Global Positioning System (GPS)
|
|
|
- Jordan Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Positioning System (GPS) MIEET 1º ano Peter Stallinga UAlg 2011 IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 1/36
2 Why knowing position? Knowing your position is needed for when you want to go somewhere (and don't get lost) This is a seemingly simple problem that is (surprisingly) difficult! IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 2/36
3 Global coordinates Position consists of: - Longitude (East-West) 0o is Greenwich (London) - Latitude (North-South) 0o is equator, 90o is N/S pole Example: Faro (airport) N W IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 3/36
4 Latitude - Latitude (North-South) can be determined by height (inclination, θ) of sun in sky (at its highest point!) θ Northern hemisphere (ex. Portugal): left to right Southern hemisphere (ex. Australia): right to left IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 4/36
5 Latitude - Latitude (North-South) can be determined by height (inclination, θ) of sun in sky (at its highest point!) When sun is aligned with horizon, on the scale we can read the inclination IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 5/36
6 Latitude - Latitude (North-South) can be determined by height (inclination, θ) of sun in sky (at its highest point! at midday) θ sun hor izo n Simple idea: Latitude = 90o θ? More complicated than that! IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 6/36
7 Latitude; Earth rotation axis Earth rotation 23.5o Plane of Earth orbit around Sun IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 7/36
8 Latitude The sun's inclination depends not only on time of day, but also on the day of the year. IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 8/36
9 Latitude - Latitude (North-South) Very complicated indeed. Sun at highest point not South Sun not always at same time of day at highest point IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 9/36
10 Latitude Position of sun at 12:00 along the year (Analemma) IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 10/36
11 Latitude The sun is not even the same size along the year. Position of sun at the year Very difficult/unreliable object to 12:00 use inalong positioning (and navigation) IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 11/36
12 Latitude - Latitude (North-South) Better use distant stars. They don't suffer from seasonal effects. They still change during a day (trajectory). Except one! IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 12/36
13 Latitude - Latitude (North-South) Better use distant stars. They don't suffer from seasonal effects. They still change during a day (trajectory). Except one! The Polar Star Long-time exposure at night IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 13/36
14 Latitude: Polar Star * Polar Star The Polar Star lies on the axis of the rotation of the Earth. All day and all year at the same position in the sky. Always at geographic North Inclination equal to latitude IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 14/36
15 Latitude: Polar Star * * θ zenith The Polar Star lies on the axis of the rotation of the Earth. All day and all year at the same position in the sky. Always at geographic North Inclination equal to latitude IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 15/36
16 Latitude: Polar Star 5x Ursa Major IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 16/36
17 Latitude: Polar Star Not even Pole Star position is fixed! Precession of Earth IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 17/36
18 Latitude: Polar Star So far we have just found only the latitude. The easiest part! IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 18/36
19 Longitude Longitude? Time! In Greenwich, the sun is at its highest point at exactly 12:00 West: 1 hour later for every 15o (360o/24 h) East: 1 hour earlier for every 15o If we know the time (GMT) when the sun is at its highest, we know the longitude! The need for precise clocks! IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 19/36
20 Longitude: Pendulum clock Period (T=1/f) of a pendulum: l Period is independent of amplitude of swing if the curve is a cycloid (Christiaan Huijgens, 17th century) IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 20/36
21 Comments With a magnetic compass we cannot measure position, only direction With a mechanical compass we can plot distance on a map (distance is speed x time) Speed was measured with a rope with knots measure how many equally spaced knots (47 feet, 3 inch) are dragged into the water in 30 seconds 1 knot is equivalent to one nautical mile per hour km/h IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 21/36
22 GPS v. 1.0 So far we are still in the preindustrial era, but we know more-or less our position on this globe. and on the Southern Hemisphere? (no North Pole Star!) and what if it is cloudy?!!! GPS. IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 22/36
23 Angle If we know the (distance) or angle to fixed objects on the globe we can also know our position. Triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by measuring angles to it from known points at either end of a fixed baseline. This is based on trigonometry (know three things of a triangle and you know everything of the triangle). For example: l, α, β. We know the distance to the ship. IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 23/36
24 Angle Note that we know where the ship is, but the ships passengers do not know where they are themselves: Lack of information!? IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 24/36
25 Distance If we know the distance (or angle) to fixed objects on the globe we can also know our position. Example: How is the epicenter of an earthquake measured? IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 25/36
