Anna Korbacz 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1 and Maik Thomas 2. Journées Systèmes de référence spatio-temporels.
|
|
|
- Earl Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 estimated from the output of the global circulation models of the atmosphere - ERA-4 reanalysis and of the ocean - OMCT Anna Korbacz 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1 and Maik Thomas 2 1 Space Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, Poland akorbacz@cbk.waw.pl 2 GeoForschungsZentrum, Potsdam, Germany presented at Journées Systèmes de référence spatio-temporels Paris, France, September 27 A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
2 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Data description and analysis 3 Results 4 Conclusions A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
3 Introduction Motivation Earlier investigation of excitation of the equatorial components of Earth rotation have revealed significant differences between effective angular momentum functions derived from ERA-4 reanalysis and nontidal OMCT and from other atmospheric and oceanic models (Korbacz et al., 27). These differences have been found smaller at shorter periods while increasing towards the longer periods. Current research is an extension of the previous work by considering the axial component of rotation expressed as changes of the length of day (LOD). The combination ERA-4 + OMCT will be compared to other available models of the atmospheric and oceanic excitation and to the ervations of LOD over a broad band of frequencies: from decadal through interannual and seasonal to intraseasonal. Korbacz A., et al., 27, Atmospheric and nontidal oceanic excitation of polar motion estimated from the output of the models ERA-4 and OMCT, Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol. 9, 9625, 27, European Geosciences Union. A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
4 Introduction General considerations According to the principle of conservation of angular momentum, changes in the LOD are excited by mass redistributions and angular momentum exchanges between the solid Earth and geophysical fluids: atmosphere, oceans, land hydrosphere and fluid core. It has been proven that variations with decadal and longer periods are excited mainly by the interactions between the core and the mantle. Changes with shorter periods are driven mostly by the dynamically coupled system atmosphere-oceans. Comparison between geophysical excitation data and geodetic ervations of LOD is much simpler than in case of polar motion - there is a linear relationship between χ 3 component of the atmospheric and oceanic angular momenta (AAM, OAM) and LOD. A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
5 Introduction Objectives of the work estimate atmospheric and oceanic excitation of LOD using a new consistent set of AAM and OAM time series: AAM: from ERA-4 reanalysis model OAM: from OMCT simulation driven by ERA-4 output fields compare to the estimates based on the alternative AAM and OAM data sets and to the excitation inferred from the Earth rotation ervations A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
6 Data description and analysis Atmospheric angular momentum (AAM) estimates AAM and AAMIB - NCEP-NCAR reanalysis data ftp://ftp.aer.com/pub/anon collaborations/sba/aamf.ncep.reanalysis temporal resolution: 6 hours data span: AAM - ERA-4 reanalysis data temporal resolution: 6 hours data span: Note: AAM series are based on the full variability of the pressure fields AAMIB series assume an isostatic ocean response to atmospheric pressure fluctuations and thus only include effects of variability in the average atmospheric pressure over the ocean A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
7 Data description and analysis Oceanic angular momentum (OAM) estimates OAM code ocean model forcing atmosphere model temporal resolution data span T6 OMCT ERA-4 3 min P1 MOM + assimil. COADS /NCEP 1 month G5 ECCO-MITgcm NCEP 1 days G3 ECCO-JPL NCEP 1 day Pas ECCO-Scripps + assimil. NCEP 1 day Note: all OAM series except T6 are referred to the inverted barometer (IB) ocean model, therefore should be combined with AAMIB when computing the aggregated oceanic-atmospheric excitation (important for PM, much less important for LOD) T6 Thomas, M., et al., 21, Geophys. Res. Lett., 28(12), P1 Ponte, R. M., 21, unpublished manuscript. G5 Gross, R. S., et al., 25, J. Geophys. Res., 11, B945. G3 Gross, R. S., et al., 23, J. Geophys. Res., 18, B8. Pas Ponte, R. M., et al., 21, Geophys. Res. Lett., 28(9), A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
8 Data description and analysis LOD data COMB22 solution - combination of Earth rotation ervations from different techniques, derived by Gross (23) data span: temporal resolution: 12 hours - time series of LOD from the COMB22 solution Gross, R. S., 2, Combinations of Earth Orientation Measurements: SPACE97, COMB97 and POLE97. J. Geodesy, vol. 73, A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
9 Data description and analysis Data analysis perform linear transformation AAM, OAM χ 3 LOD, split up the excitation functions AAM, OAM and erved: model (first order polynomial + sum of the sinusoids with periods 1, 1/2 and 1/3 year), residuals = total excitation model, compare amplitudes and phases of the seasonal harmonics, computed from the geophysical model and ervations split up residual series into four components: decadal: T > 8 years interannual: 2 < T < 8 years seasonal: 1/2 < T < 2 years intraseasonal: 2 days < T < 1/2 year compare the estimated oceanic and atmospheric excitations to the erved one in each of the selected spectral bands A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées Journées / 19 ()
10 Data description and analysis Data sets 3 AAM LOD wind (ms) AAM LOD pressure (ms) OAM LOD currents (ms).2.2 OAM LOD mass (ms) Figure: Atmospheric and oceanic contributions to LOD estimated from the models ERA-4 and OMCT. Variations with period shorter than 2 days have been removed by smoothing. Scale is the same in each panel. A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées 27 1 / 19 ()
