Recent advances in modeling precession-nutation
|
|
|
- Chastity Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recent advances in modeling precession-nutation Véronique Dehant ROB Sébastien Lambert OP Nicolas Rambaux ROB Marta Folgueira Madrid Univ Laurence Koot ROB
2 Level 3: rigid Earth nutation Level 5 oceanic/atmospheric corrections Level 2 transfer function Level 4 convolution Level 6 comparison with observation Level 1 seismic model used ROB
3 rotation axis of the mantle rotation axis of the core ROB
4 Descartes Fellows Laura Fernández Géraldine Bourda Yonghong Zhou Marta Folgueira Maciej Kalarus Sergei Bolotin Laurence Koot Kristyna Snajdrova Maria Kudryashova Sergei Bolotin Laurent Metivier Nicolas Rambaux Anna Korbacz Stefka Vojtech Alberto Escapa on FCN free mode observations, on combination of observations, on atmosphere angular momentum, on atmosphere effects on Earth orientation, on atmospheric and oceanic contributions to nutation relations between the Earth Orientation Parameters (EOP) and the variations of the Earth gravity field, on sub-diurnal Earth orientation and rotation variations, on finite method for coupling mechanisms, on dissipative and excitation mechanisms, on the expression of EOP in terms of CIP-X and Y rectangular coordinates, on influence of a non-barycentric frame on the Earth rotational motion
5 VLBI OBSERVATION STRATEGY 1. SOURCES STABILITY from ICRF, stable sources, structure index, no rotation condition, sources observed in more than 40 sessions, sources considered with local/global parameters, elevation cutoff 2. NETWORK CHOICE R1/R4 networks See Lambert et al., this session Also session from yesterday
6 What are the residuals? VLBI observations with the different strategies MHB2000 model (without atmospheric corrections) What remains should be due to the atmosphere What do we see?
7
8 Now let us consider that the model used has no inner core VLBI observations with the different strategies modified MHB2000 model (with atmospheric corrections at the prograde annual period and without inner core) transfer FCN FICN CW = R R R R R 0+ 1 function σ σ σ FCN σ σ FICN σ σ CW What remains should be due to the atmosphere (except at prograde annual period) and inner core contributions What do we see?
9 Atmosphere? Inner core
10 Geophysial parameters (direct link) Link between the FCN frequency and the core flattening and electromagnetic coupling at the CMB and the ICB σ Re FCN = Ω σ A α f q 1+ 0 h + K Re + s K Re f CMB ICB A 2 A m f Im FCN = Ω A K Im + A s K Im A CMB m Af ICB A ROB
11 Geophysial parameters (direct link) Link between the FICN frequency and the inner core flattening and electromagnetic coupling at the ICB σ ( [ Re ]) ses+ s K Re = Ω FICN 1 α υ ICB σ Im = ΩK Im FICN ICB ROB
12 T FICN K Re ICB B dip ICB /B unif ICB Q FICN K Im ICB B ICB Q FCN K Im CMB B dip CMB /B unif CMB K Re CMB B CMB T FCN α f r CMB ROB
13 Within the residuals (all VLBI strategies), where can we find the inner core parameters?
14 Contribution of the FICN on the nutations transfer function = R R R 0+ 1σ + σ σ FCN FCN + R σ σ FICN FICN RCW + σ σ CW
15 18.6 year Retro Real part of 18.6 year = mas Imaginary part of 18.6 year = 0.21 mas MHB2000
16 VLBI OBSERVATION STRATEGY 3. NEW APPROACH take the classical series or any other but fit the parameters in the time domain, and get probability distribution on the parameters See Koot et al., this session
17 Main results Bayesian approach in the time domain Almost all the same parameter values as MHB Particularly important changes for global flattening, inner core FICN frequency and quality factor Frequency approach: correlation between amplitudes of the nutations (ex: 9.3 and 18.6 years) Time approach: correlations between basic Earth parameters : probabilistic approach in which one uses the direct problem Lower uncertainties on the parameters related to a longer data set and the accounting of the error on the nutation in the time domain
18 THEORY 1. IMPROVEMENT IN RIGID NUTATION consider all coupling mechanism between tides and nutation (Lambert & Mathews) consider all coupling mechanism in the Poisson terms of the potential (Folgueira et al.)
19 THEORY 2. IMPROVEMENT IN NON-RIGID TRANSFER FUNCTION consider all possible coupling mechanisms at CMB and ICB: - electromagnetic - viscous - topographic See Folgueira et al., poster of this session
20 mantle core mantle core
21 mantle core
22 mantle core fluid pressure
23 OBSERVATION/THEORY 1. IMPROVEMENT IN ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION needs to have improvements in angular momentum of the atmosphere
24 Real part Imaginary part Atmospheric χ function Atmospheric χ function Geodetic χ function time Geodetic χ function time time time
25 OBSERVATION/THEORY 2. IMPROVEMENT IN MASS TRANSFER UNDERSTANDING not only the atmosphere plays a direct role on the nutation but the J2 changes and the nutations may be related, via the dynamical flattening entering in nutation modeling
26 Mass changes (1) Mantle convection Post-glacial rebound Core flow Ice cap
27 Mass changes (2) Atmosphere Ocean hydrology
28 OBSERVATION/THEORY 2. IMPROVEMENT IN FREE MODE MODELING can not be modeled, needs to be estimated from epoch to epoch See Lambert s work, IERS conventions + Descartes Fellows
29 Conclusions (1) Rigid nutations are well determined; The FCN frequency is quite well determined from VLBI observations, even if we consider different strategies for computing nutation series, or even considering atmospheric contamination of the amplitudes (not shown in this talk); The 18.6 year retrograde nutation is the key nutation for getting the right FICN parameters; the 0.5 year prograde nutation also helps; Different strategies for VLBI observations provide 18.6 year retrograde nutation amplitudes different with respect to MHB2000 at the level of µas; The FICN frequency and quality factor are not very well constrained; VLBI observations still need improvement;
30 Conclusions (2) The time domain approach looks very promising; The FCN free mode needs to be observed and determined; The atmosphere effects may be large and needs to be improved; nutations need to be corrected for; Many possibilities for the magnetic field deduced when considering error bars on the observed value; Other coupling mechanisms need to be considered; we believe in particular that the topographic coupling might be important; the triaxiality must be considered at the present-day level of precision. Perspectives for the planet Mars
31 ExoMars/GEP Lander Radioscience LaRa, a Space Geodesy Experiment to Mars Lander Radioscience Dehant V., Folkner W., Renotte E., Orban D., Le Maistre S., and the LaRa Team
32 Also possible: a direct link with the Earth! 7.2 GHz
33
34 Measuring Doppler shifts on Lander-Orbiter link Lander-Earth link Projection of relative velocity on line-of-sight Lander-Orbiter Dop. = r r V R r R
