EXONEST The Exoplanetary Explorer. Kevin H. Knuth and Ben Placek Department of Physics University at Albany (SUNY) Albany NY
|
|
|
- Augusta Perry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXONEST The Exoplanetary Explorer Kevin H. Knuth and Ben Placek Department of Physics University at Albany (SUNY) Albany NY
2 Kepler Mission The Kepler mission, launched in 2009, aims to explore the structure and diversity of extra-solar planetary systems.
3
4
5 Bayesian Inference Bayes theorem acts as a learning rule that allows one to update their state of knowledge about the model parameter values given acquired data. Likelihood P θ D, M, I Prior = P θ M, I P D θ, M, I P D M, I Posterior M = model θ = parameters D = data I = prior information Evidence (Z)
6 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer We have developed the EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer which is a Bayesian Inference Engine equipped with plug-and-play models of exoplanetary photometric effects. The system will be made available to the public as open-source code so that third-party development of new photometric models of exoplanetary effects can be readily incorporated.
7 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Data EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models Parameter Estimates Model Evidence EXONEST [1] takes Data from the Kepler Space Telescope, CoRoT, etc. and given a specified model, produces model-based parameter estimates as well as the Bayesian evidence for that model [1] Placek, Knuth, Angerhausen, 2014 arxiv:
8 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models Bayesian Inference Engine Central to EXONEST is the Bayesian Inference Engine, which is based on the Nested Sampling algorithm [2]. The specific current MATLAB implementation is the MultiNest algorithm [3,4,5], but we expect to change this in the near future to enable the handling of many more model parameters. [2] Sivia & Skilling, [3] Feroz et al., arxiv: [4] Feroz & Hobson, arxiv: [5] Feroz et al., arxiv:
9 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Basic Stellar and Planetary Model The basic models describing the recorded flux as originating from a star with orbiting planets are built in. This includes code for modeling the orbital dynamics, as well as describing the common parameters and their prior probabilities. Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models
10 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Instrument Likelihood The likelihood function describes the degree to which the model is expected to describe the data. We have experimented with several different likelihoods and have found that a Gaussian likelihood with the free noise parameter sigma to be most reliable. Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models
11 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Plug-and-Play The recorded flux can be described by user-defined plug-and-play forward models of both stellar and planetary configurations and photometric effects. Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models
12 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models Orbital Models For a given Keplerian planet, one of two orbital models are considered: Circular Orbit Eccentric Orbit The Eccentric Orbit model requires an additional eccentricity parameter, which must be defined with appropriate prior values. To be added in the future are three-body orbital models as in Trojan resonance dynamics and the Kozai mechanism.
13 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Transit Models Transit models accommodate both primary and secondary transits in the case of transiting planets. Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models
14 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models Photometric Models We have developed photometric models for several distinct physical effects. Two are related to the planet itself: Reflected Light Thermal Emissions Two others are related to the effect that the planet has on its host star Doppler Boosting (Beaming) Ellipsoidal Variations (Tidal Warping) We are currently investigating additional effects and their relative magnitudes.
15 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Additional Models Additional user-defined models affecting the photometric flux can be accommodated. Presently, we are considering superrotation, multiple star systems with starstar reflections, star spot models, optically thin coronal regions, etc. Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models
16 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Parameter Estimation The Nested Sampling-based Inference Engine produces estimates and uncertainties of all of the model parameters employed in the forward problem. The number of parameters employed has varied in our studies from 7 to 13 or so parameters. This is approaching the limit that MultiNest can handle, which will force us to migrate to a Nested Sampling variant that we are currently developing in-house. Additional Models
17 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models Additional Models Model Testing The main focus of the Nested Sampling Inference Engine is the computation of the Bayesian evidence of the model. The evidence is critical in Model Testing [6] which we are finding to be useful as a planet validation aid [1]. This has enabled us to verify circular or eccentric orbits, the relative importance of photometric effects, and even the probability that a system hosts multiple planets. [1] Placek, Knuth, Angerhausen, arxiv: [6] Knuth et al. arxiv.org:
18 Results
19 KOI-13b
20 KOI-13 The KOI-13 system is a pair of A-type White Dwarf stars located 1630 LY from Earth. Each star is about 2 times as massive as the Sun with a temperature of about 8500K (compared to the Sun s temperature of 5778K). This Image of the KOI-13 system was taken from the 1m RCC telescope at the Konkoly Observatory in Hungary (Szabó et al. 2011)
21 KOI-13A and KOI-13b In 2011 Kepler detected an object transiting KOI-13A at AU with a period of 25.4 hours (Szabó et al. 2011). Initially the object was thought to be a brown dwarf. Image from (Szabó et al. 2011) Note the spin-orbit mis-alignment. In 2012 Mislis and Hodgkin (2012) determined that the object was a Hot Jupiter with a mass of 8.3 Jupiter masses and a radius 1.4 times that of Jupiter.
