OCN 201 LAB FALL 2003 POLYNESIAN AND WESTERN NAVIGATION
|
|
|
- Anissa Copeland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: OCN 201 LAB FALL 2003 POLYNESIAN AND WESTERN NAVIGATION INTRODUCTION People have been sailing the seas for thousands of years, during most of which time they relied on the sun and the stars to navigate the open ocean. It wasn't until the invention of the compass and the clock, along with other advances in the fields of geophysics and astronomy, that extremely accurate navigational techniques were utilized. This lab will provide an overview of both Polynesian and modern wayfinding. You will use computer simulation, a star compass, a magnetic compass, and a GPS unit to learn more about wayfinding techniques. During this lab you should accomplish the following objectives: 1. Use maps to identify Latitude and Longitude, magnetic and true north; 2. Find the coordinates of Oahu; and 3. Learn orientation skills based on a star chart and a compass. If you need further clarification after reading the sections below, please read Appendix 3 of the class textbook, Oceanography: An Invitation to Marine Science by Tom Garrison. POLYNESIAN NAVIGATION The required reading for this section is found on the Polynesian Voyaging Society (PVS) web site at Click on the Wayfinding link and then the Wayfinding Summary link. Interested students should review the rest of the site to learn more about PVS and traditional wayfinding techniques. MODERN NAVIGATION Instead of splitting the sky into star houses, modern navigators split the globe a system of quadrants formed by imaginary lines called latitude and longitude. Latitude lines run parallel to the equator and indicate North or South positions. Longitude lines run from pole to pole and indicate positions on meridians East and West of the Greenwich meridian (designated as the zero meridian). By convention, degrees (symbol o ) and minutes (symbol ) are the units used to describe position. This is based on 360 o in a circle and 60' in a degree. When writing coordinates, the latitude always goes first. For example, the coordinate "22 o 18.5 N 155 o 34.6 W" is read as "22 degrees, 18.5 minutes North and 155 degrees, 34.6 minutes West." The distance between each line of latitude is the same and one degree of latitude is equal to 60 nautical miles (1 nautical mile = 1.15 mile). In contrast, lines of longitude are not spaced evenly. At the poles, all lines of longitude converge. At the equator, lines of longitude have their greatest spacing, which is equal to the distance between lines of latitude. For the purposes of this lab, we will assume that one degree of longitude is equal to 60 nautical miles because Hawai'i is reasonably close to the equator. To find out location relative to the latitude/longitude coordinate system, modern navigators use equipment such as charts (nautical maps), a magnetic compass, and the Global Positioning System (GPS). The basis for the magnetic compass is discussed below, followed by a brief discussion of GPS.
2 The earth's magnetic field is probably caused by motions in the liquid outer core. This magnetic field has been moving around over the history of the earth, but also the poles have been flipping sides! They also drift to a small extent. Figure 1 illustrates the movement of the North magnetic pole over the past 100 years. Right now, it seems to be 8 degrees south of the geographic North Pole. This means that depending on where you are in the world, you have to be careful to correct the reading on your compass accordingly. Figure 1: The position of the magnetic North over time. As you can see, the magnetic North in the year 2000 was on 250 o in this strange projection. That is the same as 110 o West in the system we are familiar with. Figure courtesy of USGS: The difference between the magnetic and the geographic North Pole is referred to as the declination. The declination of a map changes from year to year, so if you use an old map, you will end up travelling off course. For this laboratory, we read on our map that if we are in the Hawai`ian Islands, the magnetic North lies 10 degrees east of the geographic North, as we look towards it. That means that we must subtract 10 degrees from our compass reading to see our direction in relation to the geographic North. This direction in relation to the geographic North is known as the bearing. For example, if our compass says that we are looking in a direction of 275 o, our bearing is 265 o. 2
3 GPS uses satellites that are orbiting the earth to transmit signals to a receiver on earth. Multiple satellites transmit signals to a single receiver. By analyzing the distances between you and each of the satellites, your GPS unit determines your location. This method is referred to as triangulation and your TA will explain it further during lab. EXERCISES I. Basic Navigation Tools The TA will bring groups of students onto the roof of MSB or out into the courtyard in front of the building and demonstrate the GPS and compass. 1. What are the latitude and longitude of UH Manoa? Lat Long 2. By walking with the GPS unit turned on estimate (using your stride to measure) what is the minimum distance that you need to walk to cause the GPS display to change by its minimum value? 3. From the assigned point outside the building or on the roof, what is the bearing of a) POST, b) HIG, c) Bilger Hall? II. Modern Navigation Methods 4. Using the assigned worksheet and the chart of the main Hawaiian Islands, draw a course on the chart using the erasable marker. For this exercise, refer to the table below. You will begin by determining the coordinates (position) of Hanauma Bay. Then, go 60 nautical miles at a bearing of 140 and write down your location and position in part B. For the position, give your coordinates to the nearest minute. For the location, write down the closest land- or sea-mark. If you are in the middle of a channel, which one? If you're right next to a point or cape, which one? You get the idea 3
