Neotectonics of the Pedro de Valdivia Area, northern Chile
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Carter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neotectonics of the Pedro de Valdivia Area, northern Chile Angelo Villalobos 1*, Joaquín Cortés-Aranda 1, Luis Astudillo 1, Rodrigo Riquelme 1 and Arturo Jensen 1 (1) Universidad Católica del Norte, 0610 Avenida Angamos, Antofagasta, Chile. * Presenting Author s 1. Introduction Upper plate faulting is one of the main processes leading Cenozoic landscape evolution in the hyperarid Coastal Forearc of northern Chile (~18 S-23 S). There, predominant kinematic styles are represented by NS striking normal faults, NNW to NW trending reverse faults and EW striking reverse faults [e.g. Allmendinger and González, 2010]. Long term activity along these faults has conducted the construction of conspicuous scarps that form mountain range fronts of even 500 m height [González et al., 2003; Allmendinger et al., 2005]. The most recent expression of activity along these faults is given by scarps developed on young alluvial gravels [e.g. González et al., 2006; Cortés et al., 2012]. Despite this evidence, no important (Mw>7) earthquakes have been registered along them during historical times [e.g. Comte et al., 1994]. However, a paleoseismological survey performed during the FONDECYT project (GG) concluded that faults like Mejillones, Salar del Carmen and Chomache (Figure 1a) have triggered Mw~7 events during late Pleistocene-Holocene times. a Figure 1. a) ASTER DEM map showing the study area with the main faults and key localities. CCF= Cerro Cordón Fault; SCF= Salar del Carmen Fault; SVF= Sierra Valenzuela Fault; CF= Colupo Fault; WAF= Western Antucoya Fault; EAF= Eastern Antucoya Fault; b) WAF and EAF controlling a graben basin; and c) Normal faults leading the staircase-type topography in the area. F= Fault; HG= Halfgraben basin. In this contribution we provide neotectonic evidence of Quaternary activity along normal and reverse faults in the Carta Pedro de Valdivia area (Figure 1a). These faults are located just above the northern termination of the interplate seismogenic gap where the 1877 Iquique Mw 8.7 earthquake occurred [Comte and Pardo, 1991]. Null
2 information about the recent activity of upper plate faults in this area is available, thus we intend to give a first approach to precise the seismic hazard that they represent. 2. Structural context The Pedro de Valdivia area is located in the eastern part of the Coastal Cordillera at (Figure 1a). There, the most important faults are part of the Atacama Fault System [Arabasz, 1971], which formed in Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous as a sinistral strike slip fault [e.g. Scheuber and Andriessen, 1990]. This system extends for more than 1000 km between 21 S and 26 S and its main branch in the Pedro de Valdivia area is given by the Salar del Carmen Fault (SCF; Figure 1a). In general, structures in the study area are represented by sets of NNE and NW faults that have produced a graben and halfgraben basins that flank mountain ranges of less than 2000 ma.s.l (Figure 1b). This configuration constitutes a staircase-type topography (Figure 1c). The limits between ranges and halfgraben are dominated by piedmonts composed by at least two generations of alluvial surfaces partially buried by colluvial deposits. In most of the cases alluvial surfaces and also colluvial deposits are clearly affected by fault displacement. At the northern part of the area, near the Antucoya Mine (Figure 1a), the most important structures are given by NNE normal faults that define a graben filled with ~600 m of alluvial gravels. We named these faults as Western (WAF) and Eastern (EAF) Antucoya faults (Figure 1a-b). Further north, the Colupo Fault (CF) has promoted the uplifting of a NS mountain range where stratified crystalline rocks outcrop (Figure 1a). Also, NW reverse faults occur at this part of the area, spatially related to the intrusion of hypabyssal bodies. One of these faults is the Grava Fault (GF; Figure 1a). At the southern part, west of Algorta (Figure 1a), NNE normal faults have conducted the uplifting of NNE oriented mountain ranges where sedimentary, volcanic and intrusive rocks outcrop. The most important structures flanking mountain ranges are the Cerro Cordón, Salar del Carmen and Sierra Valenzuela faults (Figure 1a). Immediately east of these ranges, halfgraben basins filled with alluvial deposits exist (Figure 1c). 3. Neotectonic evidence Neotectonics of the Pedro de Valdivia area is mainly expressed in piedmont surfaces preserved at this part of the Coastal Cordillera. Also, in some sites we found that recent fault activity has affected crystalline rocks in the core of mountain ranges. We report two types of neotectonic features: i) Fault scarps and ii) Tensional cracks. i) Fault scarps. These morphological features have been abundantly identified in alluvial gravels and rarely affecting crystalline rocks. Scarps constructed in alluvial gravels have been produced by normal and reverse faulting. Normal fault scarps are typically 0.5 to 4 m height and are dominated by a debris slope facies [sensu Wallace, 1977]. A well example of this kind of scarps is along the Colupo Fault (CF), where several subsidiary normal faults dislocate a piedmont surface (Figure 2a). At this site, we observed knick points along gullies that dissect some of the scarps (Figure 2b). Although the topography of the area allows inferring that the dominant process conducted by faults is extension, the deformation of the youngest deposits has occurred
