Chapter 1. Introduction
|
|
|
- Amberly Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1. Introduction In this class, we will examine atmospheric phenomena that occurs at the mesoscale, including some boundary layer processes, convective storms, and hurricanes. We will emphasize the physical understanding of these phenomena, and use dynamic equations to explain their development and evolution. First, we will start with the definition of MESOSCALE Definition of Mesoscale We tend to classify weather system according to their intrinsic or characteristic time and space scales. Often theoretical considerations enter into the definition as well. Two commonly used approaches for defining the scales: Dynamical and scale-analysis approach. 1
2 Dynamical: The dynamical approach ask questions such as the following: What controls the time and space scales of certain atmospheric motion? Why are thunderstorms a particular size? Why is the planetary boundary layer (PBL) not 10 km deep? Why are raindrops not the size of baseball? Why most cyclones have diameters of a few thousand kilometers not a few hundred of km? Tornado and hurricanes are both rotating vortices, what determine their vastly different sizes? There are theoretical reasons for them! There are many different scales in the atmospheric motion. Let look at a few examples: 2
3 Hemi-spherical plot of 500mb height (color) and MSL pressure (contours) showing planetary scale waves and surface cyclones (lows) at 00UTC 15 Jan
4 National Weather Service 850mb (computer generated synoptic-scale weather chart) for northern America for 6pm CST, January 15, A cyclone/low is located over eastern U.S. Most features shown are considered synoptic scale as fine scale features are often missed by standard upper-air observation network. 4
5 ARPS Continental Scale Forecast (dx=40km) Similar forecasts can be found at 5
6 6
7 7
8 1am CST, January 17,
9 9
10 24 h forecasts by ARPS for November 2, 2000, at 32-km resolution. 10
11 11
12 12h and 24 h forecasts by ARPS for November 2, 2000, at 6-km resolution. An intense squall line is shown. 12
13 A 500mb plot showing small-scale disturbances associated with thunderstorms, in the 9km-resolution forecast of ARPS. 13
14 Atmospheric Energy Spectrum There are a few dominant time scales in the atmosphere, as is shown by the following plot of the kinetic energy spectrum plotted as a function of time: Average kinetic energy of west-east wind component in the free atmosphere (solid line) and near the ground (dashed line). (After Vinnichenko, 1970). See also Atkinson Chapter 1. 14
15 There is a local peak around 1 day associated with diurnal cycle of solar heating, and a large peak near 1 year associated with the annual cycle due to the change in the earth's rotation axis relative to the sun. These time scales are mainly determined by forcing external to the atmosphere. There is also a peak in the a few days up to about 1 month range. These scales are associated with synoptic scale cyclones up to planetary-scale waves. There isn t really any external forcing that is dominant at a period of a few days this peak must be related to the something internal to the atmosphere it is actually scale of most unstable atmospheric motion, such as those associated with baroclinic and barotropic instability. There is also a peak around 1 min. This appears to be associated with small-scale turbulent motion, including those found in convective thunderstorms and planetary boundary layer. The figure also shows that energy spectrum of the atmospheric motion is actually continuous! There appears to be a 'gap' between several hour to half an hour there remain disputes about the interpretation of this 'gap'. This 'gap' actually corresponding to the 'mesoscale' that is the subject of our study here. We know that many weather phenomena occur on the 'mesoscale', although they tend to be intermittent in both time and space. The intermittency (unlike the ever present large-scale waves and cyclones) may be the reason for the 'gap'. Mesoscale is believed to play an important role in transferring energy from the large scale down to the small scales. Quoting from Dr. A. A. White (of British Met Office) "at any one time there is not much water in the outflow pipe from a bath, but it is inconvenient if it gets blocked". It's like the mid-latitude convection it does not occur every day but we can not do without it otherwise, the heat and moisture will accumulate near the ground and we will not be able live at the surface of the earth!! 15
16 Energy Cascade As we go down scales, we see finer and finer structures. Many of these structures are due to certain types of instabilities that inherently limit the size and duration of the phenomena. Also, there exist exchanges of energy, heat, moisture and momentum among all scales. Example: A thunderstorm feeds off convective instabilities (as measured by CAPE) created by e.g., synoptic-scale cyclones. A thunderstorm can also derive part of its kinetic energy from the mean flow. The thunderstorm in turn can produce tornadoes by concentrating vorticity into small regions. Strong winds in the tornado creates turbulent eddies which then dissipate and eventually turn the kinetic energy into heat. Convective activities can also feed back into the large scale and enhancing synoptic scale cyclones. 16
