Paleoseismic investigations along a key active fault within the Gulf of Corinth, Greece
|
|
|
- Dennis Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Paleoseismic investigations along a key active fault within the Gulf of Corinth, Greece To cite this article: I K Koukouvelas et al 2008 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci View the article online for updates and enhancements. Related content - Near-Surface Fault Structures of the Seulimuem Segment Based on Electrical Resistivity Model Nazli Ismail, Muhammad Yanis, Syafrizal Idris et al. - Subsidence: Causes, Effects, and Mitigations in Geothermal Field Akta Sektiawan, Ganung Adi Prasetyo, Dida Patera Adli et al. - Assessment of Potential Environmental Risks from Saline Soils Subsidence L Ya Pobereznyi, L Ya Poberezhna, P O Maruschak et al. This content was downloaded from IP address on 19/11/2018 at 18:50
2 Paleoseismic investigations along a key active fault within the Gulf of Corinth, Greece I K Koukouvelas, S Kokkalas 1 and P Xypolias Department of Geology, University of Patras, Patras, Greece skokalas@upatras.gr Abstract. The study of paleoseismological and archaeological excavations provide clues for the evolution of Helike Fault, located along the westernmost end of the Gulf of Corinth, that displays high activity and exerts control on the landscape. In this study we present evidence from paleoseismic trenches which revealed well defined fault strands and clear colluvial stratigraphy. We focus on the two main segments of the Helike Fault and their implications on strong earthquake activity. The Helike Fault is a major tectonic structure that influenced the evolution of ancient settlements on the Helike Delta, from the Early Bronze Age through the Byzantine period, till present times. The eastern fault segment appears to control the southern Gulf morphology, while the western segment is controlling the large Aigion basin. Interbedded organic-rich soils and gravels dominate in all trenches. Fault strands that control successive scarp-derived colluvial deposits were identified within the trenches and indicate the continuous seismic activity along the fault trace. Co-seismic offsets, open cracks filled with debris and liquefaction related deformation was also recognized. At least seven seismic events were identified inside the excavated trenches, during the last 10 ka. The estimated vertical throw along the fault segments, observed within the trenches, is on the order of 1meter per event. Based on dating of colluvial wedges we estimated the Holocene slip rate on the Helike Fault, which shows an increase from ~0.3 mm/yr to 2 mm/yr in the last 2 ka. We consider the derived slip rates to be minimum values due to the implication of erosional effects and sediment accumulation from the upthrown block. The Helike fault appears to play a crucial role both in subsidence of the Helike delta plain and in shifting Kerynites river course that runs between the two Helike fault segments. The Helike Fault activity and the clustering of surface rupturing events on the Helike fault seems to fit well with the subsidence of the Helike Delta plain and its change from marsh to lake or pod over the last 5 Ka. 1. Geological setting-the Gulf of Corinth The 120-km long Gulf of Corinth offers a typical example of rapid extension in a continental region [1] (figure 1). Active normal faults strongly control the landscapes bordering the Gulf of Corinth leading to major changes of fluvial geomorphology [2], shorelines [3] and the surface of the Helike Delta [4]. In all these examples, archaeology compliments the data from geology in the interpretation of landscape evolution [4, 5]. Strong earthquakes in the area, are related to offsets on the order 1 m [i.e. 6]. However, only one earthquake during 1861 is known to have ruptured the surface within the western part of the Gulf of Corinth (figure 2). The oldest historically described earthquake that occurred in the Gulf of Corinth 1 To whom any correspondence should be addressed. c 2008 Ltd 1
3 region destroyed the cities of Helike and Boura in 373 B.C. but the faults hosting this historic event remains unknown [7, 8]. Figure 1. Tectonic map showing the active normal faults in the Gulf of Corinth and the inferred slip rates both for offshore and onshore faults (map from [9]). 2. The Helike active fault The Helike Fault is a major tectonic structure controlling the landscape of the western Gulf of Corinth (figure 2). It strongly influenced the evolution of ancient settlements on the Helike Delta from the Early Bronze Age through the Byzantine period [4, 10]. Figure 2. Structural map showing the Helike fault and the surface ruptures of the last strong 1861 earthquake event in the area. 2
4 The Helike Fault is divided into a western and eastern segment, 9 and 13 km long, respectively. The two fault segments dip north and their tips show an approaching configuration, forming the Helike step-over zone (figure 2). The easternmost segment appears to control the southern Gulf morphology. The western segment of the Helike Fault is also important in controlling the large Aigion basin [11] Paleoseismological trenching and archaeological data East Helike. Archaeology provides another mean to date the events within the paleoseismological trenches, as well as to identify the area most strongly affected by earthquakes (figure 3). Excavation of the trench T13 (figure 4) revealed the ruins of semi-circular structures built with stones of local psammite enclosing the position of a Late Roman tile-covered grave. Large clay tiles of Laconian type apparently belonging to tile-covered graves were previously discovered in trench Eli3 excavated east of T13 [12]. Figure 3. (Left) Early Bronze age architectural ruins showing offset due to earthquake. In this area archaeological evidence shows that buildings were thrown down by an earthquake accompanied by conflagration. Estimation of the event age is between BP. (Right) Part of Hellenistic pebble mosaic floor covered by a thick destruction layer of fallen clay roof tiles and plaster [10]. Interbedded organic-rich soils and gravels dominate the T13 trench. The lowermost exposed unit is a brick-orange fluvial unit (BO 1 in figure 4, right). In the trench we recognized two fault strands, the "north" and "south" fault, which control colluvial wedges. In general, colluvial wedges related to the north fault are thinner and are buried by a well preserved colluvial sequence, which is controlled by the south fault (figure 4). The displacement along the north fault is as much as 2.7 m and controls the deposition of a set of three scarp colluvial units (labeled SC 1,SC 2 and SC 3 ) and a structureless, siltysand layer (L), as shown in Fig 4. Part of the SC 3 contains scattered pebbles, many of which have subvertically oriented long axes indicating liquefaction. The contact between the SC 3 colluvium and layer L is transitional. The L layer shows wavy contacts and sill-out within fluvial or colluvial gravels producing also an apparent blister-like bulge of SC 3. All these features indicate that layer L was produced by liquefaction. Since the lower part of the SC 3 also shows liquefaction effects, we infer that the liquefaction occurred some time after the deposition of the SC 3. The unit L is 1.5 m long and extends across the 5 m width of the trench, but its presumed dyke source is beyond the faces of the trench. The SC 3 colluvium covers the upper part of the scarp, attains a maximum thickness 0.7 m, including the part disturbed by liquefaction, and is overlain by 0.6 m of yellowish-white fluvial gravels. 3