26 Distance; Earthquake Knowing that seismic waves travel at 5 km/s, knowing the time of arrival of the waves tells us the distance. Madrid: 40 s later = 200 km Faro: 80 s later = 400 km Two solutions: Apart from that: We need at least 3 (!) stations to determine the epicenter. We don't know when the earthquake happened IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 26/36
27 Distance; Earthquake Knowing that seismic waves travel at 5 km/s, knowing the time of arrival of the waves tells us the distance. We need at least 3 stations to determine the epicenter. Then we also know when the earthquake happened IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 27/36
28 Distance; Earthquake In practice difference between arrival of S-waves and P-waves is used (S-waves are transverse, P-waves are longitudinal [like sound waves]) P-waves: 5 km/s S-waves: 3 km/s The difference in arrival of P-waves and S-waves tells us directly the distance IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 28/36
29 Distance; Earthquake We can also determine the magnitude on the Richter scale Example: At 600 km, a 5.4 Richter-scale earthquake gives 2 mm amplitude of ground movement A = (1 μm) x 10M x (100 km/d) Logarithmic scale: A scale-4 earthquake is 10 times stronger than a scale-3 earthquake Power-Law scale: 10 times further away, times weaker IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 29/36
30 Own Position; inverted problem Determining our own position is the inverted problem: Instead of the epicenter firing in all directions and the different location detecting at different times All locations firing a signal at same time and I (at epicenter) will receive them at different times IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 30/36
31 Own Position; inverted problem Positions of stations should be very well known All stations should signal at exactly the same time The arrival time of the signals then tells me the distance to each of the stations and (by trilateration) I can find my own position IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 31/36
32 GPS GPS works with (24) satellites in orbit around the Earth, which allows for determining longitude, latitude and height Electromagnetic waves traveling with speed of light, c = 3x108 m/s We want position within, say, 10 m. Timing should be accurate within (10 m)/(3x108 m/s) = 33 ns. IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 32/36
33 GPS, satellites with atomic clocks GPS works with satellites in orbit around the EarthGPS works with (24) satellites in orbit around the Earth, which allows for determining longitude, latitude and height Electromagnetic waves traveling with speed of light, c = 3x108 m/s We want position within, say, 10 m. Timing should be accurate within (10 m)/(3x108 m/s) = 33 ns. Atomic clocks on all satellites. (No atomic clock needed on GPS receiver!), calibrated constantly by a ground station Relativistic (Einstein) effects important. (In fact, GPS is the result of a scientific study on relativistic effects) 4 satellites are enough, but with more (there are 24 today) we get better accuracy IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 33/36
34 Satellites in space. Where is Greenpeace?!! Geostationary (communication) satellites All satellites in Earth space IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 34/36
35 One way In GPS, only the satellites send signals. The receiver not. You do not reveal your location to anybody! The position of mobile phones can also be determined by looking at the time delays to/from the cellular towers and the signal strength. They know where you are! IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 35/36
36 One way In GPS, only the satellites send signals. The receiver not. You do not reveal your location to anybody! The position of mobile phones can also be determined by looking at the time delays to/from the cellular towers and the signal strength. They know where you are! Whatever you do, don't bring your mobile phone!! IALP 2011, GPS, UALg, Peter Stallinga 36/36
CHAPTER 2 SKILL SHEET 2: CELESTIAL NAVIGATION
 CHAPTER 2 SKILL SHEET 2: CELESTIAL NAVIGATION Before the invention of GPS technology, how were people on ships far at sea, out of the sight of land, able to tell where they were? For thousands of years
CHAPTER 2 SKILL SHEET 2: CELESTIAL NAVIGATION Before the invention of GPS technology, how were people on ships far at sea, out of the sight of land, able to tell where they were? For thousands of years
Why does Earth rotate and what s the evidence? (besides watching it from space ships or satellites) Week 18 January 5, 2015
 Why does Earth rotate and what s the evidence? (besides watching it from space ships or satellites) Week 18 January 5, 2015 The sun determines our solar time everywhere on earth as Earth rotates. Can you
Why does Earth rotate and what s the evidence? (besides watching it from space ships or satellites) Week 18 January 5, 2015 The sun determines our solar time everywhere on earth as Earth rotates. Can you
HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST
 HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST Using a globe to learn how a position on Earth can be described. Rui Dilão, Instituto Superior Técnico Curriculum topic latitude, longitude, coordinate system
HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST Using a globe to learn how a position on Earth can be described. Rui Dilão, Instituto Superior Técnico Curriculum topic latitude, longitude, coordinate system
A Sky Full of Stars - II.
 A Sky Full of Stars - II. Learning Objectives! What is the latitude of the Equator and of the Earth s North and South Poles? What is the declination of the Celestial Equator and of the Celestial Poles?!
A Sky Full of Stars - II. Learning Objectives! What is the latitude of the Equator and of the Earth s North and South Poles? What is the declination of the Celestial Equator and of the Celestial Poles?!
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation. How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?
 Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Cartesian Coordinates Need two dimensional system 2 number lines perpendicular to each other X-axis is horizontal Y-axis is vertical Position relative
 General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
LATITUDES AND LONGITUDES
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE LATITUDES AND LONGITUDES KCSE 1989 2012 Form 4 Mathematics Answer all the questions 1. 1989 Q18 P1 A globe representing the earth has a radius 0.5m. Points A(10 0 W), B (0
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE LATITUDES AND LONGITUDES KCSE 1989 2012 Form 4 Mathematics Answer all the questions 1. 1989 Q18 P1 A globe representing the earth has a radius 0.5m. Points A(10 0 W), B (0
Chapter S1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3
 Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Review of Monday s Class Spherical Trigonometry Review plane trigonometry Concepts in Spherical Trigonometry Distance measures Azimuths and bearings Basic formulas:
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Review of Monday s Class Spherical Trigonometry Review plane trigonometry Concepts in Spherical Trigonometry Distance measures Azimuths and bearings Basic formulas:
Astronomy is the oldest science! Eclipses. In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Bad Omens? Comets
 Astronomy is the oldest science! In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Eclipses Bad Omens? Comets 1 The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
Astronomy is the oldest science! In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Eclipses Bad Omens? Comets 1 The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
A reproduction of a compass from Photo by: Virginia State Parks staff/wikimedia Photo by: Virginia State Parks staff/ Wikimedia.
 What is a compass? By National Geographic, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.26.17 Word Count 838 Level 810L A reproduction of a compass from 1607. Photo by: Virginia State Parks staff/wikimedia Photo by:
What is a compass? By National Geographic, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.26.17 Word Count 838 Level 810L A reproduction of a compass from 1607. Photo by: Virginia State Parks staff/wikimedia Photo by:
The Earth and its representation
 GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 The Earth and its representation THE SOLAR SYSTEM AND THE EARTH THE SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is a planetary system. Is a group of astronomical objects who surround a star, in this
GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 The Earth and its representation THE SOLAR SYSTEM AND THE EARTH THE SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is a planetary system. Is a group of astronomical objects who surround a star, in this
Geometry of Earth Sun System
 12S56 Geometry of Earth Sun System Figure below shows the basic geometry Northern Hemisphere Winter ω equator Earth s Orbit Ecliptic ω ω SUN equator Northern Hemisphere Spring Northern Hemisphere Fall
12S56 Geometry of Earth Sun System Figure below shows the basic geometry Northern Hemisphere Winter ω equator Earth s Orbit Ecliptic ω ω SUN equator Northern Hemisphere Spring Northern Hemisphere Fall
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY
 CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Seen from the northern latitudes (mid-northern hemisphere), the star Polaris a. is never above the horizon during the day. b. always sets directly
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Seen from the northern latitudes (mid-northern hemisphere), the star Polaris a. is never above the horizon during the day. b. always sets directly
Global Positioning System (G.P.S.)
 Title: Global Positioning System (G.P.S.) (Navigation) Grade(s): 6-8 Introduction: The Global Positioning System (G.P.S.) Is a worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites
Title: Global Positioning System (G.P.S.) (Navigation) Grade(s): 6-8 Introduction: The Global Positioning System (G.P.S.) Is a worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
The Celestial Sphere. From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2 dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere.
 1 The Celestial Sphere From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2 dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere. 2 The Celestial Sphere Although we know better, it is helpful to
1 The Celestial Sphere From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2 dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere. 2 The Celestial Sphere Although we know better, it is helpful to
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008
 Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION
 Basic terms ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION *astronomical navigation *compilation *astronomical tabels *celestial observations *solution of a sight * Sun/Moon/star sight *spherical trigonometry *PZX triangle *celestial
Basic terms ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION *astronomical navigation *compilation *astronomical tabels *celestial observations *solution of a sight * Sun/Moon/star sight *spherical trigonometry *PZX triangle *celestial
Key Issue #1. How do geographers describe where things are? 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Key Issue #1 How do geographers describe where things are? Learning Outcomes 1.1.1: Explain differences between early maps and contemporary maps. 1.1.2: Describe the role of map scale and projections and
Key Issue #1 How do geographers describe where things are? Learning Outcomes 1.1.1: Explain differences between early maps and contemporary maps. 1.1.2: Describe the role of map scale and projections and
PY 124: Terrestrial Position from Celestial Observations
 The linked image cannot be displayed. The file may have been moved, renamed, or deleted. Verify that the link points to the correct file and location. The linked image cannot be displayed. The file may
The linked image cannot be displayed. The file may have been moved, renamed, or deleted. Verify that the link points to the correct file and location. The linked image cannot be displayed. The file may
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
2. Modern: A constellation is a region in the sky. Every object in the sky, whether we can see it or not, is part of a constellation.
