GIS based Estimation of snow depth in mountainous Himalayan region: A case study
|
|
|
- Beverly Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GIS based Estimation of snow depth in mountainous Himalayan region: A case study Chander Shekhar *1, S K Dewali *, Snehmani * * Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment, Chandigarh, India , India 1 Corresponding Author: cskanda@gmail.com Abstract: High reflectance in visible region and large spatial extents of seasonal snow in Indian Himalayas allow it to play important role in deciding the climatology and hydrology of Indian sub-continent. There is high spatial variability in seasonal snow cover in Himalayan in terms of the areal extents and various snow characteristics. Morphological evolution of snow cover takes place as a result of the snow deposition during various snow storms and thermo dynamical processes within snow pack. Stability of snow over a mountain slope is of importance for various recreational, developmental and transportation activities. Large mass of snow moving downhill (i.e. Snow Avalanche) can affect adversely all these activities and thus affect economy of nation. Stability of snowpack over a mountainous slope is governed by various snow, meteorological and terrain parameters. Snow depth is one of the important variable that contribute significantly in the avalanching of snow loaded slope, given favorable terrain parameters. To assess the avalanche hazard potential, accurate modeling of snow depth is necessary. In the present study, a GIS based method for estimation of the snow depth in a part of North-West Himalaya has been attempted. A hybrid method was adopted for the estimation of the snow depth to cover the limitation of limited observatory network in Himalaya. Firstly, a model factor ( ) is calculated to establish the relation between snow depth at observation points and their elevations in the study area. Snow depth is calculated at each pixel of study area using snow depth of known observation points, model factor( ), weight factors and DEM. MODIS satellite data is used to restrict the snow depth maps to snow covered areas only. Snow depth maps for one winter period 2007 to 2008 were generated and analyzed. Snow depth data of Automatic weather stations (AWS) installed in study area were used for validation. Correlation values of around ~ 0.9 have been found between modeled and measured data. Limits and limitation of the method have been discussed. The study reveals that regular monitoring of snow depth near avalanche prone areas along with other terrain and meteorological information can provide valuable inputs for snow pack stability assessment that serves as an important input to avalanche forecasters. About the Author: Mr. Chander Shekhar received his M.Sc. (Physics) degree from Panjab University, Chandigarh in 2005 and pursuing PhD (Physics) from Panjab University, Chandigarh, India. Presently, he is working as a researcher in Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment (SASE), Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO). His research interest includes study of radio-metric properties of snow, glaciers in optical region of EM Spectrum; Hyper-spectral remote sensing for snow parameters retrieval; Geo-spatial modeling of snow physical properties. E mail ID: cskanda@gmail.com Contact No: (391) Page 1 of 6
2 Introduction A large part of the Himalayan Mountain regions get covered with seasonal snow during winter season (that remains mainly from November to April). April onwards the seasonal snow starts melting and permanent snow bodies remains depending on altitude and temperature regimes. During successive snow-storms in winters, snow pack formation over the earth takes place as a group of different snow layers with different physical properties. Seasonal snowpack evolves over time due to change in microclimatic variables as the winter advances. The morphological changes in snow pack are continuously occurring as a result of which the strength and stability parameters of snow pack over a particular region are changing. Over a mountain slope, with the increase in the amount of snow during successive snow spells, the chances for downhill movements of large chunks of snow (called snow avalanche) increase given favorable terrain and weather parameters. Snow avalanches affects economy of nation in indirect manner. So, the stability of snow pack over a slope is a parameter of interest for avalanche forecaster that is further linked to number of developmental, tourism, transportation and mountain sports related activities during the winter season [1]. So accurate modeling of snow depth is important for assessing the avalanche hazard potential on a snow covered mountain. Generally, the data on snow amount deposition is collected from a distributed networks of ground observatories using snow depth measuring rod (manual method) and Automatic Weather Stations i.e. AWS that uses radiation sensors. There is observed a large spatial variability in the snow amount at relatively short distances and that too dependent on a number of factors interacting with each other in a complex fashion. Some of the factors having an influence on snow depth amount are exposure to the sun, the physical properties of the effective surface, air moisture content, the water supply of vegetation and the actual surface-atmosphere exchange characteristics [2]. Also the temporal information is not adequate which further restricts the possibilities for accurately interpolating the spatial and temporal information at regional scale. The remote sensing and GIS tool is very helpful to obtain the continuous information about the snow cover over the spatial and temporal domains. A number of attempts have been made by various researchers to interpolate the snow depth, but their usefulness is restricted as many variables causing the spatial variability (i.e. topographic variations) are not included in these models. In addition, a number of researchers have used the remote sensing based techniques for snow-cover parameters extraction in optical and microwave domains. It is observed that snow depth cannot be determined directly using VIR (Visible and Infra Red) imagery. Polari-metric SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) has also the potential to be used to measure snow depth. Over the local scale, snow depth amount can be determined from airborne digital stereo-photogrammetric and airborne laser profiling schemes. Over the global scale, snow depth patterns on the earth s surface are determined by the use of space borne passive microwave remote sensing techniques. Indirect approaches are utilized to extract the required information about snow depth [3]. Spatial interpolation of snow depth had been another indirect method in many research projects for snow depth estimation. As per these, the interpolation procedures must incorporate the effects of physical processes which determine the climate spatial distribution [4-6]. Various authors have used simple procedures, which include the latitude and longitude of weather stations. Liston et al, 2006 [7] showed that the inclusion of elevation was critical to account for strong influence of topography on snow depth amount variations. In the present study, we have integrated the topographic variable i.e. altitude (by using Digital Elevation Model) and the snow depth observations from the point network in a GIS frame work to model mean snow depth. Study area and Data used The study area covers the snow covered mountains those falls in districts of Tithwal and Kupwara in Jammu & Kashmir (India). The area negotiates and crosses the Pir Panjal ranges of Indian North West Himalayans. The geomorphology of area is typical of Pir Panjal ranges with no vegetation beyond 3300m above m.s.l. (mean sea level). This area receives heavy snowfall during winter due to western disturbances [8]. There are a number of major avalanche sites affecting the road along this axis. These avalanche sites trigger during winter due to failure of weak snow layers and causes hazard along the highway by affecting vehicular traffic and unavoidable pedestrian movements. A snap view using Landsat imagery of the study area along with reference observatory stations is shown in Figure 1 for an easy outlook. Snow meteorological data (SMD) that includes temperature, standing snow amount, fresh snow amount, wind speed and relative humidity etc. collected from four observatory locations of winter season has been used for the present study. To include the effect of terrain variables i.e. topographic variations, the high resolution (40m) Digital Elevation Model (DEM) generated from survey of India topo-sheets was employed. The data of MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectralradiometer) sensor onboard terra and aqua satellites was processed to obtain the snow and non-snow areas information for Page 2 of 6
