POLYNOMIAL MODELLING OF SOUTHERN AFRICAN SECULAR VARIATION OBSERVATIONS SINCE 2005
|
|
|
- Lynn Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POLYNOMIAL MODELLING OF SOUTHERN AFRICAN SECULAR VARIATION OBSERVATIONS SINCE 2005 P. Kotzé 1*, M. Korte 2, and M. Mandea 2,3 *1 Hermanus Magnetic Observatory, Hermanus, South Africa 2 Helmholtz-Zentrum Potsdam Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum GFZ 3 Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris ABSTRACT The COMPASS (COmprehensive Magnetic Processes under the African Southern Sub-continent) program forms part of a collaboration project between Germany and South Africa, called Inkaba ye Africa, and aims to investigate the regional geomagnetic field in this area, particularly its evolutionary behaviour. Results obtained from field surveys conducted by the Hermanus Magnetic Observatory (HMO) and the Helmholtz GeoForschungsZentrum (GFZ) in South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana, in addition to geomagnetic field data from the 4 continuous recording magnetic observatories in southern Africa at Hermanus, Hartebeesthoek, Keetmanshoop and Tsumeb, were used to model the geomagnetic field time variation by means of a polynomial approach. 1 INTRODUCTION It is well known that secular change is a comparatively local phenomenon and that it does not proceed in a regular and uniform pattern all over the Earth, giving rise to regions where the field changes more rapidly than elsewhere, such as southern Africa. COMPASS (COmprehensive Magnetic Processes under the African Southern Sub-continent), a sub-project forming part of the Inkaba yeafrica project ( aims at a better understanding of the regional geomagnetic field behaviour. Secular variation observations over southern Africa, including countries like South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana, have been conducted since 2005 as part of this collaboration between the Hermanus Magnetic Observatory (HMO) in South Africa and the German Research Centre for Geosciences in Germany. For this purpose, a total of 40 repeat stations, separated by distances ranging between 300 and 400 km, were identified. These stations form part of a network of 75 repeat stations, established by the HMO during the last 60 years and visited at regular 5 year intervals until Due to the rapid secular variation change over this area, it was necessary to conduct annual surveys at a reduced number of repeat stations. The stations were also selected to form two independent sets of 20 beacons each, enabling one to visit these at alternative years respectively. During these field surveys, 2 teams, consisting of both HMO and GFZ observers, using similar DI Flux theodolites and fluxgate variometers, obtained geomagnetic field data over southern Africa. These measurements were processed to remove daily variations etc. and then modelled by polynomial fitting as a function of latitude and longitude to derive geomagnetic field secular variation models for southern Africa. 2 FIELD SURVEYS AND DATA Continuous recording of geomagnetic field variations are conducted at Hermanus (34º 25.5 S, 19º 13.5 E), Hartebeesthoek (25º 52.9 S, 27º 42.4 E), Tsumeb (19º 12 S, 17º 35 E), and Keetmanshoop ( S, E). All these observatories comply with INTERMAGNET standards ( The primary instrument for recording of magnetic field variations is the FGE fluxgate magnetometer, manufactured by the Danish Meteorological Institute in Copenhagen, Denmark. This instrument is based on three-axis linearcore fluxgate technology, optimised for long-term stability, and records the components H, D, and Z. An Overhauser-type magnetometer further provides absolute total field information while baselines for the other components are obtained using a DI (Declinometer-Inclinometer) Flux theodolite ( IAGA95
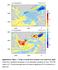
2 For field survey purposes, field stations are marked by concrete beacons, ensuring that all observation points are exactly reoccupied during surveys. Most measurements are taken on a standard 1.2m pillar while in a few cases observers had to use a tripod mounted above a clearly marked shorter beacon. The field surveys of 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, and 2009 were separated into three different sectors. At first a survey was done by only HMO field surveyors. Thereafter, two independent teams, each consisting of a staff member from HMO and GFZ, conducted a simultaneous field survey in southern Africa. A map showing the repeat station beacons visited during the 2009 survey is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Map of distribution of observatories (red asterisks) and repeat stations (numbered white dots) in the southern African region. Observatories are situated in Hermanus (HER), Tsumeb (TSU), Keetmanshoop (KMH), and Hartebeesthoek (HBK). (Figure courtesy of A Geese, GFZ) More information on the repeat station methodology is given by Korte et al. (2007). A DI fluxgate magnetometer was used as primary instrument during field surveys to obtain values of declination and inclination while an Overhauser magnetometer delivered values of total field intensity (F). Corrections for diurnal variation and other disturbing effects were made by comparing field station observations with magnetic data recorded on site with a LEMI suspended tri-axis fluxgate instrument. The data reduction to quiet internal field values according to the standard procedures described, e.g., by Newitt et al. (1996) is done in two steps. First the measured values are reduced to the quiet night time level by means of the local variometer recording. For quiet up to moderately disturbed magnetic conditions, the average of several night time hours represents the quiet internal field reasonably well (Korte et al., 2007). In order to obtain data for a common time, the quiet night time values are then further reduced to annual means utilizing the recordings of the nearest observatory and taking into account estimates of secular variation differences. 3 POLYNOMIAL MODELLING Historically, polynomial models are among the most frequently used empirical models for curve fitting and to determine the parameters that have a profound effect on a particular response function. This type of modelling is popular as polynomial models have a simple form, have well known and understood properties, have moderate flexibility of shapes, and they are computationally easy to use. However, polynomial models also have limitations such as weak interpolatory and extrapolatory properties. Polynomials may provide good fits within the range of data, but they will frequently deteriorate rapidly outside the range of the data. IAGA96