22 KOI-13b As a proof-of-concept, we examined whether the planet can be characterized using photometric effects alone (ignoring the dominant transits) Eccentric Orbit Circular Orbit Phase Phase Out-of-transit data for KOI-13b including fits (dark curve) (A) Eccentric Orbit with reflected light, Doppler beaming, and ellipsoidal variations (Log Evidence: ln Z = ± 1.1; Residual Sum of Squares: RSS = 3.45e-06) (B) Circular Orbit with reflected light, Doppler beaming, and ellipsoidal variations (Log Evidence: ln Z = ± 0.9; Residual Sum of Squares: RSS = 3.8e-06). Bayesian model testing favors the eccentric orbit (A) by a factor of exp(45)! [1] Placek, Knuth, Angerhausen, 2014 arxiv:
23 KOI-13b Ignoring transits and relying only on photometric effects we demonstrate that the planet can still be fairly well characterized. That is, Kepler could be used to detect and characterize some nontransiting planets! (Log Evidence) [1] Placek, Knuth, Angerhausen, 2014 arxiv:
24 HAT-P-7b
25 HAT-P-7b (Kepler-2b) Sinusoidally-varying light from planet Shift in baseline flux due to thermal light emission from planet Star blocks light from planet
26 HAT-P-7b (Kepler-2b) [7] Placek & Knuth 2014 arxiv:
27 HAT-P-7b (Kepler-2b) HAT-P-7b HAT-P-7b orbits an F8-type star in a circular orbit at AU with a period of 2.2 days. We estimate HAT-P-7b to a Hot Jupiter that is 1.66 times more massive than Jupiter with times the radius. Its day-side temperature is 2859 ± 33 K whereas the night-side is 1332 ± 756K. [7] Placek & Knuth 2014 arxiv:
28 KIC 54***** Discovery of a Triple Star System in a 10:1 Resonance
29 KIC 54***** Digital Sky Survey (DSS) Photometric data of KIC-54***** obtained from Kepler. (A) Quarter 13 light curve folded on the P1 = 6.45 day period, (B) Quarter 13 light curve folded on the P2 = day period (C) is the entire Q13 light curve. [8] Placek, Knuth, et al. 2014
30 KIC 54***** Eleven radial velocity measurements taken over the span of a week. The 6.45 day period is visible, but not the day period. Courtesy of Geoff Marcy and Howard Issacson [8] Placek, Knuth, et al. 2014
31 KIC 54***** Two possible models of the system. The main star is a G-star (like our sun), at least one of the other companions (C1) is M-dwarf. (A) A hierarchical arrangement (C1 and C2 orbit G with 6.45 day period, and orbit one another with day period) (B) A planetary arrangement (C1 orbits with 6.45 day period, and C2 orbits with day period) [8] Placek, Knuth, et al. 2014
32 KIC 54***** Testing the Hierarchical Model against the Planetary Model using the Radial Velocity Data The Circular Hierarchical Model has the greatest evidence [8] Placek, Knuth, et al. 2014
33 KIC 54***** The KIC 54***** system is a hierarchical triple system G-star pus two co-orbiting M-dwarfs in a 1:10 resonance (P1 = 6.45 day, P2 = day) [8] Placek, Knuth, et al. 2014
34
35 EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer Bayesian Inference Engine Basic Stellar and Planetary Model Instrument Likelihood Plug-and-Play Orbital Models Transit Models Photometric Models We have developed the EXONEST Exoplanetary Explorer which is a Bayesian Inference Engine equipped with plug-and-play models of exoplanetary photometric effects. The system will be made available to the public as open-source code so that third-party development of new photometric models of exoplanetary effects can be readily incorporated. Additional Models
36 Thank you for your kind attention meh.cc Special thanks to: Daniel Angerhausen, Jon Jenkins, Geoff Marcy, Howard Issacson, Jeff Scargle, Michael Way, John Skilling and the Kepler Mission Team