3 the study duration on days having minimum cloud free conditions [9]. Snow depth data from two AWS (Automatic Weather Station) locations have been used for validation purpose. Methodology Figure 1: The study area shown using Landsat imagery in false color composite The approach used for snow depth modeling is a hybrid approach that utilizes the physical relationship between snow depth at a particular point and the topography. GIS (Geographic Information System) software ArcGIS had been used for this analysis. To generate the snow depth map from point observation, snow depth is calculated at each pixel of the study area with respect to observation point using the elevation variation from DEM. A weighted inverse distance has also been calculated for each pixel from the four observational reference point observatories. Final snow depth map was generated by taking weighted sum of the snow depth maps of all observation points. To restrict the study to the snow cover region of the study area, MODIS images of the study period were processed. The reflectance maps were obtained and then NDSI index calculations were done to obtain the snow and non-snow areas. The snow depth maps were generated for the period Nov 2007 to April The calculated snow depth maps have been validated using data from AWS (Automatic weather station) situated in the study area. Model parameters calculation In present study, the variation of snow depth with altitude above m.s.l. had been the main focus. This is observed that variation of snow depth with altitude is non linear in Himalaya. The modeling has been done based on the model equation obtained using variation of snow depth with altitude (Point basis) as proposed by Liston et al, i.e. S p S o (1 ( E [ (1 ( E p p Eo )) ] E )) Where Eo and Ep are the altitudes of the known base station and station whose snow depth has to be determined respectively. S o is the snow depth of known base station. S p is derived snow depth amount of a station located at an altitude of E p. ' ' is called the model factor (or value). Snow depth data of four observatory locations (situated within altitude range of m above m.s.l.) of winter season along with equation (1) had been used to calculate the model parameter ( ) for the study area. The values have been calculated for all the dates of each month of study duration and then an average value of model factor is calculated for the respective month for further use in snow depth estimation at other locations. o Page 3 of 6 (1)
4 Snow depth estimation and Validation To incorporate the elevation variation, high resolution digital elevation model generated using SoI topo-sheets had been used. To calculate the Euclidean distances, the observatory location had been brought in GIS environment. Based on above equation the distance maps for each station had been generated. These distances had been normalized in the range 0 to 1 in such a way that the sum of all four distances (distance of any pixel or point from all four field stations) is one. These normalized distance maps were finally converted into the inverse distance weights ranging from 1.0 to 0.0. To generate the snow cover area information, the data from Moderate resolution Imaging Spectro-radiometer (MODIS) sensor onboard terra and aqua satellites had been utilized. The snow cover area information was used to restrict the snow depth estimation to snow covered areas only. The modeled snow depth maps of four different dates have been shown in figure 2. For validation, the snow depth amount data of two AWS locations had been utilized. Calculated values of the snow depth (from modeled maps) had been compared with measured snow depth data of AWS Figure 2: Modeled Snow Depth maps for different months (a) 22 Dec, 2007 (b) 12 Jan, 2008 (c) 18 Mar, 2008 (d) 10 April, Page 4 of 6
5 Results and Discussion Analysis of data shows that variations in the snow cover buildup among different stations are not same for all the winter months, but varying on the monthly basis. So the model factor ( ) has been calculated month wise to capture the variation of the snow depth with elevation more accurately during a particular period. This model parameter is found based on various combinations of different stations located at different altitudes and then average values have been taken for each month. Average values for months December, January, Feb, Mar, April have been , 0.001, , and respectively. The factor value is found to be decreasing for the duration December to January and then increasing from January to April. The variation in model parameter helps to decide the boundaries with in which the GIS based model for snow depth will provide good results. The higher altitude difference between the two reference observatories locations will lead to higher coverage range of prediction for the snow depth hybrid model. For validation of snow depth maps, snow depth amount values from the pixels where automatic weather station (AWS) installed were taken. These values were compared with the measured snow depth values. Figures 3 shows comparison for two different stations. A very good correlation of the predicted snow depth amount was found with the AWS site data. One probable reason the slight difference between the measured and ground AWS values may be due to the local terrain effects. The coefficients of correlation for AWS I and AWS-II have been found to be 0.98 and 0.9 respectively. Figure 3: Comparison of modeled and observed snow depth using AWS data The limiting values of elevation (minimum and maximum) for calculation of will be decided by the elevations of the observation station in the study area. In case is negative, snow depth will decrease with increase in altitude. Snow depth will become negative when product i.e. (Ep- Eo) < -1, which has no physical significance (no snow above this elevation). So (Ep- Eo) < -1 is the limit below which model cannot calculate significant snow depth values. From calculation point of view, negative snow depth values can be assigned zero values. To increase the altitude range for which model calculate snow depth, more observation points with wider altitude variations need to be included. This would be worth to mention that very limited stations data is available for the study in the used study area. This is practical problem. So Eq.(1) and interpolation methods have been used collectively to address the limitation of limited data availability. Observation data of more point locations (presently not available for this area) need to be included in the future. Also more manual observations and snow depth calculated from microwave SAR data will be used for more realistic validation. The inclusion of more parameters like slope, aspect and solar illumination corrections will further help to achieve more accurate results. This type of information can prove to be very helpful for avalanche forecasters and other snow depth based applications. Conclusions The results found based on GIS based modeling of snow depth (with-in certain limits as discussed in section 4) are found to be encouraging. The inclusion of data of more number of years and more number of stations will further help to get improved results. The integration of multispectral information for snow covered area help in improving the accuracy of results obtained by removal of the non snow area. Also this approach can be integrated with other methods of retrieving snow depth Page 5 of 6
6 information. For example in passive microwave domain, the AMSR-E sensor gives average value of snow depth over a larger area [10]. GIS model outputs snow depth maps at better resolution than passive microwave method, meaning thereby that the model could be used to focus on small topographical variations which could help deriving better outputs. Decreasing snow depth patterns in the late winter are also required to be analyzed and correlated with the ablation of snow cover. During the late winter months melting starts and the inclusion of melt factor based on slope, aspect and solar illumination conditions can provide better results. A regular monitoring of snow depth amount near avalanche prone areas along with other meteorological information can provide a valuable input for stability assessment to avalanche forecasters. Acknowledgement Authors are thankful to SASE field team members for collection of valuable snow and meteorological data during harsh and cold weather conditions in Himalayas. References 1. D. Mc Clung and I. P. Schaerer, "The Avalanche Handbook, 1 st edition," The Mountaineers Books, Seattle, WA, U.S.A., C. Daly, R. Neilson, D.L. Phillips, "A statistical topographic model for mapping climatological precipitation over mountainous terrain," J. Appl. Meteorology.,33, D.W. Cline, R.C. Bales, J Dozier, "Estimating the spatial distribution of snow in mountain basins using remote sensing and energy balance modeling," Water Resources Research, Vol. 34, No. 5, , M.F. Hutchinson and R.J. Bischof, "A new method for estimating the spatial distribution of mean seasonal and annual rainfall applied to the Hunter Valley, New South Wales," Aust. Met. Mag., 31, , D. L. Phillips, J. Dolph, D. Marks, "A comparison of geo-statistical procedures for spatial analysis of precipitation in mountainous terrain" Agric. For. Meteorology. 58, , March N. Foppa, A Stoffel, R Meister, "Snow depth mapping in the Alps: Merging of in situ and remotely-sensed data," EARSeL eproceedings 4, 1/ G.E. Liston., K. Elder, "A Meteorological Distribution System for High-Resolution Terrestrial Modeling; journal of Hydrometeorology, Vol. 7, , S.S. Sharma and A. Ganju, "Complexities of avalanche forecasting in western Himalaya an overview," Cold Region Science and Technology, 31, , NASA MODIS Specification, T. Che, X. Li, R. Jin, C. Huang, "Assimilating passive microwave remote sensing data into a land surface model to improve the estimation of snow depth," Remote Sensing of Environment, Volume 143, Pages 54-63, March Page 6 of 6
