DISTAN T EKOs. The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter. Edited by: Joel Wm. Parker CONTENTS
|
|
|
- Bathsheba Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Issue No June DISTAN T EKOs The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter Edited by: Joel Wm. Parker ekonews@boulder.swri.edu CONTENTS News & Announcements... 2 Abstracts of 8 Accepted Papers...3 Newsletter Information...8 1
2 NEWS & ANNOUNCEMENTS There were 8 new TNO discoveries announced since the previous issue of Distant EKOs: 2013 FA28, 2013 FB28, 2013 FC28, 2013 FD28, 2013 JV63, 2013 JW63, 2014 FP43, 2014 FX61 and 6 new Centaur/SDO discoveries: 2013 JU63, 2014 FU61, 2014 FB62, 2014 KL84, 2014 LR14, 2014 LJ9 Reclassified objects: 2014 FB62 (Centaur TNO) Objects recently assigned numbers: 2012 GN12 = (395699) Current number of TNOs: 1272 (including Pluto) Current number of Centaurs/SDOs: 398 Current number of Neptune Trojans: 9 Out of a total of 1679 objects: 648 have measurements from only one opposition 631 of those have had no measurements for more than a year 327 of those have arcs shorter than 10 days (for more details, see: 2
3 PAPERS ACCEPTED TO JOURNALS De-biased Populations of Kuiper Belt Objects from the Deep Ecliptic Survey E.R. Adams 1, A.A.S. Gulbis 2,3, J.L. Elliot 3,4, S.D. Benecchi 1,5, M.W. Buie 6, D.E. Trilling 7, and L.H. Wasserman 8 1 Planetary Science Institute, 1700 East Fort Lowell, Suite 106, Tucson, AZ 85719, USA 2 The Southern African Large Telescope and South African Astronomical Observatory, Cape Town, South Africa, Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Ave., Cambridge, MA, 02139, USA 4 Deceased 5 Carnegie Institution of Washington, Department of Terrestrial Magnetism, 5241 Broad Branch Road NW, Washington, DC , USA 6 Southwest Research Institute, 6220 Culebra Road, San Antonio, TX 78238, USA 7 Department of Physics & Astronomy, Northern Arizona University, S San Francisco St, Flagstaff, AZ 86011, USA 8 Lowell Observatory, 1400 W. Mars Hill Rd., Flagstaff, AZ 86001, USA The Deep Ecliptic Survey (DES) was a survey project that discovered hundreds of Kuiper Belt objects from Extensive follow-up observations of these bodies has yielded 304 objects with well-determined orbits and dynamical classifications into one of several categories: Classical, Scattered, Centaur, or 16 mean-motion resonances with Neptune. The DES search fields are well documented, enabling us to calculate the probability on each frame of detecting an object with its particular orbital parameters and absolute magnitude at a randomized point in its orbit. The detection probabilities range from a maximum of 0.32 for the 3:2 resonant object 2002 GF 32 to a minimum of for the faint Scattered object 2001 FU 185. By grouping individual objects together by dynamical classes, we can estimate the distributions of four parameters that define each class: semi-major axis, eccentricity, inclination, and object size. The orbital element distributions (a, e, and i) were fit to the largest three classes (Classical, 3:2, and Scattered) using a maximum likelihood fit. Using the absolute magnitude (H-magnitude) as a proxy for the object size, we fit a power law to the number of objects vs. H magnitude for 8 classes with at least 5 detected members (246 objects). The Classical objects are best fit with a power-law slope of α = 1.02±0.01 (observed from 5 H 7.2). Six other dynamical classes (Scattered plus 5 resonances) have consistent magnitude distributions slopes with the Classicals, provided that the absolute number of objects is scaled. Scattered objects are somewhat more numerous than Classical objects, while there are only a quarter as many 3:2 objects as Classicals. The exception to the power law relation is the Centaurs, which are non-resonant objects with perihelia closer than Neptune and therefore brighter and detectable at smaller sizes. Centaurs were observed from 7.5 < H < 11, and that population is best fit by a power law with α = 0.42 ± This is consistent with a knee in the H-distribution around H = 7.2 as reported elsewhere (Bernstein et al. 2004, Fraser et al. 2014). Based on the Classical-derived magnitude distribution, the total number of objects (H 7) in each class are: Classical (2100±300 objects), Scattered (2800±400), 3:2 (570±80), 2:1 (400 ± 50), 5:2 (270 ± 40), 7:4 (69 ± 9), 5:3 (60 ± 8). The independent estimate for the number of Centaurs in the same H range is 13 ± 5. If instead all objects are divided by inclination into Hot and Cold populations, following Fraser et al. (2014), we find that α Hot = 0.90 ±0.02, while α Cold = 1.32±0.02, in good agreement with that work. To appear in: The Astronomical Journal For preprints, contact adams@psi.edu or on the web at 3
4 New Horizons: Long-range Kuiper Belt Targets Observed by the Hubble Space Telescope S.D. Benecchi 1,2, K.S. Noll 3, H.A. Weaver 4, J.R. Spencer 5, S.A. Stern 5, M.W. Buie 5, and A.H. Parker 6 1 Planetary Science Institute, 1700 East Fort Lowell, Suite 106, Tucson, AZ 85719, USA 2 Carnegie Institution of Washington, Department of Terrestrial Magnetism, 5241 Broad Branch Road, NW, Washington, DC 20015, USA 3 NASA Goddard Space Fight Center, 8800 Greenbelt Rd. Code 693, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA 4 Space Department, Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Johns Hopkins Road, Laurel, MD 20723, USA 5 Southwest Research Institute, 1050 Walnut St., Suite 300, Boulder, CO 80302, USA 6 Department of Astronomy, University of California at Berkeley, B-20 Hearst Field Annex # 3411, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA We report on Hubble Space Telescope (HST) observations of three Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs), discovered in our dedicated ground-based search campaign, that are candidates for long-range observations from the New Horizons spacecraft: 2011 JY 31, 2011 HZ 102, and 2013 LU 35. Astrometry with HST enables both current and future critical accuracy improvements for orbit precision, required for possible New Horizons observations, beyond what can be obtained from the ground. Photometric colors of all three objects are red, typical of the Cold Classical dynamical population within which they reside; they are also the faintest KBOs to have had their colors measured. None are observed to be binary with HST above separations of 0.02 arcsec ( 700 km at 44 AU) and m 0.5. Published in: Icarus For preprints, contact susank@psi.edu or on the web at arxiv.org/abs/ and at A Study of the High-inclination Population in the Kuiper Belt II. The Twotinos J. Li 1, L.-Y. Zhou 1, and Y.-S. Sun 1 1 School of Astronomy and Space Science & Key Laboratory of Modern Astronomy and Astrophysics in Ministry of Education, Nanjing University, Nanjing , PR China As the second part of our study, in this paper we proceed to explore the dynamics of the highinclination Twotinos in the 1:2 Neptune mean motion resonance (NMMR). Depending on the inclination i, we show the existence of two critical eccentricities e a (i) and e c (i), which are lower limits of the eccentricity e for the resonant angle σ to exhibit libration and asymmetric libration, respectively. Accordingly, we have determined the libration centres σ 0 for inclined orbits, which are strongly dependent on i. With initial σ = σ 0 on a fine grid of (e,i), the stability of orbits in the 1:2 NMMR is probed by 4-Gyr integrations. It is shown that symmetric librators are totally unstable for i 30 ; while stable asymmetric librators exist for i up to 90. We further investigate the 1:2 NMMR capture and retention of planetesimals with initial inclinations i 0 90 in the planet migration model using a long time-scale of yr. We find that: (1) the 4
