possible ancestor to Sponges to Animals.
6 Size and Structure of Eukaryotic Cells compartmentalization and differentiation makes large size possible. Problem: transport and exchange limitations with increasing size Solution: compartmentalization Example: Paramecium Eukayotic compartments; nucleus, peroxisomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, central vacuole, golgi, rough ER, smooth ER Paramecium, a predaceous protist that feeds on prokaryotes and other protists Nutritional and Metabolic Diversity in Protists Ingestive Lifestyles: Predation and Scavengers Absorbtive Lifestyles; Decomposers and Parasites Photosynthetic Lifestyles; Producers, many of which are symbionts Photosynthetic unicellular dinoflagellates Paramecium giant kelp Giardia, a unicellular human parasite
7 Predation and Scavenging Parasitism pseudopodia engulf food Ciliary currents sweepd food into gullet host parasite the parasite is a red algae with nonpigmented cells Symbiosis Photosynthetic pigments host symbionts Green cells are dinoflagellates inside a heliozoan Red: chlorophyll a and phycobilins Brown: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c Green: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b Many photosynthetic groups of algae are distinguished by the accessory pigments they contain, in addition to chlorophyll a. Each of these accessory pigments interecpts different wavelengths of light Consider the diversity of feeding modes in the lineage Alveolata Ciliates -many predators and herbivores -some parasite/basorbers (eg cattle guts, fish gills) -some feed via symbiotic photosynthesizers Dinoflagellates -half or so are photosynthetic, many others are parasitic Apicomplexans -most apicomplexans are parasitic Feeding diversity in protists, like electron donor and electron acceptor diversity in prokaryotes, no doubt drove phylogenetic diversification
8 Locomotion and Structures for Support and Protection Modes of Locomotion in Protists Pseudopodia An Amoeboid Protist flagella cilia Structure of microtubules in cilia and flagella A ciliatedprotist 2 single microtubules (red) surrounded by nine paired microtubules (yellow)
9
10 A ciliated protist reference: chapter 4 in textbook Paramecium can swim in either direction relative to its long axis by beating its cilia in rhythmic, coordinated fashion that progresses from one end of the cell to the other. Amoeba extends a pseudopodium toward a Pandorina colony. At right, the amoeba surrounds colony before engulfing it
11 Source: Hickman et al 2001 Proposed mechanism of psuedopodial movement. In endoplasm, actin subunits are bound to regulatory proteins that keep them from assembling. External Structures for Support and Protection Sources: Purves et al (2002), Freeman (2002) Forams; shells are made from protein hardened with calcium carbonate Radiolarians; glassy skeletons allow light penetration for photosynthetic endosymbionts Amoeba; shell made of cemented sand grains foraminiferan with calcium carbonate tests diatomshave glasslike silicon containg sructures Diatoms Dinoflaggelates surrounded by cellulose plates
12 Multicellularity Source: Freeman 2002 True multicellarity is defined functionally Differentiation of cell function (specialization, division of labor) Differential gene expression Multicellularity has evolved independently multiple times in Protistan lineages Multicelluarity confers advantages by allowing for increased size, specialization, and complexity The initial evolution towards multicellularity begins with differentiation of gamete-producing cells, the consequence of the uniquely eukaryotic reduction division process; meiosis Multicellular Green Alga (Coleochaete orbiculairs) Clamydomonas Gonum Pandorina Volvox Morphological continuum in Volvocales from unicellular to multicelluar.
13 Reproduction, Life Cycles and Alternation of Generations Meiosis and Sexual reproduction were important Protistan innovations
14 Life Cycle of Chlamydomonas
15 Sporophytes (2n) Gametophytes (n) Life cycle of Laminaryia: an example of alternation of generations Sporophytes of this seasweed are usually found in water just below the line of the lowest tides, attached to the rocks by branching holdfasts In early spring, at end of the main growing season, cells on the surface of the blade develop into sporangia sporangia produce zoosporres by meiosis Zoospores are all structurally alike, but about half of them are capable of developing into a male gametophyte and half into a femlel gametophye. Gametophytes look nothing like the sporophytes, being short, branched filaments that grow on the surface of subtidal rocks Male gametohytes release sperm, and female gametophytes produce eggs, which remain attached tot eh gametophyte. Eggs secrete a chemical signal that attracts sperm of the same species, thereby increasing the probability of gametic union in the ocean. Sperm fertilize the eggs The zygotes grow into new sprorophytes, starting life attached to the remains of the old female gametophyte
16 Lines of evidence indicating mitochondria and chloroplasts arose as prokaryotic symbionts -membranous enzymes and transport systems -replication process -genome -protein translation machinery, including ribosomes, t-rna -similarities of mitochondrial and chloroplast ribosomes to prokaryote ribosomes Endosymbiotic Theory Lynn Margulis U. Mass., Distinguished Professor and Member of the National Academy of Science developed endosymbiotic theory 2.5 um 80 um Proteobacteria Cyanobacteria Margulis webpage
17 Phylogenetic analyses using small subunit RNA Ribosomes are comprised of one small and one large subunit. The single rrna molecule of the small subunit Ribosomes are Gene for small subunit r-rna is present in all organism good gene for determining deep branching in tree of life Sequence comparisons show that closest prokaryote relatieves of mitochondria are altpha proteobacteria. Sequence comparisons of plastids from various photosynthetic eukaryotes cluster with prokaryotic cyanobacteria (photosyntheitc machinery and metabolic pathways are shared as well.