Monitoring of Temporal Variation of Snow Depth Using Remote Sensing in Western Himalaya
 Monitoring of Temporal Variation of Snow Depth Using Remote Sensing in Western Himalaya Ruby Nanchahal*, H. S. Gusain**, Darshan Singh Sidhu* and V. D. Mishra** *PTU GZS Campus Bathinda, Punjab, 151 001,
Monitoring of Temporal Variation of Snow Depth Using Remote Sensing in Western Himalaya Ruby Nanchahal*, H. S. Gusain**, Darshan Singh Sidhu* and V. D. Mishra** *PTU GZS Campus Bathinda, Punjab, 151 001,
MONITORING OF SEASONAL SNOW COVER IN YAMUNA BASIN OF UTTARAKAHND HIMALAYA USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES
 MONITORING OF SEASONAL SNOW COVER IN YAMUNA BASIN OF UTTARAKAHND HIMALAYA USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES Anju Panwar, Devendra Singh Uttarakhand Space Application Centre, Dehradun, India ABSTRACT Himalaya
MONITORING OF SEASONAL SNOW COVER IN YAMUNA BASIN OF UTTARAKAHND HIMALAYA USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES Anju Panwar, Devendra Singh Uttarakhand Space Application Centre, Dehradun, India ABSTRACT Himalaya
Monitoring and evaluation of seasonal snow cover in Kashmir valley using remote sensing, GIS and ancillary data
 Monitoring and evaluation of seasonal snow cover in Kashmir valley using remote sensing, GIS and ancillary data HSNegi, N K Thakur, Rajeev Kumar and Manoj Kumar Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment,
Monitoring and evaluation of seasonal snow cover in Kashmir valley using remote sensing, GIS and ancillary data HSNegi, N K Thakur, Rajeev Kumar and Manoj Kumar Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment,
Estimation of snow surface temperature for NW Himalayan regions using passive microwave satellite data
 Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol 42, February 2013, pp 27-33 Estimation of snow surface temperature for NW Himalayan regions using passive microwave satellite data K K Singh 1,$,*, V D Mishra
Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol 42, February 2013, pp 27-33 Estimation of snow surface temperature for NW Himalayan regions using passive microwave satellite data K K Singh 1,$,*, V D Mishra
Using MODIS imagery to validate the spatial representation of snow cover extent obtained from SWAT in a data-scarce Chilean Andean watershed
 Using MODIS imagery to validate the spatial representation of snow cover extent obtained from SWAT in a data-scarce Chilean Andean watershed Alejandra Stehr 1, Oscar Link 2, Mauricio Aguayo 1 1 Centro
Using MODIS imagery to validate the spatial representation of snow cover extent obtained from SWAT in a data-scarce Chilean Andean watershed Alejandra Stehr 1, Oscar Link 2, Mauricio Aguayo 1 1 Centro
Snow cover monitoring and modelling in the Alps using multi temporal MODIS data
 cover monitoring and modelling in the Alps using multi temporal MODIS data Rastner P. 1, Irsara L. 1, Schellenberger T. 1, Della Chiesa S. 2, Bertoldi G. 2, Endrizzi S. 3, Notarnicola C. 1 and Zebisch
cover monitoring and modelling in the Alps using multi temporal MODIS data Rastner P. 1, Irsara L. 1, Schellenberger T. 1, Della Chiesa S. 2, Bertoldi G. 2, Endrizzi S. 3, Notarnicola C. 1 and Zebisch
Prediction of western disturbances and associated weather over Western Himalayas
 Prediction of western disturbances and associated weather over Western Himalayas H. R. Hatwar*, B. P. Yadav and Y. V. Rama Rao India Meteorological Department, Lodi Road, New Delhi 110 003, India Two cases
Prediction of western disturbances and associated weather over Western Himalayas H. R. Hatwar*, B. P. Yadav and Y. V. Rama Rao India Meteorological Department, Lodi Road, New Delhi 110 003, India Two cases
Remote Sensing of Snow GEOG 454 / 654
 Remote Sensing of Snow GEOG 454 / 654 What crysopheric questions can RS help to answer? 2 o Where is snow lying? (Snow-covered area or extent) o How much is there? o How rapidly is it melting? (Area, depth,
Remote Sensing of Snow GEOG 454 / 654 What crysopheric questions can RS help to answer? 2 o Where is snow lying? (Snow-covered area or extent) o How much is there? o How rapidly is it melting? (Area, depth,
THE INVESTIGATION OF SNOWMELT PATTERNS IN AN ARCTIC UPLAND USING SAR IMAGERY
 THE INVESTIGATION OF SNOWMELT PATTERNS IN AN ARCTIC UPLAND USING SAR IMAGERY Johansson, M., Brown, I.A. and Lundén, B. Department of Physical Geography, Stockholm University, S-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden
THE INVESTIGATION OF SNOWMELT PATTERNS IN AN ARCTIC UPLAND USING SAR IMAGERY Johansson, M., Brown, I.A. and Lundén, B. Department of Physical Geography, Stockholm University, S-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden
REVISION OF THE STATEMENT OF GUIDANCE FOR GLOBAL NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION. (Submitted by Dr. J. Eyre)
 WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION Distr.: RESTRICTED CBS/OPAG-IOS (ODRRGOS-5)/Doc.5, Add.5 (11.VI.2002) COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPEN PROGRAMME AREA GROUP ON INTEGRATED OBSERVING SYSTEMS ITEM: 4 EXPERT
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION Distr.: RESTRICTED CBS/OPAG-IOS (ODRRGOS-5)/Doc.5, Add.5 (11.VI.2002) COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPEN PROGRAMME AREA GROUP ON INTEGRATED OBSERVING SYSTEMS ITEM: 4 EXPERT
Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist Belt Area, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh
 Open Journal of Geology, 2012, 2, 294-300 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2012.24028 Published Online October 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg) Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist
Open Journal of Geology, 2012, 2, 294-300 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2012.24028 Published Online October 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg) Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist
Regional influence on road slipperiness during winter precipitation events. Marie Eriksson and Sven Lindqvist
 Regional influence on road slipperiness during winter precipitation events Marie Eriksson and Sven Lindqvist Physical Geography, Department of Earth Sciences, Göteborg University Box 460, SE-405 30 Göteborg,
Regional influence on road slipperiness during winter precipitation events Marie Eriksson and Sven Lindqvist Physical Geography, Department of Earth Sciences, Göteborg University Box 460, SE-405 30 Göteborg,
ESTIMATING SNOWMELT CONTRIBUTION FROM THE GANGOTRI GLACIER CATCHMENT INTO THE BHAGIRATHI RIVER, INDIA ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ESTIMATING SNOWMELT CONTRIBUTION FROM THE GANGOTRI GLACIER CATCHMENT INTO THE BHAGIRATHI RIVER, INDIA Rodney M. Chai 1, Leigh A. Stearns 2, C. J. van der Veen 1 ABSTRACT The Bhagirathi River emerges from
ESTIMATING SNOWMELT CONTRIBUTION FROM THE GANGOTRI GLACIER CATCHMENT INTO THE BHAGIRATHI RIVER, INDIA Rodney M. Chai 1, Leigh A. Stearns 2, C. J. van der Veen 1 ABSTRACT The Bhagirathi River emerges from
Surface energy balance of seasonal snow cover for snow-melt estimation in N W Himalaya
 Surface energy balance of seasonal snow cover for snow-melt estimation in N W Himalaya Prem Datt, P K Srivastava, PSNegiand P K Satyawali Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment (SASE), Research & Development
Surface energy balance of seasonal snow cover for snow-melt estimation in N W Himalaya Prem Datt, P K Srivastava, PSNegiand P K Satyawali Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment (SASE), Research & Development
Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region
 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region ZhangZhen 2015.07.10 1 Outline Introduction Data
Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region ZhangZhen 2015.07.10 1 Outline Introduction Data
Studying snow cover in European Russia with the use of remote sensing methods
 40 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Studying snow cover in European Russia with the use
40 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Studying snow cover in European Russia with the use
2 nd Asia CryoNet Workshop Current methods of measurement of the cryosphere in Asia consistency and issues
 2 nd Asia CryoNet Workshop Current methods of measurement of the cryosphere in Asia consistency and issues Dongqi Zhang, Cunde Xiao, Vladimir Aizen and Wolfgang Schöner Feb.5, 2016, Salekhard, Russia 1.
2 nd Asia CryoNet Workshop Current methods of measurement of the cryosphere in Asia consistency and issues Dongqi Zhang, Cunde Xiao, Vladimir Aizen and Wolfgang Schöner Feb.5, 2016, Salekhard, Russia 1.