4 Location Position Bearing Distance A. Hanauma Bay nautical miles B n miles C n miles D n miles E. You should now be at 21 N, 159 W. If that's where you ended up, good work! If not, you can recheck your route to see where you've made mistakes. Now, plot the bearing and distance to Nawiliwili Bay, Kau'ai. Put your answer in the space below. III. Polynesian Navigation Methods 5. Using the marked Hawaiian star compass rose (provided to you in class), give the direction for each of the bearings used above. Note that these legs correspond with the voyage that you plotted in the previous exercise. Also, calculate how much time would be spent on each leg of the journey if you were travelling at 15 knots (1 knot = 1 nautical mile per hour). Round to the nearest 1/4 hour. Note that this is a rather impossible speed if travelling on a vessel such as the Hokule'a when sailing in a multitude of directions, but we will use it anyhow. Degrees Hawai'ian Direction Name Distance (n miles) Time (hours) A nautical miles B nautical miles C nautical miles D nautical miles E. 4
5 6. Use the computer program "Starry Night Backyard" to identify the stars that can be used to hold the canoe's course during the above journey. Basic instructions for using Starry Night Backyard: 1) Open the program by clicking on the astronomical observatory icon on the launching dock. 2) Take a few minutes looking at the program, the menus and the clickable buttons. 3) At the top of the window with the view of the meadow you can see the following, from left to right: The date and time. You can change these by clicking on them and typing in the numbers. Speed with which time moves. You can speed time up 30 times, 300 times etc. VCR-like controls that can stop time, move time forwards or backwards etc. Elevation and location 4) Look at the menu on the left of the screen: Select View Options. To have the program label planets, stars and constellations, check the boxes marked Labels next to these items. 5) Place the computer mouse over the landscape, hold down the mouse button and move the mouse left or right. This way you can look around you in any direction you wish. 6a. Look at the menu on the top of the screen. Select View, and scroll down to Hide Daylight. Now you can see the stars and constellations obscured by daylight. Set the speed with which time moves at 3000x. Look in different directions and describe the motion of the stars as you face each direction. South East North West 6b. When facing the north, which star doesn t move? How could this star be useful in determining your bearing? 6c. (Before going on with this exercise, stop the progress of time. Go to the menu on the top of the screen, select View, and scroll down to Show Daylight. Set the time at 300x, and the hour and date mentioned below) Now, let s imagine that you are planning a voyage of the Hokule'a, with the legs used in exercises 1 and 5. The journey will commence at 7:30 PM on Friday, September 5 th, 2003 Knowing that each star can be used up to 30 degrees above the horizon, and that the stars rise and set by 1 every 4 minutes, each star can only be used for a maximum of 120 minutes. For each leg of the journey, look toward the rising stars (East) and list the stars that you could use to navigate this course. Also, list the time period for which you can use each star. Are there any time periods when you can't find one of the bright rising stars to use? If so, indicate those times (to the nearest minute). For this part, it will be useful if you change the time interval to seconds. Note that during daylight hours, you will not be able to use the stars and will have to use alternate navigation methods. 5
6 Leg Star/Constellation Time A. B. C. D. E. 7. Other than the celestial bodies (stars, moon, sun, etc.), list 3 aspects of your surroundings that could be used to determine your position and bearing while at sea (this information comes from the online reading). IV. Summary Questions 8. List 2 potential problems or sources of error that one might incur with each navigational system 9. If you were stuck in the middle of the Pacific, and had to get home as soon as possbile, which navigational system would you prefer to use? Why? 6
CHAPTER 2 SKILL SHEET 2: CELESTIAL NAVIGATION
 CHAPTER 2 SKILL SHEET 2: CELESTIAL NAVIGATION Before the invention of GPS technology, how were people on ships far at sea, out of the sight of land, able to tell where they were? For thousands of years
CHAPTER 2 SKILL SHEET 2: CELESTIAL NAVIGATION Before the invention of GPS technology, how were people on ships far at sea, out of the sight of land, able to tell where they were? For thousands of years
Stellarium Walk-through for First Time Users
 Stellarium Walk-through for First Time Users Stellarium is the computer program often demonstrated during our planetarium shows at The MOST, Syracuse s science museum. It is our hope that visitors to our
Stellarium Walk-through for First Time Users Stellarium is the computer program often demonstrated during our planetarium shows at The MOST, Syracuse s science museum. It is our hope that visitors to our
Assignment #0 Using Stellarium
 Name: Class: Date: Assignment #0 Using Stellarium The purpose of this exercise is to familiarize yourself with the Stellarium program and its many capabilities and features. Stellarium is a visually beautiful
Name: Class: Date: Assignment #0 Using Stellarium The purpose of this exercise is to familiarize yourself with the Stellarium program and its many capabilities and features. Stellarium is a visually beautiful
Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Exercise #1. Intro to the Sky
 Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Exercise #1 Partners Intro to the Sky Date Section Purpose: To develop familiarity with the daytime and nighttime sky through the use of Stellarium. Equipment: Computer
Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Exercise #1 Partners Intro to the Sky Date Section Purpose: To develop familiarity with the daytime and nighttime sky through the use of Stellarium. Equipment: Computer
Physics Lab #3:! Starry Night! Observations of the Sun and Moon!
