Report on Spring 2017 Sabbatical: Upper-Division and Graduate Coursework in Atmospheric Science
|
|
|
- Nathan Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Report on Spring 2017 Sabbatical: Upper-Division and Graduate Coursework in Atmospheric Science Division of Natural Sciences El Camino College August
2 Overview During Spring 2017, I was granted sabbatical from my usual duties as a full-time physics instructor at ECC. I used this opportunity to take upper-division and graduate courses in UCLA s Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department during UCLA s Winter and Spring Quarters, enrolling through the Concurrent Enrollment office of UCLA Extension. Between the two quarters, I took four graduate courses, for a total of eighteen quarter units, and two upper-division courses, for a total of six quarter units. A table listing the courses taken is given below. Course Number C Quarter Taken Units (Grad/ Undergrad) Course Title Winter 4 (G) Introduction to Ocean Science Winter 4 (G) Atmospheric Boundary Layer Winter 6 (G) Advanced Dynamic and Synoptic Meteorology Spring 4 (U) Numerical Methods in Atmospheric Sciences Spring 2 (U) Operational Meteorology Spring 4 (G) Atmospheric and Oceanic Turbulence My decision to take courses with UCLA s department was an outgrowth of my longstanding fascination with atmospheric processes in general and weather in particular. Nearly all subject areas in the atmospheric sciences are deeply rooted in ideas from physics. The areas of physics most foundational to the atmospheric sciences are 2
3 fluid mechanics, and thermodynamics, including in particular phase transitions, thermal transfer, and related topics. All of these topics are covered in some depth in Physics 1B. Thus, in the remainder of this report, I will describe the courses I took, as well as possible applications of what I leared to teaching Physics 1B. 202 Ocean Science (Winter 2017) This course was a graduate-level overview of oceanography. The emphasis was on physical oceanography, although chemical and biological topics, such as alkalinization due to dissolved inorganic carbon, and plankton blooms, were included. As my primary interest is in atmospheric science, I found especially interesting and useful the discussions of atmosphere-ocean interactions, such as the subtropical gyre circulations, in which anticyclonic (i.e. clockwise) ocean circulation is driven by shifts in prevailing wind direction with latitude. Another, closely related, example is the El Nino/ Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which is a consequence of variation in the tropical easterlies in the South Pacific. Most of the examples of ocean science I have mentioned here have some connection to oceanic thermal stratification (i.e. warmer, less dense water is found at the top of the ocean) which may be a good illustration of topics such as density and buoyancy in Physics 1B. 222 Boundary Layer Meteorology (Winter 2017) This course was a study of the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL). Typically the ABL is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, typically about 500 ~ 1500 m, lying between earth s surface and a capping inversion, where the air temperature increases sharply with height. 3
4 Heating of the earth s surface results in convectively-driven turbulence, which transports various physical properties such as heat, momentum, and materials (water vapor, dust, etc.) upward from the ground. Much of my workload in this course went into the production of a term paper on marine stratocumulus clouds, a well-known example of which are the June Gloom clouds regularly observed in coastal Los Angeles during late spring and early summer. This course improved my understanding of turbulence and convective heat transport, which are a somewhat minor, but still regularly covered topic in Physics 1B. Also, the physics responsible for the positive correlation between cold ocean temperatures and marine stratocumulus clouds will be readily accessible to Physics 1B students and could even motivate a homework problem. 227 Advanced Dynamic and Synoptic Meteorology (Winter 2017) Synoptic meteorology studies large-scale atmospheric processes, typically defined as those occuring at length scales of ~1000 km or greater. The most important synoptic processes typically occur in the upper troposphere, where large scale divergence (blobs of air moving away from each other) may drive large scale convergence (blobs of air moving towards each other) and therefore ascent (upward motion) near the surface. Conversely, large-scale convergence in the upper troposphere may drive large-scale divergence, and therefore subsidence (downward motion), near the surface. Among the topics studied in this course was the interpretation of soundings, which are vertical profiles of thermodynamic properties, typically dew point and temperature, most often measured by radiosondes (i.e. weather balloons ). The principles needed to analyze 4