Modelling runoff from large glacierized basins in the Karakoram Himalaya using remote sensing of the transient snowline
 Remote Sensing and Hydrology 2000 (Proceedings of a symposium held at Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA, April 2000). IAHS Publ. no. 267, 2001. 99 Modelling runoff from large glacierized basins in the Karakoram
Remote Sensing and Hydrology 2000 (Proceedings of a symposium held at Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA, April 2000). IAHS Publ. no. 267, 2001. 99 Modelling runoff from large glacierized basins in the Karakoram
Indian National (Weather) SATellites for Agrometeorological Applications
 Indian National (Weather) SATellites for Agrometeorological Applications Bimal K. Bhattacharya Agriculture-Terrestrial Biosphere- Hydrology Group Space Applications Centre (ISRO) Ahmedabad 380015, India
Indian National (Weather) SATellites for Agrometeorological Applications Bimal K. Bhattacharya Agriculture-Terrestrial Biosphere- Hydrology Group Space Applications Centre (ISRO) Ahmedabad 380015, India
Implementation of CLIMAP and GIS for Mapping the Climatic Dataset of Northern Iraq
 Implementation of CLIMAP and GIS for Mapping the Climatic Dataset of Northern Iraq Sabah Hussein Ali University of Mosul/Remote sensing Center KEYWORDS: CLIMAP, GIS, DEM, Climatic, IRAQ ABSTRACT The main
Implementation of CLIMAP and GIS for Mapping the Climatic Dataset of Northern Iraq Sabah Hussein Ali University of Mosul/Remote sensing Center KEYWORDS: CLIMAP, GIS, DEM, Climatic, IRAQ ABSTRACT The main
Analysis of meteorological measurements made over three rainy seasons in Sinazongwe District, Zambia.
 Analysis of meteorological measurements made over three rainy seasons in Sinazongwe District, Zambia. 1 Hiromitsu Kanno, 2 Hiroyuki Shimono, 3 Takeshi Sakurai, and 4 Taro Yamauchi 1 National Agricultural
Analysis of meteorological measurements made over three rainy seasons in Sinazongwe District, Zambia. 1 Hiromitsu Kanno, 2 Hiroyuki Shimono, 3 Takeshi Sakurai, and 4 Taro Yamauchi 1 National Agricultural
EVALUATION AND MONITORING OF SNOWCOVER WATER RESOURCES IN CARPATHIAN BASINS USING GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION AND SATELLITE DATA
 EVALUATION AND MONITORING OF SNOWCOVER WATER RESOURCES IN CARPATHIAN BASINS USING GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION AND SATELLITE DATA Gheorghe Stancalie, Simona Catana, Anisoara Iordache National Institute of Meteorology
EVALUATION AND MONITORING OF SNOWCOVER WATER RESOURCES IN CARPATHIAN BASINS USING GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION AND SATELLITE DATA Gheorghe Stancalie, Simona Catana, Anisoara Iordache National Institute of Meteorology
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks. Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC
 Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
URBAN WATERSHED RUNOFF MODELING USING GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES
 URBAN WATERSHED RUNOFF MODELING USING GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES DST Sponsored Research Project (NRDMS Division) By Prof. M. GOPAL NAIK Professor & Chairman, Board of Studies Email: mgnaikc@gmail.com Department
URBAN WATERSHED RUNOFF MODELING USING GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES DST Sponsored Research Project (NRDMS Division) By Prof. M. GOPAL NAIK Professor & Chairman, Board of Studies Email: mgnaikc@gmail.com Department
Remote Sensing I: Basics
 Remote Sensing I: Basics Kelly M. Brunt Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center, University of Maryland Cryospheric Science Laboratory, Goddard Space Flight Center kelly.m.brunt@nasa.gov (Based on
Remote Sensing I: Basics Kelly M. Brunt Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center, University of Maryland Cryospheric Science Laboratory, Goddard Space Flight Center kelly.m.brunt@nasa.gov (Based on
Novel Snotel Data Uses: Detecting Change in Snowpack Development Controls, and Remote Basin Snow Depth Modeling
 Novel Snotel Data Uses: Detecting Change in Snowpack Development Controls, and Remote Basin Snow Depth Modeling OVERVIEW Mark Losleben and Tyler Erickson INSTAAR, University of Colorado Mountain Research
Novel Snotel Data Uses: Detecting Change in Snowpack Development Controls, and Remote Basin Snow Depth Modeling OVERVIEW Mark Losleben and Tyler Erickson INSTAAR, University of Colorado Mountain Research
Positional accuracy of the drainage networks extracted from ASTER and SRTM for the Gorongosa National Park region - Comparative analysis
 Positional accuracy of the drainage networks extracted from ASTER and SRTM for the Gorongosa National Park region - Comparative analysis Tiago CARMO 1, Cidália C. FONTE 1,2 1 Departamento de Matemática,
Positional accuracy of the drainage networks extracted from ASTER and SRTM for the Gorongosa National Park region - Comparative analysis Tiago CARMO 1, Cidália C. FONTE 1,2 1 Departamento de Matemática,
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1
 APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
Investigations into the Spatial Pattern of Annual and Interannual Snow Coverage of Brøgger Peninsula, Svalbard,
 Investigations into the Spatial Pattern of Annual and Interannual Snow Coverage of Brøgger Peninsula, Svalbard, 2000-2007 Manfred F. Buchroithner Nadja Thieme Jack Kohler 6th ICA Mountain Cartography Workshop
Investigations into the Spatial Pattern of Annual and Interannual Snow Coverage of Brøgger Peninsula, Svalbard, 2000-2007 Manfred F. Buchroithner Nadja Thieme Jack Kohler 6th ICA Mountain Cartography Workshop
Development of Pakistan s New Area Weighted Rainfall Using Thiessen Polygon Method
 Pakistan Journal of Meteorology Vol. 9, Issue 17: July 2012 Technical Note Development of Pakistan s New Area Weighted Rainfall Using Thiessen Polygon Method Faisal, N. 1, 2, A. Gaffar 2 ABSTRACT In this
Pakistan Journal of Meteorology Vol. 9, Issue 17: July 2012 Technical Note Development of Pakistan s New Area Weighted Rainfall Using Thiessen Polygon Method Faisal, N. 1, 2, A. Gaffar 2 ABSTRACT In this
EUMETSAT STATUS AND PLANS
 1 EUM/TSS/VWG/15/826793 07/10/2015 EUMETSAT STATUS AND PLANS François Montagner, Marine Applications Manager, EUMETSAT WMO Polar Space Task Group 5 5-7 October 2015, DLR, Oberpfaffenhofen PSTG Strategic