3 mainly by reverse faulting. Scarps produced by reverse faulting are 1 to 5 m height and dominated by a debris slope facies, although free face is still preserved in some cases. The best example of this type of scarps occurs along the Grava Fault (GF), west of the Antucoya Mine (Figure 1a, 2c). There, a reverse fault promotes the uplifting of an alluvial surface in a mountain front where crystalline rocks outcrop (Figure 2c). Moreover, at this site the fault dislocates even colluvial deposits (Figure 2c). Reverse fault scarps have been also recognized affecting crystalline rocks. Along the northern termination of the Grava Fault (GV), a remarkable fault scarp puts into contact intrusive and volcanic rocks (Figure 2d). There, the fault scarp is dominated by a free face that dips 80 SW with almost no accumulation of debris facies (Figure 2d). Figure 2. a) Normal faults affecting a piedmont surface in the periphery if the Colupo Fault; b) Knick points in gullies displaced by faults showed in a); c) Grava Fault displacing alluvial gravels (AG) and colluvial deposits (CD) at the mountain front of volcanic rocks occur (J3i). The scarp is dominated by the debris slope (DS) facies; d) Grava Fault putting into contact volcanic (J3i) and hypabissal (Hyp) rocks. The free face (FF) dominates the scarp profile. ii) Tensional cracks. Tectonic cracks were identified in two kinds of sites. The first one is the periphery of the most conspicuous identified normal fault scarps (e.g. SCF). There, tensional cracks affect alluvial gravels composing the piedmont surfaces and even the sedimentary deposits of active channels (Figure 3a). These cracks are hundreds of meters long and oriented N5-20E. They present apertures of 1-15 cm and are partially filled with fine sediments arranged in subvertical layers parallel to the crack walls. Another site where these cracks exist corresponds to the hanging wall of reverse faults (Figure 3b). There, these cracks are parallel to the fault strike, providing an irregular appearance to the scarp profile. According to McCalpin [1996], these cracks are the result of the collapse of the deformed material. 4. Discussion Normal faulting has dominated the long term deformation in the study area. This is inferred from the graben-halfgraben topography that characterizes the zone. On the
4 other hand, field observation suggests that both normal and reverse faults have experienced activity during the Quaternary. We base this statement on the fact that the youngest sedimentary deposits composing piedmont surfaces and colluvium are clearly deformed. Locally, normal faulting has been observed affecting Quaternary deposits as for instance along the Colupo Fault (Figure 2a-b). Nevertheless, it seems that normal faulting is subsidiary in comparison with reverse faulting during the Quaternary. This latter deformation style has been observed, for example, along the Grava Fault (Figure 2c). Based on this evidence, we postulate that compression is the main process controlling upper plate fault activity during the Quaternary at this part of the Coastal Forearc. Figure 3. a) Tensional cracks on alluvial deposits at the periphery of normal faults in the area. b) Tensional cracks in the hangingwall block of reverse faults in the area. Scarp geometry suggests discrete slip events along normal and reverse faults in the area. Based on their heights, we interpret that the causative slip events are coherent with Mw~7 earthquakes [sensu Wells and Coppersmith, 1994]. This appears to be clearer in the case of reverse faults affecting crystalline rocks, as the Grava Fault does at its northern termination. Indeed, this fault has generated a prominent free face dominated scarp of around 1.7 m height, which was very likely constructed by a single earthquake. With the available evidence, we think that faults in the Pedro de Valdivia area must be considered active. However, we plan to develop detailed paleoseismological and neotectonic studies in the near future to constrain their seismic potential. Also, further investigations for evaluating the stress build up along them as consequence of the subduction earthquake cycle are needed. With this latter approach, we could explore the dynamical relationship between upper plate fault activity and the stages of the subduction cycle. In this way, we point to better precise the seismic risk in the Coastal Forearc due to both, the 1877 gap and upper plate fault activity. References Allmendinger, R. W., G. González, J. Yu, G. Hoke, and B. Isacks Trench-parallel shortening in the northern Chilean forearc: Tectonic and climatic implications, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 117(1), , doi: /b Allmendinger, R. W., and G. González Neogene to Quaternary tectonics of the coastal Cordillera, northern Chile, Tectonophysics, 495(1 2), , oi: /j.tecto Arabasz, W. J Geological and geophysical studies of the Atacama Fault System in northern Chile, PhD thesis, 264 pp., Calif. Inst. of Technol., Pasadena. Allmendinger, R. W., G. González, J. Yu, G. Hoke, and B. Isacks Trench-parallel shortening in the northern Chilean forearc: Tectonic and climatic implications, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 117(1), , doi: / B Comte, D., and M. Pardo Reappraisal of great historical earthquakes in the northern Chile and southern Peru seismic gaps, Nat. Hazards, 4, Cortés A., J., G. González L., S. A. Binnie, R. Robinson, S. P. H. T. Freeman, and G. Vargas E Paleoseismology of the Mejillones Fault, northern Chile: Insights from cosmogenic 10Be and optically stimulated luminescence determinations, Tectonics, 31, TC2017, doi: /2011tc González, G., Dunai, T., Carrizo, D., y Allmendinger, R Young displacements on the Atacama Fault System, northern Chile from field observations and cosmogenic 21Ne concentrations: Tectonics, v. 25, p. TC3006. González, G., Cembrano, J., Carrizo, D., Macci, A., and Schneider, H. 2003, The link between forearc tectonics and Pliocene-Quaternary deformation of the Coastal Cordillera, northern Chile. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, v. 16, p McCalpin, J Paleoseismology, Academic Press, California, USA. Scheuber, E., and P. M. Andriessen The kinematics significance of the Atacama Fault zone, northern, Chile, J. Struct. Geol., 21, Wells, D.L. y Coppersmith, K.J New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, vo. 84, pp Wallace, R. E Profiles and ages of young fault scarps, northcentral Nevada, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 88, , doi: / (1977)88<1267:PAAOYF>2.0.CO;2.
5 Save file as a word document with the first author as a file name and then it as an attachment to geosur2013@unab.cl stating whether you prefer a poster or a talk and if you are a registered student.
