P1.35 EVALUATING THE IMPACTS OF EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITIONING ON TYPHOON LOSSES VIA SYNOPTIC CASE STUDIES
|
|
|
- Hilary Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 P1.35 EVALUATING THE IMPACTS OF EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITIONING ON TYPHOON LOSSES VIA SYNOPTIC CASE STUDIES Peter J. Sousounis* and Mélicie Desflots AIR Worldwide Corporation, Boston, MA 1. MOTIVATION FOR THE STUDY The frequency of Extratropical Transitioning (XTT) in the Northwest Pacific Basin is well known. Extratropical Transitioning frequency or its significance near Japan however is less welldocumented but likely significant. For example, according to the General Insurance Association of Japan (GIAJ), 9 of the top 10 greatest meteorological insured losses in Japan s history have occurred from typhoons that have undergone XTT within 500 km of Japan s Coast (cf. Fig. 1). While the storm track information in Fig. 1 by itself is not conclusive, it is possible that the XTT process contributed to enhanced damage - especially since the process typically begins hours before the Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA) indicates completion. The significance of this high frequency is illustrated in Fig. 3, which is adapted from Klein (2000) who noted that extratropical transitioning is characterized by a growth in the asymmetry and the size of the circulation and associated cloud and precipitation shields. The asymmetry results from the presence of baroclinicity, which is typically found at higher latitudes and / or at later times of the year. The economic impacts of XTT in Japan can be dramatic. Buildings and owners in middle and high latitudes and well inland may be less well prepared for storm-force winds and heavy precipitation. Whether due to building codes that are less strict, a lack of evacuation strategies and emergency preparedness, or poor forecasting, a transitioned storm can have serious impacts. Many specific examples are cited in Jones et al. (2003). Fig. 1. Top nine meteorologically-related losses in Japan history. The numbers in the panels indicate trended losses to 2008 Japanese Yen ( ). The purple circles on tracks to the left indicate times when the storm completed XTT according to the Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA). For this study, a simple analysis was performed using JMA Track Data. Storms that underwent XTT within 500 km of the coast were counted as XTT events and those that came within 500 km but that did not transition were counted as nonxtt events. The yearly frequency is shown in Fig. 2. On average, 55% of storms that came within 500 km of the coast underwent XTT. The frequency is considerably higher over the last years. * Corresponding author address: Peter J. Sousounis, AIR-Worldwide Corporation., 131 Dartmouth Street, Boston, MA 02116; psousounis@air-worldwide.com. 2. XTT DYNAMICS The dynamics of XTT are well understood. Various authors have described the XTT process in detail (Klein et al. 2000; Ritchie and Elsberry 2001; Jones et al. 2003; Kitabatake 2007, 2008). As the tropical cyclone (TC) moves poleward, it encounters colder water and increased horizontal temperature gradients. The colder water reduces surface sensible and latent heat fluxes, which are responsible for extracting the energy from the environment (ocean) and converting it to storm energy. Cyclonic flow from the TC distorts the temperature pattern so warm (cold) advection occurs on the east (west) side. The cold advection erodes the convection on the northwest side, causing it to lose its symmetric
2 Fig. 2. Number of historical XTT and nonxtt events for Japan as defined in text. appearance. The warm advection on the east side results in warm, moist air being lifted over cold air farther north, which maintains the deep cloudiness and precipitation over the northwest and northeast quadrants. The weakening of the TC and loss of cloud symmetry are characteristic of most XTT events. As the cyclone continues moving northward into stronger baroclinicity, frontogenesis helps lift warm, moist air to cause clouds and precipitation, and helps ventilate the storm aloft, causing the central pressure at the surface to drop. As available potential energy is released, it is converted to storm energy. The transitioning cyclone begins to reorganize and may reintensify. As XTT progresses, the canonical circular symmetry that characterizes the wind and precipitation footprints of warm-core pretransitioned typhoons breaks down. This paper illustrates the impact of XTT on damage extent and distribution from both wind and flood by comparing two typhoons that impacted Japan. Typhoon Etau made landfall in Japan in August 2003 and caused relatively light damage until it reached Hokkaido at which point it had transitioned completely. In contrast, Typhoon Tokage made landfall in October 2004 in nearly the same place along Japan s coast and proceeded to cause considerable damage. Both typhoons were very comparable in strength just hours before landfall. It is hypothesized that Tokage maintained strength and increased its damaging footprint because it transitioned much earlier. This paper provides details that support that hypothesis. 3. TYPHOONS ETAU AND TOKAGE OVERVIEW Typhoon Etau formed in August It reached maximum intensity just after by-passing Okinawa, Japan at 0600 UTC on August 07 with a minimum central pressure of 945 mb and (10 min) maximum sustained winds of 85 kts according to the JMA. Etau weakened slightly just prior to landfall but then weakened more dramatically after landfall as it traveled up the spine of Honshu. Damage was minor except in Hokkaido, where damage to timber occurred from Fig. 3. Schematic showing evolution of visible cloud as typhoon undergoes XTT near Japan. Adapted from Klein (2000). Typhoon central pressure and its relationship to wind and subsequent damage is also well understood. Typhoon wind fields can be parametrically determined based on observed central pressure. Damage functions relate wind speed to damage for various types of buildings (Jain 2010). Fig. 4. Tracks of Etau 2003 (upper) and Tokage 2004 (lower) from Digital Typhoon.