35 Rotation variations Objectives Orientation in space: precession/nutation Orientation in planet: polar motion Rotation speed: length-of-day variations Þ Modeling of Interior of planets Atmosphere dynamics (CO 2 sublimation/ condensation process)
36 solid core liquid core
37 Amplitudes Amplitudes rigid Mars nutations 250 days 250 days 250 days transfer function non-rigid Mars nutations IMPORTANT FOR: retrograde terannual nutation retrograde semiannual nutation retrograde 1/4 year nutation prograde semiannual nutation ROB
38 ROB
39 ... prograde semi-annual nutation ROB
40 ROB
41
Evaluation of the accuracy of the IAU 2006/2000 precession-nutation
 Evaluation of the accuracy of the IAU 2006/2000 precession-nutation Nicole Capitaine (1), Sébastien Lambert (1), Kunliang Yao (1), Jia-cheng Liu (1)(2) (1) SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris, France (2) Nanjing
Evaluation of the accuracy of the IAU 2006/2000 precession-nutation Nicole Capitaine (1), Sébastien Lambert (1), Kunliang Yao (1), Jia-cheng Liu (1)(2) (1) SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris, France (2) Nanjing
Rotation and Interior of Terrestrial Planets
 Rotation and Interior of Terrestrial Planets Veronique Dehant and Tim Van Hoolst Royal Observatory of Belgium introduction WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT THE MEAN ROTATION AND INTERIOR OF THE PLANETS? Orbit, rotation
Rotation and Interior of Terrestrial Planets Veronique Dehant and Tim Van Hoolst Royal Observatory of Belgium introduction WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT THE MEAN ROTATION AND INTERIOR OF THE PLANETS? Orbit, rotation
Remaining error sources in the nutation at the submilliarc second level
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B5, 2275, doi:10.1029/2002jb001763, 2003 Remaining error sources in the nutation at the submilliarc second level V. Dehant, 1 M. Feissel-Vernier, 2,3 O. de
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B5, 2275, doi:10.1029/2002jb001763, 2003 Remaining error sources in the nutation at the submilliarc second level V. Dehant, 1 M. Feissel-Vernier, 2,3 O. de
Planetary and Space Science
 Planetary and Space Science 59 (211) 169 181 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Planetary and Space Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pss Revealing Mars deep interior: Future geodesy
Planetary and Space Science 59 (211) 169 181 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Planetary and Space Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pss Revealing Mars deep interior: Future geodesy
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 17 May 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 17 May 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 17 May 2017](/thumbs/72/68061426.jpg) Signatures of the Martian rotation parameters in the Doppler and range observables Marie Yseboodt, Véronique Dehant, Marie-Julie Péters Royal Observatory of Belgium, Avenue circulaire 3, Brussels, Belgium,
Signatures of the Martian rotation parameters in the Doppler and range observables Marie Yseboodt, Véronique Dehant, Marie-Julie Péters Royal Observatory of Belgium, Avenue circulaire 3, Brussels, Belgium,
5 Transformation Between the Celestial and Terrestrial Systems
 No. 32 5 Transformation Between the Celestial and Terrestrial Systems The coordinate transformation to be used to transform from the terrestrial reference system (TRS) to the celestial reference system
No. 32 5 Transformation Between the Celestial and Terrestrial Systems The coordinate transformation to be used to transform from the terrestrial reference system (TRS) to the celestial reference system
Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks
 Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks Jan Vondrák and Cyril Ron, Astronomical Inst., Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague Contents: Introduction; Description
Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks Jan Vondrák and Cyril Ron, Astronomical Inst., Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague Contents: Introduction; Description
The 3D representation of the new transformation from the terrestrial to the celestial system.
 The 3D representation of the new transformation from the terrestrial to the celestial system. Véronique Dehant, Olivier de Viron Royal Observatory of Belgium Nicole Capitaine Observatoire de Paris, France
The 3D representation of the new transformation from the terrestrial to the celestial system. Véronique Dehant, Olivier de Viron Royal Observatory of Belgium Nicole Capitaine Observatoire de Paris, France
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC EXCITATION OF EARTH ROTATION
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC EXCITATION OF EARTH ROTATION S. BÖHM, T. NILSSON, M. SCHINDELEGGER, H. SCHUH Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, Advanced Geodesy Vienna University of Technology Gußhausstraße
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC EXCITATION OF EARTH ROTATION S. BÖHM, T. NILSSON, M. SCHINDELEGGER, H. SCHUH Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, Advanced Geodesy Vienna University of Technology Gußhausstraße
Geodätische Woche The global radiational S1 tide - current Earth rotation research at TU Wien. September 17, 2015
 Geodätische Woche 2015 A. Girdiuk, M. Schindelegger, J. Böhm / TU Wien / Geodätische Woche 2015 1/14 - current Earth rotation research at TU Wien A. Girdiuk, M. Schindelegger, J. Böhm TU Wien, Geodesy
Geodätische Woche 2015 A. Girdiuk, M. Schindelegger, J. Böhm / TU Wien / Geodätische Woche 2015 1/14 - current Earth rotation research at TU Wien A. Girdiuk, M. Schindelegger, J. Böhm TU Wien, Geodesy
Astronomy and Earth s Rotation with GEODESIE
 Astronomy and Earth s Rotation with GEODESIE Sébastien Lambert SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris, PSL Research University, CNRS, Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ. Paris 06, LNE What Science can we make Answer
Astronomy and Earth s Rotation with GEODESIE Sébastien Lambert SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris, PSL Research University, CNRS, Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ. Paris 06, LNE What Science can we make Answer
THE FREE CORE NUTATION
 THE FREE CORE NUTATION D.D. MCCARTHY U. S. Naval Observatory Washington, DC 20392 USA e-mail: dmc@maia.usno.navy.mil ABSTRACT. The International Earth rotation and Reference system Service (IERS) provides
THE FREE CORE NUTATION D.D. MCCARTHY U. S. Naval Observatory Washington, DC 20392 USA e-mail: dmc@maia.usno.navy.mil ABSTRACT. The International Earth rotation and Reference system Service (IERS) provides
PRECESSION, NUTATION, AND WOBBLE OF THE EARTH
 PRECESSION, NUTATION, AND WOBBLE OF THE EARTH Earth rotation has long been used as a measure of time, together with using the stars as reference points, to determine travellers whereabouts on the globe.
