Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations. Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State
|
|
|
- Rosalind Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State
2 The Big Picture We ve found > 3000 planets, and counting. Earth s place in the Universe... We re measuring their properties. (Mass, radius, atmospheres, orbits, host stars, ) Habitable exoplanets?... so what s the physics involved? (How do they form, interact with their surroundings, change via which physical processes?)
3 The Big Picture 0 exoplanets.org 7/2/206 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] The Observed Population... so what s the physics involved? (How do they form, interact with their surroundings, change via which physical processes?)
4 The Big Picture 0 exoplanets.org 7/2/206 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Deterministic planet formation model with physical parameters α (disk mass, viscosity ): f(m,p, α) 0. Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] The Observed Population
5 The Big Picture Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Deterministic planet formation model with physical parameters α (disk mass, viscosity ): f(m,p, α) 0. Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] exoplanets.org 7/2/206 The Observed Population From the outset: ) distributions of planet properties, 2) inference on α, 3) model comparison (f vs f2 vs f3).
6 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] The Big Picture Deterministic planet formation model with physical parameters α (disk mass, viscosity ): f(m,p, α) 0. Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] exoplanets.org 7/2/206 The Observed Population From the outset: ) distributions of planet properties, 2) inference on α, 3) model comparison (f vs f2 vs f3). Straightforward, right?
7 Large Measurement Uncertainty Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, exoplanets.org 7/2/206 The Observed Population f(mtrue,ptrue, α) From the outset: ) distributions of planet properties, 2) inference on α, 3) model comparison (f vs f2 vs f3).
8 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Large Measurement Uncertainty Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, exoplanets.org 7/2/206 The Observed Population Multiple levels hierarchical modeling f(mtrue,ptrue, α) From the outset: ) distributions of planet properties, 2) inference on α, 3) model comparison (f vs f2 vs f3).
9 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Large Measurement Uncertainty Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, exoplanets.org 7/2/206 Bayesian The Observed Population Multiple levels hierarchical modeling f(mtrue,ptrue, α) From the outset: ) distributions of planet properties, 2) inference on α, 3) model comparison (f vs f2 vs f3).
10 What is Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling (HBM)? Arises naturally when want to make scientific inferences about a population based on many individuals. Regular Bayes: p(θ x) p(x θ) p(θ) posterior likelihood prior What is the probability that θ has some value, given the data? Parameters Observables Hierarchical Bayes: p(α,θ x) p(x θ,α) p(θ α) p(α) posterior likelihood prior Population Parameters Individual Parameters Mtrue, Ptrue, Observables Mobs, Pobs,
11 HBM for Exoplanets Hogg et al. 200 (orbital eccentricities) Morton & Winn, 204 Campante et al. 206 (angle between stellar spin & planet s orbit) Foreman-Mackey et al, 204 (Kepler occurrence rates) Demory 204 (geometric albedos) Rogers 205 (rocky-gaseous transition) Wolfgang & Lopez, 205 (super-earth composition distribution) Shabram et al. 206 (short-period eccentricity distribution) Wolfgang, Rogers, & Ford, 206 Chen & Kipping, submitted (mass-radius relationship) 203 SAMSI workshop on analyzing Kepler data All are some variation on this 3-level structure: (from Wolfgang et al. 206)
12 HBM for Exoplanets Hogg et al. 200 (orbital eccentricities) Morton & Winn, 204 Campante et al. 206 (angle between stellar spin & planet s orbit) Foreman-Mackey et al, 204 (Kepler occurrence rates) Demory 204 (geometric albedos) Rogers 205 (rocky-gaseous transition) Wolfgang & Lopez, 205 (super-earth composition distribution) Shabram et al. 206 (short-period eccentricity distribution) Wolfgang, Rogers, & Ford, 206 Chen & Kipping, submitted (mass-radius relationship) Already have posteriors for the observables? Can use importance sampling in multi-level models (Hogg et al. 200) More recently: full HBM using JAGS or own hierarchical MCMC code; many people moving to STAN
13 Example: Planet HBM Results Mass-radius relation : Wolfgang, Rogers, & Ford, 206 Best Fit M R Relations By Mass Radius Measurement Range of Input Method Data By Mass (M Earth ) <.6 R Earth < 4 R Earth < 8 R Earth Weiss & Marcy, 204 Power law Index γ Intrinsic Scatter σ M (M Earth ) Radius (R Earth ) RV_only TTV_dynamical_fits Weiss_dataset Weiss & Marcy, Constant C (M Earth ) Power law Index γ Intrinsic Scatter σ M (M Earth ) < RV_only.6 R Earth TTV_dynamical_fits < 4 R Earth Weiss_dataset < 8 R Earth Weiss & Marcy, Constant C (M Earth ) 0
14 Example: Planet HBM Results Mass-radius relation : Wolfgang, Rogers, & Ford, 206 Best Fit M R Relations By Mass Radius Measurement Range of Input Method Data By Mass (M Earth ) <.6 R Earth < 4 R Earth < 8 R Earth Weiss & Marcy, 204 Power law Index γ Intrinsic Scatter σ M (M Earth ) Radius (R Earth ) RV_only TTV_dynamical_fits Weiss_dataset Weiss & Marcy, 204 So what s next? Constant C (M Earth ) Power law Index γ Intrinsic Scatter σ M (M Earth ) < RV_only.6 R Earth TTV_dynamical_fits < 4 R Earth Weiss_dataset < 8 R Earth Weiss & Marcy, Constant C (M Earth ) 0
15 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Now: BIC, qualitative On the Theory Side 0. Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, exoplanets.org 7/2/206 The Observed Population f(mtrue,ptrue, α) Next: Nested Sampling? Need your help! There are many competing theories; like to quantitatively compare which is a better fit to data.
16 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] More on the Theory Side Now: parametric functions, little theory 0. Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, exoplanets.org 7/2/206 The Observed Population f(mtrue,ptrue, α) Next: incorporate emulator functions Planet formation is complicated, and f(m α) involves expensive computer simulations.