17 Most of the energy transfer in the atmosphere is downscale starting from differential heating with latitude and land-sea contrast on the planetary scales. (Energy in the atmosphere can also transfer upscale). We call the energy transfer among scales energy cascade. What does this have to do with the mesoscale? It turned out that the definition of the mesoscale is not that easy. Historically, the mesoscale was first defined as the scale between the visually observable thunderstorm scale and the scale that can be observed by synoptic observation network i.e., it is a scale that could not be observed (read Atkinson Chapter 1, in particular page 5). The mesoscale was, in early 50's, anticipated to be observed by the weather radars. 17
18 Rough Definition of Mesoscale: The scale for which both ageostrophic advection and Coriolis parameter f are important which is smaller than the Rossby radius of deformation (L =NH/f ~ 1000km). Does that help you? For now, let's use a more qualitative definition and try to relate the scale to something more concrete. Consider that the word mesoscale defines meteorological events having spatial dimensions of the order of one to two states, not an individual thunderstorms or cumulus clouds, and not a synoptic-scale cyclones (whose scale is on the order of several thousands of km). Typical thunderstorms are actually sub-meoscale scale, we call their scale the convective scale. Orlanski's classification of scales (see more discussions on this table in Atkinson Chapter 1) 18
19 19
20 Atmospheric scale definitions, where L H is horizontal scale length proposed by Thunis and Borstein (1996) 20
21 Definition of scales via scale analysis on equations of motion (Read Chapter 1 of Atkinson. Fujita also has a chapter on this topic in book edited by Ray 1985). Some (time and spatial) scales in the atmosphere are obvious: Time scales: diurnal cycle annual cycle inertial oscillation period due to earth rotation the Coriolis parameter f. advective time scale time taken to advect over certain distance Spatial scales: global related to earth's radius scale height of the atmosphere related to the total mass of the atmosphere and gravity scale fixed geographical features mountain height, width, width of continents, oceans, lakes Scale analysis (you should have learned this tool in Dynamics I) is a very useful method for establishing the importance of various processes in the atmosphere and terms in the governing equations. Based on the relative importance of these processes/terms, we can deduce much of the behavior of motion at such scales. 21
22 Let's look at a simple example: du u u 1 p = + u = + dt t x ρ x fv What is this equation? Can you identify the terms in it? With scale analysis, we try to assign the characteristic values for each of the variables in the equation and estimate the magnitude of each term then determine their relative importance. du u U For example, ~ ~ dt t T where U is the velocity scale (typical magnitude or amplitude if described as a wave component), and T the time scale (typical length of time for velocity to change by u, or the period for oscillations). It should be emphasized here there it is the typical magnitude of change that defines the scale, which is not always the same as the magnitude of the quantity itself. The absolute temperature is a good example, the surface pressure is another. For different scales, the terms in the equation of motion have different importance leading to different behavior of the motion so there is a dynamic significance to the scale! Synoptic Scale Motion Let's do the scale analysis for the synoptic scale motion since we know pretty well about synoptic scale motion (correct?). V ~ 10 m/s (actually the typical variation or change in horizontal velocity over the typical distance) W ~ 0.1 m/s (typical magnitude or range of variation of vertical velocity) 22
23 L ~ 1000 km = 10 6 m (about the radius of a typical cyclone) H ~ 10 km (depth of the troposphere) T ~ L/V ~ 10 5 s (the time for an air parcel to travel for 1000 km) f ~ 10-4 s -1 for the mid-latitude ρ ~ 1 kg/m 3 p in horizontal ~ 10 mb = 1000 Pa (about the variation of pressure from the center to the edge of a cyclone note that it is the typical variation that determines that typical scale, not the value itself, as in this example. Using the scale of 1000mb will give you wrong result) u u u 1 p + u + w = t x z ρ x + fv V VV WV p T L H ρl fv It turned out that the time tendency and advection terms are one order of magnitude smaller for synoptic scale flows. The pressure gradient force and Coriolis force are in rough balance what kind of flow do you get in this case?? - The quasi-geostrophic flow. Similar scale analysis can be performed on the vertical equation of motion. p over vertical length scale H ~ 1000 mb = 10 5 Pa 23