11 Data description and analysis Data sets.5 AAM LOD wind (ms).5.2 AAM LOD pressure (ms).2.2 OAM LOD currents (ms).2.2 OAM LOD mass (ms) Figure: Same as in the previous figure but after removal of the model containing the first order polynomial and sum of the sinusoids with periods 1, 1/2 and 1/3 year. A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
12 Results Seasonal harmonics LOD cos (ms) T6 G3 Annual zoom AAM OAM LOD sin (ms) LOD cos (ms) T6 G3 Semiannual zoom OAM AAM LOD sin (ms) LOD cos (ms) T6 G3 Terannual.4.2 zoom LOD sin (ms) Figure: Seasonal harmonics of the atmospheric and oceanic excitation of LOD. Analysis was done over the period Note: in case of T6 shown are additionally separate contributions from AAM and OAM (dotted line) A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
13 Results Seasonal harmonics LOD cos (ms) T6 G5 P1 Annual zoom AAM OAM LOD sin (ms) LOD cos (ms) T6 G5 P1 Semiannual zoom OAM AAM LOD sin (ms) LOD cos (ms) T6 G5 P1 Terannual.2.1 zoom LOD sin (ms) Figure: Seasonal harmonics of the excitation of LOD. Analysis was done over the period A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
14 Results AAM+OAM vs. LOD: decadal component (T > 8 yrs) LOD (ms) Time (years) G5 P1 T6 Corr. with Var. reduct. (%) Standard deviation (µs) Series ( ) wind pres. curr. mass P G T A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
15 Results AAM+OAM vs. LOD: interannual component (2 yrs < T < 8 yrs).4 LOD (ms).2.2 G5 P1 T Time (years) Corr. with Var. reduct. (%) Standard deviation (µs) Series ( ) wind pres. curr. mass P G T A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
16 Results AAM+OAM vs. LOD: seasonal band (1/2 yr < T < 2 yrs) Note: Seasonal harmonics have been removed prior to this analysis..4 LOD (ms).2.2 G3 T Time (years) Corr. with Var. reduct. (%) Standard deviation (µs) Series ( ) wind pres. curr. mass G T A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
17 Results AAM+OAM vs. LOD: intraseasonal oscillations (2 d < T < 1/2 yr).4 LOD (ms).2.2 Pas G3 T Time (years) Corr. with Var. reduct. (%) Standard deviation (µs) Series ( ) wind pres. curr. mass Pas G T A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
18 Conclusions Conclusions Unlike equatorial component of Earth rotation, the axial component of T6 combination AAM+OAM does not differ significantly from other geophysical models. In case of annual and terannual harmonics in LOD there is an excellent agreement in amplitude and phase between models and ervations. For semiannual oscillation there is a high agreement in amplitude, but large phase difference ( 3 o ) occurs (land hydrology?). At decadal periods the AAM and OAM are much smaller than erved LOD, as could be expected from earlier works. For periods shorter than 8 years the atmospheric/oceanic excitation plays an important role with the highest agreement with ervations in the seasonal band. The dominating contribution to the excitation of LOD at periods shorter than 8 years comes from zonal winds. Variations of the atmospheric pressure and the ocean play a minor role. A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
19 Acknowledgements Conclusions Anna Korbacz would like to express her sincere thanks for the travel grant provided by the Descartes-Nutation consortium. This work has been supported by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education under grant No. N /3972. A. Korbacz et al. Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 Journées 27 Journées / 19 ()
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC EXCITATION OF EARTH ROTATION
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC EXCITATION OF EARTH ROTATION S. BÖHM, T. NILSSON, M. SCHINDELEGGER, H. SCHUH Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, Advanced Geodesy Vienna University of Technology Gußhausstraße
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC EXCITATION OF EARTH ROTATION S. BÖHM, T. NILSSON, M. SCHINDELEGGER, H. SCHUH Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, Advanced Geodesy Vienna University of Technology Gußhausstraße
Contribution of non-tidal oceanic mass variations to Earth rotation determined from space geodesy and ocean data
 Earth FOR584 rotation Earth and rotation global and dynamic global processes dynamic processes Contribution of non-tidal oceanic mass variations to Earth rotation determined from space geodesy and ocean
Earth FOR584 rotation Earth and rotation global and dynamic global processes dynamic processes Contribution of non-tidal oceanic mass variations to Earth rotation determined from space geodesy and ocean
The global S 1 tide and Earth s nutation
 Journées 2014 St. Petersburg 22 24 September Michael SCHINDELEGGER Johannes BÖHM, David SALSTEIN The global S 1 tide and Earth s nutation Session 4: Earth s rotation and geodynamics Motivation & Background
Journées 2014 St. Petersburg 22 24 September Michael SCHINDELEGGER Johannes BÖHM, David SALSTEIN The global S 1 tide and Earth s nutation Session 4: Earth s rotation and geodynamics Motivation & Background
23. EL NINO IMPACT ON ATMOSPHERIC AND GEODETIC EXCITATION FUNCTIONS OF POLAR MOTION
 23. EL NINO IMPACT ON ATMOSPHERIC AND GEODETIC EXCITATION FUNCTIONS OF POLAR MOTION B. Kolaczek, M. Nuzhdina, J. Nastula and W. Kosek Space Research Centre Polish Academy of Sciences Warsaw, Poland On
23. EL NINO IMPACT ON ATMOSPHERIC AND GEODETIC EXCITATION FUNCTIONS OF POLAR MOTION B. Kolaczek, M. Nuzhdina, J. Nastula and W. Kosek Space Research Centre Polish Academy of Sciences Warsaw, Poland On
Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks
 Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks Jan Vondrák and Cyril Ron, Astronomical Inst., Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague Contents: Introduction; Description
Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks Jan Vondrák and Cyril Ron, Astronomical Inst., Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague Contents: Introduction; Description
OBSERVING AND MODELING LONG-PERIOD TIDAL VARIATIONS IN POLAR MOTION
 OBSERVING AND MODELING LONG-PERIOD TIDAL VARIATIONS IN POLAR MOTION R.S. GROSS 1, S.R. DICKMAN 2 1 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena, CA 91109,
OBSERVING AND MODELING LONG-PERIOD TIDAL VARIATIONS IN POLAR MOTION R.S. GROSS 1, S.R. DICKMAN 2 1 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena, CA 91109,
Note: This is the accepted manuscript and may marginally differ from the published version.