17 Emulators: An example Sub-Neptune compositions: Wolfgang & Lopez, 205 Wanted to understand BOTH: Population-wide Distributions Internal Structure Models Likelihood - compositions of individual super-earths (fraction of mass in a gaseous envelope: fenv) - the distribution of this composition parameter over the Kepler population (μ, σ). Now: internal structure models described by power laws Next: internal structure models described by nonparametric/ marginally parametric distributions
18 On the Data Side 0 Harder exoplanets.org 7/2/206 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Harder Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, Harder The Observed Population f(mtrue,ptrue, α)
19 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] 0 Harder Now: ignore p(detect) or cut stellar sample On the Data Side Harder 0. Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, exoplanets.org 7/2/206 Harder The Observed Population f(mtrue,ptrue, α) Next: characterize and include p(detect) Non-trivial detection functions are present in the observed population
20 Example: Including p(det) Kepler occurrence rates: Foreman-Mackey et al. 204 p(det) characterized by injecting synthetic transit signals in data and running detection algorithm on them (Petigura et al. 204) Grid of recovery fraction vs. radius and period Incorporated with inferred occurrence rate (Poisson point process)
21 Example: Including p(det) Kepler occurrence rates: Foreman-Mackey et al. 204 p(det) characterized by injecting synthetic transit signals in data and running detection algorithm on them (Petigura et al. 204) But p(det) not always known... or even characterizable! Grid of recovery fraction vs. radius and period Incorporated with inferred occurrence rate (Poisson point process)
22 More on the Data Side Mass, radius, period is not what we actually observe, and current likelihoods p(mobs Mtrue) very simple 0 Harder exoplanets.org 7/2/206 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Harder Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, Harder The Observed Population f(mtrue,ptrue, α)
23 More on the Data Side Mass, radius, period is not what we actually observe, and current likelihoods p(mobs Mtrue) very simple 0 Harder exoplanets.org 7/2/206 Next: inference on population directly from RVs vs. time, flux vs. time Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Harder Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days] Mtrue, Ptrue, Harder The Observed Population f(mtrue,ptrue, α)
24 Even more on the Data Side But we don t actually observe RVs vs. time or flux vs. time either... our real data is light on a detector 0 exoplanets.org 7/2/206 Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] Mass of Star [Solar Mass] Orbital Period [Days]
25 Even more on the Data Side But we don t actually observe RVs vs. time or flux vs. time either... our real data is light on a detector Next next: > 3 level HBMs, inference straight from the actual data Planet Mass [Jupiter Mass] exoplanets.org 7/2/ Orbital Period [Days] 0. Mass of Star [Solar Mass]
26 Next: Super-Earth Compositions Understanding selection effects in mass-radius space: Wolfgang, Jontof-Hutter, & Ford, in prep. figure courtesy of Daniel Jontof-Hutter But how exactly to evaluate the hierarchical model with unknown number of non-detections?
27 Next: Super-Earth Compositions Characterizing Joint Mass-Radius-Flux Distribution: Wolfgang, Jontof-Hutter, Rogers & Ford, in prep.
28 Next: Super-Earth Compositions Characterizing Joint Mass-Radius-Flux Distribution: Wolfgang, Jontof-Hutter, Rogers & Ford, in prep. Fc But many options for parameterizations hierarchical model comparisons? Poisson point process?
29 Next: Super-Earth Compositions Initial Sub-Neptune compositions: Wolfgang & Lopez, in prep. Population-wide Distributions Internal Structure Models Likelihood Need emulator function more accurate than power laws but still computationally easy.
30 Summary: Where we are: ~ a dozen exoplanet astronomers working on very simple hierarchical models describing distributions of planet properties Where we can go this year at SAMSI: ) Incorporate survey detection efficiency 2) Develop emulator functions to include computationally expensive theoretical simulations directly into HBM 3) Compare different theoretical models via hierarchical model comparison 4) Implement more realistic likelihoods: inference from lower-level data
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations
 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations You ve found planets in your data (or not)...... now what?! Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State Why Astrostats? This week: a sample of
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations You ve found planets in your data (or not)...... now what?! Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State Why Astrostats? This week: a sample of
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling
 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling Making scientific inferences about a population based on many individuals Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State Astronomical Populations Once we discover an
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling Making scientific inferences about a population based on many individuals Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State Astronomical Populations Once we discover an
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling
 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling Making scientific inferences about a population based on many individuals Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State Astronomical Populations Once we discover an
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling Making scientific inferences about a population based on many individuals Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State Astronomical Populations Once we discover an
Future Opportunities for Collaborations: Exoplanet Astronomers & Statisticians
 Future Opportunities for Collaborations: Exoplanet Astronomers & Statisticians Eric B. Ford Penn State Astronomy & Astrophysics Center for Astrostatistics Center for Exoplanets & Habitable Worlds Institute