5 soundings are likely accessible to Physics 1B students, and this topic might make for interesting extra credit projects. 180 Numerical Methods in Atmospheric Sciences (Spring 2017) This course was an introduction to techniques used in numerical simulation of atmospheric processes. Initially I had not intended to take this course, as I already have a broad familiarity with numerical methods. However, I did learn quite a bit about numerical methods for fluid mechanics generally and atmospheric sciences in particular that I did not already know. My final project was a simulation of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability, in which a denser fluid initially sits atop a lighter fluid. This was great fun to code and to execute. In regards to my work at ECC, we currently have essentially no component of scientific coding in our courses, although it might make sense to incorporate that topic, at least mildly, into our Physics 1 Series. Also, I have been wanting to produce animations of thermal transfer processes to show in class for some time. The material learned in this course would be relevant to that. 186 Operational Meteorology (Spring 2017) This course consisted of thrice-weekly meetings with an expert forecaster to discuss current weather charts, with the goal of explaining current weather and forecasting future weather. The data most frequently used included soundings (discussed earlier), constant pressure charts, and radar and satellite imagery. As much as I like the idea of including an element of weather forecasting in Physics 1B, it would really be too far afield from the 5
6 main subject matter. In the future it might make sense to incorporate some aspects of weather forecasting as extra credit. This would be a long-term project, however. 201C Atmospheric and Oceanic Turbulence (Spring 2017) This course was a high-level survey of a variety of topics related to turbulence. Most, but not all of the topics were applications to the atmospheric and oceanic contexts, such as boundary layer turbulence or geostrophic turbulence. As there were neither exams nor collected homework, the great bulk of my workload for the course was the preparation of a literature review on turbulent entrainment in cumulus clouds, with a particular focus on the interaction between the turbulent forward cascade (the process by which the entrained parcel is spun into ever-smaller fragments by the turbulence) and the distribution of cloud droplet sizes. The product of this work was a twenty-page single-spaced paper (including references and figures) and a fifteen-minute presentation. Although turbulence is not a major topic in Physics 1B, it does come up in relation to the drag force acting on objects moving through a fluid, and I have a better understanding of the topic now than I did prior to taking 201C. 6
ESCI 110: 2 s.h. Introduction to Earth Sciences Programs ESCI 322: 3 s.h. Environmental Hydrology ESCI 241: 4 s.h. Meteorology (G2, L)
 ESCI 110: 2 s.h. Introduction to Earth Sciences Programs General introduction to each of the earth sciences disciplines and to college life. 2 hrs. lec. Offered in fall. Restricted to earth sciences majors.
ESCI 110: 2 s.h. Introduction to Earth Sciences Programs General introduction to each of the earth sciences disciplines and to college life. 2 hrs. lec. Offered in fall. Restricted to earth sciences majors.
Climate vs. Weather. Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Climate: The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
 Weather and Climate Climate vs. Weather Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Temperature, humidity, cloud cover, precipitation, winds, visibility, air pressure, air pollution, etc Climate: The
Weather and Climate Climate vs. Weather Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Temperature, humidity, cloud cover, precipitation, winds, visibility, air pressure, air pollution, etc Climate: The
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Meteorology Division B Team Name: Team Number: Student Names: and
 Meteorology Division B Team Name: Team Number: Student Names: and You have 50 minutes to complete and revise this test. 1. Do not turn this page until you are told to do so. 2. Write your team name and
Meteorology Division B Team Name: Team Number: Student Names: and You have 50 minutes to complete and revise this test. 1. Do not turn this page until you are told to do so. 2. Write your team name and
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS)
 Atmospheric Science-ATS (ATS) 1 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS) Courses ATS 150 Science of Global Climate Change Credits: 3 (3-0-0) Physical basis of climate change. Energy budget of the earth, the greenhouse
Atmospheric Science-ATS (ATS) 1 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS) Courses ATS 150 Science of Global Climate Change Credits: 3 (3-0-0) Physical basis of climate change. Energy budget of the earth, the greenhouse
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Computer Models of the Earth s Climate
 Computer Models of the Earth s Climate DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES MATH DAY, 3-25-13 Climate Models Climate Models Climate Models Mathematical model: uses equations to describe
Computer Models of the Earth s Climate DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES MATH DAY, 3-25-13 Climate Models Climate Models Climate Models Mathematical model: uses equations to describe
Fluid Circulation Review. Vocabulary. - Dark colored surfaces absorb more energy.
 Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
6.2 Meteorology. A meteorologist is a person who uses scientific principles to explain, understand, observe, or forecast Earth s weather.
