Chapter 24. Tropical Cyclones. Tropical Cyclone Classification 4/19/17
|
|
|
- Felix Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Cyclones Most destructive storms on the planet Originate over tropical waters, but their paths often take them over land and into midlatitudes Names Hurricane (Atlantic and eastern Pacific) Typhoon (western Pacific) Cyclones (Indian Ocean) Tropical Cyclone Classification Classified according to the maximum average sustained wind speed. What is this in the U.S.? Rest of the world? 1
2 Tropical Cyclone Phases Tropical Wave* Tropical Disturbance Tropical Depression Tropical Storm Hurricane Tropical Wave Elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which moves east to west across the tropics causing areas of cloudiness and thunderstorms. May serve as the precursor to tropical cyclone development Tropical Disturbance Loosely organized thunderstorms km in diameter that maintains it s identity for at least 24 hours No noticeable closed circulation 2
3 Tropical Depression Occurs when a cluster of thunderstorms has an identifiable surface pressure drop and closed wind circulation Winds do not exceed 34kts Assigned a number to identify it (ie Tropical depression #5) Tropical Storm System is given an actual name when winds exceed 34 kts Maintains tropical storm status as long as winds are sustained between 34 and 64 kts Hurricane Winds must exceed 64kts for a storm to become a hurricane 3
4 Alphabetical Skip letters Q,U,X,Y,Z Hurricane Names Alternate male/female Use names from English, Spanish and French languages, repeats every six years What happens when the list of names is exhausted? Has it ever happened and when? Saffir-Simpson Scale Rates hurricanes on scale of 1 (weakest) to 5 (strongest) Was based on combination of wind speed, central pressure and storm surge Revised in 2010 to be based solely on max sustained wind speed How many storms have been rated a category 5 in the Atlantic since 1924 through 2010? Hurricane Records When was the last Category 5 to hit the U.S.? Has more than 1 Category 5 struck land in one season? If so, when? What hurricane holds the record for the lowest pressure in the Atlantic basin? What area of the world is most prone to Hurricane damage? 4
5 Hurricane Tracks Hurricane Stats (1/3, ½, 2/3) of all tropical cyclones occur in the northern hemisphere Never originate within 5 degrees of equator and never cross it Rarely originate north (south) of 25 degrees Average of 80 tropical storms develop globally each year, 50% -70% reach hurricane strength Western Pacific produces highest number Form over all tropical oceans except south Atlantic and southeast Pacific Hurricane Tracks Easterly surface (Trade) winds in the tropics guide hurricane movement Coriolis can also affect hurricane movement. How? Eventually northward movement pushes them into the westerlies 5
6 4/19/17 Erratic Tracks Erratic Tracks Primary Hurricane Structures Eye Eyewall Spiral Rainbands 6
7 Cross-Sectional Structure Double Eyewalls Develops typically only in strongest of hurricanes Forms from outer rainbands contracting into closed ring around the inner rainband Eyewall Replacement Cycle Inner eyewall eventually weakens and dissipates as the outer eyewall contracts and intensifies A new outer eyewall may form again Hurricane usually a peak intensity when the inner eyewall contracts before dissipating 7
8 Storm Surge Abnormal rise in sea level associated with the movement of a hurricane over a coastal region Surge varies from one side of hurricane to the other depending on whether winds blow towards or away from shore Low pressure center also causes a rise Biggest right is typically just to the right of the eyewall as it makes landfall Tropical Cyclone Formation Surface convergence is required as a trigger for thunderstorms Develop in three ways ITCZ Tropical Waves Occluded systems from mid-latitudes ITCZ Intersection of the north and south Hadley cells If it intrudes far enough north/south, coriolis can begin to spin the thunderstorms 8
9 4/19/17 Tropical Waves Embedded in easterly flow at low levels High pressure ridges bulge southward, low pressure troughs bulge northward Flow around the trough is counterclockwise and is less than the geostrophic value Air then decelerates from the ridge crest to trough base and undergoes convergence Air must then rise Tropical Waves Tropical Waves 9
10 Mid-Latitude Origins Occluded systems at mid-latitudes may intrude far enough south that they move into the tropics Strong vertical shear is offset by latent heat release, which can reduce wind shear Most common in the fall, why? Tropical Cyclone Development Environments Sea surface temperature must exceed (60, 70, 80) Fahrenheit Surface layer of warm water must be a minimum of (100, 200, 300) feet deep Weak vertical shear (speed and direction) Mid-troposphere must be sufficiently moist Location must be > 5 degrees north of equator Sea Surface Temperatures Heat needed to maintain deep convection North Atlantic only maintains warm temps from July Nov Western Pacific temperature is typically always above 80 10
11 Depth of Warm Water Hurricanes stir the ocean, requiring a deep layer of warm water to maintain ocean temperatures to counter any cold upwelling Weak Wind Shear Strong wind shear carries clouds downstream, dispersing the latent heat that was released in their formation Vortex cannot form in upper-level flow in the presence of strong winds Moist Mid-Levels Dry air aloft forms evaporative-cooled downdrafts that can suppress the rate of thunderstorm growth 11