Future Opportunities for Collaborations: Exoplanet Astronomers & Statisticians Eric B. Ford Penn State Astronomy & Astrophysics Center for Astrostatistics Center for Exoplanets & Habitable Worlds Institute
Convergence Diagnostics For Markov chain Monte Carlo. Eric B. Ford (Penn State) Bayesian Computing for Astronomical Data Analysis June 9, 2017
 Convergence Diagnostics For Markov chain Monte Carlo Eric B. Ford (Penn State) Bayesian Computing for Astronomical Data Analysis June 9, 2017 MCMC: A Science & an Art Science: If your algorithm is designed
Convergence Diagnostics For Markov chain Monte Carlo Eric B. Ford (Penn State) Bayesian Computing for Astronomical Data Analysis June 9, 2017 MCMC: A Science & an Art Science: If your algorithm is designed
Search for & Characterizing Small Planets with NASA s Kepler Mission
 Search for & Characterizing Small Planets with NASA s Kepler Mission Eric Ford University of Florida SAMSI Astrostatistics Workshop September 21, 2012 Image credit: NASA/ESA/StSci Golden Age for Planet
Search for & Characterizing Small Planets with NASA s Kepler Mission Eric Ford University of Florida SAMSI Astrostatistics Workshop September 21, 2012 Image credit: NASA/ESA/StSci Golden Age for Planet
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 3 Sep 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 3 Sep 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 3 Sep 2014](/thumbs/86/94158400.jpg) Exoplanet population inference and the abundance of Earth analogs from noisy, incomplete catalogs Daniel Foreman-Mackey 1,2, David W. Hogg 2,3,4, Timothy D. Morton 5 ABSTRACT arxiv:1406.3020v2 [astro-ph.ep]
Exoplanet population inference and the abundance of Earth analogs from noisy, incomplete catalogs Daniel Foreman-Mackey 1,2, David W. Hogg 2,3,4, Timothy D. Morton 5 ABSTRACT arxiv:1406.3020v2 [astro-ph.ep]
Kepler s Multiple Planet Systems
 Kepler s Multiple Planet Systems TITech & Kobe Univ. February 2018 Jack J. Lissauer NASA Ames Outline Solar System & Exoplanets Kepler Mission Kepler planets and planetery systems Principal Kepler findings
Kepler s Multiple Planet Systems TITech & Kobe Univ. February 2018 Jack J. Lissauer NASA Ames Outline Solar System & Exoplanets Kepler Mission Kepler planets and planetery systems Principal Kepler findings
EXONEST The Exoplanetary Explorer. Kevin H. Knuth and Ben Placek Department of Physics University at Albany (SUNY) Albany NY
 EXONEST The Exoplanetary Explorer Kevin H. Knuth and Ben Placek Department of Physics University at Albany (SUNY) Albany NY Kepler Mission The Kepler mission, launched in 2009, aims to explore the structure
EXONEST The Exoplanetary Explorer Kevin H. Knuth and Ben Placek Department of Physics University at Albany (SUNY) Albany NY Kepler Mission The Kepler mission, launched in 2009, aims to explore the structure
The California-Kepler Survey. III. A Gap in the Radius Distribution of Small Planets
 The California-Kepler Survey. III. A Gap in the Radius Distribution of Small Planets BJ Fulton, Erik Petigura, Andrew Howard, Howard Isaacson, Geoffrey Marcy, Phillip Cargile, Leslie Hebb, Lauren Weiss,
The California-Kepler Survey. III. A Gap in the Radius Distribution of Small Planets BJ Fulton, Erik Petigura, Andrew Howard, Howard Isaacson, Geoffrey Marcy, Phillip Cargile, Leslie Hebb, Lauren Weiss,
The Kepler Catalog A Tale of Evaporation
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. report_corrected c ESO 2016 September 2, 2016 The Kepler Catalog A Tale of Evaporation Corentin C. Cadiou, 1 James E. Owen 2 and Fred C. Adams 3 1 Sorbonne Universités,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. report_corrected c ESO 2016 September 2, 2016 The Kepler Catalog A Tale of Evaporation Corentin C. Cadiou, 1 James E. Owen 2 and Fred C. Adams 3 1 Sorbonne Universités,
Super-Earths as Failed Cores in Orbital Migration Traps
 Super-Earths as Failed Cores in Orbital Migration Traps Yasuhiro Hasegawa (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology) Hasegawa 2016, ApJ, 832, 83 Copyright 2017. All rights reserved.
Super-Earths as Failed Cores in Orbital Migration Traps Yasuhiro Hasegawa (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology) Hasegawa 2016, ApJ, 832, 83 Copyright 2017. All rights reserved.
Probabilistic modeling and Inference in Astronomy
 Probabilistic modeling and Inference in Astronomy Dan Foreman-Mackey Sagan Fellow, University of Washington github.com/dfm // @exoplaneteer // dfm.io Dan Foreman-Mackey Sagan Fellow, University of Washington
Probabilistic modeling and Inference in Astronomy Dan Foreman-Mackey Sagan Fellow, University of Washington github.com/dfm // @exoplaneteer // dfm.io Dan Foreman-Mackey Sagan Fellow, University of Washington
Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Department of Statistics The University of Auckland https://www.stat.auckland.ac.nz/~brewer/ Emphasis I will try to emphasise the underlying ideas of the methods. I will not be teaching specific software
Department of Statistics The University of Auckland https://www.stat.auckland.ac.nz/~brewer/ Emphasis I will try to emphasise the underlying ideas of the methods. I will not be teaching specific software
Update on SysSim: Determining the Distribution of Exoplanetary Architectures
 Update on SysSim: Determining the Distribution of Exoplanetary Architectures Darin Ragozzine (UF / Florida Tech), Eric Ford (UF / Penn State) ExoStats 2014 CMU June 19, 2014 Invitation to Join BayCEP Bayesian
Update on SysSim: Determining the Distribution of Exoplanetary Architectures Darin Ragozzine (UF / Florida Tech), Eric Ford (UF / Penn State) ExoStats 2014 CMU June 19, 2014 Invitation to Join BayCEP Bayesian
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Sep 2005
 For publication in Bayesian Inference and Maximum Entropy Methods, San Jose 25, K. H. Knuth, A. E. Abbas, R. D. Morris, J. P. Castle (eds.), AIP Conference Proceeding A Bayesian Analysis of Extrasolar
For publication in Bayesian Inference and Maximum Entropy Methods, San Jose 25, K. H. Knuth, A. E. Abbas, R. D. Morris, J. P. Castle (eds.), AIP Conference Proceeding A Bayesian Analysis of Extrasolar
Probabilistic Catalogs and beyond...