 Originally published as: Seitz, F.; Stuck, J.; Thomas, M.: White noise Chandler wobble excitation. In: Plag, H. P.; Chao, B.; Gross, R.; van Dam, T. (eds.) Forcing of polar motion in the Chandler frequency
Originally published as: Seitz, F.; Stuck, J.; Thomas, M.: White noise Chandler wobble excitation. In: Plag, H. P.; Chao, B.; Gross, R.; van Dam, T. (eds.) Forcing of polar motion in the Chandler frequency
Jolanta NASTULA, Małgorzata PAŚNICKA and Barbara KOŁACZEK
 Acta Geophysica vol. 59, no. 3, Jun. 2011, pp. 561-577 DOI: 10.2478/s11600-011-0008-2 Comparison of the Geophysical Excitations of Polar Motion from the Period: 1980.0-2009.0 Jolanta NASTULA, Małgorzata
Acta Geophysica vol. 59, no. 3, Jun. 2011, pp. 561-577 DOI: 10.2478/s11600-011-0008-2 Comparison of the Geophysical Excitations of Polar Motion from the Period: 1980.0-2009.0 Jolanta NASTULA, Małgorzata
Oceanic excitation of daily to seasonal signals in Earth rotation: results from a constant-density numerical model
 Geophys. J. Int. (1997) 130,69-7 Oceanic excitation of daily to seasonal signals in Earth rotation: results from a constant-density numerical model Rui M. Ponte Atmospheric and Environmental Research,
Geophys. J. Int. (1997) 130,69-7 Oceanic excitation of daily to seasonal signals in Earth rotation: results from a constant-density numerical model Rui M. Ponte Atmospheric and Environmental Research,
Oceanic effects on polar motion determined from an ocean model and satellite altimetry:
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.109/003jb00664, 004 Oceanic effects on polar motion determined from an ocean model and satellite altimetry: 1993 001 J.-L. Chen and C. R. Wilson 1 Center
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.109/003jb00664, 004 Oceanic effects on polar motion determined from an ocean model and satellite altimetry: 1993 001 J.-L. Chen and C. R. Wilson 1 Center
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations. Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis
 Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
Seasonal polar motion excitation from numerical models of atmosphere, ocean, and continental hydrosphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb007127, 2010 Seasonal polar motion excitation from numerical models of atmosphere, ocean, and continental hydrosphere H. Dobslaw, 1 R. Dill,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb007127, 2010 Seasonal polar motion excitation from numerical models of atmosphere, ocean, and continental hydrosphere H. Dobslaw, 1 R. Dill,
Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop
 Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop T. van Dam (Uni. Lux), J. Ray (NGS/NOAA), X. Collilieux (IGN) Introduction Review the history of the GGFC Discuss the 2012 Workshop Review recommendations
Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop T. van Dam (Uni. Lux), J. Ray (NGS/NOAA), X. Collilieux (IGN) Introduction Review the history of the GGFC Discuss the 2012 Workshop Review recommendations
arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011](/thumbs/95/122563786.jpg) On the correlation between air temperature and the core Earth processes: Further investigations using a continuous wavelet analysis arxiv:1103.4924v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011 Abstract Stefano Sello
On the correlation between air temperature and the core Earth processes: Further investigations using a continuous wavelet analysis arxiv:1103.4924v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011 Abstract Stefano Sello
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2011) 184, 651 660 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04869.x The understanding of length-of-day variations from satellite gravity and laser ranging measurements
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2011) 184, 651 660 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04869.x The understanding of length-of-day variations from satellite gravity and laser ranging measurements
Geodätische Woche The global radiational S1 tide - current Earth rotation research at TU Wien. September 17, 2015
 Geodätische Woche 2015 A. Girdiuk, M. Schindelegger, J. Böhm / TU Wien / Geodätische Woche 2015 1/14 - current Earth rotation research at TU Wien A. Girdiuk, M. Schindelegger, J. Böhm TU Wien, Geodesy
Geodätische Woche 2015 A. Girdiuk, M. Schindelegger, J. Böhm / TU Wien / Geodätische Woche 2015 1/14 - current Earth rotation research at TU Wien A. Girdiuk, M. Schindelegger, J. Böhm TU Wien, Geodesy
Tests on the validity of atmospheric torques on Earth computed from atmospheric model outputs
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2068, doi:10.1029/2001jb001196, 2003 Tests on the validity of atmospheric torques on Earth computed from atmospheric model outputs O. de Viron and V.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2068, doi:10.1029/2001jb001196, 2003 Tests on the validity of atmospheric torques on Earth computed from atmospheric model outputs O. de Viron and V.
Analysis of Chandler wobble excitation, reconstructed from observations of the polar motion of the Earth
 Analysis of Chandler wobble excitation, reconstructed from observations of the polar motion of the Earth Leonid Zotov wolftempus@gmail.com Sternberg Astronomical Institute Lomonosov Moscow State University
Analysis of Chandler wobble excitation, reconstructed from observations of the polar motion of the Earth Leonid Zotov wolftempus@gmail.com Sternberg Astronomical Institute Lomonosov Moscow State University
Atmospheric, hydrological, and ocean current contributions to Earth s annual wobble and length-of-day signals based on output from a climate model
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B1, 2057, doi:10.1029/2001jb000457, 2003 Atmospheric, hydrological, and ocean current contributions to Earth s annual wobble and length-of-day signals based
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B1, 2057, doi:10.1029/2001jb000457, 2003 Atmospheric, hydrological, and ocean current contributions to Earth s annual wobble and length-of-day signals based
Atmospheric angular momentum time-series: characterization of their internal noise and creation of a combined series
 J Geod (2006) 79: 663 674 DOI 10.1007/s00190-005-0019-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE L. Koot O. de Viron V. Dehant Atmospheric angular momentum time-series: characterization of their internal noise and creation of
J Geod (2006) 79: 663 674 DOI 10.1007/s00190-005-0019-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE L. Koot O. de Viron V. Dehant Atmospheric angular momentum time-series: characterization of their internal noise and creation of
17. SIGNATURE OF EL NINO IN LENGTH OF DAY AS MEASURED BY VLBI
 17. SIGNATURE OF EL NINO IN LENGTH OF DAY AS MEASURED BY VLBI John M. Gipson, NVI Inc./GSFC, Greenbelt, MD Chopo Ma, Goddard Spaceflight Center, Greenbelt, MD INTRODUCTION Very Long Baseline Interferometry
17. SIGNATURE OF EL NINO IN LENGTH OF DAY AS MEASURED BY VLBI John M. Gipson, NVI Inc./GSFC, Greenbelt, MD Chopo Ma, Goddard Spaceflight Center, Greenbelt, MD INTRODUCTION Very Long Baseline Interferometry
Mutual comparison of the combinations of the Earth orientation parameters obtained by different techniques
 Mutual comparison of the combinations of the Earth orientation parameters obtained by different techniques C. Ron, J. Vondrák Astronomical Institute, Boční II 141, 141 31 Praha 4, Czech Republic Abstract.