 Physics 10293 Lab #3: Starry Night Observations of the Sun and Moon Introduction Today, we are going to use the Starry Night software to learn about motion of the stars, sun and moon on the celestial sphere.
Physics 10293 Lab #3: Starry Night Observations of the Sun and Moon Introduction Today, we are going to use the Starry Night software to learn about motion of the stars, sun and moon on the celestial sphere.
Physics Lab #5: Starry Night Observations of the Sun and Moon
 Physics 10293 Lab #5: Starry Night Observations of the Sun and Moon Introduction Today, we are going to use the Starry Night software to learn about motion of the stars, sun and moon on the celestial sphere.
Physics 10293 Lab #5: Starry Night Observations of the Sun and Moon Introduction Today, we are going to use the Starry Night software to learn about motion of the stars, sun and moon on the celestial sphere.
Understanding Positional Astronomy Part 2 Celestial Co-ordinates Difficulty: Intermediate
 Exercise: Understanding Positional Astronomy Part 2 Celestial Co-ordinates Difficulty: Intermediate Objectives In Part 1 you learned about Celestial Sphere and how the stars appear to move across the night
Exercise: Understanding Positional Astronomy Part 2 Celestial Co-ordinates Difficulty: Intermediate Objectives In Part 1 you learned about Celestial Sphere and how the stars appear to move across the night
Astro 101 Lab #2. Start up the Stellarium program. If you do not remember how to use the user interface, please refer to Lab#1 or the user s guide.
 Name: Astro 101 Lab #2 Lab objectives 1) Learn about how the Sun s path, through the sky, changes with the changing seasons. 2) Learn about how the Sun s path changes while viewing it at different locations
Name: Astro 101 Lab #2 Lab objectives 1) Learn about how the Sun s path, through the sky, changes with the changing seasons. 2) Learn about how the Sun s path changes while viewing it at different locations
1. Label a few examples of lines of latitude and lines of longitude on the globe above left.
 Oceanography 2 Location, Direction, and Distance on Nautical Charts Please read Appendix III in the textbook for reference. Learning Objectives for the first nautical chart Lab 1. Use the latitude-longitude
Oceanography 2 Location, Direction, and Distance on Nautical Charts Please read Appendix III in the textbook for reference. Learning Objectives for the first nautical chart Lab 1. Use the latitude-longitude
Background Information
 Oceanography LAB #1: Marine Charts and Navigation Background Information Latitude and Longitude A coordinate is an address a means of designating location. Most coordinate systems involve a network of
Oceanography LAB #1: Marine Charts and Navigation Background Information Latitude and Longitude A coordinate is an address a means of designating location. Most coordinate systems involve a network of
COMPUTER ACTIVITY 3: THE SEASONS: LENGTH OF THE DAY
 NAME ASTRONOMY 20 SECTION DAY/ S. V. LLOYD COMPUTER ACTIVITY 3: THE SEASONS: LENGTH OF THE DAY Overview Software Configuration The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes in the Sun's path
NAME ASTRONOMY 20 SECTION DAY/ S. V. LLOYD COMPUTER ACTIVITY 3: THE SEASONS: LENGTH OF THE DAY Overview Software Configuration The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes in the Sun's path
HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST
 HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST Using a globe to learn how a position on Earth can be described. Rui Dilão, Instituto Superior Técnico Curriculum topic latitude, longitude, coordinate system
HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST Using a globe to learn how a position on Earth can be described. Rui Dilão, Instituto Superior Técnico Curriculum topic latitude, longitude, coordinate system
Astro Navigation (i.e. Celestial Navigation)
 Name: Partner First Name: Astro Navigation (i.e. Celestial Navigation) Over the course of human lifetimes, the stars don t appear to change positions much. We can use that in order to determine locations
Name: Partner First Name: Astro Navigation (i.e. Celestial Navigation) Over the course of human lifetimes, the stars don t appear to change positions much. We can use that in order to determine locations
Section 2. Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate.
 Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Charts and Chart Work with Poole Sailing
 with Poole Sailing Nautical charts are a mine of information but they need to be up to date. Corrections to charts are published by the Hydrographic Office monthly as Notices to Mariners both in print
with Poole Sailing Nautical charts are a mine of information but they need to be up to date. Corrections to charts are published by the Hydrographic Office monthly as Notices to Mariners both in print
Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator
![Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator](/thumbs/83/88077665.jpg) Earth Science Regents Interactive Path of the Sun University of Nebraska Resources Copyright 2011 by Z. Miller Name Period COMPANION WEBSITES: http://www.analemma.com/ http://www.stellarium.org/ INTRODUCTION:
Earth Science Regents Interactive Path of the Sun University of Nebraska Resources Copyright 2011 by Z. Miller Name Period COMPANION WEBSITES: http://www.analemma.com/ http://www.stellarium.org/ INTRODUCTION:
Google Earth. Overview: Targeted Alaska Grade Level Expectations: Objectives: Materials: Grades 5-8
 Overview: Students become familiar with using the Google Earth interface to navigate around the planet. Using the zoom and tilt features, students practice moving around the planet with the navigation
Overview: Students become familiar with using the Google Earth interface to navigate around the planet. Using the zoom and tilt features, students practice moving around the planet with the navigation
USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB
 USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB 1. Explain the main differences between using a star wheel and a star chart to find things in the night sky. 2. Explain the terms Hour Angle, Meridian and
USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB 1. Explain the main differences between using a star wheel and a star chart to find things in the night sky. 2. Explain the terms Hour Angle, Meridian and
Astronomy 101 Lab: Stellarium Tutorial
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Stellarium Tutorial Please install the Stellarium software on your computer using the instructions in the procedure. If you own a laptop, please bring it to class. You will submit
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Stellarium Tutorial Please install the Stellarium software on your computer using the instructions in the procedure. If you own a laptop, please bring it to class. You will submit
Activities: Map and Compass
 Activities: Map and Compass Determining General Directions Modified with permission from Outdoor Living Skills Series: Map and Compass, Missouri Department of Conservation Overview: Students use the sun
Activities: Map and Compass Determining General Directions Modified with permission from Outdoor Living Skills Series: Map and Compass, Missouri Department of Conservation Overview: Students use the sun
Astro 101 Lab #1. To advance time forward and backward, click on the arrow toolbar. From left to right, the buttons will
 Name: Astro 101 Lab #1 Lab objectives 1) Learn how to use the Stellarium planetarium program, by becoming familiar with the user interface and configuring the planetarium to your present location on Earth.