 Department of Statistics The University of Auckland https://www.stat.auckland.ac.nz/ brewer/ Probabilistic catalogs So, what is a probabilistic catalog? And what s beyond? Finite Mixture Models Finite
Department of Statistics The University of Auckland https://www.stat.auckland.ac.nz/ brewer/ Probabilistic catalogs So, what is a probabilistic catalog? And what s beyond? Finite Mixture Models Finite
Characterizing Small Planets via Spectroscopy of their Host Stars Johanna Teske in collaboration with
 Characterizing Small Planets via Spectroscopy of their Host Stars Johanna Teske in collaboration with Robert Wilson, Steven Majewski, Katia Cunha, Verne Smith, Diogo Souto, Chad Bender, Suvrath Mahadevan,
Characterizing Small Planets via Spectroscopy of their Host Stars Johanna Teske in collaboration with Robert Wilson, Steven Majewski, Katia Cunha, Verne Smith, Diogo Souto, Chad Bender, Suvrath Mahadevan,
Statistical Tools and Techniques for Solar Astronomers
 Statistical Tools and Techniques for Solar Astronomers Alexander W Blocker Nathan Stein SolarStat 2012 Outline Outline 1 Introduction & Objectives 2 Statistical issues with astronomical data 3 Example:
Statistical Tools and Techniques for Solar Astronomers Alexander W Blocker Nathan Stein SolarStat 2012 Outline Outline 1 Introduction & Objectives 2 Statistical issues with astronomical data 3 Example:
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 5 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 5 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 5 Oct 2018](/thumbs/87/96791169.jpg) Planet Occurrence Rate Density Models Including Stellar Effective Temperature Daniel Garrett arxiv:1810.02847v1 [astro-ph.ep] 5 Oct 2018 Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Cornell University,
Planet Occurrence Rate Density Models Including Stellar Effective Temperature Daniel Garrett arxiv:1810.02847v1 [astro-ph.ep] 5 Oct 2018 Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Cornell University,
Observational Cosmology Journal Club
 Observational Cosmology Journal Club 07/09/2018 Shijie Wang 1. Heller, R. (2018). Formation of hot Jupiters through disk migration and evolving stellar tides. Retrieved from arxiv.1806.06601 2. Rey, J.,
Observational Cosmology Journal Club 07/09/2018 Shijie Wang 1. Heller, R. (2018). Formation of hot Jupiters through disk migration and evolving stellar tides. Retrieved from arxiv.1806.06601 2. Rey, J.,
Imprints of Formation on Exoplanets
 Imprints of Formation on Exoplanets The role of Stellar Mass and Metallicity ILARIA PASCUCCI Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, Department of Planetary Sciences The University of Arizona https://almascience.nrao.edu/alma-science/planet-forming-disks
Imprints of Formation on Exoplanets The role of Stellar Mass and Metallicity ILARIA PASCUCCI Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, Department of Planetary Sciences The University of Arizona https://almascience.nrao.edu/alma-science/planet-forming-disks
Occurrence of 1-4 REarth Planets Orbiting Sun-Like Stars
 Occurrence of 1-4 REarth Planets Orbiting Sun-Like Stars Geoff Marcy, Erik Petigura, Andrew Howard Planet Density vs Radius + Collaborators: Lauren Weiss, Howard Isaacson, Rea Kolbl, Lea Hirsch Thanks
Occurrence of 1-4 REarth Planets Orbiting Sun-Like Stars Geoff Marcy, Erik Petigura, Andrew Howard Planet Density vs Radius + Collaborators: Lauren Weiss, Howard Isaacson, Rea Kolbl, Lea Hirsch Thanks
Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry. Exoplanets
 Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry Exoplanets Outline What is an exoplanet? Why are they interesting? How can we find them? Exolife?? The future... Jon Thaler Exoplanets 2 What is an Exoplanet? Most
Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry Exoplanets Outline What is an exoplanet? Why are they interesting? How can we find them? Exolife?? The future... Jon Thaler Exoplanets 2 What is an Exoplanet? Most
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets. Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017
 Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
GJ 436. Michaël Gillon (Geneva)
 Michaël Gillon (Geneva) Michelson Summer Workshop - July 25, 2007 2004: first hot Neptunes detected by radial velocity Among them: b (Butler et al. 2004, Maness et al. 2007) M * ~ 0.44 M Sun (M2.5V) R
Michaël Gillon (Geneva) Michelson Summer Workshop - July 25, 2007 2004: first hot Neptunes detected by radial velocity Among them: b (Butler et al. 2004, Maness et al. 2007) M * ~ 0.44 M Sun (M2.5V) R
Exoplanets: a dynamic field
 Exoplanets: a dynamic field Alexander James Mustill Amy Bonsor, Melvyn B. Davies, Boris Gänsicke, Anders Johansen, Dimitri Veras, Eva Villaver The (transiting) exoplanet population Solar System Hot Jupiters:
Exoplanets: a dynamic field Alexander James Mustill Amy Bonsor, Melvyn B. Davies, Boris Gänsicke, Anders Johansen, Dimitri Veras, Eva Villaver The (transiting) exoplanet population Solar System Hot Jupiters:
Parameter Estimation. William H. Jefferys University of Texas at Austin Parameter Estimation 7/26/05 1
 Parameter Estimation William H. Jefferys University of Texas at Austin bill@bayesrules.net Parameter Estimation 7/26/05 1 Elements of Inference Inference problems contain two indispensable elements: Data
Parameter Estimation William H. Jefferys University of Texas at Austin bill@bayesrules.net Parameter Estimation 7/26/05 1 Elements of Inference Inference problems contain two indispensable elements: Data
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling with Approximate Bayesian Computation
 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling with Approximate Bayesian Computation Jessi Cisewski Carnegie Mellon University June 2014 Goal of lecture Bring the ideas of Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling (HBM), Approximate
