Today in Astronomy 142: the Big Bang
|
|
|
- Delphia Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Today in Astronomy 142: the Big Bang The Universe: expanding, isotropic, and homogeneous. Big-Bang and Steady- State cosmology. Alpher, Herman and decoupling. Penzias and Wilson and the detection of the Big Bang s blast. Bob Wilson (left) and Arno Penzias (right) with the horn antenna they used to discover the cosmic microwave background (Bell Laboratories). 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
2 Hubble and the structure of the Universe When last seen (in lecture on 4 April 2013), Hubble had shown that the Universe expands, according to vr = H 0 d. Two more of Hubble s conclusions about the distribution of galaxies in the Universe, based on a huge collection of observations with the world s largest telescopes during the 1920s and early 1930s (Hubble 1934): The Universe is isotropic: on large scales the distribution of galaxies on the sky looks the same in all directions, from our viewpoint. Edwin Hubble at the Newtonian focus of the Hooker 100-inch (Life). 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
3 Hubble and the structure of the Universe (continued) By small scale, here, we mean similar to or smaller than the typical distance between galaxy clusters; by large scale, much greater than the typical distance between clusters, but still small compared to the observed size of the Universe. Recall: galaxies are typically 1Mpc apart; cluster cores are typically less than a few Mpc in radius; clusters are typically 10 Mpc apart. Obviously the Universe is not uniform on small scales; the sky is full of stars, galaxies, and clusters of galaxies, containing mass at relatively high density, with virtually empty space in between. By this definition we will turn out still to be OK with the assumption of Euclidean geometry, despite what comes next 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
4 Hubble and the structure of the Universe (continued) The Hubble Space Telescope/ACS Ultra Deep Field (Beckwith et al. 2004). 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
5 Isotropy of the Universe on large scales: modern measurements Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey: SDSS covered 28% of the sky (3.55 ster = ) centered on the Galactic poles, and identified all the galaxies brighter than R = Next page 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
6 Isotropy of the Universe on large scales: modern measurements (continued) Each dot is a galaxy; each smudge or filament a cluster or supercluster. Isotropy on the scale represented by these circles s diameter means that approximately the same numbers of galaxies are contained within them, no matter where on the sky we put them, which is evidently true here. Sloan Digital Sky Survey 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
7 Hubble and the structure of the Universe (continued) The Universe is homogeneous: the number density of galaxies is uniform on large scales. In other words, the Universe looks the same from any viewpoint. This Hubble found by observing great numbers of galaxies in chosen parts of the sky and plotting the number per solid angle brighter than flux f0, N( f > f0), as a function of, thus seeing that f 0 ( ) 32 N f > f0 = Af0. (See Homework #6, and the lecture notes for 19 March.) Nowadays you can see this in a glance, too (next page). Since the Universe is homogeneous and expanding, we would see the same recession no matter where we stood. That is, there is no unique center in space for the expansion, as in an ordinary explosion and blast wave. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
8 Homogeneity of the Universe on large scales: modern measurements Redshifts and colorcoded luminosity (blue-red = low-high) of the galaxies in the SDSS stripes along the celestial equator, 2.5 wide, ignoring the Milky Way. Sloan Digital Sky Survey 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
9 Homogeneity of the Universe on large scales: modern measurements (continued) Homogeneity on the scale of these circles s diameter means that approximately the same numbers of galaxies are contained within them, no matter where we put them within the Universe s volume, which is evidently true in this picture. Sloan Digital Sky Survey 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
10 Why the expansion looks the same from all viewpoints In Euclidean (flat) space, is along r, so v = v v v = dr dt BC BA CA = H0( rba rca ) = H0 rbc. Thus observers in galaxies B and C see the same Hubble law that we do: the expansion looks the same from A, B and C. C r CA r BC r BA A (Milky Way) B 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
11 Early post-hubble cosmology Theorists immediately applied Einstein s general theory of relativity to isotropic, homogeneous, expanding universes, and revealed a problem: All such model universes displayed a mass-density singularity at the origin. In fact it can be proven, quite generally, that this is so (Hawking and Penrose, 1970). Typical distance between galaxies, in units of the present distance Such singularities unphysical at first glance should arouse the suspicion of theoretical physicists. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring Singularity Open universe (expands forever) Closed universe t (years)??