5 Figure 4. (Left) The paleoseismological trench T13 across the east Helike fault, showing the south and north fault strands. The post-roman colluvial wedge covering much of the trench stratigraphy corresponds to SC4 colluvial wedge. (Right) Detailed view of the north fault strand with the successive colluvial wedges and the location of samples dated. In another trench, excavated by the Helike Project just west of T13 in 2003, we discovered a well built tile-covered grave containing the skeleton of an adult man oriented E-W, not accompanied by grave goods [5]. Judging from the type of the tiles used for the construction of the graves, we dated them to the Late Roman period. The graves encountered in trenches T27, T13 and Eli3, were found, respectively, at 2.1, 2.5 and 3.0 m below the surface. They seem to have suffered destruction and erosion by the flow of a minor nearby torrent, which had formed a small scale fan underlying the graves. Above this fan is the colluvial deposit SC4 controlled by the south fault (figure 4). The discovery of the tombs allows one to distinguish between pre-roman and post-roman seismic events, and to infer that the third event on the north fault occurred between 1530 and 1230 BP West Helike. Across the West Helike Fault segment we excavated two trenches, given that promising sites for paleoseismological trenching are missing (figure 5). Figure 5. Excavated paleoseismological trench across the west Helike fault, showing the succession of a series of colluvial wedges adjacent to the fault zone. 4
6 Within the trenches interbedded organic-rich soils and gravels are dominant. The West Helike 1 section is not unaffected by man-made disturbance and is characterized by a series of well preserved colluvial wedges within a scarp-graben system (figure 5). The graben is defined by an antithetic fault and includes a zone accumulating about 2.5 m of throw and tilt of the strata within the hanging-wall towards the Helike fault. Within this graben we recognized four colluvial wedges interpreted to be related with surface rupturing events. All events were dated from samples taken inside trenches with the C 14 method. Two additional events were recognized within the We2 trench. Significant is that some of these events are directly comparable with events in the East Helike Fault segment and some of them are correlated with damages in the archaeological excavations (see also figure 6 right). 3. Results-Conclusions 1. The Holocene slip rate on both segments of the Helike Fault is not constant (figure 6, left). This result, together with the long-term average lip rate of 0.5 mm/yr for the Helike Fault estimated by [11] suggests that the fault built up its displacement during very short periods of high slip rate (>1.2 mm/yr) and much longer periods with low slip rate (<0.5 mm/yr). Figure 6. (Left) Summary of the displacement vs. time for the two segments of the Helike Fault. Estimated time for faulting and displacements for the East Helike Fault segment as is published in [12, 13], while data for the West Helike Fault segment as in this study. Dashed lines correspond to the slip rate of the Helike Fault. (Right) Calibration graph of all dated samples on the Helike fault trenches. The range of possible ages is shown only for the best level of confidence (2σ = 95%). The results from the trenches show the age range for colluvial sedimentation. 2. The recognized switch from low to high slip periods is marked by surface rupturing earthquakes. Changes of the fault slip rate fit well with a model for clustering of earthquakes with periods of longer recurrence intervals. Thus, the Helike Fault activity resembles clustering similar to that of other major faults in the Eastern Mediterranean region, i.e. the North Anatolian Fault. 3. Recurrence intervals, estimated from our paleoseismological study, are almost identical for both faults in the order of yrs, as well as the throw per event which is in the order of ~1m. However, in general the throw per event in the East Helike Fault segment is in general 20% larger than in the West Helike Fault. 4. For the last two events it appears that the two fault segments were activated as a linked fault system. References [1] Doutsos T and Kokkalas S 2001 J. Struct. Geol [2] Koukouvelas 1998 J. Geody [3] Stewart I 1996 Annali di Geofisica [4] Soter S and Katsonopoulou D 1999 Geoarchaeology
7 [5] Katsonopoulou D 2003 Tekmeria (Paestum) [6] Roberts G P and Koukouvelas I K 1996 Annali di Geophysica [7] Marinatos S N 1960 Archaeology [8] Katsonopoulou D 2000 The Earthquake of 373 BC. Literary and Archaeological Evidence. Ancient Helike and Aigialeia: Archaeological Sites in Geologically Active Regions Proceedings of the Third International Conference, October 2000 eds D Katsonopoulou, S Soter and I Koukouvelas (Athens, Greece: The Helike Society) p. 4. [9] Zygouri V, Verroios S, Kokkalas S, Xypolias P and Koukouvelas I K 2008 Tectonophysics doi: /j.tecto [10] Katsonopoulou D, Soter S and Koukouvelas I 2004 Historical earthquakes in the area of Helike. The evidence of geoarchaeology. 5th International Symposium on Eastern Mediterranean Geology, (Thessaloniki, Greece, April 2004) eds A A Chatzipetros and S B Pavlides (Thessaloniki, Greece: University of Thessaloniki) pp [11] Doutsos T and Poulimenos G J. Struct. Geol [12] Koukouvelas I, Stamatopoulos L, Katsonopoulou D and Pavlides S 2001 J. Struct. Geol [13] Koukouvelas I K, Katsonopoulou D, Soter S and Xypolias P 2005 Terra Nova
The Search for Ancient Helike: a GPR Case Study. Doria L. Kutrubes 1 Radar Solutions International. Steven Soter Smithsonian Institution
 The Search for Ancient Helike: a GPR Case Study Doria L. Kutrubes 1 Radar Solutions International Steven Soter Smithsonian Institution Dora Katsonopoulou American School of Classical Studies at Athens
The Search for Ancient Helike: a GPR Case Study Doria L. Kutrubes 1 Radar Solutions International Steven Soter Smithsonian Institution Dora Katsonopoulou American School of Classical Studies at Athens
4. Geotechnical and Geological Aspects. 4.1 Geotechnical Aspects
 4. Geotechnical and Geological Aspects 4.1 Geotechnical Aspects A preliminary reconnaissance of the geotechnical conditions of Duzce, Kaynasli, and Bolu urban areas was done during the Turkey Expedition
4. Geotechnical and Geological Aspects 4.1 Geotechnical Aspects A preliminary reconnaissance of the geotechnical conditions of Duzce, Kaynasli, and Bolu urban areas was done during the Turkey Expedition