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling with Approximate Bayesian Computation Jessi Cisewski Carnegie Mellon University June 2014 Goal of lecture Bring the ideas of Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling (HBM), Approximate
ICML Scalable Bayesian Inference on Point processes. with Gaussian Processes. Yves-Laurent Kom Samo & Stephen Roberts
 ICML 2015 Scalable Nonparametric Bayesian Inference on Point Processes with Gaussian Processes Machine Learning Research Group and Oxford-Man Institute University of Oxford July 8, 2015 Point Processes
ICML 2015 Scalable Nonparametric Bayesian Inference on Point Processes with Gaussian Processes Machine Learning Research Group and Oxford-Man Institute University of Oxford July 8, 2015 Point Processes
Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology
 Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology A. Sozzetti INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino Detection/Characterization Detection (Visible): - Doppler spectroscopy (95%) -
Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology A. Sozzetti INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino Detection/Characterization Detection (Visible): - Doppler spectroscopy (95%) -
Multiplanet Systems as Laboratories for Planet Formation
 Multiplanet Systems as Laboratories for Planet Formation Lauren Weiss Parrent Fellow IfA, University of Hawaii Treasure Island California-Kepler Survey (CKS) Keck/HIRES Spectra of 1305 Kepler Planet-hosting
Multiplanet Systems as Laboratories for Planet Formation Lauren Weiss Parrent Fellow IfA, University of Hawaii Treasure Island California-Kepler Survey (CKS) Keck/HIRES Spectra of 1305 Kepler Planet-hosting
Extrasolar planets and their hosts: Why exoplanet science needs X-ray observations
 Extrasolar planets and their hosts: Why exoplanet science needs X-ray observations Dr. Katja Poppenhaeger Sagan Fellow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Exoplanets Exoplanets in 2005 (from the
Extrasolar planets and their hosts: Why exoplanet science needs X-ray observations Dr. Katja Poppenhaeger Sagan Fellow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Exoplanets Exoplanets in 2005 (from the
Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara
 A Diversity of Worlds: Toward a Theoretical Framework for the Structures of Planetary Systems Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara Strange New Worlds. Slide credit: Scott Gaudi ~1500
A Diversity of Worlds: Toward a Theoretical Framework for the Structures of Planetary Systems Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara Strange New Worlds. Slide credit: Scott Gaudi ~1500
Orbital Obliquities of Small Planets from CHARA Stellar Diameters
 Orbital Obliquities of Small Planets from CHARA Stellar Diameters Samuel Quinn & Russel White Georgia State University CHARA Meeting March 19, 2015 Hébrard+ (2011) How do planets migrate? Giant planets
Orbital Obliquities of Small Planets from CHARA Stellar Diameters Samuel Quinn & Russel White Georgia State University CHARA Meeting March 19, 2015 Hébrard+ (2011) How do planets migrate? Giant planets
Data-driven models of stars
 Data-driven models of stars David W. Hogg Center for Cosmology and Particle Physics, New York University Center for Data Science, New York University Max-Planck-Insitut für Astronomie, Heidelberg 2015
Data-driven models of stars David W. Hogg Center for Cosmology and Particle Physics, New York University Center for Data Science, New York University Max-Planck-Insitut für Astronomie, Heidelberg 2015
Non-Parametric Bayes
 Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt UBC Machine Learning Reading Group January 2016 Current Hot Topics in Machine Learning Bayesian learning includes: Gaussian processes. Approximate inference. Bayesian
Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt UBC Machine Learning Reading Group January 2016 Current Hot Topics in Machine Learning Bayesian learning includes: Gaussian processes. Approximate inference. Bayesian
Bayesian Model Selection & Extrasolar Planet Detection
 Bayesian Model Selection & Extrasolar Planet Detection Eric B. Ford UC Berkeley Astronomy Dept. Wednesday, June 14, 2006 SCMA IV SAMSI Exoplanets Working Group: Jogesh Babu, Susie Bayarri, Jim Berger,
Bayesian Model Selection & Extrasolar Planet Detection Eric B. Ford UC Berkeley Astronomy Dept. Wednesday, June 14, 2006 SCMA IV SAMSI Exoplanets Working Group: Jogesh Babu, Susie Bayarri, Jim Berger,
Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4)
 Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4) Tom Loredo Dept. of Astronomy, Cornell University http://www.astro.cornell.edu/staff/loredo/bayes/ Bayesian
Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4) Tom Loredo Dept. of Astronomy, Cornell University http://www.astro.cornell.edu/staff/loredo/bayes/ Bayesian
Final Report for Summer Program on Modern Statistical and Computational Methods for Analysis of Kepler Data, June 2013
 Final Report for Summer Program on Modern Statistical and Computational Methods for Analysis of Kepler Data, 10-28 June 2013 Summary. This three-week Summer Research Program can be viewed as a follow up
Final Report for Summer Program on Modern Statistical and Computational Methods for Analysis of Kepler Data, 10-28 June 2013 Summary. This three-week Summer Research Program can be viewed as a follow up
Extrasolar planets. Lecture 23, 4/22/14
 Extrasolar planets Lecture 23, 4/22/14 Extrasolar planets Extrasolar planets: planets around other stars Also called exoplanets 1783 exoplanets discovered as of 4/21/14 Orbitting 1105 different stars Number
Extrasolar planets Lecture 23, 4/22/14 Extrasolar planets Extrasolar planets: planets around other stars Also called exoplanets 1783 exoplanets discovered as of 4/21/14 Orbitting 1105 different stars Number
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia.
 Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Extrasolar Planets. Properties Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets. Exoplanets Introduction. Importance of the study of extrasolar planets
 Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Exoplanet Mass, Radius, and the Search for Habitable Worlds
 Sara Seager Exoplanet Mass, Radius, and the Search for Habitable Worlds O ur sun is one amongst hundreds of billions of stars in our galaxy. Based on the number of times the planetary dice must have been
Sara Seager Exoplanet Mass, Radius, and the Search for Habitable Worlds O ur sun is one amongst hundreds of billions of stars in our galaxy. Based on the number of times the planetary dice must have been
Extrasolar Planets. Today. Dwarf Planets. Extrasolar Planets. Next week. Review Tuesday. Exam Thursday. also, Homework 6 Due
 Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Statistical validation of PLATO 2.0 planet candidates
 Statistical validation of PLATO 2.0 planet candidates Rodrigo F. Díaz Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille José Manuel Almenara, Alexandre Santerne, Claire Moutou, Anthony Lehtuillier, Magali Deleuil
Statistical validation of PLATO 2.0 planet candidates Rodrigo F. Díaz Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille José Manuel Almenara, Alexandre Santerne, Claire Moutou, Anthony Lehtuillier, Magali Deleuil
Testing Theories of Planet Formation & Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems using Orbital Properties of Exoplanets
 Testing Theories of Planet Formation & Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems using Orbital Properties of Exoplanets Eric B. Ford Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (Starting at UF in August
Testing Theories of Planet Formation & Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems using Orbital Properties of Exoplanets Eric B. Ford Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (Starting at UF in August
The Physics of Exoplanets
 The Physics of Exoplanets Heike Rauer Institut für Planetenforschung, DLR, Berlin-Adlershof, Zentrum für Astronomie und Astrophysik, TU Berlin Formation in protoplanetary disk, migration Loss of primary,
The Physics of Exoplanets Heike Rauer Institut für Planetenforschung, DLR, Berlin-Adlershof, Zentrum für Astronomie und Astrophysik, TU Berlin Formation in protoplanetary disk, migration Loss of primary,
Kevin France University of Colorado AXIS Science Workshop August 6 th 2018
 Kevin France University of Colorado AXIS Science Workshop August 6 th 2018 Star-Planet Interactions at High-energies Introduction: In the solar system: Solar Influences, Living with a Star, etc. Afar:
Kevin France University of Colorado AXIS Science Workshop August 6 th 2018 Star-Planet Interactions at High-energies Introduction: In the solar system: Solar Influences, Living with a Star, etc. Afar:
Kepler Planets back to the origin
 Kepler Planets back to the origin Acknowledgements to the Kepler Team Yanqin Wu (Toronto) + Yoram Lithwick, James Owen, Ji-Wei Xie, Nikhil Mahajan, Bonan Pu, Ari Silburt Kepler planets: an Unexpected population
Kepler Planets back to the origin Acknowledgements to the Kepler Team Yanqin Wu (Toronto) + Yoram Lithwick, James Owen, Ji-Wei Xie, Nikhil Mahajan, Bonan Pu, Ari Silburt Kepler planets: an Unexpected population
Delicious Diameters of Dwarfs (in particular, the juicy red ones)
 Delicious Diameters of Dwarfs (in particular, the juicy red ones) Tabetha Boyajian GSU / Hubble Fellow In collaboration with a whole bunch of y all Radical Radii of Red Stars Tabetha Boyajian GSU / Hubble
Delicious Diameters of Dwarfs (in particular, the juicy red ones) Tabetha Boyajian GSU / Hubble Fellow In collaboration with a whole bunch of y all Radical Radii of Red Stars Tabetha Boyajian GSU / Hubble
What is to expect from the transit method. M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France
 What is to expect from the transit method M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France Transit - method Occurrence: only if the planet orbital plane is close to
What is to expect from the transit method M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France Transit - method Occurrence: only if the planet orbital plane is close to
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Michaël Gillon (Université de Liège, Belgium)
 12th Meeting of the FNRS Contact Group Astronomie & Astrophysique 17 May 2011 Planetarium, Brussels Michaël Gillon (Université de Liège, Belgium) michael.gillon@ulg.ac.be ~1% pour Soleil + Jupiter Brown
12th Meeting of the FNRS Contact Group Astronomie & Astrophysique 17 May 2011 Planetarium, Brussels Michaël Gillon (Université de Liège, Belgium) michael.gillon@ulg.ac.be ~1% pour Soleil + Jupiter Brown
Discovering Exoplanets Transiting Bright and Unusual Stars with K2
 Discovering Exoplanets Transiting Bright and Unusual Stars with K2 PhD Thesis Proposal, Department of Astronomy, Harvard University Andrew Vanderburg Advised by David Latham April 18, 2015 After four years
Discovering Exoplanets Transiting Bright and Unusual Stars with K2 PhD Thesis Proposal, Department of Astronomy, Harvard University Andrew Vanderburg Advised by David Latham April 18, 2015 After four years
Characterization of Transiting Planet Atmospheres
 Characterization of Transiting Planet Atmospheres Heather Knutson Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, Caltech A Bird s-eye View of Exoplanet Atmospheres Limited information available for individual
Characterization of Transiting Planet Atmospheres Heather Knutson Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, Caltech A Bird s-eye View of Exoplanet Atmospheres Limited information available for individual
The Rossiter- McLaughlin Effect
 The Rossiter- McLaughlin Effect B. Scott Gaudi The Ohio State University (special thanks to Josh Winn) Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative
The Rossiter- McLaughlin Effect B. Scott Gaudi The Ohio State University (special thanks to Josh Winn) Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative
Time: a new dimension of constraints for planet formation and evolution theory
 S. Jin, P. Mollière Max Planck Institut for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany Y. Alibert & W. Benz University of Bern, Switzerland Christoph Mordasini PLATO meeting Taormina 3.12.2014 Time: a new dimension
S. Jin, P. Mollière Max Planck Institut for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany Y. Alibert & W. Benz University of Bern, Switzerland Christoph Mordasini PLATO meeting Taormina 3.12.2014 Time: a new dimension
STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01
 STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01 Nasser Sadeghkhani a.sadeghkhani@queensu.ca There are two main schools to statistical inference: 1-frequentist
STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01 Nasser Sadeghkhani a.sadeghkhani@queensu.ca There are two main schools to statistical inference: 1-frequentist
Dynamic Exoplanets. Alexander James Mustill
 Dynamic Exoplanets Alexander James Mustill Exoplanets: not (all) like the Solar System Exoplanets: not (all) like the Solar System Solar System Lissauer et al 14 Key questions to bear in mind What is role
Dynamic Exoplanets Alexander James Mustill Exoplanets: not (all) like the Solar System Exoplanets: not (all) like the Solar System Solar System Lissauer et al 14 Key questions to bear in mind What is role
Interior Structure of Rocky and Vapor Worlds
 Interior Structure of Rocky and Vapor Worlds Diana Valencia, 4 April 2011 NASA Sagan Fellow, MIT Exploring Strange New Worlds: From Giant Planets to Super-Earths Super-Earths in the context of exoplanets
Interior Structure of Rocky and Vapor Worlds Diana Valencia, 4 April 2011 NASA Sagan Fellow, MIT Exploring Strange New Worlds: From Giant Planets to Super-Earths Super-Earths in the context of exoplanets
Chapter 13 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Calculating the Occurrence Rate of Earth-Like Planets from the NASA Kepler Mission
 Calculating the Occurrence Rate of Earth-Like Planets from the NASA Kepler Mission Jessie Christiansen Kepler Participating Scientist NASA Exoplanet Science Institute/Caltech jessie.christiansen@caltech.edu
Calculating the Occurrence Rate of Earth-Like Planets from the NASA Kepler Mission Jessie Christiansen Kepler Participating Scientist NASA Exoplanet Science Institute/Caltech jessie.christiansen@caltech.edu
Design Reference Mission. DRM approach
 Design Reference Mission The Design Reference Mission (DRM) is a set of observing programs which together provide a tool to assist with tradeoff decisions in the design of the E-ELT (examples of observing
Design Reference Mission The Design Reference Mission (DRM) is a set of observing programs which together provide a tool to assist with tradeoff decisions in the design of the E-ELT (examples of observing
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 11 May 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 11 May 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 11 May 2015](/thumbs/96/129039509.jpg) Draft version May 13, 215 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 ECCENTRICITY FROM TRANSIT PHOTOMETRY: SMALL PLANETS IN KEPLER MULTI-PLANET SYSTEMS HAVE LOW ECCENTRICITIES Vincent Van
Draft version May 13, 215 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 ECCENTRICITY FROM TRANSIT PHOTOMETRY: SMALL PLANETS IN KEPLER MULTI-PLANET SYSTEMS HAVE LOW ECCENTRICITIES Vincent Van
Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us.
 Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us. Current techniques can measure motions as small as 1 m/s (walking speed!). Sun motion due to: Jupiter:
Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us. Current techniques can measure motions as small as 1 m/s (walking speed!). Sun motion due to: Jupiter:
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Finding terrestrial planets in the habitable zones of nearby stars
 Finding terrestrial planets in the habitable zones of nearby stars Part II Astrophysics Essay Simon Hodgkin & Mark Wyatt (on sabbatical) Terrestrial? 15 Exoplanets Solar system 5 4.5 g cm 3 Winn et al.
Finding terrestrial planets in the habitable zones of nearby stars Part II Astrophysics Essay Simon Hodgkin & Mark Wyatt (on sabbatical) Terrestrial? 15 Exoplanets Solar system 5 4.5 g cm 3 Winn et al.
Asteroseismology of Exoplanet Host Stars
 Asteroseismology of Exoplanet Host Stars Daniel Huber Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii Know Thy Star, Know Thy Planet October 2017 Crash Course in Asteroseismology for more details: Aerts,
Asteroseismology of Exoplanet Host Stars Daniel Huber Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii Know Thy Star, Know Thy Planet October 2017 Crash Course in Asteroseismology for more details: Aerts,
Who was here? How can you tell? This is called indirect evidence!
 1 Who was here? How can you tell? This is called indirect evidence! 2 How does a planetary system form? The one we can study in the most detail is our solar system. If we want to know whether the solar
1 Who was here? How can you tell? This is called indirect evidence! 2 How does a planetary system form? The one we can study in the most detail is our solar system. If we want to know whether the solar
DATA LAB. Data Lab Page 1
 NOTE: This DataLab Activity Guide will be updated soon to reflect April 2015 changes DATA LAB PURPOSE. In this lab, students analyze and interpret quantitative features of their brightness graph to determine
NOTE: This DataLab Activity Guide will be updated soon to reflect April 2015 changes DATA LAB PURPOSE. In this lab, students analyze and interpret quantitative features of their brightness graph to determine
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 15 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 15 Sep 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 15 Sep 2017](/thumbs/92/108587178.jpg) Preprint 18 July 2018 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v30 Forecasted masses for seven thousand KOIs Jingjing Chen 1 & David M Kipping 1 1 Dept of Astronomy, Columbia University, 550 W 120th Street,
Preprint 18 July 2018 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v30 Forecasted masses for seven thousand KOIs Jingjing Chen 1 & David M Kipping 1 1 Dept of Astronomy, Columbia University, 550 W 120th Street,
Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa<ons of Transi<ng Systems
 June. 4, 215 @ NAOJ Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa
June. 4, 215 @ NAOJ Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa
Introduction into Bayesian statistics
 Introduction into Bayesian statistics Maxim Kochurov EF MSU November 15, 2016 Maxim Kochurov Introduction into Bayesian statistics EF MSU 1 / 7 Content 1 Framework Notations 2 Difference Bayesians vs Frequentists
Introduction into Bayesian statistics Maxim Kochurov EF MSU November 15, 2016 Maxim Kochurov Introduction into Bayesian statistics EF MSU 1 / 7 Content 1 Framework Notations 2 Difference Bayesians vs Frequentists
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems. Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? Size Difference. Brightness Difference
 Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? Size Difference Planets are small compared to interstellar distances 10 billion to 1 scale Sun is size of
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? Size Difference Planets are small compared to interstellar distances 10 billion to 1 scale Sun is size of
Extrasolar Planets. Materials Light source to mimic star Ball to mimic planet Light meter Interface
 Name: Date: Extrasolar Planets Objectives: Learn about Extrasolar planets planets orbiting other stars Explain how astronomers detect and characterize Extrasolar planets Materials Light source to mimic
Name: Date: Extrasolar Planets Objectives: Learn about Extrasolar planets planets orbiting other stars Explain how astronomers detect and characterize Extrasolar planets Materials Light source to mimic
A Bayesian Approach to the Understanding of Exoplanet Populations and the Origin of Life
 A Bayesian Approach to Understanding of Exoplanet Populations and Origin of Life Jingjing Chen Submitted in partial fulfillment of requirements for degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Graduate School of
A Bayesian Approach to Understanding of Exoplanet Populations and Origin of Life Jingjing Chen Submitted in partial fulfillment of requirements for degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Graduate School of
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets
 Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 23 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 23 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 23 Oct 2015](/thumbs/89/97966143.jpg) Draft version October 26, 2015 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 A POPULATION-BASED HABITABLE ZONE PERSPECTIVE Andras Zsom Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences,
Draft version October 26, 2015 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 A POPULATION-BASED HABITABLE ZONE PERSPECTIVE Andras Zsom Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences,
Treatment and analysis of data Applied statistics Lecture 4: Estimation
 Treatment and analysis of data Applied statistics Lecture 4: Estimation Topics covered: Hierarchy of estimation methods Modelling of data The likelihood function The Maximum Likelihood Estimate (MLE) Confidence
Treatment and analysis of data Applied statistics Lecture 4: Estimation Topics covered: Hierarchy of estimation methods Modelling of data The likelihood function The Maximum Likelihood Estimate (MLE) Confidence
The Direct Study of Exoplanet Atmospheres
 The Direct Study of Exoplanet Atmospheres David Charbonneau (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Symposium in Honor of Giovanni Fazio 27 May 2008 Statement about the Astronomy & Astrophysics 2010
