Figure 2: Mean diurnal flux ratios (symbols) and box plots (showing interquartile range (IQR) and whiskers for values within 1.5IQR) for four of the
|
|
|
- Hugo Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Loridan T & CSB Grimmond (2012) Characterization of energy flux partitioning in urban environments: links with surface seasonal properties Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology 51, doi: /JAMC-D Figure 1: Mean midday (±3 h around solar noon) Bowen ratio (Q H /Q E ) as a function of vegetation fraction. LOWESS (dashed line) regression performed using summer months and short term datasets only (i.e. only symbols). See Table 1 for site codes. The fluxes have had the Q F contribution accounted for (see section 2). Note the color scheme for numbers is reversed for Mb06 (southern hemisphere).
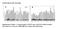
2 Figure 2: Mean diurnal flux ratios (symbols) and box plots (showing interquartile range (IQR) and whiskers for values within 1.5IQR) for four of the short term datasets. Positive (negative) values of Q H, Q E and Q indicate energy lost (gained) by the surface. The opposite is true for Q S. See Table 1 and text for site codes. Plots are ordered by decreasing mean midday latent heat flux ratio (computed at ±3 h around solar noon, see Table 2).
3 Figure 3: Geometry of the generic urban unit in the active surface model: (a) vertical (cross section) and (b) plan view. Figure 4: (a) impact of canyon orientation (θ C ) and solar azimuth angle (θ S ) on the street shading patterns (Kusaka, personal communication); where w is the normalized mean street width and l shadow the normalized portion of the street that is shaded. (b) shading patterns (cross sections) for roads and (c) walls. See text for notation.
4 Figure 5: Fraction of total, roof, road and wall materials that are active for each hour of DOY 172 in Łódź for different canyon orientation (π/8 θ C π) and for the overall average (θ C = avg; upper left).
5 Figure 6: Q /Q mean daytime (3 h around solar noon) ratio as a function of the mean midday χ tot value for all short term sites and two-month subsets of the yearly sites. LOWESS regression shown by (red) dashed line. Error bars show ± 1 standard deviation. See text for details. The non-linear regression (black curve) is eqn (25).
6 Figure 7: (a) Q /Q, (b, c, d) Q S / Q, mean (a, b) midday, (c) morning (2-3 h before solar noon) and (d) afternoon (2-3 h after solar noon) ratios as a function of the χ built values averaged over the same periods. For (b) the non-linear regression eqn is (26).
7 Figure 8: Mean midday ratios of (a) Q E / Q and (b) Q H / Q as a function of the mean midday (a) χ veg and (b) χ tot values. The non-linear regression (thick black line) for (a) is (27). For key see Figure 7. Figure 9: Mean midday (±3 h around solar noon) Bowen ratio (Q H /Q E ) as a function of midday χ veg value. The LOWESS regression is performed on all points (unlike Fig. 1). The non-linear regression (thick black line) is (29).
8 Figure 10: Theoretical flux ratio active index diagrams Figure 11: Mean midday flux ratios (capital letters) and indices (lower case and x-axis) of the four urban zones to characterize energy partitioning (UZE) (see text for class definition): (1) low active surface (winter); (2) most vegetated: Low Density ; (3) more urban: Medium Density and (4) most urban: High Density.
9 Code REF Ar93* GO95 Ar94* GR96 He08 VE08 He09 VE08 Ok03 GR04b (WH) Ch92* GR94 Vs92* GO99 Sg94 GR96 S91u GR93 Mb06 CO07 C95u* KG97 Mi95 NE99 Ma01 GR04a Vl92* GO99 Me93 OK99 Ou03 OF05 Łó01 OF06 Łó02 OF06 Tk01 MK04 Site Lat / lon Obs period Arcadia CA, USA Arcadia CA, USA Helsinki, Finland Helsinki, Finland Oklahoma City, OK, USA (wood house) Chicago, IL, USA Vancouver, BC, Canada San Gabriel CA, USA Sacramento, CA, USA Melbourne, Australia Chicago, IL, USA Miami, FL, USA Marseille, France Vancouver, BC, Canada Mexico City, Mexico Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso Łódź, Poland Łódź, Poland Tokyo, Japan N, W N, W N, E N, E N, W N, W N, W N, W N, W S, E N, W N, W N, 5 23 E N, W N, W N, 1 31 W N, E N, E N, E Jul-Aug 1993 Jul 1994 Jan-Dec 2008 Jan-Dec 2009 Jun-Aug 2003 Jul 1992 Jul/Sep 1992 Jul 1994 Aug 1991 Dec-Dec 2006 Jun-Aug 1995 May-Jun 1995 Jun-Jul 2001 Aug 1992 Dec 1993 Feb 2003 Mar-Dec 2001 Jan-Dec 2002 May 01- April 02 f urb f bld f imp Z R (m) W road (m) W roof (m) f grass Leaf-on Leaf-off (DOY) / / / / /144-81/ / / / / / /338-36/ / / / / / / /144-81/ /144-81/ / /330 N Day / Night Table 1: Characteristics of observational datasets used: location (lat/lon); observation periods; measurement footprints: plan area fractions urban (f urb ), building (f bld ) and impervious (f imp ); morphology: mean roof height (Z R ), road width (W road ) and roof width (W roof ); vegetation characteristic: plan area fraction vegetated (f veg =1-f urb ), covered by grass (f grass *f veg ) or trees/shrub (f veg *(1-f grass ); eq. 20), leaf-on (start /stop) - leaf-off (start/stop) periods (day of year); number of hours (N) analysed for day and night; reference for study details: GO95 (Grimmond and Oke 1995), GR96 (Grimmond et al. 1996), GR94 (Grimmond et al. 1994), KG97 (King and Grimmond 1997), GR04a (Grimmond et al. 2004a), OK99 (Oke et al. 1999), NE99 (Newton 1999), GR04b (Grimmond et al. 2004b), OF05 (Offerle et al. 2005), GO99 (Grimmond and Oke 1999), GR93 (Grimmond et al. 1993), CO07 (Coutts et al. 2007a,b), VE08 (Vesala et al. 2008), OF06 (Offerle et al. 2006), MK04 (Moriwaki and Kanda, 2004). *Measurement sites are in the same city but at different locations. Note that sites are grouped by classes (see section 5) with yearly sites classified according to the summer data.