12 Range from Equator Further away = more coriolis for spin Thunderstorm Organization Not fully understood how thunderstorms can organize into a vortex and rapidly develop an eyewall Strong easterly waves can provide this rotation Rotation can be understood by examining the conservation of angular momentum Wave Pouch Initially, individual thunderstorms develop within the wave Oftentimes the cold air produced by the precipitation can inhibit additional thunderstorms Large-scale rotation is necessary to help overcome this Wave pouches develop where motions at certain points in the pouch that matches wave propagation 12
13 Wave Pouch Serves two important roles: Thunderstorms within the pouch continually moisten the mid-levels, which reduces evaporation. What effect does this have on the downdrafts? Promotes the formation and intensification of the early vortex Wave Pouch Wave Pouch 13
14 Storm Surge Enhancements Tidal Cycle Waves Shoreline shape Other Effects Heavy rains (sometimes up to inches of rain in a matter of days) Inland Flooding High Winds Tornadoes Forecasting Data primarily collected from aircraft observations Dropsondes Numerical models Erratic behavior typically not forecast because of poor model initialization data 14
15 Hurricane Watches Issued for tropical storms and hurricanes that pose a threat within 48 hours Hurricane Warnings Issued for areas when tropical storm or hurricane conditions will be present in 36 hours Other Warnings Coastal Flood Watches/Warnings Heavy Surf Advisories 15
16 Impact of Climate Change on Hurricanes 16
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones
 Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
Hurricanes. April 14, 2009
 Tropical Weather & Hurricanes Chapter 15 April 14, 2009 Tropical meteorology Tropics characterized by seasonal wet and drier periods- wet when sun is nearly overhead at noon and inter-tropical convergence
Tropical Weather & Hurricanes Chapter 15 April 14, 2009 Tropical meteorology Tropics characterized by seasonal wet and drier periods- wet when sun is nearly overhead at noon and inter-tropical convergence
(April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2
 Lecture #17 (April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2 Hurricane Katrina August 2005 All tropical cyclone tracks (1945-2006). Hurricane Formation While moving westward, tropical disturbances
Lecture #17 (April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2 Hurricane Katrina August 2005 All tropical cyclone tracks (1945-2006). Hurricane Formation While moving westward, tropical disturbances
Hurricanes. Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator.
 Hurricanes Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator. They are responsible for weather that can devastate entire communities: Heavy rain --
Hurricanes Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator. They are responsible for weather that can devastate entire communities: Heavy rain --
ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 19 Tropical Cyclones Dr. DeCaria
 ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 19 Tropical Cyclones Dr. DeCaria READING: Chapter 16 GENERAL A tropical cyclone is a large, low-pressure system that forms over the tropical oceans. Tropical cyclones are classified
ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 19 Tropical Cyclones Dr. DeCaria READING: Chapter 16 GENERAL A tropical cyclone is a large, low-pressure system that forms over the tropical oceans. Tropical cyclones are classified
Hurricane Recipe. Hurricanes
 Hurricanes A hurricane is a powerful, rotating storm that forms over warm oceans near the Equator. Hurricanes have strong, rotating winds (at least 74 miles per hour), a huge amount of rain, low air pressure,
Hurricanes A hurricane is a powerful, rotating storm that forms over warm oceans near the Equator. Hurricanes have strong, rotating winds (at least 74 miles per hour), a huge amount of rain, low air pressure,
Tropical Cyclones. Objectives
 Tropical Cyclones FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 2 8/8/2012 Objectives From this lecture you should understand: Global tracks of TCs and the seasons when they are most common General circulation
Tropical Cyclones FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 2 8/8/2012 Objectives From this lecture you should understand: Global tracks of TCs and the seasons when they are most common General circulation
CHAPTER 12 TROPICAL WEATHER SYSTEMS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 12 TROPICAL WEATHER SYSTEMS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A hurricane differs from an extra-tropical cyclone in that a hurricane a. has no fronts. b. develops within a uniform warm and humid air
CHAPTER 12 TROPICAL WEATHER SYSTEMS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A hurricane differs from an extra-tropical cyclone in that a hurricane a. has no fronts. b. develops within a uniform warm and humid air
Ch. 11: Hurricanes. Be able to. Define what hurricane is. Identify the life and death of a hurricane. Identify the ways we track hurricanes.