Name: Astro 101 Lab #1 Lab objectives 1) Learn how to use the Stellarium planetarium program, by becoming familiar with the user interface and configuring the planetarium to your present location on Earth.
The Mass of Jupiter Student Guide
 The Mass of Jupiter Student Guide Introduction: In this lab, you will use astronomical observations of Jupiter and its satellites to measure the mass of Jupiter. We will use the program Stellarium to simulate
The Mass of Jupiter Student Guide Introduction: In this lab, you will use astronomical observations of Jupiter and its satellites to measure the mass of Jupiter. We will use the program Stellarium to simulate
Physics Lab #2: Learning Starry Night, Part 1
 Physics 10293 Lab #2: Learning Starry Night, Part 1 Introduction In this lab, we'll learn how to use the Starry Night software to explore the sky, and at the same time, you ll get a preview of many of
Physics 10293 Lab #2: Learning Starry Night, Part 1 Introduction In this lab, we'll learn how to use the Starry Night software to explore the sky, and at the same time, you ll get a preview of many of
CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM
 Name Partner(s) Section Date CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM You have had the opportunity to look at two different tools to display the night sky, the celestial sphere and the star chart.
Name Partner(s) Section Date CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM You have had the opportunity to look at two different tools to display the night sky, the celestial sphere and the star chart.
Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography
 5 Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
5 Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
GPS Measurement Protocol
 GPS Measurement Protocol Purpose To determine the latitude, longitude, and elevation of your school and of all your GLOBE sites Overview The GPS receiver will be used to determine the latitude, longitude
GPS Measurement Protocol Purpose To determine the latitude, longitude, and elevation of your school and of all your GLOBE sites Overview The GPS receiver will be used to determine the latitude, longitude
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map
 What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3
 Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS
 NAME(S)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ASTRONOMY 25 Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD Overview The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes
NAME(S)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ASTRONOMY 25 Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD Overview The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes
Indoor Lab #2: The Starry Sky
 17 Indoor Lab #2: The Starry Sky Objectives: To tour the sky and explore the way in which it moves, using the sky simulation program Starry Night Pro. Check out the information sheet on SN first, and try
17 Indoor Lab #2: The Starry Sky Objectives: To tour the sky and explore the way in which it moves, using the sky simulation program Starry Night Pro. Check out the information sheet on SN first, and try
Physics Lab #6:! Mercury!
 Physics 10293 Lab #6: Mercury Introduction Today we will explore the motions in the sky of the innermost planet in our solar system: Mercury. Both Mercury and Venus were easily visible to the naked eye
Physics 10293 Lab #6: Mercury Introduction Today we will explore the motions in the sky of the innermost planet in our solar system: Mercury. Both Mercury and Venus were easily visible to the naked eye
FYI. 0 You will need to take notes this information will come in handy when going through this unit and on the cok.
 FYI 0 You will need to take notes this information will come in handy when going through this unit and on the cok. One of the best ways to get started as a backyard astronomer is to learn the constellations.
FYI 0 You will need to take notes this information will come in handy when going through this unit and on the cok. One of the best ways to get started as a backyard astronomer is to learn the constellations.
ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION
 Basic terms ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION *astronomical navigation *compilation *astronomical tabels *celestial observations *solution of a sight * Sun/Moon/star sight *spherical trigonometry *PZX triangle *celestial
Basic terms ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION *astronomical navigation *compilation *astronomical tabels *celestial observations *solution of a sight * Sun/Moon/star sight *spherical trigonometry *PZX triangle *celestial
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere
 The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
SkyGlobe Planetarium
 SkyGlobe Planetarium Introduction: This exercise will simulate the night sky and demonstrate a number of principles of the celestial sphere and the motions of the Earth and planets. Getting Started: 1.
SkyGlobe Planetarium Introduction: This exercise will simulate the night sky and demonstrate a number of principles of the celestial sphere and the motions of the Earth and planets. Getting Started: 1.