3 Fig. 5. NHC Enhanced satellite imagery (from Digital Typhoon) for Typhoons Etau 2003 (upper row) and Tokage 2004 (lower row) at times shown. flooding and mudslides as the storm was transitioning. Enhanced satellite imagery in Fig. 5 shows Typhoon Etau remaining tropical through at least 0000 UTC on August 08 (note presence of eye at that time). Afterwards, interaction with an approaching weak trough began the transitioning process (note comma head and tail). Table 1. Summary of housing damage from Typhoons Etau 2003 and Tokage 204. Housing Damage Etau Tokage Completely destroyed Halfly destroyed Partially destroyed Inundation above floor Inundation below floor Insured Loss (B ) Typhoon Tokage formed in October 2004 and reached maximum intensity on October 17 with (10 min) maximum sustained winds of 85 kts and minimum central pressure of 940 mb according to the JMA. While it is not unusual for the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) to report different intensities for storms than the JMA, in the case of Tokage and Etau, the JTWC reported that Tokage was stronger than Etau 24 hours before landfall but considerably weaker at landfall. JMA showed that Tokage and Etau were the same strength 24 hours before landfall. Tokage was the worst storm to strike Japan since Typhoon Mireille in There were 69 deaths from the high winds, flooding and mudslides, and 17 persons were still unaccounted for several days after the storm. Enhanced satellite imagery (Fig. 5) shows Typhoon Tokage beginning transition between October 19 and 20. By 0000 UTC October 20, the southwest erosion of the cloud mass indicates that the cold advection is already in progress. The satellite imagery shows a Tokage with a well defined comma head and tail just after it exits Honshu. Damage from Tokage was severe from flooding especially in some of the interior and prefectures on the Sea of Japan (northern) side. Inspection of Table 1 shows that Tokage clearly resulted in more damage from both wind (indicated by destroyed) and flood (indicated by inundation) than Etau. 4. DIAGNOSING THE DIFFERENCES Six-hourly data from the Japanese 25-Year ReAnalyisis Project (JRA-25) at 20 km resolution and 3-hourly data from the Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission (TRMM) at 0.25 degree resolution is used to evaluate Etau and Tokage. For each storm, the panels in Fig. 6 show sealevel pressure, six-hourly accumulated precipitation (centered on the times for each storm show the conditions at landfall, while the left panels show the pre-landfall conditions when the storms are near Okinawa and beginning to curve towards the northeast. Note that Tokage is
4 remained the same size if not expanded slightly. A noteworthy feature of the Tokage windspeed footprint is that it extends on the left hand side over the Sea of Japan. Precipitation is also considerably heavier, which was likely attributable primarily to frontal uplift. According to the phase space diagrams for typhoons Etau (2003) and Tokage (2004) shown in Fig. 7, which were derived following the methodology described in Hart (2003) and using the 6 hourly JRA-25 reanalysis fields, Etau made landfall as a tropical system while Tokage was already exhibiting extratropical characteristics. As indicated by the cool colors, while Typhoon Tokage was making landfall, its maximum wind speed was located mainly on the left hand side (LHS) of the storm track. Fig. 6. Sea-level pressure and precipitation for Etau and Tokage for times shown. Heavy contour shows 35 kt isotach. See text for more details. moving more quickly than Etau, which is likely associated with its transitioning. The pre-landfall comparison from the JRA perspective shows that Etau is about 10 mb weaker even though the JMA shows the storms to have nearly identical central pressure. The extent of the 35 kt winds is comparable in both although the Tokage footprint is a bit wider in the east-west direction. The pre-landfall precipitation footprint for Etau is noticeably smaller and more symmetric. At landfall, the wind and precipitation footprints are markedly different. Specifically, Etau has shrunk from both perspectives, while Tokage has Vertical north-south cross sections through the storm center for selected times (not shown) illustrate the lateral extent of the wind field as well as the strength of horizontal (potential) temperature gradients. Both storms were associated with an upper level jet streak as is shown in Fig. 8. For Etau, however, this feature proved to be inconsequential as is evidenced by its weakening with time. Even though the storm moved into a region of slightly higher baroclinicity, the wind speeds weakened considerably at landfall. For Tokage, the jet streak was much stronger and even strengthened a bit more at landfall. Baroclinicity was also considerably higher. These ingredients likely played a role in maintaining the intensity and horizontal extent of Tokage as it began undergoing XTT. In fact, the juxtaposition of not one but three separate jet streaks at 300 mb during the period when Tokage was approaching and making landfall, likely assisted the enhancement of its surface wind field especially on the left hand Fig. 7. XTT phase space diagrams for Typhoons Etau and Tokage.
5 The extratropical structure of Typhoon Tokage and its evolution around landfall time, lead to far greater observed and modeled losses than Typhoon Etau (compare Figs. 10 and 11). The two typhoons inflicted comparable losses to prefectures of high exposure, namely Osaka (for Typhoon Etau) and Tokyo (for Typhoon Tokage). However, the expanded wind and precipitation of Typhoon Tokage reached and affected most of the prefectures in Japan. The atypically strong winds and precipitation on the left hand side of the track of Typhoon Tokage induced significant losses in the prefectures facing the Sea of Japan. Despite the fact that Typhoon Tokage (2004) made landfall with approximately the same central pressure as Typhoon Etau (2003) and despite its faster filling rate than Typhoon Etau, the winds of Typhoon Tokage were higher than the ones from Typhoon Etau over the main islands of Japan. Fig hpa geopotential heights and windspeeds for times shown. White circles and arrows indicate ageostrophic flow. Plus and minus signs indicate ascent and descent. Purple arrow indicates surface ageostrophic flow. (north) side. Specifically, Tokage was moving towards the northeast and approaching the right entrance region of the main jet, which is typically an area of enhanced upper level divergence and ascent (circled + sign) as shown in Carlson (1991). Additionally the presumed ageostrophic circulation associated with this feature probably resulted in enhanced southerly (northerly) flow at 300 mb (the surface) as indicated by the white (purple) arrow and was likely primarily responsible for maintaining the strength of Tokage s wind field at the surface. The approach and positioning of the other two jet streaks also constructively enhanced the impact of the main jet streak, resulting in a broad region of upper level divergence and ascent that surrounded Tokage. Etau did not enter such an environment, which is less probable during summer months and so was susceptible to the typical post landfall deterioration from friction and its loss of surface heat fluxes. 5. LOSS COMPARISON The loss estimates for Typhoon Etau (2003) and Typhoon Tokage (2004) were obtained using the AIR Japan typhoon model with the wind speeds from the JRA km re-analysis data and the precipitation estimates from the TRMM satellite and an industry exposure distribution developed at AIR (Fig. 9). The significant enhancement of the winds and precipitation on the left hand side of Typhoon Tokage were probably a response to the interaction between the extratropical system and a strong jet, which was present over Northern Japan hours prior to landfall of Tokage. The resulting structure of the wind and precipitation fields of Typhoon Tokage produced significant losses in Japan making Tokage the fifth highest loss by typhoon in Japan. according to GIAJ. Additional experiments are planned to evaluate specific impacts of track, size, or intensity differences not associated with the XTT process. Fig. 9. Spatial distribution of industry exposure for Japan.