37 Key to Model Parameters M * or Ms Mass of Star (Solar mass units) R * or Rs Radius of Star (Solar radii) Mp Mass of Planet (Jupiter mass units) Rp Radius of Planet (Jupiter radii) Ag Geometric Albedo (unit less [0,1]) Td Day-side Temperature (Kelvin) Tn Night-side Temperature (Kelvin) T or P Orbital Period (days) e Orbital Eccentricity (unit less [0,1]) i Inclination of Orbital Plane (degrees) Mo Mean Anomaly (radians) ω Argument of the Perisatron (radians) K Radial Velocity Semi-amplitude (m/s) γ Systemic Velocity (Radial Component) (m/s) σ Noise level (parts per million)
Bayesian Evidence and Model Selection: A Tutorial in Two Acts
 Bayesian Evidence and Model Selection: A Tutorial in Two Acts Kevin H. Knuth Depts. of Physics and Informatics, University at Albany, Albany NY USA Based on the paper: Knuth K.H., Habeck M., Malakar N.K.,
Bayesian Evidence and Model Selection: A Tutorial in Two Acts Kevin H. Knuth Depts. of Physics and Informatics, University at Albany, Albany NY USA Based on the paper: Knuth K.H., Habeck M., Malakar N.K.,
EXONEST: The Bayesian Exoplanetary Explorer
 entropy Article EXONEST: The Bayesian Exoplanetary Explorer Kevin H. Knuth 1, * ID, Ben Placek 2, Daniel Angerhausen 3,4, Jennifer L. Carter 1, Bryan D Angelo 1, Anthony D. Gai 1 and Bertrand Carado 1
entropy Article EXONEST: The Bayesian Exoplanetary Explorer Kevin H. Knuth 1, * ID, Ben Placek 2, Daniel Angerhausen 3,4, Jennifer L. Carter 1, Bryan D Angelo 1, Anthony D. Gai 1 and Bertrand Carado 1
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us.
 Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us. Current techniques can measure motions as small as 1 m/s (walking speed!). Sun motion due to: Jupiter:
Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us. Current techniques can measure motions as small as 1 m/s (walking speed!). Sun motion due to: Jupiter:
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia.
 Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Dynamical Tides in Binaries
 Dynamical Tides in Binaries I. Merging White Dwarf Binaries II. Kepler KOI-54 III. Hot Jupiter Systems Dong Lai Cornell University 4/5/2012, IAS, Princeton Equilibrium Tide M, R M Equilibrium Tide M, R
Dynamical Tides in Binaries I. Merging White Dwarf Binaries II. Kepler KOI-54 III. Hot Jupiter Systems Dong Lai Cornell University 4/5/2012, IAS, Princeton Equilibrium Tide M, R M Equilibrium Tide M, R
Transiting Extrasolar Planets
 Transiting Extrasolar Planets Recent Progress, XO Survey, and the Future Christopher J. Burke Solar System Has Predominately Circular Orbits Top View Side View Planet Formation NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt
Transiting Extrasolar Planets Recent Progress, XO Survey, and the Future Christopher J. Burke Solar System Has Predominately Circular Orbits Top View Side View Planet Formation NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 30 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 30 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 30 Jan 2018](/thumbs/92/109753642.jpg) Draft version August 26, 2018 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX61 BAYESIAN MODEL TESTING OF ELLIPSOIDAL VARIATIONS ON STARS DUE TO HOT JUPITERS Anthony D. Gai 1 and Kevin H. Knuth 1 1 Department
Draft version August 26, 2018 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX61 BAYESIAN MODEL TESTING OF ELLIPSOIDAL VARIATIONS ON STARS DUE TO HOT JUPITERS Anthony D. Gai 1 and Kevin H. Knuth 1 1 Department
II. Results from Transiting Planets. 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect
 II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
II Planet Finding.