1 EUM/TSS/VWG/15/826793 07/10/2015 EUMETSAT STATUS AND PLANS François Montagner, Marine Applications Manager, EUMETSAT WMO Polar Space Task Group 5 5-7 October 2015, DLR, Oberpfaffenhofen PSTG Strategic
Analysis of Rainfall and Other Weather Parameters under Climatic Variability of Parbhani ( )
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.295
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.295
INVISIBLE WATER COSTS
 Every Drop Every Counts... Drop Counts... INVISIBLE WATER COSTS Corn - 108.1 gallons per pound How much water it takes to produce... Apple - 18.5 gallons to grow Beef - 1,581 gallons per pound Oats - 122.7
Every Drop Every Counts... Drop Counts... INVISIBLE WATER COSTS Corn - 108.1 gallons per pound How much water it takes to produce... Apple - 18.5 gallons to grow Beef - 1,581 gallons per pound Oats - 122.7
Gulmarg, Kashmir, India: Potential Site for Optical Astronomical Observations
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (June 2017) 38:18 Indian Academy of Sciences DOI 10.1007/s12036-017-9438-9 Gulmarg, Kashmir, India: Potential Site for Optical Astronomical Observations AJAZ AHMAD DAR 1,2,3 and MANZOOR
J. Astrophys. Astr. (June 2017) 38:18 Indian Academy of Sciences DOI 10.1007/s12036-017-9438-9 Gulmarg, Kashmir, India: Potential Site for Optical Astronomical Observations AJAZ AHMAD DAR 1,2,3 and MANZOOR
Analyzing and Visualizing Precipitation and Soil Moisture in ArcGIS
 Analyzing and Visualizing Precipitation and Soil Moisture in ArcGIS Wenli Yang, Pham Long, Peisheng Zhao, Steve Kempler, and Jennifer Wei * NASA Goddard Earth Science Data and Information Services Center
Analyzing and Visualizing Precipitation and Soil Moisture in ArcGIS Wenli Yang, Pham Long, Peisheng Zhao, Steve Kempler, and Jennifer Wei * NASA Goddard Earth Science Data and Information Services Center
Comparing different MODIS snow products with distributed simulation of the snowpack in the French Alps
 Comparing different MODIS snow products with distributed simulation of the snowpack in the French Alps Luc Charrois 1, Marie Dumont 1,*, Pascal Sirguey 2, Samuel Morin 1, Matthieu Lafaysse 1 and Fatima
Comparing different MODIS snow products with distributed simulation of the snowpack in the French Alps Luc Charrois 1, Marie Dumont 1,*, Pascal Sirguey 2, Samuel Morin 1, Matthieu Lafaysse 1 and Fatima
Memo. I. Executive Summary. II. ALERT Data Source. III. General System-Wide Reporting Summary. Date: January 26, 2009 To: From: Subject:
 Memo Date: January 26, 2009 To: From: Subject: Kevin Stewart Markus Ritsch 2010 Annual Legacy ALERT Data Analysis Summary Report I. Executive Summary The Urban Drainage and Flood Control District (District)
Memo Date: January 26, 2009 To: From: Subject: Kevin Stewart Markus Ritsch 2010 Annual Legacy ALERT Data Analysis Summary Report I. Executive Summary The Urban Drainage and Flood Control District (District)
SNOWMELT RUNOFF ESTIMATION OF A HIMALIYAN WATERSHED THROUGH REMOTE SENSING, GIS AND SIMULATION MODELING
 SNOWMELT RUNOFF ESTIMATION OF A HIMALIYAN WATERSHED THROUGH REMOTE SENSING, GIS AND SIMULATION MODELING A. Alam g, *, A. H. Sheikh g, S. A. Bhat g, A. M.Shah g g Department of Geology & Geophysics University
SNOWMELT RUNOFF ESTIMATION OF A HIMALIYAN WATERSHED THROUGH REMOTE SENSING, GIS AND SIMULATION MODELING A. Alam g, *, A. H. Sheikh g, S. A. Bhat g, A. M.Shah g g Department of Geology & Geophysics University
Central Asia Regional Flash Flood Guidance System 4-6 October Hydrologic Research Center A Nonprofit, Public-Benefit Corporation
 http://www.hrcwater.org Central Asia Regional Flash Flood Guidance System 4-6 October 2016 Hydrologic Research Center A Nonprofit, Public-Benefit Corporation FFGS Snow Components Snow Accumulation and
http://www.hrcwater.org Central Asia Regional Flash Flood Guidance System 4-6 October 2016 Hydrologic Research Center A Nonprofit, Public-Benefit Corporation FFGS Snow Components Snow Accumulation and
1.Introduction 2.Relocation Information 3.Tourism 4.Population & Demographics 5.Education 6.Employment & Income 7.City Fees & Taxes 8.
 1.Introduction 2.Relocation Information 3.Tourism 4.Population & Demographics 5.Education 6.Employment & Income 7.City Fees & Taxes 8.Recreation & Activities 9.Climate Data 10.Economic Development History
1.Introduction 2.Relocation Information 3.Tourism 4.Population & Demographics 5.Education 6.Employment & Income 7.City Fees & Taxes 8.Recreation & Activities 9.Climate Data 10.Economic Development History
NASA Flood Monitoring and Mapping Tools
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration ARSET Applied Remote Sensing Training http://arset.gsfc.nasa.gov @NASAARSET NASA Flood Monitoring and Mapping Tools www.nasa.gov Outline Overview of Flood
National Aeronautics and Space Administration ARSET Applied Remote Sensing Training http://arset.gsfc.nasa.gov @NASAARSET NASA Flood Monitoring and Mapping Tools www.nasa.gov Outline Overview of Flood
Satellite-based Lake Surface Temperature (LST) Homa Kheyrollah Pour Claude Duguay
 Satellite-based Lake Surface Temperature (LST) Homa Kheyrollah Pour Claude Duguay Lakes in NWP models Interaction of the atmosphere and underlying layer is the most important issue in climate modeling
Satellite-based Lake Surface Temperature (LST) Homa Kheyrollah Pour Claude Duguay Lakes in NWP models Interaction of the atmosphere and underlying layer is the most important issue in climate modeling
Colorado Alpine Dust Deposition and Associated Continental Winds 1
 Hydrology Days 2010 Colorado Alpine Dust Deposition and Associated Continental Winds 1 Morgan Phillips 2 Colorado Climate Center and Bureau of Land Management Abstract. The winter and early spring of 2008-2009
Hydrology Days 2010 Colorado Alpine Dust Deposition and Associated Continental Winds 1 Morgan Phillips 2 Colorado Climate Center and Bureau of Land Management Abstract. The winter and early spring of 2008-2009
Remote Sensing of SWE in Canada
 Remote Sensing of SWE in Canada Anne Walker Climate Research Division, Environment Canada Polar Snowfall Hydrology Mission Workshop, June 26-28, 2007 Satellite Remote Sensing Snow Cover Optical -- Snow
Remote Sensing of SWE in Canada Anne Walker Climate Research Division, Environment Canada Polar Snowfall Hydrology Mission Workshop, June 26-28, 2007 Satellite Remote Sensing Snow Cover Optical -- Snow
The indicator can be used for awareness raising, evaluation of occurred droughts, forecasting future drought risks and management purposes.