12 Early post-hubble cosmology (continued) Accordingly, many leading cosmologists Einstein, de Sitter, Hoyle, Gold, Burbidge, Arp, Chairman Mao promulgated steady-state models of the Universe, in which singularities are not realized like, for example, the singularity at r = 0 for the force between two finite-size masses in Newtonian gravity. and in which the density of the Universe is constant on the (time) average despite the Hubble expansion. which they did by positing steady creation of matter out of nothing, considering this violation of energy conservation less fishy than mass-density singularities. Big Bang was originally Sir Fred Hoyle s pejorative term for models with mass-density singularities. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
13 Early post-hubble cosmology (continued) Unintimidated, those who worried less about singularities than energy conservation notably George Gamow adopted Big Bang as the short description of their class of models. Observational tests gradually started going in favor of Big Bang cosmology in the 1950s e.g. number counts of faint radio galaxies, which indicated a peak in the volume density of these objects in the early Universe (= higher density at earlier times and galaxy evolution). but the best observational test, proposed in the late 1940s by Gamow s students Ralph Alpher and Bob Herman, was ignored and almost forgotten. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
14 Early post- Hubble cosmology (continued) ( ) 32 N f > f0 = Af 0 again: radio source count as a function of brightness (Pooley & Ryle 1968). If the Universe were uniform and constant in density, and galaxies never changed, a line with slope -3/2 (dashed line) would have been obtained. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
15 Alpher, Herman and Decoupling Alpher and Herman presumed that the Universe started off very hot and dense, and cooled as it expanded, down to the very low temperature range corresponding to the darkness of the night sky. Then A&H identified an Event undergone by the expansion at a specific temperature: decoupling, meaning that atoms could suddenly form in large quantities from free electrons and nuclei, because the photons had cooled (redshifted) sufficiently during the expansion that they were incapable of ionizing atoms. In hydrogen, in the laboratory, this transition takes place at about T = 3000 K. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
16 Alpher, Herman and Decoupling (continued) This event is called decoupling because at temperatures above 3000 K, matter is opaque to radiation at the same (blackbody) temperature, as the average photon will be absorbed by ionization of the first neutral atom it finds. Thus matter and radiation are tightly coupled by ionization and recombination in the early Universe. But, by the same token, matter below 3000 K is transparent to radiation at the same temperature. Thus radiation and matter decouple live separate thermodynamic lives, are no longer in equilibrium after the Universe cools past this point. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
17 Alpher, Herman and Decoupling (continued) A&H realized that this means the Universe has a photosphere, just like a star does: the decoupling surface. Since the Universe is transparent after decoupling, we should be able to see all the way to the 3000 K surface. Since the Universe is opaque before decoupling, the surface emits like any other 3000 K black body. The light started off visible, but owing to our great distance of its source it would be redshifted to much longer wavelengths April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring Intensity (erg/sec/cm2/ster) Wavelength (µm) 1500 K 3000 K 6000 K
18 Alpher, Herman and Decoupling (continued) A&H also realized that, since the decoupling surface is close to the original singularity, the light should appear isotropic to us. In analogy with a black-hole singularity: Light emitted from within a black hole horizon cannot escape (and therefore must fall into the singularity), no matter what direction it is emitted: all light paths within the horizon end at the singularity. (See next slide.) By the same token since light can travel in either direction along these paths light emitted from the surroundings of the singularity would seem to an observer within the horizon to arrive from all directions, rather than one particular direction. It would look as if the singularity s surroundings filled the sky. (See the slide after next.) 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
19 Within a black-hole horizon Us (emitting light) Paths of light through warped space Singularity 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
20 Analogy with the Universal singularity Us (looking at the sky) Paths of light through warped space Singularity Decoupling surface 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
21 Alpher, Herman and Decoupling (continued) Finally, A&H realized that the spectrum of redshifted blackbody radiation would appear to be that of a colder, black body (they estimated 5 K), and noted that a steady-state Universe would be incapable of producing such radiation. Recall : λ 0 1 z λ = + (z = redshift, sub-0 = present time) At decoupling surface, the energy per unit time, area, solid angle and bandwidth it emits, S λ, is given by the Planck function at the decoupling temperature T: ( ) S = B T λ 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring λ
22 Alpher, Herman and Decoupling (continued) Other quantities in small bandwidth dλ at wavelength λ: 4π Energy density duλ = Bλ ( T ) dλ c 4π λ Photon number density dnλ = Bλ ( T ) dλ c hc Number of photons 3 4π λ in cube on a side dnλ = Bλ ( T ) dλ c hc 3 Same as for a present- 4π dn 0 λ = 0 λ = S d 0 λ λ day cube on a side c hc Thus we can obtain the present, observed spectrum of the decoupling surface, S λ April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
23 Alpher, Herman and Decoupling (continued) 3 λ dλ Sλ = B T 0 λ λ dλ ( ) But these lengths change by the same factor as the U expands: 0 = λλ 0 = dλdλ hc 1 2hc 1 = = = B λ hc exp 1 λ 0 hc exp 0 1 λkt λ0k T λ ( T ) where T = T., That is, the spectrum of the decoupling surface, as presently observed, should be a blackbody at temperature T 0 = T April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
24 Penzias, Wilson and the Cosmic Background In 1965, Bob Wilson and Arno Penzias (Bell Telephone Laboratories) were working on a very sensitive microwave receiver and antenna they built for satellite communication. They were trying to tune it up to reach ideal performance, but persistently found extra noise power for which they couldn t account. They knew nothing of the Alpher-Herman prediction. The extra power was like that of a blackbody with temperature 2.7 K. It was the same no matter which direction they pointed their antenna. ( If it comes from the sky, it s isotropic.) They were grasping at straws for an explanation, when they were paid a visit by radio astronomer Bernie Burke, a professor at MIT. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
25 Penzias, Wilson and the Cosmic Background (continued) Burke knew of efforts at Princeton led by Dicke and Peebles to build a sensitive microwave receiver and antenna to look for the Big Bang radiation predicted by Alpher and Herman, but were having technical troubles. He introduced the Bell Labs group to the Princeton group. It was quickly noticed that Penzias and Wilson had indeed detected that relict radiation, now called the cosmic microwave background (CMB). Thus the blast from the Big Bang is seen directly. This is the sturdiest support for Big Bang models of the origin of the Universe. For this immensely influential discovery, Penzias and Wilson shared the 1978 Nobel Prize in Physics. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
26 The cosmic microwave background The CMB is extremely isotropic. COBE image of the sky at λ = 5.7 mm. Color code: blue (red) is 0 K (4.0 K). Same, with blue (red) K (2.731 K); dominated by the dipole anisotropy from our Galaxy s 570 km/s motion relative to the average expansion. Next page: WMAP all-sky image with Galaxy and dipole removed. 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
27 The cosmic microwave background (continued) From WMAP: Bennett et al ( TT) max = April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
28 The cosmic microwave background (continued) Intensity (MJy/sterad) Only T was adjusted in fitting the curve to the data points. COBE measurements of the background intensity as a function of frequency. (Courtesy of Ned Wright and the COBE FIRAS team.) Pretty good blackbody 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring Wavenumber, ν c (cm ) For this result, John Mather (NASA/GSFC) shared the 2006 Nobel prize in physics.