 6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
6/17. Universe from Smallest to Largest:
 6/17 Universe from Smallest to Largest: 1. Quarks and Leptons fundamental building blocks of the universe size about 0 (?) importance: quarks combine together to form neutrons and protons. One of the leptons
6/17 Universe from Smallest to Largest: 1. Quarks and Leptons fundamental building blocks of the universe size about 0 (?) importance: quarks combine together to form neutrons and protons. One of the leptons
NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation
 NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation Q610065 look at it The angle between the plane of the ecliptic and the plane of equator is approx? 23.5 degrees In which two months of the year is the difference
NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation Q610065 look at it The angle between the plane of the ecliptic and the plane of equator is approx? 23.5 degrees In which two months of the year is the difference
Lecture 4: August 30, 2010
 Lecture 4: August 30, 2010 How many hospitals are there in the USA? Announcements: First homework has been posted Due Friday (10 th ) First Observatory Opportunity Thursday Night September 2, 8:30pm Will
Lecture 4: August 30, 2010 How many hospitals are there in the USA? Announcements: First homework has been posted Due Friday (10 th ) First Observatory Opportunity Thursday Night September 2, 8:30pm Will
Introduction To Astronomy Lesson 1
 Introduction To Astronomy Lesson 1 Topics for this Lesson Earth Based Coordinates The Celestial Sphere and Sky Coordinates The North Star Measuring Distances on the Sky The Motion of Objects in the Sky
Introduction To Astronomy Lesson 1 Topics for this Lesson Earth Based Coordinates The Celestial Sphere and Sky Coordinates The North Star Measuring Distances on the Sky The Motion of Objects in the Sky
Fundamentals of Satellite technology
 Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
1. Which graph best represents the altitude of Polaris observed at northern latitude positions on the Earth's surface?
 1. Which graph best represents the altitude of Polaris observed at northern latitude positions on the Earth's surface? A) 4. The diagram below shows an observer measuring the altitude of Polaris. B) C)
1. Which graph best represents the altitude of Polaris observed at northern latitude positions on the Earth's surface? A) 4. The diagram below shows an observer measuring the altitude of Polaris. B) C)
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Review of Last Class Almanacs: Paper and electronics Paper Almanacs: Nautical Almanac Electronic: Available on many web sites Homework #1 solutions 10/17/2006 12.215
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Review of Last Class Almanacs: Paper and electronics Paper Almanacs: Nautical Almanac Electronic: Available on many web sites Homework #1 solutions 10/17/2006 12.215
Module 2: Mapping Topic 2 Content: Determining Latitude and Longitude Notes
 Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Complete the following: a. Lines of latitude are parallel to the equator. Name:
 Name: Date: Social Studies Introduction: Basic Geography Period: Latitude Latitude is defined as a measurement of distance in degrees north and south of the equator. The word latitude is derived from the
Name: Date: Social Studies Introduction: Basic Geography Period: Latitude Latitude is defined as a measurement of distance in degrees north and south of the equator. The word latitude is derived from the
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy
 PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
SUB-PROBLEM 2: HOW DO SUN AND EARTH MOVE FOR THE EXISTING CYCLES AND SYMMETRIES TO OCCUR? (The invention of a Sun/Earth model)
 SUB-PROBLEM 2: HOW DO SUN AND EARTH MOVE FOR THE EXISTING CYCLES AND SYMMETRIES TO OCCUR? (The invention of a Sun/Earth model) We have made several advancements in the problem of interest proposed at the
SUB-PROBLEM 2: HOW DO SUN AND EARTH MOVE FOR THE EXISTING CYCLES AND SYMMETRIES TO OCCUR? (The invention of a Sun/Earth model) We have made several advancements in the problem of interest proposed at the
Period: Name: Astronomy Part 3A. Earth s Rotation: Video Notes Sheets. Earth Science with Mr. Sammartano Hommocks Middle School, Team 8-3
 Name: Period: Astronomy Part 3A Earth s Rotation: Video Notes Sheets Earth Science with Mr. Sammartano Hommocks Middle School, Team 8-3 PROOF #1 What is the Shape of the Earth? How do we know the Earth
Name: Period: Astronomy Part 3A Earth s Rotation: Video Notes Sheets Earth Science with Mr. Sammartano Hommocks Middle School, Team 8-3 PROOF #1 What is the Shape of the Earth? How do we know the Earth
Tonight. {01} The map. Relative space. What does a map do? Types of maps GEOG 201 2/17/2010. Instructor: Pesses 1
 Tonight {01} The map What makes a map Measuring the Earth Map Interpretation & GPS Spring 2010 M. Pesses What does a map do? Shows where things are Shows spatial (topological) relationships Shows patterns,
Tonight {01} The map What makes a map Measuring the Earth Map Interpretation & GPS Spring 2010 M. Pesses What does a map do? Shows where things are Shows spatial (topological) relationships Shows patterns,
The Sun. Fabio Peron Università IUAV - Venezia. Earth-Sun relationships. The Sun. Photosphere (Emits much of the solar radiant power)
 Università IUAV Venezia Corso di Fisica Tecnica Ambientale Laboratorio Integrato Innovazione-Sostenibilità Sun and solar radiation Fabio Peron Università IUAV - Venezia The Sun The Sun Earth-Sun relationships
Università IUAV Venezia Corso di Fisica Tecnica Ambientale Laboratorio Integrato Innovazione-Sostenibilità Sun and solar radiation Fabio Peron Università IUAV - Venezia The Sun The Sun Earth-Sun relationships
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 12 Lecture - 1 Global Positioning System (Refer Slide Time: 00:20) Welcome to this video lecture
Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 12 Lecture - 1 Global Positioning System (Refer Slide Time: 00:20) Welcome to this video lecture
Issue 1 1st October Contents. MONDO - All the time in the world [05] Installation and Adjustment...[08] Use of the MONDO...