18 Protists and Human Health: Plasmodium and Malaria P. falciparum is the most widespread and dangerous of the four: untreated it can lead to fatal cerebral malaria. The distribution of malaria varies greatly from country to country and within the countries themselves. In 1990, 75% of all recorded cases outside of Africa were concentrated in nine countries Infected Red Blood Cells Infected mosquito bites and infects person; sporozoites and enter liver cells After several days, undergo multiple divisions to become merozoites (specialized spore) that uses apical complex to penetrate RBC Merozite Apex Red blood cell 0.5 um Merozoites reproduce asexually in RBC s and lyse cells at 48 or 72 hr intervals (species specific); coordinated lysing of cells causes periodic chills and fever. Some merozoite infect new RBC s, some divide to form gametocytes; gametocytes that infect a biting female mosquite compete the life cycle in her body. Gametocytes form gametes and fertilization occurs in mosquito digestive tract; zygote is the only dipolid stage in the life cycle Oocyst develops in wall of mosquito gut. Thousands of sporozoites develop in the oocyst and then migrate to mosquites salivary gland
19 Source: Freeman 2002 HUMAN IMMUNE-DEFENSE AGAINST PLASMODIUM Plasmodium Infection Interpretation Strain Rate cp26 cp29 cp26 and cp29 strains together cp27 cp28 Low Low High High Average HLA-B53 binds to these proteins. Immune resonse is effective Immune response fails when these strains infect the same person HLA-B53 does not bind to these proteins. Immune response is not as effective Co-evolutonary Arm Race Strong association between HLA-B53 allele and protection against malaria found in West Africa HLA-B53 in infected liver cells bind to particular sporozoite protein and display protein-protein complex before they produce merozoites Recognition breaks down in people coinfected by certain strains NS leads to iimmune system adaptations for protection and to pathogen adaptations to overcome them
Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny
 Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny Protistans, Part 1 Lecture VIII Protistans Lecture Themes structure and function; recurring evolutionary themes and unifying features the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny Protistans, Part 1 Lecture VIII Protistans Lecture Themes structure and function; recurring evolutionary themes and unifying features the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
Lecture #10 2/11 Dr. Kopeny
 Lecture #10 2/11 Dr. Kopeny Locomotion and Structures for Support and Protection Modes of Locomotion in Protists Pseudopodia An Amoeboid Protist flagella cilia Structure of microtubules in cilia and flagella
Lecture #10 2/11 Dr. Kopeny Locomotion and Structures for Support and Protection Modes of Locomotion in Protists Pseudopodia An Amoeboid Protist flagella cilia Structure of microtubules in cilia and flagella
What Are the Protists?
 Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.29 - PROTISTS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
!! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
Symbiosis. Symbiosis is a close association between of two or more organisms. Endosymbiosis living within another
 PROTISTS Protists constitute several kingdoms within the domain Eukarya Protists obtain their nutrition in a variety of ways Algae are autotrophic protists Protozoans are heterotrophic protists Fungus
PROTISTS Protists constitute several kingdoms within the domain Eukarya Protists obtain their nutrition in a variety of ways Algae are autotrophic protists Protozoans are heterotrophic protists Fungus
METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph
 CH. 22 PROTISTS METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph 6 Kingdoms 1. Eubacteria prokaryotes; single cell; heterotroph
CH. 22 PROTISTS METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph 6 Kingdoms 1. Eubacteria prokaryotes; single cell; heterotroph
PROTISTS. Chapter 25 Biology II
 PROTISTS Chapter 25 Biology II Vocabulary- Protists (44 words) 1. Protist 2. binary fission 3. conjugation 4. Multiple fission 5. pseudopodium 6. test 7. Amoeboid movement 8. cilium 9. Pellicle 10. oral
PROTISTS Chapter 25 Biology II Vocabulary- Protists (44 words) 1. Protist 2. binary fission 3. conjugation 4. Multiple fission 5. pseudopodium 6. test 7. Amoeboid movement 8. cilium 9. Pellicle 10. oral
Importance of Protists
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Chapter 22: Protists
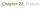 Chapter 22: Protists Protists Protistans are Unlike Prokaryotes Have a nucleus and organelles Have proteins associated with DNA Use microtubules in a cytoskeleton, spindle apparatus, and cilia and flagella
Chapter 22: Protists Protists Protistans are Unlike Prokaryotes Have a nucleus and organelles Have proteins associated with DNA Use microtubules in a cytoskeleton, spindle apparatus, and cilia and flagella
Kingdom Protista. Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 EXIT 2/16/2005
 Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Chapter 28 / Protists. I. Introduction A. Eukaryotes 1. 1 st eukaryotic organisms 2. most are unicellular 3. considered simple. Part I: Protozoans
 Randa, Bio 1151 1 Chapter 28 / Protists I. Introduction A. Eukaryotes 1. 1 st eukaryotic organisms 2. most are unicellular 3. considered simple B. Protist diversity (ecological grouping) 1. comprised of:
Randa, Bio 1151 1 Chapter 28 / Protists I. Introduction A. Eukaryotes 1. 1 st eukaryotic organisms 2. most are unicellular 3. considered simple B. Protist diversity (ecological grouping) 1. comprised of:
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor. Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells
 Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells 1 Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells 1 Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity
 http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells
 Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Kingdom Protista. The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Protists 9/11/2017. Endosymbiosis
 Protists Chapter 28 Most eukaryotes are single-celled organisms Protists are eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells have organelles and are more complex than prokaryotic cells Most protists are unicellular, but there
Protists Chapter 28 Most eukaryotes are single-celled organisms Protists are eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells have organelles and are more complex than prokaryotic cells Most protists are unicellular, but there
Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes. Chapter 22 Part 1
 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Chapter 22 Part 1 Impacts, Issues The Malaria Menace Plasmodium, a single-celled protist, causes malaria but also manipulates its mosquito and human hosts to maximize its
Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Chapter 22 Part 1 Impacts, Issues The Malaria Menace Plasmodium, a single-celled protist, causes malaria but also manipulates its mosquito and human hosts to maximize its
1. General Features of Protists
 Chapter 28: Protists 1. General Features of Protists 2. Survey of the Protista A. The Excavata B. The SAR Clade C. The Archaeplastida D. The Unikonta 1. General Features of Protists All Protists are Eukaryotes
Chapter 28: Protists 1. General Features of Protists 2. Survey of the Protista A. The Excavata B. The SAR Clade C. The Archaeplastida D. The Unikonta 1. General Features of Protists All Protists are Eukaryotes
Kingdom Protista. Protista
 Kingdom Protista Protista Traditionally a kingdom level taxon Current evidence places organisms in as many as 3-5 kingdoms We will classify all: Unicellular or simple colonial Eukaryotic Organisms that
Kingdom Protista Protista Traditionally a kingdom level taxon Current evidence places organisms in as many as 3-5 kingdoms We will classify all: Unicellular or simple colonial Eukaryotic Organisms that
Life Science. Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista
 Life Science Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista Protista Junk drawer kingdom a little bit of everything, some w/ cell walls (composition varies), some w/out. All are Eukaryotes, autotrophs and heterotrophs represented.
Life Science Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista Protista Junk drawer kingdom a little bit of everything, some w/ cell walls (composition varies), some w/out. All are Eukaryotes, autotrophs and heterotrophs represented.
Chapter 21 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes. Cengage Learning 2016
 Chapter 21 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Protists Eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals Structurally less complex Play important ecological roles as producers or predators of microorganisms
Chapter 21 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Protists Eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals Structurally less complex Play important ecological roles as producers or predators of microorganisms
Protists. There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group
 There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group Traditional Classification There are three divisions of the Kingdom Protista: Protozoa,
There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group Traditional Classification There are three divisions of the Kingdom Protista: Protozoa,
19.1 Diversity of Protists. KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms.
 19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
Kingdom Protista. The following organisms will be examined in the lab today: Volvox, Oedogonium, Spirogyra, Ulva
 Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Notes - Microbiology Protista
 Notes - Microbiology Protista Part 1 Animal like Protists - Kingdom Protista is a very diverse group of organisms. There are over 115 000 different kinds, with traits that fit with fungi, plants, and animals.
Notes - Microbiology Protista Part 1 Animal like Protists - Kingdom Protista is a very diverse group of organisms. There are over 115 000 different kinds, with traits that fit with fungi, plants, and animals.