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building
 Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI
 STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI LAURA K.O. SMITH AND SARAHTSETSEG PUREDORG Princeton University, Mongolian University of Science and Technology Sponsors: Ramon Gonzalez-Mieres
STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI LAURA K.O. SMITH AND SARAHTSETSEG PUREDORG Princeton University, Mongolian University of Science and Technology Sponsors: Ramon Gonzalez-Mieres
Normal and reverse faulting driven by the subduction zone earthquake cycle in the northern Chilean fore arc
 Click Here for Full Article Normal and reverse faulting driven by the subduction zone earthquake cycle in the northern Chilean fore arc John P. Loveless, 1,2 Richard W. Allmendinger, 1 Matthew E. Pritchard,
Click Here for Full Article Normal and reverse faulting driven by the subduction zone earthquake cycle in the northern Chilean fore arc John P. Loveless, 1,2 Richard W. Allmendinger, 1 Matthew E. Pritchard,
Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source
 Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Deformation of Rocks. Orientation of Deformed Rocks
 Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand
 Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand Piyaphong Chenrai Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand Piyaphong Chenrai Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
Recent crustal deformation in the Antofagasta region (northern Chile) and the subduction process
 Geophys. J. Int. (1998) 132, 302 338 Recent crustal deformation in the Antofagasta region (northern Chile) and the subduction process B. Delouis,1,* H. Philip,2 L. Dorbath1,3 and A. Cisternas1 1 Institut
Geophys. J. Int. (1998) 132, 302 338 Recent crustal deformation in the Antofagasta region (northern Chile) and the subduction process B. Delouis,1,* H. Philip,2 L. Dorbath1,3 and A. Cisternas1 1 Institut
Structural deformation across the southwest Mina deflection, California-Nevada: Field studies in the Huntoon Springs area.
 Structural deformation across the southwest Mina deflection, California-Nevada: Field studies in the Huntoon Springs area. Eliya R. Hogan Advisor: Jeff Lee Introduction and purpose of study: The Mina deflection
Structural deformation across the southwest Mina deflection, California-Nevada: Field studies in the Huntoon Springs area. Eliya R. Hogan Advisor: Jeff Lee Introduction and purpose of study: The Mina deflection
PALEOSEISMOLOGY: SITES (17)
 GG 454 February 8, 2002 1 PALEOSEISMOLOGY: SITES (17) Schedule Updates and Reminders: Reading for this lecture: Big Picture - Skim "Applications" in PP 1360 Reading for next lecture: Handouts from Active
GG 454 February 8, 2002 1 PALEOSEISMOLOGY: SITES (17) Schedule Updates and Reminders: Reading for this lecture: Big Picture - Skim "Applications" in PP 1360 Reading for next lecture: Handouts from Active
December 21, Chapter 11 mountain building E.notebook. Feb 19 8:19 AM. Feb 19 9:28 AM
 Mountains form along convergent plate boundaries. Typically (usually) if you look at a mountain range, you know that it is at a plate boundary (active continental margin) or has been some time in the past
Mountains form along convergent plate boundaries. Typically (usually) if you look at a mountain range, you know that it is at a plate boundary (active continental margin) or has been some time in the past
Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station
 Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station Scott Lindvall SSC TI Team Lead Palo Verde SSC SSHAC Level 3 Project Tuesday, March 19, 2013 1 Questions from
Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station Scott Lindvall SSC TI Team Lead Palo Verde SSC SSHAC Level 3 Project Tuesday, March 19, 2013 1 Questions from
Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the west of Kunlunshan pass earthquake ( M S 811) with high spatial resolution satellite images
 48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,. M S 811.,2005,48 (2) :321 326 Shan X J, Li J H, Ma C. Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the West of Kunlunshan Pass
48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,. M S 811.,2005,48 (2) :321 326 Shan X J, Li J H, Ma C. Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the West of Kunlunshan Pass
Upper plate reverse fault reactivation and the unclamping of the megathrust during the 2014 Northern Chile earthquake sequence
 GSA Data Repository 2015235 Supplemental Information for Upper plate reverse fault reactivation and the unclamping of the megathrust during the 2014 Northern Chile earthquake sequence Geological background
GSA Data Repository 2015235 Supplemental Information for Upper plate reverse fault reactivation and the unclamping of the megathrust during the 2014 Northern Chile earthquake sequence Geological background
WESTERN STATES SEISMIC POLICY COUNCIL POLICY RECOMMENDATION Definitions of Recency of Surface Faulting for the Basin and Range Province
 WESTERN STATES SEISMIC POLICY COUNCIL POLICY RECOMMENDATION 15-3 Definitions of Recency of Surface Faulting for the Basin and Range Province Policy Recommendation 15-3 WSSPC recommends that each state
WESTERN STATES SEISMIC POLICY COUNCIL POLICY RECOMMENDATION 15-3 Definitions of Recency of Surface Faulting for the Basin and Range Province Policy Recommendation 15-3 WSSPC recommends that each state
From Punchbowl to Panum: Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain
 From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
Lecture # 6. Geological Structures
 1 Lecture # 6 Geological Structures ( Folds, Faults and Joints) Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 The wavy undulations
1 Lecture # 6 Geological Structures ( Folds, Faults and Joints) Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 The wavy undulations
Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny
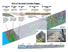 Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny AA. Accretionary Prism BB. Forearc Basin Sediment scraped off of subducting plate Sediment derived from the volcanic arc CC. Volcanic Arc Magmatic intrusion into the
Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny AA. Accretionary Prism BB. Forearc Basin Sediment scraped off of subducting plate Sediment derived from the volcanic arc CC. Volcanic Arc Magmatic intrusion into the
Earthquakes in Barcelonnette!