29 How far away is the decoupling surface? The redshift of decoupling can be obtained almost trivially: λ0 T 3000 K 1 + z = = 1100 λ T K z The most distant galaxy hitherto detected has z = 9.4 (detected via gamma-ray burst); the most distant quasar has z = 7.1. A few hints of higher-redshift objects have appeared at z ~ 11. So: substantially further away than any galaxy. John Mather (NASA photo) 16 April 2013 Astronomy 142, Spring
Today in Astronomy 102: the Big Bang
 Today in Astronomy 102: the Big Bang Cosmological models: Big Bang and Steady State. Observational tests of the models, and direct observation of the Big Bang. The cosmic microwave background: the appearance
Today in Astronomy 102: the Big Bang Cosmological models: Big Bang and Steady State. Observational tests of the models, and direct observation of the Big Bang. The cosmic microwave background: the appearance
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter. Olber s Paradox. Cosmology. Olber s Paradox. Assumptions 4/20/18
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter Cosmology ³The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³Key moments: ²Einstein General Theory of Relativity ²Hubble
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter Cosmology ³The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³Key moments: ²Einstein General Theory of Relativity ²Hubble
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D.
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter 17-2 Cosmology ³ The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³ Key moments: ² Einstein General Theory of Relativity
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter 17-2 Cosmology ³ The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³ Key moments: ² Einstein General Theory of Relativity
Lecture #24: Plan. Cosmology. Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe
 Lecture #24: Plan Cosmology Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe Reminder: Redshifts and the Expansion of the Universe Early 20 th century astronomers noted: Spectra from most
Lecture #24: Plan Cosmology Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe Reminder: Redshifts and the Expansion of the Universe Early 20 th century astronomers noted: Spectra from most
Island Universes. Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe.
 Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
Implications of the Hubble Law: - it is not static, unchanging - Universe had a beginning!! - could not have been expanding forever HUBBLE LAW:
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe. Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is changing (getting bigger!) - it is not static, unchanging
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Model Universe Including Pressure
 Model Universe Including Pressure The conservation of mass within the expanding shell was described by R 3 ( t ) ρ ( t ) = ρ 0 We now assume an Universe filled with a fluid (dust) of uniform density ρ,
Model Universe Including Pressure The conservation of mass within the expanding shell was described by R 3 ( t ) ρ ( t ) = ρ 0 We now assume an Universe filled with a fluid (dust) of uniform density ρ,
Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006
 Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Information Makeup quiz Wednesday, May 31, 5-6PM, Planetarium Review Session, Monday, June 5 6PM, Planetarium Cosmology Study of the universe
Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Information Makeup quiz Wednesday, May 31, 5-6PM, Planetarium Review Session, Monday, June 5 6PM, Planetarium Cosmology Study of the universe
26. Cosmology. Significance of a dark night sky. The Universe Is Expanding
 26. Cosmology Significance of a dark night sky The Universe is expanding The Big Bang initiated the expanding Universe Microwave radiation evidence of the Big Bang The Universe was initially hot & opaque
26. Cosmology Significance of a dark night sky The Universe is expanding The Big Bang initiated the expanding Universe Microwave radiation evidence of the Big Bang The Universe was initially hot & opaque
Chapter 17 Cosmology
 Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
COSMOLOGY The Universe what is its age and origin?
 COSMOLOGY The Universe what is its age and origin? REVIEW (SUMMARY) Oppenheimer Volkhoff limit: upper limit to mass of neutron star remnant more than 1.4 M à neutron degeneracy Supernova à extremely dense
COSMOLOGY The Universe what is its age and origin? REVIEW (SUMMARY) Oppenheimer Volkhoff limit: upper limit to mass of neutron star remnant more than 1.4 M à neutron degeneracy Supernova à extremely dense
The Cosmic Microwave Background
 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney June 26, 2018 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney November 28, 2016 Cosmic star formation history inf 10 4 3 2 1 0 z Peak of
The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney June 26, 2018 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney November 28, 2016 Cosmic star formation history inf 10 4 3 2 1 0 z Peak of
PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall 2016
 PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall 2016 Online evaluations open Announcements Final Exam Thursday, 15 December, 10am - 12, noon In-class NPB 1002
PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall 2016 Online evaluations open Announcements Final Exam Thursday, 15 December, 10am - 12, noon In-class NPB 1002
Introduction and Fundamental Observations
 Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Introduction and Fundamental Observations Prelude Cosmology is the study of the universe taken as a whole ruthless simplification necessary (e.g. homogeneity)! Cosmology
Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Introduction and Fundamental Observations Prelude Cosmology is the study of the universe taken as a whole ruthless simplification necessary (e.g. homogeneity)! Cosmology
Introduction. How did the universe evolve to what it is today?
 Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Astronomy 210 Final. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Outline
 Astronomy 210 Final This Class (Lecture 40): The Big Bang Next Class: The end HW #11 Due next Weds. Final is May 10 th. Review session: May 6 th or May 9 th? Designed to be 2 hours long 1 st half is just
Astronomy 210 Final This Class (Lecture 40): The Big Bang Next Class: The end HW #11 Due next Weds. Final is May 10 th. Review session: May 6 th or May 9 th? Designed to be 2 hours long 1 st half is just
Astronomy 1 Winter Lecture 24; March
 Astronomy 1 Winter 2011 Lecture 24; March 7 2011 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to special relativity Introduction to general relativity Introduction to black holes, stellar and supermassive Today..