Microbial Diversity. Bacteria Archaea Protista Fungi. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Microbial Diversity Bacteria Archaea Protista Fungi Figure 19-1 Three common prokaryote shapes Figure 19-2 The prokaryote flagellum Figure 19-2b The structure of the bacterial flagellum cell wall wheelandaxle
Microbial Diversity Bacteria Archaea Protista Fungi Figure 19-1 Three common prokaryote shapes Figure 19-2 The prokaryote flagellum Figure 19-2b The structure of the bacterial flagellum cell wall wheelandaxle
Kingdom Protista. Lab Exercise 20. Introduction. Contents. Objectives
 Lab Exercise Kingdom Protista Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Animal-like Protists 2 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists 3 Activity.3 Plant-like Protists 3 Resutls Section 5 Introduction This
Lab Exercise Kingdom Protista Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Animal-like Protists 2 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists 3 Activity.3 Plant-like Protists 3 Resutls Section 5 Introduction This
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
(4, , ) BIO1130
 1 Geological time scale and building height (1floor 60Ma, 72 floors, 12 feet/floor) Major Eons (Ma) Phanerozoic (550 Ma to present time, top 9 floors ) Proterozoic (2,500 550 Ma, 33 rd -63 rd ) Archaean
1 Geological time scale and building height (1floor 60Ma, 72 floors, 12 feet/floor) Major Eons (Ma) Phanerozoic (550 Ma to present time, top 9 floors ) Proterozoic (2,500 550 Ma, 33 rd -63 rd ) Archaean
Chapter 5 - Eukaryotic microorganisms
 Chapter 5 - Eukaryotic microorganisms Some things to think about as we discuss the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms Relate importance of differences between prokaryotic pathogens
Chapter 5 - Eukaryotic microorganisms Some things to think about as we discuss the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms Relate importance of differences between prokaryotic pathogens
There are two commonly accepted theories for how eukaryotic cells evolved: infolding and endosymbiosis. Infolding
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
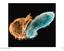 1 4.5 bya 3.5 2.5 1.5 500 mya 1.8 bya 1.5 bya 1.3 bya 1.2 bya 750 mya 635 mya 600 mya 0.5 cm 550 mya 535 mya 1 cm 20 µm (a) A 1.8-billionyear-old fossil eukaryote (b) Tappania, a 1.5-billion-year-old fossil
1 4.5 bya 3.5 2.5 1.5 500 mya 1.8 bya 1.5 bya 1.3 bya 1.2 bya 750 mya 635 mya 600 mya 0.5 cm 550 mya 535 mya 1 cm 20 µm (a) A 1.8-billionyear-old fossil eukaryote (b) Tappania, a 1.5-billion-year-old fossil
29/11/2012. Characteristics. Protist Diversity. Characteristics. Kingdom Protista. Examples of Plant-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Protists (Eukarya) Ch Feb 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine. Life can be divided into 3 domains. 1.5bya. Prokaryotes = bacteria + archaea
 Protists (Eukarya) Ch 29 26 Feb 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine 1 Life can be divided into 3 domains 3.8bya 1.5bya Prokaryotes = bacteria + archaea Prokaryote was ancestral and only form for billions
Protists (Eukarya) Ch 29 26 Feb 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine 1 Life can be divided into 3 domains 3.8bya 1.5bya Prokaryotes = bacteria + archaea Prokaryote was ancestral and only form for billions
Protists (Eukarya) Ch Feb 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine
 Protists (Eukarya) Ch 29 26 Feb 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine 1 Life can be divided into 3 domains 3.8bya 1.5bya Prokaryotes = bacteria + archaea Prokaryote was ancestral and only form for billions
Protists (Eukarya) Ch 29 26 Feb 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine 1 Life can be divided into 3 domains 3.8bya 1.5bya Prokaryotes = bacteria + archaea Prokaryote was ancestral and only form for billions
PROTISTS James Bier
 PROTISTS 2013-2015 James Bier Objectives 1. List the characteristics shared among the protists. 2. Describe secondary endosymbiosis and the evidence for this hypothesis. 3. List the five major taxa of
PROTISTS 2013-2015 James Bier Objectives 1. List the characteristics shared among the protists. 2. Describe secondary endosymbiosis and the evidence for this hypothesis. 3. List the five major taxa of
The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells
 The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells This domain is divided into four fairly distinct kingdoms: - Protists (Protista) - Plants
The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells This domain is divided into four fairly distinct kingdoms: - Protists (Protista) - Plants
Chp. 26 Notes The Protista Kingdom
 Chp. 26 Notes The Protista Kingdom Most protists are unicellular, microscopic organisms, but a few are complex and multicellular. These are the most diverse (different) organisms according to life cycles,
Chp. 26 Notes The Protista Kingdom Most protists are unicellular, microscopic organisms, but a few are complex and multicellular. These are the most diverse (different) organisms according to life cycles,
Biology. Slide 1of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Protists & Fungi. Words to Know: Chapters 19 & 20. Label the paramecium diagram above. (pg. 548)
 Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Pearson Education, Inc.