10 Mean midday (±3 h around solar noon) Mean midnight (12 h after solar noon) Site Q Ratios Q Ratios Code (W m -2 ) Q Q S Q E Q H Q E +Q H Q F χ tot χ built χ veg (W m -2 ) Q Q S Q E Q H Q F (a) Short term sites, ordered by increasing day time Q E + Q H Me Ou Vl Mi Sg Ok S91u Vs Ar Ar Ch C95u Ma (b) Łódź 2002 Łó02_JF Łó02_MA Łó02_MJ Łó02_JA Łó02_SO Łó02_ND (c) Helsinki 2009 He09_JF He09_MA He09_MJ He09_JA He09_SO He09_ND (d) Melbourne 2006 Mb06_JA Mb06_SO Mb06_ND Mb06_JF Mb06_MA Mb06_MJ (e) Tokyo 2001 TK01_JF TK01_MA TK01_MJ TK01_JA TK01_SO TK01_ND Table 2: Mean midday (±3 solar noon) and midnight (±3 12 h after solar noon) values of Q, flux ratios (Q / Q, Q S / Q, Q E / Q, Q H / Q, Q F / Q ) and mean midday active surface indices (χ tot, χ built, χ veg ) for each site. Long term sites are separated in two-month subsets (JF: January- February; MA: March-April; MJ: May-June; JA: July-August; SO: September-October; ND: November- December) and only one year is shown for Łódź and Helsinki campaigns (Łó02 and HEe9). (b-e): the
11 periods with largest radiative forcing (Q ) are shown in bold for comparison with (a). See text for details. SITE BSPR BSPA ALLS f urb Z R W roof W road Mean daytime Q (W m -2 ) χ tot χ built χ veg Urban class (UZE) 4: most urban: High Density 3: more urban: Medium Density 2: most vegetated: Low Density Q / Q (P/O) / / / Q S / Q (P/O) / / / Q E / Q (P/O) / / / Q H / Q E (P/O) / / / Mean daytime Q* (P/O) (W m -2 ) / / / Mean daytime Q E (P/O) ( W m -2 ) 67.8 / / / Mean daytime Q S (P/O) (W m -2 ) / / / Mean daytime Q H (P [eq. 29] /O) ( W m -2 ) / / / Mean daytime Q H (P [eq. 28]) ( W m -2 ) Table 3: Evaluation of the FRAISE predictive relations (eq and 24) with the Basel Urban Boundary Layer Experiment (BUBBLE, Christen and Vogt, 2004; Rotach et al. 2004) data. Note the ratios correspond to those presented in eq. 5 while the flux estimates include the Q F contribution. Averaging windows differs from the ones used in Christen and Vogt (2004, their Table 5). P/O: Predicted/ Observed
Urban micrometeorological flux observations and surface characterization State of art observational techniques and use of data in urban modeling"
 Urban micrometeorological flux observations and surface characterization State of art observational techniques and use of data in urban modeling" Sue Grimmond 1,2 1 Atmospheric Science Program, Geography,
Urban micrometeorological flux observations and surface characterization State of art observational techniques and use of data in urban modeling" Sue Grimmond 1,2 1 Atmospheric Science Program, Geography,
Multi site evaluation of an urban landsurface model: intra urban heterogeneity, seasonality and parameter complexity requirements
 Multi site evaluation of an urban landsurface model: intra urban heterogeneity, seasonality and parameter complexity requirements Article Published Version Loridan, T. and Grimmond, C.S.B. (2012) Multi
Multi site evaluation of an urban landsurface model: intra urban heterogeneity, seasonality and parameter complexity requirements Article Published Version Loridan, T. and Grimmond, C.S.B. (2012) Multi
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
MODELING URBAN THERMAL ANISOTROPY
 MODELING URBAN THERMAL ANISOTROPY J. A. Voogt a, *, E. S. Krayenhoff a a Department of Geography, University of Western Ontario, London ON N6A 5C2 Canada -javoogt@uwo.ca KEY WORDS: surface temperature,
MODELING URBAN THERMAL ANISOTROPY J. A. Voogt a, *, E. S. Krayenhoff a a Department of Geography, University of Western Ontario, London ON N6A 5C2 Canada -javoogt@uwo.ca KEY WORDS: surface temperature,
Urban Energy Balance Obtained from the Comprehensive Outdoor Scale Model Experiment. Part I: Basic Features of the Surface Energy Balance
 VOLUME 49 J O U R N A L O F A P P L I E D M E T E O R O L O G Y A N D C L I M A T O L O G Y JULY 2010 Urban Energy Balance Obtained from the Comprehensive Outdoor Scale Model Experiment. Part I: Basic
VOLUME 49 J O U R N A L O F A P P L I E D M E T E O R O L O G Y A N D C L I M A T O L O G Y JULY 2010 Urban Energy Balance Obtained from the Comprehensive Outdoor Scale Model Experiment. Part I: Basic
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER)
 L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities
 WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and 2001-2002 Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities Phoenix Tucson Flagstaff Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 October 0.7 0.0
WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and 2001-2002 Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities Phoenix Tucson Flagstaff Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 October 0.7 0.0
Motions of the Sun Model Exploration
 Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
Global Climates. Name Date
 Global Climates Name Date No investigation of the atmosphere is complete without examining the global distribution of the major atmospheric elements and the impact that humans have on weather and climate.