Finite element fault rupture propagation modelling in the Corinth Canal Greece
 Coastal Engineering VII, WIT Press, Southampton, pp. 305-311 Finite element fault rupture propagation modelling in the Corinth Canal Greece F. Gkika, G-A. Tselentis & L. Danciu Seismological Laboratory,
Coastal Engineering VII, WIT Press, Southampton, pp. 305-311 Finite element fault rupture propagation modelling in the Corinth Canal Greece F. Gkika, G-A. Tselentis & L. Danciu Seismological Laboratory,
MORPHOTECTONIC ANALYSIS IN THE ELIKI FAULT ZONE (GULF OF CORINTH, GREECE)
 ελτίο της Ελληνικής Γεωλογικής Εταιρίας τοµ. XXXVI, 2004 Πρακτικά 10 ου ιεθνούς Συνεδρίου, Θεσ/νίκη Απρίλιος 2004 Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece vol. XXXVI, 2004 Proceedings of the 10 th
ελτίο της Ελληνικής Γεωλογικής Εταιρίας τοµ. XXXVI, 2004 Πρακτικά 10 ου ιεθνούς Συνεδρίου, Θεσ/νίκη Απρίλιος 2004 Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece vol. XXXVI, 2004 Proceedings of the 10 th
PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE
 PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE E. PAPADIMITRIOU & L. PELLI EUROPEAN CENTER OF PREVENTING & FORECASTING OF EARTHQUAKES Confronting the problem SEISMIC RISK R SEISMIC
PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE E. PAPADIMITRIOU & L. PELLI EUROPEAN CENTER OF PREVENTING & FORECASTING OF EARTHQUAKES Confronting the problem SEISMIC RISK R SEISMIC
Active Tectonics. Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape. Edward A. Keller University of California, Santa Barbara
 Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
P128 Subsurface Fault and Colluvial Wedge Detection Using Resistivity, Refraction Tomography and Seismic Reflection
 P128 Subsurface Fault and Colluvial Wedge Detection Using Resistivity, Refraction Tomography and Seismic Reflection S.M. Hanafy* (King Abdullah University of Science & Technology) SUMMARY Electric resistivity
P128 Subsurface Fault and Colluvial Wedge Detection Using Resistivity, Refraction Tomography and Seismic Reflection S.M. Hanafy* (King Abdullah University of Science & Technology) SUMMARY Electric resistivity
S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura, and Y. Niwa International Research Institute of Disaster Science, Tohoku University, Japan
 The first surface-rupturing earthquake in 20 years on a HERP major active fault: Mw=6.2 2014 Nagano, Japan, event along the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line is not characteristic S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura,
The first surface-rupturing earthquake in 20 years on a HERP major active fault: Mw=6.2 2014 Nagano, Japan, event along the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line is not characteristic S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura,
PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE
 PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE R.PAPADHMHTRIOU, L.PELLI EUROPEAN CENTER OF PREVENTING & FORECASTING OF EARTHQUAKES Confronting the problem SEISMIC RISK R SEISMIC
PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE R.PAPADHMHTRIOU, L.PELLI EUROPEAN CENTER OF PREVENTING & FORECASTING OF EARTHQUAKES Confronting the problem SEISMIC RISK R SEISMIC
Fault Behavior and Characteristic Earthquakes: Examples From the Wasatch and San Andreas Fault Zones
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 89, NO. B7, PAGES 5681-5698, JULY IO, 1984 Fault Behavior and Characteristic Earthquakes: Examples From the Wasatch and San Andreas Fault Zones DAVID P. SCHWARTZ AND
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 89, NO. B7, PAGES 5681-5698, JULY IO, 1984 Fault Behavior and Characteristic Earthquakes: Examples From the Wasatch and San Andreas Fault Zones DAVID P. SCHWARTZ AND
PALEOSEISMOLOGY: SITES (17)
 GG 454 February 8, 2002 1 PALEOSEISMOLOGY: SITES (17) Schedule Updates and Reminders: Reading for this lecture: Big Picture - Skim "Applications" in PP 1360 Reading for next lecture: Handouts from Active
GG 454 February 8, 2002 1 PALEOSEISMOLOGY: SITES (17) Schedule Updates and Reminders: Reading for this lecture: Big Picture - Skim "Applications" in PP 1360 Reading for next lecture: Handouts from Active
SCEC Earthquake Gates Workshop Central Death Valley Focus Area
 SCEC Earthquake Gates Workshop Central Death Valley Focus Area Fault Gates: Rheology, fault geometry, stress history or directionality? How do we recognize or suspect a fault gate? Paleoseismic or historic
SCEC Earthquake Gates Workshop Central Death Valley Focus Area Fault Gates: Rheology, fault geometry, stress history or directionality? How do we recognize or suspect a fault gate? Paleoseismic or historic
STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI
 STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI LAURA K.O. SMITH AND SARAHTSETSEG PUREDORG Princeton University, Mongolian University of Science and Technology Sponsors: Ramon Gonzalez-Mieres
STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI LAURA K.O. SMITH AND SARAHTSETSEG PUREDORG Princeton University, Mongolian University of Science and Technology Sponsors: Ramon Gonzalez-Mieres
GSA Data Repository item
 GSA Data Repository item 2007167 A 25,000-year record of earthquakes on the Owens Valley fault near Lone Pine, California: Implications for recurrence intervals, slip rates, and segmentation models, by
GSA Data Repository item 2007167 A 25,000-year record of earthquakes on the Owens Valley fault near Lone Pine, California: Implications for recurrence intervals, slip rates, and segmentation models, by
General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone
 General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone David Hoffman University of Missouri Rolla Natural Hazards Mitigation Institute Civil, Architectural & Environmental
General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone David Hoffman University of Missouri Rolla Natural Hazards Mitigation Institute Civil, Architectural & Environmental
Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand
 Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand Piyaphong Chenrai Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand Piyaphong Chenrai Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
A palaeoseismological investigation of the Cadell Fault Zone, Victoria, Australia
 A palaeoseismological investigation of the Cadell Fault Zone, Victoria, Australia Amy Heath FM Global, Melbourne, Australia. Dan Clarke, Gary Gibson, Kevin McCue, Russ Van Dissen Geoscience Australia,
A palaeoseismological investigation of the Cadell Fault Zone, Victoria, Australia Amy Heath FM Global, Melbourne, Australia. Dan Clarke, Gary Gibson, Kevin McCue, Russ Van Dissen Geoscience Australia,
Location, Location, Location: the Construction and Preservation of Roman Burial Mounds in the Dutch River Delta
 Special Volume 3 (2012), pp. 155 159 Marjolein T.I.J. Bouman Kirsten van Kappel Linda P. Verniers Location, Location, Location: the Construction and Preservation of Roman Burial Mounds in the Dutch River
