Originally published as:
|
|
|
- Amice Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Originally published as: Mandea, M., Olsen, N. (2009): Geomagnetic and Archeomagnetic Jerks: Where Do We Stand?. - Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 90, 24,
2 From geomagnetic jerks to archeomagnetic jerks: where do we stand? Mioara Mandea 1 and Nils Olsen 2 1 Helmholtz-Zentrum Potsdam, Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum, Potsdam, Germany 2 DTU National Space Institute, Juliane Maries Vej 30, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark March 4, 2009 The Earth s magnetic field is mainly generated by a self-sustaining dynamo in the fluid outer core. This part, known as the core or main field, is not constant but changes with time, a phenomena denoted as secular variation. There is, however, no common agreement about the definition of the term secular variation in the geomagnetic literature: while some authors use this term for the temporal changes of the core field in general, others refer to its linear part (first time derivative), only. Two more terms are link to the core field temporal variations: geomagnetic jerk and archeomagnetic jerk. They have been introduced to describe a specific magnetic field signature in the observations (which means that a phenomenological classification is used). We suggest that a characterization of magnetic field changes based on the physics of the underlying core process may be more useful and such a classification is proposed here, in order to avoid misunderstanding in terminology. Let us recall, that whether something is perceived as a trend or not depends on the timescale in consideration: what appears to be a linear change over a timescale of years to decades may turn out to be more complicated when looking at the century to millennium timescale. Indeed, the secular variation for the last few centuries over which direct measurements are available is far from linear, and abrupt changes in its rate of change have been observed and discussed. These events characterized by a sudden change in the trend of the first time derivative of the magnetic field, correspond to a step in the second time derivative, and have been named geomagnetic jerks. It becomes generally agreed that these events originate in the Earth s core and that they occur over short timescales. But how short is short? Recently, using additional information provided by geomagnetic field models and latest satellite data (Mandea and Olsen, 2006; Olsen and Mandea, 2007), new characteristics of the secular variation have been found, both regarding spatial resolution and the duration of sudden changes. In this context a 1
3 problem arises: should every very short-term fluctuations of the core magnetic field that occurs on timescales of just a few months to a couple of years, be called for a geomagnetic jerk? The terminology has become further complicated by the use of the term archeomagnetic jerk (Gallet et al., 2003). The idea behind this designation is to denote sharp features at a timescale intermediate between geomagnetic jerks (1 to 2 yrs in a centennial time series) and excursions (10 3 to 10 4 yrs in a time series of 10 5 to 10 6 yrs length). However, the term archeomagnetic jerk is used to characterize a sudden change in the magnetic field itself, contrary to the classical definition of a geomagnetic jerk. The term archeomagnetic jerk may therefore be misleading. As an example for geomagnetic jerks observed from historical data, the zoom part of Figure 1 shows the temporal changes of the declination annual means, dd/dt, since the first observatory was installed in the Paris region. Also shown are predictions of dd/dt for Chambon-la-Forêt observatory, as given by the gufm1 (Jackson et al. (2000)) and the preliminary CALSK10 model (M. Korte, pers. comm.). These curves indicate that there are linear segments of constant slope of dd/dt, lasting from a few decades (e.g to 1970) to a century (e.g. the 18th century), as well as short-term abrupt changes on decadal or even subdecadal timescales. The estimations deduced from the preliminary CALSK10 model indicate periods characterized by important accelerations, as around 7000BC, with a change of about 0.5 in some 100 years, or, starting with the 18th century, of more than 0.3 in less the 200 years. In the following we suggest a classification of the magnetic field temporal changes based on the physics of the underlying core process. Geomagnetic jerks have been explained by invoking torsional oscillations in the fluid outer core (Bloxham, 2002). The torsional oscillations consist of time-dependent axisymmetric and equatorial symmetric zonal flows, with typical periods of several decades. Theoretical considerations suggest that such oscillations should be contained in core flows, and because of their timescale they can be observed in historical data. For core dynamics the torsional oscillations are very important as they are the most robust observed dynamic feature inside the core and provide a crucial link between magnetic field observation and dynamo theory. We suggest that changes in the geomagnetic field due to the torsional oscillations are denoted geomagnetic jerks. Torsional oscillations may only give a snapshot of the dynamo on a decadal timescale. No direct information are available for very short timescales (less than a couple of years) or at the timescale of magnetic field generation (more than thousands of years). Magnetic field changes arising on these timescales are discussed in the following, with a suggestion on how to denote them. Rapid secular variation fluctuations Can we find flows in the core that are consistent with very rapid changes of the field, as observed newly using 2
4 Figure 1: Temporal evolution of the declination for the site of Chambon-la-Foret given by the preliminary CALSK10 model (blue dots). The zoom part indicates the secular variation recorded in Paris region and adjusted to the Chambon-laFore t observatory (black dots), and the corresponding estimations for the same site given by the gufm1 model (red curve) and the preliminary CALSK10 model (blue curve). 3
5 magnetic satellite data (Mandea and Olsen, 2006; Olsen and Mandea, 2007) and in agreement with the observed change in the Length-of-Day (LOD)? Recently, Olsen and Mandea (2008) have shown that changes in the magnetic field occurring over only a few months as well as the fluid flow at the top of the core generating them, can be resolved. The derived time-dependent core flow, fitting the recent secular variation behavior and being in agreement with the LOD variation, is spatially rather localized and involves rapid variations over short timescales of only a few months, with surprisingly large local accelerations. We suggest to call these changes rapid secular variation fluctuations or shortly rapid fluctuations. Archeomagnetic jerks Can we find flows that are consistent with changes observed in the secular variation covering a few millennia, and also with the LOD variations on a millennial timescale? Dumberry and Bloxham (2006) have shown that the amplitudes and characteristic timescales of the observed LOD changes can be explained by zonal flow variations deduced from secular variation, on millennial timescales. Changes in the magnetic field configuration are generated by convective motions, which in turn produce observable secular variation. Recently, Wardinski and Korte (2008) found that a toroidal flow explains better the long-term variation in the geomagnetic field secular variations compared to a geostrophic flow. The significant periodicities for the large scale zonal flows range from some 540 to 1050 years. We suggest that the term archeomagnetic jerk should be used to denote these long-term changes in the secular variation, rather than the field direction, as initially suggested. We hope that our suggestion on terminology of geomagnetic field changes will help to better track the different temporal variations revealed by observations, as well as in developments concerning the dynamics of the fluid core. Acknowledgments We would like to thank Monika Korte for providing the preliminary CALSK10 model. 4