24 w w w 1 p + u + w = g t x z ρ z W VW WW p T L H ρh g 10 Clearly, the vertical acceleration is much smaller than the vertical pressure gradient term and the gravitational term, which are of the same order of magnitude. The balance between these two terms gives the hydrostatic balance, and this balance is a very good approximation for synoptic scale flows. Also, the vertical motion is much smaller than u v w the horizontal motion. We can deduce the latter from the mass continuity equation ( ). x y z Therefore, we obtain, based on the scale analysis along, the following basic properties of flows at the synopticscale flows: such flows are quasi-two-dimensional, quasi-geostrophic and hydrostatic. We saw a good example of horizontal scale determining the dynamics of motion! In summary, synoptic (and up) scale flows are quasi-two dimensional (because w << u ) hydrostatic (we can see it by performing scale analysis for vertical equation of motion) Coriolis force is a dominant term in the equation of motion and it is in rough balance with the PGF, the flow is quasi-geostrophic 24
25 Mesoscale Motion What about the mesoscale? We said earlier we define the mesoscale to be on the order of hundreds of kilometers in space and hours in time. Repeat the scale analysis done earlier: u u u 1 p + u + w = t x z ρ x + fv V VV WV p T L H ρl fv we see that the all terms in the equation are of the same magnitude none of them can be neglected we no longer have geostrophy! For the vertical direction, the hydrostatic approximation is still reasonable good for the mesoscale. In the vertical direction: 25
26 w w w 1 p + u + w = g t x z ρ z W VW WW p T L H ρh g 10 Therefore, mesoscale motion is not geostrophic (i.e., ageostrophic component is significant see earlier definition), the Coriolis force remains important, and hydrostatic balance is roughly satisfied. The motion is quasitwo-dimensional (w<<u or v). This can be a dynamic definition of the mesoscale, or in Orlanski's definition, the meso-β scale. In summary, meso-β scale flows are quasi-two dimensional nearly hydrostatic Coriolis force is non-negligible When we go one step further down the scale, looking at cumulus convection or even supercell storms, L ~ 10 km, V ~ 10 m/s, T ~ 1000 s, we get 26
27 u u u 1 p + u + w = t x z ρ x + fv V VV WV p T L H ρl fv Now we see that the Coriolis force is an order of magnitude smaller, it can therefore be neglected when studying cumulus convection that lasted for an hour or so. Again, the acceleration term is as important as the PGF. The scale analysis of the vertical equation of motion, based on the Bousinessq equations of motion (see e.g., page 354 of Bluestein) is as follows: w w w 1 p' θ ' + u + w = + g t x z ρ z θ W VW WW p θ g T L H ρh θ Here we are using the vertical mean density as the density scale in PGF term. The Bousinessq form of equation is used because it is the residual between the PGF and buoyancy force terms that drives the vertical motion, therefore we want estimate the terms in terms of the deviations/perturbations from the hydrostatically balanced base state. 27
28 Clearly, the vertical acceleration term is now important therefore hydrostatic approximation is no longer good. According to Orlanski's definition, this falls into the meso-γ range, sometimes it's referred to as small scale or convective scale. At this scale, the flow will be agostrophic, nonhydrostatic, and three dimensional (w ~ u and v). In summary, meso-γ, small or convective scale flows are three dimensional nonhydrostatic ageostrophic and the Coriolis force is negligible As one goes further down to the micro-scales, the basic dynamics becomes similar to the small scale flows the flow is three dimensional nonhydrostatic ageostrophic and the Coriolis force is negligible. 28
29 Summary There are more than one way to define the scales of weather systems. The definition can be based on the time or space scale or both of the system. It can also be based on certain physically meaningful non-dimensional parameter (for example, Rossby number based on Lagrangian time scale as advocated by Emanuel 1986). The most important is to know the key characteristics associated with weather systems/disturbances at each of these scales, as revealed by the scale analysis. The scale analysis can lead to non-dimensional parameters in nondimensionalized governing equations. Physically, the last approach (that based on non-dimensional parameters) makes most sense. Reference Emanuel, K. A., 1986: Overview and definition of mesoscale meteorology. In: P.S. Ray (Editor), Mesoscale Meteorology and Forecasting. American Meteorological Society, Boston, In the course, we will focus on the meso β (or classical mesoscale) and meso-γ (or small or convective scale), with some coverage on meso-α and micro-α scale (e.g., tornadoes). 29
Introduction to Mesoscale Meteorology: Part I
 Introduction to Mesoscale Meteorology: Part I Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu January 13, 2015 1 / 35 Overview Administrative Junk Who the heck is Jeremy Gibbs? Course Information Policies
Introduction to Mesoscale Meteorology: Part I Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu January 13, 2015 1 / 35 Overview Administrative Junk Who the heck is Jeremy Gibbs? Course Information Policies
Introduction to Mesoscale Meteorology
 Introduction to Mesoscale Meteorology Overview Scale Definitions Synoptic Synoptic derived from Greek synoptikos meaning general view of the whole. Also has grown to imply at the same time or simultaneous.
Introduction to Mesoscale Meteorology Overview Scale Definitions Synoptic Synoptic derived from Greek synoptikos meaning general view of the whole. Also has grown to imply at the same time or simultaneous.
