Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic
|
|
|
- Donna Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y Z Y Z Example Examples C H 3 C Cl C H 3 C Cl Br Br Br Br H rxn (kcal/mol) 46 H 3 C H 3 C Add lone pairs and curved arrows as needed to the heterolysis example in Model A curved arrow (two barbs on arrowhead) shows the movement of an electron pair. a. How many electrons does a fish hook arrow (one barb on arrowhead) move? b. How many fish hooks are required to show a homolysis reaction? 3. Add lone pairs, unpaired electrons, and fish hooks to the homolysis examples in Model Radical (or free radical) refers to an atom with an unpaired electron. It can also refer to the molecule that contains this atom. a. Draw the radicals that appear in the examples in Model 1 here: b. What kind of reaction, heterolysis or homolysis (circle one), produces radicals? c. How many radicals does a homolysis produce? d. Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for Br 2 2Br. Assume the barrier for the reverse reaction, radical recombination, is very small. PE Br 2 2 Br
2 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) 2 e. Why is homolysis of Br-Br and H 3 C-C nonexistent at room temperature? 1 Model 2 Halogenation of Alkanes Gives Mixtures Chlorine (Cl 2 ) and bromine (Br 2 ) react with alkanes when irradiated with ultraviolet light (signified by UV or h ). The following reactions are typical: C H 3 H C H 2 C C H 2 C H X 2 h X X X 2 = Cl 2 32% 42% 26% X X 2 = Br 2 <1% 9% 91% Similar halogenations occur with F 2, but are very fast, release large quantities of energy, and generate large amounts of corrosive, toxic HF. Halogenation does not occur to a significant extent with I Classify the reactions in Model 2 as substitution, addition, or elimination. 6. C-X and C-O bonds are treated the same way when calculating oxidation numbers. Classify the reactions in Model 2 as reduction, oxidation, or neither. 7. Which substitution of H by X occurs with greater selectivity, H Cl or H Br? 8. Which type of H appears to be replaced most quickly by Br: 1 H, 2 H or 3 H? Which type of H is replaced most slowly? (fastest) >> >> (slowest) Fact The speed of H Br is negatively correlated with the strength of the alkane CH bond: 3 CH (weakest) < 2 CH < 1 CH < CH 4 (strongest) 9. What are the number of 1, 2 and 3 H in 2,5-dimethylhexane, the starting material in Model 2? 1 Activity 6, Model 5 contained these data: half-life of a molecule protected by a barrier of 130 kj/mol was days at 100 C and forever at 25 C (1 kcal/mol 4.2 kj/mol so 46 and 88 kcal/mol 190 and 370 kj/mol, respectively).
3 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) Use the data in Model 2 to construct supporting explanations for, or complete, the following statements: a. If every H in 2,5-dimethylhexane were equally reactive, the product distribution would be 67% 1 X and 22% 2 X and just 11% 3 X. b. Equal amounts of 1 X and 2 X would be produced if each 2 H were times as reactive as each 1 H. c. Equal amounts of 1 X and 3 X would be produced if each 3 H were times as reactive as each 1 H. 11. Use the data in Model 2 to complete these statements: a. Each 3 H in 2,5-dimethylhexane reacts about times faster with Br 2 than each 2 H. b. Each 3 H in 2,5-dimethylhexane reacts (faster, slower, at about the same rate) with Cl 2 (than, as) each 2 H. Model 3 Halogenation Occurs by a Radical Chain Mechanism A chain mechanism is one that consumes a species necessary for the reaction and then produces that species again so that the reaction can continue. The individual steps in a chain mechanism are called propagation steps. Propagation step #1 Propagation step #2 12. According to the examples in Model 3, how many fish hooks are needed a. To show the breaking of a covalent bond: b. To show the forming of a covalent bond: 13. Cross out any species that appears both as a reactant and as a product in the sum equation in Model 3. Write a net equation for the two-step chain in Model 3 based on the remaining species.