Mutual comparison of the combinations of the Earth orientation parameters obtained by different techniques C. Ron, J. Vondrák Astronomical Institute, Boční II 141, 141 31 Praha 4, Czech Republic Abstract.
Multivariate autoregressive models as tools for UT1-UTC predictions
 Multivariate autoregressive models as tools for UT1-UTC predictions Tomasz Niedzielski 1,2, Wiesław Kosek 1 1 Space Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences, Poland 2 Oceanlab, University of Aberdeen,
Multivariate autoregressive models as tools for UT1-UTC predictions Tomasz Niedzielski 1,2, Wiesław Kosek 1 1 Space Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences, Poland 2 Oceanlab, University of Aberdeen,
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Mandea, M., Olsen, N. (2009): Geomagnetic and Archeomagnetic Jerks: Where Do We Stand?. - Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 90, 24, 208-208 From geomagnetic jerks
Originally published as: Mandea, M., Olsen, N. (2009): Geomagnetic and Archeomagnetic Jerks: Where Do We Stand?. - Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 90, 24, 208-208 From geomagnetic jerks
Surface Mass Loads from GRACE, GPS, and Earth Rotation
 Surface Mass Loads from GRACE,, and Earth Rotation R. Gross *, G. Blewitt, H.-P. Plag, P. Clarke, D. Lavallée, T. van Dam *Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA Nevada
Surface Mass Loads from GRACE,, and Earth Rotation R. Gross *, G. Blewitt, H.-P. Plag, P. Clarke, D. Lavallée, T. van Dam *Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA Nevada
Mechanical energy input to the world oceans due to. atmospheric loading
 Mechanical energy input to the world oceans due to atmospheric loading Wei Wang +, Cheng Chun Qian +, & Rui Xin Huang * +Physical Oceanography Laboratory, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, Shandong,
Mechanical energy input to the world oceans due to atmospheric loading Wei Wang +, Cheng Chun Qian +, & Rui Xin Huang * +Physical Oceanography Laboratory, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, Shandong,
Tropical stratospheric zonal winds in ECMWF ERA-40 reanalysis, rocketsonde data, and rawinsonde data
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L09806, doi:10.1029/2004gl022328, 2005 Tropical stratospheric zonal winds in ECMWF ERA-40 reanalysis, rocketsonde data, and rawinsonde data Mark P. Baldwin Northwest
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L09806, doi:10.1029/2004gl022328, 2005 Tropical stratospheric zonal winds in ECMWF ERA-40 reanalysis, rocketsonde data, and rawinsonde data Mark P. Baldwin Northwest
Uncertainties in Seasonal Wind Torques over the Ocean
 15 FEBRUARY 2003 PONTE ET AL. 715 Uncertainties in Seasonal Wind Torques over the Ocean RUI M. PONTE, AMALA MAHADEVAN, JAYENDRAN RAJAMONY, AND RICHARD D. ROSEN Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc.,
15 FEBRUARY 2003 PONTE ET AL. 715 Uncertainties in Seasonal Wind Torques over the Ocean RUI M. PONTE, AMALA MAHADEVAN, JAYENDRAN RAJAMONY, AND RICHARD D. ROSEN Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc.,
Relationships between mass redistribution, station position, geocenter, and Earth rotation: Results from IGS GNAAC analysis
 Relationships between mass redistribution, station position, geocenter, and Earth rotation: Results from IGS GNAAC analysis Geoff Blewitt Mackay School of Earth Sciences and Engineering University of Nevada,
Relationships between mass redistribution, station position, geocenter, and Earth rotation: Results from IGS GNAAC analysis Geoff Blewitt Mackay School of Earth Sciences and Engineering University of Nevada,
Characterisation and implications of intradecadal variations in length-of-day
 Characterisation and implications of intradecadal variations in length-of-day R. Holme 1 & O. de Viron 2 1 School of Environmental Sciences, University of Liverpool, L69 3GP, UK. holme@liv.ac.uk 2 Univ.
Characterisation and implications of intradecadal variations in length-of-day R. Holme 1 & O. de Viron 2 1 School of Environmental Sciences, University of Liverpool, L69 3GP, UK. holme@liv.ac.uk 2 Univ.
State-of-the-art physical models for calculating atmospheric pressure loading effects
 State-of-the-art physical models for calculating atmospheric pressure loading effects Dudy D. Wijaya, Böhm J., Schindelegger M., Karbon M., Schuh H. Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, TU Vienna Geodätische
State-of-the-art physical models for calculating atmospheric pressure loading effects Dudy D. Wijaya, Böhm J., Schindelegger M., Karbon M., Schuh H. Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, TU Vienna Geodätische
Low degree gravity changes from GRACE, Earth rotation, geophysical models, and satellite laser ranging
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005397, 2008 Low degree gravity changes from GRACE, Earth rotation, geophysical models, and satellite laser ranging J. L. Chen 1 and C. R.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005397, 2008 Low degree gravity changes from GRACE, Earth rotation, geophysical models, and satellite laser ranging J. L. Chen 1 and C. R.