Global Climates Name Date No investigation of the atmosphere is complete without examining the global distribution of the major atmospheric elements and the impact that humans have on weather and climate.
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
The impact of urban geometry on the radiant environment in outdoor spaces
 ICUC9 9 th International Conference on Urban Climate 20 th -24 th July 2015, Toulouse, France The impact of urban geometry on the radiant environment in outdoor spaces Christina Chatzipoulka*, Marialena
ICUC9 9 th International Conference on Urban Climate 20 th -24 th July 2015, Toulouse, France The impact of urban geometry on the radiant environment in outdoor spaces Christina Chatzipoulka*, Marialena
March 21. Observer located at 42 N. Horizon
 March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
The Climate of Bryan County
 The Climate of Bryan County Bryan County is part of the Crosstimbers throughout most of the county. The extreme eastern portions of Bryan County are part of the Cypress Swamp and Forest. Average annual
The Climate of Bryan County Bryan County is part of the Crosstimbers throughout most of the county. The extreme eastern portions of Bryan County are part of the Cypress Swamp and Forest. Average annual
Causes of high PM 10 values measured in Denmark in 2006
 Causes of high PM 1 values measured in Denmark in 26 Peter Wåhlin and Finn Palmgren Department of Atmospheric Environment National Environmental Research Institute Århus University Denmark Prepared 2 October
Causes of high PM 1 values measured in Denmark in 26 Peter Wåhlin and Finn Palmgren Department of Atmospheric Environment National Environmental Research Institute Århus University Denmark Prepared 2 October
Overview and first results of the Montreal Urban Snow Experiment (MUSE) 2005
 Overview and first results of the Montreal Urban Snow Experiment (MUSE) 2005 A. LEMONSU 1 Environment Canada, Meteorological Research Division, Dorval, Canada S. BÉLAIR Environment Canada, Meteorological
Overview and first results of the Montreal Urban Snow Experiment (MUSE) 2005 A. LEMONSU 1 Environment Canada, Meteorological Research Division, Dorval, Canada S. BÉLAIR Environment Canada, Meteorological
Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia
 Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Meiry Sakamoto Uiversidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil Colombia Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Convective System (CS)
Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Meiry Sakamoto Uiversidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil Colombia Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Convective System (CS)
TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET
 TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET Activity Description: Students will use a data table to make a graph for the length of day and average high temperature in Utah. They will then answer questions based
TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET Activity Description: Students will use a data table to make a graph for the length of day and average high temperature in Utah. They will then answer questions based
Calculations Equation of Time. EQUATION OF TIME = apparent solar time - mean solar time
 Calculations Equation of Time APPARENT SOLAR TIME is the time that is shown on sundials. A MEAN SOLAR DAY is a constant 24 hours every day of the year. Apparent solar days are measured from noon one day
Calculations Equation of Time APPARENT SOLAR TIME is the time that is shown on sundials. A MEAN SOLAR DAY is a constant 24 hours every day of the year. Apparent solar days are measured from noon one day
The Climate of Marshall County
 The Climate of Marshall County Marshall County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
The Climate of Marshall County Marshall County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
Practice Seasons Moon Quiz
 1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
The Climate of Grady County
 The Climate of Grady County Grady County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 33 inches in northern
The Climate of Grady County Grady County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 33 inches in northern
The Climate of Pontotoc County
 The Climate of Pontotoc County Pontotoc County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeast Oklahoma. Average
The Climate of Pontotoc County Pontotoc County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeast Oklahoma. Average
What Is the Relationship Between Earth s Tilt and the Seasons?