![Issue 1 1st October Contents. MONDO - All the time in the world [05] Installation and Adjustment...[08] Use of the MONDO... Issue 1 1st October Contents. MONDO - All the time in the world [05] Installation and Adjustment...[08] Use of the MONDO...](/thumbs/81/83426404.jpg) MONDO - Manual Issue 1 1st October 2004 Contents MONDO - All the time in the world [05] Installation and Adjustment.....[08] Use of the MONDO............[13] [03] [04] ILLUSTRATION 1: MONDO MONDO All
MONDO - Manual Issue 1 1st October 2004 Contents MONDO - All the time in the world [05] Installation and Adjustment.....[08] Use of the MONDO............[13] [03] [04] ILLUSTRATION 1: MONDO MONDO All
Earth s Time Zones. Time Zones In The United States
 Name: Mr. DeLeo Date: Period: Earth s Time Zones Goal: Students will understand why humans have developed time zones on Earth, and how to figure out time at different positions on Earth. Background: One
Name: Mr. DeLeo Date: Period: Earth s Time Zones Goal: Students will understand why humans have developed time zones on Earth, and how to figure out time at different positions on Earth. Background: One
drinking straw, protractor, string, and rock. observer on Earth. Sun across the sky on March 21 as seen by an
 1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
OCN 201 LAB FALL 2003 POLYNESIAN AND WESTERN NAVIGATION
 Name: OCN 201 LAB FALL 2003 POLYNESIAN AND WESTERN NAVIGATION INTRODUCTION People have been sailing the seas for thousands of years, during most of which time they relied on the sun and the stars to navigate
Name: OCN 201 LAB FALL 2003 POLYNESIAN AND WESTERN NAVIGATION INTRODUCTION People have been sailing the seas for thousands of years, during most of which time they relied on the sun and the stars to navigate
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY
 CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In one way of naming stars, a letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation. a. English b. Arabic c. Greek d. Cyrillic
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In one way of naming stars, a letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation. a. English b. Arabic c. Greek d. Cyrillic
CURVED SPACE. 6 mon line of latitude. But you can get there in 3,605 miles if you fly
 CURVED SPACE - J7 - ing your compass for 3,707 miles almost straight east, along their com 6 mon line of latitude. But you can get there in 3,605 miles if you fly CURVED SPACE along a great circle, heading
CURVED SPACE - J7 - ing your compass for 3,707 miles almost straight east, along their com 6 mon line of latitude. But you can get there in 3,605 miles if you fly CURVED SPACE along a great circle, heading
EARTHS SHAPE AND POLARIS PRACTICE 2017
 1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
Constellations In ancient times, constellations only referred to the brightest stars that appeared to form groups, representing mythological figures.
 Chapter 2: The Sky Constellations In ancient times, constellations only referred to the brightest stars that appeared to form groups, representing mythological figures. Constellations Today, constellations
Chapter 2: The Sky Constellations In ancient times, constellations only referred to the brightest stars that appeared to form groups, representing mythological figures. Constellations Today, constellations
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky
 Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Observing the Night Sky: Locating Objects
 Observing the Night Sky: Locating Objects As I left the house this morning, there was a bright bluish light above and to the left of my neighbors house (approximately East) and a big very bright object
Observing the Night Sky: Locating Objects As I left the house this morning, there was a bright bluish light above and to the left of my neighbors house (approximately East) and a big very bright object
WHERE ARE YOU? LOCATING BY THE SUN
 WHERE ARE YOU? LOCATING BY THE SUN Sakari Ekko EAAE Summer School Working Group (Finland) Abstract In this workshop, we first find our location on the globe by the Sun and Polaris, the Pole Star. After
WHERE ARE YOU? LOCATING BY THE SUN Sakari Ekko EAAE Summer School Working Group (Finland) Abstract In this workshop, we first find our location on the globe by the Sun and Polaris, the Pole Star. After
Astronomy 11. No, this course isn t all about Star Wars
 Astronomy 11 No, this course isn t all about Star Wars Earth s Rotation How fast are people on the equator moving? s=d/t =circumference/24 hours =(40,000 km)/24 hours =1670 km/h That s Mach 1.4! What
Astronomy 11 No, this course isn t all about Star Wars Earth s Rotation How fast are people on the equator moving? s=d/t =circumference/24 hours =(40,000 km)/24 hours =1670 km/h That s Mach 1.4! What
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere
 The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH
 UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH How many planets are there in our Solar System? What is the Equator? Why does life exist in our planet? Does The Earth move? What is a map? 1. Planet Earth TOPICS 2. Movements
UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH How many planets are there in our Solar System? What is the Equator? Why does life exist in our planet? Does The Earth move? What is a map? 1. Planet Earth TOPICS 2. Movements
Meridian Circle through Zenith, North Celestial Pole, Zenith Direction Straight Up from Observer. South Celestial Pole
 Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work- Effects of Latitude In chapters 3 and 4we will learn why our view of the heavens depends on our position on the Earth, the time of day, and the day of the year. We will
Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work- Effects of Latitude In chapters 3 and 4we will learn why our view of the heavens depends on our position on the Earth, the time of day, and the day of the year. We will
Author: Seth Stein, William Deering Professor of Earth & Planetary Sciences, Northwestern University. Background for Calais & Stein paper
 Background for Calais & Stein paper The GPS data reported here are important for understanding earthquakes in the central U.S. Large (magnitude 7) earthquakes on the New Madrid Fault system shook the Midwest