 Ch. 11: Hurricanes Be able to Define what hurricane is. Identify the life and death of a hurricane. Identify the ways we track hurricanes. What are Hurricanes? Smaller than mid-latitude cyclones. Don t
Ch. 11: Hurricanes Be able to Define what hurricane is. Identify the life and death of a hurricane. Identify the ways we track hurricanes. What are Hurricanes? Smaller than mid-latitude cyclones. Don t
- tornadoes. Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book. Outline. - cyclones and anti-cyclones. -tropical storms. -Storm surge
 (1 of 16) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - cyclones and anti-cyclones - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 16) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their
(1 of 16) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - cyclones and anti-cyclones - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 16) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their
Tuesday, September 13, 16
 Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers
 Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Atmospheric Circulation
 Atmospheric Circulation Introductory Oceanography Instructor: Ray Rector Atmospheric Circulation Key Topics Composition and Structure Solar Heating and Convection The Coriolis Effect Global Wind Patterns
Atmospheric Circulation Introductory Oceanography Instructor: Ray Rector Atmospheric Circulation Key Topics Composition and Structure Solar Heating and Convection The Coriolis Effect Global Wind Patterns
- tornadoes. Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book. Outline. -tropical storms. -Storm surge
 (1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 12) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their relationship to air masses Also
(1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 12) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their relationship to air masses Also
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 6 Content: Severe Weather Notes
 Severe weather can pose a risk to you and your property. Meteorologists monitor extreme weather to inform the public about dangerous atmospheric conditions. Thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes are
Severe weather can pose a risk to you and your property. Meteorologists monitor extreme weather to inform the public about dangerous atmospheric conditions. Thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes are
Air Masses, Weather Systems and Hurricanes
 The Earth System - Atmosphere IV Air Masses, Weather Systems and Hurricanes Air mass a body of air which takes on physical characteristics which distinguish it from other air. Classified on the basis of
The Earth System - Atmosphere IV Air Masses, Weather Systems and Hurricanes Air mass a body of air which takes on physical characteristics which distinguish it from other air. Classified on the basis of
11/19/14. Chapter 11: Hurricanes. The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th. Lutgens Tarbuck
 Chapter 11: Hurricanes The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! Hurricanes: " Hurricanes are intense centers of
Chapter 11: Hurricanes The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! Hurricanes: " Hurricanes are intense centers of
5 Atmospheric Disturbances 7 1.Cyclones- tropical and temperate and associated weather conditions. 2.Anticyclones and associated weather conditions.
