Kingdom Protista. Lab Exercise 20. Introduction. Contents. Objectives
|
|
|
- Madeline Collins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab Exercise Kingdom Protista Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Animal-like Protists 2 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists 3 Activity.3 Plant-like Protists 3 Resutls Section 5 Introduction This kingdom has an extremely diverse group of members. Perhaps the only similar feature among all protista is that they are simple, eukaryotic organisms, and many would argue with the characterization as simple. The assemblage includes both heterotrophic (protozoa, slime molds, and water molds) and autotrophic (the algae) protists. Objectives - Be able to recognize and name the major Protista phyla - Know the characteristics of each phyla discussed Fungi, plants, and animals are believed to have their ancestral roots in the Kingdom Protista. While there is good evidence that the green algae (Chlorophyta) have given rise to plants, identification of the direct ancestors of the fungi and animals is still uncertain. Some researchers have speculated a link between the fungi and red algae. Many believe the ancestors of animals belong to the flagellated protists, although there is speculation that there may be more than one ancestor. On the BiologyOne DVD, open the Kingdom Protista simulation in the Diversity section. Here you will observe a variety of protests. Ramp. Copyright 12 by F.one Design. All rights reserved. 1
2 Activity.1 Animal-like Protists Phylum Mastigophora: Members of this phylum use a flagellum for locomotion. Examine Trypanosoma gambiense, a blood parasite which causes African Sleeping Sickness. This parasite is carried by the tsetse fly and is injected into a host s circulatory system. The trypanosome can be found among red blood cells. Phylum Sarcodina: Members of this phylum feed and move with extensions called pseudopodia ( false feet ). The most common organism in this phylum is the amoeba. The amoeba has no definite shape and, in fact, is often described as a blob of protoplasm. A nucleus, food vacuoles, and the contractile vacuole may all be present. The latter serves as a water pump, maintaining the internal fluid environment. Other representative members of this phylum include the radiolarians and the forminifera. Both have pseudopods extending from their unique outer shells of silicon and calcium carbonate, respectively. Ciliates contain two nuclei, the macronucleus controls general cellular activity while the micronucleus is involved with sexual reproduction. Similar to the amoebae, the paramecium also has contractile vacuoles. Other examples of a ciliate are the Stentor, a funnel-shaped organism and the Vorticella that often attaches itself via a small stalk to a substrate. Phylum Apicomplexa (Sporozoa): These members have no formal means of locomotion; however, they do move by flexing themselves. They are all parasitic and have a life cycle which alternates between a sexual stage and a spore-producing asexual stage. The most widely known member of this phylum is the Plasmodium, a blood parasite which causes malaria in humans. It is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito. Make your own drawings of these organism you observe in the Results Section. Phylum Ciliophora: Members of this phylum possess short hair-like projections called cilia which, similarly to pseudopods, aid in locomotion and food catching. A very common organism in this phylum is Paramecium. Paramecium Peranema Ramp. Copyright 12 by F.one Design. All rights reserved. 2
3 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists Activity.3 Plant-like Protists Phylum Myxomycota: The protists in this phylum are commonly known as the plasmodial slime molds. They resemble fungi in that their bodies form thread-like hyphae and produce spores, but they are not true fungi in that they have centrioles and flagellated cells. The plasmodial slime mold (Physarum) is a commonly known example. It is a multinucleated mass of protoplasm. Phylum Euglenophyta: Euglenoids are unicellular, photosynthetic flagellates which inhabit fresh water supplies. They have an eyespot which is very light-sensitive, a flagellum for locomotion, and a contractile vacuole. Phylum Chlorophyta: The green algae are the most diverse protists, ranging from single cells to colonies of multicellular filaments. The Acrasiomycota are the cellular slime molds. These organisms usually exist as free-living amoeba-like organisms feeding on bacteria. When its time for these organisms to reproduce, the individual cells aggregate into a mass called a pseudoplasmodium that will eventually produce