PY 124: Terrestrial Position from Celestial Observations
 The linked image cannot be displayed. The file may have been moved, renamed, or deleted. Verify that the link points to the correct file and location. The linked image cannot be displayed. The file may
The linked image cannot be displayed. The file may have been moved, renamed, or deleted. Verify that the link points to the correct file and location. The linked image cannot be displayed. The file may
STELLARIUM ACTIVITY #1: STARRISE AND STARSET
 NAME(S) ASTRONOMY 20/25 SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD STELLARIUM ACTIVITY #1: STARRISE AND STARSET Overview The sidereal day is the amount of time from starrise to the next starrise. In this activity, you
NAME(S) ASTRONOMY 20/25 SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD STELLARIUM ACTIVITY #1: STARRISE AND STARSET Overview The sidereal day is the amount of time from starrise to the next starrise. In this activity, you
Complete Sun Sight Reduction Procedure
 Caution...2 Usage...2 Conventions...2 Assumptions...2 Explanation...2 Sight #...2 DR Latitude/DR Longitude...2 Date...2 GMT/UT...3 Hs...3 D. R. I. P. S...3 Index Error...3 Complete Sun Sight Reduction
Caution...2 Usage...2 Conventions...2 Assumptions...2 Explanation...2 Sight #...2 DR Latitude/DR Longitude...2 Date...2 GMT/UT...3 Hs...3 D. R. I. P. S...3 Index Error...3 Complete Sun Sight Reduction
CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM
 Name Partner(s) Section Date CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM You have had the opportunity to look at two different tools to display the night sky, the celestial sphere and the star chart.
Name Partner(s) Section Date CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM You have had the opportunity to look at two different tools to display the night sky, the celestial sphere and the star chart.
Chapter 1: The World of Geography
 Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
COORDINATE SYSTEMS: LOCATING YOURSELF ON A SPHERE
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) COORDINATE SYSTEMS: LOCATING YOURSELF ON A SPHERE Activity 1: Getting Your Bearings 1. Close your eyes and point to the north. Did you point up? Why or why not? Up is the #1 answer.
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) COORDINATE SYSTEMS: LOCATING YOURSELF ON A SPHERE Activity 1: Getting Your Bearings 1. Close your eyes and point to the north. Did you point up? Why or why not? Up is the #1 answer.
Astronomy 50. Lab Manual
 Astronomy 50 Lab Manual Union College Spring 2008 Professor Koopmann Professor Wilkin 2 Astronomy 50 Lab Policies Spring 2008 Professor Koopmann, Professor Wilkin For this course, you are required to complete
Astronomy 50 Lab Manual Union College Spring 2008 Professor Koopmann Professor Wilkin 2 Astronomy 50 Lab Policies Spring 2008 Professor Koopmann, Professor Wilkin For this course, you are required to complete
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2
 MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
Physics Lab #4:! Starry Night Student Exercises I!
 Physics 10293 Lab #4: Starry Night Student Exercises I Introduction For today s lab, we are going to let the Starry Night software do much of the work for us. We re going to walk through some of the sample
Physics 10293 Lab #4: Starry Night Student Exercises I Introduction For today s lab, we are going to let the Starry Night software do much of the work for us. We re going to walk through some of the sample
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008
 Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
OCN 201. History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging
 OCN 201 History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging History of Settlement: Fiji by ~ 1300 BC Tonga by ~1100 BC Samoa and Marquesas by 500 BC By now there is a distinct Polynesian culture. Easter Island
OCN 201 History of Oceanography and Polynesian voyaging History of Settlement: Fiji by ~ 1300 BC Tonga by ~1100 BC Samoa and Marquesas by 500 BC By now there is a distinct Polynesian culture. Easter Island
Downloaded from
 I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
EOS 102: Dynamic Oceans Exercise 1: Navigating Planet Earth
 EOS 102: Dynamic Oceans Exercise 1: Navigating Planet Earth YOU MUST READ THROUGH THIS CAREFULLY! This exercise is designed to familiarize yourself with Google Earth and some of its basic functions while
EOS 102: Dynamic Oceans Exercise 1: Navigating Planet Earth YOU MUST READ THROUGH THIS CAREFULLY! This exercise is designed to familiarize yourself with Google Earth and some of its basic functions while
Students will explore Stellarium, an open-source planetarium and astronomical visualization software.