Draft Chapter from Mesoscale Dynamic Meteorology By Prof. Yu-lang Lin, North Carolina State University
 Draft Chapter from Mesoscale Dynamic Meteorology By Prof. Yu-lang Lin, North Carolina State University Chapter 1 Overview 1.1 Introduction The so-called mesometeorology or mesoscale meteorology is defined
Draft Chapter from Mesoscale Dynamic Meteorology By Prof. Yu-lang Lin, North Carolina State University Chapter 1 Overview 1.1 Introduction The so-called mesometeorology or mesoscale meteorology is defined
1/18/2011. Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis ESS227 Prof. Jin-Yi Yu
 Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed in an inertial system = rate of change of Ua following the motion in an inertial
Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed in an inertial system = rate of change of Ua following the motion in an inertial
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena
 The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes
 Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes VOLUME II Observations and Theory of Weather Systems HOWARD B. BLUESTEIN New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 Contents 1. THE BEHAVIOR OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE,
Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes VOLUME II Observations and Theory of Weather Systems HOWARD B. BLUESTEIN New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 Contents 1. THE BEHAVIOR OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE,
Part-8c Circulation (Cont)
 Part-8c Circulation (Cont) Global Circulation Means of Transfering Heat Easterlies /Westerlies Polar Front Planetary Waves Gravity Waves Mars Circulation Giant Planet Atmospheres Zones and Belts Global
Part-8c Circulation (Cont) Global Circulation Means of Transfering Heat Easterlies /Westerlies Polar Front Planetary Waves Gravity Waves Mars Circulation Giant Planet Atmospheres Zones and Belts Global
Goals of this Chapter
 Waves in the Atmosphere and Oceans Restoring Force Conservation of potential temperature in the presence of positive static stability internal gravity waves Conservation of potential vorticity in the presence
Waves in the Atmosphere and Oceans Restoring Force Conservation of potential temperature in the presence of positive static stability internal gravity waves Conservation of potential vorticity in the presence
Hurricanes are intense vortical (rotational) storms that develop over the tropical oceans in regions of very warm surface water.
 Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis. ESS227 Prof. Jin-Yi Yu
 Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed
Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed
Gravity Waves. Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere. Waves in the Atmosphere and Oceans. Internal Gravity (Buoyancy) Waves 2/9/2017
 Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method Properties of Wave Shallow Water Model Gravity Waves Rossby Waves Waves in the Atmosphere and Oceans Restoring Force Conservation of potential temperature
Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method Properties of Wave Shallow Water Model Gravity Waves Rossby Waves Waves in the Atmosphere and Oceans Restoring Force Conservation of potential temperature
Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001
 Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please
Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please
dv dt = f (M M g ) (1)
 Inertial, Symmetric and Conditional Symmetric Instability (CSI) The following is not meant to be a self-contained tutorial. It is meant to accompany active discussion and demonstration in the classroom.
Inertial, Symmetric and Conditional Symmetric Instability (CSI) The following is not meant to be a self-contained tutorial. It is meant to accompany active discussion and demonstration in the classroom.
The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System. Chapter 3
 The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System Chapter 3 Since the earth is rotating about its axis and since it is convenient to adopt a frame of reference fixed in the earth, we need to study
The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System Chapter 3 Since the earth is rotating about its axis and since it is convenient to adopt a frame of reference fixed in the earth, we need to study
Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001
 Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please be sure to read each question CAREFULLY
Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please be sure to read each question CAREFULLY
Balanced Flow Geostrophic, Inertial, Gradient, and Cyclostrophic Flow
 Balanced Flow Geostrophic, Inertial, Gradient, and Cyclostrophic Flow The types of atmospheric flows describe here have the following characteristics: 1) Steady state (meaning that the flows do not change
Balanced Flow Geostrophic, Inertial, Gradient, and Cyclostrophic Flow The types of atmospheric flows describe here have the following characteristics: 1) Steady state (meaning that the flows do not change
Module 9 Weather Systems
 Module 9 Weather Systems In this module the theory of atmospheric dynamics is applied to different weather phenomena. The first section deals with extratropical cyclones, low and high pressure areas of
Module 9 Weather Systems In this module the theory of atmospheric dynamics is applied to different weather phenomena. The first section deals with extratropical cyclones, low and high pressure areas of
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations
 Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations Section 3.1 Basic Equations in Isobaric Coordinates 3.1 For some (in fact many) applications we assume that the change of the Coriolis
Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations Section 3.1 Basic Equations in Isobaric Coordinates 3.1 For some (in fact many) applications we assume that the change of the Coriolis
NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules)
 NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules) Certain physical laws of motion and conservation of energy (for example, Newton's Second Law of Motion and the First Law of Thermodynamics) govern
NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules) Certain physical laws of motion and conservation of energy (for example, Newton's Second Law of Motion and the First Law of Thermodynamics) govern
MODEL TYPE (Adapted from COMET online NWP modules) 1. Introduction
 MODEL TYPE (Adapted from COMET online NWP modules) 1. Introduction Grid point and spectral models are based on the same set of primitive equations. However, each type formulates and solves the equations
MODEL TYPE (Adapted from COMET online NWP modules) 1. Introduction Grid point and spectral models are based on the same set of primitive equations. However, each type formulates and solves the equations
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) Fair Weather over Land
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) Fair Weather over Land
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #2 Page 1 of 8
 1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
Measurement of Rotation. Circulation. Example. Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity 1/31/2017
 Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes
 NAME: SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100 total points.)