5 capture efficiency of the 1:2 NMMR decreases drastically with the increase of i 0, and it goes to 0 when i 0 60 ; (2) the probability of discovering Twotinos with i > 25, beyond observed values, is roughly estimated to be 0.1 per cent; (3) more particles are captured into the leading rather than the trailing asymmetric resonance for i 0 10, but this number difference appears to be the opposite at i 0 = 20 and is continuously varying for even larger i 0 ; (4) captured Twotinos residing in the trailing resonance or having i > 15 are practically outside the Kozai mechanism, like currently observed samples. To appear in: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Preprints available on the web at Extreme Trans-Neptunian Objects and the Kozai Mechanism: Signaling the Presence of Trans-Plutonian Planets? C. de la Fuente Marcos 1 and R. de la Fuente Marcos 1 1 Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Ciudad Universitaria, E-28040, Madrid, Spain The existence of an outer planet beyond Pluto has been a matter of debate for decades and the recent discovery of 2012 VP 113 has just revived the interest for this controversial topic. This Sednalike object has the most distant perihelion of any known minor planet and the value of its argument of perihelion is close to 0. This property appears to be shared by almost all known asteroids with semimajor axis greater than 150 au and perihelion greater than 30 au (the extreme trans-neptunian objects or ETNOs), and this fact has been interpreted as evidence for the existence of a super-earth at 250 au. In this scenario, a population of stable asteroids may be shepherded by a distant, undiscovered planet larger than the Earth that keeps the value of their argument of perihelion librating around 0 as a result of the Kozai mechanism. Here, we study the visibility of these ETNOs and confirm that the observed excess of objects reaching perihelion near the ascending node cannot be explained in terms of any observational biases. This excess must be a true feature of this population and its possible origin is explored in the framework of the Kozai effect. The analysis of several possible scenarios strongly suggest that at least two trans-plutonian planets must exist. To appear in: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Letters For preprints, contact nbplanet@fis.ucm.es or on the web at Large Retrograde Centaurs: Visitors from the Oort Cloud? C. de la Fuente Marcos 1 and R. de la Fuente Marcos 1 1 Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Ciudad Universitaria, E-28040, Madrid, Spain Among all the asteroid dynamical groups, Centaurs have the highest fraction of objects moving in retrograde orbits. The distribution in absolute magnitude, H, of known retrograde Centaurs with semi-major axes in the range 6 34 AU exhibits a remarkable trend: 10% have H < 10 mag, the rest have H > 12 mag. The largest objects, namely (342842) 2008 YB 3, 2011 MM 4 and 2013 LU 28, move in almost polar, very eccentric paths; their nodal points are currently located near perihelion and aphelion. In the group of retrograde Centaurs, they are obvious outliers both in terms of dynamics and size. Here, we show that these objects are also trapped in retrograde resonances that make them unstable. Asteroid 2013 LU 28, the largest, is a candidate transient co-orbital to Uranus and it may 5
6 be a recent visitor from the trans-neptunian region. Asteroids and 2011 MM 4 are temporarily submitted to various high-order retrograde resonances with the Jovian planets but may be ejected towards the trans-neptunian region within the next few hundred kyr. Asteroid 2011 MM 4 is far more stable. Our analysis shows that the large retrograde Centaurs form an heterogeneous group that may include objects from various sources. Asteroid 2011 MM 4 could be a visitor from the Oort cloud but an origin in a relatively stable closer reservoir cannot be ruled out. Minor bodies like 2011 MM 4 may represent the remnants of the primordial planetesimals and signal the size threshold for catastrophic collisions in the early Solar System. To appear in: Astrophysics and Space Science For preprints, contact nbplanet@fis.ucm.es or on the web at On the State of Methane and Nitrogen Ice on Pluto and Triton: Implications of the Binary Phase Diagram L.M. Trafton 1 1 University of Texas at Austin, Department of Astronomy, 2515 Speedway, C1400, Austin, TX , USA Compositional analyses of Pluto s surface ice in the literature typically include large areas on the body where CH 4 and other volatiles are segregated in the pure form from the solid solution N 2 :CH 4 in which CH 4 is diluted. However, the existence of continent-size areas of pure CH 4 are in conflict with both of the alternative models that successfully explain the enhancement of CH 4 in Pluto s atmosphere, the Detailed Balancing thermal equilibrium model and the Hot Methane Patch model. Pluto s spectrum includes an apparently unshiftedch 4 component while Triton s does not, and 93% of the concentration range of the binary phase diagram at 38 K shows that these species exist as a mixture of two saturated solid solution phases. Recognizing this, we propose that both of these saturated phases are present on Pluto and the CH 4 -rich phase of the mixture, CH 4 :N 2, is the source of the relatively unshifted CH 4 spectrum attributed to pure CH 4. We also propose that CH 4 is less abundant in Triton s ice to the point where either the ice is not saturated or the saturated CH 4 :N 2 phase has not been detected. In this scenario, the partial vapor pressures do not change when the relative proportions of these saturated phases are varied in the mixture. Thus, the partial vapor pressures are independent of N 2 CH 4 concentrations if both saturated phases are present. Accordingly, the longitudinal and seasonal variations of CH 4 and N 2 features in Pluto s spectrum would be attributed to spatial variations in the relative proportions of these species. This may occur during volatile transport in the sublimation wind through extensive influences. The lower, unsaturated, values of the mole fraction of CH 4 in the ice reported by Owen et al. (1993) and Cruikshank et al. (1998), and by Doute et al. (1999) based on a compositional analysis of Pluto s surface, were not obtained using optical constants for components consistent with the constraints of the phase diagram. To appear in: Icarus For preprints, contact lmt@astro.as.utexas.edu 6