 Water and Weather 6.2 Meteorology A meteorologist is a person who uses scientific principles to explain, understand, observe, or forecast Earth s weather. 6.2 Water in the Atmosphere Dew point is the temperature
Water and Weather 6.2 Meteorology A meteorologist is a person who uses scientific principles to explain, understand, observe, or forecast Earth s weather. 6.2 Water in the Atmosphere Dew point is the temperature
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts. Lecture 12 AOS 101
 Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
This course is based on notes from a variety of textbooks, National Weather Service Manuals, and online modules (e.g.,
 ESCI 6216 Synoptic Meteorology MWF, 9:10-10:05 a.m., JN 222 Course Syllabus Fall 2014 Instructor: Office: Phone: E-Mail: Website: Dr. Dorian J. Burnette 230, Johnson Hall 901-678-4452 djbrntte@memphis.edu
ESCI 6216 Synoptic Meteorology MWF, 9:10-10:05 a.m., JN 222 Course Syllabus Fall 2014 Instructor: Office: Phone: E-Mail: Website: Dr. Dorian J. Burnette 230, Johnson Hall 901-678-4452 djbrntte@memphis.edu
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE (ATM)
 Atmospheric Science (ATM) 1 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE (ATM) ATM 102. Introduction to Weather and Climate. 3 Credit Hours. The structure, physics, dynamics and thermodynamics of the atmosphere. Weather, weather
Atmospheric Science (ATM) 1 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE (ATM) ATM 102. Introduction to Weather and Climate. 3 Credit Hours. The structure, physics, dynamics and thermodynamics of the atmosphere. Weather, weather
no eddies eddies Figure 3. Simulated surface winds. Surface winds no eddies u, v m/s φ0 =12 φ0 =0
 References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES (ATM OCN)
 Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences (ATM OCN) 1 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES (ATM OCN) ATM OCN 100 WEATHER AND CLIMATE Nature and variability of wind, temperature, cloud and precipitation. Storm systems,
Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences (ATM OCN) 1 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES (ATM OCN) ATM OCN 100 WEATHER AND CLIMATE Nature and variability of wind, temperature, cloud and precipitation. Storm systems,
Seasonal Climate Watch February to June 2018
 Seasonal Climate Watch February to June 2018 Date issued: Jan 26, 2018 1. Overview The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is expected to remain in a weak La Niña phase through to early autumn (Feb-Mar-Apr).
Seasonal Climate Watch February to June 2018 Date issued: Jan 26, 2018 1. Overview The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is expected to remain in a weak La Niña phase through to early autumn (Feb-Mar-Apr).
DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE
 Department of Atmospheric Science 1 DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE Office in Atmospheric Science Building, Foothills Campus, Room 118 (970) 491-8682 www.atmos.colostate.edu (http://www.atmos.colostate.edu)
Department of Atmospheric Science 1 DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE Office in Atmospheric Science Building, Foothills Campus, Room 118 (970) 491-8682 www.atmos.colostate.edu (http://www.atmos.colostate.edu)
Weather & Ocean Currents
 Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Global Circulation. Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern
 Global Circulation Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern Wind rose shows % frequency of winds around the compass 1 Global Circulation
Global Circulation Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern Wind rose shows % frequency of winds around the compass 1 Global Circulation
b. The boundary between two different air masses is called a.
 NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate
 Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place"
 Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
Clouds and turbulent moist convection
 Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013
 1 Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013 by William Gray and Phil Klotzbach Preliminary Draft - March 2014 (Final draft by early June) ABSTRACT This paper discusses the causes of the unusual dearth
1 Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013 by William Gray and Phil Klotzbach Preliminary Draft - March 2014 (Final draft by early June) ABSTRACT This paper discusses the causes of the unusual dearth
1. Mass and volume: a. What is the volume of the liquid in the graduated cylinder pictured to the right? (1 point)
 Potter Name: Date: Hour: Score: /7 Learning Check 4.1 LT 4.1 Density: I can explain the role density plays to help form some currents. 1. Mass and volume: a. What is the volume of the liquid in the graduated
Potter Name: Date: Hour: Score: /7 Learning Check 4.1 LT 4.1 Density: I can explain the role density plays to help form some currents. 1. Mass and volume: a. What is the volume of the liquid in the graduated
Weather Systems. Section
 Section 1 12.2 Objectives Compare and contrast the three major wind systems. Identify four types of fronts. Distinguish between highand low-pressure systems. Review Vocabulary convection: the transfer
Section 1 12.2 Objectives Compare and contrast the three major wind systems. Identify four types of fronts. Distinguish between highand low-pressure systems. Review Vocabulary convection: the transfer
Transient/Eddy Flux. Transient and Eddy. Flux Components. Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Why transients/eddies matter to zonal and time means?
 Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Upper Ocean Circulation
 Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Critical Thinking Review
 Critical Thinking Review (wk3) Cognitive Skill of the Week: Analysis Analysis is the examination of a system (or complex), its components (or ingredients), and the linkages among these components. One
Critical Thinking Review (wk3) Cognitive Skill of the Week: Analysis Analysis is the examination of a system (or complex), its components (or ingredients), and the linkages among these components. One
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228)
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection
 Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND NWP Products for Thunderstorm Forecasting Contents Model choice Identifying parameters important for convection: Low-level convergence High relative
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND NWP Products for Thunderstorm Forecasting Contents Model choice Identifying parameters important for convection: Low-level convergence High relative
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
Goals of this Chapter
 Waves in the Atmosphere and Oceans Restoring Force Conservation of potential temperature in the presence of positive static stability internal gravity waves Conservation of potential vorticity in the presence
Waves in the Atmosphere and Oceans Restoring Force Conservation of potential temperature in the presence of positive static stability internal gravity waves Conservation of potential vorticity in the presence
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection
 Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Empirical thunderstorm forecasting techniques Contents Necessary conditions for convection: Instability Low-level moisture Trigger mechanism Forecasting
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Empirical thunderstorm forecasting techniques Contents Necessary conditions for convection: Instability Low-level moisture Trigger mechanism Forecasting
A - Lecture 3 Total Hours per Week : 3 Total Number of Weeks : 13
 https://horizon.mcgill.ca/pban1/bzskcpwf.p_display_form?form_mode=view_printable&... Page 1 of 3 11/16/2016 New Course Program Affected? Program Change Form Submitted? New Data Subject/Course/Term ATOC
https://horizon.mcgill.ca/pban1/bzskcpwf.p_display_form?form_mode=view_printable&... Page 1 of 3 11/16/2016 New Course Program Affected? Program Change Form Submitted? New Data Subject/Course/Term ATOC
Answer each section in a separate booklet.
 DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 150 Internal Examiners: Dr S Pillay & Mr J Lutchmiah External Examiner: Dr J Odindi NOTE: This paper consists of 8 pages and an MCQ answer sheet. Please ensure that you have
DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 150 Internal Examiners: Dr S Pillay & Mr J Lutchmiah External Examiner: Dr J Odindi NOTE: This paper consists of 8 pages and an MCQ answer sheet. Please ensure that you have
The Behaviour of the Atmosphere
 3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
Weather and the Atmosphere. RAP Short Course
 Weather and the Atmosphere RAP Short Course Syllabus 1) Vertical structure and composition of the atmosphere, basic weather variables 2) Warming Earth and its atmosphere the diurnal and seasonal cycles
Weather and the Atmosphere RAP Short Course Syllabus 1) Vertical structure and composition of the atmosphere, basic weather variables 2) Warming Earth and its atmosphere the diurnal and seasonal cycles
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Lecture 19. Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Weather Studies Introduction to Atmospheric Science
 Weather Studies Introduction to Atmospheric Science American Meteorological Society Chapter 1 Monitoring The Weather Credit: This presentation was prepared for AMS by Michael Leach, Professor of Geography
Weather Studies Introduction to Atmospheric Science American Meteorological Society Chapter 1 Monitoring The Weather Credit: This presentation was prepared for AMS by Michael Leach, Professor of Geography
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13
 ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
Quiz 2 Review Questions
 Quiz 2 Review Questions Chapter 7 Lectures: Winds and Global Winds and Global Winds cont 1) What is the thermal circulation (thermal wind) and how does it form? When we have this type of circulation, how
Quiz 2 Review Questions Chapter 7 Lectures: Winds and Global Winds and Global Winds cont 1) What is the thermal circulation (thermal wind) and how does it form? When we have this type of circulation, how
Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY
 Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY 3.1 The TKE budget Derivation : The definition of TKE presented is TKE/m= e = 0.5 ( u 2 + v 2 + w 2 ). we recognize immediately that TKE/m is nothing more than the
Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY 3.1 The TKE budget Derivation : The definition of TKE presented is TKE/m= e = 0.5 ( u 2 + v 2 + w 2 ). we recognize immediately that TKE/m is nothing more than the
Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001
 Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please
Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring
 Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring 1 Typical flow of making one month forecast Textbook P.66 Observed data Atmospheric and Oceanic conditions Analysis Numerical model Ensemble forecast
Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring 1 Typical flow of making one month forecast Textbook P.66 Observed data Atmospheric and Oceanic conditions Analysis Numerical model Ensemble forecast
Measurement of Rotation. Circulation. Example. Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity 1/31/2017
 Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B
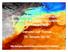 Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
Instructions, Instructor Notes and Answer Key for Ocean Gyre Circulation and Patterns of Global Primary Productivity
 Instructions, Instructor Notes and Answer Key for Ocean Gyre Circulation and Patterns of Global Primary Productivity Instructions for activity: The instructions below are described for individual student
Instructions, Instructor Notes and Answer Key for Ocean Gyre Circulation and Patterns of Global Primary Productivity Instructions for activity: The instructions below are described for individual student
Anticipation Guide #2
 Weather Systems Anticipation Guide #2 Density differences in the atmosphere are responsible for redistributing earth s heat When air is heated it rises, cools and expands releasing energy mt air masses
Weather Systems Anticipation Guide #2 Density differences in the atmosphere are responsible for redistributing earth s heat When air is heated it rises, cools and expands releasing energy mt air masses
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate
 Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
Meteorology Today. 1 Aug st Lt Libby Haynes Capt Kim Mevers
 Meteorology 1950 - Today 1 Aug 2018 1 st Lt Libby Haynes Capt Kim Mevers What is meteorology? Is it important to you? Meteorology is the science of the atmosphere embracing both weather and climate. It
Meteorology 1950 - Today 1 Aug 2018 1 st Lt Libby Haynes Capt Kim Mevers What is meteorology? Is it important to you? Meteorology is the science of the atmosphere embracing both weather and climate. It
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
 Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Warming after a cold winter will disappear quickly as it did in 2007 By Joseph D Aleo
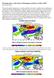 Warming after a cold winter will disappear quickly as it did in 2007 By Joseph D Aleo The pop in global temperatures, even the satellite, the last few months seems surprising to some in the Northern Hemisphere
Warming after a cold winter will disappear quickly as it did in 2007 By Joseph D Aleo The pop in global temperatures, even the satellite, the last few months seems surprising to some in the Northern Hemisphere
ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005
 ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005 true/false /25 multiple choice /25 short answer /23 essay /10 total /83 or % True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. (25 questions 1% each) 1.
ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005 true/false /25 multiple choice /25 short answer /23 essay /10 total /83 or % True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. (25 questions 1% each) 1.
Global Weather Trade Winds etc.notebook February 17, 2017
 Global Weather 1 north pole northern hemisphere equator southern hemisphere south pole 2 We have seasons because of the Earth's tilt The seasons are opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres winter
Global Weather 1 north pole northern hemisphere equator southern hemisphere south pole 2 We have seasons because of the Earth's tilt The seasons are opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres winter
Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class)
 Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class) 1. General Circulation Briefly describe where each of the following features is found in the earth s general
Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class) 1. General Circulation Briefly describe where each of the following features is found in the earth s general
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY. Metr Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts. Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation.