PRECESSION, NUTATION, AND WOBBLE OF THE EARTH Earth rotation has long been used as a measure of time, together with using the stars as reference points, to determine travellers whereabouts on the globe.
Anna Korbacz 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1 and Maik Thomas 2. Journées Systèmes de référence spatio-temporels.
 Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 estimated from the output of the global circulation models of the atmosphere - ERA-4 reanalysis and of the ocean - OMCT Anna Korbacz 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1 and Maik
Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 estimated from the output of the global circulation models of the atmosphere - ERA-4 reanalysis and of the ocean - OMCT Anna Korbacz 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1 and Maik
The global S 1 tide and Earth s nutation
 Journées 2014 St. Petersburg 22 24 September Michael SCHINDELEGGER Johannes BÖHM, David SALSTEIN The global S 1 tide and Earth s nutation Session 4: Earth s rotation and geodynamics Motivation & Background
Journées 2014 St. Petersburg 22 24 September Michael SCHINDELEGGER Johannes BÖHM, David SALSTEIN The global S 1 tide and Earth s nutation Session 4: Earth s rotation and geodynamics Motivation & Background
Abstract. By integrating the truncated complex scalar gravitational. of which are expanded to second order in ellipticity. A modied ellipticity
 A New Nutation Model Of Nonrigid Earth With Ocean And Atmosphere Cheng-li Huang, Wen-jing Jin, Xing-hao Liao Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, UCAR, NAO, CAS, Shanghai, 200030, P.R.China (email: clhuang@center.shao.ac.cn)
A New Nutation Model Of Nonrigid Earth With Ocean And Atmosphere Cheng-li Huang, Wen-jing Jin, Xing-hao Liao Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, UCAR, NAO, CAS, Shanghai, 200030, P.R.China (email: clhuang@center.shao.ac.cn)
IAU 2006 NFA GLOSSARY
 IAU 2006 NFA GLOSSARY Prepared by the IAU Division I Working Group Nomenclature for Fundamental Astronomy'' (latest revision: 20 November 2007) Those definitions corresponding to the IAU 2000 resolutions
IAU 2006 NFA GLOSSARY Prepared by the IAU Division I Working Group Nomenclature for Fundamental Astronomy'' (latest revision: 20 November 2007) Those definitions corresponding to the IAU 2000 resolutions
Introduction Fundamental definitions Motivation
 1 Introduction Fundamental definitions Motivation 1.1 Rotation and global shape of the Earth At a very elementary level, the Earth is considered to be an axially symmetric ellipsoid, rotating with uniform
1 Introduction Fundamental definitions Motivation 1.1 Rotation and global shape of the Earth At a very elementary level, the Earth is considered to be an axially symmetric ellipsoid, rotating with uniform
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations. Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis
 Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
Analysis Strategies And Software For Geodetic VLBI
 Analysis Strategies And Software For Geodetic VLBI Rüdiger Haas Presentation at the 7th EVN Symposium, Toledo, 2004 Outline: Observing stategies and observables Data analysis strategies Data analysis software
Analysis Strategies And Software For Geodetic VLBI Rüdiger Haas Presentation at the 7th EVN Symposium, Toledo, 2004 Outline: Observing stategies and observables Data analysis strategies Data analysis software
Defining Sources Selection and Celestial Reference Frame Stability
 The 17th of March, 2016 at Ekudeni, South Africa 9th IVS General Meeting Defining Sources Selection and Celestial Reference Frame Stability GATTANO C.¹, LAMBERT S.¹ ¹ SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris, PSL
The 17th of March, 2016 at Ekudeni, South Africa 9th IVS General Meeting Defining Sources Selection and Celestial Reference Frame Stability GATTANO C.¹, LAMBERT S.¹ ¹ SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris, PSL
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Mathematical models in GPS" Mathematical models used in GPS"
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME. Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol.2, No.3 (139), 87-94, 2005 COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON Department of Galaxies
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol.2, No.3 (139), 87-94, 2005 COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON Department of Galaxies
Grupo demecanica Celeste, Facultad de Ciencias, Valladolid, Spain. Dept. Applied Mathematics, University of Alicante, Alicante, Spain
 Advances in the Unied Theory of the Rotation of the Nonrigid Earth Juan Getino Grupo demecanica Celeste, Facultad de Ciencias, Valladolid, Spain Jose M.Ferrandiz Dept. Applied Mathematics, University of
Advances in the Unied Theory of the Rotation of the Nonrigid Earth Juan Getino Grupo demecanica Celeste, Facultad de Ciencias, Valladolid, Spain Jose M.Ferrandiz Dept. Applied Mathematics, University of
ASTRONOMICAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS AND FRAMES, ASTROMETRIC TECHNIQUES AND CATALOGS
 1 ASTRONOMICAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS AND FRAMES, ASTROMETRIC TECHNIQUES AND CATALOGS Jan Vondrák, Astronomical Institute Prague P PART 1: Reference systems and frames used in astronomy:! Historical outline,
1 ASTRONOMICAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS AND FRAMES, ASTROMETRIC TECHNIQUES AND CATALOGS Jan Vondrák, Astronomical Institute Prague P PART 1: Reference systems and frames used in astronomy:! Historical outline,
Love Numbers and Gravimetric Factor for Diurnal Tides. Piravonu M. Mathews
 Journal of the Geodetic Society of Japan Vol. 46, No. 4, (2001), pp. 231-236 Love Numbers and Gravimetric Factor for Diurnal Tides Piravonu M. Mathews Department of Theoretical Physics, University of Madras
Journal of the Geodetic Society of Japan Vol. 46, No. 4, (2001), pp. 231-236 Love Numbers and Gravimetric Factor for Diurnal Tides Piravonu M. Mathews Department of Theoretical Physics, University of Madras
The VLBI contribution to precession (present and future)
 The VLBI contribution to precession (present and future) N.Capitaine (1) and P. Wallace (2) (1) Observatoire de Paris/Syrte (2) RAL, HMNAO Precession-nutation parameters Classical: equinox-based fixed
The VLBI contribution to precession (present and future) N.Capitaine (1) and P. Wallace (2) (1) Observatoire de Paris/Syrte (2) RAL, HMNAO Precession-nutation parameters Classical: equinox-based fixed
Estimation of Geodetic and Geodynamical Parameters with VieVS