3 Different methods to model the geomagnetic field on a regional scale were reviewed by Haines (1990). In geomagnetism, polynomials have been applied with great success to derive regional models of secular variation (Shu et.al., 1996). Polynomials have been used extensively to model ground magnetic field measurements to derive secular variation models for southern Africa (Kotzé, 2003). The field surveys conducted since 2005 however enabled polynomial-based secular variation models to be derived. We selected a two-dimensional polynomial presentation (Xu et al., 1992): Where is the magnitude of secular variation for each component of the geomagnetic field at the point with geographic coordinates θ and γ, is a numerical coefficient, and and are the coordinates of the centre of the modelled area: = 26 S and = 24 E. Since secular variation is not measured directly but is derived as a time derivative of the geomagnetic field, one can model the main field and then differentiate the corresponding field model to get a secular variation model, or one can numerically differentiate the main field data and then fit a secular variation model directly. The latter derivative fit approach has been applied in this study of observatory and repeat station data. First central differences from annual mean observatory data as well as repeat stations, divided by their respective time intervals in years, are used as input data to our secular variation model. As observatory data, in general, are more accurate than repeat survey data (because of better baseline control and because seasonal and other shortterm variations are more effectively removed by using annual means), we weighted observatory and repeat station secular variation data in a ratio 1:0.7 in the least-squares solution. This ratio was determined by minimizing the RMS difference between model fits and survey data. There are 120 vector differences from 40 repeat stations and 12 vector differences from the 4 observatories, providing a total of 132 data values for a particular time interval. Secular variation models for the periods , , , and were subsequently derived. The least-squares routine used to fit the data is the stepwise regression procedure described by Efroymson (1960) that has the ability of both entering and removing variables at given levels of statistical significance. The scatter about the fit for declination secular variation is less than 1 min/y. 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Results obtained in this investigation by modelling secular variation over southern Africa for the period by means of a polynomial modelling approach reveal a very dynamic geomagnetic field pattern. In particular, the declination secular variation is dominated by an eastward changing pattern in the north-western part of the region while the south-eastern region of southern Africa is under the influence of a westward variation (Figure 2). The annual field survey results reveal a rapid change from year to year. This is quite evident when observing the annual movement of particularly the zero secular variation contour line as displayed in Figure 2. Of particular interest is to note that the westward change in declination secular variation in the southern part of the region, centred around Cape Agulhas, has slowed down from 8min/year in to approximately 4 min/year in In contrast to this, the eastward change in the declination secular variation as displayed in the northern part of Namibia stayed constant around 8 min/year. This indicates a decreasing gradient in the orientation of the geomagnetic field of southern Africa in a north-west, south-eastern direction as revealed during the period The pattern displayed by the Z-component secular variation (Figure 3) clearly indicates that southern Africa is dominated by a central region where the vertical component of the magnetic field is declining at a rapid rate between 20 and 40 nt/year. Over the south-western part of the subcontinent, the decay of Z is the most prominent, characterised by a rapid change between 2007 and 2008, reminiscent of a geomagnetic jerk that occurred in this time interval (Kotzé, 2010). A plot of dy/dt and dd/dt versus time (Figure 4) for the Hermanus (HER) observatory confirms that indeed an extremely strong secular variation impulse occurred around following a linear fit to the data. For the Y-component in particular, the secular variation changed from -15 nt/y at to -2 nt/y at and then started to change back to -10 nt/y at The strength of this jerk is IAGA97
4 more than 15 nt/y 2, which is more than 3 times stronger than the global geomagnetic jerk of 1982/3. A similar pattern can be observed for D during Figure 2. Secular variation of Declination for the periods , , , and for southern Africa IAGA98
5 Figure 3. Secular variation of Z for the periods , , , and for southern Africa IAGA99
6 Figure 4. Plots showing the occurrence of a geomagnetic jerk as observed during 2007 at the Hermanus Magnetic Observatory in the secular variation patterns of both the Y and D field components. Since the first magnetic field measurements started in the nineteenth century, a continuous decrease of the Earth s magnetic dipole moment has been observed. The change in the field strength is, however, not evenly distributed over the globe. In particular, the most rapid decrease of the core field is observed across the Southern Atlantic region. The southern African and south Atlantic regions have shown a particularly striking geomagnetic field behaviour over the last decades (Bloxham & Gubbins, 1985; Mandea et al., 2007). Therefore southern Africa provides an ideal opportunity to study these geomagnetic field changes, as confirmed by the field surveys since Since the establishment of the Hermanus Magnetic Observatory in South Africa in 1941, the total field intensity across southern Africa has decreased by 20%. This rapid and substantial changes observed across the southern African region can largely be attributed to the close proximity of the South Atlantic Anomaly. The growth and position changing of patches of the reverse flux under the southern African region, from 1840 onwards, may be responsible for changes in dipole moment (Gubbins & Bloxham, 1985; Bloxham & Jackson, 1992; Jackson et al., 2000). Most interestingly in this regard, it has been shown recently (Dormy & Mandea, 2005) that patches of intense secular variation appear in the South Atlantic hemisphere that are very rapidly displaced in a south-east north-west direction, consistent with observations of the present study. 6 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We wish to thank the Geological Survey of Namibia, Ministry of Mines and Energy, as well as the Geological Survey of Botswana for continuous support in carrying out repeat station measurements in these countries. For organisation and successful execution of the repeat station surveys we thank B. Pretorius and E. Julies from the Hermanus Magnetic Observatory. Support provided by the Geological Survey of Namibia in the operation of the magnetic observatory in Tsumeb is acknowledged. 7 REFERENCES Bloxham, J. & Gubbins, D. (1985) The secular variation of the Earth's magnetic field. Nature, 317, Bloxham, J. & Jackson, A. (1992)Time-dependent mapping of the magnetic field at the core-mantle boundary, Journal of Geophysical Research, 97, 19,537-19,563 IAGA100