7 Gas Transfer in the Pluto-Charon System: A Charon Atmosphere O.J. Tucker 1, R.E. Johnson 2,3, and L.A. Young 4 1 Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic and Space Sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA 2 Department of Engineering Physics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22904, USA 3 Department of Physics, New York University, NY, NY 10003, USA 4 Southwest Research Institute, Boulder, CO 80302, USA Recent hybrid fluid/molecular kinetic models demonstrated that Plutos upper atmosphere is warmer and more extended than previously thought (Erwin et al., 2013; Tucker et al. 2012). Here we examine the effect of Charon on the molecular escape rate from Plutos extended atmosphere, simulate the spatial distribution of N 2 in this binary system, and describe the resulting accumulation of N 2 on Charon. These Monte Carlo simulations are carried out for approximate solar medium conditions at 33 AU. Including Charons gravity and orbital motion,the atmosphere on the Plutos Charon-facing hemisphere is more strongly bound to the system and is more extended than the atmosphere on Plutos anti-charon hemisphere. Accounting for Charons gravity the net escape from the system is reduced by 5%. Most of the loss is direct from Plutos exobase region with 1-2% due to scattering by Charon. About 0.2% of the flux from Plutos exobase impinges on Charon: N 2 /s at nominal solar medium conditions. This is a source of condensed N 2 for Charons night side and forms a tenuous atmosphere. For the approximate range of surface temperatures, the residence time of N 2 on the surface can range from a fraction of a second to 10s of years with the near surface line of sight column densities varying from N 2 /m 2 up to > N 2 /m 2. Such an atmosphere could be detectable during the solar occultation that will occur during the New Horizon encounter providing a measure of the transfer of gas between bodies in this binary system. To appear in: Icarus For preprints, contact ojtucker@umich.edu or on the web at The Effect of Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities on the Thickness of Undifferentiated Crust on Kuiper Belt Objects M.E. Rubin 1, S.J. Desch 1, and M. Neveu 1 1 School of Earth and Space Exploration, Arizona State University, P.O. Box , Tempe, AZ , USA Previous calculations of the internal structure and thermal evolution of Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs) by Desch et al. (Desch, S.J., Cook, J.C., Doggett, T.C., Porter, S.B. [2009]. Icarus 202, ) have predicted that KBOs should only partially differentiate, with rock and ice separating into a rocky core and icy mantle, below an undifferentiated crust of ice and rock. This crust is thermally insulating and enhances the ability of subsurface liquid to persist within KBOs. A dense rock/ice layer resting on an icy mantle is gravitationally unstable and prone to Rayleigh-Taylor (RT) instabilities, and may potentially overturn. Here we calculate the ability of RT instabilities to act in KBOs, and determine the thickness of undifferentiated crusts. We have used previously calculated growth rates of the RT instability to determine the critical viscosity of ice needed for the RT instability to operate. We calculate the viscosity of ice at the cold temperatures and long timescales relevant to KBOs. We find that crustal overturn is only possible where the temperature exceeds about 150 K, and that RT instabilities cannot act on geological timescales within about 60 km of the surfaces of a KBO like Charon. Although this crustal thickness is less than the 85 km previously calculated by Desch et al. (Desch, S.J., Cook, J.C., Doggett, T.C., Porter, S.B. [2009]. Icarus 202, ), it is still significant, representing 25% of the mass of 7
8 the KBO. We conclude that while RT instabilities may act in KBOs, they do not completely overturn their crusts. We calculate that Saturns moon Rhea should only partially differentiate, resulting in a moment of inertia C/MR Published in: Icarus, 236, 122 (2014 July) The Distant EKOs Newsletter is dedicated to provide researchers with easy and rapid access to current work regarding the Kuiper belt (observational and theoretical studies), directly related objects (e.g., Pluto, Centaurs), and other areas of study when explicitly applied to the Kuiper belt. We accept submissions for the following sections: Abstracts of accepted papers Titles of submitted (but not yet accepted) papers and conference articles Thesis abstracts Short articles, announcements, or editorials Status reports of on-going programs Requests for collaboration or observing coordination Table of contents/outlines of books Announcements for conferences Job advertisements General news items deemed of interest to the Kuiper belt community A L A TEX template for submissions is appended to each issue of the newsletter, and is sent out regularly to the distribution list. Please use that template, and send your submission to: ekonews@boulder.swri.edu The Distant EKOs Newsletter is available on the World Wide Web at: Recent and back issues of the newsletter are archived there in various formats. The web pages also contain other related information and links. Distant EKOs is not a refereed publication, but is a tool for furthering communication among people interested in Kuiper belt research. Publication or listing of an article in the newsletter or the web page does not constitute an endorsement of the article s results or imply validity of its contents. When referencing an article, please reference the original source; Distant EKOs is not a substitute for peer-reviewed journals. Moving...?? If you move or your address changes, please send the editor your new address. If the newsletter bounces back from an address for three consecutive issues, the address will be deleted from the mailing list. All address changes, submissions, and other correspondence should be sent to: ekonews@boulder.swri.edu 8
The Planet Pluto. & Kuiper Belt. The Search for PLANET X Pluto Discovered. Note how Pluto Moved in 6 days. Pluto (Hades): King of the Underworld
 X The Planet Pluto & Kuiper Belt Updated May 9, 2016 The Search for PLANET X Recall Neptune was predicted from observed changes in orbit of Uranus Lowell & Pickering suggest small changes in Neptune s
X The Planet Pluto & Kuiper Belt Updated May 9, 2016 The Search for PLANET X Recall Neptune was predicted from observed changes in orbit of Uranus Lowell & Pickering suggest small changes in Neptune s
The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter CONTENTS
 Issue No. 45 March 2006 DISTAN T EKOs The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter Edited by: Joel Wm. Parker ekonews@boulder.swri.edu www.boulder.swri.edu/ekonews CONTENTS News & Announcements.................................
Issue No. 45 March 2006 DISTAN T EKOs The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter Edited by: Joel Wm. Parker ekonews@boulder.swri.edu www.boulder.swri.edu/ekonews CONTENTS News & Announcements.................................
Earth, Uranus, Neptune & Pluto
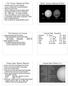 14a. Uranus, Neptune & Pluto The discovery of Uranus & Neptune Uranus is oddly tilted & nearly featureless Neptune is cold & blue Uranus & Neptune are like yet dislike Jupiter The magnetic fields of Uranus
14a. Uranus, Neptune & Pluto The discovery of Uranus & Neptune Uranus is oddly tilted & nearly featureless Neptune is cold & blue Uranus & Neptune are like yet dislike Jupiter The magnetic fields of Uranus
Pluto Data: Numbers. 14b. Pluto, Kuiper Belt & Oort Cloud. Pluto Data (Table 14-5)
 14b. Pluto, Kuiper Belt & Oort Cloud Pluto Pluto s moons The Kuiper Belt Resonant Kuiper Belt objects Classical Kuiper Belt objects Pluto Data: Numbers Diameter: 2,290.km 0.18. Earth Mass: 1.0. 10 22 kg
14b. Pluto, Kuiper Belt & Oort Cloud Pluto Pluto s moons The Kuiper Belt Resonant Kuiper Belt objects Classical Kuiper Belt objects Pluto Data: Numbers Diameter: 2,290.km 0.18. Earth Mass: 1.0. 10 22 kg
ASTEROIDS, COMETS, AND TRANS-NEPTUNIAN OBJECTS:
 ASTEROIDS, COMETS, AND TRANS-NEPTUNIAN OBJECTS: SMALL BODIES IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM Rosemary E. Pike ASIAA TIARA Summer School 2018 On the Origins of the Solar System SMALL BODIES IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM Formation
ASTEROIDS, COMETS, AND TRANS-NEPTUNIAN OBJECTS: SMALL BODIES IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM Rosemary E. Pike ASIAA TIARA Summer School 2018 On the Origins of the Solar System SMALL BODIES IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM Formation