4 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) a. Draw the species in Model 3 that justifies calling the mechanism a chain mechanism. b. Why can t we use the consumption of alkane, RH, to justify calling this a chain mechanism? c. Why can t we use the production of HX to justify calling this a chain mechanism? d. T or F. Propagation step #1 consumes and produces the same radical. If T, draw the radical that appears as a reactant and product in step # Two commonly observed steps in radical chain mechanisms are hydrogen atom transfer and halogen atom transfer. Label each propagation step in Model 3 with its appropriate name. Fact 24.2 Fish hook rules: The examples in Model 3 show that every electron that participates in a radical reaction must be guided by a fish hook. Fish hooks start at bonds or unpaired electrons, never at atoms. Fish hooks meet where new bonds are required. A fish hook that points to an atom delivers an unpaired electron to that atom. More rules: Never mix curved arrows and fish hooks in the same drawing. An unpaired electron on one atom never jumps to another atom. 16. According to Fact 24.2, why are 3 fish hooks used in each atom transfer reaction in Model 3? 17. The fish hooks in the following drawings violates one or more rules in Fact Find and describe all of the fish hooks violations. Y Z Y Z X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
5 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) 5 Model 4 Bu 3 SnH Reduces Haloalkanes by a Radical Chain Mechanism Bu = CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 (n-butyl), Bu 3 SnH = tributyl tin hydride. The same column in the periodic table that contains C also contains Si, Ge (germanium), Sn (tin), and Pb (lead). 15. Add fish hooks to the reactants of each step in Model Write the net reaction for Model 4 under the line. a. What tin-containing species is consumed in the net reaction? b. What tin-containing species is produced by the net reaction? c. What is the tin-containing reagent that reduces haloalkanes? 17. What radical in Model 4 justifies calling this a radical chain mechanism? 18. Label each propagation step in Model 4 as either hydrogen atom transfer or halogen transfer. Model 5 NBS Creates Allylic & Benzylic Bromides by a Radical Chain Mechanism O Br N O N-Bromosuccinimide NBS
6 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) How many propagation steps appear in the mechanism in Model 5? 20. Succ stands for succinimide. This compound is related to NBS by replacing Br with H. Draw Succ. 21. Label propagation steps in Model 5 that involve radicals as hydrogen atom transfer or halogen transfer as needed. 22. Draw fish hooks on the reactants of propagation steps in Model 5 that involve radicals. 23. Label allyl radical wherever it appears in Model 5. Draw fish hooks needed to interconvert the two resonance structures in propagation step # Propagation step #2 is very fast, but does not involve radicals. It probably looks something like this: a. Add lone pairs and curved arrows to the reactants. b. Draw the resonance structure implied by the curved arrows on the conjugate acid of NBS. c. Add lone pairs and curved arrows where needed to the Br s in the ion pair intermediates. Also add lone pairs to the products of the Br transfer. d. The HO-C=N structure is an unstable short-lived tautomer of succinimide. You have seen an analogous pair of tautomers in connection with vinyl alcohols. Draw brackets around the unstable tautomer below (BVA!) and draw the more stable compound that it turns into. H H O 3 C H C C
7 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) 7 Fact 24.3 Selectivity of allylic/benzylic bromination reflects the fact that the speed of H Br is negatively correlated with the strength of the alkane CH bond: Benzylic CH (weakest) < Allylic CH < 3 CH < 2 CH < 1 CH < CH 4 (strongest) Fact 24.4 NBS (reagent recipe shown below) gives exclusively allylic and benzylic bromination. Example: Br NBS (PhCOO) 2, 25. Use Fact 24.4 to predict the products of these reactions: NBS (PhCOO) 2, NBS (PhCOO) 2, draw dibromo product Model 6 Initiation Steps Create Chain-Carrying Radicals Model 1 provided evidence that covalent bonds will not undergo homolysis spontaneously. Exceptions to this rule-of-thumb are 1) molecules that contain unusually weak bonds (these break when heated) or 2) molecules that undergo homolysis after they absorb UV radiation (this can excite an electron from a BMO to an ABMO). The chemical agents that produce radicals are called radical initiators and the chemical reactions that lead to chain-carrying radicals are called initiation steps.