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell
 1522 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES VOLUME 60 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell IOANA M. DIMA AND JOHN M. WALLACE Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
1522 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES VOLUME 60 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell IOANA M. DIMA AND JOHN M. WALLACE Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
Recent advances in modeling precession-nutation
 Recent advances in modeling precession-nutation Véronique Dehant ROB Sébastien Lambert OP Nicolas Rambaux ROB Marta Folgueira Madrid Univ Laurence Koot ROB v.dehant@oma.be Level 3: rigid Earth nutation
Recent advances in modeling precession-nutation Véronique Dehant ROB Sébastien Lambert OP Nicolas Rambaux ROB Marta Folgueira Madrid Univ Laurence Koot ROB v.dehant@oma.be Level 3: rigid Earth nutation
Global reference systems and Earth rotation
 current realizations and scientific problems Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2, Tomasz Liwosz 1, Jerzy Rogowski 1, Jan Kryński 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Geodetic Astronomy Warsaw University of Technology 2
current realizations and scientific problems Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2, Tomasz Liwosz 1, Jerzy Rogowski 1, Jan Kryński 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Geodetic Astronomy Warsaw University of Technology 2
Low-Frequency Exchange of Mass Between Ocean Basins
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Marine Science Faculty Publications College of Marine Science 11-5-2009 Low-Frequency Exchange of Mass Between Ocean Basins Don P. Chambers University of South
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Marine Science Faculty Publications College of Marine Science 11-5-2009 Low-Frequency Exchange of Mass Between Ocean Basins Don P. Chambers University of South
Wavelet analysis in TEC measurements obtained using dual-frequency space and satellite techniques
 Wavelet analysis in TEC measurements obtained using dual-frequency space and satellite techniques A. Krankowski (1), W. Kosek, (2), Th. Hobiger (3), H. Schuh (3) (1) Institute of Geodesy, Warmia and Mazury
Wavelet analysis in TEC measurements obtained using dual-frequency space and satellite techniques A. Krankowski (1), W. Kosek, (2), Th. Hobiger (3), H. Schuh (3) (1) Institute of Geodesy, Warmia and Mazury
Geomagnetic jerks and a high-resolution length-of-day profile for core studies
 Geophys. J. Int. (25) 16, 435 439 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.24.251.x FA S T T R AC K PAPER Geomagnetic jerks and a high-resolution length-of-day profile for core studies R. Holme 1 and O. de Viron 2 1 Department
Geophys. J. Int. (25) 16, 435 439 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.24.251.x FA S T T R AC K PAPER Geomagnetic jerks and a high-resolution length-of-day profile for core studies R. Holme 1 and O. de Viron 2 1 Department
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN
 JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
Understanding Earth Rotation Part 2: Physical Foundations and Interpretation
 Understanding Earth Rotation Part 2: Physical Foundations and Interpretation Prof. Dr. Florian Seitz Technische Universität München (TUM) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI) Munich, Germany
Understanding Earth Rotation Part 2: Physical Foundations and Interpretation Prof. Dr. Florian Seitz Technische Universität München (TUM) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI) Munich, Germany
Consistency of Earth Rotation, Gravity, and Shape Measurements
 Consistency of Earth Rotation, Gravity, and Shape Measurements Richard S. Gross*, David A. Lavallée, Geoffrey Blewitt, and Peter J. Clarke *Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology
Consistency of Earth Rotation, Gravity, and Shape Measurements Richard S. Gross*, David A. Lavallée, Geoffrey Blewitt, and Peter J. Clarke *Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology
El Nifio impact on atmospheric polar motion excitation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 105, NO. B2, PAGES 3081-3087, FEBRUARY 10, 2000 El Nifio impact on atmospheric polar motion excitation B. Kotaczek, M. Nuzhdina l, J. Nastula, and W. Kosek Space Research
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 105, NO. B2, PAGES 3081-3087, FEBRUARY 10, 2000 El Nifio impact on atmospheric polar motion excitation B. Kotaczek, M. Nuzhdina l, J. Nastula, and W. Kosek Space Research
The Dynamics of Atmospherically Driven Intraseasonal Polar Motion
 2290 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 The Dynamics of Atmospherically Driven Intraseasonal Polar Motion STEVEN B. FELDSTEIN Earth and Environmental Systems Institute,
2290 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 The Dynamics of Atmospherically Driven Intraseasonal Polar Motion STEVEN B. FELDSTEIN Earth and Environmental Systems Institute,
Ocean Bottom Pressure Changes Lead to a Decreasing Length-of-Day in a Warming Climate
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, Ocean Bottom Pressure Changes Lead to a Decreasing Length-of-Day in a Warming Climate Felix W. Landerer, Johann H. Jungclaus, Jochem Marotzke Max
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, Ocean Bottom Pressure Changes Lead to a Decreasing Length-of-Day in a Warming Climate Felix W. Landerer, Johann H. Jungclaus, Jochem Marotzke Max
Remaining error sources in the nutation at the submilliarc second level
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B5, 2275, doi:10.1029/2002jb001763, 2003 Remaining error sources in the nutation at the submilliarc second level V. Dehant, 1 M. Feissel-Vernier, 2,3 O. de
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B5, 2275, doi:10.1029/2002jb001763, 2003 Remaining error sources in the nutation at the submilliarc second level V. Dehant, 1 M. Feissel-Vernier, 2,3 O. de
Spatial and Temporal Variations of Global Frictional Torque during the Period
 128 JOURNAL OF METEOROLOGICAL RESEARCH VOL.30 Spatial and Temporal Variations of Global Frictional Torque during the Period 1948 2011 GONG He 1 ( å), HUANG Mei 2 ( p), ZHU Lin 3 (Á»), GUO Shengli 1 (H
128 JOURNAL OF METEOROLOGICAL RESEARCH VOL.30 Spatial and Temporal Variations of Global Frictional Torque during the Period 1948 2011 GONG He 1 ( å), HUANG Mei 2 ( p), ZHU Lin 3 (Á»), GUO Shengli 1 (H
Empiric Models of the Earth s Free Core Nutation
 ISSN 38-946, Solar System Research, 27, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 492 497. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 27. Original Russian Text Z.M. Malkin, 27, published in Astronomicheskii Vestnik, 27, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp.
ISSN 38-946, Solar System Research, 27, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 492 497. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 27. Original Russian Text Z.M. Malkin, 27, published in Astronomicheskii Vestnik, 27, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp.