Astronomy 1 Winter 2011 Lecture 24; March 7 2011 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to special relativity Introduction to general relativity Introduction to black holes, stellar and supermassive Today..
Cosmology. Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick.
 Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
A brief history of cosmological ideas
 A brief history of cosmological ideas Cosmology: Science concerned with the origin and evolution of the universe, using the laws of physics. Cosmological principle: Our place in the universe is not special
A brief history of cosmological ideas Cosmology: Science concerned with the origin and evolution of the universe, using the laws of physics. Cosmological principle: Our place in the universe is not special
Cosmology. An Analogy 11/28/2010. Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe
 Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
John Mather Visit Nobel Prize in Physics 2006 for Cosmic Microwave Background measurements
 John Mather Visit Nobel Prize in Physics 006 for Cosmic Microwave Background measurements NEXT WEEK Wednesday :0-:00 BPS 00 BS session with astro students & faculty. Wednesday 8PM BPS 0 (refreshments at
John Mather Visit Nobel Prize in Physics 006 for Cosmic Microwave Background measurements NEXT WEEK Wednesday :0-:00 BPS 00 BS session with astro students & faculty. Wednesday 8PM BPS 0 (refreshments at
Cosmology. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16
 Cosmology Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16 Expansion of the Universe 1923 - Edwin Hubble resolved Andromeda Nebula into separate stars. 1929 - Hubble compared radial velocity versus distance for 18 nearest galaxies.
Cosmology Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16 Expansion of the Universe 1923 - Edwin Hubble resolved Andromeda Nebula into separate stars. 1929 - Hubble compared radial velocity versus distance for 18 nearest galaxies.
Chapter 26: Cosmology
 Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Galaxy A has a redshift of 0.3. Galaxy B has a redshift of 0.6. From this information and the existence of the Hubble Law you can conclude that
 Galaxy A has a redshift of 0.3. Galaxy B has a redshift of 0.6. From this information and the existence of the Hubble Law you can conclude that A) Galaxy B is two times further away than Galaxy A. B) Galaxy
Galaxy A has a redshift of 0.3. Galaxy B has a redshift of 0.6. From this information and the existence of the Hubble Law you can conclude that A) Galaxy B is two times further away than Galaxy A. B) Galaxy
II. The Universe Around Us. ASTR378 Cosmology : II. The Universe Around Us 23
 II. The Universe Around Us ASTR378 Cosmology : II. The Universe Around Us 23 Some Units Used in Astronomy 1 parsec distance at which parallax angle is 1 ; 1 pc = 3.086 10 16 m ( 3.26 light years; 1 kpc
II. The Universe Around Us ASTR378 Cosmology : II. The Universe Around Us 23 Some Units Used in Astronomy 1 parsec distance at which parallax angle is 1 ; 1 pc = 3.086 10 16 m ( 3.26 light years; 1 kpc
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology
 Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology Lecture 2; January 8 2014 Previously on PHYS133 Units in astrophysics Olbers paradox The night sky is dark. Inconsistent with and eternal, static and infinite
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology Lecture 2; January 8 2014 Previously on PHYS133 Units in astrophysics Olbers paradox The night sky is dark. Inconsistent with and eternal, static and infinite
Lecture 03. The Cosmic Microwave Background
 The Cosmic Microwave Background 1 Photons and Charge Remember the lectures on particle physics Photons are the bosons that transmit EM force Charged particles interact by exchanging photons But since they
The Cosmic Microwave Background 1 Photons and Charge Remember the lectures on particle physics Photons are the bosons that transmit EM force Charged particles interact by exchanging photons But since they
Astro-2: History of the Universe
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 7; May 2 2013 Previously on astro-2 A scientific theory is a logically self-consistent model or framework for describing the behavior of a related set of natural
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 7; May 2 2013 Previously on astro-2 A scientific theory is a logically self-consistent model or framework for describing the behavior of a related set of natural
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence
 CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN
 Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. Peering out/back into the Universe As
Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. Peering out/back into the Universe As
The Big Bang Theory was first proposed in the late 1920 s. This singularity was incredibly dense and hot.
 The Big Bang Theory was first proposed in the late 1920 s. It states that there was an infinitely small, infinitely dense point that contained everything that is the universe. This singularity was incredibly
The Big Bang Theory was first proposed in the late 1920 s. It states that there was an infinitely small, infinitely dense point that contained everything that is the universe. This singularity was incredibly
Astronomy: The Big Picture. Outline. What does Hubble s Law mean?
 Last Homework is due Friday 11:50 am Honor credit need to have those papers this week! Estimated grades are posted. Does not include HW 8 or Extra Credit THE FINAL IS DECEMBER 15 th : 7-10pm! Astronomy:
Last Homework is due Friday 11:50 am Honor credit need to have those papers this week! Estimated grades are posted. Does not include HW 8 or Extra Credit THE FINAL IS DECEMBER 15 th : 7-10pm! Astronomy:
1920s 1990s (from Friedmann to Freedman)
 20 th century cosmology 1920s 1990s (from Friedmann to Freedman) theoretical technology available, but no data 20 th century: birth of observational cosmology Hubble s law ~1930 Development of astrophysics
20 th century cosmology 1920s 1990s (from Friedmann to Freedman) theoretical technology available, but no data 20 th century: birth of observational cosmology Hubble s law ~1930 Development of astrophysics
The Big Bang Theory. Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra
 The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
The Early Universe: A Journey into the Past
 Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity Galileo and falling
Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity Galileo and falling
i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE?