 Barcelonnette in the Ubaye valley : the landscape results of large deformations during the alpine orogene (40 5 Myr in this area) and the succession of Quaternary glaciations. The sedimentary rocks are
Barcelonnette in the Ubaye valley : the landscape results of large deformations during the alpine orogene (40 5 Myr in this area) and the succession of Quaternary glaciations. The sedimentary rocks are
S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura, and Y. Niwa International Research Institute of Disaster Science, Tohoku University, Japan
 The first surface-rupturing earthquake in 20 years on a HERP major active fault: Mw=6.2 2014 Nagano, Japan, event along the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line is not characteristic S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura,
The first surface-rupturing earthquake in 20 years on a HERP major active fault: Mw=6.2 2014 Nagano, Japan, event along the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line is not characteristic S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura,
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11
 Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
2. Tsunami Source Details
 2. Tsunami Source Details The Northland area faces a range of potential tsunamigenic sources that include several local and distant fault systems and underwater landslides. A NIWA study (Goff et al. 2006)
2. Tsunami Source Details The Northland area faces a range of potential tsunamigenic sources that include several local and distant fault systems and underwater landslides. A NIWA study (Goff et al. 2006)
KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B
 GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
7 Ground Motion Models
 7 Ground Motion Models 7.1 Introduction Ground motion equations are often called attenution relations but they describe much more than just the attenutation of the ground motion; they describe the probability
7 Ground Motion Models 7.1 Introduction Ground motion equations are often called attenution relations but they describe much more than just the attenutation of the ground motion; they describe the probability
Hosgri-San Simeon Fault Zone Geologic Slip Rate
 Hosgri-San Simeon Fault Zone Geologic Slip Rate Insert picture(s) here Kathryn Hanson AMEC E&I Diablo Canyon SSHAC Project SSC Workshop 2 November 7, 2012 What insights have your geologic investigations
Hosgri-San Simeon Fault Zone Geologic Slip Rate Insert picture(s) here Kathryn Hanson AMEC E&I Diablo Canyon SSHAC Project SSC Workshop 2 November 7, 2012 What insights have your geologic investigations
Hints of active deformation in the southern Adriatic foreland: Holocene tectonics along the Apulia offshore (Italy)
 Hints of active deformation in the southern Adriatic foreland: Holocene tectonics along the Apulia offshore (Italy) Domenico Ridente^, Umberto Fracassi*, Daniela Di Bucci, Fabio Trincardi^ ^ & Gianluca
Hints of active deformation in the southern Adriatic foreland: Holocene tectonics along the Apulia offshore (Italy) Domenico Ridente^, Umberto Fracassi*, Daniela Di Bucci, Fabio Trincardi^ ^ & Gianluca
entered a rapid development phase. Annual increased proven reserves are above 500 billion cubic meters (bcm) from 2003, and annual natural gas product
 (), entered a rapid development phase. Annual increased proven reserves are above 500 billion cubic meters (bcm) from 2003, and annual natural gas production has increased from 50bcm in 2000 to nearly
(), entered a rapid development phase. Annual increased proven reserves are above 500 billion cubic meters (bcm) from 2003, and annual natural gas production has increased from 50bcm in 2000 to nearly
Unit 4 Lesson 7 Mountain Building
 Indiana Standards 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in the mantle cause lithospheric plates to move causing fast changes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and slow changes like creation of mountains
Indiana Standards 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in the mantle cause lithospheric plates to move causing fast changes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and slow changes like creation of mountains
Data Repository of Paper: The role of subducted sediments in plate interface dynamics as constrained by Andean forearc (paleo)topography
 Data Repository of Paper: The role of subducted sediments in plate interface dynamics as constrained by Andean forearc (paleo)topography Nicolás J. Cosentino 1*, Felipe Aron 2,3, Jorge G. F. Crempien 2,3,
Data Repository of Paper: The role of subducted sediments in plate interface dynamics as constrained by Andean forearc (paleo)topography Nicolás J. Cosentino 1*, Felipe Aron 2,3, Jorge G. F. Crempien 2,3,
EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE MECHANISMS SHOW MOTION
 6-1 6: EARTHQUAKE FOCAL MECHANISMS AND PLATE MOTIONS Hebgen Lake, Montana 1959 Ms 7.5 1 Stein & Wysession, 2003 Owens Valley, California 1872 Mw ~7.5 EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE
6-1 6: EARTHQUAKE FOCAL MECHANISMS AND PLATE MOTIONS Hebgen Lake, Montana 1959 Ms 7.5 1 Stein & Wysession, 2003 Owens Valley, California 1872 Mw ~7.5 EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE
29. IMPLICATIONS OF DEEP SEA DRILLING, SITES 186 AND 187 ON ISLAND ARC STRUCTURE
 29. IMPLICATIONS OF DEEP SEA DRILLING, SITES 186 AND 187 ON ISLAND ARC STRUCTURE John A. Grow 1, Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California INTRODUCTION Pacific
29. IMPLICATIONS OF DEEP SEA DRILLING, SITES 186 AND 187 ON ISLAND ARC STRUCTURE John A. Grow 1, Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California INTRODUCTION Pacific
Active Tectonics. Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape. Edward A. Keller University of California, Santa Barbara
 Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter Pearson Education, Inc.
 Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter 10 Structural Geology Structural geologists study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. A working knowledge of rock structures
Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter 10 Structural Geology Structural geologists study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. A working knowledge of rock structures
Zoning surface rupture hazard along normal faults: insight from the 2009 M w 6.3 L Aquila, central Italy, earthquake and other global earthquakes
 Zoning surface rupture hazard along normal faults: insight from the 2009 M w 6.3 L Aquila, central Italy, earthquake and other global earthquakes Boncio, P., Galli, P., Naso, G., Pizzi, A. Bulletin of
Zoning surface rupture hazard along normal faults: insight from the 2009 M w 6.3 L Aquila, central Italy, earthquake and other global earthquakes Boncio, P., Galli, P., Naso, G., Pizzi, A. Bulletin of
Crustal Deformation. (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer Mapping geologic structures
 Crustal Deformation (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer 2005 Mapping geologic structures When conducting a study of a region, a geologist identifies and describes the dominant rock structures
Crustal Deformation (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer 2005 Mapping geologic structures When conducting a study of a region, a geologist identifies and describes the dominant rock structures
CRUSTAL DEFORMATION. Chapter 10
 CRUSTAL DEFORMATION and dgeologic Structures t Chapter 10 Deformation Df Deformation involves: Stress the amount of force applied to a given area. Types of Stress: Confining Stress stress applied equally
CRUSTAL DEFORMATION and dgeologic Structures t Chapter 10 Deformation Df Deformation involves: Stress the amount of force applied to a given area. Types of Stress: Confining Stress stress applied equally
Learning Objectives (LO) What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Geology 15 West Valley College. Exam IV: Sierra Nevada
 Geology 15 West Valley College Name Exam IV: Sierra Nevada 1) On the diagram above, where is the Arc- Trench Gap? a. 1 and 3 c. 7 and 8 d. 6 e. 5 and 10 2) On the diagram above, where is the subduction
Geology 15 West Valley College Name Exam IV: Sierra Nevada 1) On the diagram above, where is the Arc- Trench Gap? a. 1 and 3 c. 7 and 8 d. 6 e. 5 and 10 2) On the diagram above, where is the subduction
Unit 4 Lesson 3 Mountain Building. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Stressed Out How can tectonic plate motion cause deformation? The movement of tectonic plates causes stress on rock structures. Stress is the amount of force per unit area that is placed on an object.