spores. The Oomycota are the water molds. These organisms range from single celled organisms to highly branched filamentous organisms. A large group within this phylum is aquatic, feeding on dead organic material. These organisms can reproduce sexually or asexually. Observe the micrographs of the fungus-like protists in the Kingdom Protista simulation on the BiologyOne DVD. Make your own drawings of these organisms in the Results Section. Phylum Chrysophyta: The diatoms are by far the most widely known members of this phylum. They are photosynthetic and are abundant in both fresh and marine environments. They play a very significant role in aquatic ecology, serving as the first step in the food chain. Their shell is made up of silica; therefore, they leave behind a large fossil record. These deposits, called diatomaceous earth, are mined and used in many industrial processes. Phylum Pyrrophyta: Members in this phylum are commonly called dinoflagellates. They are unicellular and often are armored with cellulose cell walls. Dinoflagellates are responsible for causing the red tides seen off the coasts of California and Peru which are often very toxic to marine life. Assortment of Diatoms Ramp. Copyright 12 by F.one Design. All rights reserved. 3
4 Phylum Rhodophyta: The red algae are multicellular with a body frame that is delicate and feather-like. They prefer warm, marine environments. In addition to containing chlorophyll, they also have red and blue pigments. These pigments allow the red algae to capture sunlight that penetrates the deep depths of the ocean. Although the red color is the most distinctive, this algae may also be purple to green-black. Phylum Phaeophyta: The brown algae are multicellular and macroscopic. This phylum includes the large kelp (Sargassum and Laminaria) which can grow to 60 to 100 meters in length. The rockweed (Fucus), commonly found attached to rocks along coastal shores, is another member of this phylum. The brown algae tend to inhabit cold, marine environments. From an industrial standpoint, brown algae are used for fertilizers, to make ice cream smooth, and used in cosmetics and paints. Phylum Chlorophyta: This is a very large, very diverse group often referred to as the green algae. While most are aquatic, they can also be found in most damp terrestrial locations, in symbiotic associations with lichens and even on the surface of snow. Members of this group are thought to have given rise to the plant kingdom. Observe the micrographs of the plant-like protists in the Kingdom Protista simulation on the BiologyOne DVD. Make your own drawings of these organisms in the Results Section. Microasterias Spyrogyra Crucigenia Closterium Ramp. Copyright 12 by F.one Design. All rights reserved. 4
5 Lab Exercise Name Results Section Activity.1 Animal-like Protists Ramp. Copyright 12 by F.one Design. All rights reserved. 5
6 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists Ramp. Copyright 12 by F.one Design. All rights reserved. 6
7 Activity.3 Plant-like Protists Ramp. Copyright 12 by F.one Design. All rights reserved. 7
Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5
 Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5 5.2 Kingdom Protista (pp. 140-151) Kingdom Protista general characterisitcs and groups Protists are a very diverse kingdom of living things that do not fit into any other
Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5 5.2 Kingdom Protista (pp. 140-151) Kingdom Protista general characterisitcs and groups Protists are a very diverse kingdom of living things that do not fit into any other
5/10/2013. Protists. Kingdom Protista. Called the Junk Drawer. 3 Subkingdoms of Protists. Protozoans Algae Slime molds
 Protists Kingdom Protista Called the Junk Drawer 3 Subkingdoms of Protists Protozoans Algae Slime molds 1 Protozoans Animal-like Superphyla: Sarcodines ( Sarcodina ) Ciliates ( Ciliophora ) Flagellates
Protists Kingdom Protista Called the Junk Drawer 3 Subkingdoms of Protists Protozoans Algae Slime molds 1 Protozoans Animal-like Superphyla: Sarcodines ( Sarcodina ) Ciliates ( Ciliophora ) Flagellates
Kingdom Protista. Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 EXIT 2/16/2005
 Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
PROTISTS. Chapter 25 Biology II
 PROTISTS Chapter 25 Biology II Vocabulary- Protists (44 words) 1. Protist 2. binary fission 3. conjugation 4. Multiple fission 5. pseudopodium 6. test 7. Amoeboid movement 8. cilium 9. Pellicle 10. oral
PROTISTS Chapter 25 Biology II Vocabulary- Protists (44 words) 1. Protist 2. binary fission 3. conjugation 4. Multiple fission 5. pseudopodium 6. test 7. Amoeboid movement 8. cilium 9. Pellicle 10. oral