 Estimation of Geodetic and Geodynamical Parameters with VieVS, IVS 2010 General Meeting Proceedings, p.202 206 http://ivscc.gsfc.nasa.gov/publications/gm2010/spicakova.pdf Estimation of Geodetic and Geodynamical
Estimation of Geodetic and Geodynamical Parameters with VieVS, IVS 2010 General Meeting Proceedings, p.202 206 http://ivscc.gsfc.nasa.gov/publications/gm2010/spicakova.pdf Estimation of Geodetic and Geodynamical
Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop
 Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop T. van Dam (Uni. Lux), J. Ray (NGS/NOAA), X. Collilieux (IGN) Introduction Review the history of the GGFC Discuss the 2012 Workshop Review recommendations
Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop T. van Dam (Uni. Lux), J. Ray (NGS/NOAA), X. Collilieux (IGN) Introduction Review the history of the GGFC Discuss the 2012 Workshop Review recommendations
Precession, nutation, and space geodetic determination of the Earth s variable gravity field
 Precession, nutation, and space geodetic determination of the Earth s variable gravity field G. Bourda, N. apitaine To cite this version: G. Bourda, N. apitaine. Precession, nutation, and space geodetic
Precession, nutation, and space geodetic determination of the Earth s variable gravity field G. Bourda, N. apitaine To cite this version: G. Bourda, N. apitaine. Precession, nutation, and space geodetic
Reference system and non-rotating origin: the NRO for the rest of us Olivier de Viron, Véronique Dehant, and Nicole Capitaine
 Reference system and non-rotating origin: the NRO for the rest of us Olivier de Viron, Véronique Dehant, and Nicole Capitaine Abstract The concept of Non Rotating Origin has been introduced in the method
Reference system and non-rotating origin: the NRO for the rest of us Olivier de Viron, Véronique Dehant, and Nicole Capitaine Abstract The concept of Non Rotating Origin has been introduced in the method
Second-order torque on the tidal redistribution and the Earth s rotation ABSTRACT
 A&A 453, 363 369 (2006) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054516 c ESO 2006 Astronomy & Astrophysics Second-order torque on the tidal redistribution and the Earth s rotation S. B. Lambert 1, andp.m.mathews 2 1
A&A 453, 363 369 (2006) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054516 c ESO 2006 Astronomy & Astrophysics Second-order torque on the tidal redistribution and the Earth s rotation S. B. Lambert 1, andp.m.mathews 2 1
Gravimetry of the Planets - J.P. Barriot
 Gravimetry of the Planets - J.P. Barriot Programme of the training Thursday 18 November 9h-12h30 (with coffee break at 10h30) "Current tectonic and geomorphology of Mars", Ernst Hauber 14h30-18h (with
Gravimetry of the Planets - J.P. Barriot Programme of the training Thursday 18 November 9h-12h30 (with coffee break at 10h30) "Current tectonic and geomorphology of Mars", Ernst Hauber 14h30-18h (with
ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS
 ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS Markus Rothacher, Gerhard Beutler Astronomical Institute, University of Berne CH-3012 Berne, Switzerland ABSTRACT Satellite space-geodetic measurements have been
ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS Markus Rothacher, Gerhard Beutler Astronomical Institute, University of Berne CH-3012 Berne, Switzerland ABSTRACT Satellite space-geodetic measurements have been
PRESS KIT: Scientific work of the Royal Observatory of Belgium on the Mars Express mission
 PRESS KIT: Scientific work of the Royal Observatory of Belgium on the Mars Express mission Royal Observatory of Belgium Avenue Circulaire, 3 - Ringlaan 3 1180 BRUXELLES BRUSSEL Contact : Véronique Dehant,
PRESS KIT: Scientific work of the Royal Observatory of Belgium on the Mars Express mission Royal Observatory of Belgium Avenue Circulaire, 3 - Ringlaan 3 1180 BRUXELLES BRUSSEL Contact : Véronique Dehant,
New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts
 Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
Global reference systems and Earth rotation
 current realizations and scientific problems Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2, Tomasz Liwosz 1, Jerzy Rogowski 1, Jan Kryński 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Geodetic Astronomy Warsaw University of Technology 2
current realizations and scientific problems Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2, Tomasz Liwosz 1, Jerzy Rogowski 1, Jan Kryński 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Geodetic Astronomy Warsaw University of Technology 2
OBSERVING AND MODELING LONG-PERIOD TIDAL VARIATIONS IN POLAR MOTION
 OBSERVING AND MODELING LONG-PERIOD TIDAL VARIATIONS IN POLAR MOTION R.S. GROSS 1, S.R. DICKMAN 2 1 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena, CA 91109,
OBSERVING AND MODELING LONG-PERIOD TIDAL VARIATIONS IN POLAR MOTION R.S. GROSS 1, S.R. DICKMAN 2 1 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena, CA 91109,
Effects of zonal deformations and the Earth s rotation rate variations on precession-nutation
 A&A 428, 255 260 (2004) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20035952 c ESO 2004 Astronomy & Astrophysics Effects of zonal deformations and the Earth s rotation rate variations on precession-nutation S. Lambert 1 and
A&A 428, 255 260 (2004) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20035952 c ESO 2004 Astronomy & Astrophysics Effects of zonal deformations and the Earth s rotation rate variations on precession-nutation S. Lambert 1 and
The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part I : General concepts
 The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part I : General concepts Zuheir ALTAMIMI Laboratoire de Recherche en Géodésie Institut national de l information géographique et forestière (IGN),
The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part I : General concepts Zuheir ALTAMIMI Laboratoire de Recherche en Géodésie Institut national de l information géographique et forestière (IGN),
Earth. Properties of Earth. Earth's Interior. Earth is the planet that we know best
 Earth Earth is the planet that we know best Our observations of the other planets are all compared to the conditions and properties of Earth Properties of Earth Semimajor Axis Orbital Eccentricity Orbital
Earth Earth is the planet that we know best Our observations of the other planets are all compared to the conditions and properties of Earth Properties of Earth Semimajor Axis Orbital Eccentricity Orbital
Understanding the Earth core and nutation. Abstract Book
 Understanding the Earth core and nutation. Abstract Book Brussels, September 2016 ii Contents Monday Talks 1 Drilling the Earth down to the core with VLBI. (Sebastien Lambert, Cesar Gattano)..................................
