SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Christine Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE216 Recent intensification of wind-driven circulation in the Pacific and the ongoing warming hiatus (a) Observed wind trends 6N N 2N 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18E 12W 6W (b) IPO wind trends 6N N 2N 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18E 12W 6W (c) Observed minus IPO wind trends 6N N 2N 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18E 12W 6W Figure S1 Observed wind trends during (a) Observed trends in surface wind stress (N/m 2 /year) shown as vectors with the strength of the zonal wind stress trend overlaid in colour shading (N/m 2 /year). Maximum vector scale is indicated. (b) As in (a) but showing the wind stress trends derived from a regression of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation (IPO) index. (c) As in (a), but showing the component of the wind stress trends not accounted for by typical IPO variability (i.e., panel (a) minus panel (b)). The recent observed wind trends (panel (a)) are thus seen to be significantly stronger than those typically associated with the IPO (panel (b)). N/m 2 /year 1 Australian Research Council (ARC) Centre of Excellence for Climate System Science, The University of New South Wales, Sydney 252, Australia, 2 Climate Change Research Centre, University of New South Wales, Sydney, 252, Australia, 3 National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado 837, USA, International Pacific Research Center, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 1 Pope Road,Honolulu, Hawaii 96822, USA, 5 CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research, Station Street, Aspendale, Victoria 3195, Australia, 6 National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory, Seattle, Washington 98115, USA. * e- mail: M.England@unsw.edu.au NATURE CLIMATE CHANGE Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
2 (a) Surface u x 1e (b) Surface v 8 (c) 1-2m u x 1e x 1e (d) 1-2m v x 1e Figure S2 Recent Pacific basin upper ocean current trends estimated from an ocean reanalysis. The reanalysis product analyzed is the Simple Ocean Data Assimilation (SODA) retrospective analysis of the global ocean1. Trends are computed over all available SODA data since January 1992 (Jan Dec 28). The ocean current trends are shown at the surface (a,b) and averaged over depths 1-2m (c,d). The ocean velocity trends are shown as two components; (left) zonal velocity trends and (right) meridional velocity trends. Note the different velocity scales used in panels (b,d) to highlight the sign of the meridional velocity trends, including the increased divergence away from the Equator at the surface (panel b) and the recharge of heat toward the Equator at depth (panel d). Outside the tropics, velocity trend estimates are dominated by small-scale noise. Positive values indicate eastward flow (a,c) and northward flow (b,d). Units are m/s/year throughout. The circulation is shown depth averaged over 1-2m as observations are sparse in the ocean interior. (a) Observed surface air temperature trend 6N N 2N 2S S 6S (b) CMIP5 surface air temperature trend 6N N 2N 2S S 6S Figure S3 Observed trends in air temperature compared to CMIP5 projections. (a) Observed air temperature trends ( C/year) during (b) As in (a) but showing the air temperature trends in the multimodel ensemble mean of CMIP5 model simulations, using historical forcing up until 25 followed by the RCP.5 emissions scenario during (c) The difference between the observed air temperature trends ( C/year) during and those of the multi-model ensemble mean of CMIP5 model simulations (i.e., panel (a) minus panel (b)). Subtracting the model estimated air temperature response to anthropogenic forcing (b) from the trends (a) reveals the Pacific Ocean cooling signature even more strongly (c). (c) Observed minus CMIP5 6N N 2N 2S S 6S o C/year 21 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
3 (a) 2 m x 1e (b) 8 m x 1e 8 6 (c) 17 m 2 (d) 285 m Figure S Model upper ocean circulation anomalies due to the observed Pacific Ocean wind trends. Vectors show the ocean current trends at depths of (a) 2-m (b) 8-m (c) 17-m and (d) 285-m. The vector scale is indicated in each panel. Overlaid in colour are the meridional velocity trends, with a different colour scale used in panel (a). Units throughout are m/sec/year o C/year Figure S5 Model depth-integrated ocean circulation anomalies due to the observed Pacific Ocean wind trends. Contours show the depth-integrated stream-function trends spanning the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Contour interval is.1 Sv/year, with contours drawn at ±.5, ±.15, ±.25, ±.35, and ±.5 Sv/year. Solid (dashed) contours indicate a clockwise (anticlockwise) circulation. Overlaid in colour are the sea surface temperature trends in the model experiment including both historical CO 2 forcing and observed Pacific Ocean wind trends. Units are C/year. Apart from the changes in the equatorial circulation and tropical gyres (main text), note also the strengthened Indonesian Throughflow via the Sverdrup relation and Island Rule 2, and the enhanced Southern Hemisphere supergyre 3, particularly the Indian Ocean component including the Agulhas Current and its retroflection. 21 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