19.1 Diversity of Protists. KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms.
 19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
Protists. Plant Like Animal Like Fungus Like. What are the three main groups of protists?*
 Protists & Fungi Protists Single celled or multi-celled organisms that live in moist areas Eukaryotic organisms Characteristics of plants, animals and fungi Grouped in to three main groups* Plant Like
Protists & Fungi Protists Single celled or multi-celled organisms that live in moist areas Eukaryotic organisms Characteristics of plants, animals and fungi Grouped in to three main groups* Plant Like
Protists & Fungi. Words to Know: Chapters 19 & 20. Label the paramecium diagram above. (pg. 548)
 Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
There are two commonly accepted theories for how eukaryotic cells evolved: infolding and endosymbiosis. Infolding
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists. There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group
 There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group Traditional Classification There are three divisions of the Kingdom Protista: Protozoa,
There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group Traditional Classification There are three divisions of the Kingdom Protista: Protozoa,
Life Science. Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista
 Life Science Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista Protista Junk drawer kingdom a little bit of everything, some w/ cell walls (composition varies), some w/out. All are Eukaryotes, autotrophs and heterotrophs represented.
Life Science Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista Protista Junk drawer kingdom a little bit of everything, some w/ cell walls (composition varies), some w/out. All are Eukaryotes, autotrophs and heterotrophs represented.
General Characteristics of Protists
 General Characteristics of Protists Protists are: Eukaryotic Unicellular Most solitary, though some colonize. Some Autotrophic, some Heterotrophic Share characteristics with plants, animals and fungi.
General Characteristics of Protists Protists are: Eukaryotic Unicellular Most solitary, though some colonize. Some Autotrophic, some Heterotrophic Share characteristics with plants, animals and fungi.
Chapter 28 / Protists. I. Introduction A. Eukaryotes 1. 1 st eukaryotic organisms 2. most are unicellular 3. considered simple. Part I: Protozoans
 Randa, Bio 1151 1 Chapter 28 / Protists I. Introduction A. Eukaryotes 1. 1 st eukaryotic organisms 2. most are unicellular 3. considered simple B. Protist diversity (ecological grouping) 1. comprised of:
Randa, Bio 1151 1 Chapter 28 / Protists I. Introduction A. Eukaryotes 1. 1 st eukaryotic organisms 2. most are unicellular 3. considered simple B. Protist diversity (ecological grouping) 1. comprised of:
29/11/2012. Characteristics. Protist Diversity. Characteristics. Kingdom Protista. Examples of Plant-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Importance of Protists
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Kingdom Protista. Protista
 Kingdom Protista Protista Traditionally a kingdom level taxon Current evidence places organisms in as many as 3-5 kingdoms We will classify all: Unicellular or simple colonial Eukaryotic Organisms that
Kingdom Protista Protista Traditionally a kingdom level taxon Current evidence places organisms in as many as 3-5 kingdoms We will classify all: Unicellular or simple colonial Eukaryotic Organisms that
Kingdom Protista. The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Observing and Classifying Protozoa
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Observing and Classifying Protozoa Background The name protozoa actually means first animals. This name was given because many protozoa share characteristics with animals. However,
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Observing and Classifying Protozoa Background The name protozoa actually means first animals. This name was given because many protozoa share characteristics with animals. However,
Name Date Class CHAPTER 19
 Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 19 Section 1: Introduction to Protists In your textbook, read about protists. Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A Column B 1. protist
Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 19 Section 1: Introduction to Protists In your textbook, read about protists. Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A Column B 1. protist
Protista and Fungi. Fungi. Protista
 Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
Notes - Microbiology Protista
 Notes - Microbiology Protista Part 1 Animal like Protists - Kingdom Protista is a very diverse group of organisms. There are over 115 000 different kinds, with traits that fit with fungi, plants, and animals.
Notes - Microbiology Protista Part 1 Animal like Protists - Kingdom Protista is a very diverse group of organisms. There are over 115 000 different kinds, with traits that fit with fungi, plants, and animals.