Stressed Out How can tectonic plate motion cause deformation? The movement of tectonic plates causes stress on rock structures. Stress is the amount of force per unit area that is placed on an object.
Chapter 15 Structures
 Chapter 15 Structures Plummer/McGeary/Carlson (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TECTONIC FORCES AT WORK Stress & Strain Stress Strain Compressive stress Shortening strain Tensional stress stretching
Chapter 15 Structures Plummer/McGeary/Carlson (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TECTONIC FORCES AT WORK Stress & Strain Stress Strain Compressive stress Shortening strain Tensional stress stretching
Case Study 1: 2014 Chiang Rai Sequence
 Case Study 1: 2014 Chiang Rai Sequence Overview Mw 6.1 earthquake on 5 May 2014 at 11:08:43 UTC Largest recorded earthquake in Thailand Fault Orientation How does the orientation of the fault affect the
Case Study 1: 2014 Chiang Rai Sequence Overview Mw 6.1 earthquake on 5 May 2014 at 11:08:43 UTC Largest recorded earthquake in Thailand Fault Orientation How does the orientation of the fault affect the
Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting
 Crustal Deformation AKA Structural geology (adapted from Brunkel, 2012) Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting How Rocks Deform: 4 Controls
Crustal Deformation AKA Structural geology (adapted from Brunkel, 2012) Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting How Rocks Deform: 4 Controls
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Landsat TM processing in the investigation of active fault zones, South Lajas Valley Fault Zone and Cerro Goden Fault Zone as an example
 Landsat TM processing in the investigation of active fault zones, South Lajas Valley Fault Zone and Cerro Goden Fault Zone as an example ANTONIO E. CAMERON-GONZÁLEZ 1 1 Department of Geology, University
Landsat TM processing in the investigation of active fault zones, South Lajas Valley Fault Zone and Cerro Goden Fault Zone as an example ANTONIO E. CAMERON-GONZÁLEZ 1 1 Department of Geology, University
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Basin & Range / Mojave Desert
 Basin & Range / Mojave Desert Basin & Range vs. Great Basin 1 2/20/2016 An overview of the last horst Basin and Range / Mojave Desert Summary: Granitic, volcanic, marine sedimentary, non marine sedimentary,
Basin & Range / Mojave Desert Basin & Range vs. Great Basin 1 2/20/2016 An overview of the last horst Basin and Range / Mojave Desert Summary: Granitic, volcanic, marine sedimentary, non marine sedimentary,
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education
 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
The Quaternary Dextral Shearing in the Southeastern. Tibetan Plateau
 The Quaternary Dextral Shearing in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau SHEN Jun Wang Yipeng REN Jinwei CAO Zhongquan Institute of Geology of China Seismological Bureau, Beijing 100029, China Tel:8610-62009121,
The Quaternary Dextral Shearing in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau SHEN Jun Wang Yipeng REN Jinwei CAO Zhongquan Institute of Geology of China Seismological Bureau, Beijing 100029, China Tel:8610-62009121,
Paleoseismic investigations along a key active fault within the Gulf of Corinth, Greece
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Paleoseismic investigations along a key active fault within the Gulf of Corinth, Greece To cite this article: I K Koukouvelas et al 2008 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Paleoseismic investigations along a key active fault within the Gulf of Corinth, Greece To cite this article: I K Koukouvelas et al 2008 IOP Conf.