6 References Bloxham, J. (2002). Time-independent and time-dependent behaviour of highlatitude flux bundles at the core-mantle boundary. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29:1854,doi: /2001GL Dumberry, M. and Bloxham, J. (2006). Azimuthal flows in the Earth s core and changes in length of day at millennial timescales. Geophys. J. Int., 165: Gallet, Y., Genevey, A., and Courtillot, V. (2003). On the possible occurrance of archaeomagnetic jerks in the geomagnetic field over the past three millennia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 214: Jackson, A., Jonkers, A. R. T., and Walker, M. R. (2000). Four centuries of geomagnetic secular variation from historical records. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A, 358: Mandea, M. and Olsen, N. (2006). A new approach to directly determine the secular variation from magnetic satellite observations. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33(L15306). doi: /2006gl Olsen, N. and Mandea, M. (2007). Investigation of a secular variation impulse using satellite data: The 2003 geomagnetic jerk. Earth Planet. Science Lett, 255: doi: /j.epsl Olsen, N. and Mandea, M. (2008). Rapidly changing flows in the earth s core. Nature Geosciences, 1: Wardinski, I. and Korte, M. (2008). The evolution of the core-surface flow over the last seven thousands years. J. Geophys. Res. doi: /2007jb
The evolution of the core-surface flow over the last seven thousands years
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005024, 2008 The evolution of the core-surface flow over the last seven thousands years I. Wardinski 1 and M. Korte 1 Received 1 March 2007;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005024, 2008 The evolution of the core-surface flow over the last seven thousands years I. Wardinski 1 and M. Korte 1 Received 1 March 2007;
Core field acceleration pulse as a common cause of the 2003 and 2007 geomagnetic jerks
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042019, 2010 Core field acceleration pulse as a common cause of the 2003 and 2007 geomagnetic jerks A. Chulliat, 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042019, 2010 Core field acceleration pulse as a common cause of the 2003 and 2007 geomagnetic jerks A. Chulliat, 1
POLYNOMIAL MODELLING OF SOUTHERN AFRICAN SECULAR VARIATION OBSERVATIONS SINCE 2005
 POLYNOMIAL MODELLING OF SOUTHERN AFRICAN SECULAR VARIATION OBSERVATIONS SINCE 2005 P. Kotzé 1*, M. Korte 2, and M. Mandea 2,3 *1 Hermanus Magnetic Observatory, Hermanus, South Africa Email: pkotze@hmo.ac.za
POLYNOMIAL MODELLING OF SOUTHERN AFRICAN SECULAR VARIATION OBSERVATIONS SINCE 2005 P. Kotzé 1*, M. Korte 2, and M. Mandea 2,3 *1 Hermanus Magnetic Observatory, Hermanus, South Africa Email: pkotze@hmo.ac.za
THE RELIABILITY OF EARTH S MAGNETIC POLES IN THE MODERN, HISTORICAL AND ANCIENT MODELS. T.I. Zvereva, S.V. Starchenko
 THE RELIABILITY OF EARTH S MAGNETIC POLES IN THE MODERN, HISTORICAL AND ANCIENT MODELS T.I. Zvereva, S.V. Starchenko Pushkov institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, ionosphere and Radio wave Propagation (IZMIRAN),
THE RELIABILITY OF EARTH S MAGNETIC POLES IN THE MODERN, HISTORICAL AND ANCIENT MODELS T.I. Zvereva, S.V. Starchenko Pushkov institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, ionosphere and Radio wave Propagation (IZMIRAN),
The geomagnetic dipole moment over the last 7000 years new results from a global model
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 236 (25) 348 358 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl The geomagnetic dipole moment over the last 7 years new results from a global model M. Korte a, *, C.G. Constable b a GeoForschungsZentrum
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 236 (25) 348 358 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl The geomagnetic dipole moment over the last 7 years new results from a global model M. Korte a, *, C.G. Constable b a GeoForschungsZentrum
Centennial to millennial geomagnetic secular variation
 Geophys. J. Int. (2006) 167, 43 52 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03088.x Centennial to millennial geomagnetic secular variation M. Korte 1 and C. G. Constable 2 1 GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg,
Geophys. J. Int. (2006) 167, 43 52 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03088.x Centennial to millennial geomagnetic secular variation M. Korte 1 and C. G. Constable 2 1 GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg,
arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011](/thumbs/95/122563786.jpg) On the correlation between air temperature and the core Earth processes: Further investigations using a continuous wavelet analysis arxiv:1103.4924v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011 Abstract Stefano Sello
On the correlation between air temperature and the core Earth processes: Further investigations using a continuous wavelet analysis arxiv:1103.4924v1 [physics.data-an] 25 Mar 2011 Abstract Stefano Sello
Korte, M., Mandea, M. (2008): Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia. - Earth Planets and Space, 60, 9,
 Originally published as: Korte, M., Mandea, M. (28): Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia. - Earth Planets and Space, 6, 9, 937-948 http://www.terrapub.co.jp/journals/eps/pdf/28/69/69937.pdf
Originally published as: Korte, M., Mandea, M. (28): Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia. - Earth Planets and Space, 6, 9, 937-948 http://www.terrapub.co.jp/journals/eps/pdf/28/69/69937.pdf
Geomagnetic jerks and a high-resolution length-of-day profile for core studies
 Geophys. J. Int. (25) 16, 435 439 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.24.251.x FA S T T R AC K PAPER Geomagnetic jerks and a high-resolution length-of-day profile for core studies R. Holme 1 and O. de Viron 2 1 Department
Geophys. J. Int. (25) 16, 435 439 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.24.251.x FA S T T R AC K PAPER Geomagnetic jerks and a high-resolution length-of-day profile for core studies R. Holme 1 and O. de Viron 2 1 Department
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer CHAOS-2 - A geomagnetic field model derived from one decade of continuous satellite data Citation for published version: Olsen, N, Mandea, M, Sabaka, TJ & Tøffner-Clausen, L
Edinburgh Research Explorer CHAOS-2 - A geomagnetic field model derived from one decade of continuous satellite data Citation for published version: Olsen, N, Mandea, M, Sabaka, TJ & Tøffner-Clausen, L
Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia
 Earth Planets Space, 6, 937 948, 28 Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia M. Korte and M. Mandea GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, elegrafenberg, 14473 Potsdam, Germany
Earth Planets Space, 6, 937 948, 28 Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia M. Korte and M. Mandea GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, elegrafenberg, 14473 Potsdam, Germany
Modelling the southern African geomagnetic field secular variation using ground survey data for 2005
 P. B. KOTZÉ, M. MANDEA AND M. KORTE 187 Modelling the southern African geomagnetic field secular variation using ground survey data for 2005 P. B. Kotzé Hermanus Magnetic Observatory, Hermanus, South Africa
P. B. KOTZÉ, M. MANDEA AND M. KORTE 187 Modelling the southern African geomagnetic field secular variation using ground survey data for 2005 P. B. Kotzé Hermanus Magnetic Observatory, Hermanus, South Africa
Azimuthal flows in the Earth s core and changes in length of day at millennial timescales
 Geophys. J. Int. (6) 165, 3 46 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-46X.6.93.x GJI Geomagnetism, rock magnetism and palaeomagnetism Azimuthal flows in the Earth s core and changes in length of day at millennial timescales
Geophys. J. Int. (6) 165, 3 46 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-46X.6.93.x GJI Geomagnetism, rock magnetism and palaeomagnetism Azimuthal flows in the Earth s core and changes in length of day at millennial timescales
This is an author produced version of Rapid dynamics of the Earth's core.