6 Fig. 10. Insured loss distribution for Typhoon Etau using AIR Japan Typhoon Model with analyzed wind and precipitation fields. JRA-25 20km reanalysis derived Surface windspeed (mph) footprint (upper left). TRMMderived precipitation (mm) footprint (upper right). Model estimated losses from wind damage (lower left). Model estimate losses from flood damage (lower right). A transitioning typhoon over Japan can have a social impact comparable to or more significant than a non-transitioning typhoon. As each year, 5 out of 8 storms that come within 500 km of the Japanese coast undergo extratropical transition and as shown by the significant losses induced by Tokage as the system made landfall in Japan as an extratropical cyclone, a better understanding of the extratropical transition process might help to develop more accurate building codes and ultimately save lives. Acknowledgements We gratefully acknowledge the availability and use of JRA25-20 km Reanalysis Data and TRMM Data for this study. REFERENCES circulation characteristics. Mon. Wea. Rev., 128, Hart, R. E., 2003: A cyclone phase space derived from thermal wind and thermal asymmetry. Mon. Wea. Rev., 131, Jones, S., and Coauthors, 2003: The extratropical transition of tropical cyclones: Forecast challenges, current understanding, and future directions. Wea. Forecasting, 18, Kitabatake, N., 2008: Extratropical transition of tropical cyclones in the western North Pacific: Their frontal evolution. Mon. Wea. Rev., 136, Klein, P. M., P. A. Harr and R. L Elsberry, 2000: Extratropical transition of western North Pacific tropical cyclones: An overview and conceptual model of the transformation stage, Wea. Forecasting, 15, Ritchie, E. A. and R. L. Elsberry, 2001: Simulations of the transformation stage of the extratropical transition of tropical cyclones. Mon. Wea. Rev., 129, Carlson, T. N., 1991: Mid-latitude Weather Systems. Routledge, New York, 507 p. Harr, P. A., R. L. Elsberry and T. F. Hogan, 2000: Extratropical transition of tropical cyclones over the western North Pacific, Part II: The impact of midlatitude
7 Fig. 11. Similar to Fig. 10 but for Typhoon Tokage.
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997)
 Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
A Climatology of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones in the Western North Pacific
 A Climatology of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones in the Western North Pacific Naoko KITABATAKE (Meteorological Research Institute / Japan Meteorological Agency) 1 Outline 1. Topic 1:
A Climatology of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones in the Western North Pacific Naoko KITABATAKE (Meteorological Research Institute / Japan Meteorological Agency) 1 Outline 1. Topic 1:
Tropical-Extratropical Transition
 Tropical-Extratropical Transition Extratropical Transition A significant number of tropical cyclones move into the midlatitudes and transform into extratropical cyclones. This process is generally referred
Tropical-Extratropical Transition Extratropical Transition A significant number of tropical cyclones move into the midlatitudes and transform into extratropical cyclones. This process is generally referred
Features of the wind fields associated with Typhoon 0418 (Songda) compared with those of Typhoon 9119 (Mireille)
 Features of the wind fields associated with Typhoon 0418 (Songda) compared with those of Typhoon 9119 (Mireille) by Fumiaki Fujibe 1, Naoko Kitabatake 2, Kotaro Bessho 2 and Shunsuke Hoshino 3 ABSTRACT
Features of the wind fields associated with Typhoon 0418 (Songda) compared with those of Typhoon 9119 (Mireille) by Fumiaki Fujibe 1, Naoko Kitabatake 2, Kotaro Bessho 2 and Shunsuke Hoshino 3 ABSTRACT
The Impact of air-sea interaction on the extratropical transition of tropical cyclones
 The Impact of air-sea interaction on the extratropical transition of tropical cyclones Sarah Jones Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung Universität Karlsruhe / Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe 1. Introduction
The Impact of air-sea interaction on the extratropical transition of tropical cyclones Sarah Jones Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung Universität Karlsruhe / Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe 1. Introduction
and 24 mm, hPa lapse rates between 3 and 4 K km 1, lifted index values
 3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
2D.1 DETERMINATION OF A CONSISTENT TIME FOR THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES
 2D.1 DETERMINATION OF A CONSISTENT TIME FOR THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES David E. Kofron*, Elizabeth A. Ritchie, and J. Scott Tyo University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION
2D.1 DETERMINATION OF A CONSISTENT TIME FOR THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES David E. Kofron*, Elizabeth A. Ritchie, and J. Scott Tyo University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION
1. INTRODUCTION: 2. DATA AND METHODOLOGY:
 27th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, 24-28 April 2006, Monterey, CA 3A.4 SUPERTYPHOON DALE (1996): A REMARKABLE STORM FROM BIRTH THROUGH EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION TO EXPLOSIVE REINTENSIFICATION
27th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, 24-28 April 2006, Monterey, CA 3A.4 SUPERTYPHOON DALE (1996): A REMARKABLE STORM FROM BIRTH THROUGH EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION TO EXPLOSIVE REINTENSIFICATION
David E. Kofron*, Miguel F. Piñeros, Elizabeth A. Ritchie, and J. Scott Tyo University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION
 15.4 DEFINING THE LIFECYCLE OF THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES USING THE DEVIATION ANGLE VARIANCE TECHNIQUE FOR REMOTELY-SENSED IMAGERY David E. Kofron*, Miguel F. Piñeros, Elizabeth