Kingdom Protista. The following organisms will be examined in the lab today: Volvox, Oedogonium, Spirogyra, Ulva
 Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote. grouping for organisms that don't fit into other kingdoms
 Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote include more than 200,000 species
Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote include more than 200,000 species
Bio 134. Ch. 19 Protists
 Bio 134 Ch. 19 Protists Main Idea! Protists form a diverse group of organisms that are subdivided based on their method of obtaining nutrients What do all protists have in common?! They are all eukaryotes
Bio 134 Ch. 19 Protists Main Idea! Protists form a diverse group of organisms that are subdivided based on their method of obtaining nutrients What do all protists have in common?! They are all eukaryotes
Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi
 Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi Ch. 19: Protists Major Concepts 1. Protists make up a diverse catch-all kingdom of organisms. 2. Algae are photosynthetic protists that are major producers in the biosphere. 3.
Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi Ch. 19: Protists Major Concepts 1. Protists make up a diverse catch-all kingdom of organisms. 2. Algae are photosynthetic protists that are major producers in the biosphere. 3.
VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists:
 VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists: 1. Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus to organize their hereditary material. 2. Some protists help their host
VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists: 1. Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus to organize their hereditary material. 2. Some protists help their host
METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph
 CH. 22 PROTISTS METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph 6 Kingdoms 1. Eubacteria prokaryotes; single cell; heterotroph
CH. 22 PROTISTS METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph 6 Kingdoms 1. Eubacteria prokaryotes; single cell; heterotroph
The Protistans. Includes protozoans and algae All single celled eukaryotes
 Includes protozoans and algae All single celled eukaryotes The Protistans Protozoa - Unicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic - Inhabit water and soil - Some normal microbiota of animals - Few cause disease
Includes protozoans and algae All single celled eukaryotes The Protistans Protozoa - Unicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic - Inhabit water and soil - Some normal microbiota of animals - Few cause disease
Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote. grouping for organisms that don't fit into other kingdoms
 Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote grouping for organisms that don't
Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote grouping for organisms that don't
CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI
 CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI Name Day M T W Th F Weekly Lifeline Period B_ Check Question What is a parasite? KICK-OFF LEARNING LOG KICK-OFF Response (1) A parasite is an organism that feeds off of another
CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI Name Day M T W Th F Weekly Lifeline Period B_ Check Question What is a parasite? KICK-OFF LEARNING LOG KICK-OFF Response (1) A parasite is an organism that feeds off of another
The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity
 http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
Objective 1: I can describe protists. Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus.
 Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor. Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells
 Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells 1 Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells 1 Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells
 Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Protists 9/11/2017. Endosymbiosis
 Protists Chapter 28 Most eukaryotes are single-celled organisms Protists are eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells have organelles and are more complex than prokaryotic cells Most protists are unicellular, but there
Protists Chapter 28 Most eukaryotes are single-celled organisms Protists are eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells have organelles and are more complex than prokaryotic cells Most protists are unicellular, but there
Chapter 7. Protists. Protists( 원생동물 )
 Protists( 원생동물 ) - currently 100,000 species, 35,000 species found in fossils - lying in classification gap bwtn prokaryote and smallest animal and plants - all are unicellular, some exist as colonies
Protists( 원생동물 ) - currently 100,000 species, 35,000 species found in fossils - lying in classification gap bwtn prokaryote and smallest animal and plants - all are unicellular, some exist as colonies
Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike.
 SECTION 19.1 DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. VOCABULARY protist Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. 1. Are protists
SECTION 19.1 DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. VOCABULARY protist Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. 1. Are protists
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES
 ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES I. Protists - Commonly called protozoans - All single celled eukaryotes Three most important phyla: 1. Sarcomastigophora: includes the amebas and the flagellates 2.
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES I. Protists - Commonly called protozoans - All single celled eukaryotes Three most important phyla: 1. Sarcomastigophora: includes the amebas and the flagellates 2.
Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1
 Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1 1. What are protists? 2. Why is it easier to define protists by what they are not, rather than by what they are? Completion On the lines provided, complete the following
Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1 1. What are protists? 2. Why is it easier to define protists by what they are not, rather than by what they are? Completion On the lines provided, complete the following
Name Class Date. 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Kinds of Protists 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits? PROTIST PRODUCERS 2. What is the name for protists that
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Kinds of Protists 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits? PROTIST PRODUCERS 2. What is the name for protists that
Eukarya. Eukarya includes all organisms with eukaryotic cells Examples: plants animals fungi algae single-celled animal-like protozoa
 Eukarya Eukarya includes all organisms with eukaryotic cells Examples: plants animals fungi algae single-celled animal-like protozoa Protists Eukaryotic; but comprises its own Kingdom Protista Algae -
Eukarya Eukarya includes all organisms with eukaryotic cells Examples: plants animals fungi algae single-celled animal-like protozoa Protists Eukaryotic; but comprises its own Kingdom Protista Algae -
Study Guide B. Answer Key. Protists and Fungi
 Protists and Fungi Answer Key SECTION 1. DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS 1. eukaryotes 2. protists may be single-celled, colonial, or multicellular 3. No, the size of protists range from microscopic to very large.
Protists and Fungi Answer Key SECTION 1. DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS 1. eukaryotes 2. protists may be single-celled, colonial, or multicellular 3. No, the size of protists range from microscopic to very large.
Chapter 22: Protists
 Chapter 22: Protists Protists Protistans are Unlike Prokaryotes Have a nucleus and organelles Have proteins associated with DNA Use microtubules in a cytoskeleton, spindle apparatus, and cilia and flagella
Chapter 22: Protists Protists Protistans are Unlike Prokaryotes Have a nucleus and organelles Have proteins associated with DNA Use microtubules in a cytoskeleton, spindle apparatus, and cilia and flagella
The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells
 The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells This domain is divided into four fairly distinct kingdoms: - Protists (Protista) - Plants
The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells This domain is divided into four fairly distinct kingdoms: - Protists (Protista) - Plants
Symbiosis. Symbiosis is a close association between of two or more organisms. Endosymbiosis living within another
 PROTISTS Protists constitute several kingdoms within the domain Eukarya Protists obtain their nutrition in a variety of ways Algae are autotrophic protists Protozoans are heterotrophic protists Fungus
PROTISTS Protists constitute several kingdoms within the domain Eukarya Protists obtain their nutrition in a variety of ways Algae are autotrophic protists Protozoans are heterotrophic protists Fungus
EVOLUTION OF METAZOANS
 EVOLUTION OF METAZOANS All multicellular animals are called metazoans and single celled animals, Protozoa Metazoa (Meta= later; zoa = animals) after Metazoa (Meta= later; zoa = animals) after the Protozoans
EVOLUTION OF METAZOANS All multicellular animals are called metazoans and single celled animals, Protozoa Metazoa (Meta= later; zoa = animals) after Metazoa (Meta= later; zoa = animals) after the Protozoans
Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes. Chapter 22 Part 1
 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Chapter 22 Part 1 Impacts, Issues The Malaria Menace Plasmodium, a single-celled protist, causes malaria but also manipulates its mosquito and human hosts to maximize its
Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Chapter 22 Part 1 Impacts, Issues The Malaria Menace Plasmodium, a single-celled protist, causes malaria but also manipulates its mosquito and human hosts to maximize its
Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus.
 7ch8 Protists Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus. protists are a diverse group with many different adaptations share some characteristics with plants,
7ch8 Protists Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus. protists are a diverse group with many different adaptations share some characteristics with plants,
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.29 - PROTISTS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
!! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
20-1 The Kingdom Protista
 20-1 The Kingdom Protista Protists are that are not members of the Plant, Animal, or Fungi Kingdoms. The Kingdom Protista may include more than 200,000 species. Most, but not all, protists are. One way
20-1 The Kingdom Protista Protists are that are not members of the Plant, Animal, or Fungi Kingdoms. The Kingdom Protista may include more than 200,000 species. Most, but not all, protists are. One way
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
PROTISTS James Bier
 PROTISTS 2013-2015 James Bier Objectives 1. List the characteristics shared among the protists. 2. Describe secondary endosymbiosis and the evidence for this hypothesis. 3. List the five major taxa of
PROTISTS 2013-2015 James Bier Objectives 1. List the characteristics shared among the protists. 2. Describe secondary endosymbiosis and the evidence for this hypothesis. 3. List the five major taxa of
Microbial Diversity. Bacteria Archaea Protista Fungi. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Microbial Diversity Bacteria Archaea Protista Fungi Figure 19-1 Three common prokaryote shapes Figure 19-2 The prokaryote flagellum Figure 19-2b The structure of the bacterial flagellum cell wall wheelandaxle
Microbial Diversity Bacteria Archaea Protista Fungi Figure 19-1 Three common prokaryote shapes Figure 19-2 The prokaryote flagellum Figure 19-2b The structure of the bacterial flagellum cell wall wheelandaxle
Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Eukaryotic microorganisms Fungi Algae Water
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Eukaryotic microorganisms Fungi Algae Water
Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain
 Protista Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain All protists are eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Protists are really just all of the Eukaryotes that don t fit into the Animal,
Protista Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain All protists are eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Protists are really just all of the Eukaryotes that don t fit into the Animal,
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
What is a Protist? A protist is any organism that is not: a plant, an animal, a fungus or a prokaryote.