Background for Calais & Stein paper The GPS data reported here are important for understanding earthquakes in the central U.S. Large (magnitude 7) earthquakes on the New Madrid Fault system shook the Midwest
What Is a Globe? Hemispheres. Main Idea Globes and maps provide different ways of showing features of the earth. Terms to Know
 r Main Idea Globes and maps provide different ways of showing features of the earth. Terms to Know hemisphere latitude longitude scale bar scale relief elevation contour line What Is a Globe? A globe is
r Main Idea Globes and maps provide different ways of showing features of the earth. Terms to Know hemisphere latitude longitude scale bar scale relief elevation contour line What Is a Globe? A globe is
compass 1 of 5 For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
Astron 104 Laboratory #2 The Celestial Sphere
 Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #2 The Celestial Sphere Basic Setup Once the celestial sphere is properly setup, it will serve as an exact model of the heavens relative to your location on Earth.
Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #2 The Celestial Sphere Basic Setup Once the celestial sphere is properly setup, it will serve as an exact model of the heavens relative to your location on Earth.
NAVIGATION READER 10th edition October 2015
 NAVIGATION READER 10 th edition 13-18 October 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction p. 3 2. The earth p. 4 A layout of the earth p. 4 Latitude and longitude p. 4 3. The sea chart p. 6 Determining latitude
NAVIGATION READER 10 th edition 13-18 October 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction p. 3 2. The earth p. 4 A layout of the earth p. 4 Latitude and longitude p. 4 3. The sea chart p. 6 Determining latitude
Scientists observe the environment around them using their five senses.
 Earth Science Notes Topics 1: Observation and Measurement Topic 2: The Changing Environment Review book pages 1-38 Scientists observe the environment around them using their five senses. When scientists
Earth Science Notes Topics 1: Observation and Measurement Topic 2: The Changing Environment Review book pages 1-38 Scientists observe the environment around them using their five senses. When scientists
Chapter 6: Latitude by Noon Sight
 Chapter 6: Latitude by oon ight When the sun is crossing the meridian of the boat, it is straight south or north of the boat and at its highest altitude over the horizon for the day. The local meridian
Chapter 6: Latitude by oon ight When the sun is crossing the meridian of the boat, it is straight south or north of the boat and at its highest altitude over the horizon for the day. The local meridian
Making a Sundial. Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory. iau.org/astroedu
 Making a Sundial Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory Age 6-10 Supervised Unsupervised Core skills Asking questions, Developing and using models, Analysing
Making a Sundial Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory Age 6-10 Supervised Unsupervised Core skills Asking questions, Developing and using models, Analysing
Chapter 1: The World of Geography
 Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Geographic Grid -Latitudes and Longitudes
 GEOGRAPHY STD 9 Geographic Grid -Latitudes and Longitudes 2018-2019 Q1. Define Geographic Grid. The network of latitudes and longitudes are known as Geographic Grid. They help us to locate places on the
GEOGRAPHY STD 9 Geographic Grid -Latitudes and Longitudes 2018-2019 Q1. Define Geographic Grid. The network of latitudes and longitudes are known as Geographic Grid. They help us to locate places on the
LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations
 LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations Name School The amount of solar energy striking the Earth s atmosphere is not uniform; distances, angles and seasons play a dominant role on this distribution of radiation. Needless
LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations Name School The amount of solar energy striking the Earth s atmosphere is not uniform; distances, angles and seasons play a dominant role on this distribution of radiation. Needless
Map Skills Test. 1. What do we call a person who makes maps? a. mapographer b. cartographer c. geologist d. archaeologist
 Map Skills Test 1. What do we call a person who makes maps? a. mapographer b. cartographer c. geologist d. archaeologist 2. What is the name of the 0 latitude line? a. Equator b. Arctic Circle c. First
Map Skills Test 1. What do we call a person who makes maps? a. mapographer b. cartographer c. geologist d. archaeologist 2. What is the name of the 0 latitude line? a. Equator b. Arctic Circle c. First
GEOGRAPHY STD.9 LATITUDE & LONGITUDE
 GEOGRAPHY STD.9 LATITUDE & LONGITUDE 1. What is the Earth Grid? A. The complete network of meridians & parallels is called the earth Grid. 2. What is Latitude? A. The latitude of a place is the distance
GEOGRAPHY STD.9 LATITUDE & LONGITUDE 1. What is the Earth Grid? A. The complete network of meridians & parallels is called the earth Grid. 2. What is Latitude? A. The latitude of a place is the distance
DUMMIES guide to Astro-Navigation
 DUMMIES guide to Astro-Navigation The idea of this booklet is to give you the nuts and bolts in the process of gaining a position on your chart through celestial navigation without a deep understanding
DUMMIES guide to Astro-Navigation The idea of this booklet is to give you the nuts and bolts in the process of gaining a position on your chart through celestial navigation without a deep understanding
Background Information
 Oceanography LAB #1: Marine Charts and Navigation Background Information Latitude and Longitude A coordinate is an address a means of designating location. Most coordinate systems involve a network of
Oceanography LAB #1: Marine Charts and Navigation Background Information Latitude and Longitude A coordinate is an address a means of designating location. Most coordinate systems involve a network of
The following terms are some of the vocabulary that students should be familiar with in order to fully master this lesson.
 Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
ASTRO Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky
 ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky ABSTRACT Today we will be calibrating your hand as an angular measuring device, and then heading down to the planetarium to see the night sky in motion.
ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky ABSTRACT Today we will be calibrating your hand as an angular measuring device, and then heading down to the planetarium to see the night sky in motion.
+ 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ
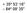 + 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ N 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ W (the precise location of Farragut High School!) Spherical Coordinates Mapping a Sphere The student will be able to: HW: 1 Utilize and convert SI units
+ 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ N 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ W (the precise location of Farragut High School!) Spherical Coordinates Mapping a Sphere The student will be able to: HW: 1 Utilize and convert SI units
Earth is rotating on its own axis
 Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Astronomy. The Seasons
 Astronomy The Seasons The seasons are caused by the inclination of the Earth s axis: when a hemisphere is tipped toward the Sun, the Sun is more directly above it. At the Summer Solstice the tilt is most
Astronomy The Seasons The seasons are caused by the inclination of the Earth s axis: when a hemisphere is tipped toward the Sun, the Sun is more directly above it. At the Summer Solstice the tilt is most
CELESTIAL COORDINATES
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 27 Celestial Coordinates CELESTIAL COORDINATES GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES The Earth's geographic coordinate system is familiar to everyone - the north and south poles are defined by
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 27 Celestial Coordinates CELESTIAL COORDINATES GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES The Earth's geographic coordinate system is familiar to everyone - the north and south poles are defined by
Contents [1] CIELO - Celestial times...[3] Measuring time by the Sun...[3] Time zones...[4]
![Contents [1] CIELO - Celestial times...[3] Measuring time by the Sun...[3] Time zones...[4] Contents [1] CIELO - Celestial times...[3] Measuring time by the Sun...[3] Time zones...[4]](/thumbs/77/75592191.jpg) CIELO MANUAL Contents CIELO - Celestial times....................[3] Measuring time by the Sun..............[3] Time zones..........................[4] Adjusting the sundial and reading the time.....[5]
CIELO MANUAL Contents CIELO - Celestial times....................[3] Measuring time by the Sun..............[3] Time zones..........................[4] Adjusting the sundial and reading the time.....[5]
Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics
 SOAR: The Sky in Motion Life on the Tilted Teacup Ride The Year Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics Celestial Coordinates Right Ascension RA or From prime meridian (0 h ) to 23 h
SOAR: The Sky in Motion Life on the Tilted Teacup Ride The Year Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics Celestial Coordinates Right Ascension RA or From prime meridian (0 h ) to 23 h
A Sense of Scale and The Motions of Earth. The guitar player Pablo Picasso (1910)
 A Sense of Scale and The Motions of Earth The guitar player Pablo Picasso (1910) Announcements n Notes from the first lecture are available on the class web site (www.astro.umass.edu/~calzetti/astro100).
A Sense of Scale and The Motions of Earth The guitar player Pablo Picasso (1910) Announcements n Notes from the first lecture are available on the class web site (www.astro.umass.edu/~calzetti/astro100).