15.4 DEFINING THE LIFECYCLE OF THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES USING THE DEVIATION ANGLE VARIANCE TECHNIQUE FOR REMOTELY-SENSED IMAGERY David E. Kofron*, Miguel F. Piñeros, Elizabeth
THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TYPHOON WINNIE (1997): SELF-AMPLIFICATION AFTER LANDFALL
 THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TYPHOON WINNIE (1997): SELF-AMPLIFICATION AFTER LANDFALL Chih-Shin Liu *1,2 and George Tai-Jen Chen 2 1 Weather Forecast Center, Central Weather Bureau, 2 Department of
THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TYPHOON WINNIE (1997): SELF-AMPLIFICATION AFTER LANDFALL Chih-Shin Liu *1,2 and George Tai-Jen Chen 2 1 Weather Forecast Center, Central Weather Bureau, 2 Department of
Extratropical transition of tropical cyclones: Operational forecasting challenges. Matthew Kucas Joint Typhoon Warning Center Pearl Harbor, HI, USA
 Extratropical transition of tropical cyclones: Operational forecasting challenges Matthew Kucas Joint Typhoon Warning Center Pearl Harbor, HI, USA Outline Motivation for discussion Brief overview of tropical
Extratropical transition of tropical cyclones: Operational forecasting challenges Matthew Kucas Joint Typhoon Warning Center Pearl Harbor, HI, USA Outline Motivation for discussion Brief overview of tropical
A Preliminary Climatology of Extratropical Transitions in the Southwest Indian Ocean
 A Preliminary Climatology of Extratropical Transitions in the Southwest Indian Ocean Kyle S. Griffin Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences, University at Albany, State University of New
A Preliminary Climatology of Extratropical Transitions in the Southwest Indian Ocean Kyle S. Griffin Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences, University at Albany, State University of New
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones
 Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
- tornadoes. Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book. Outline. - cyclones and anti-cyclones. -tropical storms. -Storm surge
 (1 of 16) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - cyclones and anti-cyclones - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 16) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their
(1 of 16) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - cyclones and anti-cyclones - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 16) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their
Heavy Rain/Flooding September 8-10 Associated with Tropical Storm Etau
 Heavy Rain/Flooding September 8-10 Associated with Tropical Storm Etau Wx Files Vol.32 September 24, 2015 Tropical Storm Etau made landfall over the Chita Peninsula in Aichi just after 10:00 AM on September
Heavy Rain/Flooding September 8-10 Associated with Tropical Storm Etau Wx Files Vol.32 September 24, 2015 Tropical Storm Etau made landfall over the Chita Peninsula in Aichi just after 10:00 AM on September
Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps
 Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps Case Study: October 2011 Nor easter FIU MET 3502 Synoptic Hurricane Forecasts Genesis: on large scale weather maps or satellite images, look for tropical waves (Africa
Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps Case Study: October 2011 Nor easter FIU MET 3502 Synoptic Hurricane Forecasts Genesis: on large scale weather maps or satellite images, look for tropical waves (Africa
(April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2
 Lecture #17 (April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2 Hurricane Katrina August 2005 All tropical cyclone tracks (1945-2006). Hurricane Formation While moving westward, tropical disturbances
Lecture #17 (April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2 Hurricane Katrina August 2005 All tropical cyclone tracks (1945-2006). Hurricane Formation While moving westward, tropical disturbances
ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 19 Tropical Cyclones Dr. DeCaria
 ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 19 Tropical Cyclones Dr. DeCaria READING: Chapter 16 GENERAL A tropical cyclone is a large, low-pressure system that forms over the tropical oceans. Tropical cyclones are classified
ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 19 Tropical Cyclones Dr. DeCaria READING: Chapter 16 GENERAL A tropical cyclone is a large, low-pressure system that forms over the tropical oceans. Tropical cyclones are classified
Extratropical transition of North Atlantic tropical cyclones in variable-resolution CAM5
 Extratropical transition of North Atlantic tropical cyclones in variable-resolution CAM5 Diana Thatcher, Christiane Jablonowski University of Michigan Colin Zarzycki National Center for Atmospheric Research
Extratropical transition of North Atlantic tropical cyclones in variable-resolution CAM5 Diana Thatcher, Christiane Jablonowski University of Michigan Colin Zarzycki National Center for Atmospheric Research
Hurricanes. April 14, 2009
 Tropical Weather & Hurricanes Chapter 15 April 14, 2009 Tropical meteorology Tropics characterized by seasonal wet and drier periods- wet when sun is nearly overhead at noon and inter-tropical convergence
Tropical Weather & Hurricanes Chapter 15 April 14, 2009 Tropical meteorology Tropics characterized by seasonal wet and drier periods- wet when sun is nearly overhead at noon and inter-tropical convergence
Predicting Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change
 Predicting Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 phone: (831)656-3787 fax: (831)656-3061 email: paharr@nps.navy.mil
Predicting Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 phone: (831)656-3787 fax: (831)656-3061 email: paharr@nps.navy.mil
Summary of November Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge
 Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) Why has the weather been so violent?