7 Dormy, E. & Mandea, M. (2005) Tracking geomagnetic impulses down to the core-mantle boundary, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 237, Efroymson, M.A. (1960) Multiple regression analysis, in Mathematical Methods for Digital Computers, A. Ralston & H.S. Wilf (Eds.), pp , John Wiley, New York. Gubbins, D. & Bloxham, J. (1985) Geomagnetic field analysis III. Magnetic fields at the core-mantle boundary. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 80, Haines, G. V. (1990) Regional magnetic field modelling - A review, Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity, 42, Jackson, A., Jonkers, A.R.T., & Walker, M.R. (2000) Four centuries of geomagnetic secular variation from historical records. Philosophical Transaction of the Royal Society, London, Series A, 358, Korte, M., Mandea, M., Kotzé, P., Nahayo, E., & Pretorius, B. (2007) Improved observations at the southern African geomagnetic repeat station network, South African Journal of Geology, 110, Korte, M., Mandea, M., Linthe, H.-J., Geese [Hemshorn], A., Kotzé, P., & Ricaldi, E. (2009) New geomagnetic field observations in the South Atlantic Anomaly region, Annals of Geophysics, 52, Kotzé, P.B. (2003) The time-varying geomagnetic field of Southern Africa, Earth Planets and Space, 55, Kotzé, P. B., Mandea, M., & Korte, M. (2007) Modelling the southern African geomagnetic field secular variation using ground survey data for 2005, South African Journal of Geology, 110, Kotzé, P. (2010) The 2007 geomagnetic jerk as observed at the Hermanus Magnetic Observatory, Physics Comment, 2(4), 5-6. Linthe, H.-J., Kotzé, P., Mandea, M., &Theron, H. (2007) Keetmanshoop A new observatory in Namibia. Publications of the Institute of Geophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences, C-99 (398), Mandea, M., Korte, M. Mozzoni, D., & Kotzé, P. (2007) The magnetic field changing over the southern African continent - a unique behaviour, South African Journal of Geology, 110, Newitt, L.R., Barton, C.E., Bitterly, J. (1996) Guide for geomagnetic repeat station surveys, International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy. Shu, Y., An, C., Golovkov, V.P., Rotanova, N.M., & Bondar, T. N. (1996) Analysis of geomagnetic secular variations in eastern Asia during the last 30 years, Geomagn. Aeronomy, 35, Xu, Y., Wang, Y., & Z. (1992) An analysis and the models of the geomagnetic secular variation in China for , Acta Geophys. Sin., 35, IAGA101
Modelling the southern African geomagnetic field secular variation using ground survey data for 2005
 P. B. KOTZÉ, M. MANDEA AND M. KORTE 187 Modelling the southern African geomagnetic field secular variation using ground survey data for 2005 P. B. Kotzé Hermanus Magnetic Observatory, Hermanus, South Africa
P. B. KOTZÉ, M. MANDEA AND M. KORTE 187 Modelling the southern African geomagnetic field secular variation using ground survey data for 2005 P. B. Kotzé Hermanus Magnetic Observatory, Hermanus, South Africa
Hermanus Magnetic Observatory
 Hermanus Magnetic Observatory A facility of the National Research Foundation Magnetic Results 2009 Hermanus, Hartebeesthoek and Keetmanshoop observatories 1. INTRODUCTION The Hermanus Magnetic Observatory
Hermanus Magnetic Observatory A facility of the National Research Foundation Magnetic Results 2009 Hermanus, Hartebeesthoek and Keetmanshoop observatories 1. INTRODUCTION The Hermanus Magnetic Observatory
New geomagnetic field observations in the South Atlantic Anomaly region
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 52, N. 1, February 2009 New geomagnetic field observations in the South Atlantic Anomaly region Monika Korte ( 1 ), Mioara Mandea ( 1 ), Hans-Joachim Linthe ( 1 ), Anne Hemshorn
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 52, N. 1, February 2009 New geomagnetic field observations in the South Atlantic Anomaly region Monika Korte ( 1 ), Mioara Mandea ( 1 ), Hans-Joachim Linthe ( 1 ), Anne Hemshorn
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Mandea, M., Olsen, N. (2009): Geomagnetic and Archeomagnetic Jerks: Where Do We Stand?. - Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 90, 24, 208-208 From geomagnetic jerks
Originally published as: Mandea, M., Olsen, N. (2009): Geomagnetic and Archeomagnetic Jerks: Where Do We Stand?. - Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 90, 24, 208-208 From geomagnetic jerks
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR EUROPEAN MAGNETIC REPEAT STATION SURVEYS
 RECOMMENDATIONS FOR EUROPEAN MAGNETIC REPEAT STATION SURVEYS Andrzej Sas Uhrynowski, Monika Korte, Jean Jacques Schott and Gerhard Schwarz, Coordination Committee for common European repeat station surveys.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR EUROPEAN MAGNETIC REPEAT STATION SURVEYS Andrzej Sas Uhrynowski, Monika Korte, Jean Jacques Schott and Gerhard Schwarz, Coordination Committee for common European repeat station surveys.
THE RELIABILITY OF EARTH S MAGNETIC POLES IN THE MODERN, HISTORICAL AND ANCIENT MODELS. T.I. Zvereva, S.V. Starchenko
 THE RELIABILITY OF EARTH S MAGNETIC POLES IN THE MODERN, HISTORICAL AND ANCIENT MODELS T.I. Zvereva, S.V. Starchenko Pushkov institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, ionosphere and Radio wave Propagation (IZMIRAN),
THE RELIABILITY OF EARTH S MAGNETIC POLES IN THE MODERN, HISTORICAL AND ANCIENT MODELS T.I. Zvereva, S.V. Starchenko Pushkov institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, ionosphere and Radio wave Propagation (IZMIRAN),
International Geomagnetic Reference Field the eighth generation
 Earth Planets Space, 52, 1119 1124, 2000 International Geomagnetic Reference Field the eighth generation Mioara Mandea 1 and Susan Macmillan 2 1 Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, B.P. 89, 4 Place
Earth Planets Space, 52, 1119 1124, 2000 International Geomagnetic Reference Field the eighth generation Mioara Mandea 1 and Susan Macmillan 2 1 Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, B.P. 89, 4 Place
Core field acceleration pulse as a common cause of the 2003 and 2007 geomagnetic jerks
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042019, 2010 Core field acceleration pulse as a common cause of the 2003 and 2007 geomagnetic jerks A. Chulliat, 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042019, 2010 Core field acceleration pulse as a common cause of the 2003 and 2007 geomagnetic jerks A. Chulliat, 1
Geomagnetic observations on Tristan da Cunha, South Atlantic Ocean
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 52, N. 1, February 2009 Geomagnetic observations on Tristan da Cunha, South Atlantic Ocean Jürgen Matzka ( 1 ), Nils Olsen ( 2 ), Cathrine Fox Maule ( 1 ), Lars William Pedersen
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 52, N. 1, February 2009 Geomagnetic observations on Tristan da Cunha, South Atlantic Ocean Jürgen Matzka ( 1 ), Nils Olsen ( 2 ), Cathrine Fox Maule ( 1 ), Lars William Pedersen
KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY King Edward d Point Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin May 2018 18/05/KE King Edward Point (UK) Maps British Antarctic Survey KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1.
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY King Edward d Point Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin May 2018 18/05/KE King Edward Point (UK) Maps British Antarctic Survey KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1.
KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY King Edward d Point Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin September 2018 18/09/KE King Edward Point (UK) Maps British Antarctic Survey KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY King Edward d Point Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin September 2018 18/09/KE King Edward Point (UK) Maps British Antarctic Survey KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA
KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY King Edward d Point Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin October 2018 18/10/KE King Edward Point (UK) Maps British Antarctic Survey KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY King Edward d Point Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin October 2018 18/10/KE King Edward Point (UK) Maps British Antarctic Survey KING EDWARD POINT OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Ascension Island Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2017 17/03/AS Crown copyright; Ordnance Survey ASCENSION ISLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Ascension
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Ascension Island Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2017 17/03/AS Crown copyright; Ordnance Survey ASCENSION ISLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Ascension
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Jim Carrigan Observatory Prudhoe Bay Monthly Magnetic Bulletin May 2014 14/05/JC JIM CARRIGAN OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Jim Carrigan observatory is the fourth
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Jim Carrigan Observatory Prudhoe Bay Monthly Magnetic Bulletin May 2014 14/05/JC JIM CARRIGAN OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Jim Carrigan observatory is the fourth
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Fort McMurray Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin February 2016 16/02/FM Fort McMurray FORT McMURRAY OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction The British Geological Survey
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Fort McMurray Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin February 2016 16/02/FM Fort McMurray FORT McMURRAY OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction The British Geological Survey
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Fort McMurray Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2017 17/03/FM Fort McMurray FORT McMURRAY OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction The British Geological Survey (BGS)
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Fort McMurray Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2017 17/03/FM Fort McMurray FORT McMURRAY OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction The British Geological Survey (BGS)
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Hartland Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin June /06/HA
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Hartland Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin June 2016 16/06/HA HARTLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Hartland observatory is one of three geomagnetic observatories
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Hartland Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin June 2016 16/06/HA HARTLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Hartland observatory is one of three geomagnetic observatories
Westward drift in secular variation of the main geomagnetic field inferred from IGRF
 Earth Planets Space, 55, 131 137, 2003 Westward drift in secular variation of the main geomagnetic field inferred from IGRF Zi-Gang Wei and Wen-Yao Xu Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy
Earth Planets Space, 55, 131 137, 2003 Westward drift in secular variation of the main geomagnetic field inferred from IGRF Zi-Gang Wei and Wen-Yao Xu Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin July 2011 11/07/PS Jason Islands West Falkland King George Bay Queen Charlotte Bay Weddell Island Caracass Island Saunders Island
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin July 2011 11/07/PS Jason Islands West Falkland King George Bay Queen Charlotte Bay Weddell Island Caracass Island Saunders Island
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Hartland Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March /03/HA
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Hartland Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2010 10 /03/HA HARTLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Hartland observatory is one of three geomagnetic observatories
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Hartland Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2010 10 /03/HA HARTLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Hartland observatory is one of three geomagnetic observatories
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Ascension Island Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin December 2008 08/12/AS Crown copyright; Ordnance Survey ASCENSION ISLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Ascension
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Ascension Island Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin December 2008 08/12/AS Crown copyright; Ordnance Survey ASCENSION ISLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Ascension
Unusual behaviour of the IGRF during the period
 Earth Planets Space, 52, 1227 1233, 2000 Unusual behaviour of the IGRF during the 1945 1955 period Wen-yao Xu Institute of Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China (Received February
Earth Planets Space, 52, 1227 1233, 2000 Unusual behaviour of the IGRF during the 1945 1955 period Wen-yao Xu Institute of Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China (Received February
Stability analysis of geomagnetic baseline data obtained at Cheongyang observatory in Korea
 https://doi.org/10.5194/gi-6-231-2017 Author(s) 2017. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Stability analysis of geomagnetic baseline data obtained at Cheongyang
https://doi.org/10.5194/gi-6-231-2017 Author(s) 2017. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Stability analysis of geomagnetic baseline data obtained at Cheongyang
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Lerwick Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin September /09/LE
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Lerwick Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin September 2010 10/09/LE LERWICK OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Lerwick observatory is one of three geomagnetic observatories
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Lerwick Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin September 2010 10/09/LE LERWICK OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Lerwick observatory is one of three geomagnetic observatories
Geomagnetic Measurements in Macedonia
 Geomagnetic Measurements in Macedonia T. Delipetrov 1*, J. Rasson 2, M. Delipetrev 1 1 Faculty of Mining and Geology, Goce Delcev 89 2000 Stip, R. Macedonia 2 Institut Royal Meteorologique, Centre de Physique
Geomagnetic Measurements in Macedonia T. Delipetrov 1*, J. Rasson 2, M. Delipetrev 1 1 Faculty of Mining and Geology, Goce Delcev 89 2000 Stip, R. Macedonia 2 Institut Royal Meteorologique, Centre de Physique
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2010
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Eskdalemuir Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2010 10/03/ES Crown copyright; Ordnance Survey ESKDALEMUIR OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Eskdalemuir observatory
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Eskdalemuir Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2010 10/03/ES Crown copyright; Ordnance Survey ESKDALEMUIR OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1. Introduction Eskdalemuir observatory
Correlation Between IGRF2000 Model and Measured Geomagnetic Data on the Territory of the Republic of Macedonia from 2003 and 2004 Measurements
 PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., C-99 (398), 2007 Correlation Between IGRF2000 Model and Measured Geomagnetic Data on the Territory of the Republic of Macedonia from 2003 and 2004 Measurements Sanja
PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., C-99 (398), 2007 Correlation Between IGRF2000 Model and Measured Geomagnetic Data on the Territory of the Republic of Macedonia from 2003 and 2004 Measurements Sanja
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin July 2010 10/07/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So un d
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin July 2010 10/07/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So un d
Magnetic field nomenclature
 Magnetic field nomenclature Declination trend angle between horizontal projection of F and true North Inclination plunge angle between horizontal and F Magnetic equator location on surface where field
Magnetic field nomenclature Declination trend angle between horizontal projection of F and true North Inclination plunge angle between horizontal and F Magnetic equator location on surface where field
Establishment of Abdus Salam Geomagnetic Observatory Sonmiani, Pakistan: Site Selection to INTERMAGNET Certification
 Pakistan Space & Upper Atmosphere Research Commission Establishment of Abdus Salam Geomagnetic Observatory Sonmiani, Pakistan: Site Selection to INTERMAGNET Certification G. Murtaza Space Science Department
Pakistan Space & Upper Atmosphere Research Commission Establishment of Abdus Salam Geomagnetic Observatory Sonmiani, Pakistan: Site Selection to INTERMAGNET Certification G. Murtaza Space Science Department
IGRF-12 GFZ candidates
 IGRF-12 GFZ candidates V. Lesur 1, M. Rother 1, I. Wardinski 1, R. Schachtschneider 1, M. Hamoudi 2, A. Chambodut 3 October 1, 2014 1 Helmholtz Centre Potsdam, GFZ German Research centre for Geosciences,
IGRF-12 GFZ candidates V. Lesur 1, M. Rother 1, I. Wardinski 1, R. Schachtschneider 1, M. Hamoudi 2, A. Chambodut 3 October 1, 2014 1 Helmholtz Centre Potsdam, GFZ German Research centre for Geosciences,
Monthly Geomagnetic Bulletin
 HARTLAND OBSERVATORY Monthly Geomagnetic Bulletin BRISTOL CHANNEL December 2002 02/12/HA Hartland NERC 2002 1. HARTLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1.1 Introduction This bulletin is published to meet the
HARTLAND OBSERVATORY Monthly Geomagnetic Bulletin BRISTOL CHANNEL December 2002 02/12/HA Hartland NERC 2002 1. HARTLAND OBSERVATORY MAGNETIC DATA 1.1 Introduction This bulletin is published to meet the
Temperature Tests on Modern Magnetometers
 PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., C-99 (398), 2007 Temperature Tests on Modern Magnetometers András CSONTOS, László HEGYMEGI and Balázs HEILIG Eötvös Loránd Geophysical Institute Budapest, Kolombusz
PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., C-99 (398), 2007 Temperature Tests on Modern Magnetometers András CSONTOS, László HEGYMEGI and Balázs HEILIG Eötvös Loránd Geophysical Institute Budapest, Kolombusz
A COMPARISON BETWEEN COMPUTER DERIVED (FMI METHOD) AND HAND SCALED K INDICES AT PORT AUX FRANCAIS AND PORT ALFRED FRENCH OBSERVATORIES
 A COMPARISON BETWEEN COMPUTER DERIVED (FMI METHOD) AND HAND SCALED K INDICES AT PORT AUX FRANCAIS AND PORT ALFRED FRENCH OBSERVATORIES M. BITTERLY 1, M. MENVIELLE 2,4, J. BITTERLY 1 and A. BERTHELIER 3,4
A COMPARISON BETWEEN COMPUTER DERIVED (FMI METHOD) AND HAND SCALED K INDICES AT PORT AUX FRANCAIS AND PORT ALFRED FRENCH OBSERVATORIES M. BITTERLY 1, M. MENVIELLE 2,4, J. BITTERLY 1 and A. BERTHELIER 3,4
Global Models of the Magnetic Field in Historical Times: Augmenting Declination Observations with Archeo- and Paleo- Magnetic Data D.