4 a) Trend ( ) o C/decade b) o S 3 o S 2 o S 1 o S o 1 o N 2 o N 3 o N o N Decadal trend difference < > o C/decade Figure S6 Zonally-averaged Pacific basin linear trend in potential temperature for the last two decades. (a) Latitude-depth zonal mean temperature trends averaged over five reanalysis products, with stippling used to indicate regions where all five reanalysis products agree on the sign of the trends. (b) Depth profiles of the difference in temperature trends between 2-21 compared to 199-2, summed over the tropics (1 N 1 S), averaged over five reanalysis products. Values to the right of the zero dashed line indicate greater warming in the 2 s compared to the 199 s. The cooling near the surface at the Equator has persisted since the 199 s consistent with the 2-year trade wind trends. Solid bold line in panel (b) refers to depths where at least four of the five reanalysis products agree on the sign of the trend difference. The red profile highlights the ORAS reanalysis, which also assimilates ERA interim winds. The reanalysis products include: (1) SODA 1 (Jan 1992 Dec 28), (2) ECMWF ORAS,5 (Jan 1992 Dec 29), (3) GFDL-ECDA 6 (Jan 1992 Dec 21), () ECCO-JPL (Jan 1993 Dec 211; and (5) NCEP-GODAS 7 (Jan 1992 Dec 211). Figure S7 Twenty-year trends in tropical Pacific winds vs. decadal trends in global surface air temperature (SAT) in observations and models. The global SAT trends are calculated over the last decade of each 2- year wind trend period; so for example, the wind stress trend for the 2-year period is plotted against the decadal SAT trend from Model trends are sampled during the period and observations from Only those CMIP5 model experiments that, like observations, include at least one hiatus decade during are shown, as defined by a negative decadal trend in global mean SAT. The wind stress trends are computed over the region 6 N 6 S and W, corresponding to where the Interdecadal 21 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
5 Pacific Oscillation (IPO) exhibits maximum regression onto Pacific Ocean wind stress. Wind stress is positive for westerly winds, so negative values indicate acceleration in the Pacific trade winds. A best-fit linear regression is shown separately for both observations and models, along with correlations and an associated significance level (p-value). Of the total of 3 model hiatus decades (SAT trend < ) simulated post 199, 26 occur during the last decade of a 2-year positive trend in Pacific trade winds. The observed and model correlations are significant at 99% confidence level. In contrast, the corresponding scatter plot shows little correlation when observed global SAT and Pacific wind trends are compared decade-by-decade. This suggests that the multi-decade Pacific trade wind trend has played a key role in the current hiatus, not just the most recent 1-yrs of Pacific winds. a) SAT trends (control) 6N N 2N o C/year.8. 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18 12W 6W b) SAT trends (wind trends) 6N N 2N 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18 12W 6W o C/year Figure S8 Average coupled climate model trends in surface air temperature during (a) In the 12-member control ensemble set wherein the ocean component feels the model s seasonal-mean cycle of Pacific winds over the latitude band 5 N 5 S. Elsewhere the ocean model is forced by the atmospheric GCM, which freely adjusts to the evolving ocean SST field. (b) In the wind trend 12-member ensemble set, which is identical to control, only with the additional wind anomaly imposed corresponding to the observed Pacific wind trends over As per control, this prescribed wind forcing is limited to the latitude band 5 N 5 S; elsewhere the ocean model is forced by the atmospheric GCM. Stippling indicates where the trend ensemble-means are statistically significant at the 95% confidence level given the linear-regression standard error over the period The significance of the trend ensemble-mean is evaluated using a two-tailed student t-test by first setting each trend sample to zero (i.e., no trend) if not greater than the 95% linear-regression standard error. The SAT trend patterns in the Pacific sector agree well with the observed (Fig. 2d), although the peak tropical cooling is slightly too large, and there are regions of cooling elsewhere in the tropics that do not match observed, such as in the Indian/Atlantic sectors. This could be due in part to the model s low climate sensitivity (see Methods), although another coupled model study 8 also simulates cooling over the Indian and Atlantic Oceans during the recent hiatus, which matches observations better for that part of the recent record. Note the different colour scales used above. 21 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
6 Figure S9 Observed range in 2-year trends in tropical Pacific trade winds compared to the range captured by CMIP5 models. In the top panel the ranges are shown separately during the periods (solid fill) and (solid + unfilled combined) to emphasize the anomalous nature of the recent observed trends. The lower panel shows the corresponding analysis using available preindustrial CMIP5 model runs. The observed and model wind stress trends are computed over the region 6 N 6 S and W, corresponding to where the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation (IPO) exhibits maximum regression onto Pacific Ocean wind stress. Wind stress is positive for westerly winds, so negative values indicate acceleration in the Pacific trade winds. The maximum observed Pacific trade wind acceleration occurs during (-.19 N/m 2 per year), indicated by the vertical dashed line, while the simulated maximum across 8 CMIP5 historical model experiments is generally less than half this magnitude. The symbol x denotes the simulated and observed model mean Pacific trade wind trend during (a) and (b) all available years (for observed this is ). No historical or preindustrial simulation ever captures 2-year Pacific wind trends at the magnitude of the recent observed trade wind acceleration. 21 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