Understanding the Earth core and nutation. Abstract Book Brussels, September 2016 ii Contents Monday Talks 1 Drilling the Earth down to the core with VLBI. (Sebastien Lambert, Cesar Gattano)..................................
1 General Definitions and Numerical Standards
 This chapter provides general definitions for some topics and the values of numerical standards that are used in the document. Those are based on the most recent reports of the appropriate working groups
This chapter provides general definitions for some topics and the values of numerical standards that are used in the document. Those are based on the most recent reports of the appropriate working groups
IVS Working Group 2 for Product Specification and Observing Programs
 IVS Working Group 2 for Product Specification and Observing Programs Final Report (13 th of February 2002) Harald Schuh (hschuh@luna.tuwien.ac.at) *) Patrick Charlot (charlot@observ.u-bordeaux.fr) Hayo
IVS Working Group 2 for Product Specification and Observing Programs Final Report (13 th of February 2002) Harald Schuh (hschuh@luna.tuwien.ac.at) *) Patrick Charlot (charlot@observ.u-bordeaux.fr) Hayo
AST111, Lecture 1b. Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements
 AST111, Lecture 1b Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements Planetary properties (continued): Measuring Mass The orbital period of a moon about a planet depends
AST111, Lecture 1b Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements Planetary properties (continued): Measuring Mass The orbital period of a moon about a planet depends
The rotational motion of Vesta
 The rotational motion of Vesta Nicolas Rambaux To cite this version: Nicolas Rambaux. The rotational motion of Vesta. 12 p. Accepted for publication in Astronomy and Astrophysics. 2013.
The rotational motion of Vesta Nicolas Rambaux To cite this version: Nicolas Rambaux. The rotational motion of Vesta. 12 p. Accepted for publication in Astronomy and Astrophysics. 2013.
Comparison between high precision precession models for the ecliptic and the equator
 A&A 421, 365 379 (2004) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20035942 c ESO 2004 Astronomy & Astrophysics Comparison between high precision precession models for the ecliptic and the equator N. Capitaine 1,P.T.Wallace
A&A 421, 365 379 (2004) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20035942 c ESO 2004 Astronomy & Astrophysics Comparison between high precision precession models for the ecliptic and the equator N. Capitaine 1,P.T.Wallace
Information on internal structure from shape, gravity field and rotation
 Information on internal structure from shape, gravity field and rotation Seismological information is available only for the Earth and in limited amounts for the Moon. Various geodetic data put constraints
Information on internal structure from shape, gravity field and rotation Seismological information is available only for the Earth and in limited amounts for the Moon. Various geodetic data put constraints
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate
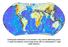 Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
Empiric Models of the Earth s Free Core Nutation
 ISSN 38-946, Solar System Research, 27, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 492 497. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 27. Original Russian Text Z.M. Malkin, 27, published in Astronomicheskii Vestnik, 27, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp.
ISSN 38-946, Solar System Research, 27, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 492 497. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 27. Original Russian Text Z.M. Malkin, 27, published in Astronomicheskii Vestnik, 27, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp.
Introduction to geodetic VLBI
 Introduction to geodetic VLBI David Mayer Andreas Hellerschmied Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Introduction to geodetic VLBI David Mayer Andreas Hellerschmied Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy, IAG
 The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy, IAG Hans-Peter Plag (1), Markus Rothacher (2), Richard Gross (3), Srinivas Bettadpur (4) (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines
The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy, IAG Hans-Peter Plag (1), Markus Rothacher (2), Richard Gross (3), Srinivas Bettadpur (4) (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines
Towards sub-microarsecond rigid Earth nutation series in. Abstract. The nonrigid Earth nutation series adopted by the IAU (International
 Towards sub-microarsecond rigid Earth nutation series in the Hamiltonian theory J. Souchay and M. Folgueira 1 Observatoire de Paris, 61 Avenue de l'observatoire. 75014 Paris, France Abstract. The nonrigid
Towards sub-microarsecond rigid Earth nutation series in the Hamiltonian theory J. Souchay and M. Folgueira 1 Observatoire de Paris, 61 Avenue de l'observatoire. 75014 Paris, France Abstract. The nonrigid
On the definition and use of the ecliptic in modern astronomy
 On the definition and use of the ecliptic in modern astronomy Nicole Capitaine (1), Michael Soffel (2) (1) : Observatoire de Paris / SYRTE (2) : Lohrmann Observatory, Dresden Technical University Introduction
On the definition and use of the ecliptic in modern astronomy Nicole Capitaine (1), Michael Soffel (2) (1) : Observatoire de Paris / SYRTE (2) : Lohrmann Observatory, Dresden Technical University Introduction
SIO15 Midterm 1, Monday Oct. 30, 2017 TEST VARIATION: 2
 SIO15 Midterm 1, Monday Oct. 30, 2017 TEST VARIATION: 2 1) Over the last 20 years, which of these natural disasters killed the most people in the U.S.? a) heat waves b) hurricanes c) lightning strikes
SIO15 Midterm 1, Monday Oct. 30, 2017 TEST VARIATION: 2 1) Over the last 20 years, which of these natural disasters killed the most people in the U.S.? a) heat waves b) hurricanes c) lightning strikes
Geodesy and interior structure of Mercury
 Geodesy and interior structure of Mercury Tim Van Hoolst and the ROB planets team Royal Observatory of Belgium February 26, 2007 Outline 1 Tidal potential Potential Response 2 Interior structure models
Geodesy and interior structure of Mercury Tim Van Hoolst and the ROB planets team Royal Observatory of Belgium February 26, 2007 Outline 1 Tidal potential Potential Response 2 Interior structure models
Influence of the inner core on the rotation of the Earth revisited
 Influence of the inner core on the rotation of the Earth revisited A. Escapa 1, J. M. Ferrándiz 1, & J. Getino 2 1 Dept. Applied Mathematics. University of Alicante. Spain 2 Dept. Applied Mathematics.
Influence of the inner core on the rotation of the Earth revisited A. Escapa 1, J. M. Ferrándiz 1, & J. Getino 2 1 Dept. Applied Mathematics. University of Alicante. Spain 2 Dept. Applied Mathematics.
Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment. Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute
 Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Land uplift is just one consequence of the physical
Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Land uplift is just one consequence of the physical
The Martian Climate Revisited
 Peter L. Read and Stephen R. Lewis The Martian Climate Revisited Atmosphere and Environment of a Desert Planet Springer Published in association with Praxis Publishing Chichester, UK Contents Preface Abbreviations
Peter L. Read and Stephen R. Lewis The Martian Climate Revisited Atmosphere and Environment of a Desert Planet Springer Published in association with Praxis Publishing Chichester, UK Contents Preface Abbreviations
Planetary Interiors. Earth s Interior Structure Hydrostatic Equilibrium Heating Constituent Relations Gravitational Fields Isostasy Magnetism
 Planetary Interiors Earth s Interior Structure Hydrostatic Equilibrium Heating Constituent Relations Gravitational Fields Isostasy Magnetism Isostasy Courtesy of U of Leeds Now apply this idea to topography
Planetary Interiors Earth s Interior Structure Hydrostatic Equilibrium Heating Constituent Relations Gravitational Fields Isostasy Magnetism Isostasy Courtesy of U of Leeds Now apply this idea to topography
Tests on the validity of atmospheric torques on Earth computed from atmospheric model outputs
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2068, doi:10.1029/2001jb001196, 2003 Tests on the validity of atmospheric torques on Earth computed from atmospheric model outputs O. de Viron and V.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2068, doi:10.1029/2001jb001196, 2003 Tests on the validity of atmospheric torques on Earth computed from atmospheric model outputs O. de Viron and V.
Free polar motion of a triaxial and elastic body in Hamiltonian formalism: Application to the Earth and Mars
 A&A 43, 111 1113 (5) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:4131 c ESO 5 Astronomy & Astrophysics Free polar motion of a triaxial and elastic body in Hamiltonian formalism: Application to the Earth and Mars M. Folgueira 1,
A&A 43, 111 1113 (5) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:4131 c ESO 5 Astronomy & Astrophysics Free polar motion of a triaxial and elastic body in Hamiltonian formalism: Application to the Earth and Mars M. Folgueira 1,
New transfer functions for nutations of a nonrigid Earth
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 102, NO. B12, PAGES 27,659-27,687, DECEMBER 10, 1997 New transfer functions for nutations of a nonrigid Earth V. Dehant and P. Defraigne Royal Observatory of Belgium,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 102, NO. B12, PAGES 27,659-27,687, DECEMBER 10, 1997 New transfer functions for nutations of a nonrigid Earth V. Dehant and P. Defraigne Royal Observatory of Belgium,
9. Moon, Mercury, Venus
 9. Moon, Mercury, Venus All the heavier elements were manufactured by stars later, either by thermonuclear fusion reactions deep in their interiors or by the violent explosions that mark the end of massive
9. Moon, Mercury, Venus All the heavier elements were manufactured by stars later, either by thermonuclear fusion reactions deep in their interiors or by the violent explosions that mark the end of massive
EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS
 EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS Francis Nimmo Last Week Applications of fluid dynamics to geophysical problems Navier-Stokes equation describes fluid flow: Convection requires solving the coupled equations
EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS Francis Nimmo Last Week Applications of fluid dynamics to geophysical problems Navier-Stokes equation describes fluid flow: Convection requires solving the coupled equations
Interaction between subdaily Earth rotation parameters and GPS orbits Natalia Panafidina, Urs Hugentobler, Manuela Seitz
 Interaction between subdaily Earth rotation parameters and GPS orbits Natalia Panafidina, Urs Hugentobler, Manuela Seitz Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI) Centrum für Geodätische Erdsystemforschung
Interaction between subdaily Earth rotation parameters and GPS orbits Natalia Panafidina, Urs Hugentobler, Manuela Seitz Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI) Centrum für Geodätische Erdsystemforschung
3.3 Analysis Coordinator
 1. Introduction 2. Analysis of ITRF2014 post-seismic parameterization In this report we outline the activities of the Analysis Coordinator during 2015. The main activities were analysis of the ITRF2014
1. Introduction 2. Analysis of ITRF2014 post-seismic parameterization In this report we outline the activities of the Analysis Coordinator during 2015. The main activities were analysis of the ITRF2014
VLBA Astrometry of Planetary Orbiters
 VLBA Astrometry of Planetary Orbiters Dayton Jones (1), Ed Fomalont (2), Vivek Dhawan (2), Jon Romney (2), William Folkner (1), Robert Jacobson (1), Gabor Lanyi (1), and James Border (1) (1) Jet Propulsion
VLBA Astrometry of Planetary Orbiters Dayton Jones (1), Ed Fomalont (2), Vivek Dhawan (2), Jon Romney (2), William Folkner (1), Robert Jacobson (1), Gabor Lanyi (1), and James Border (1) (1) Jet Propulsion
Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz
 GGOS and Reference Systems Introduction 2015-10-12 Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz Torsten Mayer-Gürr 1 Course and exam Lecture Monday 14:00 16:00, A111 (ST01044)
GGOS and Reference Systems Introduction 2015-10-12 Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz Torsten Mayer-Gürr 1 Course and exam Lecture Monday 14:00 16:00, A111 (ST01044)
From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed?