 5 Atmospheric Disturbances 7 1.Cyclones- tropical and temperate and associated weather conditions. 2.Anticyclones and associated weather conditions. atmospheric disturbances (weather systems) that are
5 Atmospheric Disturbances 7 1.Cyclones- tropical and temperate and associated weather conditions. 2.Anticyclones and associated weather conditions. atmospheric disturbances (weather systems) that are
Hurricanes and Tropical Weather Systems:
 Hurricanes and Tropical Weather Systems: An influence on weather in parts of the USA Meteorology 411 Iowa State University Week 2 Bill Gallus Classification/Terminology Tropical Disturbance enhanced convection
Hurricanes and Tropical Weather Systems: An influence on weather in parts of the USA Meteorology 411 Iowa State University Week 2 Bill Gallus Classification/Terminology Tropical Disturbance enhanced convection
Section 13-1: Thunderstorms
 Section 13-1: Thunderstorms Chapter 13 Main Idea: The intensity and duration of thunderstorms depend on the local conditions that create them. Air-mass thunderstorm Mountain thunderstorm Sea-breeze thunderstorm
Section 13-1: Thunderstorms Chapter 13 Main Idea: The intensity and duration of thunderstorms depend on the local conditions that create them. Air-mass thunderstorm Mountain thunderstorm Sea-breeze thunderstorm
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Hurricanes. Environmental Geology Mr. Paul Lowrey. Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman
 Environmental Geology Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman Hurricanes EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Environmental Geology Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman Hurricanes EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Chapter 18/19. Ch 18
 Chapter 18/19 Ch 18 Pressure Force of the weight of the air above At sea level: 14.7 lbs/in2 Decreases with altitude Inches of mercury (29.92 @ sea level) Barometer - instrument used to measure air pressure
Chapter 18/19 Ch 18 Pressure Force of the weight of the air above At sea level: 14.7 lbs/in2 Decreases with altitude Inches of mercury (29.92 @ sea level) Barometer - instrument used to measure air pressure
HURRICANES. Source:
 HURRICANES Source: http://www.dc.peachnet.edu/~pgore/students/w97/matheson/hpage.htm What is a hurricane? Violent cyclonic storm that develops in the tropical region Wind speeds are > 74 mph Source: http://www.google.com/imgres?hl=en&sa=x&biw=1920&bih=955&tbm=
HURRICANES Source: http://www.dc.peachnet.edu/~pgore/students/w97/matheson/hpage.htm What is a hurricane? Violent cyclonic storm that develops in the tropical region Wind speeds are > 74 mph Source: http://www.google.com/imgres?hl=en&sa=x&biw=1920&bih=955&tbm=
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Climate & Earth System Science. Atmosphere Ocean Interactions. A: Structure of the Ocean.
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Thunderstorms. Stages in the development of a thunderstorm
 Severe Weather Outcomes: S2-4-04 Explain the formation and dynamics of selected severe weather phenomena... S2-4-05 Collect, interpret, and analyze meteorological data related to a severe weather event.
Severe Weather Outcomes: S2-4-04 Explain the formation and dynamics of selected severe weather phenomena... S2-4-05 Collect, interpret, and analyze meteorological data related to a severe weather event.
Tropical Cyclone Genesis: What we know, and what we don t!
 Tropical Cyclone Genesis: What we know, and what we don t! Allison Wing! NSF Postdoctoral Research Fellow! Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory! Columbia University! Overview! Climatology! What We Know! Theories!
Tropical Cyclone Genesis: What we know, and what we don t! Allison Wing! NSF Postdoctoral Research Fellow! Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory! Columbia University! Overview! Climatology! What We Know! Theories!
Huracan: evil Taino & Mayan god of winds & destruction
 Huracan: evil Taino & Mayan god of winds & destruction Profile of a Tropical Cyclone! Hurricane = typhoon = cyclone! All different words for the same thing Eye: clear area in the center Eyewall: clouds
Huracan: evil Taino & Mayan god of winds & destruction Profile of a Tropical Cyclone! Hurricane = typhoon = cyclone! All different words for the same thing Eye: clear area in the center Eyewall: clouds
2) What general circulation wind belt is the place of origin for hurricanes? A) westerlies B) trade winds C) doldrums D) horse latitudes
 Meteo 1010 Homework 6 1) What is the difference between a typhoon and a hurricane? A) A hurricane is a true tropical cyclone, but a typhoon is not. B) A hurricane is stronger than a typhoon. C) They represent
Meteo 1010 Homework 6 1) What is the difference between a typhoon and a hurricane? A) A hurricane is a true tropical cyclone, but a typhoon is not. B) A hurricane is stronger than a typhoon. C) They represent
Name Earth Science Pd. Hurricanes. Directions: Read the information, view diagrams and answer the questions in the worksheet.
 Hurricanes Directions: Read the information, view diagrams and answer the questions in the worksheet. Hurricane Basics The ingredients for a hurricane include a pre-existing weather disturbance, warm tropical
Hurricanes Directions: Read the information, view diagrams and answer the questions in the worksheet. Hurricane Basics The ingredients for a hurricane include a pre-existing weather disturbance, warm tropical
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes!
 Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
LECTURE #17: Severe Weather: Introduction to Hurricanes
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #17: Severe Weather: Introduction to Hurricanes Date: 15 March 2018 I. Hurricane Overview hurricanes o what they are? o how they form? storm stages:
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #17: Severe Weather: Introduction to Hurricanes Date: 15 March 2018 I. Hurricane Overview hurricanes o what they are? o how they form? storm stages:
Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT
 Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT Standard 1: Air Masses Air Mass An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given altitude When an air mass
Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT Standard 1: Air Masses Air Mass An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given altitude When an air mass
Tropical Cyclones: When Nature Attacks!! AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Tropical Cyclone: African Easterly Jet
 Tropical Cyclones: When Nature Attacks!! AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Really powerful low pressure systems Lecture 25 Nov 27 2018 1 Tropical
Tropical Cyclones: When Nature Attacks!! AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Really powerful low pressure systems Lecture 25 Nov 27 2018 1 Tropical
Lecture 18 Hurricanes
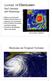 Lecture 18 Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology What is a hurricane? What is the structure or anatomy of a hurricane? How to build a hurricane - hurricane energy Hurricane climatology - when and
Lecture 18 Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology What is a hurricane? What is the structure or anatomy of a hurricane? How to build a hurricane - hurricane energy Hurricane climatology - when and
Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time. It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the
 Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY EARTH 365. Fall 2018 Test #2. November :00pm 7:15pm
 1 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY EARTH 365 Fall 2018 Test #2 November 6 2018 6:00pm 7:15pm 200 points (4 points each answer) Answer on the answer sheet provided.
1 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY EARTH 365 Fall 2018 Test #2 November 6 2018 6:00pm 7:15pm 200 points (4 points each answer) Answer on the answer sheet provided.
Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology by Professor Steven Businger. Hurricane Katrina
 Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology by Professor Steven Businger Hurricane Katrina Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology by Professor Steven Businger What is a hurricane? What is the structure
Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology by Professor Steven Businger Hurricane Katrina Hurricanes Part I Structure and Climatology by Professor Steven Businger What is a hurricane? What is the structure
Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011
 Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011 Instructions: Write your name (last name and first name) on your bubble sheet. Write your student identification number on the bubble sheet, and carefully and completely
Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011 Instructions: Write your name (last name and first name) on your bubble sheet. Write your student identification number on the bubble sheet, and carefully and completely
4/29/2011. Mid-latitude cyclones form along a
 Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
b. The boundary between two different air masses is called a.
 NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
Hurricane Glossary. Southeast Coastal Ocean Observing Regional Association. Definitions selected & adapted from weather.com
 Hurricane Glossary Southeast Coastal Ocean Observing Regional Association Definitions selected & adapted from weather.com Atmospheric Pressure: The pressure exerted by the atmosphere at a given point.
Hurricane Glossary Southeast Coastal Ocean Observing Regional Association Definitions selected & adapted from weather.com Atmospheric Pressure: The pressure exerted by the atmosphere at a given point.
Chapter 21. Weather Patterns and Severe Storms
 Chapter 21 Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1 Air Masses Air Masses and Weather Air Masses An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture
Chapter 21 Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1 Air Masses Air Masses and Weather Air Masses An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture
Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Air Masses Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. high pressure poles low pressure equator wind
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Air Masses Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. high pressure poles low pressure equator wind
General Atmospheric Circulation
 General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
Homework 8: Hurricane Damage (adapted from Pipkin et al.)
 1 Homework 8: Hurricane Damage (adapted from Pipkin et al.) Tropical cyclones have a significant impact on coastal areas of the world. In the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Oceans they are called hurricanes
1 Homework 8: Hurricane Damage (adapted from Pipkin et al.) Tropical cyclones have a significant impact on coastal areas of the world. In the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Oceans they are called hurricanes
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Hurricane: an organized tropical storm system featuring vigorous convection and sustained winds in excess of 64 knots (74 mph)
 Hurricane: an organized tropical storm system featuring vigorous convection and sustained winds in excess of 64 knots (74 mph) The storms have different names, depending on where they form: Western Hemisphere:
Hurricane: an organized tropical storm system featuring vigorous convection and sustained winds in excess of 64 knots (74 mph) The storms have different names, depending on where they form: Western Hemisphere:
1. The and the act as one interdependent system. 2. Why do we have to study both to understand the relationship?
 Ch. 6 Questions Air Sea Interaction (pg. 162) 1. The and the act as one interdependent system. 2. Why do we have to study both to understand the relationship? 3. energy heats up the of the Earth and creates,
Ch. 6 Questions Air Sea Interaction (pg. 162) 1. The and the act as one interdependent system. 2. Why do we have to study both to understand the relationship? 3. energy heats up the of the Earth and creates,
1. Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs) > 27 and extending to some depth.