7 Global mean SAT anomaly Global mean air temperature anomalies Observed 5 year running mean Model average warming (control) Model (contol + Pacific wind trend) Year Figure S1 Twentieth century annual average global air temperature anomalies compared with two model simulations during Observations are shown as annual values (grey bars) with the 5-year running mean superimposed (black solid line). The model simulation curves show (i) the average warming rate during in the control experiment with 2 th Century CO 2 forcing (red) and (ii) the impact of added wind stress anomalies between 5 S and 5 N in the Pacific Ocean following a regression of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation Index onto the ERA-interim wind climatology. The simulation suggests that interdecadal variations in Pacific winds contributed to part of the cooling during the first two decades of the hiatus ( ), but not to the latter part, during , when other processes dominated; foremost the large increase in post World War II aerosols 9,1. Thus both cooling due to external forcing (aerosols) and cooling due to variability in the IPO (which may be internally generated or externally forced) appear to have contributed to the mid-2 th Century hiatus in surface warming. References in Supplementary Material 1. Carton, J.A., G.A. Chepurin, X. Cao, and B. Giese, 2: A Simple Ocean Data Assimilation retrospective analysis of the global ocean Part I: Methodology, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 3, Godfrey, J. S., 1989: A Sverdrup model of the depthintegrated flow from the world ocean allowing for island circulations. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., 5, Cai, W. J., 26: Antarctic ozone depletion causes an intensification of the southern ocean super-gyre circulation. Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L3712, 1.129/25GL Balmaseda M.A., K. Mogensen, A. Weaver, 213: Evaluation of the ECMWF Ocean Reanalysis ORAS. Quart. J. Roy. Met. Soc., in press. 5. Mogensen, K., M.A. Balmaseda, A. Weaver, 212: The NEMOVAR ocean data assimilation system as implemented in the ECMWF ocean analysis for System. ECMWF Technical Memorandum pp. 6. Chang Y.-S., S. Zhang, A. Rosati, T. L. Delworth, and W. F. Stern, 212: An assessment of oceanic variability for from the GFDL ensemble coupled data assimilation. Clim. Dyn.,, Nishida, T, 211: Validation of the Global Ocean Data Assimilation System (GODAS) data in the NOAA National Centre for Environmental System (NCEP) by theory, comparative studies, applications and sea truth. IOTC-211-WPB Kosaka, Y., and S.-P. Xie, 213: Recent globalwarming hiatus tied to equatorial Pacific surface cooling. Nature, doi:1.138/nature Stott, P.A., et al., 2: External control of 2th century temperature by natural and anthropogenic forcings. Science, 29, Wilcox L. J., Highwood E. J. and Dunstone N. J., 213: The influence of anthropogenic aerosol on multi-decadal variations of historical global climate Environ. Res. Lett., 8, Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability
 Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability Gerald A. Meehl 1, Julie M. Arblaster 1,2, Cecilia M. Bitz 3, Christine T.Y. Chung 4, and Haiyan
Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability Gerald A. Meehl 1, Julie M. Arblaster 1,2, Cecilia M. Bitz 3, Christine T.Y. Chung 4, and Haiyan
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1353 Enhanced warming over the global subtropical western boundary currents Lixin Wu 1, Wenju Cai 2, Liping Zhang 1, Hisashi Nakamura 3, Axel Timmermann 4,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1353 Enhanced warming over the global subtropical western boundary currents Lixin Wu 1, Wenju Cai 2, Liping Zhang 1, Hisashi Nakamura 3, Axel Timmermann 4,
Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming
 Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming Gerald A. Meehl 1, Haiyan Teng 1, and Julie M. Arblaster 1,2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO 2. CAWCR,
Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming Gerald A. Meehl 1, Haiyan Teng 1, and Julie M. Arblaster 1,2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO 2. CAWCR,
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods and obtained
 Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods 1999 2013 and 1979 1998 obtained from ERA-interim. Vectors are horizontal wind at 850
Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods 1999 2013 and 1979 1998 obtained from ERA-interim. Vectors are horizontal wind at 850
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1530 Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. Annual tropical Atlantic SST anomalies (top
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1530 Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. Annual tropical Atlantic SST anomalies (top
Doing science with multi-model ensembles
 Doing science with multi-model ensembles Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Biological and Energy Research Regional and Global Climate Modeling Program Why use a multi-model ensemble