8 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) Three radical initiators are shown in Model 6. Circle the non-radical reactant (if an abbreviation is provided, circle that instead) and label it as light-sensitive initiator or heat-sensitive initiator. 27. Draw fish hooks for the initiation steps shown in Model The two heat-sensitive initiators produce allyl-like radicals in the first step. Draw another resonance structure for each of these radicals. 29. Initiators, like catalysts, can be added in small amounts. However, the justification for this is different. a. Which substance, an initiator or a catalyst, is not consumed during a reaction? b. Construct an explanation for why initiators can be used successfully in small amounts. 30. Each initiation sequence in Model 6 includes a molecule that will act as the reactant for the desired reaction. This molecule must be present in large amounts. Circle these molecules and label them reactant. 31. Each initiation sequence in Model 6 produces a radical that can carry a chain mechanism forward. Circle these radicals and label them chain carriers. 7 O 2 Creates Allylic Peroxides by a Radical Chain Mechanism Triplet O 2, is ubiquitous in the natural environment and can create radicals for chain mechanisms. Here are the initiation steps leading to allylic peroxides.
9 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) 9 Allyl radical carries a chain mechanism that consumes more O 2 and leads to allylic peroxides. 32. Label all allyl radicals that appear in Model What radical carries the chain mechanism in Model 7, i.e., is consumed and regenerated? 34. Use Fact 24.2 to explain why O 2 reacts much faster with allylic CH (and benzylic CH) than with alkyl CH. What kind of CH bond might be even more O 2 -sensitive than allylic CH? 28. Combine the initiation steps in Model 7 and draw the net reaction. 29. How many propagation steps are there in the chain mechanism in Model 7? 30. Combine the propagation steps in Model 7 and draw the net reaction. 31. Complete the sentence: According to Model 7, the H and allyl groups bonded to O 2 in the allyl peroxide come from (the same/different) alkene(s). 32. Termination steps are reactions that destroy radicals needed for the chain to continue. Termination steps often involve radical recombination. a. Draw the product of each radical recombination. b. Describe how each radical recombination would affect the rate of allyl peroxide formation (raise/lower the rate).
10 Ch201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (Ch. 12) 10 c. A chain reaction can run indefinitely as long as there are available reactants. In practice, a chain might repeat 100 s or 1000 s of times before termination occurs. o Are the concentrations of short-lived chain-carrying radicals lower than, about the same as, or higher than, the concentrations of the reactants? o o Which kind of collision is likely to occur more often: radical-radical or radical-reactant? Which kind of reaction probably occurs more often: propagation step or termination step?
Organic Chemistry. Radical Reactions
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
The C-X bond gets longerand weakergoing down the periodic table.
 Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.8 - HALOALKANES, HALOGENATION AND RADICALS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3
 Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules
Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
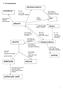 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
10. Alkyl Halides. What Is an Alkyl Halide. An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen
 10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
What are radicals? H. Cl. Chapter 10 Radical Reactions. Production of radicals. Reactions of radicals. Electronic structure of methyl radical
 What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions
 Grossman, CE 230 Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so
Grossman, CE 230 Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so
4.15 Halogenation of Alkanes RH + X 2 RX + HX
 4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A
 An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Introduction Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of radicals (also called free radicals) Radicals are highly reactive, short-lived species Single-barbed arrows are
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Introduction Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of radicals (also called free radicals) Radicals are highly reactive, short-lived species Single-barbed arrows are
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems 13.1 Introduction Allyl radical C 2 C C 2 C C C Allyl cation C 2 C C 2 C C C 1,3-Butadiene C 2 C C C 2 C C C C Molecules with delocalized π bonds are called conjugated unsaturated
Conjugated Unsaturated Systems 13.1 Introduction Allyl radical C 2 C C 2 C C C Allyl cation C 2 C C 2 C C C 1,3-Butadiene C 2 C C C 2 C C C C Molecules with delocalized π bonds are called conjugated unsaturated
dihalogenoalkane H 2, KOH alcoholic heat under reflux Elimination PCl 5, PBr 3, PI 3 Heat under reflux substitution KOH aqueous heat under reflux
 7. AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) 2, l 2 room temp Electrophilic addition KO aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7. AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) 2, l 2 room temp Electrophilic addition KO aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light. This is the overall reaction, but a more complex mixture of products is actually formed
 8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical
 C h a p t e r E l e v e n: Radical Reactions α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 11: Radical
C h a p t e r E l e v e n: Radical Reactions α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 11: Radical
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch Handouts 1
 Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more H atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms.
 aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
Study of Chemical Reactions
 Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
What is the major product of the following reaction?