 Learning Set 2 Why Are There Differences in Temperature? Review Images and Graphics While reading about Earth s tilt and the seasons, pay particular attention to the graphics included. How do they help
Learning Set 2 Why Are There Differences in Temperature? Review Images and Graphics While reading about Earth s tilt and the seasons, pay particular attention to the graphics included. How do they help
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
The Climate of Payne County
 The Climate of Payne County Payne County is part of the Central Great Plains in the west, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Payne County is also part of the Crosstimbers in the
The Climate of Payne County Payne County is part of the Central Great Plains in the west, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Payne County is also part of the Crosstimbers in the
The Climate of Kiowa County
 The Climate of Kiowa County Kiowa County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 24 inches in northwestern
The Climate of Kiowa County Kiowa County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 24 inches in northwestern
The Climate of Haskell County
 The Climate of Haskell County Haskell County is part of the Hardwood Forest. The Hardwood Forest is characterized by its irregular landscape and the largest lake in Oklahoma, Lake Eufaula. Average annual
The Climate of Haskell County Haskell County is part of the Hardwood Forest. The Hardwood Forest is characterized by its irregular landscape and the largest lake in Oklahoma, Lake Eufaula. Average annual
The Climate of Seminole County
 The Climate of Seminole County Seminole County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
The Climate of Seminole County Seminole County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
Project No India Basin Shadow Study San Francisco, California, USA
 Project No. 432301 India Basin Shadow Study San Francisco, California, USA Numerical Modelling Studies 04 th June 2018 For Build Inc. Report Title: India Basin Shadow Study San Francisco, California, USA
Project No. 432301 India Basin Shadow Study San Francisco, California, USA Numerical Modelling Studies 04 th June 2018 For Build Inc. Report Title: India Basin Shadow Study San Francisco, California, USA
The Climate of Murray County
 The Climate of Murray County Murray County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition between prairies and the mountains of southeastern Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from
The Climate of Murray County Murray County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition between prairies and the mountains of southeastern Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from
Evaluation of the coupled COSMO-CLM/DCEP model with observations from BUBBLE
 QuarterlyJournalof theroyalmeteorologicalsociety Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 140: 2465 2483, October 2014 B DOI:10.1002/qj.2311 Evaluation of the coupled COSMO-CLM/ model with observations from BUBBLE S. Schubert*
QuarterlyJournalof theroyalmeteorologicalsociety Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 140: 2465 2483, October 2014 B DOI:10.1002/qj.2311 Evaluation of the coupled COSMO-CLM/ model with observations from BUBBLE S. Schubert*
1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture.
 Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
The Climate of Texas County
 The Climate of Texas County Texas County is part of the Western High Plains in the north and west and the Southwestern Tablelands in the east. The Western High Plains are characterized by abundant cropland
The Climate of Texas County Texas County is part of the Western High Plains in the north and west and the Southwestern Tablelands in the east. The Western High Plains are characterized by abundant cropland
Seasons Quiz Please Do Not Write on this Paper Obrigado
 Seasons Quiz Please Do Not Write on this Paper Obrigado Use this diagram of the sun and Earth's path around the sun to answer the next two questions. The N indicates North and Earth is traveling from A
Seasons Quiz Please Do Not Write on this Paper Obrigado Use this diagram of the sun and Earth's path around the sun to answer the next two questions. The N indicates North and Earth is traveling from A
Estimation of Hourly Solar Radiation on Horizontal and Inclined Surfaces in Western Himalayas
 Smart Grid and Renewable Energy, 2011, 2, 45-55 doi:10.4236/sgre.2011.21006 Published Online February 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/sgre) 45 Estimation of Hourly Solar Radiation on Horizontal and
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy, 2011, 2, 45-55 doi:10.4236/sgre.2011.21006 Published Online February 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/sgre) 45 Estimation of Hourly Solar Radiation on Horizontal and
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018
 Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
dt urb (z)/dt = M(z) (T rur (z) T urb (z)) / x (1)
 5.5 SENSITIVITY TESTING OF AN URBAN SURFACE SCHEME COUPLED TO A 1-D BOUNDARY LAYER MODEL E. Scott Krayenhoff * and James A. Voogt University of Western Ontario, London ON Canada 1. INTRODUCTION Many applications
5.5 SENSITIVITY TESTING OF AN URBAN SURFACE SCHEME COUPLED TO A 1-D BOUNDARY LAYER MODEL E. Scott Krayenhoff * and James A. Voogt University of Western Ontario, London ON Canada 1. INTRODUCTION Many applications
Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed
 Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed David Bosch USDA-ARS, Tifton, GA Jeff Arnold ARS Temple, TX and Peter Allen Baylor University, TX SEWRU Objectives 1. Project changes
Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed David Bosch USDA-ARS, Tifton, GA Jeff Arnold ARS Temple, TX and Peter Allen Baylor University, TX SEWRU Objectives 1. Project changes
P7.7 A CLIMATOLOGICAL STUDY OF CLOUD TO GROUND LIGHTNING STRIKES IN THE VICINITY OF KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLORIDA
 P7.7 A CLIMATOLOGICAL STUDY OF CLOUD TO GROUND LIGHTNING STRIKES IN THE VICINITY OF KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLORIDA K. Lee Burns* Raytheon, Huntsville, Alabama Ryan K. Decker NASA, Marshall Space Flight