 This is an author produced version of Rapid dynamics of the Earth's core. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/76955/ Article: Cox, GA and Brown, WJ (213) Rapid
This is an author produced version of Rapid dynamics of the Earth's core. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/76955/ Article: Cox, GA and Brown, WJ (213) Rapid
Anna Korbacz 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1 and Maik Thomas 2. Journées Systèmes de référence spatio-temporels.
 Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 estimated from the output of the global circulation models of the atmosphere - ERA-4 reanalysis and of the ocean - OMCT Anna Korbacz 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1 and Maik
Geophysical excitation of LOD/UT1 estimated from the output of the global circulation models of the atmosphere - ERA-4 reanalysis and of the ocean - OMCT Anna Korbacz 1, Aleksander Brzeziński 1 and Maik
Geomagnetic dipole moment collapse by convective mixing in the core
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L10305, doi:10.1029/2009gl038130, 2009 Geomagnetic dipole moment collapse by convective mixing in the core Lijun Liu 1 and Peter Olson
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L10305, doi:10.1029/2009gl038130, 2009 Geomagnetic dipole moment collapse by convective mixing in the core Lijun Liu 1 and Peter Olson
Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Estimation of core angular momentum (CAM) variation is systematically studied Stronger core flow constraints steepen estimates of the CAM secular trend Estimation of the 6
RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Estimation of core angular momentum (CAM) variation is systematically studied Stronger core flow constraints steepen estimates of the CAM secular trend Estimation of the 6
Characterisation and implications of intradecadal variations in length-of-day
 Characterisation and implications of intradecadal variations in length-of-day R. Holme 1 & O. de Viron 2 1 School of Environmental Sciences, University of Liverpool, L69 3GP, UK. holme@liv.ac.uk 2 Univ.
Characterisation and implications of intradecadal variations in length-of-day R. Holme 1 & O. de Viron 2 1 School of Environmental Sciences, University of Liverpool, L69 3GP, UK. holme@liv.ac.uk 2 Univ.
(This is a sample cover image for this issue. The actual cover is not yet available at this time.)
 (This is a sample cover image for this issue. The actual cover is not yet available at this time.) This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author
(This is a sample cover image for this issue. The actual cover is not yet available at this time.) This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author
IGRF-12 GFZ candidates
 IGRF-12 GFZ candidates V. Lesur 1, M. Rother 1, I. Wardinski 1, R. Schachtschneider 1, M. Hamoudi 2, A. Chambodut 3 October 1, 2014 1 Helmholtz Centre Potsdam, GFZ German Research centre for Geosciences,
IGRF-12 GFZ candidates V. Lesur 1, M. Rother 1, I. Wardinski 1, R. Schachtschneider 1, M. Hamoudi 2, A. Chambodut 3 October 1, 2014 1 Helmholtz Centre Potsdam, GFZ German Research centre for Geosciences,
Tracking geomagnetic impulses at the core mantle boundary
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 237 (25) 3 39 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Tracking geomagnetic impulses at the core mantle boundary Emmanuel Dormy a,b, *, Mioara Mandea a,c a Institut de Physique
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 237 (25) 3 39 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Tracking geomagnetic impulses at the core mantle boundary Emmanuel Dormy a,b, *, Mioara Mandea a,c a Institut de Physique
2. Magnetic Mixing Flows LXXXXX
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, LXXXXX, doi:10.1029/2009gl038130, 2009 2 Geomagnetic dipole moment collapse by convective mixing in the core 3 Lijun Liu 1 and Peter Olson
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, LXXXXX, doi:10.1029/2009gl038130, 2009 2 Geomagnetic dipole moment collapse by convective mixing in the core 3 Lijun Liu 1 and Peter Olson
Constraints on core-mantle electromagnetic coupling from torsional oscillation normal modes
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005135, 2008 Constraints on core-mantle electromagnetic coupling from torsional oscillation normal modes M. Dumberry 1,2 and J. E. Mound 1
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005135, 2008 Constraints on core-mantle electromagnetic coupling from torsional oscillation normal modes M. Dumberry 1,2 and J. E. Mound 1
Unusual behaviour of the IGRF during the period
 Earth Planets Space, 52, 1227 1233, 2000 Unusual behaviour of the IGRF during the 1945 1955 period Wen-yao Xu Institute of Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China (Received February
Earth Planets Space, 52, 1227 1233, 2000 Unusual behaviour of the IGRF during the 1945 1955 period Wen-yao Xu Institute of Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China (Received February
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Continuous geomagnetic field models for the past 7 millennia: 2. CALS7K Article Volume 6, Number
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Continuous geomagnetic field models for the past 7 millennia: 2. CALS7K Article Volume 6, Number
Talks. December 2011.