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Winkelnkemper, T., F. Seitz: Simulation of historic and future atmospheric angular momentum effects on length of day variations with GCMs. In: Observing our Changing Earth, Sideris,
Originally published as: Winkelnkemper, T., F. Seitz: Simulation of historic and future atmospheric angular momentum effects on length of day variations with GCMs. In: Observing our Changing Earth, Sideris,
Wave-driven equatorial annual oscillation induced and modulated by the solar cycle
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L20811, doi:10.1029/2005gl023090, 2005 Wave-driven equatorial annual oscillation induced and modulated by the solar cycle Hans G. Mayr, 1 John G. Mengel, 2 and Charles
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L20811, doi:10.1029/2005gl023090, 2005 Wave-driven equatorial annual oscillation induced and modulated by the solar cycle Hans G. Mayr, 1 John G. Mengel, 2 and Charles
Axial Atmospheric Angular Momentum Budget at Diurnal and Subdiurnal Periodicities
 156 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 Axial Atmospheric Angular Momentum Budget at Diurnal and Subdiurnal Periodicities FRANÇOIS LOTT LMD/IPSL CNRS, Ecole Normale
156 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 Axial Atmospheric Angular Momentum Budget at Diurnal and Subdiurnal Periodicities FRANÇOIS LOTT LMD/IPSL CNRS, Ecole Normale
MOTIVATION. New view of Arctic cyclone activity from the Arctic System Reanalysis
 New view of Arctic cyclone activity from the Arctic System Reanalysis Natalia Tilinina 1, Sergey Gulev 1 and David H.Bromwich 2 1) P.P. Shirshov Institute of Oceanology, Moscow 2) Byrd Polar Research Center,
New view of Arctic cyclone activity from the Arctic System Reanalysis Natalia Tilinina 1, Sergey Gulev 1 and David H.Bromwich 2 1) P.P. Shirshov Institute of Oceanology, Moscow 2) Byrd Polar Research Center,
Hydrological and oceanic effects on polar motion from GRACE and models
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006635, 2010 Hydrological and oceanic effects on polar motion from GRACE and models Shuanggen Jin, 1,2 Don P. Chambers,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006635, 2010 Hydrological and oceanic effects on polar motion from GRACE and models Shuanggen Jin, 1,2 Don P. Chambers,
Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L20601, doi:10.1029/2008gl035490, 2008 Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean Denis L. Volkov, 1 Tong Lee, 1 and Lee-Lueng Fu 1 Received 28 July 2008;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L20601, doi:10.1029/2008gl035490, 2008 Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean Denis L. Volkov, 1 Tong Lee, 1 and Lee-Lueng Fu 1 Received 28 July 2008;
Hydrological Mass Variations due to Extreme Weather Conditions in Central Europe from Regional GRACE 4D Expansions
 Hydrological Mass Variations due to Extreme Weather Conditions in Central Europe from Regional GRACE 4D Expansions Florian Seitz 1, Michael Schmidt 2, C.K. Shum 3, Yiqun Chen 3 1 Earth Oriented Space Science
Hydrological Mass Variations due to Extreme Weather Conditions in Central Europe from Regional GRACE 4D Expansions Florian Seitz 1, Michael Schmidt 2, C.K. Shum 3, Yiqun Chen 3 1 Earth Oriented Space Science
By STEVEN B. FELDSTEINI and WALTER A. ROBINSON* University of Colorado, USA 2University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA. (Received 27 July 1993)
 Q. J. R. Meteorol. SOC. (1994), 12, pp. 739-745 551.513.1 Comments on Spatial structure of ultra-low frequency variability of the flow in a simple atmospheric circulation model by I. N. James and P. M.
Q. J. R. Meteorol. SOC. (1994), 12, pp. 739-745 551.513.1 Comments on Spatial structure of ultra-low frequency variability of the flow in a simple atmospheric circulation model by I. N. James and P. M.
THE FREE CORE NUTATION
 THE FREE CORE NUTATION D.D. MCCARTHY U. S. Naval Observatory Washington, DC 20392 USA e-mail: dmc@maia.usno.navy.mil ABSTRACT. The International Earth rotation and Reference system Service (IERS) provides
THE FREE CORE NUTATION D.D. MCCARTHY U. S. Naval Observatory Washington, DC 20392 USA e-mail: dmc@maia.usno.navy.mil ABSTRACT. The International Earth rotation and Reference system Service (IERS) provides
The Rotational and Gravitational Signature of Recent Great Earthquakes
 The Rotational and Gravitational Signature of Recent Great Earthquakes Richard S. Gross Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109 8099, USA 7th IVS General Meeting
The Rotational and Gravitational Signature of Recent Great Earthquakes Richard S. Gross Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109 8099, USA 7th IVS General Meeting
Intraseasonal and seasonal variations in in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean. Y. Masumoto, H. Hase, Y. Kuroda, and H. Sasaki
 Intraseasonal and seasonal variations in in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean -A -A high-resolution OGCM and and ADCP Observation- Y. Masumoto, H. Hase, Y. Kuroda, and H. Sasaki FRCGC/IORGC/ESC JAMSTEC
Intraseasonal and seasonal variations in in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean -A -A high-resolution OGCM and and ADCP Observation- Y. Masumoto, H. Hase, Y. Kuroda, and H. Sasaki FRCGC/IORGC/ESC JAMSTEC
Coordinated Ocean-ice Reference Experiments phase II (CORE-II)
 Coordinated Ocean-ice Reference Experiments phase II (CORE-II) Gokhan Danabasoglu, Stephen G. Yeager, William G. Large National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, USA Stephen M. Griffies NOAA
Coordinated Ocean-ice Reference Experiments phase II (CORE-II) Gokhan Danabasoglu, Stephen G. Yeager, William G. Large National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, USA Stephen M. Griffies NOAA
Salinity variability associated with changes in the hydrological cycle variables
 Salinity variability associated with changes in the hydrological cycle variables Olga Sato Paulo Polito olga.sato@usp.br Oceanographic Institute of the University of SÃčo Paulo Olga Sato (IOUSP) Salinity
Salinity variability associated with changes in the hydrological cycle variables Olga Sato Paulo Polito olga.sato@usp.br Oceanographic Institute of the University of SÃčo Paulo Olga Sato (IOUSP) Salinity
Basic mechanism for abrupt monsoon transitions
 Basic mechanism for abrupt monsoon transitions Anders Levermann, Jacob Schewe, Vladimir Petoukhov, and Hermann Held Earth System Analysis, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Potsdam, Germany,
Basic mechanism for abrupt monsoon transitions Anders Levermann, Jacob Schewe, Vladimir Petoukhov, and Hermann Held Earth System Analysis, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Potsdam, Germany,
Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions
 EGU2009-3768 Session G4 EGU General Assembly 2009 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 2009 Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions Are we able to Detect and Identify
EGU2009-3768 Session G4 EGU General Assembly 2009 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 2009 Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions Are we able to Detect and Identify
Inverse Barometer correction comparison for TOPEX/Poseidon mission between Corrections based on JRA-55 and ERA-Interim atmospheric reanalyses
 Inverse Barometer correction comparison for TOPEX/Poseidon mission between Corrections based on JRA-55 and ERA-Interim atmospheric reanalyses The JRA-55 correction is referred to as JRA55 in the following