Chapter 2. Earthquake and Damage
 EDM Report on the Chi-Chi, Taiwan Earthquake of September 21, 1999 2.1 Earthquake Fault 2.1.1 Tectonic Background The island of Taiwan is located in the complex junction where the Eurasian and Philippine
EDM Report on the Chi-Chi, Taiwan Earthquake of September 21, 1999 2.1 Earthquake Fault 2.1.1 Tectonic Background The island of Taiwan is located in the complex junction where the Eurasian and Philippine
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
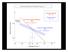 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS
 UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS ROCK DEFORMATION Tectonic forces exert different types of stress on rocks in different geologic environments. STRESS The first, called confining stress
UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS ROCK DEFORMATION Tectonic forces exert different types of stress on rocks in different geologic environments. STRESS The first, called confining stress
caribbean basins, tectonics and hydrocarbons university of texas institute for geophysics
 Copyright by Trevor John Aitken 2005 CENOZOIC STRATIGRAPHIC AND TECTONIC HISTORY OF THE GRENADA AND TOBAGO BASINS AS DETERMINED FROM MARINE SEISMIC DATA, WELLS, AND ONLAND GEOLOGY by Trevor John Aitken,
Copyright by Trevor John Aitken 2005 CENOZOIC STRATIGRAPHIC AND TECTONIC HISTORY OF THE GRENADA AND TOBAGO BASINS AS DETERMINED FROM MARINE SEISMIC DATA, WELLS, AND ONLAND GEOLOGY by Trevor John Aitken,
Apparent and True Dip
 Apparent and True Dip Cross-bedded building stone. The contact immediately below A appears to dip gently to the right, but at B, the contact appears to dip to the left. But it's not a syncline! Both of
Apparent and True Dip Cross-bedded building stone. The contact immediately below A appears to dip gently to the right, but at B, the contact appears to dip to the left. But it's not a syncline! Both of
Name Class Date. Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One)
 Name Class Date Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One) 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? Define the problem or question Form a hypothesis (MUST BE TESTABLE) o (identify variables)
Name Class Date Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One) 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? Define the problem or question Form a hypothesis (MUST BE TESTABLE) o (identify variables)
INTRODUCTION. Climate
 INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
TECHNICAL REPORT: REGIONAL GEOLOGY AND TECTONICS Resume. Huachon Project, Cerro de Pasco departments, Peru. By: AFC Logistic SAC
 TECHNICAL REPORT: REGIONAL GEOLOGY AND TECTONICS Resume Huachon Project, Cerro de Pasco departments, Peru By: AFC Logistic SAC December 2016 1. INTRODUCTION GPM Metals Peru, in its portfolio of generating
TECHNICAL REPORT: REGIONAL GEOLOGY AND TECTONICS Resume Huachon Project, Cerro de Pasco departments, Peru By: AFC Logistic SAC December 2016 1. INTRODUCTION GPM Metals Peru, in its portfolio of generating
Material Database of reflection surveys in Japan and pattern of active faults in seismic reflection profile
 Bull. of Yamagata Univ., Nat. Sci., Vol.15, No.4, Feb. 2004 Material Database of reflection surveys in Japan and pattern of active faults in seismic reflection profile Yosuke NAKAMURA, Akiko HASEMI, Tomotsugu
Bull. of Yamagata Univ., Nat. Sci., Vol.15, No.4, Feb. 2004 Material Database of reflection surveys in Japan and pattern of active faults in seismic reflection profile Yosuke NAKAMURA, Akiko HASEMI, Tomotsugu
What Causes Rock to Deform?
 Crustal Deformation Earth, Chapter 10 Chapter 10 Crustal Deformation What Causes Rock to Deform? Deformation is a general term that refers to all changes in the shape or position of a rock body in response
Crustal Deformation Earth, Chapter 10 Chapter 10 Crustal Deformation What Causes Rock to Deform? Deformation is a general term that refers to all changes in the shape or position of a rock body in response
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard. Earthquake Environment
 Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
THE SONORA EARTHQUAKE OF 1887
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. Vol. 67, No. 4, pp. 1219-1223. August 1977 THE SONORA EARTHQUAKE OF 1887 BY JOHN RANDOLPH SUMNER* INTRODUCTION The 1887 Sonoran earthquake is historically
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. Vol. 67, No. 4, pp. 1219-1223. August 1977 THE SONORA EARTHQUAKE OF 1887 BY JOHN RANDOLPH SUMNER* INTRODUCTION The 1887 Sonoran earthquake is historically
Tectonic Movements in the Central Kyushu, Japan
 /-,**.. +0 - +0,, +0, +* Tectonic Movements in the Central Kyushu, Japan Keiji TAKEMURA Beppu Geothermal Res. Lab., Kyoto University Abstract The central part of Kyushu, Japan is a locus of active arc-volcanism
/-,**.. +0 - +0,, +0, +* Tectonic Movements in the Central Kyushu, Japan Keiji TAKEMURA Beppu Geothermal Res. Lab., Kyoto University Abstract The central part of Kyushu, Japan is a locus of active arc-volcanism
Earthquake and Volcano Clustering at Mono Basin (California)
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Paris Earthquake and Volcano Clustering at Mono Basin (California) D. La Marra *,1, A. Manconi 2,3 and M. Battaglia 1 1 Dept of Earth Sciences,
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Paris Earthquake and Volcano Clustering at Mono Basin (California) D. La Marra *,1, A. Manconi 2,3 and M. Battaglia 1 1 Dept of Earth Sciences,
How mountains are made. We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later)
 How mountains are made We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later) http://www.ilike2learn.com/ilike2learn/mountainmaps/mountainranges.html Continent-continent plate convergence Less dense,
How mountains are made We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later) http://www.ilike2learn.com/ilike2learn/mountainmaps/mountainranges.html Continent-continent plate convergence Less dense,
Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes
 Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes Mathew Pritchard Teh-Ru A. Song Yuri Fialko Luis Rivera Mark Simons UJNR Earthquake Research Panel, Morioka, Japan - Nov 6, 2002 Goals Accurate and high
Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes Mathew Pritchard Teh-Ru A. Song Yuri Fialko Luis Rivera Mark Simons UJNR Earthquake Research Panel, Morioka, Japan - Nov 6, 2002 Goals Accurate and high
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20
 Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Crustal Deformation. Earth Systems 3209
 Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Section 3 Deforming Earth s Crust
 Section 3 Deforming Earth s Crust Key Concept Tectonic plate motions deform Earth s crust. Deformation causes rock layers to bend and break and causes mountains to form. What You Will Learn Stress is placed
Section 3 Deforming Earth s Crust Key Concept Tectonic plate motions deform Earth s crust. Deformation causes rock layers to bend and break and causes mountains to form. What You Will Learn Stress is placed
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
ABSTRACT. Key words: InSAR; GPS; northern Chile; subduction zone.