NAME: SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100 total points.)
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines
 A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines Note: Lecture notes presented here based on course Daily Weather Laboratory
A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines Note: Lecture notes presented here based on course Daily Weather Laboratory
Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY
 Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY 3.1 The TKE budget Derivation : The definition of TKE presented is TKE/m= e = 0.5 ( u 2 + v 2 + w 2 ). we recognize immediately that TKE/m is nothing more than the
Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY 3.1 The TKE budget Derivation : The definition of TKE presented is TKE/m= e = 0.5 ( u 2 + v 2 + w 2 ). we recognize immediately that TKE/m is nothing more than the
Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity
 Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity 1. Observed Planetary Wave Patterns After upper air observations became routine, it became easy to produce contour
Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity 1. Observed Planetary Wave Patterns After upper air observations became routine, it became easy to produce contour
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place"
 Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
 Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Chapter 2. Quasi-Geostrophic Theory: Formulation (review) ε =U f o L <<1, β = 2Ω cosθ o R. 2.1 Introduction
 Chapter 2. Quasi-Geostrophic Theory: Formulation (review) 2.1 Introduction For most of the course we will be concerned with instabilities that an be analyzed by the quasi-geostrophic equations. These are
Chapter 2. Quasi-Geostrophic Theory: Formulation (review) 2.1 Introduction For most of the course we will be concerned with instabilities that an be analyzed by the quasi-geostrophic equations. These are
ESCI 110: 2 s.h. Introduction to Earth Sciences Programs ESCI 322: 3 s.h. Environmental Hydrology ESCI 241: 4 s.h. Meteorology (G2, L)
 ESCI 110: 2 s.h. Introduction to Earth Sciences Programs General introduction to each of the earth sciences disciplines and to college life. 2 hrs. lec. Offered in fall. Restricted to earth sciences majors.
ESCI 110: 2 s.h. Introduction to Earth Sciences Programs General introduction to each of the earth sciences disciplines and to college life. 2 hrs. lec. Offered in fall. Restricted to earth sciences majors.
SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER
 SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER Basic Meteorological Terminology Adiabatic - Referring to a process without the addition or removal of heat. A temperature change may come about as a result of a change in the
SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER Basic Meteorological Terminology Adiabatic - Referring to a process without the addition or removal of heat. A temperature change may come about as a result of a change in the
Chapter 9. Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation
 Chapter 9 Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling. We examined in the last chapter some consequences of the dynamical balances for low frequency, nearly
Chapter 9 Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling. We examined in the last chapter some consequences of the dynamical balances for low frequency, nearly
Examples of Pressure Gradient. Pressure Gradient Force. Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances. Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion 2/2/2015
 Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems
 The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
196 7 atmospheric oscillations:
 196 7 atmospheric oscillations: 7.4 INTERNAL GRAVITY (BUOYANCY) WAVES We now consider the nature of gravity wave propagation in the atmosphere. Atmospheric gravity waves can only exist when the atmosphere
196 7 atmospheric oscillations: 7.4 INTERNAL GRAVITY (BUOYANCY) WAVES We now consider the nature of gravity wave propagation in the atmosphere. Atmospheric gravity waves can only exist when the atmosphere
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #1 Page 1 of 7
 1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation. 1. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic. 2. The atmosphere is approximately geostrophic.
 Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation For large-scale flow in the atmosphere, we have learned about two very important characteristics:. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic.. The atmosphere is approximately
Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation For large-scale flow in the atmosphere, we have learned about two very important characteristics:. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic.. The atmosphere is approximately
Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte
 Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte In order to inform prospective M.S. Earth Science students as to what graduate-level courses are offered across the broad disciplines of
Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte In order to inform prospective M.S. Earth Science students as to what graduate-level courses are offered across the broad disciplines of
Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology
 Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology B. Legras, http://www.lmd.ens.fr/legras III Frontogenesis (pre requisite: quasi-geostrophic equation, baroclinic instability in the Eady and Phillips models ) Recommended
Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology B. Legras, http://www.lmd.ens.fr/legras III Frontogenesis (pre requisite: quasi-geostrophic equation, baroclinic instability in the Eady and Phillips models ) Recommended
Changes in Density Within An Air are Density Velocity Column Fixed due and/or With Respect to to Advection Divergence the Earth
 The Continuity Equation: Dines Compensation and the Pressure Tendency Equation 1. General The Continuity Equation is a restatement of the principle of Conservation of Mass applied to the atmosphere. The
The Continuity Equation: Dines Compensation and the Pressure Tendency Equation 1. General The Continuity Equation is a restatement of the principle of Conservation of Mass applied to the atmosphere. The
Transient/Eddy Flux. Transient and Eddy. Flux Components. Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Why transients/eddies matter to zonal and time means?
 Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
The Integration of WRF Model Forecasts for Mesoscale Convective Systems Interacting with the Mountains of Western North Carolina
 Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2006 The University of North Carolina at Asheville Asheville, North Carolina April 6-8, 2006 The Integration of WRF Model Forecasts
Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2006 The University of North Carolina at Asheville Asheville, North Carolina April 6-8, 2006 The Integration of WRF Model Forecasts
For the operational forecaster one important precondition for the diagnosis and prediction of
 Initiation of Deep Moist Convection at WV-Boundaries Vienna, Austria For the operational forecaster one important precondition for the diagnosis and prediction of convective activity is the availability
Initiation of Deep Moist Convection at WV-Boundaries Vienna, Austria For the operational forecaster one important precondition for the diagnosis and prediction of convective activity is the availability
Practical Atmospheric Analysis
 Chapter 12 Practical Atmospheric Analysis With the ready availability of computer forecast models and statistical forecast data, it is very easy to prepare a forecast without ever looking at actual observations,
Chapter 12 Practical Atmospheric Analysis With the ready availability of computer forecast models and statistical forecast data, it is very easy to prepare a forecast without ever looking at actual observations,
Dynamic Meteorology (Atmospheric Dynamics)
 Lecture 1-2012 Dynamic Meteorology (Atmospheric Dynamics) Lecturer: Aarnout van Delden Office: BBG, room 615 a.j.vandelden@uu.nl http://www.staff.science.uu.nl/~delde102/index.php Students (background
Lecture 1-2012 Dynamic Meteorology (Atmospheric Dynamics) Lecturer: Aarnout van Delden Office: BBG, room 615 a.j.vandelden@uu.nl http://www.staff.science.uu.nl/~delde102/index.php Students (background
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate
 Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Contents. Parti Fundamentals. 1. Introduction. 2. The Coriolis Force. Preface Preface of the First Edition
 Foreword Preface Preface of the First Edition xiii xv xvii Parti Fundamentals 1. Introduction 1.1 Objective 3 1.2 Importance of Geophysical Fluid Dynamics 4 1.3 Distinguishing Attributes of Geophysical
Foreword Preface Preface of the First Edition xiii xv xvii Parti Fundamentals 1. Introduction 1.1 Objective 3 1.2 Importance of Geophysical Fluid Dynamics 4 1.3 Distinguishing Attributes of Geophysical
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS)
 Atmospheric Science-ATS (ATS) 1 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS) Courses ATS 150 Science of Global Climate Change Credits: 3 (3-0-0) Physical basis of climate change. Energy budget of the earth, the greenhouse
Atmospheric Science-ATS (ATS) 1 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS) Courses ATS 150 Science of Global Climate Change Credits: 3 (3-0-0) Physical basis of climate change. Energy budget of the earth, the greenhouse
Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday. Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1
 Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1 Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Pressure Atmospheric Pressure & Its Measurement Ideal Gas Law (Equation of State) Pressure Gradient
Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1 Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Pressure Atmospheric Pressure & Its Measurement Ideal Gas Law (Equation of State) Pressure Gradient
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation
 3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
Scale Analysis of the Equations of Motion
 hen are curvature terms important? Important for GCMs and large-scale (global) weather. ere, we consider sub-global scale referred to as synoptic scale. Scale Analysis of the Equations of Motion e use
hen are curvature terms important? Important for GCMs and large-scale (global) weather. ere, we consider sub-global scale referred to as synoptic scale. Scale Analysis of the Equations of Motion e use
LECTURE 28. The Planetary Boundary Layer
 LECTURE 28 The Planetary Boundary Layer The planetary boundary layer (PBL) [also known as atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)] is the lower part of the atmosphere in which the flow is strongly influenced
LECTURE 28 The Planetary Boundary Layer The planetary boundary layer (PBL) [also known as atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)] is the lower part of the atmosphere in which the flow is strongly influenced
BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere. Potential temperature θ. Rossby Ertel potential vorticity
 BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere Need to introduce a new measure of the buoyancy Potential temperature θ In a compressible fluid, the relevant measure
BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere Need to introduce a new measure of the buoyancy Potential temperature θ In a compressible fluid, the relevant measure
Synoptic Meteorology I: Other Force Balances
 Synoptic Meteorology I: Other Force Balances For Further Reading Section.1.3 of Mid-Latitude Atmospheric Dynamics by J. Martin provides a discussion of the frictional force and considerations related to
Synoptic Meteorology I: Other Force Balances For Further Reading Section.1.3 of Mid-Latitude Atmospheric Dynamics by J. Martin provides a discussion of the frictional force and considerations related to
Eliassen-Palm Theory
 Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
Synoptic Meteorology
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
Dynamics Rotating Tank
 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science - IACETH Atmospheric Physics Lab Work Dynamics Rotating Tank Large scale flows on different latitudes of the rotating Earth Abstract The large scale atmospheric
Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science - IACETH Atmospheric Physics Lab Work Dynamics Rotating Tank Large scale flows on different latitudes of the rotating Earth Abstract The large scale atmospheric
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Geostrophic and Quasi-Geostrophic Balances
 Geostrophic and Quasi-Geostrophic Balances Qiyu Xiao June 19, 2018 1 Introduction Understanding how the atmosphere and ocean behave is important to our everyday lives. Techniques such as weather forecasting
Geostrophic and Quasi-Geostrophic Balances Qiyu Xiao June 19, 2018 1 Introduction Understanding how the atmosphere and ocean behave is important to our everyday lives. Techniques such as weather forecasting
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997)
 Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
MET 4300/5355 Severe Weather
 MET 4300/5355 Severe Weather Lecture 1 Introduction Course Organization Tu/Th 11:00AM-12:15 PM, AHC5 Rm357 Haiyan Jiang, 305-348-2984, AHC5 Rm371, haiyan.jiang@fiu.edu Office Hours Tu 12:15-1:15 PM, or
MET 4300/5355 Severe Weather Lecture 1 Introduction Course Organization Tu/Th 11:00AM-12:15 PM, AHC5 Rm357 Haiyan Jiang, 305-348-2984, AHC5 Rm371, haiyan.jiang@fiu.edu Office Hours Tu 12:15-1:15 PM, or
Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems
 Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems Introduction Spring Semester 2018 Heini Wernli Outline of lecture course See also www.iac.ethz.ch/edu/courses/master/modules/mesoscale-atmospheric-systems.html 20 Feb Introduction
Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems Introduction Spring Semester 2018 Heini Wernli Outline of lecture course See also www.iac.ethz.ch/edu/courses/master/modules/mesoscale-atmospheric-systems.html 20 Feb Introduction
Instabilities and Basic Convection
 Instabilities and Basic Convection Buoyant Instability (gravity is restoring force) Assume a stationary incompressible fluid (like water), so that ρ = ρ 0 + ρ/ z z and also it is in hydrostatic equilibrium
Instabilities and Basic Convection Buoyant Instability (gravity is restoring force) Assume a stationary incompressible fluid (like water), so that ρ = ρ 0 + ρ/ z z and also it is in hydrostatic equilibrium
Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD
 P1.57 GOES WMSI PROGRESS AND DEVELOPMENTS Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD 1. INTRODUCTION A multi-parameter index has
P1.57 GOES WMSI PROGRESS AND DEVELOPMENTS Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD 1. INTRODUCTION A multi-parameter index has
Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems. Surface fronts and frontogenesis. 06 March 2018 Heini Wernli. 06 March 2018 H. Wernli 1
 Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems Surface fronts and frontogenesis 06 March 2018 Heini Wernli 06 March 2018 H. Wernli 1 Temperature (degc) Frontal passage in Mainz on 26 March 2010 06 March 2018 H. Wernli
Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems Surface fronts and frontogenesis 06 March 2018 Heini Wernli 06 March 2018 H. Wernli 1 Temperature (degc) Frontal passage in Mainz on 26 March 2010 06 March 2018 H. Wernli
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination Wednesday, November 2, :00 2:50 PM
 SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination Wednesday, November 2, 2005 2:00 2:50 PM This is a closed book exam. Calculators are allowed. (101 total points.) MULTIPLE CHOICE (3 points
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination Wednesday, November 2, 2005 2:00 2:50 PM This is a closed book exam. Calculators are allowed. (101 total points.) MULTIPLE CHOICE (3 points
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries
 11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann
 Place an X here to count it double! Name: Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann If you wish to have the final exam count double and replace your midterm score, place an X in the box above. As
Place an X here to count it double! Name: Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann If you wish to have the final exam count double and replace your midterm score, place an X in the box above. As
Examples of Pressure Gradient. Pressure Gradient Force. Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances. Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion 2/7/2019
 Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
1/27/2010. With this method, all filed variables are separated into. from the basic state: Assumptions 1: : the basic state variables must
 Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification References: A Global View of Tropical Cyclones, Elsberry (ed.) Global Perspectives on Tropical Cylones:
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification References: A Global View of Tropical Cyclones, Elsberry (ed.) Global Perspectives on Tropical Cylones:
Circulation and Vorticity
 Circulation and Vorticity Example: Rotation in the atmosphere water vapor satellite animation Circulation a macroscopic measure of rotation for a finite area of a fluid Vorticity a microscopic measure
Circulation and Vorticity Example: Rotation in the atmosphere water vapor satellite animation Circulation a macroscopic measure of rotation for a finite area of a fluid Vorticity a microscopic measure
Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models. Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005)
 Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Observational motivation 2. Forced planetary waves in the stratosphere 3. Traveling planetary
Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Observational motivation 2. Forced planetary waves in the stratosphere 3. Traveling planetary