Doing science with multi-model ensembles Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Biological and Energy Research Regional and Global Climate Modeling Program Why use a multi-model ensemble
Climate Change Impacts on the Marine Environment
 Climate Change Impacts on the Marine Environment Ken Ridgway CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research Wealth from Oceans National Research Flagship www.csiro.au Acknowledgements Jeff Dunn, John Church, Katy
Climate Change Impacts on the Marine Environment Ken Ridgway CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research Wealth from Oceans National Research Flagship www.csiro.au Acknowledgements Jeff Dunn, John Church, Katy
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
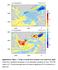 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Observed Trends in Wind Speed over the Southern Ocean
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051734, 2012 Observed s in over the Southern Ocean L. B. Hande, 1 S. T. Siems, 1 and M. J. Manton 1 Received 19 March 2012; revised 8 May 2012;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051734, 2012 Observed s in over the Southern Ocean L. B. Hande, 1 S. T. Siems, 1 and M. J. Manton 1 Received 19 March 2012; revised 8 May 2012;
Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.18/NCLIMATE2 Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming Shayne McGregor, Axel Timmermann, Malte F. Stuecker, Matthew H. England,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.18/NCLIMATE2 Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming Shayne McGregor, Axel Timmermann, Malte F. Stuecker, Matthew H. England,
Recent Walker Circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming
 Recent Walker Circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming Shayne McGregor 1, Axel Timmermann 2*, Malte F. Stuecker 3, Matthew H. England 1, Mark Merrifield 4, Fei-Fei Jin
Recent Walker Circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming Shayne McGregor 1, Axel Timmermann 2*, Malte F. Stuecker 3, Matthew H. England 1, Mark Merrifield 4, Fei-Fei Jin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction
 1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian Sea
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-017-0008-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-017-0008-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian
Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA
 27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA Andrew D. King Warmth in the east Indian Ocean increased the likelihood of the record wet July September in
27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA Andrew D. King Warmth in the east Indian Ocean increased the likelihood of the record wet July September in
Multidecadal variability in the transmission of ENSO signals to the Indian Ocean
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09706, doi:10.1029/2007gl029528, 2007 Multidecadal variability in the transmission of ENSO signals to the Indian Ocean G. Shi, 1 J. Ribbe,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09706, doi:10.1029/2007gl029528, 2007 Multidecadal variability in the transmission of ENSO signals to the Indian Ocean G. Shi, 1 J. Ribbe,
C
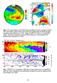 C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
Multiple Ocean Analysis Initialization for Ensemble ENSO Prediction using NCEP CFSv2
 Multiple Ocean Analysis Initialization for Ensemble ENSO Prediction using NCEP CFSv2 B. Huang 1,2, J. Zhu 1, L. Marx 1, J. L. Kinter 1,2 1 Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies 2 Department of Atmospheric,
Multiple Ocean Analysis Initialization for Ensemble ENSO Prediction using NCEP CFSv2 B. Huang 1,2, J. Zhu 1, L. Marx 1, J. L. Kinter 1,2 1 Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies 2 Department of Atmospheric,
Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2277 Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades Masato Mori 1*, Masahiro Watanabe 1, Hideo Shiogama 2, Jun Inoue 3,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2277 Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades Masato Mori 1*, Masahiro Watanabe 1, Hideo Shiogama 2, Jun Inoue 3,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 6, 515 520 Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3 XUE Feng 1, SUN Dan 2,3, and ZHOU Tian-Jun
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 6, 515 520 Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3 XUE Feng 1, SUN Dan 2,3, and ZHOU Tian-Jun
Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2820 Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss Kelly E. McCusker 1,2, John C. Fyfe 2 & Michael Sigmond 2 1 School
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2820 Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss Kelly E. McCusker 1,2, John C. Fyfe 2 & Michael Sigmond 2 1 School
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview
 The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
Assessing the Quality of Regional Ocean Reanalysis Data from ENSO Signals
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 55 61 Assessing the Quality of Regional Ocean Reanalysis Data from ENSO Signals WANG Lu 1, 2 and ZHOU Tian-Jun 1 1 State Key Laboratory of
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 55 61 Assessing the Quality of Regional Ocean Reanalysis Data from ENSO Signals WANG Lu 1, 2 and ZHOU Tian-Jun 1 1 State Key Laboratory of