 WEATHER TOPICS Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) 2009 Why has the weather been so violent? As can be seen by the following forecast map, the Fall Transition and early Winter Season of
WEATHER TOPICS Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) 2009 Why has the weather been so violent? As can be seen by the following forecast map, the Fall Transition and early Winter Season of
Simulations of the Transformation Stage of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones
 1462 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Simulations of the Transformation Stage of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones ELIZABETH A. RITCHIE AND RUSSELL L. ELSBERRY Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate
1462 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Simulations of the Transformation Stage of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones ELIZABETH A. RITCHIE AND RUSSELL L. ELSBERRY Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate
Description of the ET of Super Typhoon Choi-Wan (2009) based on the YOTC-dataset
 High Impact Weather PANDOWAE Description of the ET of Super Typhoon Choi-Wan (2009) based on the YOTC-dataset ¹, D. Anwender¹, S. C. Jones2, J. Keller2, L. Scheck¹ 2 ¹Karlsruhe Institute of Technology,
High Impact Weather PANDOWAE Description of the ET of Super Typhoon Choi-Wan (2009) based on the YOTC-dataset ¹, D. Anwender¹, S. C. Jones2, J. Keller2, L. Scheck¹ 2 ¹Karlsruhe Institute of Technology,
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
- tornadoes. Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book. Outline. -tropical storms. -Storm surge
 (1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 12) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their relationship to air masses Also
(1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 12) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their relationship to air masses Also
10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN
 10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN Andrew L. Hulme* and Jonathan E. Martin University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin
10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN Andrew L. Hulme* and Jonathan E. Martin University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream
 Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events
 National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Heavy rainfall of 23 November 2011 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 Abstract:. A fast moving mid-tropospheric
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Heavy rainfall of 23 November 2011 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 Abstract:. A fast moving mid-tropospheric
Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter
 Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter Shingo Yamada Tokyo Climate Center Japan Meteorological Agency 2006/11/02 7 th Joint Meeting on EAWM Contents 1. Verification of the Seasonal
Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter Shingo Yamada Tokyo Climate Center Japan Meteorological Agency 2006/11/02 7 th Joint Meeting on EAWM Contents 1. Verification of the Seasonal
Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Climate & Earth System Science. Atmosphere Ocean Interactions. A: Structure of the Ocean.
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework. 5-7 May 2015
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework 5-7 May 2015 Readings: Section 5.3.6 of Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology. Introduction In this and other recent lectures, we have developed
Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework 5-7 May 2015 Readings: Section 5.3.6 of Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology. Introduction In this and other recent lectures, we have developed
Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone
 Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone The Beast in the East 15-17 February 2003 Extra-tropical cyclone an area of low pressure outside of the tropics Other names for extra-tropical cyclones: Cyclone Mid-latitude
Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone The Beast in the East 15-17 February 2003 Extra-tropical cyclone an area of low pressure outside of the tropics Other names for extra-tropical cyclones: Cyclone Mid-latitude
Synoptic Meteorology
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
4/29/2011. Mid-latitude cyclones form along a
 Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
New Zealand Heavy Rainfall and Floods
 New Zealand Heavy Rainfall and Floods 1. Introduction Three days of heavy rainfall associated with a deep upper-level low (Fig. 1) brought flooding to portions of New Zealand (Fig. 2). The flooding was
New Zealand Heavy Rainfall and Floods 1. Introduction Three days of heavy rainfall associated with a deep upper-level low (Fig. 1) brought flooding to portions of New Zealand (Fig. 2). The flooding was
Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains
 Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803
 Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies 17-19 August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rain fell over the Gulf States,
Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies 17-19 August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rain fell over the Gulf States,
Chapter 24. Tropical Cyclones. Tropical Cyclone Classification 4/19/17
 Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Cyclones Most destructive storms on the planet Originate over tropical waters, but their paths often take them over land and into midlatitudes Names Hurricane (Atlantic
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Cyclones Most destructive storms on the planet Originate over tropical waters, but their paths often take them over land and into midlatitudes Names Hurricane (Atlantic
Simulations of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones: Contributions by the Midlatitude Upper-Level Trough to Reintensification
 2112 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Simulations of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones: Contributions by the Midlatitude Upper-Level Trough to Reintensification ELIZABETH A. RITCHIE Department of
2112 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Simulations of the Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones: Contributions by the Midlatitude Upper-Level Trough to Reintensification ELIZABETH A. RITCHIE Department of
1. INTRODUCTION. designed. The primary focus of this strategy was the extratropical transition (ET) of tropical cyclones based on the poleward
 P1.98 THE THORPEX PACIFIC ASIAN REGIONAL CAMPAIGN (T-PARC) OBJECTIVE ON THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES: OBSERVED CASES, THEIR STRUCTURE AND DOWNSTREAM IMPACTS P. A. Harr 1, S. C. Jones
P1.98 THE THORPEX PACIFIC ASIAN REGIONAL CAMPAIGN (T-PARC) OBJECTIVE ON THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES: OBSERVED CASES, THEIR STRUCTURE AND DOWNSTREAM IMPACTS P. A. Harr 1, S. C. Jones
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events
 National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events New Zealand heavy rain and flood event-draft by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 Abstract:. A record
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events New Zealand heavy rain and flood event-draft by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 Abstract:. A record
Heavy Rainfall and Flooding of 23 July 2009 By Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Heavy Rainfall and Flooding of 23 July 2009 By Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rains fall over Pennsylvania and eastern New
Heavy Rainfall and Flooding of 23 July 2009 By Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rains fall over Pennsylvania and eastern New
Shawn M. Milrad Atmospheric Science Program Department of Geography University of Kansas Lawrence, Kansas
 Shawn M. Milrad Atmospheric Science Program Department of Geography University of Kansas Lawrence, Kansas Eyad H. Atallah and John R. Gyakum Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences McGill University
Shawn M. Milrad Atmospheric Science Program Department of Geography University of Kansas Lawrence, Kansas Eyad H. Atallah and John R. Gyakum Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences McGill University
Paul Yura*, Frank Alsheimer, and Joseph Calderone NOAA, National Weather Service Forecast Office, Charleston South Carolina 1.