P7.7 A CLIMATOLOGICAL STUDY OF CLOUD TO GROUND LIGHTNING STRIKES IN THE VICINITY OF KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLORIDA K. Lee Burns* Raytheon, Huntsville, Alabama Ryan K. Decker NASA, Marshall Space Flight
1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude
 1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude There are many opportunities for making observations of shadows cast with a vertical stick and the Sun. Observations
1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude There are many opportunities for making observations of shadows cast with a vertical stick and the Sun. Observations
NATIONAL SPORT SCHOOL
 NATIONAL SPORT SCHOOL Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2016 Level 7-8 FORM 3 Geography Option TIME: 1h 30min Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Max. Mark Global Mark Mark DO NOT WRITE ABOVE THIS LINE Name:
NATIONAL SPORT SCHOOL Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2016 Level 7-8 FORM 3 Geography Option TIME: 1h 30min Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Max. Mark Global Mark Mark DO NOT WRITE ABOVE THIS LINE Name:
Exercise 6. Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. Introduction to the importance of solar panel orientation DISCUSSION
 Exercise 6 Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will understand how the solar illumination at any location on Earth varies over the course of a year. You
Exercise 6 Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will understand how the solar illumination at any location on Earth varies over the course of a year. You
Which graph best shows the relationship between intensity of insolation and position on the Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
 1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
b. So at 12:00 p.m., are the shadows pointing in the direction you predicted? If they are not, you must explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Section 1: Overhang. Sizing an Overhang
 Section 1: Overhang A horizontal overhang is a straightforward method for shading solar glazing in summer. Passive heating strategies call for major glazed areas (solar glazing) in a building to be oriented
Section 1: Overhang A horizontal overhang is a straightforward method for shading solar glazing in summer. Passive heating strategies call for major glazed areas (solar glazing) in a building to be oriented
Sunlight and its Properties Part I. EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz
 Sunlight and its Properties Part I EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz The Sun a Thermonuclear Furnace The sun is a hot sphere of gas whose internal temperatures reach over 20 million deg. K. Nuclear fusion reaction
Sunlight and its Properties Part I EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz The Sun a Thermonuclear Furnace The sun is a hot sphere of gas whose internal temperatures reach over 20 million deg. K. Nuclear fusion reaction
TEMPERATURE AND PRECIPITATION CHANGES IN TÂRGU- MURES (ROMANIA) FROM PERIOD
 TEMPERATURE AND PRECIPITATION CHANGES IN TÂRGU- MURES (ROMANIA) FROM PERIOD 1951-2010 O.RUSZ 1 ABSTRACT. Temperature and precipitation changes in Târgu Mures (Romania) from period 1951-2010. The analysis
TEMPERATURE AND PRECIPITATION CHANGES IN TÂRGU- MURES (ROMANIA) FROM PERIOD 1951-2010 O.RUSZ 1 ABSTRACT. Temperature and precipitation changes in Târgu Mures (Romania) from period 1951-2010. The analysis
Champaign-Urbana 1998 Annual Weather Summary
 Champaign-Urbana 1998 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY Audrey Bryan, Weather Observer 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sparc.sws.uiuc.edu The development of the El Nìno
Champaign-Urbana 1998 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY Audrey Bryan, Weather Observer 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sparc.sws.uiuc.edu The development of the El Nìno
Safety effects of lower speed limits during winter months
 Safety effects of lower speed limits during winter months Jaakko Klang Traffic Safety Engineer Centres for Economic Development, Transport and the Environment Finland 13.9.2018 1 1. Finland 13.9.2018 2
Safety effects of lower speed limits during winter months Jaakko Klang Traffic Safety Engineer Centres for Economic Development, Transport and the Environment Finland 13.9.2018 1 1. Finland 13.9.2018 2
Sierra Weather and Climate Update
 Sierra Weather and Climate Update 2014-15 Kelly Redmond Western Regional Climate Center Desert Research Institute Reno Nevada Yosemite Hydroclimate Workshop Yosemite Valley, 2015 October 8-9 Percent of
Sierra Weather and Climate Update 2014-15 Kelly Redmond Western Regional Climate Center Desert Research Institute Reno Nevada Yosemite Hydroclimate Workshop Yosemite Valley, 2015 October 8-9 Percent of
Champaign-Urbana 2001 Annual Weather Summary
 Champaign-Urbana 2001 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer January: After a cold and snowy December,
Champaign-Urbana 2001 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer January: After a cold and snowy December,
DROUGHT IN MAINLAND PORTUGAL
 DROUGHT IN MAINLAND Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior Instituto de Meteorologia, I. P. Rua C Aeroporto de Lisboa Tel.: (351) 21 844 7000 e-mail:informacoes@meteo.pt 1749-077 Lisboa Portugal
DROUGHT IN MAINLAND Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior Instituto de Meteorologia, I. P. Rua C Aeroporto de Lisboa Tel.: (351) 21 844 7000 e-mail:informacoes@meteo.pt 1749-077 Lisboa Portugal
LAB 3: THE SUN AND CLIMATE NAME: LAB PARTNER(S):
 GEOG 101L PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY LAB SAN DIEGO CITY COLLEGE SELKIN 1 LAB 3: THE SUN AND CLIMATE NAME: LAB PARTNER(S): The main objective of today s lab is for you to be able to visualize the sun s position
GEOG 101L PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY LAB SAN DIEGO CITY COLLEGE SELKIN 1 LAB 3: THE SUN AND CLIMATE NAME: LAB PARTNER(S): The main objective of today s lab is for you to be able to visualize the sun s position
Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model
 Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model Gabriella Zsebeházi Gabriella Zsebeházi and Gabriella Szépszó Hungarian Meteorological Service,
Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model Gabriella Zsebeházi Gabriella Zsebeházi and Gabriella Szépszó Hungarian Meteorological Service,
Local scale urban meteorological parameterization scheme (LUMPS): longwave radiation parameterization and seasonality related developments
 Local scale urban meteorological parameterization scheme (LUMPS): longwave radiation parameterization and seasonality related developments Article Published Version Loridan, T., Grimmond, C.S.B., Offerle,
Local scale urban meteorological parameterization scheme (LUMPS): longwave radiation parameterization and seasonality related developments Article Published Version Loridan, T., Grimmond, C.S.B., Offerle,
Reason for the Seasons Workbook
 Name Reason for the Seasons Workbook Clipart from the Florida Center for Instructional Technology (FCIT) Table of Contents What Causes the Seasons Factsheet and Activity............. 1 Angle of Light Rays
Name Reason for the Seasons Workbook Clipart from the Florida Center for Instructional Technology (FCIT) Table of Contents What Causes the Seasons Factsheet and Activity............. 1 Angle of Light Rays
Champaign-Urbana 2000 Annual Weather Summary
 Champaign-Urbana 2000 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer January: January started on a mild note,
Champaign-Urbana 2000 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer January: January started on a mild note,
Which Earth latitude receives the greatest intensity of insolation when Earth is at the position shown in the diagram? A) 0 B) 23 N C) 55 N D) 90 N
 1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
drinking straw, protractor, string, and rock. observer on Earth. Sun across the sky on March 21 as seen by an
 1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS. Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, Helsinki
 MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, 00101 Helsinki INTRODUCTION Urban heat islands have been suspected as being partially
MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, 00101 Helsinki INTRODUCTION Urban heat islands have been suspected as being partially
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, Anne Green / Richard Thompson
 Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, 2006 Anne Green / Richard Thompson http://www.physics.usyd.edu.au/ag/agschome.htm Course Coordinator: Mike Wheatland Course Goals Evaluate & interpret information,
Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, 2006 Anne Green / Richard Thompson http://www.physics.usyd.edu.au/ag/agschome.htm Course Coordinator: Mike Wheatland Course Goals Evaluate & interpret information,
The Arctic Energy Budget
 The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
Memo. I. Executive Summary. II. ALERT Data Source. III. General System-Wide Reporting Summary. Date: January 26, 2009 To: From: Subject:
 Memo Date: January 26, 2009 To: From: Subject: Kevin Stewart Markus Ritsch 2010 Annual Legacy ALERT Data Analysis Summary Report I. Executive Summary The Urban Drainage and Flood Control District (District)
Memo Date: January 26, 2009 To: From: Subject: Kevin Stewart Markus Ritsch 2010 Annual Legacy ALERT Data Analysis Summary Report I. Executive Summary The Urban Drainage and Flood Control District (District)
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: , Volume 2, Issue 4, May 2014
 Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: 3583, Volume, Issue 4, May 14 A STUDY OF INVERSIONS AND ISOTHERMALS OF AIR POLLUTION DISPERSION DR.V.LAKSHMANARAO DR. K. SAI LAKSHMI P. SATISH Assistant Professor(c), Dept. of
Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: 3583, Volume, Issue 4, May 14 A STUDY OF INVERSIONS AND ISOTHERMALS OF AIR POLLUTION DISPERSION DR.V.LAKSHMANARAO DR. K. SAI LAKSHMI P. SATISH Assistant Professor(c), Dept. of
P7: Limiting Factors in Ecosystems
 P7: Limiting Factors in Ecosystems Purpose To understand that physical factors temperature and precipitation limit the growth of vegetative ecosystems Overview Students correlate graphs of vegetation vigor
P7: Limiting Factors in Ecosystems Purpose To understand that physical factors temperature and precipitation limit the growth of vegetative ecosystems Overview Students correlate graphs of vegetation vigor
Variability and trends in daily minimum and maximum temperatures and in diurnal temperature range in Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia
 Variability and trends in daily minimum and maximum temperatures and in diurnal temperature range in Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia Jaak Jaagus Dept. of Geography, University of Tartu Agrita Briede Dept.
Variability and trends in daily minimum and maximum temperatures and in diurnal temperature range in Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia Jaak Jaagus Dept. of Geography, University of Tartu Agrita Briede Dept.
Supplementary Figure 1 Annual number of F0-F5 (grey) and F2-F5 (black) tornado observations over 30 years ( ) for Canada and United States.
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Annual number of F0-F5 (grey) and F2-F5 (black) tornado observations over 30 years (1980-2009) for Canada and United States. Supplementary Figure 2 Differences
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Annual number of F0-F5 (grey) and F2-F5 (black) tornado observations over 30 years (1980-2009) for Canada and United States. Supplementary Figure 2 Differences
Chapter 3. Regression-Based Models for Developing Commercial Demand Characteristics Investigation
 Chapter Regression-Based Models for Developing Commercial Demand Characteristics Investigation. Introduction Commercial area is another important area in terms of consume high electric energy in Japan.
Chapter Regression-Based Models for Developing Commercial Demand Characteristics Investigation. Introduction Commercial area is another important area in terms of consume high electric energy in Japan.