 Talks Oliveira, J.S., Langlais, B., Amit, H., Pais, M.A., Modeling the magnetic field of Mercury using the Time Dependent Equivalent Source Dipole method. European Geosciences Union, Vienna, Austria, April
Talks Oliveira, J.S., Langlais, B., Amit, H., Pais, M.A., Modeling the magnetic field of Mercury using the Time Dependent Equivalent Source Dipole method. European Geosciences Union, Vienna, Austria, April
Geomagnetic Field Modeling Lessons learned from Ørsted and CHAMP and prospects for Swarm
 Geomagnetic Field Modeling Lessons learned from Ørsted and CHAMP and prospects for Swarm Nils Olsen RAS Discussion Meeting on Swarm October 9 th 2009 Nils Olsen (DTU Space) Ørsted, CHAMP, and Swarm 1 /
Geomagnetic Field Modeling Lessons learned from Ørsted and CHAMP and prospects for Swarm Nils Olsen RAS Discussion Meeting on Swarm October 9 th 2009 Nils Olsen (DTU Space) Ørsted, CHAMP, and Swarm 1 /
Pacific Secular Variation A result of hot lower mantle. David Gubbins School of Earth Sciences University of Leeds
 Pacific Secular Variation A result of hot lower mantle David Gubbins School of Earth Sciences University of Leeds Thermal Core-Mantle Interaction (hot) (cold) Lateral variations in heat flux boundary condition
Pacific Secular Variation A result of hot lower mantle David Gubbins School of Earth Sciences University of Leeds Thermal Core-Mantle Interaction (hot) (cold) Lateral variations in heat flux boundary condition
GEOMAGNETIC TEMPORAL SPECTRUM
 Geomagnetic Temporal Spectrum Catherine Constable 1 GEOMAGNETIC TEMPORAL SPECTRUM Catherine Constable Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California
Geomagnetic Temporal Spectrum Catherine Constable 1 GEOMAGNETIC TEMPORAL SPECTRUM Catherine Constable Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Lesur, V., Wardinski, I., Asari, S., Minchev, B., Mandea, M. (2010): Modelling the Earth s core magnetic field under flow constraints. - Earth Planets and Space, 62, 6, 503-516
Originally published as: Lesur, V., Wardinski, I., Asari, S., Minchev, B., Mandea, M. (2010): Modelling the Earth s core magnetic field under flow constraints. - Earth Planets and Space, 62, 6, 503-516
Magnetostrophic MRI in the Earth s outer core
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L15305, doi:10.109/008gl034395, 008 Magnetostrophic MRI in the Earth s outer core Ludovic Petitdemange, 1, Emmanuel Dormy, 1,3 and Steven A. Balbus 1, Received 18
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L15305, doi:10.109/008gl034395, 008 Magnetostrophic MRI in the Earth s outer core Ludovic Petitdemange, 1, Emmanuel Dormy, 1,3 and Steven A. Balbus 1, Received 18
Calculated and observed climate change in the thermosphere, and a prediction for solar cycle 24
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L23705, doi:10.1029/2006gl027185, 2006 Calculated and observed climate change in the thermosphere, and a prediction for solar cycle 24
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L23705, doi:10.1029/2006gl027185, 2006 Calculated and observed climate change in the thermosphere, and a prediction for solar cycle 24
An ensemble Kalman filter for the time-dependent analysis of the geomagnetic field
 Technical Brief Volume 14, Number 10 2 October 2013 doi: ISSN: 1525-2027 An ensemble Kalman filter for the time-dependent analysis of the geomagnetic field Alexandre Fournier Geomagnetisme, Institut de
Technical Brief Volume 14, Number 10 2 October 2013 doi: ISSN: 1525-2027 An ensemble Kalman filter for the time-dependent analysis of the geomagnetic field Alexandre Fournier Geomagnetisme, Institut de
The second generation of the GFZ Reference Internal Magnetic Model: GRIMM-2
 Earth Planets Space, 62, 765 773, 2010 The second generation of the GFZ Reference Internal Magnetic Model: GRIMM-2 V. Lesur, I. Wardinski, M. Hamoudi, and M. Rother Helmholtz Centre Potsdam, GFZ German
Earth Planets Space, 62, 765 773, 2010 The second generation of the GFZ Reference Internal Magnetic Model: GRIMM-2 V. Lesur, I. Wardinski, M. Hamoudi, and M. Rother Helmholtz Centre Potsdam, GFZ German
Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction. Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center
 Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center Outline Solar cycle characteristics Producing the solar cycle the solar dynamo Polar magnetic fields producing
Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center Outline Solar cycle characteristics Producing the solar cycle the solar dynamo Polar magnetic fields producing
International Geomagnetic Reference Field the eighth generation
 Earth Planets Space, 52, 1119 1124, 2000 International Geomagnetic Reference Field the eighth generation Mioara Mandea 1 and Susan Macmillan 2 1 Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, B.P. 89, 4 Place
Earth Planets Space, 52, 1119 1124, 2000 International Geomagnetic Reference Field the eighth generation Mioara Mandea 1 and Susan Macmillan 2 1 Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, B.P. 89, 4 Place
The Solar Wind over the Last Five Sunspot Cycles and The Sunspot Cycle over the Last Three Centuries
 The Solar Wind over the Last Five Sunspot Cycles and The Sunspot Cycle over the Last Three Centuries C.T. Russell, J.G. Luhmann, L.K. Jian, and B.J.I. Bromage IAU Division E: Sun and Heliosphere Mini Symposium:
The Solar Wind over the Last Five Sunspot Cycles and The Sunspot Cycle over the Last Three Centuries C.T. Russell, J.G. Luhmann, L.K. Jian, and B.J.I. Bromage IAU Division E: Sun and Heliosphere Mini Symposium:
What ancient scalar satellite data can tell us about the 1969 geomagnetic jerk?
 Earth Planets Space, 61, 885 894, 2009 What ancient scalar satellite data can tell us about the 1969 geomagnetic jerk? Y. Yahiat 1,M.Hamoudi 1, and M. Mandea 2 1 University of Sciences and Technology Houari
Earth Planets Space, 61, 885 894, 2009 What ancient scalar satellite data can tell us about the 1969 geomagnetic jerk? Y. Yahiat 1,M.Hamoudi 1, and M. Mandea 2 1 University of Sciences and Technology Houari
Amplitude and Rhythm of Winter Half-year Temperature Change in Eastern China for the Past 2000 Years
 Letters Article ID: 1673-1719 (2007) Suppl.-0026-05 Amplitude and Rhythm of Winter Half-year Temperature Change in Eastern China for the Past 2000 Years Ge Quansheng 1, Zheng Jingyun 1, Liu Jian 2 1 Institute
Letters Article ID: 1673-1719 (2007) Suppl.-0026-05 Amplitude and Rhythm of Winter Half-year Temperature Change in Eastern China for the Past 2000 Years Ge Quansheng 1, Zheng Jingyun 1, Liu Jian 2 1 Institute
Wavelet Analysis of CHAMP Flux Gate Magnetometer Data
 Wavelet Analysis of CHAMP Flux Gate Magnetometer Data Georgios Balasis, Stefan Maus, Hermann Lühr and Martin Rother GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Section., Potsdam, Germany gbalasis@gfz-potsdam.de Summary.
Wavelet Analysis of CHAMP Flux Gate Magnetometer Data Georgios Balasis, Stefan Maus, Hermann Lühr and Martin Rother GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Section., Potsdam, Germany gbalasis@gfz-potsdam.de Summary.
Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions
 Chapter 1 Earth Science Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions Project Representative Yozo Hamano Authors Ataru Sakuraba Yusuke Oishi
Chapter 1 Earth Science Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions Project Representative Yozo Hamano Authors Ataru Sakuraba Yusuke Oishi
Is Earth's magnetic field reversing?