 i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Hubble s discovery that most distant galaxies are receding from us tells us that we are at the center of the Universe B. The Universe started
i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Hubble s discovery that most distant galaxies are receding from us tells us that we are at the center of the Universe B. The Universe started
The Early Universe: A Journey into the Past
 The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Galileo and falling bodies Galileo Galilei: all bodies fall at the same speed force needed to accelerate a body is
The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Galileo and falling bodies Galileo Galilei: all bodies fall at the same speed force needed to accelerate a body is
Olbers Paradox. Lecture 14: Cosmology. Resolutions of Olbers paradox. Cosmic redshift
 Lecture 14: Cosmology Olbers paradox Redshift and the expansion of the Universe The Cosmological Principle Ω and the curvature of space The Big Bang model Primordial nucleosynthesis The Cosmic Microwave
Lecture 14: Cosmology Olbers paradox Redshift and the expansion of the Universe The Cosmological Principle Ω and the curvature of space The Big Bang model Primordial nucleosynthesis The Cosmic Microwave
Taking the Measure of the Universe. Gary Hinshaw University of British Columbia TRIUMF Saturday Series 24 November 2012
 Taking the Measure of the Universe Gary Hinshaw University of British Columbia TRIUMF Saturday Series 24 November 2012 The Big Bang Theory What is wrong with this picture? The Big Bang Theory The Big bang
Taking the Measure of the Universe Gary Hinshaw University of British Columbia TRIUMF Saturday Series 24 November 2012 The Big Bang Theory What is wrong with this picture? The Big Bang Theory The Big bang
CMB. Suggested Reading: Ryden, Chapter 9
 CMB Suggested Reading: Ryden, Chapter 9 1934, Richard Tolman, blackbody radiation in an expanding universe cools but retains its thermal distribution and remains a blackbody 1941, Andrew McKellar, excitation
CMB Suggested Reading: Ryden, Chapter 9 1934, Richard Tolman, blackbody radiation in an expanding universe cools but retains its thermal distribution and remains a blackbody 1941, Andrew McKellar, excitation
Chapter 22 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. The Birth of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 22 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory Our goals for learning: What were conditions like in the early universe?
Chapter 22 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory Our goals for learning: What were conditions like in the early universe?
The Expanding Universe
 Announcements (this page posted as part of lecture notes on Angel) Homework 7 due late at night Monday April 23 (6:30AM Apr 24) Homework 8 now available on Angel Due late at night Friday April 27 (6:30AM
Announcements (this page posted as part of lecture notes on Angel) Homework 7 due late at night Monday April 23 (6:30AM Apr 24) Homework 8 now available on Angel Due late at night Friday April 27 (6:30AM
Astronomy 422. Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Key concepts: The CMB Recombination Radiation and matter eras Next time: Astro 422 Peer Review - Make sure to read all 6 proposals and send in rankings
Astronomy 422 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Key concepts: The CMB Recombination Radiation and matter eras Next time: Astro 422 Peer Review - Make sure to read all 6 proposals and send in rankings
9.2 The Universe. p. 368
 9.2 The Universe p. 368 Cosmology the study of the universe, including its origin, how it is changing, and its future. The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) The American astronomer Edwin Hubble (1889-1953)
9.2 The Universe p. 368 Cosmology the study of the universe, including its origin, how it is changing, and its future. The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) The American astronomer Edwin Hubble (1889-1953)
UNIT 3 The Study of the. Universe. Chapter 7: The Night Sky. Chapter 8: Exploring Our Stellar Neighbourhood. Chapter 9:The Mysterious.
 UNIT 3 The Study of the Universe Chapter 7: The Night Sky Chapter 8: Exploring Our Stellar Neighbourhood Chapter 9:The Mysterious Universe CHAPTER 9 The Mysterious Universe In this chapter, you will: identify
UNIT 3 The Study of the Universe Chapter 7: The Night Sky Chapter 8: Exploring Our Stellar Neighbourhood Chapter 9:The Mysterious Universe CHAPTER 9 The Mysterious Universe In this chapter, you will: identify
Today. Course Evaluations Open. Modern Cosmology. The Hot Big Bang. Age & Fate. Density and Geometry. Microwave Background
 Today Modern Cosmology The Hot Big Bang Age & Fate Density and Geometry Microwave Background Course Evaluations Open Cosmology The study of the universe as a physical system Historically, people have always
Today Modern Cosmology The Hot Big Bang Age & Fate Density and Geometry Microwave Background Course Evaluations Open Cosmology The study of the universe as a physical system Historically, people have always
Testing the Big Bang Idea
 Reading: Chapter 29, Section 29.2-29.6 Third Exam: Tuesday, May 1 12:00-2:00 COURSE EVALUATIONS - please complete these online (recitation and lecture) Last time: Cosmology I - The Age of the & the Big
Reading: Chapter 29, Section 29.2-29.6 Third Exam: Tuesday, May 1 12:00-2:00 COURSE EVALUATIONS - please complete these online (recitation and lecture) Last time: Cosmology I - The Age of the & the Big
Astronomy 114. Lecture35:TheBigBang. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture35:TheBigBang Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 35 09 May 2005 Read: Ch. 28,29 Astronomy 114 1/18 Announcements PS#8 due Monday!
Astronomy 114 Lecture35:TheBigBang Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 35 09 May 2005 Read: Ch. 28,29 Astronomy 114 1/18 Announcements PS#8 due Monday!