Inverse Barometer correction comparison for TOPEX/Poseidon mission between Corrections based on JRA-55 and ERA-Interim atmospheric reanalyses The JRA-55 correction is referred to as JRA55 in the following
Effects of Unresolved High-Frequency Signals in Altimeter Records Inferred from Tide Gauge Data
 534 JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 19 Effects of Unresolved High-Frequency Signals in Altimeter Records Inferred from Tide Gauge Data RUI M. PONTE Atmospheric and Environmental Research,
534 JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 19 Effects of Unresolved High-Frequency Signals in Altimeter Records Inferred from Tide Gauge Data RUI M. PONTE Atmospheric and Environmental Research,
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 )
 3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
2. DYNAMICS OF CLIMATIC AND GEOPHYSICAL INDICES
 4 2. DYNAMICS OF CLIMATIC AND GEOPHYSICAL INDICES Regular and reliable climate observations with measurement and calculation of principal climatic indices were started only about 150 years ago, when organized
4 2. DYNAMICS OF CLIMATIC AND GEOPHYSICAL INDICES Regular and reliable climate observations with measurement and calculation of principal climatic indices were started only about 150 years ago, when organized
Excitation of Earth rotation from meteorological analyses and models
 Excitation of Earth rotation from meteorological analyses and models David A. Salstein Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc., (AER) Lexington, MA, USA www.aer.com Centrum Badan Kosmicznych, Warsaw,
Excitation of Earth rotation from meteorological analyses and models David A. Salstein Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc., (AER) Lexington, MA, USA www.aer.com Centrum Badan Kosmicznych, Warsaw,
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic
 Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis
 Extended abstract for the 3 rd WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis held in Tokyo, Japan, on Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis Yan Xue,
Extended abstract for the 3 rd WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis held in Tokyo, Japan, on Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis Yan Xue,
Interannual trends in the Southern Ocean sea surface temperature and sea level from remote sensing data
 RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF EARTH SCIENCES, VOL. 9, ES3003, doi:10.2205/2007es000283, 2007 Interannual trends in the Southern Ocean sea surface temperature and sea level from remote sensing data S. A. Lebedev 1,2
RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF EARTH SCIENCES, VOL. 9, ES3003, doi:10.2205/2007es000283, 2007 Interannual trends in the Southern Ocean sea surface temperature and sea level from remote sensing data S. A. Lebedev 1,2
Journal of Coastal Develpopment ISSN :
 Volume 15, Number 1,October 2011 : 1-8 Original Paper INTRASEASONAL VARIATIONS OF NEAR-SURFACE ZONAL CURRENT OBSERVED IN THE SOUTH-EASTERN EQUATORIAL INDIAN OCEAN Iskhaq Iskandar Department of Physics,
Volume 15, Number 1,October 2011 : 1-8 Original Paper INTRASEASONAL VARIATIONS OF NEAR-SURFACE ZONAL CURRENT OBSERVED IN THE SOUTH-EASTERN EQUATORIAL INDIAN OCEAN Iskhaq Iskandar Department of Physics,
Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign
 Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign results from combined reprocessed IGS GPS orbits and EOPs assessment of IG1 orbit repeatability items to consider for next reprocessing Jake
Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign results from combined reprocessed IGS GPS orbits and EOPs assessment of IG1 orbit repeatability items to consider for next reprocessing Jake
Mountain Torques Caused by Normal-Mode Global Rossby Waves, and the Impact on Atmospheric Angular Momentum
 1045 Mountain Torques Caused by Normal-Mode Global Rossby Waves, and the Impact on Atmospheric Angular Momentum HARALD LEJENÄS Department of Meteorology, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden ROLAND
1045 Mountain Torques Caused by Normal-Mode Global Rossby Waves, and the Impact on Atmospheric Angular Momentum HARALD LEJENÄS Department of Meteorology, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden ROLAND
The Atmospheric Dynamics of Intraseasonal Length-of-Day Fluctuations during the Austral Winter
 1SEPTEMBER 1999 FELDSTEIN 3043 The Atmospheric Dynamics of Intraseasonal Length-of-Day Fluctuations during the Austral Winter STEVEN B. FELDSTEIN Earth System Science Center, The Pennsylvania State University,
1SEPTEMBER 1999 FELDSTEIN 3043 The Atmospheric Dynamics of Intraseasonal Length-of-Day Fluctuations during the Austral Winter STEVEN B. FELDSTEIN Earth System Science Center, The Pennsylvania State University,
Tropical Pacific Ocean model error covariances from Monte Carlo simulations
 Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2005), 131, pp. 3643 3658 doi: 10.1256/qj.05.113 Tropical Pacific Ocean model error covariances from Monte Carlo simulations By O. ALVES 1 and C. ROBERT 2 1 BMRC, Melbourne, Australia
Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2005), 131, pp. 3643 3658 doi: 10.1256/qj.05.113 Tropical Pacific Ocean model error covariances from Monte Carlo simulations By O. ALVES 1 and C. ROBERT 2 1 BMRC, Melbourne, Australia
Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data
 Johannes Böhm, Arthur Niell, Paul Tregoning, and Harald Schuh Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data Geophysical Research Letters Vol. 33,
Johannes Böhm, Arthur Niell, Paul Tregoning, and Harald Schuh Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data Geophysical Research Letters Vol. 33,
Researches on predictions of Earth orientation parameters
 Researches on predictions of Earth orientation parameters Xueqing Xu Yonghong Zhou 17 Sep--213 Paris Contents Introduction of EOP prediction Our work about EOP prediction Participation of EOPC PPP JOURNÉES
Researches on predictions of Earth orientation parameters Xueqing Xu Yonghong Zhou 17 Sep--213 Paris Contents Introduction of EOP prediction Our work about EOP prediction Participation of EOPC PPP JOURNÉES
Project of Strategic Interest NEXTDATA. Deliverables D1.3.B and 1.3.C. Final Report on the quality of Reconstruction/Reanalysis products
 Project of Strategic Interest NEXTDATA Deliverables D1.3.B and 1.3.C Final Report on the quality of Reconstruction/Reanalysis products WP Coordinator: Nadia Pinardi INGV, Bologna Deliverable authors Claudia
Project of Strategic Interest NEXTDATA Deliverables D1.3.B and 1.3.C Final Report on the quality of Reconstruction/Reanalysis products WP Coordinator: Nadia Pinardi INGV, Bologna Deliverable authors Claudia
Evaluation of Temperature and Ocean Currents within Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) Using Rama Mooring Buoys Data in Indian Ocean
 International Journal of Oceans and Oceanography ISSN 0973-2667 Volume 11, Number 2 (2017), pp. 159-173 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Evaluation of Temperature and Ocean Currents
International Journal of Oceans and Oceanography ISSN 0973-2667 Volume 11, Number 2 (2017), pp. 159-173 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Evaluation of Temperature and Ocean Currents
Non-isotropic filtering of GRACE temporal gravity for geophysical signal enhancement
 Geophys. J. Int. (2005) 163, 18 25 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02756.x GJI Geodesy, potential field and applied geophysics Non-isotropic filtering of GRACE temporal gravity for geophysical signal enhancement