 INDICATOR FACT SHEET SSPI: Standardized SnowPack Index Indicator definition The availability of water in rivers, lakes and ground is mainly related to precipitation. However, in the cold climate when precipitation
INDICATOR FACT SHEET SSPI: Standardized SnowPack Index Indicator definition The availability of water in rivers, lakes and ground is mainly related to precipitation. However, in the cold climate when precipitation
CGMS Baseline. Sustained contributions to the Global Observing System. Endorsed by CGMS-46 in Bengaluru, June 2018
 CGMS Baseline Sustained contributions to the Global Observing System Best Practices for Achieving User Readiness for New Meteorological Satellites Endorsed by CGMS-46 in Bengaluru, June 2018 CGMS/DOC/18/1028862,
CGMS Baseline Sustained contributions to the Global Observing System Best Practices for Achieving User Readiness for New Meteorological Satellites Endorsed by CGMS-46 in Bengaluru, June 2018 CGMS/DOC/18/1028862,
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
PREDICTION AND MONITORING OF OCEANIC DISASTERS USING MICROWAVE REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES
 PREDICTION AND MONITORING OF OCEANIC DISASTERS USING MICROWAVE REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES O P N Calla International Centre for Radio Science, OM NIWAS A-23, Shastri Nagar, Jodhpur-342 003 Abstract The disasters
PREDICTION AND MONITORING OF OCEANIC DISASTERS USING MICROWAVE REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES O P N Calla International Centre for Radio Science, OM NIWAS A-23, Shastri Nagar, Jodhpur-342 003 Abstract The disasters
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies
 Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis
 4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis Beth L. Hall and Timothy. J. Brown DRI, Reno, NV ABSTRACT. The North American
4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis Beth L. Hall and Timothy. J. Brown DRI, Reno, NV ABSTRACT. The North American
Civil Engineering Journal
 Available online at www.civilejournal.org Civil Engineering Journal Vol. 1, No. 2, December, 2015 Comparative Study of Landsat and Aster Data by Morphometric Analysis Sujit Kumar a*, Tapasi Bhandary b
Available online at www.civilejournal.org Civil Engineering Journal Vol. 1, No. 2, December, 2015 Comparative Study of Landsat and Aster Data by Morphometric Analysis Sujit Kumar a*, Tapasi Bhandary b
Inter-linkage case study in Pakistan
 7 th GEOSS Asia Pacific Symposium GEOSS AWCI Parallel Session: 26-28 May, 2014, Tokyo, Japan Inter-linkage case study in Pakistan Snow and glaciermelt runoff modeling in Upper Indus Basin of Pakistan Maheswor
7 th GEOSS Asia Pacific Symposium GEOSS AWCI Parallel Session: 26-28 May, 2014, Tokyo, Japan Inter-linkage case study in Pakistan Snow and glaciermelt runoff modeling in Upper Indus Basin of Pakistan Maheswor
Image 1: Earth from space
 Image 1: Earth from space Credit: NASA Spacecraft: Apollo 17 Sensor: camera using visible light Image date: December 7, 1972 This image is a photograph of Earth taken by Harrison "Jack" Schmitt, an astronaut
Image 1: Earth from space Credit: NASA Spacecraft: Apollo 17 Sensor: camera using visible light Image date: December 7, 1972 This image is a photograph of Earth taken by Harrison "Jack" Schmitt, an astronaut
Land Data Assimilation at NCEP NLDAS Project Overview, ECMWF HEPEX 2004
 Dag.Lohmann@noaa.gov, Land Data Assimilation at NCEP NLDAS Project Overview, ECMWF HEPEX 2004 Land Data Assimilation at NCEP: Strategic Lessons Learned from the North American Land Data Assimilation System
Dag.Lohmann@noaa.gov, Land Data Assimilation at NCEP NLDAS Project Overview, ECMWF HEPEX 2004 Land Data Assimilation at NCEP: Strategic Lessons Learned from the North American Land Data Assimilation System
Third Grade Math and Science DBQ Weather and Climate/Representing and Interpreting Charts and Data
 Third Grade Math and Science DBQ Weather and Climate/Representing and Interpreting Charts and Data A document based question (DBQ) is an authentic assessment where students interact with content related
Third Grade Math and Science DBQ Weather and Climate/Representing and Interpreting Charts and Data A document based question (DBQ) is an authentic assessment where students interact with content related
USE OF SATELLITE INFORMATION IN THE HUNGARIAN NOWCASTING SYSTEM
 USE OF SATELLITE INFORMATION IN THE HUNGARIAN NOWCASTING SYSTEM Mária Putsay, Zsófia Kocsis and Ildikó Szenyán Hungarian Meteorological Service, Kitaibel Pál u. 1, H-1024, Budapest, Hungary Abstract The
USE OF SATELLITE INFORMATION IN THE HUNGARIAN NOWCASTING SYSTEM Mária Putsay, Zsófia Kocsis and Ildikó Szenyán Hungarian Meteorological Service, Kitaibel Pál u. 1, H-1024, Budapest, Hungary Abstract The
Global Climates. Name Date
 Global Climates Name Date No investigation of the atmosphere is complete without examining the global distribution of the major atmospheric elements and the impact that humans have on weather and climate.
Global Climates Name Date No investigation of the atmosphere is complete without examining the global distribution of the major atmospheric elements and the impact that humans have on weather and climate.
Creating a cloud-free MODIS snow cover product using spatial and temporal interpolation and temperature thresholds
 Creating a cloud-free MODIS snow cover product using spatial and temporal interpolation and temperature thresholds Justinas Kilpys, Egidijus Rimkus, Silvija Pipiraitė Vilnius University, Institute of Geosciences
Creating a cloud-free MODIS snow cover product using spatial and temporal interpolation and temperature thresholds Justinas Kilpys, Egidijus Rimkus, Silvija Pipiraitė Vilnius University, Institute of Geosciences
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLIMATE. Basic Climatology Colorado Climate Center
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLIMATE Basic Climatology Colorado Climate Center Remember These? Factor 1: Our Energy Source Factor 2: Revolution & Tilt Factor 3: Rotation!
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLIMATE Basic Climatology Colorado Climate Center Remember These? Factor 1: Our Energy Source Factor 2: Revolution & Tilt Factor 3: Rotation!
Modelling snow accumulation and snow melt in a continuous hydrological model for real-time flood forecasting
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Modelling snow accumulation and snow melt in a continuous hydrological model for real-time flood forecasting To cite this article: Ph Stanzel et al
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Modelling snow accumulation and snow melt in a continuous hydrological model for real-time flood forecasting To cite this article: Ph Stanzel et al
PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE.
 PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE. Spyridoula Vassilopoulou * Institute of Cartography
PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE. Spyridoula Vassilopoulou * Institute of Cartography
Evaluation of distributed snowpack simulation with in-situ and remote sensing information in Arveupper catchment
 Evaluation of distributed snowpack simulation with in-situ and remote sensing information in Arveupper catchment J. Revuelto 1,2, G. Lecourt 2, L. Charrois 2, T. Condom 1, M. Dumont 2, M. Lafaysse 2,,
Evaluation of distributed snowpack simulation with in-situ and remote sensing information in Arveupper catchment J. Revuelto 1,2, G. Lecourt 2, L. Charrois 2, T. Condom 1, M. Dumont 2, M. Lafaysse 2,,
HYDROLOGICAL MODELING OF HIGHLY GLACIERIZED RIVER BASINS. Nina Omani, Raghavan Srinivasan, Patricia Smith, Raghupathy Karthikeyan, Gerald North
 HYDROLOGICAL MODELING OF HIGHLY GLACIERIZED RIVER BASINS Nina Omani, Raghavan Srinivasan, Patricia Smith, Raghupathy Karthikeyan, Gerald North Problem statement Glaciers help to keep the earth cool High
HYDROLOGICAL MODELING OF HIGHLY GLACIERIZED RIVER BASINS Nina Omani, Raghavan Srinivasan, Patricia Smith, Raghupathy Karthikeyan, Gerald North Problem statement Glaciers help to keep the earth cool High
NASA Products to Enhance Energy Utility Load Forecasting
 NASA Products to Enhance Energy Utility Load Forecasting Erica Zell, Battelle zelle@battelle.org, Arlington, VA ESIP 2010 Summer Meeting, Knoxville, TN, July 20-23 Project Overview Funded by the NASA Applied
NASA Products to Enhance Energy Utility Load Forecasting Erica Zell, Battelle zelle@battelle.org, Arlington, VA ESIP 2010 Summer Meeting, Knoxville, TN, July 20-23 Project Overview Funded by the NASA Applied
Satellite derived precipitation estimates over Indian region during southwest monsoons
 J. Ind. Geophys. Union ( January 2013 ) Vol.17, No.1, pp. 65-74 Satellite derived precipitation estimates over Indian region during southwest monsoons Harvir Singh 1,* and O.P. Singh 2 1 National Centre
J. Ind. Geophys. Union ( January 2013 ) Vol.17, No.1, pp. 65-74 Satellite derived precipitation estimates over Indian region during southwest monsoons Harvir Singh 1,* and O.P. Singh 2 1 National Centre
Outline. Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring. Introduction. Satellites and their Sensors used for Flood Mapping
 Outline Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Chairman, Centre for Earth Sciences Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg. Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560
Outline Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Chairman, Centre for Earth Sciences Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg. Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560
Hydro-meteorological Analysis of Langtang Khola Catchment, Nepal
 Hydro-meteorological Analysis of Langtang Khola Catchment, Nepal Tirtha R. Adhikari 1, Lochan P. Devkota 1, Suresh.C Pradhan 2, Pradeep K. Mool 3 1 Central Department of Hydrology and Meteorology Tribhuvan
Hydro-meteorological Analysis of Langtang Khola Catchment, Nepal Tirtha R. Adhikari 1, Lochan P. Devkota 1, Suresh.C Pradhan 2, Pradeep K. Mool 3 1 Central Department of Hydrology and Meteorology Tribhuvan
CLIMATE CHANGE AND REGIONAL HYDROLOGY ACROSS THE NORTHEAST US: Evidence of Changes, Model Projections, and Remote Sensing Approaches
 CLIMATE CHANGE AND REGIONAL HYDROLOGY ACROSS THE NORTHEAST US: Evidence of Changes, Model Projections, and Remote Sensing Approaches Michael A. Rawlins Dept of Geosciences University of Massachusetts OUTLINE
CLIMATE CHANGE AND REGIONAL HYDROLOGY ACROSS THE NORTHEAST US: Evidence of Changes, Model Projections, and Remote Sensing Approaches Michael A. Rawlins Dept of Geosciences University of Massachusetts OUTLINE
Weather and Climate of the Rogue Valley By Gregory V. Jones, Ph.D., Southern Oregon University
 Weather and Climate of the Rogue Valley By Gregory V. Jones, Ph.D., Southern Oregon University The Rogue Valley region is one of many intermountain valley areas along the west coast of the United States.