Special Volume 3 (2012), pp. 155 159 Marjolein T.I.J. Bouman Kirsten van Kappel Linda P. Verniers Location, Location, Location: the Construction and Preservation of Roman Burial Mounds in the Dutch River
Present seismic activity of Sparta fault (Peloponnesus, southern Greece) and its implications
 Present seismic activity of Sparta fault (Peloponnesus, southern Greece) and its implications Papanastassiou D(1), Karastathis V(2), Liakopoulos S(3) (1) Institute of Geodynamics, National Observatory
Present seismic activity of Sparta fault (Peloponnesus, southern Greece) and its implications Papanastassiou D(1), Karastathis V(2), Liakopoulos S(3) (1) Institute of Geodynamics, National Observatory
ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR )
 PLATTE RIVER POWER AUTHORITY RAWHIDE ENERGY STATION BOTTOM ASH TRANSFER (BAT) IMPOUNDMENTS LARIMER COUNTY, CO ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR 257.62) FOR COAL COMBUSTION RESIDUALS
PLATTE RIVER POWER AUTHORITY RAWHIDE ENERGY STATION BOTTOM ASH TRANSFER (BAT) IMPOUNDMENTS LARIMER COUNTY, CO ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR 257.62) FOR COAL COMBUSTION RESIDUALS
Bonn, Germany MOUTAZ DALATI. General Organization for Remote Sensing ( GORS ), Syria Advisor to the General Director of GORS,
 Bonn, Germany Early Warning System is needed for Earthquakes disaster mitigation in Syria Case Study: Detecting and Monitoring the Active faulting zones along the Afro-Arabian-Syrian Rift System MOUTAZ
Bonn, Germany Early Warning System is needed for Earthquakes disaster mitigation in Syria Case Study: Detecting and Monitoring the Active faulting zones along the Afro-Arabian-Syrian Rift System MOUTAZ
GEOLOGY, SOILS, AND SEISMICITY
 4.9 GEOLOGY, SOILS, AND SEISMICITY 4.9.1 Introduction Information about the geological conditions and seismic hazards in the study area was summarized in the FEIR, and was based on the Geotechnical Exploration
4.9 GEOLOGY, SOILS, AND SEISMICITY 4.9.1 Introduction Information about the geological conditions and seismic hazards in the study area was summarized in the FEIR, and was based on the Geotechnical Exploration
FOLDS AND THRUST SYSTEMS IN MASS TRANSPORT DEPOSITS
 FOLDS AND THRUST SYSTEMS IN MASS TRANSPORT DEPOSITS G.I Aslop, S. Marco, T. Levi, R. Weinberger Presentation by Aaron Leonard INTRODUCTION Examine fold and thrust geometries associated with downslope movement
FOLDS AND THRUST SYSTEMS IN MASS TRANSPORT DEPOSITS G.I Aslop, S. Marco, T. Levi, R. Weinberger Presentation by Aaron Leonard INTRODUCTION Examine fold and thrust geometries associated with downslope movement
MOUSLOPOULOU V., ANDREOU C., ATAKAN K. FOUNTOULIS I.,
 ΔΗΜΟΣΙΕΥΣΗ Νο 80 MOUSLOPOULOU V., ANDREOU C., ATAKAN K. FOUNTOULIS I., (2001) Paleoseismological investigations along the Kera Fault Zone, Western Crete: Implications for Seismic Hazard Assessment. Proc.
ΔΗΜΟΣΙΕΥΣΗ Νο 80 MOUSLOPOULOU V., ANDREOU C., ATAKAN K. FOUNTOULIS I., (2001) Paleoseismological investigations along the Kera Fault Zone, Western Crete: Implications for Seismic Hazard Assessment. Proc.
Important Concepts. Earthquake hazards can be categorized as:
 Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Case Study of the Structural and Depositional-Evolution Interpretation from Seismic Data*
 Case Study of the Structural and Depositional-Evolution Interpretation from Seismic Data* Yun Ling 1, Xiangyu Guo 1, Jixiang Lin 1, and Desheng Sun 1 Search and Discovery Article #20143 (2012) Posted April
Case Study of the Structural and Depositional-Evolution Interpretation from Seismic Data* Yun Ling 1, Xiangyu Guo 1, Jixiang Lin 1, and Desheng Sun 1 Search and Discovery Article #20143 (2012) Posted April
Bulletin of Earth Sciences of Thailand
 Quantitative Seismic Geomorphology of Early Miocene to Pleistocene Fluvial System of Northern Songkhla Basin, Gulf of Thailand Oanh Thi Tran Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty
Quantitative Seismic Geomorphology of Early Miocene to Pleistocene Fluvial System of Northern Songkhla Basin, Gulf of Thailand Oanh Thi Tran Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty
Study on the Fluvial Geomorphological Meanings of Valley Plain in the River and Estimation of the Extreme River Discharge
 12th International Conference on Hydroscience & Engineering Study on the Fluvial Geomorphological Meanings of Valley Plain in the River and Estimation of the Extreme River Discharge Masaki Wakui, Shoji
12th International Conference on Hydroscience & Engineering Study on the Fluvial Geomorphological Meanings of Valley Plain in the River and Estimation of the Extreme River Discharge Masaki Wakui, Shoji
Characterisation of late Quaternary displacements on the Waitangi Fault at Aviemore Dam, New Zealand
 Characterisation of late Quaternary displacements on the Waitangi Fault at Aviemore Dam, New Zealand D.J.A. Barrell, R.J. Van Dissen, K.R. Berryman, & S.A.L. Read Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences
Characterisation of late Quaternary displacements on the Waitangi Fault at Aviemore Dam, New Zealand D.J.A. Barrell, R.J. Van Dissen, K.R. Berryman, & S.A.L. Read Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences
Geomorphic Deformation of a Small Glaciofluvial Basin by an Upstream-Facing Thrust Fault over Multiple Glacial Cycles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Geomorphic Deformation of a Small Glaciofluvial Basin by an Upstream-Facing Thrust Fault over Multiple Glacial Cycles Rachel J. Comp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Geomorphic Deformation of a Small Glaciofluvial Basin by an Upstream-Facing Thrust Fault over Multiple Glacial Cycles Rachel J. Comp
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana
 Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana Robert C. Thomas Department of Environmental Sciences, The University of Montana Western, Dillon, MT 59725, (406) 683-7615, r_thomas@umwestern.edu
Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana Robert C. Thomas Department of Environmental Sciences, The University of Montana Western, Dillon, MT 59725, (406) 683-7615, r_thomas@umwestern.edu
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 2, pp , April 2004
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 2, pp. 531 549, April 2004 Paleoseismological Trenching across the Atalanti Fault (Central Greece): Evidence for the Ancestors of the 1894
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 2, pp. 531 549, April 2004 Paleoseismological Trenching across the Atalanti Fault (Central Greece): Evidence for the Ancestors of the 1894
Geomorphology LAB FAULT-SCARP DEGRADATION
 Geomorphology LAB FAULT-SCARP DEGRADATION Nicholas Pinter (University of California, Davis) Supplies Needed calculator straight-edge ruler PURPOSE The evolution of the Earth s surface over time is governed
Geomorphology LAB FAULT-SCARP DEGRADATION Nicholas Pinter (University of California, Davis) Supplies Needed calculator straight-edge ruler PURPOSE The evolution of the Earth s surface over time is governed
Earthquakes. Building Earth s Surface, Part 2. Science 330 Summer What is an earthquake?
 Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
Late Holocene Slip Rate and Ages of Prehistoric Earthquakes along the Maacama Fault Near Willits, Mendocino County, Northern California
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 104, No. 6, pp., December 2014, doi: 10.1785/0120140003 E Late Holocene Slip Rate and Ages of Prehistoric Earthquakes along the Maacama Fault Near
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 104, No. 6, pp., December 2014, doi: 10.1785/0120140003 E Late Holocene Slip Rate and Ages of Prehistoric Earthquakes along the Maacama Fault Near
Hosgri-San Simeon Fault Zone Geologic Slip Rate
 Hosgri-San Simeon Fault Zone Geologic Slip Rate Insert picture(s) here Kathryn Hanson AMEC E&I Diablo Canyon SSHAC Project SSC Workshop 2 November 7, 2012 What insights have your geologic investigations
Hosgri-San Simeon Fault Zone Geologic Slip Rate Insert picture(s) here Kathryn Hanson AMEC E&I Diablo Canyon SSHAC Project SSC Workshop 2 November 7, 2012 What insights have your geologic investigations
Date: / Page # Version A Page 1
 Name: Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. Which best describes a major characteristic of both volcanoes and earthquakes? (1) They are centered at the poles. (2) They are located in the same geographic areas. (3) They
Name: Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. Which best describes a major characteristic of both volcanoes and earthquakes? (1) They are centered at the poles. (2) They are located in the same geographic areas. (3) They
Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures
 Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures Art Frankel U.S. Geological Survey Seattle, WA GeoPrisms-Earthscope
Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures Art Frankel U.S. Geological Survey Seattle, WA GeoPrisms-Earthscope
8.0 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 8.0 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In November 2008, Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) informed the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) that preliminary results from the Diablo Canyon Power Plant (DCPP) Long
8.0 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In November 2008, Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) informed the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) that preliminary results from the Diablo Canyon Power Plant (DCPP) Long
Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels.
 Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels. Rugged Terra Rugged terra are mountainous regions of the moon. Wrinkle Ridges Wrinkle Ridges are created through
Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels. Rugged Terra Rugged terra are mountainous regions of the moon. Wrinkle Ridges Wrinkle Ridges are created through
Correlation of gravel deposits from trenching project on Alder Creek fluvial terrace near Point Arena, California
 Correlation of gravel deposits from trenching project on Alder Creek fluvial terrace near Point Arena, California Aletha Lee Department of Geology and Geography, West Virginia University, White Hall, Morgantown,
Correlation of gravel deposits from trenching project on Alder Creek fluvial terrace near Point Arena, California Aletha Lee Department of Geology and Geography, West Virginia University, White Hall, Morgantown,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL DESCRIPTIONS OF OTHER STRATIGRAPHIC SECTIONS Cherry Creek In its middle reaches, Cherry Creek meanders between three paired terraces within a narrow bedrock valley. The highest is
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL DESCRIPTIONS OF OTHER STRATIGRAPHIC SECTIONS Cherry Creek In its middle reaches, Cherry Creek meanders between three paired terraces within a narrow bedrock valley. The highest is
Earthquakes Chapter 19
 Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
MINNESOTA DEEP TEST PROTOCOL PROJECT
 MINNESOTA DEEP TEST PROTOCOL PROJECT Mn/DOT Agreement No. 85878 OSA License No. 04-030 Authorized and Sponsored by: MINNESOTA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION FEDERAL HIGHWAY ADMINISTRATION Prepared by COMMONWEALTH
MINNESOTA DEEP TEST PROTOCOL PROJECT Mn/DOT Agreement No. 85878 OSA License No. 04-030 Authorized and Sponsored by: MINNESOTA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION FEDERAL HIGHWAY ADMINISTRATION Prepared by COMMONWEALTH
FINAL TECHNICAL REPORT. Award Title Rupture History of the San Andreas Fault in the Carrizo Plain prior to 1300 A.D.