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I
 Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I TECHNICAL REGULATIONS VOLUME I General Meteorological Standards and Recommended
Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I TECHNICAL REGULATIONS VOLUME I General Meteorological Standards and Recommended
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT I
 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT I Environmental science is the study of the interaction of humans with the natural environment. The environment includes all conditions that surround living organisms: Climate
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT I Environmental science is the study of the interaction of humans with the natural environment. The environment includes all conditions that surround living organisms: Climate
MT Dynamic Meteorology II MWF Spring :00 a.m. - 8:50 a.m. Dr. Jim Koermer Boyd 306 DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY II SYLLABUS
 MT5320.01 - Dynamic Meteorology II MWF Spring 2011 8:00 a.m. - 8:50 a.m. Dr. Jim Koermer Boyd 306 DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY II SYLLABUS COURSE DESCRIPTION: Dynamic Meteorology II involves the application of
MT5320.01 - Dynamic Meteorology II MWF Spring 2011 8:00 a.m. - 8:50 a.m. Dr. Jim Koermer Boyd 306 DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY II SYLLABUS COURSE DESCRIPTION: Dynamic Meteorology II involves the application of
Lesson IV. TOPEX/Poseidon Measuring Currents from Space
 Lesson IV. TOPEX/Poseidon Measuring Currents from Space The goal of this unit is to explain in detail the various measurements taken by the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite. Keywords: ocean topography, geoid,
Lesson IV. TOPEX/Poseidon Measuring Currents from Space The goal of this unit is to explain in detail the various measurements taken by the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite. Keywords: ocean topography, geoid,
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Introduction of climate monitoring and analysis products for one-month forecast
 Introduction of climate monitoring and analysis products for one-month forecast TCC Training Seminar on One-month Forecast on 13 November 2018 10:30 11:00 1 Typical flow of making one-month forecast Observed
Introduction of climate monitoring and analysis products for one-month forecast TCC Training Seminar on One-month Forecast on 13 November 2018 10:30 11:00 1 Typical flow of making one-month forecast Observed
Chapter 9. Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones
 Chapter 9 Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones Frontal Weather Fronts are boundary surfaces between different air masses. Warm front Cold front Stationary front Occluded front Drylines Frontal Weather
Chapter 9 Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones Frontal Weather Fronts are boundary surfaces between different air masses. Warm front Cold front Stationary front Occluded front Drylines Frontal Weather
MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES
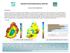 MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES CLIMATE SEPTEMBER 2018 Introduction Synoptic weather pattern over the region portrayed September as a transition month. The month started with wintry characteristics.
MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES CLIMATE SEPTEMBER 2018 Introduction Synoptic weather pattern over the region portrayed September as a transition month. The month started with wintry characteristics.
Introduction of Seasonal Forecast Guidance. TCC Training Seminar on Seasonal Prediction Products November 2013
 Introduction of Seasonal Forecast Guidance TCC Training Seminar on Seasonal Prediction Products 11-15 November 2013 1 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Regression method Single/Multi regression model Selection
Introduction of Seasonal Forecast Guidance TCC Training Seminar on Seasonal Prediction Products 11-15 November 2013 1 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Regression method Single/Multi regression model Selection
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR TEST NUMBER IS THE 5-DIGIT NUMBER AT THE TOP OF EACH PAGE.
 Instructor: Prof. Seiberling PHYSICS DEPARTMENT MET 1010 Name (print, last rst): 1st Midterm Exam Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR TEST
Instructor: Prof. Seiberling PHYSICS DEPARTMENT MET 1010 Name (print, last rst): 1st Midterm Exam Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR TEST
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight,
 The air that we breathe comes from the atmosphere, a thin gaseous layer that surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight, but this weight varies
The air that we breathe comes from the atmosphere, a thin gaseous layer that surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight, but this weight varies
2. What causes these weather changes?
 Weather Table of Contents Essential Questions... 1 Vocabulary... 2 Weather Symbols... 5 Bringing the Rain to Kapiti Plain... 7 Weather Instruments... 8 Weather Forecasting... 13 Essential Questions 1.
Weather Table of Contents Essential Questions... 1 Vocabulary... 2 Weather Symbols... 5 Bringing the Rain to Kapiti Plain... 7 Weather Instruments... 8 Weather Forecasting... 13 Essential Questions 1.
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1. Introduction In this class, we will examine atmospheric phenomena that occurs at the mesoscale, including some boundary layer processes, convective storms, and hurricanes. We will emphasize
Chapter 1. Introduction In this class, we will examine atmospheric phenomena that occurs at the mesoscale, including some boundary layer processes, convective storms, and hurricanes. We will emphasize
Study Guide. Earth Systems 1109 Weather Dynamics. Adult Basic Education Science. Prerequisites: Credit Value: 1
 Adult Basic Education Science Weather Dynamics Study Guide Prerequisites: None Credit Value: 1 Text: Science 10 ; Ritter, Plumb, et al; Nelson, 2001. Earth Systems Concentration Earth Systems 3109A Earth
Adult Basic Education Science Weather Dynamics Study Guide Prerequisites: None Credit Value: 1 Text: Science 10 ; Ritter, Plumb, et al; Nelson, 2001. Earth Systems Concentration Earth Systems 3109A Earth
Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Climate & Earth System Science. Atmosphere Ocean Interactions. A: Structure of the Ocean.
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Activity #2 - Major Ocean Surface Currents
 Activity #2 - Major Ocean Surface Currents Concepts # 3 & 6 # 3 Atmospheric cells and ocean gyres redistribute heat from low to high latitudes, which influences climate, weather, and ocean temperature.