 II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Sep 2005
 For publication in Bayesian Inference and Maximum Entropy Methods, San Jose 25, K. H. Knuth, A. E. Abbas, R. D. Morris, J. P. Castle (eds.), AIP Conference Proceeding A Bayesian Analysis of Extrasolar
For publication in Bayesian Inference and Maximum Entropy Methods, San Jose 25, K. H. Knuth, A. E. Abbas, R. D. Morris, J. P. Castle (eds.), AIP Conference Proceeding A Bayesian Analysis of Extrasolar
Extrasolar Planets. Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects
 Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Planet Detection. AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System
 Review AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM III this THURSDAY 04/8 covering LECT. 17 through We ve talked about the Terrestrial Planets and the Jovian Planets - What about planets around other
Review AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM III this THURSDAY 04/8 covering LECT. 17 through We ve talked about the Terrestrial Planets and the Jovian Planets - What about planets around other
Gravitational microlensing. Exoplanets Microlensing and Transit methods
 Gravitational microlensing Exoplanets Microlensing and s Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo May take place when a star-planet system crosses the visual of a background star, as a result of
Gravitational microlensing Exoplanets Microlensing and s Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo May take place when a star-planet system crosses the visual of a background star, as a result of
Astronomy 421. Lecture 8: Binary stars
 Astronomy 421 Lecture 8: Binary stars 1 Key concepts: Binary types How to use binaries to determine stellar parameters The mass-luminosity relation 2 Binary stars So far, we ve looked at the basic physics
Astronomy 421 Lecture 8: Binary stars 1 Key concepts: Binary types How to use binaries to determine stellar parameters The mass-luminosity relation 2 Binary stars So far, we ve looked at the basic physics
Observations of extrasolar planets
 Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Extrasolar Planets. Properties Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
III The properties of extrasolar planets
 III The properties of extrasolar planets (as of early 2016) http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 3.0 Introduction This lecture will discuss what we have found so far. It is important to remember
III The properties of extrasolar planets (as of early 2016) http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 3.0 Introduction This lecture will discuss what we have found so far. It is important to remember
Observational Cosmology Journal Club
 Observational Cosmology Journal Club 07/09/2018 Shijie Wang 1. Heller, R. (2018). Formation of hot Jupiters through disk migration and evolving stellar tides. Retrieved from arxiv.1806.06601 2. Rey, J.,
Observational Cosmology Journal Club 07/09/2018 Shijie Wang 1. Heller, R. (2018). Formation of hot Jupiters through disk migration and evolving stellar tides. Retrieved from arxiv.1806.06601 2. Rey, J.,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Dec 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Dec 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Dec 2017](/thumbs/76/73169108.jpg) EXONEST: The Bayesian Exoplanetary Explorer arxiv:1712.08894v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Dec 2017 Kevin H. Knuth 1, Ben Placek 2, Daniel Angerhausen 3, Jennifer L. Carter 1, Bryan D Angelo 1, Anthony D. Gai 1,
EXONEST: The Bayesian Exoplanetary Explorer arxiv:1712.08894v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Dec 2017 Kevin H. Knuth 1, Ben Placek 2, Daniel Angerhausen 3, Jennifer L. Carter 1, Bryan D Angelo 1, Anthony D. Gai 1,
Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler. William Cochran McDonald Observatory
 Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler William Cochran McDonald Observatory Who is Bill Cochran? Senior Research Scien;st McDonald Observatory Originally interested in outer planet atmospheres Started
Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler William Cochran McDonald Observatory Who is Bill Cochran? Senior Research Scien;st McDonald Observatory Originally interested in outer planet atmospheres Started
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets. Exoplanets Introduction. Importance of the study of extrasolar planets
 Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Chapter 13 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