 Kingdom Protista What is a Protist? There is much debate about this very diverse group of organisms. Scientists have been arguing for years over how best to classify these organisms. Eventually the protists
Kingdom Protista What is a Protist? There is much debate about this very diverse group of organisms. Scientists have been arguing for years over how best to classify these organisms. Eventually the protists
Unit 10: The simplest living beings
 Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Chp. 26 Notes The Protista Kingdom
 Chp. 26 Notes The Protista Kingdom Most protists are unicellular, microscopic organisms, but a few are complex and multicellular. These are the most diverse (different) organisms according to life cycles,
Chp. 26 Notes The Protista Kingdom Most protists are unicellular, microscopic organisms, but a few are complex and multicellular. These are the most diverse (different) organisms according to life cycles,
Name Hour Section 20-1 The Kingdom Protista (pages ) What Is a Protist? (Page 497) 1. What is a protist?
 Name Hour Section 20-1 The Kingdom Protista (pages 497-498) What Is a Protist? (Page 497) 1. What is a protist? 2. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about protists. a. All are unicellular.
Name Hour Section 20-1 The Kingdom Protista (pages 497-498) What Is a Protist? (Page 497) 1. What is a protist? 2. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about protists. a. All are unicellular.
INTRODUCTION prokaryotic eukaryotic pigments
 INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014
 Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring Protist Phylogeny. Meet the algae. Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis. Endosymbiosis. Secondary Endosymbiosis
 Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Domains and Kingdoms. Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria
 Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Name Hour. Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages )
 Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Protist Classification the Saga Continues
 Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes
 Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes OBJECTIVES 1. To observe representatives of major types of microbes. 2. To cultivate select representatives of major types of microbes. 3. Understand key
Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes OBJECTIVES 1. To observe representatives of major types of microbes. 2. To cultivate select representatives of major types of microbes. 3. Understand key
Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi)
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A protist is any organism
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A protist is any organism
Microbiology and Protista Lab
 Microbiology and Protista Lab Learning Objectives Describe the basic structures of a bacterial cell. Name the three bacterial cell shapes and recognize each under the microscope Recognize and identify
Microbiology and Protista Lab Learning Objectives Describe the basic structures of a bacterial cell. Name the three bacterial cell shapes and recognize each under the microscope Recognize and identify
You and plants have something in common! 1
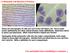 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure & Function These are micrographs of cells you saw in the Cell Types Lab. One is plant (onion epithelium), the other animal (human cheek epithelium). Determine which is which
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure & Function These are micrographs of cells you saw in the Cell Types Lab. One is plant (onion epithelium), the other animal (human cheek epithelium). Determine which is which
Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi
 complete petri dishes Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Viruses Lesson 1 Objectives Name and describe the characteristics of viruses and how they multiply. Discuss both positive and negative
complete petri dishes Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Viruses Lesson 1 Objectives Name and describe the characteristics of viruses and how they multiply. Discuss both positive and negative
1A Review Questions. Matching 6. Class 7. Order 8. Binomial nomenclature 9. Phylum 10. Species
 1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
1. General Features of Protists
 Chapter 28: Protists 1. General Features of Protists 2. Survey of the Protista A. The Excavata B. The SAR Clade C. The Archaeplastida D. The Unikonta 1. General Features of Protists All Protists are Eukaryotes
Chapter 28: Protists 1. General Features of Protists 2. Survey of the Protista A. The Excavata B. The SAR Clade C. The Archaeplastida D. The Unikonta 1. General Features of Protists All Protists are Eukaryotes
SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B. Subject: Biology. Teacher Signature
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Biology Grade 10A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Biology Grade 10A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true
Unit 4 Protists and Fungi