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 246 (2006) 1 16 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Frontiers Is Earth's magnetic field reversing? Catherine Constable a,, Monika Korte b a Institute of Geophysics and Planetary
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 246 (2006) 1 16 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Frontiers Is Earth's magnetic field reversing? Catherine Constable a,, Monika Korte b a Institute of Geophysics and Planetary
First scalar magnetic anomaly map from CHAMP satellite data indicates weak lithospheric field
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 29, NO. 14, 10.1029/2001GL013685, 2002 First scalar magnetic anomaly map from CHAMP satellite data indicates weak lithospheric field S. Maus, M. Rother, R. Holme, H.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 29, NO. 14, 10.1029/2001GL013685, 2002 First scalar magnetic anomaly map from CHAMP satellite data indicates weak lithospheric field S. Maus, M. Rother, R. Holme, H.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12574 1 Parameter space exploration and rationale for parameter choices Here we give a detailed account of the parameter space exploration (Extended Data Table 1) carried out in support
doi:10.1038/nature12574 1 Parameter space exploration and rationale for parameter choices Here we give a detailed account of the parameter space exploration (Extended Data Table 1) carried out in support
GE SPACE. Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce
 GE SPACE Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce Fit to NERC s Science Priorities Understanding the complex interactions and feedbacks within the Earth system over a range of space and time scales Fit
GE SPACE Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce Fit to NERC s Science Priorities Understanding the complex interactions and feedbacks within the Earth system over a range of space and time scales Fit
The Magnetic Field of the Earth
 The Magnetic Field of the Earth Paleomagnetism, the Core, and the Deep Mantle RONALD T. MERRILL Department of Geophysics University of Washington Seattle, Washington MICHAEL W. McELHINNY Gondwana Consultants
The Magnetic Field of the Earth Paleomagnetism, the Core, and the Deep Mantle RONALD T. MERRILL Department of Geophysics University of Washington Seattle, Washington MICHAEL W. McELHINNY Gondwana Consultants
The second generation of the GFZ Reference Internal Magnetic Model: GRIMM-2
 Originally published as: Lesur, V.., Wardinski, I., Hamoudi, M., Rother, M. (2010): The second generation of the GFZ Reference Internal Magnetic Model: GRIMM 2. Earth Planets and Space, 62, 10, 765 773
Originally published as: Lesur, V.., Wardinski, I., Hamoudi, M., Rother, M. (2010): The second generation of the GFZ Reference Internal Magnetic Model: GRIMM 2. Earth Planets and Space, 62, 10, 765 773
When did Earth s magnetic field start and how has it contributed to the preservation of life? J. A. Tarduno 1,2, 1 Dept Earth & Environmental Sciences
 When did Earth s magnetic field start and how has it contributed to the preservation of life? J. A. Tarduno 1,2, 1 Dept Earth & Environmental Sciences, University of Rochester, New York 2 Dept Physics
When did Earth s magnetic field start and how has it contributed to the preservation of life? J. A. Tarduno 1,2, 1 Dept Earth & Environmental Sciences, University of Rochester, New York 2 Dept Physics
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
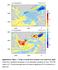 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Mount Stromlo Gravity Station Gravimetry at the ANU
 ANU COLLEGE OF SCIENCE RESEARCH SCHOOL OF EARTH SCIENCES Canberra ACT 0200 Australia Mount Stromlo Gravity Station Gravimetry at the ANU Background Terrestrial observing has been conducted at Mount Stromlo
ANU COLLEGE OF SCIENCE RESEARCH SCHOOL OF EARTH SCIENCES Canberra ACT 0200 Australia Mount Stromlo Gravity Station Gravimetry at the ANU Background Terrestrial observing has been conducted at Mount Stromlo
INTERNATIONAL SERVICE OF GEOMAGNETIC INDICES Monthly Bulletin June Page 1 of 9. International Service of Geomagnetic Indices
 INTERNATIONAL SERVICE OF GEOMAGNETIC INDICES Monthly Bulletin June 2017- Page 1 of 9 International Service of Geomagnetic Indices Monthly Bulletin June 2017 This Bulletin is freely offered to interested
INTERNATIONAL SERVICE OF GEOMAGNETIC INDICES Monthly Bulletin June 2017- Page 1 of 9 International Service of Geomagnetic Indices Monthly Bulletin June 2017 This Bulletin is freely offered to interested
Accounting for magnetic diffusion in core flow inversions from geomagnetic secular variation
 Geophys. J. Int. (2008) 175, 913 924 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03948.x Accounting for magnetic diffusion in core flow inversions from geomagnetic secular variation Hagay Amit 1 and Ulrich R. Christensen
Geophys. J. Int. (2008) 175, 913 924 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03948.x Accounting for magnetic diffusion in core flow inversions from geomagnetic secular variation Hagay Amit 1 and Ulrich R. Christensen
Rationale and geophysical evidence for quasi-geostrophic rapid dynamics within the Earth s outer core
 Rationale and geophysical evidence for quasi-geostrophic rapid dynamics within the Earth s outer core Nicolas Gillet, Nathanaël Schaeffer, Dominique Jault To cite this version: Nicolas Gillet, Nathanaël
Rationale and geophysical evidence for quasi-geostrophic rapid dynamics within the Earth s outer core Nicolas Gillet, Nathanaël Schaeffer, Dominique Jault To cite this version: Nicolas Gillet, Nathanaël
Geomagnetic activity indicates large amplitude for sunspot cycle 24
 Geomagnetic activity indicates large amplitude for sunspot cycle 24 David H. Hathaway and Robert M. Wilson NASA/National Space Science and Technology Center Huntsville, AL USA Abstract. The level of geomagnetic
Geomagnetic activity indicates large amplitude for sunspot cycle 24 David H. Hathaway and Robert M. Wilson NASA/National Space Science and Technology Center Huntsville, AL USA Abstract. The level of geomagnetic
INTERNATIONAL SERVICE OF GEOMAGNETIC INDICES Monthly Bulletin January Page 1 of 9. International Service of Geomagnetic Indices
 INTERNATIONAL SERVICE OF GEOMAGNETIC INDICES Monthly Bulletin January 2017- Page 1 of 9 International Service of Geomagnetic Indices Monthly Bulletin January 2017 This Bulletin is freely offered to interested
INTERNATIONAL SERVICE OF GEOMAGNETIC INDICES Monthly Bulletin January 2017- Page 1 of 9 International Service of Geomagnetic Indices Monthly Bulletin January 2017 This Bulletin is freely offered to interested
SIO229 PART II: GEOMAGNETISM
 SIO229 PART II: GEOMAGNETISM 1. INTRODUCTION Geomagnetism, the study of Earth s magnetic field, has a long history and has revealed much about the way the Earth works. As we shall see, the existence and
SIO229 PART II: GEOMAGNETISM 1. INTRODUCTION Geomagnetism, the study of Earth s magnetic field, has a long history and has revealed much about the way the Earth works. As we shall see, the existence and
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society. Ensemble inversion of time-dependent core flow models
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 10, Number 6 10 June 2009 Q06004, doi:10.1029/2008gc002290 ISSN: 1525-2027 Ensemble
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 10, Number 6 10 June 2009 Q06004, doi:10.1029/2008gc002290 ISSN: 1525-2027 Ensemble
FREE CORE NUTATION: NEW LARGE DISTURBANCE AND CONNECTION EVIDENCE WITH GEOMAGNETIC JERKS
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 13, No. 1 (181), 41 45, 2016 DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2015.0042 journal homepage: http://www.irsm.cas.cz/acta ORIGINAL PAPER FREE CORE NUTATION: NEW LARGE DISTURBANCE AND CONNECTION