Weather and Climate of the Rogue Valley By Gregory V. Jones, Ph.D., Southern Oregon University The Rogue Valley region is one of many intermountain valley areas along the west coast of the United States.
Spaceborne and Ground-based Global and Regional Precipitation Estimation: Multi-Sensor Synergy
 Hydrometeorology and Remote Sensing Lab (hydro.ou.edu) at The University of Oklahoma Spaceborne and Ground-based Global and Regional Precipitation Estimation: Multi-Sensor Synergy Presented by: 温逸馨 (Berry)
Hydrometeorology and Remote Sensing Lab (hydro.ou.edu) at The University of Oklahoma Spaceborne and Ground-based Global and Regional Precipitation Estimation: Multi-Sensor Synergy Presented by: 温逸馨 (Berry)
Seasonal and annual variation of Temperature and Precipitation in Phuntsholing
 easonal and annual variation of Temperature and Precipitation in Phuntsholing Leki Dorji Department of Civil Engineering, College of cience and Technology, Royal University of Bhutan. Bhutan Abstract Bhutan
easonal and annual variation of Temperature and Precipitation in Phuntsholing Leki Dorji Department of Civil Engineering, College of cience and Technology, Royal University of Bhutan. Bhutan Abstract Bhutan
CHANGE DETECTION USING REMOTE SENSING- LAND COVER CHANGE ANALYSIS OF THE TEBA CATCHMENT IN SPAIN (A CASE STUDY)
 CHANGE DETECTION USING REMOTE SENSING- LAND COVER CHANGE ANALYSIS OF THE TEBA CATCHMENT IN SPAIN (A CASE STUDY) Sharda Singh, Professor & Programme Director CENTRE FOR GEO-INFORMATICS RESEARCH AND TRAINING
CHANGE DETECTION USING REMOTE SENSING- LAND COVER CHANGE ANALYSIS OF THE TEBA CATCHMENT IN SPAIN (A CASE STUDY) Sharda Singh, Professor & Programme Director CENTRE FOR GEO-INFORMATICS RESEARCH AND TRAINING
SNOW COVER DURATION MAPS IN ALPINE REGIONS FROM REMOTE SENSING DATA
 SNOW COVER DURATION MAPS IN ALPINE REGIONS FROM REMOTE SENSING DATA D. Brander, K. Seidel, M. Zurflüh and Ch. Huggel Computer Vision Group, Communication Technology Laboratory, ETH, Zurich, Switzerland,
SNOW COVER DURATION MAPS IN ALPINE REGIONS FROM REMOTE SENSING DATA D. Brander, K. Seidel, M. Zurflüh and Ch. Huggel Computer Vision Group, Communication Technology Laboratory, ETH, Zurich, Switzerland,
A New Approach to Avalanche Forecasting and Disaster Management for Western Himalaya
 A New Approach to Avalanche Forecasting and Disaster Management for Western Himalaya Ashwagosha Ganju and Amreek Singh Synopsis Every winter snow avalanches claim a number of precious lives of civil and
A New Approach to Avalanche Forecasting and Disaster Management for Western Himalaya Ashwagosha Ganju and Amreek Singh Synopsis Every winter snow avalanches claim a number of precious lives of civil and
Understanding Michigan snowfall. Jim Keysor - NWS Gaylord
 Understanding Michigan snowfall Jim Keysor - NWS Gaylord Presentation Outline Topics Background information on lake effect Radar and lake effect snow Wind direction and lake effect Lake Enhanced snow Elevation
Understanding Michigan snowfall Jim Keysor - NWS Gaylord Presentation Outline Topics Background information on lake effect Radar and lake effect snow Wind direction and lake effect Lake Enhanced snow Elevation
Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN. SWE Maps
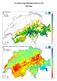 Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN SWE Maps Description The snow water equivalent maps (SWE maps) present an estimation of the distribution of snow water resources in Switzerland. The maps have
Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN SWE Maps Description The snow water equivalent maps (SWE maps) present an estimation of the distribution of snow water resources in Switzerland. The maps have
Japanese Programs on Space and Water Applications
 Japanese Programs on Space and Water Applications Tamotsu IGARASHI Remote Sensing Technology Center of Japan June 2006 COPUOS 2006 Vienna International Centre Water-related hazards/disasters may occur
Japanese Programs on Space and Water Applications Tamotsu IGARASHI Remote Sensing Technology Center of Japan June 2006 COPUOS 2006 Vienna International Centre Water-related hazards/disasters may occur
Introdution. Geography. Country overview
 The 5th Meeting of the Coordinating Group of the RA II WIGOS Satellite Project 21 October, Vladivostok city, Russky Island, Russia Far Eastern Federal University Tajikistan report Agency for Hydrometeorology
The 5th Meeting of the Coordinating Group of the RA II WIGOS Satellite Project 21 October, Vladivostok city, Russky Island, Russia Far Eastern Federal University Tajikistan report Agency for Hydrometeorology
Aniekan Eyoh 1* Department of Geoinformatics & Surveying, Faculty of Environmental Studies, University of Uyo, Nigeria
 Available online at http://euroasiapub.org/journals.php, pp. 53~62 Thomson Reuters Researcher ID: L-5236-2015 TEMPORAL APPRAISAL OF LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE DYNAMICS ACROSS THE NINE STATES OF NIGER DELTA
Available online at http://euroasiapub.org/journals.php, pp. 53~62 Thomson Reuters Researcher ID: L-5236-2015 TEMPORAL APPRAISAL OF LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE DYNAMICS ACROSS THE NINE STATES OF NIGER DELTA
Snowcover accumulation and soil temperature at sites in the western Canadian Arctic
 Snowcover accumulation and soil temperature at sites in the western Canadian Arctic Philip Marsh 1, C. Cuell 1, S. Endrizzi 1, M. Sturm 2, M. Russell 1, C. Onclin 1, and J. Pomeroy 3 1. National Hydrology
Snowcover accumulation and soil temperature at sites in the western Canadian Arctic Philip Marsh 1, C. Cuell 1, S. Endrizzi 1, M. Sturm 2, M. Russell 1, C. Onclin 1, and J. Pomeroy 3 1. National Hydrology
Usefulness of mesoscale weather forecast for avalanche forecasting
 Usefulness of mesoscale weather forecast for avalanche forecasting K. Srinivasan*, A. Ganju and S. S. Sharma Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment, Research and Development Centre, Chandigarh 160 036,
Usefulness of mesoscale weather forecast for avalanche forecasting K. Srinivasan*, A. Ganju and S. S. Sharma Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment, Research and Development Centre, Chandigarh 160 036,
Snow processes and their drivers in Sierra Nevada (Spain), and implications for modelling.