 Formation Factors for Hurricanes 1. Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs) > 27 and extending to some depth. 2. Location >5 away from the equator (usually 10 ). Coriolis force is necessary for rotation. 3. High
Formation Factors for Hurricanes 1. Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs) > 27 and extending to some depth. 2. Location >5 away from the equator (usually 10 ). Coriolis force is necessary for rotation. 3. High
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Earth Science, 11e. Weather Patterns and Severe Storms Chapter 19. Air masses. A cold Canadian air mass Figure Air masses. Air masses 9/5/2012
 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Weather & Ocean Currents
 Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Massive Storms! Hurricanes What a Hurricane Needs to Develop Warm tropical water - at least 80 F High Humidity Light wind Low Pressure Area Form between 5 and 20 latitude Hurricane Ingredients Hurricane
Massive Storms! Hurricanes What a Hurricane Needs to Develop Warm tropical water - at least 80 F High Humidity Light wind Low Pressure Area Form between 5 and 20 latitude Hurricane Ingredients Hurricane
Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 1. August 1992
 Lecture #16 (April 5, 2010, Monday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 1 August 1992 Tracks of rain accumulation & clouds from Hurricane Rita September 2005 Tropical Cyclones Around the Globe Why none here?
Lecture #16 (April 5, 2010, Monday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 1 August 1992 Tracks of rain accumulation & clouds from Hurricane Rita September 2005 Tropical Cyclones Around the Globe Why none here?
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Water in the Atmosphere The Role of Water in Earth s Surface Processes. Hurricane Warning
 Hurricane Warning 1 Earth, the lue Planet. What makes Earth blue? It has to do with all of the water on Earth. There is water in more places than the vast oceans. Water is also in the atmosphere. High
Hurricane Warning 1 Earth, the lue Planet. What makes Earth blue? It has to do with all of the water on Earth. There is water in more places than the vast oceans. Water is also in the atmosphere. High
ATMO 436a. The General Circulation. Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it
 ATMO 436a The General Circulation Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it Scales of Atmospheric Motion vs. Lifespan The general circulation Atmospheric oscillations
ATMO 436a The General Circulation Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it Scales of Atmospheric Motion vs. Lifespan The general circulation Atmospheric oscillations
Tropical-Extratropical Transition
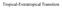 Tropical-Extratropical Transition Extratropical Transition A significant number of tropical cyclones move into the midlatitudes and transform into extratropical cyclones. This process is generally referred
Tropical-Extratropical Transition Extratropical Transition A significant number of tropical cyclones move into the midlatitudes and transform into extratropical cyclones. This process is generally referred
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification References: A Global View of Tropical Cyclones, Elsberry (ed.) Global Perspectives on Tropical Cylones:
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification References: A Global View of Tropical Cyclones, Elsberry (ed.) Global Perspectives on Tropical Cylones:
Weather Patterns and Severe Storms
 Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1 Air Masses Air Masses and Weather Air Masses An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given
Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1 Air Masses Air Masses and Weather Air Masses An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given
Cause, Assessment & Management of Flood Hazards associated with Landfalling Tropical Cyclones & Heavy Rain
 Cause, Assessment & Management of Flood Hazards associated with Landfalling Tropical Cyclones & Heavy Rain by CHEN Charng Ning, Professor Emeritus Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore Consultant,
Cause, Assessment & Management of Flood Hazards associated with Landfalling Tropical Cyclones & Heavy Rain by CHEN Charng Ning, Professor Emeritus Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore Consultant,
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Chapter 16, Part Hurricane Paths. 2. Hurricane Paths. Hurricane Paths and Damage
 Chapter 16, Part 2 Hurricane Paths and Damage 1. Hurricane Paths Start over tropical water except South Atlantic and eastern South Atlantic, where water is too cold. Initially steered by easterly winds
Chapter 16, Part 2 Hurricane Paths and Damage 1. Hurricane Paths Start over tropical water except South Atlantic and eastern South Atlantic, where water is too cold. Initially steered by easterly winds
Name: Date: Hour: Comparing the Effects of El Nino & La Nina on the Midwest (E4.2c)
 Purpose: Comparing the Effects of El Nino & La Nina on the Midwest (E4.2c) To compare the effects of El Nino and La Nina on the Midwest United States. Background Knowledge: The El Nino-Southern Oscillation
Purpose: Comparing the Effects of El Nino & La Nina on the Midwest (E4.2c) To compare the effects of El Nino and La Nina on the Midwest United States. Background Knowledge: The El Nino-Southern Oscillation