 J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 38, 715-720, 1986 Global Models of the Magnetic Field in Historical Times: Augmenting Declination Observations with Archeo- and Paleo- Magnetic Data D. GUBBINS Bullard Laboratories,
J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 38, 715-720, 1986 Global Models of the Magnetic Field in Historical Times: Augmenting Declination Observations with Archeo- and Paleo- Magnetic Data D. GUBBINS Bullard Laboratories,
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
REPORT ON THE MEASUREMENT SESSION DURING THE XIVth IAGA WORKSHOP AT CHANGCHUN MAGNETIC OBSERVATORY
 REPORT ON THE MEASUREMENT SESSION DURING THE XIVth IAGA WORKSHOP AT CHANGCHUN MAGNETIC OBSERVATORY Yufei He 1*, Dongmei Yang 1, Benliang Zou 2, Jianjun Wang 3 * 1 Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake
REPORT ON THE MEASUREMENT SESSION DURING THE XIVth IAGA WORKSHOP AT CHANGCHUN MAGNETIC OBSERVATORY Yufei He 1*, Dongmei Yang 1, Benliang Zou 2, Jianjun Wang 3 * 1 Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake
Korte, M., Mandea, M. (2008): Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia. - Earth Planets and Space, 60, 9,
 Originally published as: Korte, M., Mandea, M. (28): Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia. - Earth Planets and Space, 6, 9, 937-948 http://www.terrapub.co.jp/journals/eps/pdf/28/69/69937.pdf
Originally published as: Korte, M., Mandea, M. (28): Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia. - Earth Planets and Space, 6, 9, 937-948 http://www.terrapub.co.jp/journals/eps/pdf/28/69/69937.pdf
Time scheduling of magnetic surveys in mid-latitudes with respect to forecasting geomagnetic activity
 Earth Planets Space, 58, 735 74, 26 Time scheduling of magnetic surveys in mid-latitudes with respect to forecasting geomagnetic activity Pavel Hejda, Josef Bochníček, Josef Horáček, and Jaroslava Nejedlá
Earth Planets Space, 58, 735 74, 26 Time scheduling of magnetic surveys in mid-latitudes with respect to forecasting geomagnetic activity Pavel Hejda, Josef Bochníček, Josef Horáček, and Jaroslava Nejedlá
GE SPACE. Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce
 GE SPACE Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce Fit to NERC s Science Priorities Understanding the complex interactions and feedbacks within the Earth system over a range of space and time scales Fit
GE SPACE Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce Fit to NERC s Science Priorities Understanding the complex interactions and feedbacks within the Earth system over a range of space and time scales Fit
Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia
 Earth Planets Space, 6, 937 948, 28 Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia M. Korte and M. Mandea GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, elegrafenberg, 14473 Potsdam, Germany
Earth Planets Space, 6, 937 948, 28 Magnetic poles and dipole tilt variation over the past decades to millennia M. Korte and M. Mandea GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, elegrafenberg, 14473 Potsdam, Germany
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin July 2009 09/07/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So un d
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin July 2009 09/07/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So un d
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin May 2009 09/05/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So un d
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin May 2009 09/05/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So un d
 Name Period Parent Signature Geography/Map Skills Study Guide *For extra practice with these skills, check out Mr. Kath s website: http://rkath.weebly.com/activities--links.html Continents and Oceans of
Name Period Parent Signature Geography/Map Skills Study Guide *For extra practice with these skills, check out Mr. Kath s website: http://rkath.weebly.com/activities--links.html Continents and Oceans of
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin April 2009 09/04/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So un
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin April 2009 09/04/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So un
Annual Report of New Zealand Magnetic Observatories, 2007
 Annual Report of New Zealand Magnetic Observatories, 2007 INTRODUCTION There were no significant changes to the equipment used in the magnetic observatories in 2007. The new fluxgate at Scott Base continued
Annual Report of New Zealand Magnetic Observatories, 2007 INTRODUCTION There were no significant changes to the equipment used in the magnetic observatories in 2007. The new fluxgate at Scott Base continued
The International Geomagnetic Reference Field. Introduction. Scope of the IGRF. Applications and Availability. Inception and development
 The International Geomagnetic Reference Field Susan Macmillan 1 and Christopher Finlay 2 1 British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh, EH9 3LA, UK 2 Institut für Geophysik,
The International Geomagnetic Reference Field Susan Macmillan 1 and Christopher Finlay 2 1 British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh, EH9 3LA, UK 2 Institut für Geophysik,
Measurement Session During the XII IAGA Workshop at Belsk
 PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., C-99 (398), 2007 Measurement Session During the XII IAGA Workshop at Belsk Jan REDA and Mariusz NESKA Institute of Geophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Księcia
PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., C-99 (398), 2007 Measurement Session During the XII IAGA Workshop at Belsk Jan REDA and Mariusz NESKA Institute of Geophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Księcia
EXTREMELY QUIET 2009 STATE OF GEOMAGNETIC FIELD AS A REFERENCE LEVEL FOR AMPLITUDE OF THE LOCAL GEOMAGNETIC DISTURBANCES
 EXTREMELY QUIET 2009 STATE OF GEOMAGNETIC FIELD AS A REFERENCE LEVEL FOR AMPLITUDE OF THE LOCAL GEOMAGNETIC DISTURBANCES A.E. Levitin, L.I. Gromova, S.V. Gromov, L.A. Dremukhina Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial
EXTREMELY QUIET 2009 STATE OF GEOMAGNETIC FIELD AS A REFERENCE LEVEL FOR AMPLITUDE OF THE LOCAL GEOMAGNETIC DISTURBANCES A.E. Levitin, L.I. Gromova, S.V. Gromov, L.A. Dremukhina Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin
 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin December 2007 07/12/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So
BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Port Stanley Observatory Monthly Magnetic Bulletin December 2007 07/12/PS Jason Islands a ar C West Falkland Kin gg eor ge B Port Salavador ay Weddell Island Mount Osborne So
The World of Geography Pre-Test/Study Guide Chapter 1 Test
 Read each statement or question. On the lines below write the letter of the best answer. 1. Geographers look at the Earth 5. What are the two specific A. by studying cities first. measurements of Earth
Read each statement or question. On the lines below write the letter of the best answer. 1. Geographers look at the Earth 5. What are the two specific A. by studying cities first. measurements of Earth
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity
 Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity I. Geomagnetism The earth's magnetic field can be viewed as a simple bar magnet located near the center of
Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity I. Geomagnetism The earth's magnetic field can be viewed as a simple bar magnet located near the center of
Cardinal and Intermediate Directions:
 Name Period Parent Signature Due Date: (TBA) Geography/Map Skills Study Guide Continents and Oceans of the World: Label the continents (7) and oceans (4) on the lines below the map. 1 11 3 5 4 8 2 9 10
Name Period Parent Signature Due Date: (TBA) Geography/Map Skills Study Guide Continents and Oceans of the World: Label the continents (7) and oceans (4) on the lines below the map. 1 11 3 5 4 8 2 9 10
Theodolite-borne Vector Overhauser Magnetometer: DIMOVER
 heodolite-borne Vector Overhauser Magnetometer: DIMOVER Sapunov V *, Denisov A, Saveliev D, Kiselev S, Denisova O, Podmogov Y Khomutov S 3, Rasson J 4 Quantum Magnetometry Laboratory of USU, Mira str.,
heodolite-borne Vector Overhauser Magnetometer: DIMOVER Sapunov V *, Denisov A, Saveliev D, Kiselev S, Denisova O, Podmogov Y Khomutov S 3, Rasson J 4 Quantum Magnetometry Laboratory of USU, Mira str.,
Chapter 2 Variability and Long-Term Changes in Surface Air Temperatures Over the Indian Subcontinent
 Chapter 2 Variability and Long-Term Changes in Surface Air Temperatures Over the Indian Subcontinent A.K. Srivastava, D.R. Kothawale and M.N. Rajeevan 1 Introduction Surface air temperature is one of the
Chapter 2 Variability and Long-Term Changes in Surface Air Temperatures Over the Indian Subcontinent A.K. Srivastava, D.R. Kothawale and M.N. Rajeevan 1 Introduction Surface air temperature is one of the
V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity
 Earthq Sci (2010)23: 343 348 343 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0731-9 V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity Dongmei Yang 1, Yufei He 1 Chuanhua Chen 2 and Jiadong Qian 3 1
Earthq Sci (2010)23: 343 348 343 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0731-9 V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity Dongmei Yang 1, Yufei He 1 Chuanhua Chen 2 and Jiadong Qian 3 1
Map Skills Unit. Note taking unit
 Map Skills Unit Note taking unit Introduction To learn about the Earth, we are going to learn about two geographic tools you can use.globes and maps. Globe A globe is a round model of the planet Earth
Map Skills Unit Note taking unit Introduction To learn about the Earth, we are going to learn about two geographic tools you can use.globes and maps. Globe A globe is a round model of the planet Earth
With a group, get a bar magnet, some plastic wrap, iron filings and a compass.
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 8: The Earth's Magnetic Field Chapter 2, p. 39-41: The Seafloor as a Magnetic Tape Recorder Chapter 7, p. 213: Paleomagnetic Stratigraphy Chapter 14, p. 396-406: Earth s Magnetic Field
Name: EPS 50 Lab 8: The Earth's Magnetic Field Chapter 2, p. 39-41: The Seafloor as a Magnetic Tape Recorder Chapter 7, p. 213: Paleomagnetic Stratigraphy Chapter 14, p. 396-406: Earth s Magnetic Field
The geomagnetic indices: derivation, meaning, and availability
 The geomegnetic indices: derivation, meaning and availability The geomagnetic indices: derivation, meaning, and availability Michel MENVIELLE C.E.T.P., 4, Avenue de Neptune, F-94107 SAINT MAUR DES FOSSES,
The geomegnetic indices: derivation, meaning and availability The geomagnetic indices: derivation, meaning, and availability Michel MENVIELLE C.E.T.P., 4, Avenue de Neptune, F-94107 SAINT MAUR DES FOSSES,
(ii) Observational Geomagnetism. Lecture 5: Spherical harmonic field models
 (ii) Observational Geomagnetism Lecture 5: Spherical harmonic field models Lecture 5: Spherical harmonic field models 5.1 Introduction 5.2 How to represent functions on a spherical surface 5.3 Spherical
(ii) Observational Geomagnetism Lecture 5: Spherical harmonic field models Lecture 5: Spherical harmonic field models 5.1 Introduction 5.2 How to represent functions on a spherical surface 5.3 Spherical
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
What ancient scalar satellite data can tell us about the 1969 geomagnetic jerk?
 Earth Planets Space, 61, 885 894, 2009 What ancient scalar satellite data can tell us about the 1969 geomagnetic jerk? Y. Yahiat 1,M.Hamoudi 1, and M. Mandea 2 1 University of Sciences and Technology Houari
Earth Planets Space, 61, 885 894, 2009 What ancient scalar satellite data can tell us about the 1969 geomagnetic jerk? Y. Yahiat 1,M.Hamoudi 1, and M. Mandea 2 1 University of Sciences and Technology Houari
El Niño / Southern Oscillation
 El Niño / Southern Oscillation Student Packet 2 Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents Introduction on
El Niño / Southern Oscillation Student Packet 2 Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents Introduction on
Direction: the reference system
 Adapted from Liebenberg and Vlok 2000, The interpretation of maps, aerial photographs and satellite images. Direction: the reference system Direction provides us with one way of answering "Where?" questions.
Adapted from Liebenberg and Vlok 2000, The interpretation of maps, aerial photographs and satellite images. Direction: the reference system Direction provides us with one way of answering "Where?" questions.