 Unit 4 Protists and Fungi Objectives Topic 1: Protists Protists are eukaryotes that are not members of the kingdoms, Plantae, Animalia, or Fungi Identify the defining characteristics of animal-like, plant-like
Unit 4 Protists and Fungi Objectives Topic 1: Protists Protists are eukaryotes that are not members of the kingdoms, Plantae, Animalia, or Fungi Identify the defining characteristics of animal-like, plant-like
Biology. Slide 1of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Protists Diversity
 Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Protists Diversity For Lecture, Make sure you know the Water Molds (Oomycota) names and characteris6cs of the taxa at the levels indicated by the red arrows. Characteristics
Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Protists Diversity For Lecture, Make sure you know the Water Molds (Oomycota) names and characteris6cs of the taxa at the levels indicated by the red arrows. Characteristics
Chapter 19. Diversity of Protists and Fungi
 Chapter 19 Diversity of Protists and Fungi 1 Misfit or Junkdrawer Kingdom Very diverse: Most unicellular BUT Some multicellular Protists Some heterotrophic BUT some autotrophic Some reproduce sexually
Chapter 19 Diversity of Protists and Fungi 1 Misfit or Junkdrawer Kingdom Very diverse: Most unicellular BUT Some multicellular Protists Some heterotrophic BUT some autotrophic Some reproduce sexually
What Are the Protists?
 Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Protists: Molds Lecture 3 Spring 2014
 Meet the Protists 1 Protists: Molds Lecture 3 Spring 2014 Domain Eukarya What unites them as a group? The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells Evolution of the endomembrane system Which organelles are included in
Meet the Protists 1 Protists: Molds Lecture 3 Spring 2014 Domain Eukarya What unites them as a group? The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells Evolution of the endomembrane system Which organelles are included in
Protists: Molds Lecture 3 Spring 2014
 Protists: Molds Lecture 3 Spring 2014 Meet the Protists 1 Domain Eukarya What unites them as a group? The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells 2 Evolution of the endomembrane system Which organelles are included
Protists: Molds Lecture 3 Spring 2014 Meet the Protists 1 Domain Eukarya What unites them as a group? The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells 2 Evolution of the endomembrane system Which organelles are included
Chapter 21 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes. Cengage Learning 2016
 Chapter 21 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Protists Eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals Structurally less complex Play important ecological roles as producers or predators of microorganisms
Chapter 21 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Protists Eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals Structurally less complex Play important ecological roles as producers or predators of microorganisms
Bell Work. identify the phylum that each character belongs to. Tuesday, February 19, 13
 Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera
Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera
On the slides and live specimens find the (and know the function of) nucleus paramylon bodies cytopharynx flagellum eyespot
 Biology 3B Laboratory Protist Diversity Objectives Learn the basic characteristics that define organisms classified within the Protist taxon To learn the anatomy, life cycles and identification of representative
Biology 3B Laboratory Protist Diversity Objectives Learn the basic characteristics that define organisms classified within the Protist taxon To learn the anatomy, life cycles and identification of representative
Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny
 Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny Protistans, Part 1 Lecture VIII Protistans Lecture Themes structure and function; recurring evolutionary themes and unifying features the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny Protistans, Part 1 Lecture VIII Protistans Lecture Themes structure and function; recurring evolutionary themes and unifying features the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms
 Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms 7.L.1.1 - Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life including: Euglena
Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms 7.L.1.1 - Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life including: Euglena
Biology Chapter 20 Notes
 Biology Chapter 20 Notes Kingdom Protozoa Protist any organism that is not a plant, animal, fungus, or prokaryote. Eukaryotes Most difficult group to classify All can reproduce asexually Three categories:
Biology Chapter 20 Notes Kingdom Protozoa Protist any organism that is not a plant, animal, fungus, or prokaryote. Eukaryotes Most difficult group to classify All can reproduce asexually Three categories:
Chapter 12B: EUKARYOTES The Protists & Helminths. 1. Protists. Algae Protozoa. 2. Helminths. 1. Protists. A. Algae. B. Protozoa. A.