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes) Fall 2014
 Page 1 of 17 TIDE-1220 Tulane University New Orleans & Hurricanes Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes) Fall 2014 This document last updated on 19-Aug-2014 Before discussing the science
Page 1 of 17 TIDE-1220 Tulane University New Orleans & Hurricanes Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes) Fall 2014 This document last updated on 19-Aug-2014 Before discussing the science
Untitled.notebook May 12, Thunderstorms. Moisture is needed to form clouds and precipitation the lifting of air, or uplift, must be very strong
 Thunderstorms Moisture is needed to form clouds and precipitation the lifting of air, or uplift, must be very strong cold air and warm air must mix; creating an active circulation system that has both
Thunderstorms Moisture is needed to form clouds and precipitation the lifting of air, or uplift, must be very strong cold air and warm air must mix; creating an active circulation system that has both
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Final Exam Clicker Questions ATOC 1050 Spring 2011 Chapter 16: Mountain Snowstorms
 Final Exam Clicker Questions ATOC 1050 Spring 2011 Chapter 16: Mountain Snowstorms True or false: Mean annual snowfall in the western United States always increases from south to north. Total precipitation
Final Exam Clicker Questions ATOC 1050 Spring 2011 Chapter 16: Mountain Snowstorms True or false: Mean annual snowfall in the western United States always increases from south to north. Total precipitation
Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans. Chapter 13 The Nature of Storms
 Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans Chapter 13 The Nature of Storms NC ESES Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.5 - Understand the structure of and processes
Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans Chapter 13 The Nature of Storms NC ESES Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.5 - Understand the structure of and processes
ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005
 ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005 true/false /25 multiple choice /25 short answer /23 essay /10 total /83 or % True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. (25 questions 1% each) 1.
ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005 true/false /25 multiple choice /25 short answer /23 essay /10 total /83 or % True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. (25 questions 1% each) 1.
(What do you want to know)
 K (What do you know) W (What do you want to know) L (What have you learned) Flow of Energy Activity Sheet Purpose: Students will learn that there is more energy in warm/hot water than in cold water. This
K (What do you know) W (What do you want to know) L (What have you learned) Flow of Energy Activity Sheet Purpose: Students will learn that there is more energy in warm/hot water than in cold water. This
Hurricanes are intense vortical (rotational) storms that develop over the tropical oceans in regions of very warm surface water.
 Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Global Wind Patterns
 Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
1. What type of wind is needed for a hurricane to form? Low to medium winds, blowing in the same direction (weak wind shear).
 Explain 1. What type of wind is needed for a hurricane to form? Low to medium winds, blowing in the same direction (weak wind shear). 2. What is wind shear? Any change in wind speed or direction. When
Explain 1. What type of wind is needed for a hurricane to form? Low to medium winds, blowing in the same direction (weak wind shear). 2. What is wind shear? Any change in wind speed or direction. When
3 Severe Weather. Critical Thinking
 CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
ESCI 1010 Lab 7 Hurricanes (AKA: Typhoons, Cyclones)
 ESCI 1010 Lab 7 Hurricanes (AKA: Typhoons, Cyclones) Before Lab: Review pages 328-361 in your Weather and Climate textbook. Please pay special attention to the sections entitled: Hurricanes around the
ESCI 1010 Lab 7 Hurricanes (AKA: Typhoons, Cyclones) Before Lab: Review pages 328-361 in your Weather and Climate textbook. Please pay special attention to the sections entitled: Hurricanes around the
CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction Chapter Overview The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction Chapter Overview The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Massive Storms! 8.10C Identify the role of the oceans in the formation of weather systems such as hurricanes
 Massive Storms! 8.10C Identify the role of the oceans in the formation of weather systems such as hurricanes Instructional page: Each person in group will take on one portion or set of questions: Each
Massive Storms! 8.10C Identify the role of the oceans in the formation of weather systems such as hurricanes Instructional page: Each person in group will take on one portion or set of questions: Each
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions. Magnitudes are measured differently for different hazard types:
 Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Figure 1. Idealized global atmospheric circulation (C = surface convergence, D = surface divergence).