The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models
 1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate
 Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate Shang- Ping Xie 1 & Yu Kosaka 2 1 Scripps Inst of Oceanogr, UCSD; 2 Univ of Tokyo Develop seasonal and spa
Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate Shang- Ping Xie 1 & Yu Kosaka 2 1 Scripps Inst of Oceanogr, UCSD; 2 Univ of Tokyo Develop seasonal and spa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2988 Hemispheric climate shifts driven by anthropogenic aerosol-cloud interactions Eui-Seok Chung and Brian
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2988 Hemispheric climate shifts driven by anthropogenic aerosol-cloud interactions Eui-Seok Chung and Brian
Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation S. Pfahl 1 *,P.A.O Gorman 2 and E. M. Fischer 1 Changes in extreme
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation S. Pfahl 1 *,P.A.O Gorman 2 and E. M. Fischer 1 Changes in extreme
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes
 High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global warming?
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042743, 2010 Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042743, 2010 Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific
 Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Sea level variability in the North Indian Ocean
 Sea level variability in the North Indian Ocean M. Ravichandran ESSO-National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR) (Ministry of Earth Sciences, Govt. of India) Goa mravi@ncaor.gov.in U.Srinivasu
Sea level variability in the North Indian Ocean M. Ravichandran ESSO-National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR) (Ministry of Earth Sciences, Govt. of India) Goa mravi@ncaor.gov.in U.Srinivasu
Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake
 Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia
 Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia I. Introduction To assess the impact of large-scale environmental conditions on tropical cyclone
Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia I. Introduction To assess the impact of large-scale environmental conditions on tropical cyclone
Case studies for initialized decadal hindcasts and predictions for the Pacific region
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053423, 2012 Case studies for initialized decadal hindcasts and predictions for the Pacific region Gerald A. Meehl 1 and Haiyan Teng 1 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053423, 2012 Case studies for initialized decadal hindcasts and predictions for the Pacific region Gerald A. Meehl 1 and Haiyan Teng 1 Received
Contents of this file
 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Future changes in tropical cyclone activity in high-resolution large-ensemble simulations Kohei Yoshida 1, Masato Sugi 1, Ryo Mizuta 1, Hiroyuki
Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Future changes in tropical cyclone activity in high-resolution large-ensemble simulations Kohei Yoshida 1, Masato Sugi 1, Ryo Mizuta 1, Hiroyuki
The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Climate Forecast Applications Network (CFAN)
 Forecast of 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Activity April 5, 2018 Summary CFAN s inaugural April seasonal forecast for Atlantic tropical cyclone activity is based on systematic interactions among ENSO, stratospheric
Forecast of 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Activity April 5, 2018 Summary CFAN s inaugural April seasonal forecast for Atlantic tropical cyclone activity is based on systematic interactions among ENSO, stratospheric
Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L24701, doi:10.1029/2006gl027655, 2006 Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon Riyu Lu, 1,2 Buwen Dong, 3 and Hui Ding 2,4 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L24701, doi:10.1029/2006gl027655, 2006 Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon Riyu Lu, 1,2 Buwen Dong, 3 and Hui Ding 2,4 Received
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis
 Extended abstract for the 3 rd WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis held in Tokyo, Japan, on Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis Yan Xue,
Extended abstract for the 3 rd WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis held in Tokyo, Japan, on Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis Yan Xue,
Initialized decadal climate predictions focusing on the Pacific Gerald Meehl
 Initialized decadal climate predictions focusing on the Pacific Gerald Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder Colorado Following Zhang, Wallace and Battisti (1997) the Interdecadal Pacific
Initialized decadal climate predictions focusing on the Pacific Gerald Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder Colorado Following Zhang, Wallace and Battisti (1997) the Interdecadal Pacific
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11784 Methods The ECHO-G model and simulations The ECHO-G model 29 consists of the 19-level ECHAM4 atmospheric model and 20-level HOPE-G ocean circulation model.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11784 Methods The ECHO-G model and simulations The ECHO-G model 29 consists of the 19-level ECHAM4 atmospheric model and 20-level HOPE-G ocean circulation model.