The Direct Study of Exoplanet Atmospheres David Charbonneau (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Symposium in Honor of Giovanni Fazio 27 May 2008 Statement about the Astronomy & Astrophysics 2010
Precise Stellar Parameters are Crucial for Constraining Transiting Exoplanet Interiors
 Precise Stellar Parameters are Crucial for Constraining Transiting Exoplanet Interiors Andrew Vanderburg! NASA Sagan Fellow The University of Texas at Austin Juliette C. Becker, Lars A. Buchhave, Annelies
Precise Stellar Parameters are Crucial for Constraining Transiting Exoplanet Interiors Andrew Vanderburg! NASA Sagan Fellow The University of Texas at Austin Juliette C. Becker, Lars A. Buchhave, Annelies
COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning
 COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Trevor Cohn 2. Statistical Schools Adapted from slides by Ben Rubinstein Statistical Schools of Thought Remainder of lecture is to provide
COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Trevor Cohn 2. Statistical Schools Adapted from slides by Ben Rubinstein Statistical Schools of Thought Remainder of lecture is to provide
Lecture 13 Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference
 Lecture 13 Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference Dennis Sun Stats 253 August 11, 2014 Outline of Lecture 1 Bayesian Models 2 Modeling Correlations Using Bayes 3 The Universal Algorithm 4 BUGS 5 Wrapping Up
Lecture 13 Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference Dennis Sun Stats 253 August 11, 2014 Outline of Lecture 1 Bayesian Models 2 Modeling Correlations Using Bayes 3 The Universal Algorithm 4 BUGS 5 Wrapping Up
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing
 Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing
 Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Tidal Dissipation in Binaries
 Tidal Dissipation in Binaries From Merging White Dwarfs to Exoplanetary Systems Dong Lai Cornell University March 14, 2013, Harvard ITC Colloquium Tidal Dissipation in Binaries I. Merging White Dwarf Binaries
Tidal Dissipation in Binaries From Merging White Dwarfs to Exoplanetary Systems Dong Lai Cornell University March 14, 2013, Harvard ITC Colloquium Tidal Dissipation in Binaries I. Merging White Dwarf Binaries
(5) Multi-parameter models - Gibbs sampling. ST440/540: Applied Bayesian Analysis
 Summarizing a posterior Given the data and prior the posterior is determined Summarizing the posterior gives parameter estimates, intervals, and hypothesis tests Most of these computations are integrals
Summarizing a posterior Given the data and prior the posterior is determined Summarizing the posterior gives parameter estimates, intervals, and hypothesis tests Most of these computations are integrals
NASA's Kepler telescope uncovers a treasure trove of planets
 NASA's Kepler telescope uncovers a treasure trove of planets By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela on 03.04.14 Word Count 711 The Kepler Mission is specifically designed to survey a portion of our region
NASA's Kepler telescope uncovers a treasure trove of planets By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela on 03.04.14 Word Count 711 The Kepler Mission is specifically designed to survey a portion of our region
Definitions. Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H. Brown dwarfs: M<0.07M s No Burning. Planets No Burning. Dwarf planets. cosmic composition (H+He)
 Definitions Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H cosmic composition (H+He) Brown dwarfs: M
Definitions Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H cosmic composition (H+He) Brown dwarfs: M
Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 6: Exoplanets Due in class Tuesday, March 3, 2015
 Name: Section: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 6: Exoplanets Due in class Tuesday, March 3, 2015 Up until the mid 1990 s, we did not know if planets existed around other stars. Advancements
Name: Section: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 6: Exoplanets Due in class Tuesday, March 3, 2015 Up until the mid 1990 s, we did not know if planets existed around other stars. Advancements
Heavy meteal rules. Vardan Adibekyan Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences. The star-planet connection. 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo
 The star-planet connection Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo 1 Introduction to exoplanets Diversity of exoplanets Planet formation theories 2 Planet formation and metallicity
The star-planet connection Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo 1 Introduction to exoplanets Diversity of exoplanets Planet formation theories 2 Planet formation and metallicity
Young Solar-like Systems
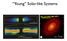 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets!
 The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets! Kepler Spacecraft Can we believe this result? What techniques and data were used to derive this important result? 1 How to
The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets! Kepler Spacecraft Can we believe this result? What techniques and data were used to derive this important result? 1 How to
Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets
 Lecture 1 Part II Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini mordasini@mpia.de Mentor Prof. T. Henning Lecture
Lecture 1 Part II Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini mordasini@mpia.de Mentor Prof. T. Henning Lecture
Hunting Habitable Shadows. Elizabeth Tasker
 Hunting Habitable Shadows Elizabeth Tasker Saturn Earth Uranus Mercury Mars Jupiter Venus Neptune Saturn Earth Uranus Mercury Mars Jupiter Venus Neptune 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004
Hunting Habitable Shadows Elizabeth Tasker Saturn Earth Uranus Mercury Mars Jupiter Venus Neptune Saturn Earth Uranus Mercury Mars Jupiter Venus Neptune 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004
[25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17)
![[25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17)](/thumbs/86/94788164.jpg) 1 [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) Upcoming Items APOD 12/2/16 1. Read chapters 24.1-24.3 for Tuesday 2. We will have a final exam review in the last discussion section (Friday, Dec 8) and also
1 [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) Upcoming Items APOD 12/2/16 1. Read chapters 24.1-24.3 for Tuesday 2. We will have a final exam review in the last discussion section (Friday, Dec 8) and also