 7B.8 AN EXAMINATION OF THE SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ENVIRONMENTS INVOLVED IN TORNADO OUTBREAKS FROM HURRICANES FRANCES (2004) AND JEANNE (2004) OVER NORTHEAST COASTAL GEORGIA AND SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA
7B.8 AN EXAMINATION OF THE SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ENVIRONMENTS INVOLVED IN TORNADO OUTBREAKS FROM HURRICANES FRANCES (2004) AND JEANNE (2004) OVER NORTHEAST COASTAL GEORGIA AND SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA
Tropical Cyclone Formation/Structure/Motion Studies
 Tropical Cyclone Formation/Structure/Motion Studies Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 phone: (831) 656-3787 fax: (831) 656-3061 email: paharr@nps.edu
Tropical Cyclone Formation/Structure/Motion Studies Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 phone: (831) 656-3787 fax: (831) 656-3061 email: paharr@nps.edu
The Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones
 The Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones Elizabeth A. Ritchie Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Center for High Performance Computing Room 125, EECE Building Albuquerque,
The Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones Elizabeth A. Ritchie Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Center for High Performance Computing Room 125, EECE Building Albuquerque,
Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples Figure 1
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples The below images, taken from the 1200 UTC 17 January 2019 GFS forecast run, provide examples of the contributions of deformation and divergence to frontogenesis.
Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples The below images, taken from the 1200 UTC 17 January 2019 GFS forecast run, provide examples of the contributions of deformation and divergence to frontogenesis.
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Massive Storms! Hurricanes What a Hurricane Needs to Develop Warm tropical water - at least 80 F High Humidity Light wind Low Pressure Area Form between 5 and 20 latitude Hurricane Ingredients Hurricane
Massive Storms! Hurricanes What a Hurricane Needs to Develop Warm tropical water - at least 80 F High Humidity Light wind Low Pressure Area Form between 5 and 20 latitude Hurricane Ingredients Hurricane
Predecessor Rain Events: A Literature Review. By: Tony Viramontez
 Predecessor Rain Events: A Literature Review By: Tony Viramontez Introduction Predecessor Rain Event (PRE): meso- and subsynopticscale regions of high-impact heavy rainfall that occur well in advance of
Predecessor Rain Events: A Literature Review By: Tony Viramontez Introduction Predecessor Rain Event (PRE): meso- and subsynopticscale regions of high-impact heavy rainfall that occur well in advance of
Impact of air-sea interaction on extratropical transition of tropical cyclones. Sarah Jones
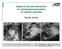 Impact of air-sea interaction on extratropical transition of tropical cyclones Sarah Jones 12.Juli 2007 15.Juli 2007 16.Juli 2007 Direct Impact of ET Ex-Hurricane Philippe: a storm or not a storm? 6 day
Impact of air-sea interaction on extratropical transition of tropical cyclones Sarah Jones 12.Juli 2007 15.Juli 2007 16.Juli 2007 Direct Impact of ET Ex-Hurricane Philippe: a storm or not a storm? 6 day
Subtropical and Hybrid Systems IWTC VII Topic 1.6
 Subtropical and Hybrid Systems IWTC VII Topic 1.6 John R. Gyakum Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences McGill University, Montreal Canada Working group: John L. Beven II, Lance F. Bosart, Fermin
Subtropical and Hybrid Systems IWTC VII Topic 1.6 John R. Gyakum Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences McGill University, Montreal Canada Working group: John L. Beven II, Lance F. Bosart, Fermin
Chapter 5. Summary and Conclusions
 Chapter 5. Summary and Conclusions Two cases of heavy rainfall were analyzed using observational data sets and model simulations. The first case was the landfall of Hurricane Floyd in North Carolina in
Chapter 5. Summary and Conclusions Two cases of heavy rainfall were analyzed using observational data sets and model simulations. The first case was the landfall of Hurricane Floyd in North Carolina in
International Journal of Integrated Sciences & Technology 2 (2016) 55-61
 International Journal of Integrated Sciences & Technology 2 (2016) 55-61 Changes in Latent Heat Energy and Moist Static Energy Contents of the Atmosphere over Bangladesh and Neighbourhood during the Formation
International Journal of Integrated Sciences & Technology 2 (2016) 55-61 Changes in Latent Heat Energy and Moist Static Energy Contents of the Atmosphere over Bangladesh and Neighbourhood during the Formation
Tropical Cyclones. Objectives
 Tropical Cyclones FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 2 8/8/2012 Objectives From this lecture you should understand: Global tracks of TCs and the seasons when they are most common General circulation
Tropical Cyclones FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 2 8/8/2012 Objectives From this lecture you should understand: Global tracks of TCs and the seasons when they are most common General circulation
SUMMARY OF THE 2011 TYPHOON SEASON
 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMISSION FOR ASIA AND THE PACIFIC AND WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION WRD/TC.44/4.1 Add. 2 06 February 2012 Typhoon Committee Forty Fourth Session 06 to 12 February 2012 Hangzhou,
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMISSION FOR ASIA AND THE PACIFIC AND WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION WRD/TC.44/4.1 Add. 2 06 February 2012 Typhoon Committee Forty Fourth Session 06 to 12 February 2012 Hangzhou,
AIR MASSES. Large bodies of air. SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate
 Large bodies of air AIR MASSES SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate Uniform in composition Light surface winds Dominated by high surface pressure The longer the air mass remains over a region,
Large bodies of air AIR MASSES SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate Uniform in composition Light surface winds Dominated by high surface pressure The longer the air mass remains over a region,
Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014
 Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014 Summary of analysis by the TCC Advisory Panel on Extreme Climatic Events In an extraordinary session held at the Japan Meteorological Agency on 3
Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014 Summary of analysis by the TCC Advisory Panel on Extreme Climatic Events In an extraordinary session held at the Japan Meteorological Agency on 3
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
Probabilistic Evaluation of Prediction and Dynamics of Super Typhoon MEGI (2010)
 Probabilistic Evaluation of Prediction and Dynamics of Super Typhoon MEGI (2010) 6 November 2012 Chuanhai Qian 1, Fuqing Zhang 2, Yihong Duan 1 1 China Meteorological Administration 2 Pennsylvania State
Probabilistic Evaluation of Prediction and Dynamics of Super Typhoon MEGI (2010) 6 November 2012 Chuanhai Qian 1, Fuqing Zhang 2, Yihong Duan 1 1 China Meteorological Administration 2 Pennsylvania State
A Tropical Cyclone with a Very Large Eye
 JANUARY 1999 PICTURES OF THE MONTH 137 A Tropical Cyclone with a Very Large Eye MARK A. LANDER University of Guam, Mangilao, Guam 9 September 1997 and 2 March 1998 1. Introduction The well-defined eye
JANUARY 1999 PICTURES OF THE MONTH 137 A Tropical Cyclone with a Very Large Eye MARK A. LANDER University of Guam, Mangilao, Guam 9 September 1997 and 2 March 1998 1. Introduction The well-defined eye
Extratropical Transition of Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclones: An Overview and Conceptual Model of the Transformation Stage
 VOLUME 15 WEATHER AND FORECASTING AUGUST 2000 Extratropical Transition of Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclones: An Overview and Conceptual Model of the Transformation Stage PETER M. KLEIN, PATRICK A.