Tracking ocean heat uptake during the surface warming hiatus. 1. Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California, San Diego,
 1 Tracking ocean heat uptake during the surface warming hiatus 2 3 Wei Liu 1*, Shang-Ping Xie 1 and Jian Lu 2 4 5 6 7 8 1. Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California, San Diego, 9500
1 Tracking ocean heat uptake during the surface warming hiatus 2 3 Wei Liu 1*, Shang-Ping Xie 1 and Jian Lu 2 4 5 6 7 8 1. Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California, San Diego, 9500
Impact of atmospheric CO 2 doubling on the North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06602, doi:10.1029/2008gl037075, 2009 Impact of atmospheric CO 2 doubling on the North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water Hyun-Chul Lee 1,2 Received 19 December 2008;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06602, doi:10.1029/2008gl037075, 2009 Impact of atmospheric CO 2 doubling on the North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water Hyun-Chul Lee 1,2 Received 19 December 2008;
The ENSO s Effect on Eastern China Rainfall in the Following Early Summer
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 26, NO. 2, 2009, 333 342 The ENSO s Effect on Eastern China Rainfall in the Following Early Summer LIN Zhongda ( ) andluriyu( F ) Center for Monsoon System Research,
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 26, NO. 2, 2009, 333 342 The ENSO s Effect on Eastern China Rainfall in the Following Early Summer LIN Zhongda ( ) andluriyu( F ) Center for Monsoon System Research,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade?
 Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade? G. Bala Divecha Center for Climate Change Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore (Email: gbala@caos.iisc.ernet.in) On 27 September
Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade? G. Bala Divecha Center for Climate Change Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore (Email: gbala@caos.iisc.ernet.in) On 27 September
particular regional weather extremes
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE2271 Amplified mid-latitude planetary waves favour particular regional weather extremes particular regional weather extremes James A Screen and Ian Simmonds
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE2271 Amplified mid-latitude planetary waves favour particular regional weather extremes particular regional weather extremes James A Screen and Ian Simmonds
Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Intensification of Northern Hemisphere Subtropical Highs in a Warming Climate Wenhong Li, Laifang Li, Mingfang Ting, and Yimin Liu 1. Data and Methods The data used in this study consists of the atmospheric
Intensification of Northern Hemisphere Subtropical Highs in a Warming Climate Wenhong Li, Laifang Li, Mingfang Ting, and Yimin Liu 1. Data and Methods The data used in this study consists of the atmospheric
ECMWF: Weather and Climate Dynamical Forecasts
 ECMWF: Weather and Climate Dynamical Forecasts Medium-Range (0-day) Partial coupling Extended + Monthly Fully coupled Seasonal Forecasts Fully coupled Atmospheric model Atmospheric model Wave model Wave
ECMWF: Weather and Climate Dynamical Forecasts Medium-Range (0-day) Partial coupling Extended + Monthly Fully coupled Seasonal Forecasts Fully coupled Atmospheric model Atmospheric model Wave model Wave
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview
 Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. Human-Induced Change in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
 3068 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 18 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Human-Induced Change in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current JOHN C. FYFE AND OLEG A. SAENKO Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis,
3068 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 18 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Human-Induced Change in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current JOHN C. FYFE AND OLEG A. SAENKO Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis,
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
No pause in the increase of hot temperature extremes
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2145 No pause in the increase of hot temperature extremes Sonia I. Seneviratne 1, Markus G. Donat 2,3, Brigitte Mueller 4,1, and Lisa V. Alexander 2,3 1 Institute