 From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed? Zuheir ALTAMIMI Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière, France Vice-President,
From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed? Zuheir ALTAMIMI Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière, France Vice-President,
Fundamental Station Wettzell - geodetic observatory -
 Fundamental Station Wettzell - geodetic observatory - Wolfgang Schlüter Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Fundamental Station Wettzell Germany Radiometer Workshop, Wettzell, 10.10.06 Evolvement
Fundamental Station Wettzell - geodetic observatory - Wolfgang Schlüter Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Fundamental Station Wettzell Germany Radiometer Workshop, Wettzell, 10.10.06 Evolvement
Elements of Geodesy. Shape of the Earth Tides Terrestrial coordinate systems Inertial coordinate systems Earth orientation parameters
 Elements of Geodesy Shape of the Earth Tides Terrestrial coordinate systems Inertial coordinate systems Earth orientation parameters E. Calais Purdue University - EAS Department Civil 3273 ecalais@purdue.edu
Elements of Geodesy Shape of the Earth Tides Terrestrial coordinate systems Inertial coordinate systems Earth orientation parameters E. Calais Purdue University - EAS Department Civil 3273 ecalais@purdue.edu
Exam# 1 Review Gator 1 Keep the first page of the exam. Scores will be published using the exam number Chapter 0 Charting the Heavens
 Exam# 1 Review Exam is Wednesday October 11 h at 10:40AM, room FLG 280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 (HB) with eraser. We provide the scantrons No use of calculator or any electronic device during
Exam# 1 Review Exam is Wednesday October 11 h at 10:40AM, room FLG 280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 (HB) with eraser. We provide the scantrons No use of calculator or any electronic device during
IERS DB Retreat, Paris, France, 23 May ICRF-3 Overview
 IERS DB Retreat, Paris, France, 23 May 2013 ICRF-3 Overview Jacobs, Ma, Gaume 2013/05/24 Ralph Gaume USNO & Chopo Ma, GSFC (presenters) Prepared by Christopher S. Jacobs, (ICRF-3 WG chair) Jet Propulsion
IERS DB Retreat, Paris, France, 23 May 2013 ICRF-3 Overview Jacobs, Ma, Gaume 2013/05/24 Ralph Gaume USNO & Chopo Ma, GSFC (presenters) Prepared by Christopher S. Jacobs, (ICRF-3 WG chair) Jet Propulsion
Using non-tidal atmospheric loading model in space geodetic data processing: Preliminary results of the IERS analysis campaign
 Using non-tidal atmospheric loading model in space geodetic data processing: Preliminary results of the IERS analysis campaign Xavier Collilieux (1), Zuheir Altamimi (1), Laurent Métivier (1), Tonie van
Using non-tidal atmospheric loading model in space geodetic data processing: Preliminary results of the IERS analysis campaign Xavier Collilieux (1), Zuheir Altamimi (1), Laurent Métivier (1), Tonie van
INPOP10a. A. Fienga, UTINAM/IMCCE
 INPOP10a A. Fienga, UTINAM/IMCCE INPOP team: J. Laskar, IMCCE, Obs. de Paris H. Manche, IMCCE, Obs. de Paris P. Kuchynka, IMCCE, Obs. de Paris M. Gastineau, IMCCE, Obs. de Paris INPOP new release: INPOP10a
INPOP10a A. Fienga, UTINAM/IMCCE INPOP team: J. Laskar, IMCCE, Obs. de Paris H. Manche, IMCCE, Obs. de Paris P. Kuchynka, IMCCE, Obs. de Paris M. Gastineau, IMCCE, Obs. de Paris INPOP new release: INPOP10a
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Expressions for IAU 2000 precession quantities. N. Capitaine 1,P.T.Wallace 2, and J. Chapront 1. 1.
 A&A 42, 567 586 (2003) DOI: 0.05/0004-636:2003539 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics Expressions for IAU 2000 precession quantities N. Capitaine,P.T.Wallace 2, and J. Chapront Observatoire de Paris, SYRTE/UMR8630-CNRS,
A&A 42, 567 586 (2003) DOI: 0.05/0004-636:2003539 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics Expressions for IAU 2000 precession quantities N. Capitaine,P.T.Wallace 2, and J. Chapront Observatoire de Paris, SYRTE/UMR8630-CNRS,
ITRF2014 Et la prise en compte des mouvements non linéaires
 ITRF2014 Et la prise en compte des mouvements non linéaires Zuheir Altamimi, Paul Rebischung, Laurent Métivier, Xavier Collilieux E-mail: zuheir.altamimi@ign.fr ITRF2014 Network Key Points Modelling of
ITRF2014 Et la prise en compte des mouvements non linéaires Zuheir Altamimi, Paul Rebischung, Laurent Métivier, Xavier Collilieux E-mail: zuheir.altamimi@ign.fr ITRF2014 Network Key Points Modelling of
REPORT OF THE IAU DIVISION 1 WORKING GROUP ON NOMENCLATURE FOR FUNDAMENTAL ASTRONOMY (NFA)
 REPORT OF THE IAU DIVISION 1 WORKING GROUP ON NOMENCLATURE FOR FUNDAMENTAL ASTRONOMY (NFA) N. CAPITAINE, Observatoire de Paris, France and C. HOHENKERK, HMNAO, UK; A.H. ANDREI, Observatorio Nacional, Brazil;
REPORT OF THE IAU DIVISION 1 WORKING GROUP ON NOMENCLATURE FOR FUNDAMENTAL ASTRONOMY (NFA) N. CAPITAINE, Observatoire de Paris, France and C. HOHENKERK, HMNAO, UK; A.H. ANDREI, Observatorio Nacional, Brazil;
Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy
 Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy Johannes Böhm 18 November 2011 @ UNESP, Presidente Prudente, Brazil The atmosphere.. is not only causing troubles in space geodesy.. but it opens up a wide field of
Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy Johannes Böhm 18 November 2011 @ UNESP, Presidente Prudente, Brazil The atmosphere.. is not only causing troubles in space geodesy.. but it opens up a wide field of
Introduction to geodetic VLBI and VieVS software
 Introduction to geodetic VLBI and VieVS software Hana Krásná and colleagues April 15, 2014 Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory, South Africa Introduction to geodetic VLBI Introduction to VieVS Our
Introduction to geodetic VLBI and VieVS software Hana Krásná and colleagues April 15, 2014 Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory, South Africa Introduction to geodetic VLBI Introduction to VieVS Our
Atmospheric angular momentum time-series: characterization of their internal noise and creation of a combined series
 J Geod (2006) 79: 663 674 DOI 10.1007/s00190-005-0019-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE L. Koot O. de Viron V. Dehant Atmospheric angular momentum time-series: characterization of their internal noise and creation of
J Geod (2006) 79: 663 674 DOI 10.1007/s00190-005-0019-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE L. Koot O. de Viron V. Dehant Atmospheric angular momentum time-series: characterization of their internal noise and creation of
Special Bureau for Loading: Potential Role Versus Reality
 Special Bureau for Loading: Potential Role Versus Reality Hans-Peter Plag Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology and Seismological Laboratory University of Nevada, Reno Special Bureau for Loading: Potential
Special Bureau for Loading: Potential Role Versus Reality Hans-Peter Plag Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology and Seismological Laboratory University of Nevada, Reno Special Bureau for Loading: Potential
Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions. J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM
 Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM IERS Conventions update: electronic access http://tai.bipm.org/iers/convupdt/listupdt.html Introduction Add a set of
Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM IERS Conventions update: electronic access http://tai.bipm.org/iers/convupdt/listupdt.html Introduction Add a set of