 page 22 STELLARIUM* OBJECTIVE: Students will explore, an open-source planetarium and astronomical visualization software. BACKGROUND & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This lab was generously provided by the Red Rocks
page 22 STELLARIUM* OBJECTIVE: Students will explore, an open-source planetarium and astronomical visualization software. BACKGROUND & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This lab was generously provided by the Red Rocks
Lab 2 Astronomical Coordinates, Time, Focal Length, Messier List and Open Clusters
 Lab 2 Astronomical Coordinates, Time, Focal Length, Messier List and Open Clusters Name: Partner(s): Boxes contain questions that you are expected to answer (in the box). You will also be asked to put
Lab 2 Astronomical Coordinates, Time, Focal Length, Messier List and Open Clusters Name: Partner(s): Boxes contain questions that you are expected to answer (in the box). You will also be asked to put
Cartesian Coordinates Need two dimensional system 2 number lines perpendicular to each other X-axis is horizontal Y-axis is vertical Position relative
 General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1
 MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
Chapter 6: Latitude by Noon Sight
 Chapter 6: Latitude by oon ight When the sun is crossing the meridian of the boat, it is straight south or north of the boat and at its highest altitude over the horizon for the day. The local meridian
Chapter 6: Latitude by oon ight When the sun is crossing the meridian of the boat, it is straight south or north of the boat and at its highest altitude over the horizon for the day. The local meridian
Where in the World? Plotting Latitude & Longitude
 Where in the World? Plotting Latitude & Longitude Background Because our planet is a sphere, we need two types of reference lines to locate positions on the Earth and to make accurate maps. These imaginary
Where in the World? Plotting Latitude & Longitude Background Because our planet is a sphere, we need two types of reference lines to locate positions on the Earth and to make accurate maps. These imaginary
Meridian Circle through Zenith, North Celestial Pole, Zenith Direction Straight Up from Observer. South Celestial Pole
 Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work- Effects of Latitude In chapters 3 and 4we will learn why our view of the heavens depends on our position on the Earth, the time of day, and the day of the year. We will
Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work- Effects of Latitude In chapters 3 and 4we will learn why our view of the heavens depends on our position on the Earth, the time of day, and the day of the year. We will
Astron 104 Laboratory #4 Orbital Motion of a Planet
 Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #4 Orbital Motion of a Planet Introduction The nature of the Solar System was first derived from careful measurements of the positions of the planets in the night
Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #4 Orbital Motion of a Planet Introduction The nature of the Solar System was first derived from careful measurements of the positions of the planets in the night
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
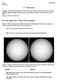 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
CHAPTER 20 SIGHT REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 20 SIGHT REDUCTION BASIC PRINCIPLES 2000. Introduction Reducing a celestial sight to obtain a line of position consists of six steps: 1. Correcting sextant altitude (hs) to obtain observed altitude
CHAPTER 20 SIGHT REDUCTION BASIC PRINCIPLES 2000. Introduction Reducing a celestial sight to obtain a line of position consists of six steps: 1. Correcting sextant altitude (hs) to obtain observed altitude
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography What is geography? Geography comes from the Greek word Geographia. Geo means earth and graphia means to describe or chart. Geographers study the earth in relation to space and
Introduction to Geography What is geography? Geography comes from the Greek word Geographia. Geo means earth and graphia means to describe or chart. Geographers study the earth in relation to space and
Butte County Fire Department
 Butte County Fire Department Basic Land Navigation Verification Sheet I verify that Print Supervisor s name has completed the Print Employee s name Basic Land Navigation self study guide on. Date Attached
Butte County Fire Department Basic Land Navigation Verification Sheet I verify that Print Supervisor s name has completed the Print Employee s name Basic Land Navigation self study guide on. Date Attached
Phys Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations
 Phys 10293 Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations Introduction Astronomers use a coordinate system that is fixed to Earth s latitude and longitude. This way, the coordinates of a star or planet are the
Phys 10293 Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations Introduction Astronomers use a coordinate system that is fixed to Earth s latitude and longitude. This way, the coordinates of a star or planet are the
Lesson 1 The View from Earth
 Lesson 1 The View from Earth Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 Math Skills 15 School to Home 16
Lesson 1 The View from Earth Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 Math Skills 15 School to Home 16
Gnomon (a thin, round stick at least a foot long and capable of being put into the ground or stood up vertically)
 Name: Partner(s): Lab #3 Celestial Navigation Due 7/2 Objectives In this lab you will take measurements of the sun s motion around noon and the north star s position in the sky. You will use this data
Name: Partner(s): Lab #3 Celestial Navigation Due 7/2 Objectives In this lab you will take measurements of the sun s motion around noon and the north star s position in the sky. You will use this data
DUMMIES guide to Astro-Navigation
 DUMMIES guide to Astro-Navigation The idea of this booklet is to give you the nuts and bolts in the process of gaining a position on your chart through celestial navigation without a deep understanding
DUMMIES guide to Astro-Navigation The idea of this booklet is to give you the nuts and bolts in the process of gaining a position on your chart through celestial navigation without a deep understanding
Cartography the art of making maps
 Cartography the art of making maps A map is a drawing or a picture of the earths surface, showing how things are related to each other by distance, direction and size. Maps are used for: Navigation Distance
Cartography the art of making maps A map is a drawing or a picture of the earths surface, showing how things are related to each other by distance, direction and size. Maps are used for: Navigation Distance
GPS Mapping. Teacher Instructions. Overview: Objectives: Materials: Answers to Student Worksheets:
 Overview: Scientists use Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers to map lava flows. GPS data are compiled by computer Geographic Information System (GIS) software into a digital map. Digital maps can
Overview: Scientists use Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers to map lava flows. GPS data are compiled by computer Geographic Information System (GIS) software into a digital map. Digital maps can
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
APPENDIX A GLOSSARY. Appendix A.1
 APPENDIX A GLOSSARY Appendix A.1 Appendix A.2 Back Bearing A back bearing is measured from the object to your position. It is the exact opposite of a direct bearing. Base Line An imaginary line on the
APPENDIX A GLOSSARY Appendix A.1 Appendix A.2 Back Bearing A back bearing is measured from the object to your position. It is the exact opposite of a direct bearing. Base Line An imaginary line on the
AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere
 AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere Name: Student number (SUID): Lab section: Group Members: 1 Introduction Following the prelab, you should be now acquainted
AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere Name: Student number (SUID): Lab section: Group Members: 1 Introduction Following the prelab, you should be now acquainted
Topic Guide: The Celestial Sphere. GCSE (9-1) Astronomy. Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0)
 Topic Guide: The Celestial Sphere GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0) The Celestial Sphere Contents Specification Points 1 The Astronomy 2 Equatorial coordinates
Topic Guide: The Celestial Sphere GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0) The Celestial Sphere Contents Specification Points 1 The Astronomy 2 Equatorial coordinates
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab
 Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Relative and Absolute Directions
 Relative and Absolute Directions Purpose Learning about latitude and longitude Developing math skills Overview Students begin by asking the simple question: Where Am I? Then they learn about the magnetic
Relative and Absolute Directions Purpose Learning about latitude and longitude Developing math skills Overview Students begin by asking the simple question: Where Am I? Then they learn about the magnetic
CHAPTER 24 THE SAILINGS
 CHAPTER 24 THE SAILINGS INTRODUCTION 2400. Introduction Dead reckoning involves the determination of one s present or future position by projecting the ship s course and distance run from a known position.