 1 4.5 bya 3.5 1.5 2.5 500 mya 1.8 bya 1.5 bya 1.3 bya 1.2 bya 550 750 mya 635 mya 600 mya mya 0.5 cm 535 mya 1 cm (a) A 1.8-billionyear-old fossil (b) Tappania, a 1.5-billion-year-old fossil that may represent
1 4.5 bya 3.5 1.5 2.5 500 mya 1.8 bya 1.5 bya 1.3 bya 1.2 bya 550 750 mya 635 mya 600 mya mya 0.5 cm 535 mya 1 cm (a) A 1.8-billionyear-old fossil (b) Tappania, a 1.5-billion-year-old fossil that may represent
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES
 ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES I. Protists - Commonly called protozoans - All single celled eukaryotes Three most important phyla: 1. Sarcomastigophora: includes the amebas and the flagellates 2.
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES I. Protists - Commonly called protozoans - All single celled eukaryotes Three most important phyla: 1. Sarcomastigophora: includes the amebas and the flagellates 2.
CHAPTERS 16 & 17: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 2012 PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES. Fig Lived alone on Earth for over 1 billion years
 CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
2.3. The Protists. why Protists Are Important
 2.3 The Protists The smallest eukaryotes and some of the largest belong to the Kingdom Protista. This kingdom is extremely diverse. Some of its members, such as amoebas and paramecia, are very small and
2.3 The Protists The smallest eukaryotes and some of the largest belong to the Kingdom Protista. This kingdom is extremely diverse. Some of its members, such as amoebas and paramecia, are very small and
The Protistans. Includes protozoans and algae All single celled eukaryotes
 Includes protozoans and algae All single celled eukaryotes The Protistans Protozoa - Unicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic - Inhabit water and soil - Some normal microbiota of animals - Few cause disease
Includes protozoans and algae All single celled eukaryotes The Protistans Protozoa - Unicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic - Inhabit water and soil - Some normal microbiota of animals - Few cause disease
Chapter 7. Protists. Protists( 원생동물 )
 Protists( 원생동물 ) - currently 100,000 species, 35,000 species found in fossils - lying in classification gap bwtn prokaryote and smallest animal and plants - all are unicellular, some exist as colonies
Protists( 원생동물 ) - currently 100,000 species, 35,000 species found in fossils - lying in classification gap bwtn prokaryote and smallest animal and plants - all are unicellular, some exist as colonies
Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5
 Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5 5.2 Kingdom Protista (pp. 140-151) Kingdom Protista general characterisitcs and groups Protists are a very diverse kingdom of living things that do not fit into any other
Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5 5.2 Kingdom Protista (pp. 140-151) Kingdom Protista general characterisitcs and groups Protists are a very diverse kingdom of living things that do not fit into any other
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014
 Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
The Microbial World. Chapter 5
 The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring Protist Phylogeny. Meet the algae. Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis. Endosymbiosis. Secondary Endosymbiosis
 Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Protist Classification the Saga Continues
 Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Viruses p.122. Viruses are very small structures which can make other organisms sick.
 Viruses p.122 Viruses are very small structures which can make other organisms sick. Illness is caused when the viruses invade an organisms cells and use that cell s resources to make more viruses. Viruses
Viruses p.122 Viruses are very small structures which can make other organisms sick. Illness is caused when the viruses invade an organisms cells and use that cell s resources to make more viruses. Viruses
Outline. Diplomonads. Excavata. Parabasalids. Euglenozoans. Diatoms. Golden algae. Brown algae. SAR clade. Dinoflagellates Apicomplexans
 BIOSC 041 PROTISTS! Reference: Chapter 28 Outline v General characteristics of protists v Our understanding of the relationships among protist groups continues to change rapidly! v One hypothesis divides
BIOSC 041 PROTISTS! Reference: Chapter 28 Outline v General characteristics of protists v Our understanding of the relationships among protist groups continues to change rapidly! v One hypothesis divides
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists
 Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Name Hour Section 20-1 The Kingdom Protista (pages ) What Is a Protist? (Page 497) 1. What is a protist?
 Name Hour Section 20-1 The Kingdom Protista (pages 497-498) What Is a Protist? (Page 497) 1. What is a protist? 2. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about protists. a. All are unicellular.
Name Hour Section 20-1 The Kingdom Protista (pages 497-498) What Is a Protist? (Page 497) 1. What is a protist? 2. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about protists. a. All are unicellular.
Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi
 Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi Ch. 19: Protists Major Concepts 1. Protists make up a diverse catch-all kingdom of organisms. 2. Algae are photosynthetic protists that are major producers in the biosphere. 3.
Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi Ch. 19: Protists Major Concepts 1. Protists make up a diverse catch-all kingdom of organisms. 2. Algae are photosynthetic protists that are major producers in the biosphere. 3.
Protists. Protists. Protist Feeding Strategies. Protist Body Plans. Endosymbiosis. Protist Reproduction 3/3/2011. Eukaryotes Not a monophyletic group
 Protists Protists Eukaryotes Not a monophyletic group Paraphyletic March 3 rd, 2011 Still use the term protist All eukaryotes except Plants, Fungi, Animals Most unicellular Some colonial Some multicelled
Protists Protists Eukaryotes Not a monophyletic group Paraphyletic March 3 rd, 2011 Still use the term protist All eukaryotes except Plants, Fungi, Animals Most unicellular Some colonial Some multicelled
Observing and Classifying Protozoa
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Observing and Classifying Protozoa Background The name protozoa actually means first animals. This name was given because many protozoa share characteristics with animals. However,
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Observing and Classifying Protozoa Background The name protozoa actually means first animals. This name was given because many protozoa share characteristics with animals. However,
Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Protists Diversity
 Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Protists Diversity For Lecture, Make sure you know the Water Molds (Oomycota) names and characteris6cs of the taxa at the levels indicated by the red arrows. Characteristics
Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Protists Diversity For Lecture, Make sure you know the Water Molds (Oomycota) names and characteris6cs of the taxa at the levels indicated by the red arrows. Characteristics
Name Class Date. 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Kinds of Protists 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits? PROTIST PRODUCERS 2. What is the name for protists that
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Kinds of Protists 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits? PROTIST PRODUCERS 2. What is the name for protists that
5/10/2013. Protists. Kingdom Protista. Called the Junk Drawer. 3 Subkingdoms of Protists. Protozoans Algae Slime molds
 Protists Kingdom Protista Called the Junk Drawer 3 Subkingdoms of Protists Protozoans Algae Slime molds 1 Protozoans Animal-like Superphyla: Sarcodines ( Sarcodina ) Ciliates ( Ciliophora ) Flagellates
Protists Kingdom Protista Called the Junk Drawer 3 Subkingdoms of Protists Protozoans Algae Slime molds 1 Protozoans Animal-like Superphyla: Sarcodines ( Sarcodina ) Ciliates ( Ciliophora ) Flagellates
Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Eukaryotic microorganisms Fungi Algae Water
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Eukaryotic microorganisms Fungi Algae Water
 Fig. 27-18e 0.5 µm Thiomargarita namibiensis containing sulfur wastes (LM) Fig. 27-18f 10 µm Fruiting bodies of Chondromyces crocatus, a myxobacterium (SEM) Fig. 27-18g 5 µm B. bacteriophorus Bdellovibrio
Fig. 27-18e 0.5 µm Thiomargarita namibiensis containing sulfur wastes (LM) Fig. 27-18f 10 µm Fruiting bodies of Chondromyces crocatus, a myxobacterium (SEM) Fig. 27-18g 5 µm B. bacteriophorus Bdellovibrio
Name Date Class CHAPTER 19
 Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 19 Section 1: Introduction to Protists In your textbook, read about protists. Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A Column B 1. protist
Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 19 Section 1: Introduction to Protists In your textbook, read about protists. Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A Column B 1. protist
Objective 1: I can describe protists. Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus.
 Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Study Guide B. Answer Key. Protists and Fungi
 Protists and Fungi Answer Key SECTION 1. DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS 1. eukaryotes 2. protists may be single-celled, colonial, or multicellular 3. No, the size of protists range from microscopic to very large.
Protists and Fungi Answer Key SECTION 1. DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS 1. eukaryotes 2. protists may be single-celled, colonial, or multicellular 3. No, the size of protists range from microscopic to very large.