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 13, No. 1 (181), 41 45, 2016 DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2015.0042 journal homepage: http://www.irsm.cas.cz/acta ORIGINAL PAPER FREE CORE NUTATION: NEW LARGE DISTURBANCE AND CONNECTION
Radial vorticity constraint in core flow modeling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008267, 2011 Radial vorticity constraint in core flow modeling S. Asari 1 and V. Lesur 1 Received 2 February 2011; revised 8 August 2011; accepted
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008267, 2011 Radial vorticity constraint in core flow modeling S. Asari 1 and V. Lesur 1 Received 2 February 2011; revised 8 August 2011; accepted
SIO 229 Part II Geomagnetism. Lecture 1 Introduction to the geomagnetic field
 SIO 229 Part II Geomagnetism Lecture 1 Introduction to the geomagnetic field Why study Earth's magnetic field Schematic picture of Earth's magnetic field interacting with the solar wind (credit: NASA)
SIO 229 Part II Geomagnetism Lecture 1 Introduction to the geomagnetic field Why study Earth's magnetic field Schematic picture of Earth's magnetic field interacting with the solar wind (credit: NASA)
Study of Geomagnetic Field Variations at Low Latitude of African Equatorial Region
 Study of Geomagnetic Field Variations at Low Latitude of African Equatorial Region Agbo G. A 1 ; Azi A. O. 2, Okoro N. O. 3 Industrial Physics Department, Ebonyi State University, P.M.B 053 Abakaliki Abstract:
Study of Geomagnetic Field Variations at Low Latitude of African Equatorial Region Agbo G. A 1 ; Azi A. O. 2, Okoro N. O. 3 Industrial Physics Department, Ebonyi State University, P.M.B 053 Abakaliki Abstract:
Case Study: Numerical Simulations of the Process by which Planets generate their Magnetic Fields. Stephan Stellmach UCSC
 Case Study: Numerical Simulations of the Process by which Planets generate their Magnetic Fields Stephan Stellmach UCSC 1 The Scientific Problem 2 The Magnetic Field of the Earth http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/image:magnetosphere_rendition.jpg
Case Study: Numerical Simulations of the Process by which Planets generate their Magnetic Fields Stephan Stellmach UCSC 1 The Scientific Problem 2 The Magnetic Field of the Earth http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/image:magnetosphere_rendition.jpg
A time-dependent model of the Earth s magnetic field and its secular variation for the period
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004401, 2006 A time-dependent model of the Earth s magnetic field and its secular variation for the period 1980 2000 I. Wardinski 1 and R.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004401, 2006 A time-dependent model of the Earth s magnetic field and its secular variation for the period 1980 2000 I. Wardinski 1 and R.
3-D modelling the electric field due to ocean tidal flow and comparison with observations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L06314, doi:10.1029/2005gl025043, 2006 3-D modelling the electric field due to ocean tidal flow and comparison with observations Alexei Kuvshinov, 1,2 Andreas Junge,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L06314, doi:10.1029/2005gl025043, 2006 3-D modelling the electric field due to ocean tidal flow and comparison with observations Alexei Kuvshinov, 1,2 Andreas Junge,
The Earth's Magnetic Field. Its History, Origin and Planetary Perspective
 The Earth's Magnetic Field Its History, Origin and Planetary Perspective RONALD T. MERRILL Geophysics Program University of Washington Seattle, USA MICHAEL W. McELHINNY Formerly, Research School of Earth
The Earth's Magnetic Field Its History, Origin and Planetary Perspective RONALD T. MERRILL Geophysics Program University of Washington Seattle, USA MICHAEL W. McELHINNY Formerly, Research School of Earth
Reply to Lockwood and Fröhlich The persistent role of the Sun in climate forcing. Svensmark, H. and Friis-Christensen, E.
 Reply to Lockwood and Fröhlich The persistent role of the Sun in climate forcing Svensmark, H. and Friis-Christensen, E. Danish National Space Center Scientific Report 3/2007 Reply to Lockwood and Fröhlich
Reply to Lockwood and Fröhlich The persistent role of the Sun in climate forcing Svensmark, H. and Friis-Christensen, E. Danish National Space Center Scientific Report 3/2007 Reply to Lockwood and Fröhlich
The Earth s rotation and atmospheric circulation:
 Geophys. J. R. astr. SOC. (1982) 71,581-587 The Earth s rotation and atmospheric circulation: 1958-1 980 Kurt Lambeck and Peter Hopgood Research SchoolofEarth Sciences, Australian Nationaf University,
Geophys. J. R. astr. SOC. (1982) 71,581-587 The Earth s rotation and atmospheric circulation: 1958-1 980 Kurt Lambeck and Peter Hopgood Research SchoolofEarth Sciences, Australian Nationaf University,
Space Weather Fundamentals. Earth s Magnetic Field
 This article was downloaded by: 10.3.98.93 On: 04 Apr 2019 Access details: subscription number Publisher: CRC Press Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
This article was downloaded by: 10.3.98.93 On: 04 Apr 2019 Access details: subscription number Publisher: CRC Press Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
PERSISTENT 22-YEAR CYCLE IN SUNSPOT ACTIVITY: EVIDENCE FOR A RELIC SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELD. 1. Introduction
 PERSISTENT 22-YEAR CYCLE IN SUNSPOT ACTIVITY: EVIDENCE FOR A RELIC SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELD K. MURSULA 1, I. G. USOSKIN 2, and G. A. KOVALTSOV 3 1 Department of Physical Sciences, FIN-90014 University of Oulu,
PERSISTENT 22-YEAR CYCLE IN SUNSPOT ACTIVITY: EVIDENCE FOR A RELIC SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELD K. MURSULA 1, I. G. USOSKIN 2, and G. A. KOVALTSOV 3 1 Department of Physical Sciences, FIN-90014 University of Oulu,
L ONG-TERM VARIATIONS OF GEOMAGNETIC ACTIVITY AND THEIR SOL AR SOURCES. Shelting B.D. 2
 L ONG-TERM VARIATIONS OF GEOMAGNETIC ACTIVITY AND THEIR SOL AR SOURCES Kirov B. 1, Obridko V.N. 2, Georgieva K. 1, Nepomnyashtaya E.V. 2, Shelting B.D. 2 1 Space Research ant Technologies Institute - BAS,
L ONG-TERM VARIATIONS OF GEOMAGNETIC ACTIVITY AND THEIR SOL AR SOURCES Kirov B. 1, Obridko V.N. 2, Georgieva K. 1, Nepomnyashtaya E.V. 2, Shelting B.D. 2 1 Space Research ant Technologies Institute - BAS,
The Unexpected Awakening of Chaitén Volcano, Chile
 Chemistry-Climate Models, p. 206 News: Gender Equity at U.S. Research Institutions, p. 207 Forum: Geomagnetic and Archeomagnetic Jerks, p. 208 Meeting: Marine Research Drilling, p. 209 About AGU: Fein
Chemistry-Climate Models, p. 206 News: Gender Equity at U.S. Research Institutions, p. 207 Forum: Geomagnetic and Archeomagnetic Jerks, p. 208 Meeting: Marine Research Drilling, p. 209 About AGU: Fein
Existence of finite rigidity layer at the base of the Earth s liquid outer core inferred from anomalous splitting of normal modes
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 54, 67 7, 22 Existence of finite rigidity layer at the base of the Earth s liquid outer core inferred from anomalous splitting of normal modes Seiji Tsuboi,2 and Masanori Saito
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 54, 67 7, 22 Existence of finite rigidity layer at the base of the Earth s liquid outer core inferred from anomalous splitting of normal modes Seiji Tsuboi,2 and Masanori Saito
Observation of magnetic diffusion in the Earth s outer core from Magsat, Ørsted, and CHAMP data
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006994, 2010 Observation of magnetic diffusion in the Earth s outer core from Magsat, Ørsted, and CHAMP data A.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006994, 2010 Observation of magnetic diffusion in the Earth s outer core from Magsat, Ørsted, and CHAMP data A.