 Snow processes and their drivers in Sierra Nevada (Spain), and implications for modelling. M.J. Polo, M.J. Pérez-Palazón, R. Pimentel, J. Herrero Granada,02 de November 2016 SECTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction
Snow processes and their drivers in Sierra Nevada (Spain), and implications for modelling. M.J. Polo, M.J. Pérez-Palazón, R. Pimentel, J. Herrero Granada,02 de November 2016 SECTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction
IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE OVER THE ARABIAN PENINSULA
 IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE OVER THE ARABIAN PENINSULA By: Talal Alharbi June, 29 2017 1 Motivation: In arid and semi-arid regions of the world the demand for fresh water resources is increasing due to: increasing
IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE OVER THE ARABIAN PENINSULA By: Talal Alharbi June, 29 2017 1 Motivation: In arid and semi-arid regions of the world the demand for fresh water resources is increasing due to: increasing
Country Presentation-Nepal
 Country Presentation-Nepal Mt.Everest, Shiva Pd. Nepal, DHM South Asia Drought Monitor Workshop Dhaka Bangladesh 2 th April 215 Overview Brief Climatology Climate activities- DHM PPCR (Pilot Program for
Country Presentation-Nepal Mt.Everest, Shiva Pd. Nepal, DHM South Asia Drought Monitor Workshop Dhaka Bangladesh 2 th April 215 Overview Brief Climatology Climate activities- DHM PPCR (Pilot Program for
Spatiotemporal variations of alpine climate, snow cover and phenology
 Spatiotemporal variations of alpine climate, snow cover and phenology S. Asam, M. Callegari, M. Matiu, G. Fiore, L. De Gregorio, A. Jacob, A. Menzel, C. Notarnicola, M. Zebisch Asam et al., Spatiotemporal
Spatiotemporal variations of alpine climate, snow cover and phenology S. Asam, M. Callegari, M. Matiu, G. Fiore, L. De Gregorio, A. Jacob, A. Menzel, C. Notarnicola, M. Zebisch Asam et al., Spatiotemporal
Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list)
 Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list) Snow/ice Sea ice motion (sat): experimental, climate model Sea ice extent (sat): operational, U.S. Navy PIPs model; Canada; others? Sea ice concentration
Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list) Snow/ice Sea ice motion (sat): experimental, climate model Sea ice extent (sat): operational, U.S. Navy PIPs model; Canada; others? Sea ice concentration
MET Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16)
 MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
Field Based Spectral Reflectance Studies to Develop NDSI Method for Snow Cover Monitoring
 Photonirvachak Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, Vol. 30, No. 1&2, 2002 Field Based Spectral Reflectance Studies to Develop NDSI Method for Snow Cover Monitoring A V KULKARNP, J SRINIVASULU
Photonirvachak Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, Vol. 30, No. 1&2, 2002 Field Based Spectral Reflectance Studies to Develop NDSI Method for Snow Cover Monitoring A V KULKARNP, J SRINIVASULU
Comparison of meteorological data from different sources for Bishkek city, Kyrgyzstan
 Comparison of meteorological data from different sources for Bishkek city, Kyrgyzstan Ruslan Botpaev¹*, Alaibek Obozov¹, Janybek Orozaliev², Christian Budig², Klaus Vajen², 1 Kyrgyz State Technical University,
Comparison of meteorological data from different sources for Bishkek city, Kyrgyzstan Ruslan Botpaev¹*, Alaibek Obozov¹, Janybek Orozaliev², Christian Budig², Klaus Vajen², 1 Kyrgyz State Technical University,
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION
 DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting
 Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD,
 J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD, 1948-2008 Richard R. Heim Jr. * NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. Introduction The Intergovernmental Panel
J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD, 1948-2008 Richard R. Heim Jr. * NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. Introduction The Intergovernmental Panel
Monitoring Sea Ice with Space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar
 Monitoring Sea Ice with Space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar Torbjørn Eltoft UiT- the Arctic University of Norway CIRFA A Centre for Research-based Innovation cirfa.uit.no Sea ice & climate Some basic
Monitoring Sea Ice with Space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar Torbjørn Eltoft UiT- the Arctic University of Norway CIRFA A Centre for Research-based Innovation cirfa.uit.no Sea ice & climate Some basic
ESTIMATION OF NEW SNOW DENSITY USING 42 SEASONS OF METEOROLOGICAL DATA FROM JACKSON HOLE MOUNTAIN RESORT, WYOMING. Inversion Labs, Wilson, WY, USA 2
 ESTIMATION OF NEW SNOW DENSITY USING 42 SEASONS OF METEOROLOGICAL DATA FROM JACKSON HOLE MOUNTAIN RESORT, WYOMING Patrick J. Wright 1 *, Bob Comey 2,3, Chris McCollister 2,3, and Mike Rheam 2,3 1 Inversion
ESTIMATION OF NEW SNOW DENSITY USING 42 SEASONS OF METEOROLOGICAL DATA FROM JACKSON HOLE MOUNTAIN RESORT, WYOMING Patrick J. Wright 1 *, Bob Comey 2,3, Chris McCollister 2,3, and Mike Rheam 2,3 1 Inversion
Current and Upcoming NASA Hurricane Measurement Missions National Hurricane Conference
 NASA Science Mission Directorate Earth Science Division Applied Sciences Program Current and Upcoming NASA Hurricane Measurement Missions National Hurricane Conference April 18, 2017 Formulation Implementation
NASA Science Mission Directorate Earth Science Division Applied Sciences Program Current and Upcoming NASA Hurricane Measurement Missions National Hurricane Conference April 18, 2017 Formulation Implementation
P6.13 GLOBAL AND MONTHLY DIURNAL PRECIPITATION STATISTICS BASED ON PASSIVE MICROWAVE OBSERVATIONS FROM AMSU
 P6.13 GLOBAL AND MONTHLY DIURNAL PRECIPITATION STATISTICS BASED ON PASSIVE MICROWAVE OBSERVATIONS FROM AMSU Frederick W. Chen*, David H. Staelin, and Chinnawat Surussavadee Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
P6.13 GLOBAL AND MONTHLY DIURNAL PRECIPITATION STATISTICS BASED ON PASSIVE MICROWAVE OBSERVATIONS FROM AMSU Frederick W. Chen*, David H. Staelin, and Chinnawat Surussavadee Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
COUNTRY PRESENTATION ON MR JAYNAL ABEDIN JOINT SECRETARY ( WORKS & DEVELOPMENT ) MINISTRY OF DEFENCE
 COUNTRY PRESENTATION ON By MR JAYNAL ABEDIN JOINT SECRETARY ( WORKS & DEVELOPMENT ) MINISTRY OF DEFENCE Bangladesh Geographical Location of Bangladesh Bangladesh Country at a Glance Physical Features 1,230
COUNTRY PRESENTATION ON By MR JAYNAL ABEDIN JOINT SECRETARY ( WORKS & DEVELOPMENT ) MINISTRY OF DEFENCE Bangladesh Geographical Location of Bangladesh Bangladesh Country at a Glance Physical Features 1,230
Dual-Frequency Ku- Band Radar Mission Concept for Snow Mass
 Dual-Frequency Ku- Band Radar Mission Concept for Snow Mass Chris Derksen Environment and Climate Change Canada Study Team: Climate Research Division/Meteorological Research Division, ECCC Canadian Space
Dual-Frequency Ku- Band Radar Mission Concept for Snow Mass Chris Derksen Environment and Climate Change Canada Study Team: Climate Research Division/Meteorological Research Division, ECCC Canadian Space
Studies of Austfonna ice cap (Svalbard) using radar altimetry with other satellite techniques
 15 Years of progress in Radar Altimetry Symposium Ocean surface topography science team (OSTST) International Doris Service (IDS) Workshop, Argo Workshop 13-18 March 2006, Venice, Italy Alexei V. Kouraev,
15 Years of progress in Radar Altimetry Symposium Ocean surface topography science team (OSTST) International Doris Service (IDS) Workshop, Argo Workshop 13-18 March 2006, Venice, Italy Alexei V. Kouraev,
Gridding of precipitation and air temperature observations in Belgium. Michel Journée Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium (RMI)
 Gridding of precipitation and air temperature observations in Belgium Michel Journée Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium (RMI) Gridding of meteorological data A variety of hydrologic, ecological,
Gridding of precipitation and air temperature observations in Belgium Michel Journée Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium (RMI) Gridding of meteorological data A variety of hydrologic, ecological,