 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
Química Orgânica I. Organic Reactions
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
3. A forward reaction has an activation energy of 50 kj and a H of 100 kj. The PE. diagram, which describes this reaction, is
 Kinetics Quiz 4 Potential Energy Diagrams 1. A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by A. Increasing the concentration of the reactant(s) B. Decreasing the concentration of the reactant(s) C. Increasing
Kinetics Quiz 4 Potential Energy Diagrams 1. A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by A. Increasing the concentration of the reactant(s) B. Decreasing the concentration of the reactant(s) C. Increasing
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions
 Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION
 REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
2. Hydrohalogenation: Propylene reacts with HBr to form 2-bromopropane.
 Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Lesmahagow High School CfE Higher Chemistry. Chemical Changes & Structure Controlling the Rate
 Lesmahagow High School CfE Higher Chemistry Chemical Changes & Structure Controlling the Rate E a Page 1 of 18 Learning Outcomes Controlling the Rate Circle a face to show how much understanding you have
Lesmahagow High School CfE Higher Chemistry Chemical Changes & Structure Controlling the Rate E a Page 1 of 18 Learning Outcomes Controlling the Rate Circle a face to show how much understanding you have
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Radical Reac)ons of Alkanes
 Radical Reac)ons of Alkanes Types of Steps in Reac)on Mechanisms Bond forma)on or breakage can be symmetrical or unsymmetrical Symmetrical- homoly)c Unsymmetrical- heteroly)c Indica)ng Steps in Mechanisms
Radical Reac)ons of Alkanes Types of Steps in Reac)on Mechanisms Bond forma)on or breakage can be symmetrical or unsymmetrical Symmetrical- homoly)c Unsymmetrical- heteroly)c Indica)ng Steps in Mechanisms
Chapter 13. Conjugated Unsaturated Systems. +,., - Allyl. What is a conjugated system? AllylicChlorination (High Temperature)
 What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
CH320/328 M Spring 2014
 CH320/328 M Spring 2014 HW Set #3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your
CH320/328 M Spring 2014 HW Set #3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your
Lecture 21 Organic Chemistry 1
 CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 21 Organic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 30, 2010 1 Self Test Question Ethanolysis of alkyl halide 1 gives ether 2 as one product; however, several
CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 21 Organic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 30, 2010 1 Self Test Question Ethanolysis of alkyl halide 1 gives ether 2 as one product; however, several
Rearrangement: a single reactant rearranges its
 Chapter 5: An overview of organic reactions 5.1 Kinds of organic reactions Even though there are hundreds of reactions to study, organic chemistry is governed by only a few key ideas that determine chemical
Chapter 5: An overview of organic reactions 5.1 Kinds of organic reactions Even though there are hundreds of reactions to study, organic chemistry is governed by only a few key ideas that determine chemical
HC- Kinetics and Thermodynamics Test Review Stations
 HC- Kinetics and Thermodynamics Test Review Stations Station 1- Collision Theory and Factors Affecting Reaction Rate 1. Explain the collision theory of reactions. 2. Fill out the following table to review
HC- Kinetics and Thermodynamics Test Review Stations Station 1- Collision Theory and Factors Affecting Reaction Rate 1. Explain the collision theory of reactions. 2. Fill out the following table to review
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Homework - Review of Chem 2310
 omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
Physical Properties: Structure:
 Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Loudon Chapter 17 Review: Allylic/Benzylic Reactivity
 Chapter 17 is all about reactions that happen at the position one away from an aromatic ring, or one away from a double bond. These are called the benzylic and allylic positions respectively. Benzyl and
Chapter 17 is all about reactions that happen at the position one away from an aromatic ring, or one away from a double bond. These are called the benzylic and allylic positions respectively. Benzyl and