Atmospheric circulation analysis for seasonal forecasting
 Training Seminar on Application of Seasonal Forecast GPV Data to Seasonal Forecast Products 18 21 January 2011 Tokyo, Japan Atmospheric circulation analysis for seasonal forecasting Shotaro Tanaka Climate
Training Seminar on Application of Seasonal Forecast GPV Data to Seasonal Forecast Products 18 21 January 2011 Tokyo, Japan Atmospheric circulation analysis for seasonal forecasting Shotaro Tanaka Climate
Jackson County 2013 Weather Data
 Jackson County 2013 Weather Data 61 Years of Weather Data Recorded at the UF/IFAS Marianna North Florida Research and Education Center Doug Mayo Jackson County Extension Director 1952-2008 Rainfall Data
Jackson County 2013 Weather Data 61 Years of Weather Data Recorded at the UF/IFAS Marianna North Florida Research and Education Center Doug Mayo Jackson County Extension Director 1952-2008 Rainfall Data
Climate impact on seasonal patterns of diarrhea diseases in Tropical area
 Climate impact on seasonal patterns of diarrhea diseases in Tropical area Akari Teshima 1, Michio Yamada 2, *Taiichi Hayashi 1, Yukiko Wagatsuma 3, Toru Terao 4 (1: DPRI, Kyoto Univ., Japan, 2: RIMS, Kyoto
Climate impact on seasonal patterns of diarrhea diseases in Tropical area Akari Teshima 1, Michio Yamada 2, *Taiichi Hayashi 1, Yukiko Wagatsuma 3, Toru Terao 4 (1: DPRI, Kyoto Univ., Japan, 2: RIMS, Kyoto
Mapping coherent structures responsible for heat exchange between land-surfaces and atmosphere using time-sequential thermography
 Mapping coherent structures responsible for heat exchange between land-surfaces and atmosphere using time-sequential thermography Andreas Christen (1), Anirban Garai (2), Atsushi Inagaki (6), Jan Kleissl
Mapping coherent structures responsible for heat exchange between land-surfaces and atmosphere using time-sequential thermography Andreas Christen (1), Anirban Garai (2), Atsushi Inagaki (6), Jan Kleissl
Winter Thermal Comfort in 19 th Century Traditional Buildings of the Town of Florina, in North-Western Greece
 PLEA2 - The 22 nd Conference on Passive and Low Energy Architecture. Beirut, Lebanon, 13-16 November 2 Winter Thermal Comfort in 19 th Century Traditional Buildings of the Town of Florina, in North-Western
PLEA2 - The 22 nd Conference on Passive and Low Energy Architecture. Beirut, Lebanon, 13-16 November 2 Winter Thermal Comfort in 19 th Century Traditional Buildings of the Town of Florina, in North-Western
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Ascension Island Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin December 2008 08/12/AS Crown copyright; Ordnance Survey ASCENSION ISLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Ascension
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Ascension Island Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin December 2008 08/12/AS Crown copyright; Ordnance Survey ASCENSION ISLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Ascension
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
225 Bush Street Suite 1700 San Francisco, CA phone fax
 225 Bush Street Suite 1700 San Francisco, CA 94104 415.896.5900 phone 415.896.0332 fax www.esassoc.com memorandum date July 29, 2009 to from subject Craig Nikitas, San Francisco Planning Department Daniel
225 Bush Street Suite 1700 San Francisco, CA 94104 415.896.5900 phone 415.896.0332 fax www.esassoc.com memorandum date July 29, 2009 to from subject Craig Nikitas, San Francisco Planning Department Daniel
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBERS
 ENGINE SERIAL NUMBERS The engine number was also the serial number of the car. Engines were numbered when they were completed, and for the most part went into a chassis within a day or so. However, some
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBERS The engine number was also the serial number of the car. Engines were numbered when they were completed, and for the most part went into a chassis within a day or so. However, some
Seasonal dynamics of a suburban energy balance in Phoenix, Arizona
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 34: 3863 3880 (2014) Published online 4 March 2014 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/joc.3947 Seasonal dynamics of a suburban
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 34: 3863 3880 (2014) Published online 4 March 2014 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/joc.3947 Seasonal dynamics of a suburban
Water vapour above Switzerland over the last 12 years
 Water vapour above Switzerland over the last 12 years June Morland*, Martine Collaud**, Klemens Hocke*, Pierre Jeannet**, Christian Mätzler* *Institute of Applied Physics, University of Bern **MeteoSwiss
Water vapour above Switzerland over the last 12 years June Morland*, Martine Collaud**, Klemens Hocke*, Pierre Jeannet**, Christian Mätzler* *Institute of Applied Physics, University of Bern **MeteoSwiss
Grade 6 Standard 2 Unit Test Astronomy
 Grade 6 Standard 2 Unit Test Astronomy Multiple Choice 1. Why does the air temperature rise in the summer? A. We are closer to the sun. B. The air becomes thicker and more dense. C. The sun s rays are
Grade 6 Standard 2 Unit Test Astronomy Multiple Choice 1. Why does the air temperature rise in the summer? A. We are closer to the sun. B. The air becomes thicker and more dense. C. The sun s rays are
FRAPPÉ/DISCOVER-AQ (July/August 2014) in perspective of multi-year ozone analysis
 FRAPPÉ/DISCOVER-AQ (July/August 2014) in perspective of multi-year ozone analysis Project Report #2: Monitoring network assessment for the City of Fort Collins Prepared by: Lisa Kaser kaser@ucar.edu ph:
FRAPPÉ/DISCOVER-AQ (July/August 2014) in perspective of multi-year ozone analysis Project Report #2: Monitoring network assessment for the City of Fort Collins Prepared by: Lisa Kaser kaser@ucar.edu ph:
Implementation Status & Results Burkina Faso TRANSPORT SECTOR PROJECT (P074030)
 losure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Implementation Status & Results Burkina Faso TRANSPORT SECTOR PROJECT (P074030) Operation Name:
losure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Implementation Status & Results Burkina Faso TRANSPORT SECTOR PROJECT (P074030) Operation Name:
One sine wave is 7.64 minutes peak to peak variation. Two sine waves is 9.86
 WHY THE SUN IS SOMETIMES FAST AND SOMETIMES SLOW As the earth orbits the sun in an ellipse, it goes faster approaching the sun and slower when receding, just like when you throw a ball up in the air and