Astroparticle physics
 Timo Enqvist University of Oulu Oulu Southern institute lecture cource on Astroparticle physics 15.09.2009 15.12.2009 10 Cosmic microwave background Content 10.0 Small introduction 10.1 Cosmic microwave
Timo Enqvist University of Oulu Oulu Southern institute lecture cource on Astroparticle physics 15.09.2009 15.12.2009 10 Cosmic microwave background Content 10.0 Small introduction 10.1 Cosmic microwave
Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang. Expansion of the Universe. Big Bang Theory. Age of the Universe. Hubble s Law. Hubble s Law
 Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang Hubble s Law Universal recession: Slipher (1912) and Hubble found that all galaxies seem to be moving away from us: the greater the distance, the higher the redshift
Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang Hubble s Law Universal recession: Slipher (1912) and Hubble found that all galaxies seem to be moving away from us: the greater the distance, the higher the redshift
Module 3: Astronomy The Universe Topic 1 Content: Cosmology Presentation Notes
 Pretend that you have been given the opportunity to travel through time to explore cosmology. Cosmology is the study of how the universe formed and what will happen to it. Watch through your viewport as
Pretend that you have been given the opportunity to travel through time to explore cosmology. Cosmology is the study of how the universe formed and what will happen to it. Watch through your viewport as
The first 400,000 years
 The first 400,000 years All about the Big Bang Temperature Chronology of the Big Bang The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) The VERY early universe Our Evolving Universe 1 Temperature and the Big Bang
The first 400,000 years All about the Big Bang Temperature Chronology of the Big Bang The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) The VERY early universe Our Evolving Universe 1 Temperature and the Big Bang
v = H o d Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d):
 Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
The Science Missions of Columbia
 The Science Missions of Columbia Tools for Viewing The Universe Tools for Viewing The Universe & Columbia Shuttle Added Corrective Optics to the Hubble Space Telescope Hubble Discovers a New View of The
The Science Missions of Columbia Tools for Viewing The Universe Tools for Viewing The Universe & Columbia Shuttle Added Corrective Optics to the Hubble Space Telescope Hubble Discovers a New View of The
Hubble's Law. H o = 71 km/s / Mpc. The further a galaxy is away, the faster it s moving away from us. V = H 0 D. Modern Data.
 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe, addressing the grandest issues: How "big" is the Universe? Does it have an "edge"? What is its large-scale structure? How did
Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe, addressing the grandest issues: How "big" is the Universe? Does it have an "edge"? What is its large-scale structure? How did
Astronomy 122 Outline
 Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 26): The Primeval Fireball Next Class: Dark Matter & Dark Energy ICES Form!!! HW10 due Friday Hubble s Law implications An expanding Universe! Run in movie in
Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 26): The Primeval Fireball Next Class: Dark Matter & Dark Energy ICES Form!!! HW10 due Friday Hubble s Law implications An expanding Universe! Run in movie in
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Abstracts of Powerpoint Talks - newmanlib.ibri.org - The Cosmos. Robert C. Newman
 The Cosmos Robert C. Newman The Cosmos Carl Sagan said: "The cosmos is all that is, or ever was, or ever will be." If Christianity is true, Sagan is mistaken. But we can perhaps define the cosmos as "All
The Cosmos Robert C. Newman The Cosmos Carl Sagan said: "The cosmos is all that is, or ever was, or ever will be." If Christianity is true, Sagan is mistaken. But we can perhaps define the cosmos as "All
A100H Exploring the Universe: Big Bang Theory. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the : Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 21, 2016 Read: Chap 23 04/26/16 slide 1 Early Final Exam: Friday 29 Apr at 10:30 am 12:30 pm, here! Emphasizes
A100H Exploring the : Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 21, 2016 Read: Chap 23 04/26/16 slide 1 Early Final Exam: Friday 29 Apr at 10:30 am 12:30 pm, here! Emphasizes
Today in Astronomy 102: relativity and the Universe
 Today in Astronomy 102: relativity and the Universe General relativity and the Universe. Hubble: the Universe is observed to be homogeneous, isotropic, and expanding Redshift and distance: Hubble s Law
Today in Astronomy 102: relativity and the Universe General relativity and the Universe. Hubble: the Universe is observed to be homogeneous, isotropic, and expanding Redshift and distance: Hubble s Law
The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments
 The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments Intersection of physics (fundamental laws) and astronomy (contents of the universe)
The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments Intersection of physics (fundamental laws) and astronomy (contents of the universe)
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008
 Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
Cosmology. Clusters of galaxies. Redshift. Late 1920 s: Hubble plots distances versus velocities of galaxies. λ λ. redshift =
 Cosmology Study of the structure and origin of the universe Observational science The large-scale distribution of galaxies Looking out to extremely large distances The motions of galaxies Clusters of galaxies
Cosmology Study of the structure and origin of the universe Observational science The large-scale distribution of galaxies Looking out to extremely large distances The motions of galaxies Clusters of galaxies
The Cosmic Microwave Background
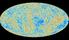 The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
The Big Bang. Olber s Paradox. Hubble s Law. Why is the night sky dark? The Universe is expanding and We cannot see an infinite Universe
 The Big Bang Olber s Paradox Why is the night sky dark? The Universe is expanding and We cannot see an infinite Universe Hubble s Law v = H0 d v = recession velocity in km/sec d = distance in Mpc H 0 =
The Big Bang Olber s Paradox Why is the night sky dark? The Universe is expanding and We cannot see an infinite Universe Hubble s Law v = H0 d v = recession velocity in km/sec d = distance in Mpc H 0 =
(Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 13: cosmic microwave background (and cosmic reionization!)