CHAPTER 24 THE SAILINGS INTRODUCTION 2400. Introduction Dead reckoning involves the determination of one s present or future position by projecting the ship s course and distance run from a known position.
2. What does the map scale tell the map reader? a ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the length given to that distance on a map
 AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4)
 Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy
 1 GEK1506 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2005 2006 GEK1506 Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy April/May 2006 Time allowed: 2 hours 1. After taking
1 GEK1506 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2005 2006 GEK1506 Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy April/May 2006 Time allowed: 2 hours 1. After taking
Astronomy 101 Lab Manual. Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora
 Astronomy 101 Lab Manual Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora victor.andersen@ccaurora.edu January 8, 2013 2 Contents 1 Angular Measures 5 1.1 Introduction............................ 5 1.1.1 Degrees,
Astronomy 101 Lab Manual Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora victor.andersen@ccaurora.edu January 8, 2013 2 Contents 1 Angular Measures 5 1.1 Introduction............................ 5 1.1.1 Degrees,
Into the Wide Blue Yonder HISTORY OF OCEAN EXPLORATION
 Into the Wide Blue Yonder HISTORY OF OCEAN EXPLORATION 3 MAIN REASONS FOR SEAFARING Food Trade Discovery of new land ANCIENT SEAFARING Biblically Noah s Ark and similar stories of floods: Not really out
Into the Wide Blue Yonder HISTORY OF OCEAN EXPLORATION 3 MAIN REASONS FOR SEAFARING Food Trade Discovery of new land ANCIENT SEAFARING Biblically Noah s Ark and similar stories of floods: Not really out
Observing the Night Sky: Locating Objects
 Observing the Night Sky: Locating Objects As I left the house this morning, there was a bright bluish light above and to the left of my neighbors house (approximately East) and a big very bright object
Observing the Night Sky: Locating Objects As I left the house this morning, there was a bright bluish light above and to the left of my neighbors house (approximately East) and a big very bright object
Last Time on Survey of Astronomy
 Last Time on Survey of Astronomy The big picture : The earth is: a single planet around a single star of hundreds of billions of stars. in a single galaxy of hundreds of billions of galaxies. The earth,
Last Time on Survey of Astronomy The big picture : The earth is: a single planet around a single star of hundreds of billions of stars. in a single galaxy of hundreds of billions of galaxies. The earth,
Physics Lab #5:! Starry Night Student Exercises II!
 Physics 10293 Lab #5: Starry Night Student Exercises II Introduction We will continue today exploring some of the useful applications of the Starry Night software to learn about motions in the sky. Step
Physics 10293 Lab #5: Starry Night Student Exercises II Introduction We will continue today exploring some of the useful applications of the Starry Night software to learn about motions in the sky. Step
Module 2: Mapping Topic 2 Content: Determining Latitude and Longitude Notes
 Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Earth Science Regents Reading Topographic Maps
 Earth Science Regents Reading Topographic Maps Name Period Quick Tutorial on Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds of Latitude and Longitude A degree of latitude on the surface of the earth is about 70 miles long.
Earth Science Regents Reading Topographic Maps Name Period Quick Tutorial on Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds of Latitude and Longitude A degree of latitude on the surface of the earth is about 70 miles long.
Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon
 Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon Based on Chapter 2 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 3 and 4 on The
Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon Based on Chapter 2 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 3 and 4 on The
Map and Compass Skills
 Map and Compass Skills Grade levels: 5-12 In a Nutshell Given a map and compass, students will be able to find a location on the map, chart a course to that location with the compass, and find that location
Map and Compass Skills Grade levels: 5-12 In a Nutshell Given a map and compass, students will be able to find a location on the map, chart a course to that location with the compass, and find that location
Map Skills Unit. Note taking unit
 Map Skills Unit Note taking unit Introduction To learn about the Earth, we are going to learn about two geographic tools you can use.globes and maps. Globe A globe is a round model of the planet Earth
Map Skills Unit Note taking unit Introduction To learn about the Earth, we are going to learn about two geographic tools you can use.globes and maps. Globe A globe is a round model of the planet Earth
Lab 2: Angles and other needed math (or the history of astronomy)
 Astronomy 101 Name(s): Lab 2: Angles and other needed math (or the history of astronomy) Purpose: This lab is an overview of much of the math skills you will need for this course. As I hope you will see
Astronomy 101 Name(s): Lab 2: Angles and other needed math (or the history of astronomy) Purpose: This lab is an overview of much of the math skills you will need for this course. As I hope you will see
Lecture 4: August 30, 2010
 Lecture 4: August 30, 2010 How many hospitals are there in the USA? Announcements: First homework has been posted Due Friday (10 th ) First Observatory Opportunity Thursday Night September 2, 8:30pm Will
Lecture 4: August 30, 2010 How many hospitals are there in the USA? Announcements: First homework has been posted Due Friday (10 th ) First Observatory Opportunity Thursday Night September 2, 8:30pm Will
Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN
 Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN I. The Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun A star always rises and sets at the same place on the horizon and, hence, it is above the horizon for the same
Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN I. The Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun A star always rises and sets at the same place on the horizon and, hence, it is above the horizon for the same
Name Class Date. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use each of the following terms in a separate sentence: year, month, day, astronomy, electromagnetic spectrum, constellation, and altitude. For each pair
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use each of the following terms in a separate sentence: year, month, day, astronomy, electromagnetic spectrum, constellation, and altitude. For each pair
Due to the fact that we are hurrying to get on the telescope this Tuesday, we will postpone the writing of a formal proposal.
 ASTRONOMY 221 SARA IMAGING EXERCISE Spring 2011 Observing Exercise 4 Introduction: The use of the SARA telescopes at Kitt Peak, Arizona and Cerro Tololo, Chile, permit us to observe fainter objects that
ASTRONOMY 221 SARA IMAGING EXERCISE Spring 2011 Observing Exercise 4 Introduction: The use of the SARA telescopes at Kitt Peak, Arizona and Cerro Tololo, Chile, permit us to observe fainter objects that
Office 307 Breshnahan Hall Phone: ext MT3121 CELESTIAL NAVIGATION II
 MT3121 CELESTIAL NAVIGATION II Learning Objective Celestial Navigation II will cover the requirements of the 1978 STCW convention as amended in 1995. The course covers the theory and practice of navigation
MT3121 CELESTIAL NAVIGATION II Learning Objective Celestial Navigation II will cover the requirements of the 1978 STCW convention as amended in 1995. The course covers the theory and practice of navigation
Global Positioning System (G.P.S.)
 Title: Global Positioning System (G.P.S.) (Navigation) Grade(s): 6-8 Introduction: The Global Positioning System (G.P.S.) Is a worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites
Title: Global Positioning System (G.P.S.) (Navigation) Grade(s): 6-8 Introduction: The Global Positioning System (G.P.S.) Is a worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites
Land Navigation Table of Contents
 Land Navigation Table of Contents Preparatory Notes to Instructor... 1 Session Notes... 5 Learning Activity: Grid Reference Four Figure... 7 Learning Activity: Grid Reference Six Figure... 8 Learning Activity:
Land Navigation Table of Contents Preparatory Notes to Instructor... 1 Session Notes... 5 Learning Activity: Grid Reference Four Figure... 7 Learning Activity: Grid Reference Six Figure... 8 Learning Activity:
Resources and Materials Promethean Board and Laptop for notes, Stellarium, and to record class discussion topics
 Photo by stillwellmike Resources and Materials Promethean Board and Laptop for notes, Stellarium, and to record class discussion topics Star trail photos Protractors Compass Pencils Paper Key Definitions
Photo by stillwellmike Resources and Materials Promethean Board and Laptop for notes, Stellarium, and to record class discussion topics Star trail photos Protractors Compass Pencils Paper Key Definitions
Tonight. {01} The map. Relative space. What does a map do? Types of maps GEOG 201 2/17/2010. Instructor: Pesses 1
 Tonight {01} The map What makes a map Measuring the Earth Map Interpretation & GPS Spring 2010 M. Pesses What does a map do? Shows where things are Shows spatial (topological) relationships Shows patterns,
Tonight {01} The map What makes a map Measuring the Earth Map Interpretation & GPS Spring 2010 M. Pesses What does a map do? Shows where things are Shows spatial (topological) relationships Shows patterns,
Local Coordinates. These are centered upon you, the observer.
 Astronomy 30, Observing #3 Name: Lab Partners: Date: Materials: This lab, with the star chart completed from the pre-lab. Some sheets of paper for sketches. A pencil with eraser. A small flashlight, ideally
Astronomy 30, Observing #3 Name: Lab Partners: Date: Materials: This lab, with the star chart completed from the pre-lab. Some sheets of paper for sketches. A pencil with eraser. A small flashlight, ideally
The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