Astro Tourism OPPORTUNITIES FOR ASTRO TOURISM IN THE NORTHERN AND WESTERN CAPE
 Astro Tourism OPPORTUNITIES FOR ASTRO TOURISM IN THE NORTHERN AND WESTERN CAPE NSTF DISCUSSION FORUM SCIENCE TOURISM PRESENTER: Lorenzo Raynard South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO) National facility
Astro Tourism OPPORTUNITIES FOR ASTRO TOURISM IN THE NORTHERN AND WESTERN CAPE NSTF DISCUSSION FORUM SCIENCE TOURISM PRESENTER: Lorenzo Raynard South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO) National facility
... Europe. Based on Bloom s Taxonomy. Environment Interactions Movement. Human & Location. Regions. Place
 ... Europe Location Place Human & Environment Interactions Movement Regions LEVEL 1 Knowledge Match Show or Label List Information Recall Details (5Ws + H) Find Information LEVEL 2 Comprehension Describe
... Europe Location Place Human & Environment Interactions Movement Regions LEVEL 1 Knowledge Match Show or Label List Information Recall Details (5Ws + H) Find Information LEVEL 2 Comprehension Describe
NATIONAL ANTARCTIC RESEARCH PROGRAM. Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica Geomagnetic Observatory
 NATIONAL ANTARCTIC RESEARCH PROGRAM Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica Geomagnetic Observatory Magnetic Observation Results 2009-2010 L. Cafarella, S. Lepidi, A. Meloni, P. Palangio, M. Pietrolungo L. Santarelli
NATIONAL ANTARCTIC RESEARCH PROGRAM Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica Geomagnetic Observatory Magnetic Observation Results 2009-2010 L. Cafarella, S. Lepidi, A. Meloni, P. Palangio, M. Pietrolungo L. Santarelli
T E M P U S P R O J E C T
 T E M P U S P R O J E C T GEOMAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS AND QUALITY STANDARDS No. IB_JEP 17072 2002 GEOMAGNETIC AND ELECTROMAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS AND QUALITY STANDARDS Todor Delipetrov Jean Rasson Gerald Duma
T E M P U S P R O J E C T GEOMAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS AND QUALITY STANDARDS No. IB_JEP 17072 2002 GEOMAGNETIC AND ELECTROMAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS AND QUALITY STANDARDS Todor Delipetrov Jean Rasson Gerald Duma
_ falian GEOMAGNETISM REPORT
 blications compactus w u t; n :0 o c r ir. iifc _ falian GEOMAGNETISM REPORT MAGNETIC OBSERVATORIES VOLUME 40 No.6 JUNE 1992 BUREAU OF MINERAL RESOURCES, GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS DEPARTMENT OF PRIMARY INDUSTRIES
blications compactus w u t; n :0 o c r ir. iifc _ falian GEOMAGNETISM REPORT MAGNETIC OBSERVATORIES VOLUME 40 No.6 JUNE 1992 BUREAU OF MINERAL RESOURCES, GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS DEPARTMENT OF PRIMARY INDUSTRIES
Heart of Africa Inkaba yeafrica Ludwig Combrinck, Monika Korte, Mioara Mandea, Pieter Kotzé, Marco Andreoli
 Heart of Africa Inkaba yeafrica Ludwig Combrinck, Monika Korte, Mioara Mandea, Pieter Kotzé, Marco Andreoli 5 th IyA Workshop 22-23 Oct 2007 Wild Coast Sun, KwaZulu-Natal Achievements and progress during
Heart of Africa Inkaba yeafrica Ludwig Combrinck, Monika Korte, Mioara Mandea, Pieter Kotzé, Marco Andreoli 5 th IyA Workshop 22-23 Oct 2007 Wild Coast Sun, KwaZulu-Natal Achievements and progress during
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for January 2018 1.1 The prevailing Northeast monsoon conditions over Southeast Asia strengthened in January
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for January 2018 1.1 The prevailing Northeast monsoon conditions over Southeast Asia strengthened in January
NATIONAL ANTARCTIC RESEARCH PROGRAM. Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica Geomagnetic Observatory
 NATIONAL ANTARCTIC RESEARCH PROGRAM Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica Geomagnetic Observatory Magnetic Observation Results 2007-2008 L. Cafarella, S. Lepidi, A. Meloni, P. Palangio, M. Pietrolungo and L. Santarelli
NATIONAL ANTARCTIC RESEARCH PROGRAM Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica Geomagnetic Observatory Magnetic Observation Results 2007-2008 L. Cafarella, S. Lepidi, A. Meloni, P. Palangio, M. Pietrolungo and L. Santarelli
The geomagnetic dipole moment over the last 7000 years new results from a global model
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 236 (25) 348 358 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl The geomagnetic dipole moment over the last 7 years new results from a global model M. Korte a, *, C.G. Constable b a GeoForschungsZentrum
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 236 (25) 348 358 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl The geomagnetic dipole moment over the last 7 years new results from a global model M. Korte a, *, C.G. Constable b a GeoForschungsZentrum
The seasonality of transportation in the Southern African subregion is considered. By
 CHAPTER 3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION This Chapter discusses the findings of the research. A seasonal air transport climatology for southern Africa is presented. The months of February, April, July and October
CHAPTER 3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION This Chapter discusses the findings of the research. A seasonal air transport climatology for southern Africa is presented. The months of February, April, July and October
THE EVOLUTION OF THE GEOMAGNETIC FIELD ON THE ROMANIAN TERRITORY. MEASUREMENTS IN THE SECULAR VARIATION NATIONAL NETWORK BETWEEN 2010 AND 2014
 THE EVOLUTION OF THE GEOMAGNETIC FIELD ON THE ROMANIAN TERRITORY. MEASUREMENTS IN THE SECULAR VARIATION NATIONAL NETWORK BETWEEN 2010 AND 2014 RĂZVAN GRECULEASA 1, VENERA DOBRICĂ 1, ANCA ISAC 2 1 Sabba
THE EVOLUTION OF THE GEOMAGNETIC FIELD ON THE ROMANIAN TERRITORY. MEASUREMENTS IN THE SECULAR VARIATION NATIONAL NETWORK BETWEEN 2010 AND 2014 RĂZVAN GRECULEASA 1, VENERA DOBRICĂ 1, ANCA ISAC 2 1 Sabba
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.97/6/IP. 33
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.97/6/IP. 33 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Seventeenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 18-22 September 2006 Item 7 of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.97/6/IP. 33 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Seventeenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 18-22 September 2006 Item 7 of the provisional
Saunderson E, 1 and Gouws D 2 South African National Space Agency, Hermanus, Western Cape, 7200, South Africa
 SpaceOps Conferences 28 May - 1 June 2018, 2018, Marseille, France 2018 SpaceOps Conference 10.2514/6.2018-2374 Evaluation of the effect of ambient temperature variation on the calibration of a Large Helmholtz
SpaceOps Conferences 28 May - 1 June 2018, 2018, Marseille, France 2018 SpaceOps Conference 10.2514/6.2018-2374 Evaluation of the effect of ambient temperature variation on the calibration of a Large Helmholtz
Italian Magnetic Network and magnetic reference fields at
 MagNetE workshop 2011 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, 55, 6, 2012; doi: 10.4401/ag-5411 Italian Magnetic Network and magnetic reference fields at 2010.0 Guido Dominici *, Antonio Meloni, Angelo Di Ponzio, Massimo
MagNetE workshop 2011 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, 55, 6, 2012; doi: 10.4401/ag-5411 Italian Magnetic Network and magnetic reference fields at 2010.0 Guido Dominici *, Antonio Meloni, Angelo Di Ponzio, Massimo
SIO 229 Part II Geomagnetism. Lecture 1 Introduction to the geomagnetic field
 SIO 229 Part II Geomagnetism Lecture 1 Introduction to the geomagnetic field Why study Earth's magnetic field Schematic picture of Earth's magnetic field interacting with the solar wind (credit: NASA)
SIO 229 Part II Geomagnetism Lecture 1 Introduction to the geomagnetic field Why study Earth's magnetic field Schematic picture of Earth's magnetic field interacting with the solar wind (credit: NASA)
EQUATORIAL ELECTROJET STRENGTH IN THE AFRICAN SECTOR DURING HIGH AND LOW SOLAR ACTIVITY YEARS
 SINET: ETHIOP. J. SCI., 26(1):77 81, 2003 Faculty of Science, Addis Ababa University, 2003 ISSN: 0379 2897 Short communication EQUATORIAL ELECTROJET STRENGTH IN THE AFRICAN SECTOR DURING HIGH AND LOW SOLAR
SINET: ETHIOP. J. SCI., 26(1):77 81, 2003 Faculty of Science, Addis Ababa University, 2003 ISSN: 0379 2897 Short communication EQUATORIAL ELECTROJET STRENGTH IN THE AFRICAN SECTOR DURING HIGH AND LOW SOLAR
First scalar magnetic anomaly map from CHAMP satellite data indicates weak lithospheric field
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 29, NO. 14, 10.1029/2001GL013685, 2002 First scalar magnetic anomaly map from CHAMP satellite data indicates weak lithospheric field S. Maus, M. Rother, R. Holme, H.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 29, NO. 14, 10.1029/2001GL013685, 2002 First scalar magnetic anomaly map from CHAMP satellite data indicates weak lithospheric field S. Maus, M. Rother, R. Holme, H.