1. Which statement is not true of nucleophillic substitution reactions?!
 Mock Exam 3 CH 235-2F Ch. 7, 8, 9, and 11 Multiple Choice: 1. Which statement is not true of nucleophillic substitution reactions? a. SN1 proceeds through a cation intermediate. b. SN2 occurs with inversion
Mock Exam 3 CH 235-2F Ch. 7, 8, 9, and 11 Multiple Choice: 1. Which statement is not true of nucleophillic substitution reactions? a. SN1 proceeds through a cation intermediate. b. SN2 occurs with inversion
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES Information taken from a presentation by: KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING General ALKANES members of a homologous series general formula is C n H 2n+2 for non-cyclic alkanes
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES Information taken from a presentation by: KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING General ALKANES members of a homologous series general formula is C n H 2n+2 for non-cyclic alkanes
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
Chapter 10 Free Radicals
 hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
REACTIONS OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: REACTIONS OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS 1. Predict the product(s) of Electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS): halogenation, sulfonation, nitration, Friedel- Crafts alkylation and
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: REACTIONS OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS 1. Predict the product(s) of Electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS): halogenation, sulfonation, nitration, Friedel- Crafts alkylation and
Organic Chemistry. Organic Reactions
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Organic Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Organic Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Bond length (pm) Bond strength (KJ/mol)
 hapter 10: Alkyl alides = F, l,, I Alkyl halide Aryl halide Vinyl halide 10.1 Naming alkyl halides- ead 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides Table 10.1 alomethane 3 -F 3 -l 3-3 -I Bond length (pm) 139 178 193
hapter 10: Alkyl alides = F, l,, I Alkyl halide Aryl halide Vinyl halide 10.1 Naming alkyl halides- ead 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides Table 10.1 alomethane 3 -F 3 -l 3-3 -I Bond length (pm) 139 178 193
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes
 Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
CH 3 Cl + Cl 2 CH 2 Cl 2 + HCl
 Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
10. Organohalides. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level. Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis
 OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
 Practice Questions : Chem 226 / Exam 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about benzene is correct?
Practice Questions : Chem 226 / Exam 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about benzene is correct?
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TOPICAL: Hydrocarbons Test 1
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TOPICAL: Hydrocarbons Test 1 Time: 22 Minutes* Number of Questions: 17 * The timing restrictions for the science topical tests are optional. If you are using this test for the sole purpose
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TOPICAL: Hydrocarbons Test 1 Time: 22 Minutes* Number of Questions: 17 * The timing restrictions for the science topical tests are optional. If you are using this test for the sole purpose
CEM 351 3rd EXAM/Version A Friday, November 21, :50 2:40 p.m. Room 138, Chemistry
 Name (print) Signature Student # Section Number CEM 351 3rd EXAM/Version A Friday, November 21, 2003 1:50 2:40 p.m. Room 138, Chemistry Key Grade? 1.(20 2.(20. 3.(20 4.(20 5.(20 6.(20 TTAL 100 Score Note:
Name (print) Signature Student # Section Number CEM 351 3rd EXAM/Version A Friday, November 21, 2003 1:50 2:40 p.m. Room 138, Chemistry Key Grade? 1.(20 2.(20. 3.(20 4.(20 5.(20 6.(20 TTAL 100 Score Note:
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
11/5/ Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Heats of Hydrogenation
 8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
Chapter 5. 3-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2. 2-Chloro-2-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-4-methylpentane
 hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University
 350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University Exam #4B, December 9, 2013 Professor T. Nalli Name General Instructions: Write your name in the space provided above and on the provided Scan-tron form.
350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University Exam #4B, December 9, 2013 Professor T. Nalli Name General Instructions: Write your name in the space provided above and on the provided Scan-tron form.