Major groups of algae
 Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B. Subject: Biology. Teacher Signature
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Biology Grade 10A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Biology Grade 10A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan &Talaro Chapter 5 Eucaryotic cells and microorganisms Chapter 5 2 3 Eucaryotic cells 3 Flagella 4 Cilia similar in overall structure to flagella, but
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan &Talaro Chapter 5 Eucaryotic cells and microorganisms Chapter 5 2 3 Eucaryotic cells 3 Flagella 4 Cilia similar in overall structure to flagella, but
VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists:
 VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists: 1. Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus to organize their hereditary material. 2. Some protists help their host
VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists: 1. Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus to organize their hereditary material. 2. Some protists help their host
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Protista and Fungi. Fungi. Protista
 Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
General Biology 1004 Chapter 15 Lecture Handout, Summer 2005 Dr. Frisby
 Slide 1 CHAPTER 15 The Evolution of Microbial Life PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell,
Slide 1 CHAPTER 15 The Evolution of Microbial Life PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell,
Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1
 Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1 1. What are protists? 2. Why is it easier to define protists by what they are not, rather than by what they are? Completion On the lines provided, complete the following
Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1 1. What are protists? 2. Why is it easier to define protists by what they are not, rather than by what they are? Completion On the lines provided, complete the following
Have cell walls made of chitin (same material is found in the skeletons of arthropods)
 Fungi are multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs that do not ingest their food but rather absorb it through their cell walls and cell membranes after breaking it down with powerful digestive enzymes. Fungi
Fungi are multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs that do not ingest their food but rather absorb it through their cell walls and cell membranes after breaking it down with powerful digestive enzymes. Fungi
What is a Protist? A protist is any organism that is not: a plant, an animal, a fungus or a prokaryote.
 Kingdom Protista What is a Protist? There is much debate about this very diverse group of organisms. Scientists have been arguing for years over how best to classify these organisms. Eventually the protists
Kingdom Protista What is a Protist? There is much debate about this very diverse group of organisms. Scientists have been arguing for years over how best to classify these organisms. Eventually the protists
Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain
 Protista Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain All protists are eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Protists are really just all of the Eukaryotes that don t fit into the Animal,
Protista Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain All protists are eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Protists are really just all of the Eukaryotes that don t fit into the Animal,
General Characteristics of Protists
 General Characteristics of Protists Protists are: Eukaryotic Unicellular Most solitary, though some colonize. Some Autotrophic, some Heterotrophic Share characteristics with plants, animals and fungi.
General Characteristics of Protists Protists are: Eukaryotic Unicellular Most solitary, though some colonize. Some Autotrophic, some Heterotrophic Share characteristics with plants, animals and fungi.
Chapter 12B: EUKARYOTES The Protists & Helminths. 1. Protists. Algae Protozoa. 2. Helminths. 1. Protists. A. Algae. B. Protozoa. A.
 Chapter 12B: EUKARYOTES The Protists & Helminths 1. Protists Algae Protozoa 2. Helminths 1. Protists A. Algae B. Protozoa A. Algae 1 Overview of the Algae Characteristics of algae: unicellular or multicellular
Chapter 12B: EUKARYOTES The Protists & Helminths 1. Protists Algae Protozoa 2. Helminths 1. Protists A. Algae B. Protozoa A. Algae 1 Overview of the Algae Characteristics of algae: unicellular or multicellular
Overview of Cells. Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory
 Overview of Cells Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryotic Cells Archaea Bacteria Come in many different shapes and sizes.5 µm 2 µm, up to 60 µm long Have large
Overview of Cells Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryotic Cells Archaea Bacteria Come in many different shapes and sizes.5 µm 2 µm, up to 60 µm long Have large
Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote. grouping for organisms that don't fit into other kingdoms
 Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote grouping for organisms that don't
Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote grouping for organisms that don't
Name Hour. Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages )
 Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Unit 10: The simplest living beings
 Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Page # In what ways are protists important? The Protists. A diverse assemblage of eukaryotes that ARENʼT fungi, plants, or animals
 In what ways are protists important? The Protists A diverse assemblage of eukaryotes that ARENʼT fungi, plants, or animals Base of many food chains - especially in aquatic settings Clarify water by filtering
In what ways are protists important? The Protists A diverse assemblage of eukaryotes that ARENʼT fungi, plants, or animals Base of many food chains - especially in aquatic settings Clarify water by filtering
Bio 134. Ch. 19 Protists
 Bio 134 Ch. 19 Protists Main Idea! Protists form a diverse group of organisms that are subdivided based on their method of obtaining nutrients What do all protists have in common?! They are all eukaryotes