UNIT 1 THE BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY
 UNIT 1 THE BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER 1 LOOKING AT THE EARTH 1 Section 1.1: The 5 Themes of Geography.Geography comes from a Greek word meaning writing about or describing the earth. Geography is: Geographers
UNIT 1 THE BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER 1 LOOKING AT THE EARTH 1 Section 1.1: The 5 Themes of Geography.Geography comes from a Greek word meaning writing about or describing the earth. Geography is: Geographers
Spherical Geometry HSC. Name:
 Spherical Geometry HSC Name: C:\Documents and Settings\tracey_h-butters\Desktop\mathematics\year_levels\math_stage6\General\hsc\spherical_geometry\spherical_geo_notes.doc 1 HSC CAPACITY MATRIX GENERAL
Spherical Geometry HSC Name: C:\Documents and Settings\tracey_h-butters\Desktop\mathematics\year_levels\math_stage6\General\hsc\spherical_geometry\spherical_geo_notes.doc 1 HSC CAPACITY MATRIX GENERAL
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography
 5 Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
5 Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
CHAPTER EXIT CHAPTER. Models of Earth. 3.1 Modeling the Planet. 3.2 Mapmaking and Technology. 3.3 Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE
 EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
SMILE Teacher Workshop 2007 Winter Teachers Workshop Maritime Science. Maritime Science
 This activity is adapted from Teach Engineering lessons and activities How to be a great navigator, The North (Wall) Star, and Vector Voyage! http://www.teachengineering.org/index.php Integrated Teaching
This activity is adapted from Teach Engineering lessons and activities How to be a great navigator, The North (Wall) Star, and Vector Voyage! http://www.teachengineering.org/index.php Integrated Teaching
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy AST0111-3 (Astronomía) Semester 2014B Prof. Thomas H. Puzia Theme Our Sky 1. Celestial Sphere 2. Diurnal Movement 3. Annual Movement 4. Lunar Movement 5. The Seasons 6. Eclipses
Introduction to Astronomy AST0111-3 (Astronomía) Semester 2014B Prof. Thomas H. Puzia Theme Our Sky 1. Celestial Sphere 2. Diurnal Movement 3. Annual Movement 4. Lunar Movement 5. The Seasons 6. Eclipses
Lesson 20: The Earth in its Orbit
 291 Lesson 20: The Earth in its Orbit Recall that the Earth s orbit around the un is an ellipse which is almost a perfect circle. The average distance from the un to the Earth is 152,100,000 km (to the
291 Lesson 20: The Earth in its Orbit Recall that the Earth s orbit around the un is an ellipse which is almost a perfect circle. The average distance from the un to the Earth is 152,100,000 km (to the
The Sky. Day sky: the Sun, occasionally the Moon. Night Sky: stars, and sometimes the Moon
 The Sky Day sky: the Sun, occasionally the Moon Night Sky: stars, and sometimes the Moon So MANY objects.how Do We Make Sense of it ALL?? Goal How to describe the locations of objects in the sky To understand
The Sky Day sky: the Sun, occasionally the Moon Night Sky: stars, and sometimes the Moon So MANY objects.how Do We Make Sense of it ALL?? Goal How to describe the locations of objects in the sky To understand
Navigating by the Stars and Planets
 Navigating by the Stars and Planets (Finding your location from measured altitudes of celestial bodies) Presented to: Chagrin Valley Astronomical Society September 1, 2012 By Ron Baker, CVAS member Historical
Navigating by the Stars and Planets (Finding your location from measured altitudes of celestial bodies) Presented to: Chagrin Valley Astronomical Society September 1, 2012 By Ron Baker, CVAS member Historical
Shape of Earth, Cycles, Distribution of Water
 Shape of Earth, Cycles, Distribution of Water What is the shape of Earth? A. Spherical B. Apple-shaped C. Pear-shaped Shape of the Earth It should be spherical: Earth condensed under gravity, thus everything
Shape of Earth, Cycles, Distribution of Water What is the shape of Earth? A. Spherical B. Apple-shaped C. Pear-shaped Shape of the Earth It should be spherical: Earth condensed under gravity, thus everything
Earth, Sun, and Stars
 Earth, Sun, and Stars Daily Patterns Earth Spins Earth is always moving, even though you don t feel it. One way Earth moves is by spinning around an imaginary line. One end of the line would come out of
Earth, Sun, and Stars Daily Patterns Earth Spins Earth is always moving, even though you don t feel it. One way Earth moves is by spinning around an imaginary line. One end of the line would come out of
Compass Basics. Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use
 Compass Basics Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use A topographic map tells you where things are and how to get to them, whether you're hiking, biking, hunting, fishing, or just interested in the world
Compass Basics Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use A topographic map tells you where things are and how to get to them, whether you're hiking, biking, hunting, fishing, or just interested in the world
Latitude and Longitude. Begin
 Latitude and Longitude Begin The Earth is divided in two halves, the top half is called the northern hemisphere, and the bottom half is called the southern hemisphere. The dividing line between the two
Latitude and Longitude Begin The Earth is divided in two halves, the top half is called the northern hemisphere, and the bottom half is called the southern hemisphere. The dividing line between the two
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES
 UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
Shape of Earth, Cycles, Distribution of Water
 Shape of Earth, Cycles, Distribution of Water What is the shape of Earth? A. Spherical B. Apple-shaped C. Pear-shaped Shape of the Earth It should be spherical: Earth condensed under gravity, thus everything
Shape of Earth, Cycles, Distribution of Water What is the shape of Earth? A. Spherical B. Apple-shaped C. Pear-shaped Shape of the Earth It should be spherical: Earth condensed under gravity, thus everything
Practice Questions: Seasons #2
 1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