Tilts and Obliquities!
 Fran Bagenal! University of Colorado! Tilts and Obliquities! Offset Tilted Dipole Approximation Earth Stanley & Bloxham 2006 Jupiter Saturn B radial @ surface Uranus Neptune Magnetic Potential 3-D harmonics
Fran Bagenal! University of Colorado! Tilts and Obliquities! Offset Tilted Dipole Approximation Earth Stanley & Bloxham 2006 Jupiter Saturn B radial @ surface Uranus Neptune Magnetic Potential 3-D harmonics
Predicting amplitude of solar cycle 24 based on a new precursor method
 Author(s) 21. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Annales Geophysicae Predicting amplitude of solar cycle 24 based on a new precursor method A. Yoshida and H. Yamagishi
Author(s) 21. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Annales Geophysicae Predicting amplitude of solar cycle 24 based on a new precursor method A. Yoshida and H. Yamagishi
HONORS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS II. The Origin of Earth s Magnetic Field and Theories on Polarity Reversal
 HONORS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS II The Origin of Earth s Magnetic Field and Theories on Polarity Reversal Aaron 11/29/2010 The Encyclopedia Britannica defines a magnetic pole as the region at each end of a magnet
HONORS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS II The Origin of Earth s Magnetic Field and Theories on Polarity Reversal Aaron 11/29/2010 The Encyclopedia Britannica defines a magnetic pole as the region at each end of a magnet
The Earth's Magnetism
 Roberto Lanza Antonio Meloni The Earth's Magnetism An Introduction for Geologists With 167 Figures and 6 Tables 4y Springer Contents 1 The Earth's Magnetic Field 1 1.1 Observations and Geomagnetic Measurements
Roberto Lanza Antonio Meloni The Earth's Magnetism An Introduction for Geologists With 167 Figures and 6 Tables 4y Springer Contents 1 The Earth's Magnetic Field 1 1.1 Observations and Geomagnetic Measurements
DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL
 DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE EARTH DIPOLE Field Structure Permanent magnetization of Core? 80% of field is dipole 20 % is non dipole 2)
DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE EARTH DIPOLE Field Structure Permanent magnetization of Core? 80% of field is dipole 20 % is non dipole 2)
The role of the Earth s mantle in controlling the frequency of geomagnetic reversals
 The role of the Earth s mantle in controlling the frequency of geomagnetic reversals Gary A. Glatzmaier*, Robert. Coe*, Lionel Hongre* & Paul H. Roberts * Earth ciences Department, University of California,
The role of the Earth s mantle in controlling the frequency of geomagnetic reversals Gary A. Glatzmaier*, Robert. Coe*, Lionel Hongre* & Paul H. Roberts * Earth ciences Department, University of California,
Fluctuations in the Earth's Rate of Rotation Related to Changes in the Geomagnetic Dipole Field
 J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 25, 195-212, 1973 Fluctuations in the Earth's Rate of Rotation Related to Changes in the Geomagnetic Dipole Field Takesi YUKUTAKE Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo,
J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 25, 195-212, 1973 Fluctuations in the Earth's Rate of Rotation Related to Changes in the Geomagnetic Dipole Field Takesi YUKUTAKE Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo,
Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse?
 IMPRS Solar System Seminar June 2002 Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse? Dieter Schmitt (Katlenburg-Lindau) 1. Geomagnetic field >99% of matter in universe is plasma: gas of electrons, ions
IMPRS Solar System Seminar June 2002 Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse? Dieter Schmitt (Katlenburg-Lindau) 1. Geomagnetic field >99% of matter in universe is plasma: gas of electrons, ions
The Magnetic Field of the Earth. Paleomagnetism, the Core, and the Deep Mantle
 The Magnetic Field of the Earth Paleomagnetism, the Core, and the Deep Mantle This is Volume 63 in the INTERNATIONAL GEOPHYSICS SERIES A series of monographs and textbooks Edited by RENATA DMOWSKA and
The Magnetic Field of the Earth Paleomagnetism, the Core, and the Deep Mantle This is Volume 63 in the INTERNATIONAL GEOPHYSICS SERIES A series of monographs and textbooks Edited by RENATA DMOWSKA and
Irregularity and Predictability of ENSO
 Irregularity and Predictability of ENSO Richard Kleeman Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York Main Reference R. Kleeman. Stochastic theories for the irregularity of ENSO. Phil. Trans. Roy.
Irregularity and Predictability of ENSO Richard Kleeman Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York Main Reference R. Kleeman. Stochastic theories for the irregularity of ENSO. Phil. Trans. Roy.