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY
 4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism - Aromatic rings typically undergo substitution, where an H is replaced with an electrophile (E+). - The rings do not typically undergo addition across
Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism - Aromatic rings typically undergo substitution, where an H is replaced with an electrophile (E+). - The rings do not typically undergo addition across
Chapter 6 and 7 Study Guide Reactions and Bonds
 Name_ Per. Block _ Multiple Choice: Chapter 6 and 7 Study Guide Reactions and Bonds 1. Copper is a good conductor of electricity because its electrons A. are positively charged B. are free to move and
Name_ Per. Block _ Multiple Choice: Chapter 6 and 7 Study Guide Reactions and Bonds 1. Copper is a good conductor of electricity because its electrons A. are positively charged B. are free to move and
Unit I: Reaction Kinetics Introduction:
 Chemistry 12 Unit I: Reaction Kinetics Introduction: Kinetics Definition: All reactions occur at different rates Examples: Slow Reactions Fast Reactions Chemists need to understand kinetics because sometimes
Chemistry 12 Unit I: Reaction Kinetics Introduction: Kinetics Definition: All reactions occur at different rates Examples: Slow Reactions Fast Reactions Chemists need to understand kinetics because sometimes
Chapter 10. BrCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CCH 2 Br CH 3. CH 3 CCH 2 CH 2 Cl CH 3 CHCH 2 CH 2 CHCH Give IUPAC names for the following alkyl halides:
 hapter 10 10.1 Give IUPA names for the following alkyl halides: (a), 3 2 2 2 I 1-iodobutane 3 (b), 3 2 2 l 1-chloro-3-methylbutane (c), 3 2 2 2 2 3 1,5-Dibromo-2,2-dimethylpentane 3 3 2 2 l (d), l 1,3-Dichloro-3-methylbutane
hapter 10 10.1 Give IUPA names for the following alkyl halides: (a), 3 2 2 2 I 1-iodobutane 3 (b), 3 2 2 l 1-chloro-3-methylbutane (c), 3 2 2 2 2 3 1,5-Dibromo-2,2-dimethylpentane 3 3 2 2 l (d), l 1,3-Dichloro-3-methylbutane
11/26/ Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds
 9.5 Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds The general concept of aromaticity can be extended to include polycyclic aromatic compounds Benzo[a]pyrene is one of the cancer-causing substances found in tobacco smoke
9.5 Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds The general concept of aromaticity can be extended to include polycyclic aromatic compounds Benzo[a]pyrene is one of the cancer-causing substances found in tobacco smoke
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
BSc. II 3 rd Semester. Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1
 BSc. II 3 rd Semester Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1 Introduction to Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are organic molecules containing a halogen atom bonded to an
BSc. II 3 rd Semester Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1 Introduction to Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are organic molecules containing a halogen atom bonded to an
Kinetics. Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 14 Yonsei University In kinetics we study the rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed at which reactions occur, kinetics also sheds light
Lecture Presentation Chapter 14 Yonsei University In kinetics we study the rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed at which reactions occur, kinetics also sheds light
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions Chemical Equation --> is a representation of a chemical reaction in which the reactants and products are expressed as formulas Reactants --> substances that undergo change
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions Chemical Equation --> is a representation of a chemical reaction in which the reactants and products are expressed as formulas Reactants --> substances that undergo change
Unit 2. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips. 1 (a) heat energy change at constant pressure
 (a) heat energy change at constant pressure This is in the spec but not so well known. Learn it. (b) N 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) N 2 O(g) (c) (i) D = (bonds broken) (bonds made) = ½(945) + (3/2)(59) 3(278) = 23
(a) heat energy change at constant pressure This is in the spec but not so well known. Learn it. (b) N 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) N 2 O(g) (c) (i) D = (bonds broken) (bonds made) = ½(945) + (3/2)(59) 3(278) = 23
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide.
 Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry. Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School
 Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
Rates, Temperature and Potential Energy Diagrams Worksheet
 SCH4U1 ER10 Name: Date: Rates, Temperature and Potential Energy Diagrams Worksheet Part 1: 1. Use the potential energy diagram shown to the right to answer the following: a. Label the axis. y axis is potential
SCH4U1 ER10 Name: Date: Rates, Temperature and Potential Energy Diagrams Worksheet Part 1: 1. Use the potential energy diagram shown to the right to answer the following: a. Label the axis. y axis is potential
Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine?
 Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine? A B C D C 4 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 Cl + C 3 + Cl 2 C 3 Cl + Cl C 3 Cl + Cl C 2 Cl + Cl (Total 1
Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine? A B C D C 4 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 Cl + C 3 + Cl 2 C 3 Cl + Cl C 3 Cl + Cl C 2 Cl + Cl (Total 1
12/27/2010. Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Some Arrow-Pushing Guidelines (Section 1.14) 1. Arrows follow electron movement.
 Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 1 Notes 1 Note: The headers and associated chapters don t actually jive with the textbook we are using this summer. But otherwise this highlights a lot of the chemistry from Organic
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 1 Notes 1 Note: The headers and associated chapters don t actually jive with the textbook we are using this summer. But otherwise this highlights a lot of the chemistry from Organic
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307 CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES R. Boikess II. Principles of Organic Reactions 1. Chemical reactions are the result of bond breaking and bond making. a. Most (but not all) bond making and
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307 CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES R. Boikess II. Principles of Organic Reactions 1. Chemical reactions are the result of bond breaking and bond making. a. Most (but not all) bond making and
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
trans-cyclooctene 4-fluoro-1-butanol 2-cyclohexenol 4. (5 pts) Provide structural formula for each of the following molecules: Br OH Cl OH
 CEMISTRY 313-01 MIDTERM # 2 answer key March 12, 2009 Statistics: Average: 72 pts (72%); ighest: 98 pts (98%); Lowest: 21 pts (21%) umber of students performing at or above average: 22 (50%) umber of students
CEMISTRY 313-01 MIDTERM # 2 answer key March 12, 2009 Statistics: Average: 72 pts (72%); ighest: 98 pts (98%); Lowest: 21 pts (21%) umber of students performing at or above average: 22 (50%) umber of students
Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat #
 Test 4 Name Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat # Part 1. Multiple Choice. Choose the one best answer, and clearly mark that answer
Test 4 Name Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat # Part 1. Multiple Choice. Choose the one best answer, and clearly mark that answer
Organic Chemistry CHM 224
 rganic Chemistry CHM 224 Exam I Review Questions This set of questions is a compilation of old exams and additional questions, and does not represent the typical length of an exam - this is WAY longer!
rganic Chemistry CHM 224 Exam I Review Questions This set of questions is a compilation of old exams and additional questions, and does not represent the typical length of an exam - this is WAY longer!
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems. Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Organic Chemistry Worksheets
 Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
17.3 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC ANIONS
 798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
Allyl radicals are especially stable due to resonance ( and double bond switch places):
 Ch 10 Alkyl Halides Nomenclature Rules The parent is the longest alkyl chain or ring. The #1 C for a chain is at the end that is nearest to the first substituent. The #1 C for a ring possesses the first
Ch 10 Alkyl Halides Nomenclature Rules The parent is the longest alkyl chain or ring. The #1 C for a chain is at the end that is nearest to the first substituent. The #1 C for a ring possesses the first
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
H C C C C H. Secondary halogenoalkane Two carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen
 3.3 alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; omo for ; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically lassifying oalkanes
3.3 alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; omo for ; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically lassifying oalkanes
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
Ch.10 Alkyl Halides. Organic halides are valuable as industrial solvents, inhaled anesthetics in medicine, refrigerants, and pesticides.
 Ch.10 Alkyl alides Organic halides are valuable as industrial solvents, inhaled anesthetics in medicine, refrigerants, and pesticides. F F C C F Trichloroethylene (a solvent) alothane (an inhaled anesthetic)
Ch.10 Alkyl alides Organic halides are valuable as industrial solvents, inhaled anesthetics in medicine, refrigerants, and pesticides. F F C C F Trichloroethylene (a solvent) alothane (an inhaled anesthetic)