Bio 134 Ch. 19 Protists Main Idea! Protists form a diverse group of organisms that are subdivided based on their method of obtaining nutrients What do all protists have in common?! They are all eukaryotes
Creating a Dichotomous Key
 Dichotomous Keys A tool used that allows users to determine the identity of unknown species Keys consist of a series of choices, where the user selects from a series of connected pairs Each pair of choices
Dichotomous Keys A tool used that allows users to determine the identity of unknown species Keys consist of a series of choices, where the user selects from a series of connected pairs Each pair of choices
Protists. Chapter 28. Overview: Living Small. Concept 28.1: Most eukaryotes are single-celled organisms
 Chapter 28 Protists Overview: Living Small Even a low-power microscope can reveal a great variety of organisms in a drop of pond water Protist is the informal name of the group of mostly unicellular eukaryotes
Chapter 28 Protists Overview: Living Small Even a low-power microscope can reveal a great variety of organisms in a drop of pond water Protist is the informal name of the group of mostly unicellular eukaryotes
Taxonomy the science of the naming and categorization of organisms according to their evolutionary similarities
 Chapter 13 Early Life Forms and the Viruses - Life originated on earth more than 3.8 billion years ago - Its origin and subsequent evolution have been linked to the physical and chemical evolution of the
Chapter 13 Early Life Forms and the Viruses - Life originated on earth more than 3.8 billion years ago - Its origin and subsequent evolution have been linked to the physical and chemical evolution of the
Key Points PROTISTA. Functional arrangements. General. All of these groups are polyphyletic 9/18/14
 PROTISTA The paraphyletic, nonfungi, non-animal, nonplant Eucarya + Even MORE new words to remember! Key Points Origin of eukaryotes via symbiosis Origin of classification based on functional (ecological)
PROTISTA The paraphyletic, nonfungi, non-animal, nonplant Eucarya + Even MORE new words to remember! Key Points Origin of eukaryotes via symbiosis Origin of classification based on functional (ecological)
1A Review Questions. Matching 6. Class 7. Order 8. Binomial nomenclature 9. Phylum 10. Species
 1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
CELLS. Single Celled Organisms. The Building Blocks of Life. Junior Science
 CELLS Single Celled Organisms The Building Blocks of Life Junior Science Lesson Objectives Know what is meant by unicellular and multicellular organisms. List the six kingdoms of life. Explain the difference
CELLS Single Celled Organisms The Building Blocks of Life Junior Science Lesson Objectives Know what is meant by unicellular and multicellular organisms. List the six kingdoms of life. Explain the difference
Chapter 21 Protists BIOLOGY II
 Chapter 21 Protists BIOLOGY II Section 1 Characteristics of Protists Diversity Most diverse of all organisms ALL are eukaryotic Are eukaryotic organisms that cannot be classified as fungi, plants, or animals
Chapter 21 Protists BIOLOGY II Section 1 Characteristics of Protists Diversity Most diverse of all organisms ALL are eukaryotic Are eukaryotic organisms that cannot be classified as fungi, plants, or animals
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Chapter 16. The Origin and Evolution of Microbial Life: Prokaryotes and Protists. Lecture by Joan Sharp
 Chapter 16 The Origin and Evolution of Microbial Life: Prokaryotes and Protists PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture
Chapter 16 The Origin and Evolution of Microbial Life: Prokaryotes and Protists PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture
Chapter 21: Protists
 Chapter 21: Protists Section 1: Characteristics of Protists Gamete: a haploid reproductive cell that unites with another gamete to form a zygote Zygote: the cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 21: Protists Section 1: Characteristics of Protists Gamete: a haploid reproductive cell that unites with another gamete to form a zygote Zygote: the cell that results from the fusion of gametes
BIOL110 Exam 2 Practice Test Solutions
 www.liontutors.com BIOL110 Exam 2 Practice Test Solutions Problem #1: D The Golgi apparatus receives the products from the ER and glycosylates them. The Endomembrane system is a network of membrane-bound
www.liontutors.com BIOL110 Exam 2 Practice Test Solutions Problem #1: D The Golgi apparatus receives the products from the ER and glycosylates them. The Endomembrane system is a network of membrane-bound
Protists 2/14/2012. Chapter 28. Overview: Living Small. Concept 28.1: Most eukaryotes are single-celled organisms
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 28 Protists Overview: Living Small
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 28 Protists Overview: Living Small
20-1 The Kingdom Protista
 20-1 The Kingdom Protista Protists are that are not members of the Plant, Animal, or Fungi Kingdoms. The Kingdom Protista may include more than 200,000 species. Most, but not all, protists are. One way
20-1 The Kingdom Protista Protists are that are not members of the Plant, Animal, or Fungi Kingdoms. The Kingdom Protista may include more than 200,000 species. Most, but not all, protists are. One way
v How long ago is Earth thought to have formed? v What is thought to have been the first genetic material? v Are we tetrapods?
 Biosc 41 Announcements 9/29 v Quick review followed by lecture quiz (history & phylogeny) v Lecture: Protists v Lab: Protozoa (animal-like protists) v Lab exam 1 is Wed! (does not cover today s lab) Review:
Biosc 41 Announcements 9/29 v Quick review followed by lecture quiz (history & phylogeny) v Lecture: Protists v Lab: Protozoa (animal-like protists) v Lab exam 1 is Wed! (does not cover today s lab) Review:
BIOLOGY. Protists CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 28 Protists Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Living Small Even a low-power microscope can reveal
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 28 Protists Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Living Small Even a low-power microscope can reveal