 Chapter 12B: EUKARYOTES The Protists & Helminths 1. Protists Algae Protozoa 2. Helminths 1. Protists A. Algae B. Protozoa A. Algae 1 Overview of the Algae Characteristics of algae: unicellular or multicellular
Chapter 12B: EUKARYOTES The Protists & Helminths 1. Protists Algae Protozoa 2. Helminths 1. Protists A. Algae B. Protozoa A. Algae 1 Overview of the Algae Characteristics of algae: unicellular or multicellular
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P AND CHAPTER 16 P
 BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
Page # In what ways are protists important? The Protists. A diverse assemblage of eukaryotes that ARENʼT fungi, plants, or animals
 In what ways are protists important? The Protists A diverse assemblage of eukaryotes that ARENʼT fungi, plants, or animals Base of many food chains - especially in aquatic settings Clarify water by filtering
In what ways are protists important? The Protists A diverse assemblage of eukaryotes that ARENʼT fungi, plants, or animals Base of many food chains - especially in aquatic settings Clarify water by filtering
Biology. Slide 1of 34. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists 2of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists Similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi Like fungi, g, funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb
Biology 1of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists 2of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists Similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi Like fungi, g, funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb
The Microbial World. Chapter 5
 The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi
 KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING
 Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Different ideas about origins Generation Until mid-1800s Life can emerge from materials Flies on meat; mice in dirty laundry; frogs in ponds; etc.
 1 Bio 1101 Lecture 12 (Guided Notes) Chapter 15 -- Evolution of Microbial Life 2 3 Evolution of Earliest Life Different ideas about origins Generation Until mid-1800s Life can emerge from materials Flies
1 Bio 1101 Lecture 12 (Guided Notes) Chapter 15 -- Evolution of Microbial Life 2 3 Evolution of Earliest Life Different ideas about origins Generation Until mid-1800s Life can emerge from materials Flies
Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Lab: Pond Water M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Pond Water Lab Introduction: Why Study Pond Microlife? Right, what are all those little things really good for? Well, for one thing, without bacteria no fish, no frogs, no birds,
Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Pond Water Lab Introduction: Why Study Pond Microlife? Right, what are all those little things really good for? Well, for one thing, without bacteria no fish, no frogs, no birds,
Chapter 21: Protists
 Chapter 21: Protists Section 1: Characteristics of Protists Gamete: a haploid reproductive cell that unites with another gamete to form a zygote Zygote: the cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 21: Protists Section 1: Characteristics of Protists Gamete: a haploid reproductive cell that unites with another gamete to form a zygote Zygote: the cell that results from the fusion of gametes
2.3. The Protists. why Protists Are Important
 2.3 The Protists The smallest eukaryotes and some of the largest belong to the Kingdom Protista. This kingdom is extremely diverse. Some of its members, such as amoebas and paramecia, are very small and
2.3 The Protists The smallest eukaryotes and some of the largest belong to the Kingdom Protista. This kingdom is extremely diverse. Some of its members, such as amoebas and paramecia, are very small and
Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants
 Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants Distinguishing Characteristics: Photosynthetic Live in aqueous environments (ie. In or near water) Lack internal tubes to move water and materials from one part of the
Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants Distinguishing Characteristics: Photosynthetic Live in aqueous environments (ie. In or near water) Lack internal tubes to move water and materials from one part of the
biology Slide 1of 33 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1of 33 2of 33 General characteristics of Plantlike Protists Commonly called algae Found in ponds and lakes Lack true roots, true leaves and stems (differ from true plants) Most are autotrophic
biology 1of 33 2of 33 General characteristics of Plantlike Protists Commonly called algae Found in ponds and lakes Lack true roots, true leaves and stems (differ from true plants) Most are autotrophic
Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista
 Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista Domain Eubacteria Domain Archae The Prokaryotes Cell type: Prokaryotes Found in: Domain Bacteria Domain Archae Cell type: Prokaryotes Two Domains: Bacteria and Archae Do
Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista Domain Eubacteria Domain Archae The Prokaryotes Cell type: Prokaryotes Found in: Domain Bacteria Domain Archae Cell type: Prokaryotes Two Domains: Bacteria and Archae Do