Understanding Projections
 GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create
A comparative study of the bottomside profile parameters over Wuhan with IRI-2001 for
 Earth Planets Space, 58, 601 605, 2006 A comparative study of the bottomside profile parameters over Wuhan with IRI-2001 for 1999 2004 Huajiao Chen 1,2,3, Libo Liu 1, Weixing Wan 1, Baiqi Ning 1, and Jiuhou
Earth Planets Space, 58, 601 605, 2006 A comparative study of the bottomside profile parameters over Wuhan with IRI-2001 for 1999 2004 Huajiao Chen 1,2,3, Libo Liu 1, Weixing Wan 1, Baiqi Ning 1, and Jiuhou
StudyofEquatorialElectrojetusingChainofStationsalongtheDipEquator
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: A Physics and Space Science Volume 17 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2017 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: A Physics and Space Science Volume 17 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2017 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Positioning System (GPS)
 Global Positioning System (GPS) MIEET 1º ano Peter Stallinga UAlg 2011 IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 1/36 Why knowing position? Knowing your position is needed for when you want to go somewhere
Global Positioning System (GPS) MIEET 1º ano Peter Stallinga UAlg 2011 IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 1/36 Why knowing position? Knowing your position is needed for when you want to go somewhere
Magnetic measurements, apparatus and metrology
 Geoinformation Issues Magnetic measurements, apparatus and metrology Elzbieta Welker Institute of Geodesy and Cartography, 27 Modzelewskiego St., 02-679, Warsaw, Poland Tel.: +48 22 3291913, Fax: +48 22
Geoinformation Issues Magnetic measurements, apparatus and metrology Elzbieta Welker Institute of Geodesy and Cartography, 27 Modzelewskiego St., 02-679, Warsaw, Poland Tel.: +48 22 3291913, Fax: +48 22
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Name three countries in Europe.
 Name three countries in Europe. I will be able to identify the 5 themes of geography for Europe and locate the countries and capitals of Europe and the major physical features. People: Past: Through the
Name three countries in Europe. I will be able to identify the 5 themes of geography for Europe and locate the countries and capitals of Europe and the major physical features. People: Past: Through the
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
Credibility of climate predictions revisited
 European Geosciences Union General Assembly 29 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 29 Session CL54/NP4.5 Climate time series analysis: Novel tools and their application Credibility of climate predictions revisited
European Geosciences Union General Assembly 29 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 29 Session CL54/NP4.5 Climate time series analysis: Novel tools and their application Credibility of climate predictions revisited
Map Skills Lesson 1. Materials: maps, pencils, Lesson 1 Worksheet, strips of paper, grid paper
 Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
Ionospheric Scintillation Impact Report: South African SKA Site
 NW RA NorthWest Research Associates, Inc. University of Arizona Science and Technology Park : South African SKA Site Prepared for the University of Manchester, Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics NWRA
NW RA NorthWest Research Associates, Inc. University of Arizona Science and Technology Park : South African SKA Site Prepared for the University of Manchester, Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics NWRA
Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills
 Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills Standard(s) of Learning: WHI.1 The student will improve skills in historical research and geographical analysis by a) Identifying, analyzing, and interpreting
Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills Standard(s) of Learning: WHI.1 The student will improve skills in historical research and geographical analysis by a) Identifying, analyzing, and interpreting
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
ENVI.2030L - Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity
 I. Geomagnetism Name ENVI.2030L - Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity The earth's magnetic field can be viewed as a simple bar magnet located near the center of the earth and inclined
I. Geomagnetism Name ENVI.2030L - Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity The earth's magnetic field can be viewed as a simple bar magnet located near the center of the earth and inclined
SHORT COMMUNICATION EXPLORING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE NORTH ATLANTIC OSCILLATION AND RAINFALL PATTERNS IN BARBADOS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 6: 89 87 (6) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:./joc. SHORT COMMUNICATION EXPLORING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 6: 89 87 (6) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:./joc. SHORT COMMUNICATION EXPLORING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
An Assessment of the BGS δdδi Vector Magnetometer
 PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., C-99 (398), 007 An Assessment of the BGS δdδi Vector Magnetometer Santiago MARSAL, J. Miquel TORTA and John C. RIDDICK Observatori de l Ebre, CSIC Universitat Ramon
PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., C-99 (398), 007 An Assessment of the BGS δdδi Vector Magnetometer Santiago MARSAL, J. Miquel TORTA and John C. RIDDICK Observatori de l Ebre, CSIC Universitat Ramon
Latitude and Longitude
 Latitude and Longitude Finding Your Location on a Sphere Coordinate Systems n When you are locating a point on a flat surface you can use Cartesian coordinates of x and y. n The point 2, 3 is plotted on
Latitude and Longitude Finding Your Location on a Sphere Coordinate Systems n When you are locating a point on a flat surface you can use Cartesian coordinates of x and y. n The point 2, 3 is plotted on
Gan Magnetic Observatory. Maldive Islands South Indian Ocean Annual Report
 Gan Magnetic Observatory Maldive Islands South Indian Ocean 2016 Annual Report 1 Institut für Geophysik, Zürich Gan Magnetic Observatory Maldive Islands South Indian Ocean 2016 Annual Report Report Editor
Gan Magnetic Observatory Maldive Islands South Indian Ocean 2016 Annual Report 1 Institut für Geophysik, Zürich Gan Magnetic Observatory Maldive Islands South Indian Ocean 2016 Annual Report Report Editor
A Preliminary Climatology of Extratropical Transitions in the Southwest Indian Ocean
 A Preliminary Climatology of Extratropical Transitions in the Southwest Indian Ocean Kyle S. Griffin Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences, University at Albany, State University of New
A Preliminary Climatology of Extratropical Transitions in the Southwest Indian Ocean Kyle S. Griffin Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences, University at Albany, State University of New