VOLUME 15 WEATHER AND FORECASTING AUGUST 2000 Extratropical Transition of Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclones: An Overview and Conceptual Model of the Transformation Stage PETER M. KLEIN, PATRICK A.
A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA
 J12B.4 A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA John Billet* and Keith Lynch NOAA/NWS Wakefield, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Hurricane Gaston made landfall north of Charleston, SC on Sunday morning
J12B.4 A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA John Billet* and Keith Lynch NOAA/NWS Wakefield, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Hurricane Gaston made landfall north of Charleston, SC on Sunday morning
Hurricanes. Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator.
 Hurricanes Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator. They are responsible for weather that can devastate entire communities: Heavy rain --
Hurricanes Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator. They are responsible for weather that can devastate entire communities: Heavy rain --
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
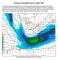 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
TOWARDS A BETTER UNDERSTANDING OF AND ABILITY TO FORECAST THE WIND FIELD EXPANSION DURING THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION PROCESS
 P1.17 TOWARDS A BETTER UNDERSTANDING OF AND ABILITY TO FORECAST THE WIND FIELD EXPANSION DURING THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION PROCESS Clark Evans* and Robert E. Hart Florida State University Department
P1.17 TOWARDS A BETTER UNDERSTANDING OF AND ABILITY TO FORECAST THE WIND FIELD EXPANSION DURING THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION PROCESS Clark Evans* and Robert E. Hart Florida State University Department
Synoptic Meteorology II: Petterssen-Sutcliffe Development Theory Application March 2015
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Petterssen-Sutcliffe Development Theory Application 10-12 March 2015 In our lecture on Petterssen-Sutcliffe Development Theory, we outlined the principle of selfdevelopment in
Synoptic Meteorology II: Petterssen-Sutcliffe Development Theory Application 10-12 March 2015 In our lecture on Petterssen-Sutcliffe Development Theory, we outlined the principle of selfdevelopment in
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts. Lecture 12 AOS 101
 Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions. Magnitudes are measured differently for different hazard types:
 Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
The purpose of this thesis is to present two multiscale analyses of inland tropical
 I. Introduction 1.1 General Purpose The purpose of this thesis is to present two multiscale analyses of inland tropical cyclone (TC) midlatitude jet interactions. More specifically, the main focus will
I. Introduction 1.1 General Purpose The purpose of this thesis is to present two multiscale analyses of inland tropical cyclone (TC) midlatitude jet interactions. More specifically, the main focus will
Precipitation Structure and Processes of Typhoon Nari (2001): A Modeling Propsective
 Precipitation Structure and Processes of Typhoon Nari (2001): A Modeling Propsective Ming-Jen Yang Institute of Hydrological Sciences, National Central University 1. Introduction Typhoon Nari (2001) struck
Precipitation Structure and Processes of Typhoon Nari (2001): A Modeling Propsective Ming-Jen Yang Institute of Hydrological Sciences, National Central University 1. Introduction Typhoon Nari (2001) struck
Department of Atmospheric Sciences, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
 10A.4 TROPICAL CYCLONE FORMATIONS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA CHENG-SHANG LEE 1 AND YUNG-LAN LIN* 1, 2 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 2 Taipei Aeronautic Meteorological
10A.4 TROPICAL CYCLONE FORMATIONS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA CHENG-SHANG LEE 1 AND YUNG-LAN LIN* 1, 2 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 2 Taipei Aeronautic Meteorological
Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013
 1 Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013 by William Gray and Phil Klotzbach Preliminary Draft - March 2014 (Final draft by early June) ABSTRACT This paper discusses the causes of the unusual dearth
1 Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013 by William Gray and Phil Klotzbach Preliminary Draft - March 2014 (Final draft by early June) ABSTRACT This paper discusses the causes of the unusual dearth
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Evolution of Tropical Cyclone Characteristics and Forecast Assessment
 Evolution of Tropical Cyclone Characteristics and Forecast Assessment Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 Telephone : (831) 656-3787 FAX: (831) 656-3061
Evolution of Tropical Cyclone Characteristics and Forecast Assessment Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 Telephone : (831) 656-3787 FAX: (831) 656-3061
Predicting Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change
 Predicting Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 Telephone: (831)656-3787 FAX:(831)656-3061 email:
Predicting Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 Telephone: (831)656-3787 FAX:(831)656-3061 email:
The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview
 The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview A fast moving short-wave (Fig. 1) with -1σ 500 hpa height
The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview A fast moving short-wave (Fig. 1) with -1σ 500 hpa height
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena
 The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers
 Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems
 Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology & Bolin Centre for Climate Research George Tselioudis Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Lecture 1 Extratropical cyclones
Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology & Bolin Centre for Climate Research George Tselioudis Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Lecture 1 Extratropical cyclones
7 December 2016 Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency
 Summary of the 2016 Asian Summer Monsoon 7 December 2016 Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency This report summarizes the characteristics of the surface climate and atmospheric/oceanographic