Control Volume. Dynamics and Kinematics. Basic Conservation Laws. Lecture 1: Introduction and Review 1/24/2017
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Review of fundamental mathematical tools Fundamental and apparent forces Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Review of fundamental mathematical tools Fundamental and apparent forces Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study
IV. Atmospheric Science Section
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines IV. Atmospheric Science Section 1. Introduction, Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Learning objectives: Understand the basic characteristics
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines IV. Atmospheric Science Section 1. Introduction, Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Learning objectives: Understand the basic characteristics
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones
 Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 )
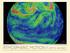 http://earth.nullschool.net/ ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 ) INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office:
http://earth.nullschool.net/ ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 ) INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office:
GEF 1100 Klimasystemet. Chapter 7: Balanced flow
 GEF1100 Autumn 2016 27.09.2016 GEF 1100 Klimasystemet Chapter 7: Balanced flow Prof. Dr. Kirstin Krüger (MetOs, UiO) 1 Lecture Outline Ch. 7 Ch. 7 Balanced flow 1. Motivation 2. Geostrophic motion 2.1
GEF1100 Autumn 2016 27.09.2016 GEF 1100 Klimasystemet Chapter 7: Balanced flow Prof. Dr. Kirstin Krüger (MetOs, UiO) 1 Lecture Outline Ch. 7 Ch. 7 Balanced flow 1. Motivation 2. Geostrophic motion 2.1
Chapter 3. Stability theory for zonal flows :formulation
 Chapter 3. Stability theory for zonal flows :formulation 3.1 Introduction Although flows in the atmosphere and ocean are never strictly zonal major currents are nearly so and the simplifications springing
Chapter 3. Stability theory for zonal flows :formulation 3.1 Introduction Although flows in the atmosphere and ocean are never strictly zonal major currents are nearly so and the simplifications springing
1/25/2010. Circulation and vorticity are the two primary
 Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics
 Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics M 1 ( ) e R ε er Tropical v Midlatitude Meteorology Why is the general circulation and synoptic weather systems in the tropics different to the those in the
Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics M 1 ( ) e R ε er Tropical v Midlatitude Meteorology Why is the general circulation and synoptic weather systems in the tropics different to the those in the
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
1/3/2011. This course discusses the physical laws that govern atmosphere/ocean motions.
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2)
 Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
THE INFLUENCE OF THE GREAT LAKES ON NORTHWEST SNOWFALL IN THE SOUTHERN APPALACHIANS
 P2.18 THE INFLUENCE OF THE GREAT LAKES ON NORTHWEST SNOWFALL IN THE SOUTHERN APPALACHIANS Robbie Munroe* and Doug K. Miller University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, North Carolina B. Holloway
P2.18 THE INFLUENCE OF THE GREAT LAKES ON NORTHWEST SNOWFALL IN THE SOUTHERN APPALACHIANS Robbie Munroe* and Doug K. Miller University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, North Carolina B. Holloway
Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability
 Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability J. H. LaCasce, University of Oslo J. Pedlosky, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution P. E. Isachsen, Norwegian Meteorological
Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability J. H. LaCasce, University of Oslo J. Pedlosky, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution P. E. Isachsen, Norwegian Meteorological
psio 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Answer key
 NAME: psio 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Answer key Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100
NAME: psio 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Answer key Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100
The Behaviour of the Atmosphere
 3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
Dust devils, water spouts, tornados
 Balanced flow Things we know Primitive equations are very comprehensive, but there may be a number of vast simplifications that may be relevant (e.g., geostrophic balance). Seems that there are things
Balanced flow Things we know Primitive equations are very comprehensive, but there may be a number of vast simplifications that may be relevant (e.g., geostrophic balance). Seems that there are things
The perturbation pressure, p, can be represented as the sum of a hydrostatic pressure perturbation p h and a nonhydrostatic pressure perturbation p nh
 z = The perturbation pressure, p, can be represented as the sum of a hydrostatic pressure perturbation p h and a nonhydrostatic pressure perturbation p nh, that is, p = p h + p nh. (.1) The former arises
z = The perturbation pressure, p, can be represented as the sum of a hydrostatic pressure perturbation p h and a nonhydrostatic pressure perturbation p nh, that is, p = p h + p nh. (.1) The former arises
ERTH 465 Fall Lab 3. Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness. (300 points)
 Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 3 Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness (300 points) 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show
Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 3 Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness (300 points) 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show