The final publication is available at Springer. DOI: / _6
 Originally published as: Seitz, F., H. Schuh: Earth Rotation. In: Sciences of Geodesy I: Advances and Future Directions, Xu, G. (Ed.), 185 227, Springer, Heidelberg, ISBN 978 3 642 11744, 21. The final
Originally published as: Seitz, F., H. Schuh: Earth Rotation. In: Sciences of Geodesy I: Advances and Future Directions, Xu, G. (Ed.), 185 227, Springer, Heidelberg, ISBN 978 3 642 11744, 21. The final
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 30 Aug 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 30 Aug 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 30 Aug 2018](/thumbs/86/93331603.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. article c ESO 218 August 31, 218 Long-term orbital and rotational motions of Ceres and Vesta T. Vaillant, J. Laskar, N. Rambaux, and M. Gastineau ASD/IMCCE, Observatoire
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. article c ESO 218 August 31, 218 Long-term orbital and rotational motions of Ceres and Vesta T. Vaillant, J. Laskar, N. Rambaux, and M. Gastineau ASD/IMCCE, Observatoire
GG S. Internal Vision of GGOS. Markus Rothacher. GFZ Potsdam
 Internal Vision of GGOS Markus Rothacher GFZ Potsdam GGOS Retreat DGFI in Munich February 15-16, 2006 Contents Motivation Four Levels of Products of the IAG Services: First Level: Raw Data Collection Second
Internal Vision of GGOS Markus Rothacher GFZ Potsdam GGOS Retreat DGFI in Munich February 15-16, 2006 Contents Motivation Four Levels of Products of the IAG Services: First Level: Raw Data Collection Second
Overview of the Solar System
 The Solar System Overview of the Solar System Basics Source: Nine Planets - A Multimedia Tour of the Solar System * By Bill Arnett The solar system consists of the Sun, the nine planets, about 90 satellites
The Solar System Overview of the Solar System Basics Source: Nine Planets - A Multimedia Tour of the Solar System * By Bill Arnett The solar system consists of the Sun, the nine planets, about 90 satellites
Solution for Homework# 3. Chapter 5 : Review & Discussion
 Solution for Homework# 3 Chapter 5 : Review & Discussion. The largest telescopes are reflecting telescopes, primarily because of 3 distinct disadvantages of the refracting telescope. When light passes
Solution for Homework# 3 Chapter 5 : Review & Discussion. The largest telescopes are reflecting telescopes, primarily because of 3 distinct disadvantages of the refracting telescope. When light passes
Earth Science 104. Earth s Place in the Cosmos, Structure History of Astronomy
 Earth Science 104 Earth s Place in the Cosmos, Structure History of Astronomy No lab this week Must pass lab to pass this class Instructors will give percent lab grade to one another Introduction Get Lab
Earth Science 104 Earth s Place in the Cosmos, Structure History of Astronomy No lab this week Must pass lab to pass this class Instructors will give percent lab grade to one another Introduction Get Lab
Update on the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) : ITRF2014. Zuheir Altamimi
 Update on the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) : ITRF2014 Zuheir Altamimi Head of the IERS ITRF Product Center IAG Vice President IGN, France E-mail: zuheir.altamimi@ign.fr Key Points Introduction:
Update on the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) : ITRF2014 Zuheir Altamimi Head of the IERS ITRF Product Center IAG Vice President IGN, France E-mail: zuheir.altamimi@ign.fr Key Points Introduction:
Linking the Planetary Ephemeris to the ICRF. W. M. Folkner
 Linking the Planetary Ephemeris to the ICRF W. M. Folkner 28 August 2012 2012. Government sponsorship acknowledged. This document has been reviewed for export control and does NOT contain controlled technical
Linking the Planetary Ephemeris to the ICRF W. M. Folkner 28 August 2012 2012. Government sponsorship acknowledged. This document has been reviewed for export control and does NOT contain controlled technical
The celestial reference system and its role in the epoch of global geodetic technologies
 Reports on Geodesy, vol. 92, no. 1, 2012 The celestial reference system and its role in the epoch of global geodetic technologies Jerzy B. Rogowski 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2 1 Warsaw University of Technology,
Reports on Geodesy, vol. 92, no. 1, 2012 The celestial reference system and its role in the epoch of global geodetic technologies Jerzy B. Rogowski 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2 1 Warsaw University of Technology,
Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS)
 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS) Laura Sánchez 1, Johannes Ihde 2, Roland
Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS) Laura Sánchez 1, Johannes Ihde 2, Roland
Surface Mass Loads from GRACE, GPS, and Earth Rotation
 Surface Mass Loads from GRACE,, and Earth Rotation R. Gross *, G. Blewitt, H.-P. Plag, P. Clarke, D. Lavallée, T. van Dam *Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA Nevada
Surface Mass Loads from GRACE,, and Earth Rotation R. Gross *, G. Blewitt, H.-P. Plag, P. Clarke, D. Lavallée, T. van Dam *Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA Nevada
Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI)
 Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) A brief Note compiled by: Prof. Madhav N. Kulkarni, IIT Bombay Since the inception of the Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) system in 1967, this
Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) A brief Note compiled by: Prof. Madhav N. Kulkarni, IIT Bombay Since the inception of the Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) system in 1967, this
Can we see evidence of post-glacial geoidal adjustment in the current slowing rate of rotation of the Earth?
 Can we see evidence of post-glacial geoidal adjustment in the current slowing rate of rotation of the Earth? BARRETO L., FORTIN M.-A., IREDALE A. In this simple analysis, we compare the historical record
Can we see evidence of post-glacial geoidal adjustment in the current slowing rate of rotation of the Earth? BARRETO L., FORTIN M.-A., IREDALE A. In this simple analysis, we compare the historical record
Astronomy 6570 Physics of the Planets. Precession: Free and Forced
 Astronomy 6570 Physics of the Planets Precession: Free and Forced Planetary Precession We have seen above how information concerning the distribution of density within a planet (in particular, the polar
Astronomy 6570 Physics of the Planets Precession: Free and Forced Planetary Precession We have seen above how information concerning the distribution of density within a planet (in particular, the polar
the precession-nutation parameters and Greenwich sidereal time, which Ephemeris Pole (CEP) has to be extended in order to be consistent with
 Denition of the Celestial Ephemeris Pole and the Celestial Ephemeris Origin Nicole Capitaine DANOF/UMR8630-CNRS, Observatoire deparis 61, avenue de l'observatoire, 75014 - Paris, France, capitain@danof.obspm.fr
Denition of the Celestial Ephemeris Pole and the Celestial Ephemeris Origin Nicole Capitaine DANOF/UMR8630-CNRS, Observatoire deparis 61, avenue de l'observatoire, 75014 - Paris, France, capitain@danof.obspm.fr
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry
 Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