 page - Laboratory Exercise #8 - Introduction to Atmospheric Science: Global Circulation and Weather Makers Section A - Global Atmospheric Circulation: To understand weather you need to understand how the
page - Laboratory Exercise #8 - Introduction to Atmospheric Science: Global Circulation and Weather Makers Section A - Global Atmospheric Circulation: To understand weather you need to understand how the
Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans. Chapter 13 The Nature of Storms
 Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans Chapter 13 The Nature of Storms NC ESES Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.5 - Understand the structure of and processes
Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans Chapter 13 The Nature of Storms NC ESES Unit 6: The Atmosphere and the Oceans NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.5 - Understand the structure of and processes
Space Atmospheric Gases. the two most common gases; found throughout all the layers a form of oxygen found in the stratosphere
 Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars
 Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
FORMATION OF AIR MASSES
 Chapter 24: Weather (air mass, fronts, Weather instruments, and forecasting the weather) Name: Period: Due Date: Air Mass Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term
Chapter 24: Weather (air mass, fronts, Weather instruments, and forecasting the weather) Name: Period: Due Date: Air Mass Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term
Middle-Latitude Cyclone
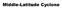 Middle-Latitude Cyclone What is a mid-latitude cyclone? - The mid-latitude cyclone is a synoptic scale low pressure system that has cyclonic (counter-clockwise in northern hemisphere) flow that is found
Middle-Latitude Cyclone What is a mid-latitude cyclone? - The mid-latitude cyclone is a synoptic scale low pressure system that has cyclonic (counter-clockwise in northern hemisphere) flow that is found
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns. Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
Global Weather Trade Winds etc.notebook February 17, 2017
 Global Weather 1 north pole northern hemisphere equator southern hemisphere south pole 2 We have seasons because of the Earth's tilt The seasons are opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres winter
Global Weather 1 north pole northern hemisphere equator southern hemisphere south pole 2 We have seasons because of the Earth's tilt The seasons are opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres winter
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts. Lecture 12 AOS 101
 Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Storms. Tropical Cyclone?
 Storms Tropical Cyclone? Tropical Cyclone: low pressure storm forming in the tropics (Start as Thunder Storms). They form around a center, producing heavy winds and rains. Storms What strengthens a Tropical
Storms Tropical Cyclone? Tropical Cyclone: low pressure storm forming in the tropics (Start as Thunder Storms). They form around a center, producing heavy winds and rains. Storms What strengthens a Tropical
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
Canes on Canes: Keeping South Florida Prepared During the Calm Before the Storm. Matt Onderlinde and Pete Finocchio
 Canes on Canes: Keeping South Florida Prepared During the Calm Before the Storm Matt Onderlinde and Pete Finocchio Outline The Science of Hurricanes Why and When South Floridians Must Be Weather-Ready
Canes on Canes: Keeping South Florida Prepared During the Calm Before the Storm Matt Onderlinde and Pete Finocchio Outline The Science of Hurricanes Why and When South Floridians Must Be Weather-Ready
Weather Elements (air masses, fronts & storms)
 Weather Elements (air masses, fronts & storms) S6E4. Obtain, evaluate and communicate information about how the sun, land, and water affect climate and weather. A. Analyze and interpret data to compare
Weather Elements (air masses, fronts & storms) S6E4. Obtain, evaluate and communicate information about how the sun, land, and water affect climate and weather. A. Analyze and interpret data to compare
I. Air Masses A. Defined: large body of air, 1600 km or more across, with similar temperature and moisture at similar altitudes 1.
 I. Air Masses A. Defined: large body of air, 1600 km or more across, with similar temperature and moisture at similar altitudes 1. Brings these characteristics with it as it moves to different areas 2.
I. Air Masses A. Defined: large body of air, 1600 km or more across, with similar temperature and moisture at similar altitudes 1. Brings these characteristics with it as it moves to different areas 2.