A New Lithospheric Field Model based on CHAMP and Swarm Magnetic Satellite Data
 A New Lithospheric Field Model based on CHAMP and Swarm Magnetic Satellite Data Nils Olsen 1, Dhananjay Ravat 2, Christopher C Finlay 1, Livia K. Kother 1 1 DTU Space, Technical University of Denmark 2
A New Lithospheric Field Model based on CHAMP and Swarm Magnetic Satellite Data Nils Olsen 1, Dhananjay Ravat 2, Christopher C Finlay 1, Livia K. Kother 1 1 DTU Space, Technical University of Denmark 2
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research
 Pausata, F., LeGrande, A., & Roberts, W. H. G. (2016). How Will Sea Ice Loss Affect the Greenland Ice Sheet?: On the Puzzling Features of Greenland Ice-Core Isotopic Composition; Copenhagen, Denmark, 26
Pausata, F., LeGrande, A., & Roberts, W. H. G. (2016). How Will Sea Ice Loss Affect the Greenland Ice Sheet?: On the Puzzling Features of Greenland Ice-Core Isotopic Composition; Copenhagen, Denmark, 26
INVESTIGATIONS OF THE STRUCTURE OF THE DIURNAL VARIATIONS OF GEOMAGNETIC FIELD
 Geologica Macedonica, Vol. 26, No. 1, pp. 37 51 (2012) GEOME 2 ISSN 0352 1206 Manuscript received: May 6, 2012 UDC: 556.385 Accepted: October 10, 2012 Original scientific paper INVESTIGATIONS OF THE STRUCTURE
Geologica Macedonica, Vol. 26, No. 1, pp. 37 51 (2012) GEOME 2 ISSN 0352 1206 Manuscript received: May 6, 2012 UDC: 556.385 Accepted: October 10, 2012 Original scientific paper INVESTIGATIONS OF THE STRUCTURE
LONG-TERM VARIATIONS OF SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELDS DERIVED FROM GEOMAGNETIC DATA K.Georgieva 1, B.Kirov 1, Yu.A.Nagovitsyn 2
 1. Introduction LONG-TERM VARIATIONS OF SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELDS DERIVED FROM GEOMAGNETIC DATA K.Georgieva 1, B.Kirov 1, Yu.A.Nagovitsyn 2 1 Space Research and Technologies Institute, Bulgarian Academy of
1. Introduction LONG-TERM VARIATIONS OF SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELDS DERIVED FROM GEOMAGNETIC DATA K.Georgieva 1, B.Kirov 1, Yu.A.Nagovitsyn 2 1 Space Research and Technologies Institute, Bulgarian Academy of
Magnetic field nomenclature
 Magnetic field nomenclature Declination trend angle between horizontal projection of F and true North Inclination plunge angle between horizontal and F Magnetic equator location on surface where field
Magnetic field nomenclature Declination trend angle between horizontal projection of F and true North Inclination plunge angle between horizontal and F Magnetic equator location on surface where field
Diffusive magnetic images of upwelling patterns in the core
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. B12, 2348, doi:10.1029/2001jb000384, 2002 Diffusive magnetic images of upwelling patterns in the core Peter Olson, Ikuro Sumita, 1 and Jonathan Aurnou 2 Department
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. B12, 2348, doi:10.1029/2001jb000384, 2002 Diffusive magnetic images of upwelling patterns in the core Peter Olson, Ikuro Sumita, 1 and Jonathan Aurnou 2 Department
Four decades of European geomagnetic secular variation and acceleration
 Vol,,9 --9 :9 Pagina 7 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL., N. October 9 Four decades of European geomagnetic secular variation and acceleration Giuliana Verbanac ( ), Monika Korte ( ) and Mioara Mandea ( ) ( )
Vol,,9 --9 :9 Pagina 7 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL., N. October 9 Four decades of European geomagnetic secular variation and acceleration Giuliana Verbanac ( ), Monika Korte ( ) and Mioara Mandea ( ) ( )
Meridional Flow, Torsional Oscillations, and the Solar Magnetic Cycle
 Meridional Flow, Torsional Oscillations, and the Solar Magnetic Cycle David H. Hathaway NASA/MSFC National Space Science and Technology Center Outline 1. Key observational components of the solar magnetic
Meridional Flow, Torsional Oscillations, and the Solar Magnetic Cycle David H. Hathaway NASA/MSFC National Space Science and Technology Center Outline 1. Key observational components of the solar magnetic
Preferred spatio-temporal patterns as non-equilibrium currents
 Preferred spatio-temporal patterns as non-equilibrium currents Escher Jeffrey B. Weiss Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Colorado, Boulder Arin Nelson, CU Baylor Fox-Kemper, Brown U Royce
Preferred spatio-temporal patterns as non-equilibrium currents Escher Jeffrey B. Weiss Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Colorado, Boulder Arin Nelson, CU Baylor Fox-Kemper, Brown U Royce
Spectral Studies of Ionospheric and Solar Wind Electric Fields: Case Studies and Long-Duration Analysis Using Magnetometer Data
 Spectral Studies of Ionospheric and Solar Wind Electric Fields: Case Studies and Long-Duration Analysis Using Magnetometer Data M. C. Kelley, M. J. Nicolls, and G. Sachdeva Cornell University, Ithaca,
Spectral Studies of Ionospheric and Solar Wind Electric Fields: Case Studies and Long-Duration Analysis Using Magnetometer Data M. C. Kelley, M. J. Nicolls, and G. Sachdeva Cornell University, Ithaca,
Planetary dynamos: Dipole-multipole transition and dipole reversals
 Planetary dynamos: Dipole-multipole transition and dipole reversals Ulrich Christensen Max-Planck-Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany in collaboration with Hagay Amit, Julien
Planetary dynamos: Dipole-multipole transition and dipole reversals Ulrich Christensen Max-Planck-Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany in collaboration with Hagay Amit, Julien
Westward drift in secular variation of the main geomagnetic field inferred from IGRF
 Earth Planets Space, 55, 131 137, 2003 Westward drift in secular variation of the main geomagnetic field inferred from IGRF Zi-Gang Wei and Wen-Yao Xu Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy
Earth Planets Space, 55, 131 137, 2003 Westward drift in secular variation of the main geomagnetic field inferred from IGRF Zi-Gang Wei and Wen-Yao Xu Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy
The time-averaged magnetic field in numerical dynamos with non-uniform boundary heat flow
 Geophys. J. Int. (2002) 151, 809 823 The time-averaged magnetic field in numerical dynamos with non-uniform boundary heat flow Peter Olson 1 and U. R. Christensen 2 1 Department of Earth and Planetary
Geophys. J. Int. (2002) 151, 809 823 The time-averaged magnetic field in numerical dynamos with non-uniform boundary heat flow Peter Olson 1 and U. R. Christensen 2 1 Department of Earth and Planetary
HISTORICAL ECLIPSES AND EARTH'S ROTATION
 HISTORICAL ECLIPSES AND EARTH'S ROTATION F. Richard Stephenson University of Durham CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Principal Symbols 1 Variations in the length of the day: a historical perspective
HISTORICAL ECLIPSES AND EARTH'S ROTATION F. Richard Stephenson University of Durham CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Principal Symbols 1 Variations in the length of the day: a historical perspective
Comment on Effects of fast and slow solar wind on the correlation between interplanetary medium and geomagnetic activity by P.
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A10, 1386, doi:10.1029/2002ja009746, 2003 Correction published 20 January 2004 Comment on Effects of fast and slow solar wind on the correlation between interplanetary
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A10, 1386, doi:10.1029/2002ja009746, 2003 Correction published 20 January 2004 Comment on Effects of fast and slow solar wind on the correlation between interplanetary
Convection-driven spherical dynamos: remarks on bistability and on simple models of the Solar cycle
 University of Cambridge DAMTP, Astrophysics Group Seminar 2014-11-17 Convection-driven spherical dynamos: remarks on bistability and on simple models of the Solar cycle R.D. Simitev F.H. Busse School of
University of Cambridge DAMTP, Astrophysics Group Seminar 2014-11-17 Convection-driven spherical dynamos: remarks on bistability and on simple models of the Solar cycle R.D. Simitev F.H. Busse School of
Time-average and time-dependent parts of core flow
 Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 155 (2006) 120 139 Time-average and time-dependent parts of core flow Hagay Amit, Peter Olson Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Johns Hopkins University,
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 155 (2006) 120 139 Time-average and time-dependent parts of core flow Hagay Amit, Peter Olson Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Johns Hopkins University,