WHY THE SUN IS SOMETIMES FAST AND SOMETIMES SLOW As the earth orbits the sun in an ellipse, it goes faster approaching the sun and slower when receding, just like when you throw a ball up in the air and
ENERGY AND RADIATION BALANCE OF A CENTRAL EUROPEAN CITY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 24: 1395 1421 (2004) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/joc.1074 ENERGY AND RADIATION BALANCE OF A
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 24: 1395 1421 (2004) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/joc.1074 ENERGY AND RADIATION BALANCE OF A
Constructing a typical meteorological year -TMY for Voinesti fruit trees region and the effects of global warming on the orchard ecosystem
 Constructing a typical meteorological year -TMY for Voinesti fruit trees region and the effects of global warming on the orchard ecosystem ARMEANU ILEANA*, STĂNICĂ FLORIN**, PETREHUS VIOREL*** *University
Constructing a typical meteorological year -TMY for Voinesti fruit trees region and the effects of global warming on the orchard ecosystem ARMEANU ILEANA*, STĂNICĂ FLORIN**, PETREHUS VIOREL*** *University
P3.20 A CLIMATOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DIURNAL PATTERNS OF PRECIPITATION OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF WESTERN COLORADO
 P3.20 A CLIMATOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DIURNAL PATTERNS OF PRECIPITATION OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF WESTERN COLORADO Jeffrey D. Colton*, J.D. Ramey Jr., B. Avery, and M.P. Meyers National Weather
P3.20 A CLIMATOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DIURNAL PATTERNS OF PRECIPITATION OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF WESTERN COLORADO Jeffrey D. Colton*, J.D. Ramey Jr., B. Avery, and M.P. Meyers National Weather
Public Library Use and Economic Hard Times: Analysis of Recent Data
 Public Library Use and Economic Hard Times: Analysis of Recent Data A Report Prepared for The American Library Association by The Library Research Center University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign April
Public Library Use and Economic Hard Times: Analysis of Recent Data A Report Prepared for The American Library Association by The Library Research Center University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign April
Earth s Motion. Lesson Outline LESSON 1. A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than
 Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region
 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region ZhangZhen 2015.07.10 1 Outline Introduction Data
Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region ZhangZhen 2015.07.10 1 Outline Introduction Data
Land Cover, Climate, and the Summer Surface Energy Balance in Phoenix, AZ, and Portland, OR
 Portland State University PDXScholar Institute for Sustainable Solutions Publications and Presentations Institute for Sustainable Solutions 11-1-2012 Land Cover, Climate, and the Summer Surface Energy
Portland State University PDXScholar Institute for Sustainable Solutions Publications and Presentations Institute for Sustainable Solutions 11-1-2012 Land Cover, Climate, and the Summer Surface Energy
APPENDIX B SHADOW STUDY
 APPENDIX B SHADOW STUDY Shadow Study Methodology and Analysis Douglas Avenue Multi-Family Residential Development Project Methodology Panorama evaluated for accuracy the building foot print data provided
APPENDIX B SHADOW STUDY Shadow Study Methodology and Analysis Douglas Avenue Multi-Family Residential Development Project Methodology Panorama evaluated for accuracy the building foot print data provided
5. In which diagram is the observer experiencing the greatest intensity of insolation? A) B)
 1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
Time Series Analysis
 Time Series Analysis A time series is a sequence of observations made: 1) over a continuous time interval, 2) of successive measurements across that interval, 3) using equal spacing between consecutive
Time Series Analysis A time series is a sequence of observations made: 1) over a continuous time interval, 2) of successive measurements across that interval, 3) using equal spacing between consecutive
January 2009 Videmus Stellae
 January 2009 January Schedule of Events Sun Mon Tu e Wed Thu Fri Sat Jan 6th: ATM Sub at Paul Lind s Garage at 1900 Jan 9th: SAC General at Grand Canyon University at 1930 in room 105 of the Fleming Bldg.
January 2009 January Schedule of Events Sun Mon Tu e Wed Thu Fri Sat Jan 6th: ATM Sub at Paul Lind s Garage at 1900 Jan 9th: SAC General at Grand Canyon University at 1930 in room 105 of the Fleming Bldg.
Remote Sensing of Urban Surface Temperatures
 Remote Sensing of Urban Surface Temperatures James Voogt University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada This work is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Remote Sensing of Urban Surface Temperatures James Voogt University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada This work is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Multivariate Regression Model Results
 Updated: August, 0 Page of Multivariate Regression Model Results 4 5 6 7 8 This exhibit provides the results of the load model forecast discussed in Schedule. Included is the forecast of short term system
Updated: August, 0 Page of Multivariate Regression Model Results 4 5 6 7 8 This exhibit provides the results of the load model forecast discussed in Schedule. Included is the forecast of short term system
Which table correctly shows the dates on which the apparent paths of the Sun were observed? A) B) C) D)
 1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
R.L. Kellogg, Ph.D. North American Sundial Society June 2013
 R.L. Kellogg, Ph.D. North American Sundial Society June 2013 1 Analemmatic Sundials The Human Sundial The Analemmatic Sundial or Human Sundial was first described by M. de Vaulezard in 1640 in a Treatise
R.L. Kellogg, Ph.D. North American Sundial Society June 2013 1 Analemmatic Sundials The Human Sundial The Analemmatic Sundial or Human Sundial was first described by M. de Vaulezard in 1640 in a Treatise
A Report on a Statistical Model to Forecast Seasonal Inflows to Cowichan Lake
 A Report on a Statistical Model to Forecast Seasonal Inflows to Cowichan Lake Prepared by: Allan Chapman, MSc, PGeo Hydrologist, Chapman Geoscience Ltd., and Former Head, BC River Forecast Centre Victoria
A Report on a Statistical Model to Forecast Seasonal Inflows to Cowichan Lake Prepared by: Allan Chapman, MSc, PGeo Hydrologist, Chapman Geoscience Ltd., and Former Head, BC River Forecast Centre Victoria