 (Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 13: cosmic microwave background (and cosmic reionization!) Welcome back! (four pictures on class website; add your own to http://s304.photobucket.com/albums/nn172/rugbt/) Results:
(Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 13: cosmic microwave background (and cosmic reionization!) Welcome back! (four pictures on class website; add your own to http://s304.photobucket.com/albums/nn172/rugbt/) Results:
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 26. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 26 Cosmology Units of Chapter 26 26.1 The Universe on the Largest Scales 26.2 The Expanding Universe 26.3 The Fate of the
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 26 Cosmology Units of Chapter 26 26.1 The Universe on the Largest Scales 26.2 The Expanding Universe 26.3 The Fate of the
Distances to Quasars. Quasars. The Luminosity Puzzle. Seyfert Galaxies. Seyfert galaxies have
 Quasars In 1963 Martin Schmidt was trying to understand some unidentified lines in the optical spectra from a star that had a strong radio signal He realized that the lines were Balmer lines that were
Quasars In 1963 Martin Schmidt was trying to understand some unidentified lines in the optical spectra from a star that had a strong radio signal He realized that the lines were Balmer lines that were
Cosmology. Big Bang and Inflation
 Cosmology Big Bang and Inflation What is the Universe? Everything we can know about is part of the universe. Everything we do know about is part of the universe. Everything! The Universe is expanding If
Cosmology Big Bang and Inflation What is the Universe? Everything we can know about is part of the universe. Everything we do know about is part of the universe. Everything! The Universe is expanding If
Universal redshift, the Hubble constant The cosmic background radiation until COBE
 Universal redshift, the Hubble constant The cosmic background radiation until COBE Sylwester Radomski Gesellschaft fuer Schwerionenforschung November 11, 2004 1 1 Dimensions in the Universe The scale of
Universal redshift, the Hubble constant The cosmic background radiation until COBE Sylwester Radomski Gesellschaft fuer Schwerionenforschung November 11, 2004 1 1 Dimensions in the Universe The scale of
Cosmology: Building the Universe.
 Cosmology: Building the Universe. The term has several different meanings. We are interested in physical cosmology - the study of the origin and development of the physical universe, and all the structure
Cosmology: Building the Universe. The term has several different meanings. We are interested in physical cosmology - the study of the origin and development of the physical universe, and all the structure
Physics Nobel Prize 2006
 Physics Nobel Prize 2006 Ghanashyam Date The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai http://www.imsc.res.in shyam@imsc.res.in Nov 4, 2006. Organization of the Talk Organization of the Talk Nobel Laureates
Physics Nobel Prize 2006 Ghanashyam Date The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai http://www.imsc.res.in shyam@imsc.res.in Nov 4, 2006. Organization of the Talk Organization of the Talk Nobel Laureates
Energy Source for Active Galactic Nuclei
 Quasars Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei Bright radio sources Name comes from Quasi-Stellar Radio Source, as they appeared to be stars! Can have clouds of gas near
Quasars Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei Bright radio sources Name comes from Quasi-Stellar Radio Source, as they appeared to be stars! Can have clouds of gas near
Cosmology: The History of the Universe
 Cosmology: The History of the Universe The Universe originated in an explosion called the Big Bang. Everything started out 13.7 billion years ago with zero size and infinite temperature. Since then, it
Cosmology: The History of the Universe The Universe originated in an explosion called the Big Bang. Everything started out 13.7 billion years ago with zero size and infinite temperature. Since then, it
Chapter 18. Cosmology in the 21 st Century
 Chapter 18 Cosmology in the 21 st Century Guidepost This chapter marks a watershed in our study of astronomy. Since Chapter 1, our discussion has focused on learning to understand the universe. Our outward
Chapter 18 Cosmology in the 21 st Century Guidepost This chapter marks a watershed in our study of astronomy. Since Chapter 1, our discussion has focused on learning to understand the universe. Our outward
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
Astronomy Hour Exam 2 March 10, 2011 QUESTION 1: The half-life of Ra 226 (radium) is 1600 years. If you started with a sample of 100 Ra 226
 Astronomy 101.003 Hour Exam 2 March 10, 2011 QUESTION 1: The half-life of Ra 226 (radium) is 1600 years. If you started with a sample of 100 Ra 226 atoms, approximately how many Ra 226 atoms would be left
Astronomy 101.003 Hour Exam 2 March 10, 2011 QUESTION 1: The half-life of Ra 226 (radium) is 1600 years. If you started with a sample of 100 Ra 226 atoms, approximately how many Ra 226 atoms would be left
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint
 Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
A100 Exploring the Universe Big Bang Theory and the Early Universe. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100 Exploring the Universe and the Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100-mdw@courses.umass.edu December 02, 2014 Read: Chap 23 12/04/14 slide 1 Assignment on Chaps 22 23, at the end of next week,
A100 Exploring the Universe and the Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100-mdw@courses.umass.edu December 02, 2014 Read: Chap 23 12/04/14 slide 1 Assignment on Chaps 22 23, at the end of next week,
The Dawn of Time - II. A Cosmos is Born
 The Dawn of Time - II. A Cosmos is Born Learning Objectives! Why does Olbers paradox show the Universe began?! How does Hubble s Law tell us the age of the Universe? If Hubble s Constant is large, is the
The Dawn of Time - II. A Cosmos is Born Learning Objectives! Why does Olbers paradox show the Universe began?! How does Hubble s Law tell us the age of the Universe? If Hubble s Constant is large, is the
If there is an edge to the universe, we should be able to see our way out of the woods. Olber s Paradox. This is called Olber s Paradox
 Suppose the Universe were not expanding, but was in some kind of steady state. How should galaxy recession velocities correlate with distance? They should a) be directly proportional to distance. b) reverse
Suppose the Universe were not expanding, but was in some kind of steady state. How should galaxy recession velocities correlate with distance? They should a) be directly proportional to distance. b) reverse
Chapter 1 Introduction. Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS
 Chapter 1 Introduction Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS 2008 1 Ptolemäus (85 165 b.c.) Kopernicus (1473 1543) Kepler (1571 1630) Newton (1643 1727) Kant (1724 1630) Herschel (1738 1822) Einstein (1917)
Chapter 1 Introduction Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS 2008 1 Ptolemäus (85 165 b.c.) Kopernicus (1473 1543) Kepler (1571 1630) Newton (1643 1727) Kant (1724 1630) Herschel (1738 1822) Einstein (1917)
Lecture 32: Astronomy 101
 Lecture 32: Evidence for the Big Bang Astronomy 101 The Three Pillars of the Big Bang Threefundamental pieces of evidence: Expansion of the Universe: Explains Hubble s Law Primordial Nucleosynthesis: Formation
Lecture 32: Evidence for the Big Bang Astronomy 101 The Three Pillars of the Big Bang Threefundamental pieces of evidence: Expansion of the Universe: Explains Hubble s Law Primordial Nucleosynthesis: Formation
Evidence is Clear. Students consider observations and inferences about the Steady State and Big Bang theories.