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2145 No pause in the increase of hot temperature extremes Sonia I. Seneviratne 1, Markus G. Donat 2,3, Brigitte Mueller 4,1, and Lisa V. Alexander 2,3 1 Institute
The 1970 s shift in ENSO dynamics: A linear inverse model perspective
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 1612 1617, doi:1.12/grl.5264, 213 The 197 s shift in ENSO dynamics: A linear inverse model perspective Christopher M. Aiken, 1 Agus Santoso, 1 Shayne McGregor, 1 and
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 1612 1617, doi:1.12/grl.5264, 213 The 197 s shift in ENSO dynamics: A linear inverse model perspective Christopher M. Aiken, 1 Agus Santoso, 1 Shayne McGregor, 1 and
Surface ozone variability and the jet position: Implications for projecting future air quality
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 2839 2844, doi:10.1002/grl.50411, 2013 Surface ozone variability and the jet position: Implications for projecting future air quality Elizabeth A. Barnes 1 and Arlene
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 2839 2844, doi:10.1002/grl.50411, 2013 Surface ozone variability and the jet position: Implications for projecting future air quality Elizabeth A. Barnes 1 and Arlene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1189 Different magnitudes of projected subsurface ocean warming around Greenland and Antarctica Jianjun Yin 1*, Jonathan T. Overpeck 1, Stephen M. Griffies 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1189 Different magnitudes of projected subsurface ocean warming around Greenland and Antarctica Jianjun Yin 1*, Jonathan T. Overpeck 1, Stephen M. Griffies 2,
The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Outlook by JMA. Hiroyuki Sugimoto. El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
The North Atlantic Oscillation as a driver of rapid climate change in the Northern Hemisphere
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2738 The North Atlantic Oscillation as a driver of rapid climate change in the Northern Hemisphere Thomas L. Delworth, Fanrong Zeng, Gabriel A. Vecchi, Xiaosong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2738 The North Atlantic Oscillation as a driver of rapid climate change in the Northern Hemisphere Thomas L. Delworth, Fanrong Zeng, Gabriel A. Vecchi, Xiaosong
Forcing of anthropogenic aerosols on temperature trends of the subthermocline
 Forcing of anthropogenic aerosols on temperature trends of the subthermocline southern Indian Ocean Tim Cowan* 1,2, Wenju Cai 1, Ariaan Purich 1, Leon Rotstayn 1 and Matthew H. England 2 1 CSIRO Marine
Forcing of anthropogenic aerosols on temperature trends of the subthermocline southern Indian Ocean Tim Cowan* 1,2, Wenju Cai 1, Ariaan Purich 1, Leon Rotstayn 1 and Matthew H. England 2 1 CSIRO Marine
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT
 REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2017 2019 MEMBER STATE: Sweden.... 1 Principal InvestigatorP0F P: Wilhelm May... Affiliation: Address: Centre for Environmental and Climate Research, Lund University Sölvegatan
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2017 2019 MEMBER STATE: Sweden.... 1 Principal InvestigatorP0F P: Wilhelm May... Affiliation: Address: Centre for Environmental and Climate Research, Lund University Sölvegatan
Influence of eddy driven jet latitude on North Atlantic jet persistence and blocking frequency in CMIP3 integrations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045700, 2010 Influence of eddy driven jet latitude on North Atlantic jet persistence and blocking frequency in CMIP3 integrations Elizabeth A.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045700, 2010 Influence of eddy driven jet latitude on North Atlantic jet persistence and blocking frequency in CMIP3 integrations Elizabeth A.
Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model
 ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model E. Scoccimarro
ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model E. Scoccimarro
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate
 Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
Attribution of anthropogenic influence on seasonal sea level pressure
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L23709, doi:10.1029/2009gl041269, 2009 Attribution of anthropogenic influence on seasonal sea level pressure N. P. Gillett 1 and P. A.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L23709, doi:10.1029/2009gl041269, 2009 Attribution of anthropogenic influence on seasonal sea level pressure N. P. Gillett 1 and P. A.