 FINAL TECHNICAL REPORT Award Title Rupture History of the San Andreas Fault in the Carrizo Plain prior to 1300 A.D. Lisa Grant Ludwig Principal Investigator: with Sinan O. Akciz Program in Public Health
FINAL TECHNICAL REPORT Award Title Rupture History of the San Andreas Fault in the Carrizo Plain prior to 1300 A.D. Lisa Grant Ludwig Principal Investigator: with Sinan O. Akciz Program in Public Health
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. GEOLOGY AND SOILS
 IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. GEOLOGY AND SOILS The following section is a summary of the geotechnical report conducted for the proposed project. The Report of Geotechnical Investigation Proposed
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. GEOLOGY AND SOILS The following section is a summary of the geotechnical report conducted for the proposed project. The Report of Geotechnical Investigation Proposed
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Controls on clastic systems in the Angoche basin, Mozambique: tectonics, contourites and petroleum systems
 P2-2-13 Controls on clastic systems in the Angoche basin, Mozambique: tectonics, contourites and petroleum systems Eva Hollebeek, Olivia Osicki, Duplo Kornpihl Schlumberger, London, UK Introduction Offshore
P2-2-13 Controls on clastic systems in the Angoche basin, Mozambique: tectonics, contourites and petroleum systems Eva Hollebeek, Olivia Osicki, Duplo Kornpihl Schlumberger, London, UK Introduction Offshore
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan
 Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan Angelier, J., Chang, T.Y., Hu, J.C., Chang, C.P., Siame, L., Lee, J.C., Deffontaines, B., Chu, H.T, Lu, C.Y., Does extrusion occur
Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan Angelier, J., Chang, T.Y., Hu, J.C., Chang, C.P., Siame, L., Lee, J.C., Deffontaines, B., Chu, H.T, Lu, C.Y., Does extrusion occur
Description of faults
 GLG310 Structural Geology Description of faults Horizontal stretch Crustal thickness Regional elevation Regional character Issues Normal Thrust/reverse Strike-slip >1 1 in one direction and < 1 in
GLG310 Structural Geology Description of faults Horizontal stretch Crustal thickness Regional elevation Regional character Issues Normal Thrust/reverse Strike-slip >1 1 in one direction and < 1 in
B.C. s Offshore Oil and Gas: a Guide to the Geology and Resources.
 B.C. s Offshore Oil and Gas: a Guide to the Geology and Resources. Introduction Beneath the offshore regions of British Columbia are four moderately large, geologically young sedimentary basins (Figure
B.C. s Offshore Oil and Gas: a Guide to the Geology and Resources. Introduction Beneath the offshore regions of British Columbia are four moderately large, geologically young sedimentary basins (Figure
Paleoearthquakes and slip rates of the North Tabriz Fault, NW Iran: preliminary results
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N. 5, October 2003 Paleoearthquakes and slip rates of the North Tabriz Fault, NW Iran: preliminary results Khaled Hessami ( 1 ), Daniela Pantosti ( 2 ), Hadi Tabassi ( 1
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N. 5, October 2003 Paleoearthquakes and slip rates of the North Tabriz Fault, NW Iran: preliminary results Khaled Hessami ( 1 ), Daniela Pantosti ( 2 ), Hadi Tabassi ( 1
Seismic Hazard Assessment of Switzerland, Falko Bethmann October 1 st, 2008
 Seismic Hazard Assessment of Switzerland, 2004 Falko Bethmann October 1 st, 2008 Outline Definition of earthquake sources Definition of seismic recurrence characteristics for each source Ground motion
Seismic Hazard Assessment of Switzerland, 2004 Falko Bethmann October 1 st, 2008 Outline Definition of earthquake sources Definition of seismic recurrence characteristics for each source Ground motion
Late Holocene Rupture History of the Alpine Fault in South Westland, New Zealand
 Western Washington University Western CEDAR Geology Faculty and Staff Publications Geology 4-2012 Late Holocene Rupture History of the Alpine Fault in South Westland, New Zealand Kelvin Berryman Alan Cooper
Western Washington University Western CEDAR Geology Faculty and Staff Publications Geology 4-2012 Late Holocene Rupture History of the Alpine Fault in South Westland, New Zealand Kelvin Berryman Alan Cooper
Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan
 Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan Abstract Longitudinal Valley was the suture zone between the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Peinanshan was the southest segment of the
Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan Abstract Longitudinal Valley was the suture zone between the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Peinanshan was the southest segment of the
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Appendix C - Geotechnical Report. Landmark Consultants, Inc.
 Appendix C - Geotechnical Report Landmark Consultants, Inc. LCI Report No. LP18128 Fault Map Regional Review of the current Alquist-Priolo Earthquake Fault Zone maps (CGS, 2000a) indicates that
Appendix C - Geotechnical Report Landmark Consultants, Inc. LCI Report No. LP18128 Fault Map Regional Review of the current Alquist-Priolo Earthquake Fault Zone maps (CGS, 2000a) indicates that
NUCLEAR POWER PLANT SITE SELECTION
 NUCLEAR POWER PLANT SITE SELECTION ABDELATY B. SALMAN Ex-Chairman Nuclear Materials Authority, Cairo, Egypt I. Introduction The aim of this article is to present the requirements and characteristics for
NUCLEAR POWER PLANT SITE SELECTION ABDELATY B. SALMAN Ex-Chairman Nuclear Materials Authority, Cairo, Egypt I. Introduction The aim of this article is to present the requirements and characteristics for
COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009
 Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009 Geologic landforms Purpose: By studying aerial photographs you will learn to identify different kinds of geologic features based on their different morphologies and learn
Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009 Geologic landforms Purpose: By studying aerial photographs you will learn to identify different kinds of geologic features based on their different morphologies and learn
depression above scarp scarp
 1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
Earthquake Damage Scenario
 Chapter 2. Earthquake Damage Scenario CHAPTER 2. EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO 2.1 Earthquake Scenario Setting and Ground Motion 2.1.1 Fault in the Philippines The Philippines is located in latitude 5 to
Chapter 2. Earthquake Damage Scenario CHAPTER 2. EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO 2.1 Earthquake Scenario Setting and Ground Motion 2.1.1 Fault in the Philippines The Philippines is located in latitude 5 to
Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY
 Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY A Technical Report By MARTINEZ BRAVO Delvin Abdiel (MEE10515) Disaster
Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY A Technical Report By MARTINEZ BRAVO Delvin Abdiel (MEE10515) Disaster
Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1
 Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1 Magdy Torab* 2 * Prof. of Geomorphology, Department of Geography, Damanhour University, Egypt 3 E-mail: magdytorab@hotmail.com.
Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1 Magdy Torab* 2 * Prof. of Geomorphology, Department of Geography, Damanhour University, Egypt 3 E-mail: magdytorab@hotmail.com.
Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System
 SRL complex earthquakes 5/22/09 1 Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System Niels Bohr once observed How wonderful that we have met with a paradox. Now we have some hope of making progress. This situation
SRL complex earthquakes 5/22/09 1 Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System Niels Bohr once observed How wonderful that we have met with a paradox. Now we have some hope of making progress. This situation
Movement on hidden faults within the Hamilton Basin. Dr Vicki Moon PEngGeol, Dr Willem de Lange & Michael Cummins School of Science
 Movement on hidden faults within the Hamilton Basin Dr Vicki Moon PEngGeol, Dr Willem de Lange & Michael Cummins School of Science Introduction In May 2015 we presented evidence suggesting 3 fault zones
Movement on hidden faults within the Hamilton Basin Dr Vicki Moon PEngGeol, Dr Willem de Lange & Michael Cummins School of Science Introduction In May 2015 we presented evidence suggesting 3 fault zones
Exploring the Belgian Maas valley between Neeroeteren and Bichterweert for evidence of active faulting
 Geologica Belgica International Meeting Aardk. Mededel., 2002, XX, 000-000 Exploring the Belgian Maas valley between Neeroeteren and Bichterweert for evidence of active faulting K. Vanneste, K. Verbeeck
Geologica Belgica International Meeting Aardk. Mededel., 2002, XX, 000-000 Exploring the Belgian Maas valley between Neeroeteren and Bichterweert for evidence of active faulting K. Vanneste, K. Verbeeck
Structural Geology of the Mountains
 Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Preliminary Observations of the January 8, 2006 Kythira Island (South Western Greece) Earthquake (Mw 6.9).
 Preliminary Observations of the January 8, 2006 Kythira Island (South Western Greece) Earthquake (Mw 6.9). Following the earthquake of January 8 2006, EERI members Dr. E. Lekkas, Professor of Dynamic Tectonics
Preliminary Observations of the January 8, 2006 Kythira Island (South Western Greece) Earthquake (Mw 6.9). Following the earthquake of January 8 2006, EERI members Dr. E. Lekkas, Professor of Dynamic Tectonics
RECENT COMPREHENSIVE TSUNAMI MODELING FOR COASTAL OREGON
 RECENT COMPREHENSIVE TSUNAMI MODELING FOR COASTAL OREGON Speaker: George R. Priest, Oregon Dept. of Geology and Mineral Industries Pardee Keynote Symposium Great Earthquakes, the Cascadia Subduction Zone,
RECENT COMPREHENSIVE TSUNAMI MODELING FOR COASTAL OREGON Speaker: George R. Priest, Oregon Dept. of Geology and Mineral Industries Pardee Keynote Symposium Great Earthquakes, the Cascadia Subduction Zone,
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Pearson Education, Inc.
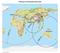 Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Magnitude 6.3 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Structural Style in the Peel Region, NWT and Yukon
 Structural Style in the Peel Region, NWT and Yukon Adriana Taborda* Husky Energy and University of Calgary, Calgary, AB Adriana.Taborda@huskyenergy.ca and Deborah Spratt University of Calgary, Calgary,
Structural Style in the Peel Region, NWT and Yukon Adriana Taborda* Husky Energy and University of Calgary, Calgary, AB Adriana.Taborda@huskyenergy.ca and Deborah Spratt University of Calgary, Calgary,
Luca Guerrieri Valerio Comerci Eutizio Vittori
 Earthquake Environmental Effects induced by the 1908 December 28 th Messina earthquake: an in-situ contribute to the Messina supersite (GEO Task DI-09-01a Vulnerability Mapping and Risk Assessment Luca
Earthquake Environmental Effects induced by the 1908 December 28 th Messina earthquake: an in-situ contribute to the Messina supersite (GEO Task DI-09-01a Vulnerability Mapping and Risk Assessment Luca
Active fault traces along Bhuj Fault and Katrol Hill Fault, and trenching survey at Wandhay, Kachchh, Gujarat, India
 Active fault traces along Bhuj Fault and Katrol Hill Fault, and trenching survey at Wandhay, Kachchh, Gujarat, India Michio Morino 1,, Javed N Malik 2,, Prashant Mishra 2,, Chandrashekhar Bhuiyan 2, and
Active fault traces along Bhuj Fault and Katrol Hill Fault, and trenching survey at Wandhay, Kachchh, Gujarat, India Michio Morino 1,, Javed N Malik 2,, Prashant Mishra 2,, Chandrashekhar Bhuiyan 2, and
Landslides Classification
 ENVIRONMENTAL GEOTECHNICS Landslides Classification Prof. Ing. Marco Favaretti University of Padova Department of Civil, Environmental and Architectural Engineering, Via Ognissanti, 39 Padova (Italy) phone:
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOTECHNICS Landslides Classification Prof. Ing. Marco Favaretti University of Padova Department of Civil, Environmental and Architectural Engineering, Via Ognissanti, 39 Padova (Italy) phone:
Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2015 Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard Solomon Buckman University
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2015 Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard Solomon Buckman University
Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018 Questions? Lecture Final Exam Lecture Section 1 Friday May 4, 8:00-10:00am Lecture Section 2 Friday May 4, 3:10-5:10 pm Final Exam is 70% new material
Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018 Questions? Lecture Final Exam Lecture Section 1 Friday May 4, 8:00-10:00am Lecture Section 2 Friday May 4, 3:10-5:10 pm Final Exam is 70% new material
Geo736: Seismicity and California s Active Faults Introduction
 Geo736: Seismicity and California s Active Faults Course Notes: S. G. Wesnousky Spring 2018 Introduction California sits on the boundary of the Pacific - North American plate boundary (Figure 1). Relative
Geo736: Seismicity and California s Active Faults Course Notes: S. G. Wesnousky Spring 2018 Introduction California sits on the boundary of the Pacific - North American plate boundary (Figure 1). Relative
Analysis of Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Spreading Data from the 2010 Darfield and 2011 Christchurch Earthquakes
 Analysis of Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Spreading Data from the 2010 Darfield and 2011 Christchurch Earthquakes K. Robinson, B. A. Bradley, & M. Cubrinovski University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New
Analysis of Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Spreading Data from the 2010 Darfield and 2011 Christchurch Earthquakes K. Robinson, B. A. Bradley, & M. Cubrinovski University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN THE TSUNAMI RESEARCH IN GREECE: A SHORT REVIEW GERASSIMOS A. PAPADOPOULOS
 CHAPTER 7 RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN THE TSUNAMI RESEARCH IN GREECE: A SHORT REVIEW GERASSIMOS A. PAPADOPOULOS Institute of Geodynamics, National Observatory of Athens, 11810 Athens, Greece In: S. L. SOLOVIEV,
CHAPTER 7 RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN THE TSUNAMI RESEARCH IN GREECE: A SHORT REVIEW GERASSIMOS A. PAPADOPOULOS Institute of Geodynamics, National Observatory of Athens, 11810 Athens, Greece In: S. L. SOLOVIEV,
Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis
 Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis 5 Characteristics of the Ocean Trenches Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter.
Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis 5 Characteristics of the Ocean Trenches Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter.
Offshore Evidence for Uplift Rate Boundaries. Hans AbramsonWard Diablo Canyon SSHAC SSC Workshop 2 November 7, 2012
 Offshore Evidence for Uplift Rate Boundaries Hans AbramsonWard Diablo Canyon SSHAC SSC Workshop 2 November 7, 2012 Questions asked by the TI team Discuss your ability to distinguish and correlate offshore
Offshore Evidence for Uplift Rate Boundaries Hans AbramsonWard Diablo Canyon SSHAC SSC Workshop 2 November 7, 2012 Questions asked by the TI team Discuss your ability to distinguish and correlate offshore
DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
 III. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION 3.1. Rift Geometry Identification Based on recent analysis of modern and ancient rifts, many previous workers concluded that the basic structural unit of continental
III. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION 3.1. Rift Geometry Identification Based on recent analysis of modern and ancient rifts, many previous workers concluded that the basic structural unit of continental
Physical Geology Lab. Teacher Check (show your screen to your teacher) Part ONE: Dynamic Earth. Continents Over Time.
 Physical Geology Lab Name Hour Part ONE: Dynamic Earth Earth s Structure Name the Layer: The only liquid layer Only a few miles thick (under oceans) Mostly solid iron and nickel Made of hot, semi-solid
Physical Geology Lab Name Hour Part ONE: Dynamic Earth Earth s Structure Name the Layer: The only liquid layer Only a few miles thick (under oceans) Mostly solid iron and nickel Made of hot, semi-solid
Fault growth & linkage
 Fault growth & linkage Important to understand fault growth, interaction & linkage Continental extension and basin formation Controls on subsurface fluid flow Hydrocarbon exploration & production Minerals
Fault growth & linkage Important to understand fault growth, interaction & linkage Continental extension and basin formation Controls on subsurface fluid flow Hydrocarbon exploration & production Minerals
Mw 7.8, Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia Wed, 2 March 2016 at 12:49:48 UTC M /03/03
 Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Seismogenic structure of 1935 Hsinchu-Taichung (M GR =7.1) earthquake, Miaoli, western Taiwan 1935 (M GR =7.1)
 Seismogenic structure of 1935 Hsinchu-Taichung (M GR =7.1) earthquake, Miaoli, western Taiwan 1935 (M GR =7.1) Y.N. Nina Lin; Y.G. Chen; Y.M. Wu (Inst. of Geosciences, NTU); K.M. Yang (Exploration and
Seismogenic structure of 1935 Hsinchu-Taichung (M GR =7.1) earthquake, Miaoli, western Taiwan 1935 (M GR =7.1) Y.N. Nina Lin; Y.G. Chen; Y.M. Wu (Inst. of Geosciences, NTU); K.M. Yang (Exploration and
Arthur Saller 1. Search and Discovery Article #51393 (2017)** Posted June 26, Abstract
 PS Mixed Carbonates and Siliciclastics North of the Mahakam Delta, Offshore East Kalimantan, Indonesia* Arthur Saller 1 Search and Discovery Article #51393 (2017)** Posted June 26, 2017 *Adapted from poster
PS Mixed Carbonates and Siliciclastics North of the Mahakam Delta, Offshore East Kalimantan, Indonesia* Arthur Saller 1 Search and Discovery Article #51393 (2017)** Posted June 26, 2017 *Adapted from poster
Lecture # 6. Geological Structures
 1 Lecture # 6 Geological Structures ( Folds, Faults and Joints) Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 The wavy undulations
1 Lecture # 6 Geological Structures ( Folds, Faults and Joints) Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 The wavy undulations
Neotectonics of the Pedro de Valdivia Area, northern Chile
 Neotectonics of the Pedro de Valdivia Area, northern Chile Angelo Villalobos 1*, Joaquín Cortés-Aranda 1, Luis Astudillo 1, Rodrigo Riquelme 1 and Arturo Jensen 1 (1) Universidad Católica del Norte, 0610
Neotectonics of the Pedro de Valdivia Area, northern Chile Angelo Villalobos 1*, Joaquín Cortés-Aranda 1, Luis Astudillo 1, Rodrigo Riquelme 1 and Arturo Jensen 1 (1) Universidad Católica del Norte, 0610
Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting
 Crustal Deformation AKA Structural geology (adapted from Brunkel, 2012) Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting How Rocks Deform: 4 Controls
Crustal Deformation AKA Structural geology (adapted from Brunkel, 2012) Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting How Rocks Deform: 4 Controls
Late Quaternary left-lateral slip rate of the Haiyuan fault, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau
 TECTONICS, VOL. 28,, doi:10.1029/2008tc002302, 2009 Late Quaternary left-lateral slip rate of the Haiyuan fault, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau Chuanyou Li, 1 Pei-zhen Zhang, 1 Jinhui Yin,
TECTONICS, VOL. 28,, doi:10.1029/2008tc002302, 2009 Late Quaternary left-lateral slip rate of the Haiyuan fault, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau Chuanyou Li, 1 Pei-zhen Zhang, 1 Jinhui Yin,
2.2.7 Backbarrier flats
 FIGURE 24. VERTICAL PHOTOGRAPH SHOWING THE DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL PARABOLIC DUNES FROM BLOWOUTS IN A LARGE RELICT FOREDUNE NORTHWEST OF HUNTER'S CREEK. PHOTOGRAPH COURTESY OF CAR'T'ER HOLT HARVEY FORESTS
FIGURE 24. VERTICAL PHOTOGRAPH SHOWING THE DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL PARABOLIC DUNES FROM BLOWOUTS IN A LARGE RELICT FOREDUNE NORTHWEST OF HUNTER'S CREEK. PHOTOGRAPH COURTESY OF CAR'T'ER HOLT HARVEY FORESTS
Earthquakes and Faulting
 Earthquakes and Faulting Crustal Strength Profile Quakes happen in the strong, brittle layers Great San Francisco Earthquake April 18, 1906, 5:12 AM Quake lasted about 60 seconds San Francisco was devastated
Earthquakes and Faulting Crustal Strength Profile Quakes happen in the strong, brittle layers Great San Francisco Earthquake April 18, 1906, 5:12 AM Quake lasted about 60 seconds San Francisco was devastated
KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B
 GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon
 Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