 ASPERITIES, BARRIERS AND TRANSITION ZONE IN THE NORTH CHILE SEISMIC GAP: STATE OF THE ART AFTER THE 007 MW 7.7 TOCOPILLA EARTHQUAKE INFERRED BY GPS AND INSAR DATA Marta Bejar Pizarro, Daniel Carrizo, Anne
ASPERITIES, BARRIERS AND TRANSITION ZONE IN THE NORTH CHILE SEISMIC GAP: STATE OF THE ART AFTER THE 007 MW 7.7 TOCOPILLA EARTHQUAKE INFERRED BY GPS AND INSAR DATA Marta Bejar Pizarro, Daniel Carrizo, Anne
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March
 Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
NATURAL ENVIRONMENT. Geophysics
 NATURAL ENVIRONMENT Geophysics Geodynamics Alpine, Carpathian and Dinaric mountain belts surround the Pannonian (Carpathian) Basin, of Neogene through Quaternary in age. The Cenozoic evolution of the Alpine-Pannonian
NATURAL ENVIRONMENT Geophysics Geodynamics Alpine, Carpathian and Dinaric mountain belts surround the Pannonian (Carpathian) Basin, of Neogene through Quaternary in age. The Cenozoic evolution of the Alpine-Pannonian
Comment on: Cenozoic evolution of the eastern Danish North Sea by M. Huuse, H. Lykke-Andersen and O. Michelsen, [Marine Geology 177, 243^269]
![Comment on: Cenozoic evolution of the eastern Danish North Sea by M. Huuse, H. Lykke-Andersen and O. Michelsen, [Marine Geology 177, 243^269] Comment on: Cenozoic evolution of the eastern Danish North Sea by M. Huuse, H. Lykke-Andersen and O. Michelsen, [Marine Geology 177, 243^269]](/thumbs/93/112023617.jpg) Marine Geology 186 (2002) 571^575 Discussion Comment on: Cenozoic evolution of the eastern Danish North Sea by M. Huuse, H. Lykke-Andersen and O. Michelsen, [Marine Geology 177, 243^269] P. Japsen, T.
Marine Geology 186 (2002) 571^575 Discussion Comment on: Cenozoic evolution of the eastern Danish North Sea by M. Huuse, H. Lykke-Andersen and O. Michelsen, [Marine Geology 177, 243^269] P. Japsen, T.
Present seismic activity of Sparta fault (Peloponnesus, southern Greece) and its implications
 Present seismic activity of Sparta fault (Peloponnesus, southern Greece) and its implications Papanastassiou D(1), Karastathis V(2), Liakopoulos S(3) (1) Institute of Geodynamics, National Observatory
Present seismic activity of Sparta fault (Peloponnesus, southern Greece) and its implications Papanastassiou D(1), Karastathis V(2), Liakopoulos S(3) (1) Institute of Geodynamics, National Observatory
SONGS SSC. Tom Freeman GeoPentech PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 SONGS SSC Tom Freeman GeoPentech PRELIMINARY RESULTS Focused Questions Summarize the tectonic setting What is the seismogenic thickness? Are you including deep ruptures in the upper mantle (~30 km)? Do
SONGS SSC Tom Freeman GeoPentech PRELIMINARY RESULTS Focused Questions Summarize the tectonic setting What is the seismogenic thickness? Are you including deep ruptures in the upper mantle (~30 km)? Do
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/ngeo739 Supplementary Information to variability and distributed deformation in the Marmara Sea fault system Tobias Hergert 1 and Oliver Heidbach 1,* 1 Geophysical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/ngeo739 Supplementary Information to variability and distributed deformation in the Marmara Sea fault system Tobias Hergert 1 and Oliver Heidbach 1,* 1 Geophysical
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 10 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 10 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 10 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II
 EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY - EES 1005 LABORATORY FIVE GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II Introduction Geologic maps of orogenic belts are much more complex than maps of the stable interior. Just
EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY - EES 1005 LABORATORY FIVE GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II Introduction Geologic maps of orogenic belts are much more complex than maps of the stable interior. Just
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures. But first a short review
 How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first a short review Where do we see deep earthquakes? What is happening there? What can happen at a plate boundary? 1. Plates can move apart
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first a short review Where do we see deep earthquakes? What is happening there? What can happen at a plate boundary? 1. Plates can move apart
You must take the exam in the lecture section for which you are registered. Any exceptions must be cleared with the instructor in advance.
 Geo 101, Fall 2000 Review Questions for Final Exam GEOLOGIC TIME AND FOLDING AND FAULTING THE FINAL EXAM FOR MWF CLASS WILL BE TUESDAY 1400 THE FINAL EXAM FOR TR CLASS WILL BE FRIDAY 930 These questions
Geo 101, Fall 2000 Review Questions for Final Exam GEOLOGIC TIME AND FOLDING AND FAULTING THE FINAL EXAM FOR MWF CLASS WILL BE TUESDAY 1400 THE FINAL EXAM FOR TR CLASS WILL BE FRIDAY 930 These questions
ESTIMATION OF SEDIMENT THICKNESS BY USING MICROTREMOR OBSERVATIONS AT PALU CITY, INDONESIA. Pyi Soe Thein. 11 November 2013
 ESTIMATION OF SEDIMENT THICKNESS BY USING MICROTREMOR OBSERVATIONS AT PALU CITY, INDONESIA By Pyi Soe Thein 11 November 2013 Outlines Introduction Research objectives Research analyses Microtremor Single
ESTIMATION OF SEDIMENT THICKNESS BY USING MICROTREMOR OBSERVATIONS AT PALU CITY, INDONESIA By Pyi Soe Thein 11 November 2013 Outlines Introduction Research objectives Research analyses Microtremor Single
Structural Modelling of Inversion Structures: A case study on South Cambay Basin
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 065 Structural Modelling of Inversion Structures: A case study on South Cambay Basin Dr. Mayadhar Sahoo & S.K Chakrabarti Summary The inversion in
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 065 Structural Modelling of Inversion Structures: A case study on South Cambay Basin Dr. Mayadhar Sahoo & S.K Chakrabarti Summary The inversion in
P128 Subsurface Fault and Colluvial Wedge Detection Using Resistivity, Refraction Tomography and Seismic Reflection