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Cat Response
 2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution
 CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution Several `high-top models in CMIP5 Key question What are
CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution Several `high-top models in CMIP5 Key question What are
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why
 Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052006, 2012 The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models Seon Tae Kim 1 and Jin-Yi Yu 1 Received 12 April 2012; revised 14 May 2012; accepted 15 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052006, 2012 The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models Seon Tae Kim 1 and Jin-Yi Yu 1 Received 12 April 2012; revised 14 May 2012; accepted 15 May
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall?
 Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate
 SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate Chris Reason Oceanography Dept, Univ. Cape Town Overview of southern African climate and tropical Atlantic SST South American monsoon, Benguela
SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate Chris Reason Oceanography Dept, Univ. Cape Town Overview of southern African climate and tropical Atlantic SST South American monsoon, Benguela
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12310 We present here two additional Tables (Table SI-1, 2) and eight further Figures (Figures SI-1 to SI-8) to provide extra background information to the main figures of the paper.
doi:10.1038/nature12310 We present here two additional Tables (Table SI-1, 2) and eight further Figures (Figures SI-1 to SI-8) to provide extra background information to the main figures of the paper.
Significant changes to ENSO strength and impacts in the twenty-first century: Results from CMIP5
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052759, 2012 Significant changes to ENSO strength and impacts in the twenty-first century: Results from CMIP5 S. L. Stevenson 1 Received 14 June
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052759, 2012 Significant changes to ENSO strength and impacts in the twenty-first century: Results from CMIP5 S. L. Stevenson 1 Received 14 June
Atmospheric driving forces for the Agulhas Current in the subtropics
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15605, doi:10.1029/2007gl030200, 2007 Atmospheric driving forces for the Agulhas Current in the subtropics A. Fetter, 1 J. R. E. Lutjeharms,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15605, doi:10.1029/2007gl030200, 2007 Atmospheric driving forces for the Agulhas Current in the subtropics A. Fetter, 1 J. R. E. Lutjeharms,
ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L13711, doi:10.1029/2005gl025653, 2006 ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling Sang-Wook Yeh, 1 Young-Gyu Park, 1 and Ben
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L13711, doi:10.1029/2005gl025653, 2006 ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling Sang-Wook Yeh, 1 Young-Gyu Park, 1 and Ben
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
AMOC Impacts on Climate
 AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Moving from Global to Regional Projections of Climate Change
 Moving from Global to Regional Projections of Climate Change Mat Collins College of Engineering, Mathematics and Physical Sciences, University of Exeter, UK Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Joint Met Office
Moving from Global to Regional Projections of Climate Change Mat Collins College of Engineering, Mathematics and Physical Sciences, University of Exeter, UK Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Joint Met Office
The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051977, 2012 The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle Harry van Loon 1,2 and Gerald A. Meehl 1 Received 9 April 2012;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051977, 2012 The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle Harry van Loon 1,2 and Gerald A. Meehl 1 Received 9 April 2012;
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Downscaling Global Warming with a Regional Ocean- Atmosphere Model over the Tropical Atlantic
 Downscaling Global Warming with a Regional Ocean- Atmosphere Model over the Tropical Atlantic Role of equatorial ocean dynamics: equatorial upwelling and ocean mesoscale variability Hyodae Seo and Shang-Ping
Downscaling Global Warming with a Regional Ocean- Atmosphere Model over the Tropical Atlantic Role of equatorial ocean dynamics: equatorial upwelling and ocean mesoscale variability Hyodae Seo and Shang-Ping
Data assimilation for ocean climate studies
 Data assimilation for ocean climate studies James Carton, Gennady Chepurin, Steven Penny, and David Behringer (thanks Eugenia) University of Maryland, NOAA/NCEP, College Park, MD USA Chl concentration
Data assimilation for ocean climate studies James Carton, Gennady Chepurin, Steven Penny, and David Behringer (thanks Eugenia) University of Maryland, NOAA/NCEP, College Park, MD USA Chl concentration
Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3275 Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target Jianping Huang 1 *, Haipeng Yu 1,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3275 Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target Jianping Huang 1 *, Haipeng Yu 1,
GPC Exeter forecast for winter Crown copyright Met Office
 GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