Geophys. J. Int. (2005) 163, 18 25 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02756.x GJI Geodesy, potential field and applied geophysics Non-isotropic filtering of GRACE temporal gravity for geophysical signal enhancement
Impact of the 2002 stratospheric warming in the southern hemisphere on the tropical cirrus clouds and convective activity
 The Third International SOWER meeting,, Lake Shikotsu,, July 18-20, 2006 1 Impact of the 2002 stratospheric warming in the southern hemisphere on the tropical cirrus clouds and convective activity Eguchi,
The Third International SOWER meeting,, Lake Shikotsu,, July 18-20, 2006 1 Impact of the 2002 stratospheric warming in the southern hemisphere on the tropical cirrus clouds and convective activity Eguchi,
CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS. Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 1850
 CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 185 2.1 Datasets 2.1.1 OLR The primary data used in this study are the outgoing
CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 185 2.1 Datasets 2.1.1 OLR The primary data used in this study are the outgoing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE216 Recent intensification of wind-driven circulation in the Pacific and the ongoing warming hiatus (a) Observed wind trends 6N N 2N 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18E 12W
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE216 Recent intensification of wind-driven circulation in the Pacific and the ongoing warming hiatus (a) Observed wind trends 6N N 2N 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18E 12W
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
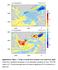 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions
 EGU2009-3768 Session G4 EGU General Assembly 2009 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 2009 Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions Are we able to Detect and Identify
EGU2009-3768 Session G4 EGU General Assembly 2009 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 2009 Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions Are we able to Detect and Identify
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. On the Interpretation of Antarctic Temperature Trends
 3885 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Interpretation of Antarctic Temperature Trends MICHIEL R. VAN DEN BROEKE Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Research, Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands 9August1999and3April2000
3885 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Interpretation of Antarctic Temperature Trends MICHIEL R. VAN DEN BROEKE Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Research, Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands 9August1999and3April2000
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE. V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva
 HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
The Earth s rotation and atmospheric circulation:
 Geophys. J. R. astr. SOC. (1982) 71,581-587 The Earth s rotation and atmospheric circulation: 1958-1 980 Kurt Lambeck and Peter Hopgood Research SchoolofEarth Sciences, Australian Nationaf University,
Geophys. J. R. astr. SOC. (1982) 71,581-587 The Earth s rotation and atmospheric circulation: 1958-1 980 Kurt Lambeck and Peter Hopgood Research SchoolofEarth Sciences, Australian Nationaf University,
Vertical Moist Thermodynamic Structure of the MJO in AIRS Observations: An Update and A Comparison to ECMWF Interim Reanalysis
 Vertical Moist Thermodynamic Structure of the MJO in AIRS Observations: An Update and A Comparison to ECMWF Interim Reanalysis Baijun Tian 1 Duane Waliser 1, Eric Fetzer 1, and Yuk Yung 2 1.Jet Propulsion
Vertical Moist Thermodynamic Structure of the MJO in AIRS Observations: An Update and A Comparison to ECMWF Interim Reanalysis Baijun Tian 1 Duane Waliser 1, Eric Fetzer 1, and Yuk Yung 2 1.Jet Propulsion
Dynamics of the Atmosphere. General circulation of the atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing
 The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing Thomas Krismer, Marco Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology Hamburg Introduction 1) The Quasi Biennial Oscillation is driven
The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing Thomas Krismer, Marco Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology Hamburg Introduction 1) The Quasi Biennial Oscillation is driven
COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME. Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol.2, No.3 (139), 87-94, 2005 COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON Department of Galaxies
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol.2, No.3 (139), 87-94, 2005 COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON Department of Galaxies
Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations
 Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations Hans-Peter Plag(1), Geoff Blewitt, Tom A. Herring (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology and Seismological Laboratory University
Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations Hans-Peter Plag(1), Geoff Blewitt, Tom A. Herring (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology and Seismological Laboratory University
J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE
 J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE E Fischer* (1), SI Seneviratne (1), D Lüthi (1), PL Vidale (2), and C Schär (1) 1 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate
J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE E Fischer* (1), SI Seneviratne (1), D Lüthi (1), PL Vidale (2), and C Schär (1) 1 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate
Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data
 Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data Rong Fu 1, Mike Young 1, Hui Wang 2, Weiqing Han 3 1 School
Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data Rong Fu 1, Mike Young 1, Hui Wang 2, Weiqing Han 3 1 School
Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission
 Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission Sergei Rudenko (1,2), Saskia Esselborn (1), Tilo Schöne (1) (1) GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences,
Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission Sergei Rudenko (1,2), Saskia Esselborn (1), Tilo Schöne (1) (1) GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences,
Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites
 13-01-08 Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Christian Baumann (1), Rolf Dach (1), Gerhard
13-01-08 Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Christian Baumann (1), Rolf Dach (1), Gerhard
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
What have we learned about our climate by using networks and nonlinear analysis tools?
 What have we learned about our climate by using networks and nonlinear analysis tools? Cristina Masoller Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya www.fisica.edu.uy/~cris LINC conference Wien, April 2015 ITN
What have we learned about our climate by using networks and nonlinear analysis tools? Cristina Masoller Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya www.fisica.edu.uy/~cris LINC conference Wien, April 2015 ITN