 P128 Subsurface Fault and Colluvial Wedge Detection Using Resistivity, Refraction Tomography and Seismic Reflection S.M. Hanafy* (King Abdullah University of Science & Technology) SUMMARY Electric resistivity
P128 Subsurface Fault and Colluvial Wedge Detection Using Resistivity, Refraction Tomography and Seismic Reflection S.M. Hanafy* (King Abdullah University of Science & Technology) SUMMARY Electric resistivity
Lecture Outline Friday March 2 thru Wednesday March 7, 2018
 Lecture Outline Friday March 2 thru Wednesday March 7, 2018 Questions? Lecture Exam Friday March 9, 2018 Same time, Same room Bring Pencils and WSU ID 50 question Multiple Choice, Computer Graded Interlude
Lecture Outline Friday March 2 thru Wednesday March 7, 2018 Questions? Lecture Exam Friday March 9, 2018 Same time, Same room Bring Pencils and WSU ID 50 question Multiple Choice, Computer Graded Interlude
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5
 Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana
 Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana Robert C. Thomas Department of Environmental Sciences, The University of Montana Western, Dillon, MT 59725, (406) 683-7615, r_thomas@umwestern.edu
Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana Robert C. Thomas Department of Environmental Sciences, The University of Montana Western, Dillon, MT 59725, (406) 683-7615, r_thomas@umwestern.edu
Young displacements on the Atacama Fault System, northern Chile from field observations and cosmogenic 21 Ne concentrations
 TECTONICS, VOL. 25,, doi:10.1029/2005tc001846, 2006 Young displacements on the Atacama Fault System, northern Chile from field observations and cosmogenic 21 Ne concentrations Gabriel González L., 1 Tibor
TECTONICS, VOL. 25,, doi:10.1029/2005tc001846, 2006 Young displacements on the Atacama Fault System, northern Chile from field observations and cosmogenic 21 Ne concentrations Gabriel González L., 1 Tibor
Mountain Building. Mountain Building
 Mountain Building Mountain building has occurred during the recent geologic past American Cordillera the western margin of the Americas from Cape Horn to Alaska Includes the Andes and Rocky Mountains Alpine
Mountain Building Mountain building has occurred during the recent geologic past American Cordillera the western margin of the Americas from Cape Horn to Alaska Includes the Andes and Rocky Mountains Alpine
Non-ideal Subduction
 Subduction zone cross sections Earthquake locations : black = teleseismic est. gray = local-array est. red line = top of slab seismicity blue line = center of slab seismicity Non-ideal Subduction Oblique
Subduction zone cross sections Earthquake locations : black = teleseismic est. gray = local-array est. red line = top of slab seismicity blue line = center of slab seismicity Non-ideal Subduction Oblique
The Omega fault is an Atirro fault splay that branches westward off of the main trace at
 This supplemental information file for Neotectonic faulting and forearc sliver motion along the Atirro-Río Sucio fault system, Costa Rica, Central America by Montero et al. contains descriptions of secondary
This supplemental information file for Neotectonic faulting and forearc sliver motion along the Atirro-Río Sucio fault system, Costa Rica, Central America by Montero et al. contains descriptions of secondary
Topics Laramide Orogeny: Late Cretaceous to Early Eocene Reading: GSA DNAG volume 3, Ch. 6
 Topics Laramide Orogeny: Late Cretaceous to Early Eocene Reading: GSA DNAG volume 3, Ch. 6 Late Cretaceous to early Eocene New patterns developed 5 main regions Tectonic interpretations Post-Laramide events
Topics Laramide Orogeny: Late Cretaceous to Early Eocene Reading: GSA DNAG volume 3, Ch. 6 Late Cretaceous to early Eocene New patterns developed 5 main regions Tectonic interpretations Post-Laramide events
John Baldwin and Brian Gray Lettis Consultants International, Inc. Alexis Lavine AMEC Josh Goodman and Janet Sowers Fugro Consultants, Inc.
 John Baldwin and Brian Gray Lettis Consultants International, Inc. Alexis Lavine AMEC Josh Goodman and Janet Sowers Fugro Consultants, Inc. December 1, 2011 Pacific Gas & Electric SSHAC Workshop 1 San
John Baldwin and Brian Gray Lettis Consultants International, Inc. Alexis Lavine AMEC Josh Goodman and Janet Sowers Fugro Consultants, Inc. December 1, 2011 Pacific Gas & Electric SSHAC Workshop 1 San
MOUSLOPOULOU V., ANDREOU C., ATAKAN K. FOUNTOULIS I.,
 ΔΗΜΟΣΙΕΥΣΗ Νο 80 MOUSLOPOULOU V., ANDREOU C., ATAKAN K. FOUNTOULIS I., (2001) Paleoseismological investigations along the Kera Fault Zone, Western Crete: Implications for Seismic Hazard Assessment. Proc.
ΔΗΜΟΣΙΕΥΣΗ Νο 80 MOUSLOPOULOU V., ANDREOU C., ATAKAN K. FOUNTOULIS I., (2001) Paleoseismological investigations along the Kera Fault Zone, Western Crete: Implications for Seismic Hazard Assessment. Proc.
11.1 Rock Deformation
 Tarbuck Lutgens Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock
Tarbuck Lutgens Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock
Motion on Upper-Plate Faults During Subduction Zone Earthquakes: Case of the Atacama Fault System, Northern Chile
 Smith ScholarWorks Geosciences: Faculty Publications Geosciences 12-12-2008 Motion on Upper-Plate Faults During Subduction Zone Earthquakes: Case of the Atacama Fault System, Northern Chile John P. Loveless
Smith ScholarWorks Geosciences: Faculty Publications Geosciences 12-12-2008 Motion on Upper-Plate Faults During Subduction Zone Earthquakes: Case of the Atacama Fault System, Northern Chile John P. Loveless
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building. Fig. 10.1
 Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Characterisation of late Quaternary displacements on the Waitangi Fault at Aviemore Dam, New Zealand
 Characterisation of late Quaternary displacements on the Waitangi Fault at Aviemore Dam, New Zealand D.J.A. Barrell, R.J. Van Dissen, K.R. Berryman, & S.A.L. Read Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences
Characterisation of late Quaternary displacements on the Waitangi Fault at Aviemore Dam, New Zealand D.J.A. Barrell, R.J. Van Dissen, K.R. Berryman, & S.A.L. Read Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences