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 15. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets
Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets
Earth, Uranus, Neptune & Pluto. 14a. Uranus & Neptune. The Discovery of Uranus. Uranus Data: Numbers. Uranus Data (Table 14-1)
 14a. Uranus & Neptune The discovery of Uranus & Neptune Uranus is oddly tilted & nearly featureless Neptune is cold & blue Uranus & Neptune are like yet dislike Jupiter The magnetic fields of Uranus &
14a. Uranus & Neptune The discovery of Uranus & Neptune Uranus is oddly tilted & nearly featureless Neptune is cold & blue Uranus & Neptune are like yet dislike Jupiter The magnetic fields of Uranus &
Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects
 Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects 1 What about Pluto? Pluto used to be considered a planet Pluto is one of a large number of Trans-Neptunian Objects, not even the largest one! Discovery
Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects 1 What about Pluto? Pluto used to be considered a planet Pluto is one of a large number of Trans-Neptunian Objects, not even the largest one! Discovery
Transneptunian Binaries and Collision Families: Probes of our Local Dust Disk
 Transneptunian Binaries and Collision Families: Probes of our Local Dust Disk Susan D. Benecchi, STScI Collaborators: Keith Noll, Will Grundy, Denise Stephens, Hal Levison, and the Deep Ecliptic Survey
Transneptunian Binaries and Collision Families: Probes of our Local Dust Disk Susan D. Benecchi, STScI Collaborators: Keith Noll, Will Grundy, Denise Stephens, Hal Levison, and the Deep Ecliptic Survey
Transneptunian objects. Minor bodies in the outer Solar System. Transneptunian objects
 Transneptunian objects Minor bodies in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Around 1980 it was proposed that the hypothetical disk of small bodies beyond Neptune (called
Transneptunian objects Minor bodies in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Around 1980 it was proposed that the hypothetical disk of small bodies beyond Neptune (called
Astronomy. Uranus Neptune & Remote Worlds
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Uranus Neptune & Remote Worlds Uranus and Neptune Orbits and Atmospheres Internal Structure Magnetic Fields Rings Uranus's
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Uranus Neptune & Remote Worlds Uranus and Neptune Orbits and Atmospheres Internal Structure Magnetic Fields Rings Uranus's
Which of the following statements best describes the general pattern of composition among the four jovian
 Part A Which of the following statements best describes the general pattern of composition among the four jovian planets? Hint A.1 Major categories of ingredients in planetary composition The following
Part A Which of the following statements best describes the general pattern of composition among the four jovian planets? Hint A.1 Major categories of ingredients in planetary composition The following
Solar System Research Teacher Notes The Sun
 The Sun G-type main sequence star (G2V), also known as a yellow dwarf Mass = 1.99 x 10 30 kg or 333,000 Earths. Volume = 1.41 x 10 18 km 3 or 1,300,000 Earths. Density (average) = 1.41 g/cm 3 or 0.255
The Sun G-type main sequence star (G2V), also known as a yellow dwarf Mass = 1.99 x 10 30 kg or 333,000 Earths. Volume = 1.41 x 10 18 km 3 or 1,300,000 Earths. Density (average) = 1.41 g/cm 3 or 0.255
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Comparative Planetology Studying the similarities among and differences between the planets
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Comparative Planetology Studying the similarities among and differences between the planets
Lecture 25: The Outer Planets
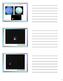 Lecture 25: The Outer Planets Neptune Uranus Pluto/Charon Uranus and three moons Neptune and two moons 1 The Outer Planets Uranus Discovered by William Herschel in 1781, who realized that this extended
Lecture 25: The Outer Planets Neptune Uranus Pluto/Charon Uranus and three moons Neptune and two moons 1 The Outer Planets Uranus Discovered by William Herschel in 1781, who realized that this extended
Issue No. 77 October DISTAN T EKOs. The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter. Edited by: Joel Wm. Parker CONTENTS
 Issue No. 77 October 2011 DISTAN T EKOs The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter Edited by: Joel Wm. Parker ekonews@boulder.swri.edu www.boulder.swri.edu/ekonews CONTENTS News & Announcements... 2 Abstracts
Issue No. 77 October 2011 DISTAN T EKOs The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter Edited by: Joel Wm. Parker ekonews@boulder.swri.edu www.boulder.swri.edu/ekonews CONTENTS News & Announcements... 2 Abstracts
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review
 Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan November 16, 2017 I Jupiter 1. How do Jupiter s mass, size, day and year compare to Earth s? Mass: 318 Earth masses (or about 1/1000th the mass of the Sun). Radius:
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan November 16, 2017 I Jupiter 1. How do Jupiter s mass, size, day and year compare to Earth s? Mass: 318 Earth masses (or about 1/1000th the mass of the Sun). Radius:
7. Our Solar System. Planetary Orbits to Scale. The Eight Planetary Orbits
 7. Our Solar System Terrestrial & Jovian planets Seven large satellites [moons] Chemical composition of the planets Asteroids & comets The Terrestrial & Jovian Planets Four small terrestrial planets Like
7. Our Solar System Terrestrial & Jovian planets Seven large satellites [moons] Chemical composition of the planets Asteroids & comets The Terrestrial & Jovian Planets Four small terrestrial planets Like
New Horizons Mission To Pluto Fran Bagenal University of Colorado
 New Horizons Mission To Pluto Fran Bagenal University of Colorado Compared to Earth at 1AU what is the flux of sunlight at 33 AU? Pluto orbits the Sun every 248 years 2 nd Kuiper Belt object discovered
New Horizons Mission To Pluto Fran Bagenal University of Colorado Compared to Earth at 1AU what is the flux of sunlight at 33 AU? Pluto orbits the Sun every 248 years 2 nd Kuiper Belt object discovered
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 15. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 Exoplanets Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Solar System Regularities and Irregularities 15.3
Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 Exoplanets Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Solar System Regularities and Irregularities 15.3
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 16 Jun 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 16 Jun 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 16 Jun 2014](/thumbs/82/85265299.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (2014) Printed 17 June 2014 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Extreme trans-neptunian objects and the Kozai mechanism: signalling the presence of trans-plutonian planets
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (2014) Printed 17 June 2014 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Extreme trans-neptunian objects and the Kozai mechanism: signalling the presence of trans-plutonian planets
as the orbits of distant planetoids are expected to be randomized over billions of year by the gravity of the four giant planets.
 Dynamics of Extreme Outer Solar System Objects Principle investigators/supervisors: Denis Gaidashev (Matematiska Institution); Erik Zackrisson (Institutionen fo r fysik och astronomi) 1. Purpose and aims
Dynamics of Extreme Outer Solar System Objects Principle investigators/supervisors: Denis Gaidashev (Matematiska Institution); Erik Zackrisson (Institutionen fo r fysik och astronomi) 1. Purpose and aims
Characteristics and Origin of the Quadruple System at Pluto
 Characteristics and Origin of the Quadruple System at Pluto S.A. Stern 1, H.A. Weaver 2, A.J. Steffl 1, M.J. Mutchler 3, W.J. Merline 1, M.W. Buie 4, E.F. Young 1, L.A. Young 1, & J.R. Spencer 1 Submitted
Characteristics and Origin of the Quadruple System at Pluto S.A. Stern 1, H.A. Weaver 2, A.J. Steffl 1, M.J. Mutchler 3, W.J. Merline 1, M.W. Buie 4, E.F. Young 1, L.A. Young 1, & J.R. Spencer 1 Submitted
Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants. Discovery of Uranus. Bode s Law. Discovery of Neptune
 Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants Discovery of Uranus Discovery of Uranus & Neptune Properties Density & Composition Internal Heat Source Magnetic fields Rings Uranus Rotational Axis by William Herschel
Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants Discovery of Uranus Discovery of Uranus & Neptune Properties Density & Composition Internal Heat Source Magnetic fields Rings Uranus Rotational Axis by William Herschel
Astronomy Wed. Oct. 6
 Astronomy 301 - Wed. Oct. 6 Guest lectures, Monday and today: Prof. Harriet Dinerstein Monday: The outer planets & their moons Today: asteroids, comets, & the Kuiper Belt; formation of the Solar System
Astronomy 301 - Wed. Oct. 6 Guest lectures, Monday and today: Prof. Harriet Dinerstein Monday: The outer planets & their moons Today: asteroids, comets, & the Kuiper Belt; formation of the Solar System
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley ANNOUNCEMENTS Keep up with reading! Always posted on course web site. Reading material
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley ANNOUNCEMENTS Keep up with reading! Always posted on course web site. Reading material
Our Planetary System. Chapter 7
 Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Lecture 24: Saturn. The Solar System. Saturn s Rings. First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: (where we have used Earth units)
 Lecture 24: Saturn The Solar System First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: Planet Distance Density Mass Mercury 0.4 1.0 0.06 Venus 0.7 0.9 0.8 Earth 1.0 1.0 1.0 Mars 1.5 0.7 0.1 (asteroid)
Lecture 24: Saturn The Solar System First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: Planet Distance Density Mass Mercury 0.4 1.0 0.06 Venus 0.7 0.9 0.8 Earth 1.0 1.0 1.0 Mars 1.5 0.7 0.1 (asteroid)
Survey of the Solar System. The Sun Giant Planets Terrestrial Planets Minor Planets Satellite/Ring Systems
 Survey of the Solar System The Sun Giant Planets Terrestrial Planets Minor Planets Satellite/Ring Systems Definition of a dwarf planet 1. Orbits the sun 2. Is large enough to have become round due to the
Survey of the Solar System The Sun Giant Planets Terrestrial Planets Minor Planets Satellite/Ring Systems Definition of a dwarf planet 1. Orbits the sun 2. Is large enough to have become round due to the
Object Type Moons Rings Planet Terrestrial none none. Max Distance from Sun. Min Distance from Sun. Avg. Distance from Sun 57,910,000 km 0.
 Mercury Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. It is extremely hot on the side of the planet facing the sun and very cold on the other. There is no water on the surface. There is practically no atmosphere.
Mercury Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. It is extremely hot on the side of the planet facing the sun and very cold on the other. There is no water on the surface. There is practically no atmosphere.
1. The Sun is the largest and brightest object in the universe. 2. The period that the Earth takes to revolve once around the Sun is approximately a
 PLEASE ANSWER YOUR QUESTIONS ON THIS PROVIDED QUESTION PAPER. EACH QUESTION IS FOLLOWED BY ANSWERS MARKED A AND B, OR A, B, C AND D. ONLY ONE ANSWER IS CORRECT. CHOOSE THE MOST CORRECT ANSWER AND CIRCLE
PLEASE ANSWER YOUR QUESTIONS ON THIS PROVIDED QUESTION PAPER. EACH QUESTION IS FOLLOWED BY ANSWERS MARKED A AND B, OR A, B, C AND D. ONLY ONE ANSWER IS CORRECT. CHOOSE THE MOST CORRECT ANSWER AND CIRCLE
The orbit evolution of 32 plutinos over 100 million year
 A&A 368, 700 705 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010056 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics The orbit evolution of 32 plutinos over 100 million year X.-S. Wan 1 and T.-Y. Huang 1,2 1 Astronomy Department,
A&A 368, 700 705 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010056 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics The orbit evolution of 32 plutinos over 100 million year X.-S. Wan 1 and T.-Y. Huang 1,2 1 Astronomy Department,
on it, can still ripen a bunch of grapes as though it had nothing else in the Universe to do. Galileo Galilei
 The Sun, with all the planets revolving around it, and depending on it, can still ripen a bunch of grapes as though it had nothing else in the Universe to do. Galileo Galilei What We Will Learn Today Where
The Sun, with all the planets revolving around it, and depending on it, can still ripen a bunch of grapes as though it had nothing else in the Universe to do. Galileo Galilei What We Will Learn Today Where
The search for Planet X Lowell Observatory, Flagstaff, Arizona. Overview. Andy Lubenow
 The discovery of two new satellites of Pluto Max Mutchler Space Telescope Science Institute Open Night 3 January 2006 Andy Lubenow 1956-2005 Hubble Pluto Satellite Search Team reporting the discovery to
The discovery of two new satellites of Pluto Max Mutchler Space Telescope Science Institute Open Night 3 January 2006 Andy Lubenow 1956-2005 Hubble Pluto Satellite Search Team reporting the discovery to
Report to Planetary Science Decadal Survey Primitive Bodies Panel. Perspectives from the Previous PBP Experience,
 Report to Planetary Science Decadal Survey Primitive Bodies Panel Perspectives from the Previous PBP Experience, 2001-2002 Primitive Bodies Panel Meeting, Sept. 9, 2009, Washington, DC Dale Cruikshank
Report to Planetary Science Decadal Survey Primitive Bodies Panel Perspectives from the Previous PBP Experience, 2001-2002 Primitive Bodies Panel Meeting, Sept. 9, 2009, Washington, DC Dale Cruikshank
LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS. NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Io Above Jupiter s Clouds on New Year's Day, Credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
 LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS Can see basic features through Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope especially useful because of sharp imaging. Distances from Kepler s 3 rd law, diameters from
LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS Can see basic features through Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope especially useful because of sharp imaging. Distances from Kepler s 3 rd law, diameters from
ABSTACT KUIPER BINARY OBJECT FORMATION
 KUIPER BINARY OBJECT FORMATION R. C. Nazzario, K Orr, C. Covington, D. Kagan, and T. W. Hyde Center for Astrophysics, Space Physics and Engineering Research, Baylor University, Waco, TX 76798-7310, USA,
KUIPER BINARY OBJECT FORMATION R. C. Nazzario, K Orr, C. Covington, D. Kagan, and T. W. Hyde Center for Astrophysics, Space Physics and Engineering Research, Baylor University, Waco, TX 76798-7310, USA,
Jupiter and Saturn. Guiding Questions. Long orbital periods of Jupiter and Saturn cause favorable viewing times to shift
 Jupiter and Saturn 1 2 Guiding Questions 1. Why is the best month to see Jupiter different from one year to the next? 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn?
Jupiter and Saturn 1 2 Guiding Questions 1. Why is the best month to see Jupiter different from one year to the next? 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn?
The Solar System - I. Alexei Gilchrist. [The Story of the Solar System]
![The Solar System - I. Alexei Gilchrist. [The Story of the Solar System] The Solar System - I. Alexei Gilchrist. [The Story of the Solar System]](/thumbs/89/99064825.jpg) The Solar System - I Alexei Gilchrist [The Story of the Solar System] Some resources Section 13.3 of Voyages (references and links at end) References noted in these slides The Story of the Solar System,
The Solar System - I Alexei Gilchrist [The Story of the Solar System] Some resources Section 13.3 of Voyages (references and links at end) References noted in these slides The Story of the Solar System,
Moon Obs #1 Due! Moon visible: early morning through afternoon. 6 more due June 13 th. 15 total due June 25 th. Final Report Due June 28th
 Moon Obs #1 Due! Moon visible: early morning through afternoon 6 more due June 13 th 15 total due June 25 th Final Report Due June 28th Our Solar System Objectives Overview of what is in our solar system
Moon Obs #1 Due! Moon visible: early morning through afternoon 6 more due June 13 th 15 total due June 25 th Final Report Due June 28th Our Solar System Objectives Overview of what is in our solar system
Comets and Kuiper Belt Objects 4/24/07
 and Kuiper Belt Objects Announcements Reading Assignment -- Chapter 30 quiz today In-class activity and course evaluations on Thursday Public lecture tonight 7:30PM, this room Prof. Alfed McEwan, Mars
and Kuiper Belt Objects Announcements Reading Assignment -- Chapter 30 quiz today In-class activity and course evaluations on Thursday Public lecture tonight 7:30PM, this room Prof. Alfed McEwan, Mars
Edmonds Community College ASTRONOMY 100 Sample Test #2 Fall Quarter 2006
 Edmonds Community College ASTRONOMY 100 Sample Test #2 Fall Quarter 2006 Instructor: L. M. Khandro 10/19/06 Please Note: the following test derives from a course and text that covers the entire topic of
Edmonds Community College ASTRONOMY 100 Sample Test #2 Fall Quarter 2006 Instructor: L. M. Khandro 10/19/06 Please Note: the following test derives from a course and text that covers the entire topic of
Our Solar System. Lesson 5. Distances Between the Sun and the Planets
 Our Solar System Lesson 5 T he Solar System consists of the Sun, the Moon, planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, meteors and other celestial bodies. All these celestial bodies are bound to the Sun
Our Solar System Lesson 5 T he Solar System consists of the Sun, the Moon, planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, meteors and other celestial bodies. All these celestial bodies are bound to the Sun
Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)
![Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)](/thumbs/77/76655554.jpg) Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Lecture #11: Plan. Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets
 Lecture #11: Plan Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets Mercury (review) Density = 5.4 kg / liter.. ~ Earth s Rocky mantle + iron/nickel core Slow spin: 59 days (orbital period = 88 days) No satellites
Lecture #11: Plan Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets Mercury (review) Density = 5.4 kg / liter.. ~ Earth s Rocky mantle + iron/nickel core Slow spin: 59 days (orbital period = 88 days) No satellites
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM. James Martin. Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC
 OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
Today. The Little Things. Comets. Dwarf Planets. Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then.
 Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
The Solar System 6/23
 6/23 The Solar System I. Earth A. Earth is the prototype terrestrial planet 1. Only planet in the solar system (we know of so far) with life 2. Temperature 290 K B. Physical Characteristics 1. Mass: 6
6/23 The Solar System I. Earth A. Earth is the prototype terrestrial planet 1. Only planet in the solar system (we know of so far) with life 2. Temperature 290 K B. Physical Characteristics 1. Mass: 6
Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Outer Worlds 4/19/07
 The : Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto Reading Assignment Finish Chapter 17 Announcements 6 th homework due on Tuesday, April 24 Quiz on Tuesday, April 24 (will cover all lectures since the last exam and Chapters
The : Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto Reading Assignment Finish Chapter 17 Announcements 6 th homework due on Tuesday, April 24 Quiz on Tuesday, April 24 (will cover all lectures since the last exam and Chapters
28-Aug-17. A Tour of Our Solar System and Beyond. The Sun
 A Tour of Our Solar System and Beyond The Sun diameter = 1,390,000 km = 864,000 mi >99.8% of the mass of the entire solar system surface temperature 5800 C 600 x 10 6 tons H -> 596 x 10 6 tons He per second
A Tour of Our Solar System and Beyond The Sun diameter = 1,390,000 km = 864,000 mi >99.8% of the mass of the entire solar system surface temperature 5800 C 600 x 10 6 tons H -> 596 x 10 6 tons He per second
Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System
 Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System Astronomy 241 is the first part of a year-long introduction to astrophysics. It uses basic classical mechanics and thermodynamics to analyze
Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System Astronomy 241 is the first part of a year-long introduction to astrophysics. It uses basic classical mechanics and thermodynamics to analyze
Universe Now. 5. Minor planets and other small bodies in the Solar System
 Universe Now 5. Minor planets and other small bodies in the Solar System An overview of the known Solar System The Sun 4 terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars 4 Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn,
Universe Now 5. Minor planets and other small bodies in the Solar System An overview of the known Solar System The Sun 4 terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars 4 Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn,
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM
 Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 17 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 22, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 17 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 22, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018
 Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018 Tidal locking We always see the same face of the Moon. This means: period of orbit = period of spin Top view of Moon orbiting Earth Earth Why? The tidal bulge in the solid
Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018 Tidal locking We always see the same face of the Moon. This means: period of orbit = period of spin Top view of Moon orbiting Earth Earth Why? The tidal bulge in the solid
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review
 Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan December 6, 2016 I The Outer Planets in General 1. How do the sizes, masses and densities of the outer planets compare with the inner planets? The outer planets
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan December 6, 2016 I The Outer Planets in General 1. How do the sizes, masses and densities of the outer planets compare with the inner planets? The outer planets
1 of 5 5/2/2015 5:50 PM
 1 of 5 5/2/2015 5:50 PM 1. A comet that has a semi-major axis of 100 AU must have a period of about 10 years. 20 years. 100 years. 1000 years. 2. Astronomers believe chondrite meteorites are about 4.6
1 of 5 5/2/2015 5:50 PM 1. A comet that has a semi-major axis of 100 AU must have a period of about 10 years. 20 years. 100 years. 1000 years. 2. Astronomers believe chondrite meteorites are about 4.6
Planets: Name Distance from Sun Satellites Year Day Mercury 0.4AU yr 60 days Venus yr 243 days* Earth 1 1 yr 1 day Mars 1.
 The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014
 1 Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014 2 Pluto -- Basic Information Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 Period: P orb = 248 years Distance: a = 39.5 AU 3 moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra) Demoted
1 Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014 2 Pluto -- Basic Information Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 Period: P orb = 248 years Distance: a = 39.5 AU 3 moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra) Demoted
SOLAR SYSTEM B Division
 SOLAR SYSTEM B Division Team Name: Team #: Student Names: IMAGE SHEET A E B C D F G H Spectrum I Spectrum II SS2014 Spectrum III Spectrum IV Spectrum V Spectrum VI 1. A. What satellite is pictured in Image
SOLAR SYSTEM B Division Team Name: Team #: Student Names: IMAGE SHEET A E B C D F G H Spectrum I Spectrum II SS2014 Spectrum III Spectrum IV Spectrum V Spectrum VI 1. A. What satellite is pictured in Image
Overview of Solar System
 Overview of Solar System The solar system is a disk Rotation of sun, orbits of planets all in same direction. Most planets rotate in this same sense. (Venus, Uranus, Pluto are exceptions). Angular momentum
Overview of Solar System The solar system is a disk Rotation of sun, orbits of planets all in same direction. Most planets rotate in this same sense. (Venus, Uranus, Pluto are exceptions). Angular momentum
SOLAR SYSTEM 2019 SAMPLE EXAM
 SOLAR SYSTEM 2019 SAMPLE EXAM Team Name: Team #: No calculators are allowed. All questions are of equal weight unless otherwise noted. Turn in all materials when you have completed the test! Make sure
SOLAR SYSTEM 2019 SAMPLE EXAM Team Name: Team #: No calculators are allowed. All questions are of equal weight unless otherwise noted. Turn in all materials when you have completed the test! Make sure
Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017
 Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017 Today: Chapter 12, Pluto and Debris March 24: Exam #2, Ch. 5-12 (9:00-9:50) March 27: Mastering Astronomy HW Chapter 11 & 12 1 Chapter 12: Meteorites, Asteroids, Comets
Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017 Today: Chapter 12, Pluto and Debris March 24: Exam #2, Ch. 5-12 (9:00-9:50) March 27: Mastering Astronomy HW Chapter 11 & 12 1 Chapter 12: Meteorites, Asteroids, Comets
Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets. 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal
 Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal What is a storm on Saturn like? The Giant Planets, Part 1 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal What is a storm on Saturn like? The Giant Planets, Part 1 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Chapter Outline. Earth and Other Planets. The Formation of the Solar System. Clue #1: Planetary Orbits. Clues to the Origin of the Solar System
 Chapter Outline Earth and Other Planets The Formation of the Solar System Exploring the Solar System Chapter 16 Great Idea: Earth, one of the planets that orbit the Sun, formed 4.5 billion years ago from
Chapter Outline Earth and Other Planets The Formation of the Solar System Exploring the Solar System Chapter 16 Great Idea: Earth, one of the planets that orbit the Sun, formed 4.5 billion years ago from
Astronomy 1001/1005 Midterm (200 points) Name:
 Astronomy 1001/1005 Midterm (00 points) Name: Instructions: Mark your answers on this test AND your bubble sheet You will NOT get your bubble sheet back One page of notes and calculators are allowed Use
Astronomy 1001/1005 Midterm (00 points) Name: Instructions: Mark your answers on this test AND your bubble sheet You will NOT get your bubble sheet back One page of notes and calculators are allowed Use
Chapters 7&8. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements.
![Chapters 7&8. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements. Chapters 7&8. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements.](/thumbs/81/83429897.jpg) ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements The Solar System Comparative
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements The Solar System Comparative
37. Planetary Geology p
 37. Planetary Geology p. 656-679 The Solar System Revisited We will now apply all the information we have learned about the geology of the earth to other planetary bodies to see how similar, or different,
37. Planetary Geology p. 656-679 The Solar System Revisited We will now apply all the information we have learned about the geology of the earth to other planetary bodies to see how similar, or different,
9. Formation of the Solar System
 9. Formation of the Solar System The evolution of the world may be compared to a display of fireworks that has just ended: some few red wisps, ashes, and smoke. Standing on a cool cinder, we see the slow
9. Formation of the Solar System The evolution of the world may be compared to a display of fireworks that has just ended: some few red wisps, ashes, and smoke. Standing on a cool cinder, we see the slow
Planetarium observing is over. Nighttime observing starts next week.
 Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now. Planetarium observing is over. Solar observing is over. Nighttime observing starts next week. Outline Switch Gears Solar System Introduction The
Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now. Planetarium observing is over. Solar observing is over. Nighttime observing starts next week. Outline Switch Gears Solar System Introduction The
The Main Point. Basic Properties of Mars. Observations. Lecture #19: Mars
 Mars: Overview General properties Telescopic observations Space missions Atmospheric Characteristics Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Mars), 9.4, 10.4 Lecture #19: Mars The Main Point Changes in the Martian surface
Mars: Overview General properties Telescopic observations Space missions Atmospheric Characteristics Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Mars), 9.4, 10.4 Lecture #19: Mars The Main Point Changes in the Martian surface
The Outermost Planets. The 7 Wanderers known since Antiquity. Uranus and Neptune distinctly Blue-ish!
 The Outermost Planets The 7 Wanderers known since Antiquity. Uranus and Neptune distinctly Blue-ish! Uranus Uranus and 3 of its moons, barely visible from Earth. Discovered by William Herschel 1781. (Accidentally!)
The Outermost Planets The 7 Wanderers known since Antiquity. Uranus and Neptune distinctly Blue-ish! Uranus Uranus and 3 of its moons, barely visible from Earth. Discovered by William Herschel 1781. (Accidentally!)
Astronomy November, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System. Mid-term Exam 3. Practice Version. Name (written legibly):
 Astronomy 101 16 November, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System Mid-term Exam 3 Practice Version Name (written legibly): Honor Pledge: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
Astronomy 101 16 November, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System Mid-term Exam 3 Practice Version Name (written legibly): Honor Pledge: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 16 4 Moons SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.d, 8.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How did Earth s moon
CHAPTER 16 4 Moons SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.d, 8.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How did Earth s moon
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More
 12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Dwarf planets Following the discovery of multiple objects similar to Pluto (and one that was even bigger than Pluto) a new classification for planets
The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Dwarf planets Following the discovery of multiple objects similar to Pluto (and one that was even bigger than Pluto) a new classification for planets
Modeling the Orbits of the Outer Planets
 Name Modeling the Orbits of the Outer Planets (a NASA New Horizons activity) Materials Paper clip Scissors Glue Pencil and crayons or markers Planet sheets Safety Concerns: Scissors. Discuss safe and proper
Name Modeling the Orbits of the Outer Planets (a NASA New Horizons activity) Materials Paper clip Scissors Glue Pencil and crayons or markers Planet sheets Safety Concerns: Scissors. Discuss safe and proper
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 14. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 14 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 14 Solar System Debris Units of Chapter 14 14.1 Asteroids What Killed the Dinosaurs? 14.2 Comets 14.3 Beyond Neptune 14.4
Lecture Outlines Chapter 14 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 14 Solar System Debris Units of Chapter 14 14.1 Asteroids What Killed the Dinosaurs? 14.2 Comets 14.3 Beyond Neptune 14.4
3. The moon with the most substantial atmosphere in the Solar System is A) Iapetus B) Io C) Titan D) Triton E) Europa
 Spring 2013 Astronomy - Test 2 Test form A Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form A on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Spring 2013 Astronomy - Test 2 Test form A Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form A on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Uranus & Neptune, The Ice Giants
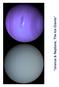 Uranus & Neptune, The Ice Giants What We Will Learn Today How & When were Uranus & Neptune discovered? How are the interiors and weather on these planets? Why is Neptune as warm as Uranus? What are their
Uranus & Neptune, The Ice Giants What We Will Learn Today How & When were Uranus & Neptune discovered? How are the interiors and weather on these planets? Why is Neptune as warm as Uranus? What are their
Lecture 38. The Jovian Planets; Kuiper Belt. Tides; Roche Limit; Rings Jupiter System Saturn, Uranus, Neptune rings Plutinos and KBO's
 Lecture 38 The Jovian Planets; Kuiper Belt Tides; Roche Limit; Rings Jupiter System Saturn, Uranus, Neptune rings Plutinos and KBO's Apr 26, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 38 1 Jovian System Jovian System Solar
Lecture 38 The Jovian Planets; Kuiper Belt Tides; Roche Limit; Rings Jupiter System Saturn, Uranus, Neptune rings Plutinos and KBO's Apr 26, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 38 1 Jovian System Jovian System Solar
What is it like? When did it form? How did it form. The Solar System. Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1
 What is it like? When did it form? How did it form The Solar System Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1 Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 2 The planets all orbit the sun in the same direction. The Sun spins in the same
What is it like? When did it form? How did it form The Solar System Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1 Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 2 The planets all orbit the sun in the same direction. The Sun spins in the same
The Main Point. Planetary Ring Systems
 Lecture #31: Satellites and Rings II Ring Systems Overview of rings: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. What are rings made of? How do they form? Reading: Chapter 11.3. The Main Point All of the giant planets
Lecture #31: Satellites and Rings II Ring Systems Overview of rings: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. What are rings made of? How do they form? Reading: Chapter 11.3. The Main Point All of the giant planets
AST111, Lecture 1b. Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements
 AST111, Lecture 1b Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements Planetary properties (continued): Measuring Mass The orbital period of a moon about a planet depends
AST111, Lecture 1b Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements Planetary properties (continued): Measuring Mass The orbital period of a moon about a planet depends
Astronomy. physics.wm.edu/~hancock/171/ A. Dayle Hancock. Small 239. Office hours: MTWR 10-11am
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets
 Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets 2-28-2018 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune ASTR-101 Section 004 Bulk Properties of Terrestrial and Jovian Planets All Jovian planets have strong magnetic fields
Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets 2-28-2018 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune ASTR-101 Section 004 Bulk Properties of Terrestrial and Jovian Planets All Jovian planets have strong magnetic fields
Outline. Question of Scale. Planets Dance. Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now.
 Outline Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now. Planetarium observing is over. Switch Gears Solar System Introduction The Planets, the Asteroid belt, the Kupier objects, and the Oort cloud
Outline Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now. Planetarium observing is over. Switch Gears Solar System Introduction The Planets, the Asteroid belt, the Kupier objects, and the Oort cloud
Small Bodies of the Outer Solar System
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 5, 37 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della Supplementi Small Bodies of the Outer Solar System E. Dotto 1 and M.A. Barucci 2 1 INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, Via Frascati 33, 00040
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 5, 37 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della Supplementi Small Bodies of the Outer Solar System E. Dotto 1 and M.A. Barucci 2 1 INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, Via Frascati 33, 00040
Astronomers Universe. More information about this series at
 Astronomers Universe More information about this series at http://www.springer.com/series/6960 ThiS is a FM Blank Page John Wilkinson The Solar System in Close-Up John Wilkinson Castlemaine, Victoria Australia
Astronomers Universe More information about this series at http://www.springer.com/series/6960 ThiS is a FM Blank Page John Wilkinson The Solar System in Close-Up John Wilkinson Castlemaine, Victoria Australia
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section X
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section X Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section X Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of
IX. Dwarf Planets A. A planet is defined to be an object that is large enough to coalesce into a sphere and to have cleared its orbit of other
 7/1 VII. VIII. Uranus A. Gas Giant 1. Rings but not visible 2. HUGE axial tilt 97! 3. Mostly hydrogen and helium 4. Medium rotation rate 5. Cold 55 K at the cloud tops B. Physical characteristics 1. Mass:
7/1 VII. VIII. Uranus A. Gas Giant 1. Rings but not visible 2. HUGE axial tilt 97! 3. Mostly hydrogen and helium 4. Medium rotation rate 5. Cold 55 K at the cloud tops B. Physical characteristics 1. Mass:
Whipple: Exploring the Solar System Beyond Neptune Using a Survey for Occultations of Bright Stars
 Whipple: Exploring the Solar System Beyond Neptune Using a Survey for Occultations of Bright Stars Charles Alcock 1, Matthew Holman 1, Matthew Lehner 2,3,1, Stephen Murray 1, Pavlos Protopapas 1,4 and
Whipple: Exploring the Solar System Beyond Neptune Using a Survey for Occultations of Bright Stars Charles Alcock 1, Matthew Holman 1, Matthew Lehner 2,3,1, Stephen Murray 1, Pavlos Protopapas 1,4 and
Smallest Kuiper Belt Object Ever Detected
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Smallest Kuiper Belt Object Ever Detected Taken from: Hubble 2009: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Smallest Kuiper Belt Object Ever Detected Taken from: Hubble 2009: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope
Astronomy. physics.wm.edu/~hancock/171/ A. Dayle Hancock. Small 239. Office hours: MTWR 10-11am. Page 1
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology I Terrestrial and Jovian planets Similarities/differences between planetary satellites Surface and atmosphere
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology I Terrestrial and Jovian planets Similarities/differences between planetary satellites Surface and atmosphere
Unusual Moon Information
 Saturn s Numbers Saturn is 1.35 billion km from the Sun minimum. Saturn is 1.5 billion km from the Sun maximum. One day on Saturn takes about 10.67 hours. One full rotation around the sun takes about 29.5
Saturn s Numbers Saturn is 1.35 billion km from the Sun minimum. Saturn is 1.5 billion km from the Sun maximum. One day on Saturn takes about 10.67 hours. One full rotation around the sun takes about 29.5
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION
 Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 4 The Solar System Lecture Presentation 4.0 What can be seen with the naked eye? Early astronomers knew about the Sun, Moon, stars, Mercury,
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 4 The Solar System Lecture Presentation 4.0 What can be seen with the naked eye? Early astronomers knew about the Sun, Moon, stars, Mercury,
Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System
 Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System Guiding Questions 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon? 3. How do astronomers
Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System Guiding Questions 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon? 3. How do astronomers
3. The name of a particularly large member of the asteroid belt is A) Halley B) Charon C) Eris D) Ceres E) Triton
 Summer 2013 Astronomy - Test 2 Test form A Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form A on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Summer 2013 Astronomy - Test 2 Test form A Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form A on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Saturn. Slightly smaller 1/3 the mass density 700 kg/m 3. Interior - light elements, lack of rocky materials. Voyager 2, NASA
 Saturn Slightly smaller 1/3 the mass density 700 kg/m 3 Interior - light elements, lack of rocky materials Voyager 2, NASA 1 Saturn - Atmosphere belts - driven by rapid rotation period - 10 hrs 14 min
Saturn Slightly smaller 1/3 the mass density 700 kg/m 3 Interior - light elements, lack of rocky materials Voyager 2, NASA 1 Saturn - Atmosphere belts - driven by rapid rotation period - 10 hrs 14 min
[12] Overview of the Solar System (10/5/17)
![[12] Overview of the Solar System (10/5/17) [12] Overview of the Solar System (10/5/17)](/thumbs/81/82937356.jpg) 1 [12] Overview of the Solar System (10/5/17) Upcoming Items Voyager Family Portrait 1. Read Ch. 8.1 & 8.2 by next class and do the self-study quizzes 2. Midterm #1 on Tuesday Good luck to all of you!
1 [12] Overview of the Solar System (10/5/17) Upcoming Items Voyager Family Portrait 1. Read Ch. 8.1 & 8.2 by next class and do the self-study quizzes 2. Midterm #1 on Tuesday Good luck to all of you!
The Formation of the Solar System
 The Formation of the Solar System Basic Facts to be explained : 1. Each planet is relatively isolated in space. 2. Orbits nearly circular. 3. All roughly orbit in the same plane. 4. Planets are all orbiting
The Formation of the Solar System Basic Facts to be explained : 1. Each planet is relatively isolated in space. 2. Orbits nearly circular. 3. All roughly orbit in the same plane. 4. Planets are all orbiting