Summary of the 2016 Asian Summer Monsoon 7 December 2016 Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency This report summarizes the characteristics of the surface climate and atmospheric/oceanographic
Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann
 Place an X here to count it double! Name: Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann If you wish to have the final exam count double and replace your midterm score, place an X in the box above. As
Place an X here to count it double! Name: Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann If you wish to have the final exam count double and replace your midterm score, place an X in the box above. As
Examination of Tropical Cyclogenesis using the High Temporal and Spatial Resolution JRA-25 Dataset
 Examination of Tropical Cyclogenesis using the High Temporal and Spatial Resolution JRA-25 Dataset Masato Sugi Forecast Research Department, Meteorological Research Institute, Japan Correspondence: msugi@mri-jma.go.jp
Examination of Tropical Cyclogenesis using the High Temporal and Spatial Resolution JRA-25 Dataset Masato Sugi Forecast Research Department, Meteorological Research Institute, Japan Correspondence: msugi@mri-jma.go.jp
Lower-Tropospheric Height Tendencies Associated with the Shearwise and Transverse Components of Quasigeostrophic Vertical Motion
 JULY 2007 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2803 Lower-Tropospheric Height Tendencies Associated with the Shearwise and Transverse Components of Quasigeostrophic Vertical Motion JONATHAN E. MARTIN
JULY 2007 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2803 Lower-Tropospheric Height Tendencies Associated with the Shearwise and Transverse Components of Quasigeostrophic Vertical Motion JONATHAN E. MARTIN
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
1. Introduction. 2. Verification of the 2010 forecasts. Research Brief 2011/ February 2011
 Research Brief 2011/01 Verification of Forecasts of Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific and Number of Tropical Cyclones Making Landfall in South China and the Korea and Japan region
Research Brief 2011/01 Verification of Forecasts of Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific and Number of Tropical Cyclones Making Landfall in South China and the Korea and Japan region
Understanding the Microphysical Properties of Developing Cloud Clusters during TCS-08
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding the Microphysical Properties of Developing Cloud Clusters during TCS-08 PI: Elizabeth A. Ritchie Department
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding the Microphysical Properties of Developing Cloud Clusters during TCS-08 PI: Elizabeth A. Ritchie Department
Reduction of the Radius of Probability Circle. in Typhoon Track Forecast
 Reduction of the Radius of Probability Circle in Typhoon Track Forecast Nobutaka MANNOJI National Typhoon Center, Japan Meteorological Agency Abstract RSMC Tokyo - Typhoon Center of the Japan Meteorological
Reduction of the Radius of Probability Circle in Typhoon Track Forecast Nobutaka MANNOJI National Typhoon Center, Japan Meteorological Agency Abstract RSMC Tokyo - Typhoon Center of the Japan Meteorological
Evolution of Tropical Cyclone Characteristics
 Evolution of Tropical Cyclone Characteristics Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 Telephone : (831) 656-3787 FAX: (831) 656-3061 email: paharr@nps.navy.mil
Evolution of Tropical Cyclone Characteristics Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 Telephone : (831) 656-3787 FAX: (831) 656-3061 email: paharr@nps.navy.mil
Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and Michael M. Bell. Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California, USA
 Latent heating rate profiles at different tropical cyclone stages during 2008 Tropical Cyclone Structure experiment: Comparison of ELDORA and TRMM PR retrievals Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and
Latent heating rate profiles at different tropical cyclone stages during 2008 Tropical Cyclone Structure experiment: Comparison of ELDORA and TRMM PR retrievals Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events
 National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Heavy Rain 7-8 December 2011 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 Abstract:. A mid-level short-wave
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Heavy Rain 7-8 December 2011 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 Abstract:. A mid-level short-wave
Lecture 18 Hurricanes
 Lecture 18 Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology What is a hurricane? What is the structure or anatomy of a hurricane? How to build a hurricane - hurricane energy Hurricane climatology - when and
Lecture 18 Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology What is a hurricane? What is the structure or anatomy of a hurricane? How to build a hurricane - hurricane energy Hurricane climatology - when and
Storm Summary for Hurricane Joaquin
 Storm Summary for Hurricane Joaquin Wednesday, September 30, 2015 at 5 PM EDT (Output from Hurrevac, based on National Hurricane Center Forecast Advisory #12) Joaquin is currently a Category 1 hurricane
Storm Summary for Hurricane Joaquin Wednesday, September 30, 2015 at 5 PM EDT (Output from Hurrevac, based on National Hurricane Center Forecast Advisory #12) Joaquin is currently a Category 1 hurricane
Mélicie Desflots* RSMAS, University of Miami, Miami, Florida
 15B.6 RAPID INTENSITY CHANGE IN HURRICANE LILI (2002) Mélicie Desflots* RSMAS, University of Miami, Miami, Florida 1. INTRODUCTION Rapid intensity change in tropical cyclones is one of the most difficult
15B.6 RAPID INTENSITY CHANGE IN HURRICANE LILI (2002) Mélicie Desflots* RSMAS, University of Miami, Miami, Florida 1. INTRODUCTION Rapid intensity change in tropical cyclones is one of the most difficult
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997
 Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Massive Storms! 8.10C Identify the role of the oceans in the formation of weather systems such as hurricanes
 Massive Storms! 8.10C Identify the role of the oceans in the formation of weather systems such as hurricanes Instructional page: Each person in group will take on one portion or set of questions: Each
Massive Storms! 8.10C Identify the role of the oceans in the formation of weather systems such as hurricanes Instructional page: Each person in group will take on one portion or set of questions: Each
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems
 The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017
 Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