Activity #2 - Major Ocean Surface Currents Concepts # 3 & 6 # 3 Atmospheric cells and ocean gyres redistribute heat from low to high latitudes, which influences climate, weather, and ocean temperature.
Surface Circulation. Key Ideas
 Surface Circulation The westerlies and the trade winds are two of the winds that drive the ocean s surface currents. 1 Key Ideas Ocean water circulates in currents. Surface currents are caused mainly by
Surface Circulation The westerlies and the trade winds are two of the winds that drive the ocean s surface currents. 1 Key Ideas Ocean water circulates in currents. Surface currents are caused mainly by
Course Catalog - Spring 2015
 Course Catalog - Spring 2015 Atmospheric Sciences Atmospheric Sciences Head of Department: Robert Rauber Department Office: 101 Atmospheric Sciences Building, 105 South Gregory Street, Urbana Phone: 333-2046
Course Catalog - Spring 2015 Atmospheric Sciences Atmospheric Sciences Head of Department: Robert Rauber Department Office: 101 Atmospheric Sciences Building, 105 South Gregory Street, Urbana Phone: 333-2046
25.1 Air Masses. Section 25.1 Objectives
 Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Types of Ocean Currents Surface currents Deep currents 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Measuring Surface Currents Direct methods Floating device tracked
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Types of Ocean Currents Surface currents Deep currents 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Measuring Surface Currents Direct methods Floating device tracked
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW
 2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
NIWA Outlook: September October November 2013
 September-November 2013 Issued: 30 August 2013 Hold mouse over links and press ctrl + left click to jump to the information you require: Overview Regional predictions for the next three months: Northland,
September-November 2013 Issued: 30 August 2013 Hold mouse over links and press ctrl + left click to jump to the information you require: Overview Regional predictions for the next three months: Northland,
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes!
 Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton
 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
4. Atmospheric transport. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 4. Atmospheric transport Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 Forces in the atmosphere: Gravity g Pressure-gradient ap = ( 1/ ρ ) dp / dx for x-direction (also y, z directions)
4. Atmospheric transport Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 Forces in the atmosphere: Gravity g Pressure-gradient ap = ( 1/ ρ ) dp / dx for x-direction (also y, z directions)
NATS 101, Section 13, Fall 2010 Midterm Examination #2 October 22, 2010
 EXAM NUMBER NATS 101, Section 13, Fall 2010 Midterm Examination #2 October 22, 2010 Name: KEY SID: Instructions: Write your name and student ID on ALL pages of the exam. In the multiple-choice/fill in
EXAM NUMBER NATS 101, Section 13, Fall 2010 Midterm Examination #2 October 22, 2010 Name: KEY SID: Instructions: Write your name and student ID on ALL pages of the exam. In the multiple-choice/fill in
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES. Weather. atmosphere. Weather and climate
 GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
The general circulation: midlatitude storms
 The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
Atmospheric Circulation
 Atmospheric Circulation Introductory Oceanography Instructor: Ray Rector Atmospheric Circulation Key Topics Composition and Structure Solar Heating and Convection The Coriolis Effect Global Wind Patterns
Atmospheric Circulation Introductory Oceanography Instructor: Ray Rector Atmospheric Circulation Key Topics Composition and Structure Solar Heating and Convection The Coriolis Effect Global Wind Patterns
Seasonal Climate Watch November 2017 to March 2018
 Seasonal Climate Watch November 2017 to March 2018 Date issued: Oct 26, 2017 1. Overview The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) continues to develop towards a La Niña state, and is expected to be in at
Seasonal Climate Watch November 2017 to March 2018 Date issued: Oct 26, 2017 1. Overview The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) continues to develop towards a La Niña state, and is expected to be in at
SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER
 SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER Basic Meteorological Terminology Adiabatic - Referring to a process without the addition or removal of heat. A temperature change may come about as a result of a change in the
SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER Basic Meteorological Terminology Adiabatic - Referring to a process without the addition or removal of heat. A temperature change may come about as a result of a change in the
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change
 Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation. Dr. Michael J Passow
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation Dr. Michael J Passow What Processes Lift Air? Clouds require three things: water vapor, a condensation nucleus, and cooling Cooling usually
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation Dr. Michael J Passow What Processes Lift Air? Clouds require three things: water vapor, a condensation nucleus, and cooling Cooling usually