 The Evidence is Clear! Summary Students consider observations and inferences about the Steady State and Big Bang theories. Objectives Distinguish between data collected from empirical observations and
The Evidence is Clear! Summary Students consider observations and inferences about the Steady State and Big Bang theories. Objectives Distinguish between data collected from empirical observations and
Olbers Paradox. Why is the sky dark? Possible answers:
 Olbers Paradox Why is the sky dark? If the universe were infinitely big and infinitely old, there should be no dark patches in the sky (Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers (1757-- 1840) ) Possible answers: Dust? No,
Olbers Paradox Why is the sky dark? If the universe were infinitely big and infinitely old, there should be no dark patches in the sky (Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers (1757-- 1840) ) Possible answers: Dust? No,
Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014
![Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014](/thumbs/75/72758061.jpg) 1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
The Big Bang. Mr. Mike Partridge Earth & Space Science J.H. Reagan High School, Houston, TX
 The Big Bang Mr. Mike Partridge Earth & Space Science J.H. Reagan High School, Houston, TX Notes Outlines Theories of the Universe Static Universe What is the Big Bang Theory What is the evidence supporting
The Big Bang Mr. Mike Partridge Earth & Space Science J.H. Reagan High School, Houston, TX Notes Outlines Theories of the Universe Static Universe What is the Big Bang Theory What is the evidence supporting
The History and Philosophy of Astronomy
 Astronomy 350L (Spring 2005) The History and Philosophy of Astronomy (Lecture 25: Steady State vs Big Bang) Instructor: Volker Bromm TA: Amanda Bauer The University of Texas at Austin Steady State vs Big
Astronomy 350L (Spring 2005) The History and Philosophy of Astronomy (Lecture 25: Steady State vs Big Bang) Instructor: Volker Bromm TA: Amanda Bauer The University of Texas at Austin Steady State vs Big
Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 35, April 23
 Assignments: ICES available online Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 35, April 23 HW11 due next Friday: last homework! note: lowest HW score dropped but: HW11 material will be on Exam 3, so be sure to
Assignments: ICES available online Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 35, April 23 HW11 due next Friday: last homework! note: lowest HW score dropped but: HW11 material will be on Exam 3, so be sure to
ASTR 1P02 Test 2, March 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY. Test 2: March 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02, Section 2 Number of students: 1193
 ASTR 1P02 Test 2, March 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 2: March 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02, Section 2 Number of students: 1193 Examination date: 4 March 2017 Time limit: 50 min Time of
ASTR 1P02 Test 2, March 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 2: March 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02, Section 2 Number of students: 1193 Examination date: 4 March 2017 Time limit: 50 min Time of
IB Physics - Astronomy
 Solar System Our Solar System has eight planets. The picture below shows their relative sizes, but NOT their relative distances. A planet orbits the sun, and has gravitationally cleared its orbital area
Solar System Our Solar System has eight planets. The picture below shows their relative sizes, but NOT their relative distances. A planet orbits the sun, and has gravitationally cleared its orbital area
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
Revision Guide for Chapter 12
 Revision Guide for Chapter 12 Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes The speed of light... 4 Doppler effect... 4 Expansion of the Universe... 5 Microwave background radiation... 5 Galaxy... 6 Summary
Revision Guide for Chapter 12 Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes The speed of light... 4 Doppler effect... 4 Expansion of the Universe... 5 Microwave background radiation... 5 Galaxy... 6 Summary
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 First, we have the in-class presentations Then I will return the test I will collect HW#5 HW#6 is posted and due next Wednesday Includes elements from the test Soon, we will get
This week at Astro 3303 First, we have the in-class presentations Then I will return the test I will collect HW#5 HW#6 is posted and due next Wednesday Includes elements from the test Soon, we will get
Lecture 20 Cosmology, Inflation, dark matter
 The Nature of the Physical World November 19th, 2008 Lecture 20 Cosmology, Inflation, dark matter Arán García-Bellido 1 News Exam 2: good job! Ready for pick up after class or in my office Average: 74/100
The Nature of the Physical World November 19th, 2008 Lecture 20 Cosmology, Inflation, dark matter Arán García-Bellido 1 News Exam 2: good job! Ready for pick up after class or in my office Average: 74/100
Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it
 Cosmology Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it is? Are other universes possible? Would they
Cosmology Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it is? Are other universes possible? Would they
Cosmology. Chapter 18. Cosmology. Observations of the Universe. Observations of the Universe. Motion of Galaxies. Cosmology
 Cosmology Chapter 18 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole How big is the Universe? What shape is it? How old is it? How did it form? What will happen
Cosmology Chapter 18 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole How big is the Universe? What shape is it? How old is it? How did it form? What will happen
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