DETECTING TRANSITING PLANETS WITH COROT. Stefania Carpano ESAC (25th of November 2009)
 DETECTING TRANSITING PLANETS WITH COROT Stefania Carpano ESAC (25th of November 2009) Outline 1) Introduction: Exoplanet science and detection methods Detection of exoplanets using the transit method The
DETECTING TRANSITING PLANETS WITH COROT Stefania Carpano ESAC (25th of November 2009) Outline 1) Introduction: Exoplanet science and detection methods Detection of exoplanets using the transit method The
3.4 Transiting planets
 64 CHAPTER 3. TRANSITS OF PLANETS: MEAN DENSITIES 3.4 Transiting planets A transits of a planet in front of its parent star occurs if the line of sight is very close to the orbital plane. The transit probability
64 CHAPTER 3. TRANSITS OF PLANETS: MEAN DENSITIES 3.4 Transiting planets A transits of a planet in front of its parent star occurs if the line of sight is very close to the orbital plane. The transit probability
Occurrence of 1-4 REarth Planets Orbiting Sun-Like Stars
 Occurrence of 1-4 REarth Planets Orbiting Sun-Like Stars Geoff Marcy, Erik Petigura, Andrew Howard Planet Density vs Radius + Collaborators: Lauren Weiss, Howard Isaacson, Rea Kolbl, Lea Hirsch Thanks
Occurrence of 1-4 REarth Planets Orbiting Sun-Like Stars Geoff Marcy, Erik Petigura, Andrew Howard Planet Density vs Radius + Collaborators: Lauren Weiss, Howard Isaacson, Rea Kolbl, Lea Hirsch Thanks
10/16/ Detecting Planets Around Other Stars. Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds
 10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion. Exoplanets Doppler method
 Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion Exoplanets The reflex motion of the star is proportional to M p /M * This introduces an observational bias that favours the detection
Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion Exoplanets The reflex motion of the star is proportional to M p /M * This introduces an observational bias that favours the detection
What is to expect from the transit method. M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France
 What is to expect from the transit method M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France Transit - method Occurrence: only if the planet orbital plane is close to
What is to expect from the transit method M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France Transit - method Occurrence: only if the planet orbital plane is close to
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets. Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017
 Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Planet Occurrence Within 0.25 AU
 Planet Occurrence Within 0.25 AU Andrew W. Howard UC Berkeley California Planet Search Team: Geoff Marcy, Debra Fischer, John Johnson, Jason Wright, Howard Isaacson, Julien Spronck, Jeff ValenO, Jay Anderson,
Planet Occurrence Within 0.25 AU Andrew W. Howard UC Berkeley California Planet Search Team: Geoff Marcy, Debra Fischer, John Johnson, Jason Wright, Howard Isaacson, Julien Spronck, Jeff ValenO, Jay Anderson,
The Plethora of Exoplanets Could Any Have Life? Kevin H Knuth University at Albany Spring 2015
 The Plethora of Exoplanets Could Any Have Life? Kevin H Knuth University at Albany Spring 2015 For there is a single general space, a single vast immensity which we may freely call Void; in it are innumerable
The Plethora of Exoplanets Could Any Have Life? Kevin H Knuth University at Albany Spring 2015 For there is a single general space, a single vast immensity which we may freely call Void; in it are innumerable
Finding terrestrial planets in the habitable zones of nearby stars
 Finding terrestrial planets in the habitable zones of nearby stars Part II Astrophysics Essay Simon Hodgkin & Mark Wyatt (on sabbatical) Terrestrial? 15 Exoplanets Solar system 5 4.5 g cm 3 Winn et al.
Finding terrestrial planets in the habitable zones of nearby stars Part II Astrophysics Essay Simon Hodgkin & Mark Wyatt (on sabbatical) Terrestrial? 15 Exoplanets Solar system 5 4.5 g cm 3 Winn et al.
4 1 Extrasolar Planets
 Extrasolar Planets 4 1 Introduction 4 2 So far: have looked at planets around our Sun Physics question: Is our Solar System normal? = Are there planets around other stars? can then compare solar system
Extrasolar Planets 4 1 Introduction 4 2 So far: have looked at planets around our Sun Physics question: Is our Solar System normal? = Are there planets around other stars? can then compare solar system
HD Transits HST/STIS First Transiting Exo-Planet. Exoplanet Discovery Methods. Paper Due Tue, Feb 23. (4) Transits. Transits.
 Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Analysis of Radial Velocity Measurements
 Analysis of Radial Velocity Measurements Sistemas Planetários - 2nd project - 2011/2012 João Faria 1. Introduction The existence of solar systems other than our own has been speculated for a long time,
Analysis of Radial Velocity Measurements Sistemas Planetários - 2nd project - 2011/2012 João Faria 1. Introduction The existence of solar systems other than our own has been speculated for a long time,
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets. PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009
 Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture: atmospheric temperature structure of irradiated planets isothermal
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture: atmospheric temperature structure of irradiated planets isothermal
Tidal Dissipation in Binaries
 Tidal Dissipation in Binaries From Merging White Dwarfs to Exoplanetary Systems Dong Lai Cornell University March 14, 2013, Harvard ITC Colloquium Tidal Dissipation in Binaries I. Merging White Dwarf Binaries
Tidal Dissipation in Binaries From Merging White Dwarfs to Exoplanetary Systems Dong Lai Cornell University March 14, 2013, Harvard ITC Colloquium Tidal Dissipation in Binaries I. Merging White Dwarf Binaries
Extrasolar planets. Lecture 23, 4/22/14
 Extrasolar planets Lecture 23, 4/22/14 Extrasolar planets Extrasolar planets: planets around other stars Also called exoplanets 1783 exoplanets discovered as of 4/21/14 Orbitting 1105 different stars Number
Extrasolar planets Lecture 23, 4/22/14 Extrasolar planets Extrasolar planets: planets around other stars Also called exoplanets 1783 exoplanets discovered as of 4/21/14 Orbitting 1105 different stars Number
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems
 Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Recent Results on Circumbinary Planets
 Recent Results on Circumbinary Planets Jerome A. Orosz with thanks to Bill Welsh, Don Short, Gur Windmiller, Dan Fabrycky, Josh Carter, Laurance Doyle, The Kepler EB and TTV Working Groups Importance of
Recent Results on Circumbinary Planets Jerome A. Orosz with thanks to Bill Welsh, Don Short, Gur Windmiller, Dan Fabrycky, Josh Carter, Laurance Doyle, The Kepler EB and TTV Working Groups Importance of
Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission
 Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Member, TESS Follow-up Observing Program Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2018 1 The Big Picture Is
Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Member, TESS Follow-up Observing Program Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2018 1 The Big Picture Is
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census
 Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
SPICA Science for Transiting Planetary Systems
 SPICA Science for Transiting Planetary Systems Norio Narita Takuya Yamashita National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 2009/06/02 SPICA Science Workshop @ UT 1 Outline For Terrestrial/Jovian Planets 1.
SPICA Science for Transiting Planetary Systems Norio Narita Takuya Yamashita National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 2009/06/02 SPICA Science Workshop @ UT 1 Outline For Terrestrial/Jovian Planets 1.
Actuality of Exoplanets Search. François Bouchy OHP - IAP
 Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS. Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence
 The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence CHEOPS Characterizing Exoplanets Satellite Science Workshop
The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence CHEOPS Characterizing Exoplanets Satellite Science Workshop
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations. Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State
 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State The Big Picture We ve found > 3000 planets, and counting. Earth s place in the Universe... We re
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State The Big Picture We ve found > 3000 planets, and counting. Earth s place in the Universe... We re
Observations of Extrasolar Planets
 Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Signal processing in Python for the detection and characterization of extrasolar planets
 Signal processing in Python for the detection and characterization of extrasolar planets Institut d astrophysique spatial Université Paris-Sud 11 29 August 2011 1 Personal background 2 3 4 5 1 Personal
Signal processing in Python for the detection and characterization of extrasolar planets Institut d astrophysique spatial Université Paris-Sud 11 29 August 2011 1 Personal background 2 3 4 5 1 Personal
Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa<ons of Transi<ng Systems
 June. 4, 215 @ NAOJ Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa
June. 4, 215 @ NAOJ Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa
Other planetary systems
 Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
Search for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs. Norio Narita (NAOJ)
 Search for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs Norio Narita (NAOJ) Outline Introduction of Current Status of Exoplanet Studies Motivation for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs Roadmap and
Search for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs Norio Narita (NAOJ) Outline Introduction of Current Status of Exoplanet Studies Motivation for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs Roadmap and
2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Thought Question Suppose you found a star with the same mass as the Sun moving back and forth with a period of 16 months. What could you conclude? A. It has a planet orbiting at less than 1 AU. B. It has
Thought Question Suppose you found a star with the same mass as the Sun moving back and forth with a period of 16 months. What could you conclude? A. It has a planet orbiting at less than 1 AU. B. It has
Additional Keplerian Signals in the HARPS data for Gliese 667C from a Bayesian re-analysis
 Additional Keplerian Signals in the HARPS data for Gliese 667C from a Bayesian re-analysis Phil Gregory, Samantha Lawler, Brett Gladman Physics and Astronomy Univ. of British Columbia Abstract A re-analysis
Additional Keplerian Signals in the HARPS data for Gliese 667C from a Bayesian re-analysis Phil Gregory, Samantha Lawler, Brett Gladman Physics and Astronomy Univ. of British Columbia Abstract A re-analysis
Searching for Extra-Solar Planets
 Searching for Extra-Solar Planets Until 1996, astronomers only knew about planets orbiting our sun. Though other planetary systems were suspected to exist, none had been found. Now, thirteen years later,
Searching for Extra-Solar Planets Until 1996, astronomers only knew about planets orbiting our sun. Though other planetary systems were suspected to exist, none had been found. Now, thirteen years later,
AST111, Lecture 1b. Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements
 AST111, Lecture 1b Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements Planetary properties (continued): Measuring Mass The orbital period of a moon about a planet depends
AST111, Lecture 1b Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements Planetary properties (continued): Measuring Mass The orbital period of a moon about a planet depends
Monitoring the Behavior of Star Spots Using Photometric Data
 Monitoring the Behavior of Star Spots Using Photometric Data P. Ioannidis 1 and J.H.M.M. Schmitt 1 1 Hamburger Sternwarte, Gojenbergsweg 112, 21029 HH - Germany Abstract. We use high accuracy photometric
Monitoring the Behavior of Star Spots Using Photometric Data P. Ioannidis 1 and J.H.M.M. Schmitt 1 1 Hamburger Sternwarte, Gojenbergsweg 112, 21029 HH - Germany Abstract. We use high accuracy photometric
Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology
 Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology A. Sozzetti INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino Detection/Characterization Detection (Visible): - Doppler spectroscopy (95%) -
Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology A. Sozzetti INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino Detection/Characterization Detection (Visible): - Doppler spectroscopy (95%) -
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview. PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009
 Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, KITP Public Lecture
 Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets
 Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Planet is Much Fainter than Star!
 Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
Kozai-Lidov oscillations
 Kozai-Lidov oscillations Kozai (1962 - asteroids); Lidov (1962 - artificial satellites) arise most simply in restricted three-body problem (two massive bodies on a Kepler orbit + a test particle) e.g.,
Kozai-Lidov oscillations Kozai (1962 - asteroids); Lidov (1962 - artificial satellites) arise most simply in restricted three-body problem (two massive bodies on a Kepler orbit + a test particle) e.g.,
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets
 Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Black Hole and Host Galaxy Mass Estimates
 Black Holes Black Hole and Host Galaxy Mass Estimates 1. Constraining the mass of a BH in a spectroscopic binary. 2. Constraining the mass of a supermassive BH from reverberation mapping and emission line
Black Holes Black Hole and Host Galaxy Mass Estimates 1. Constraining the mass of a BH in a spectroscopic binary. 2. Constraining the mass of a supermassive BH from reverberation mapping and emission line
Astronomy 111 Exam Review Problems (Real exam will be Tuesday Oct 25, 2016)
 Astronomy 111 Exam Review Problems (Real exam will be Tuesday Oct 25, 2016) Actual Exam rules: you may consult only one page of formulas and constants and a calculator while taking this test. You may not
Astronomy 111 Exam Review Problems (Real exam will be Tuesday Oct 25, 2016) Actual Exam rules: you may consult only one page of formulas and constants and a calculator while taking this test. You may not
Design Reference Mission. DRM approach
 Design Reference Mission The Design Reference Mission (DRM) is a set of observing programs which together provide a tool to assist with tradeoff decisions in the design of the E-ELT (examples of observing
Design Reference Mission The Design Reference Mission (DRM) is a set of observing programs which together provide a tool to assist with tradeoff decisions in the design of the E-ELT (examples of observing
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
Planet Detection! Estimating f p!
 Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Can We See Them?! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Can We See Them?! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
SOLAR SYSTEM 2019 SAMPLE EXAM
 SOLAR SYSTEM 2019 SAMPLE EXAM Team Name: Team #: No calculators are allowed. All questions are of equal weight unless otherwise noted. Turn in all materials when you have completed the test! Make sure
SOLAR SYSTEM 2019 SAMPLE EXAM Team Name: Team #: No calculators are allowed. All questions are of equal weight unless otherwise noted. Turn in all materials when you have completed the test! Make sure
4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets. 4.1 Expected properties of extrasolar planets. Sizes of gas giants, brown dwarfs & low-mass stars
 4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets Reminder: Direct imaging is challenging: The proximity to its host star: 1 AU at 1 for alpha Cen 0.15 for the 10th most nearby solar-type star The low ratio of planet
4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets Reminder: Direct imaging is challenging: The proximity to its host star: 1 AU at 1 for alpha Cen 0.15 for the 10th most nearby solar-type star The low ratio of planet
Physical Parameters of KID , a Low-Mass, Double- Lined Eclipsing Binary
 Physical Parameters of KID 6131659, a Low-Mass, Double- Lined Eclipsing Binary Gideon Bass Jerome Orosz, William Welsh, Gur Windmiller, Trevor Gregg, Tara Fetherolf, Richard Wade, Samuel Quinn Paper available
Physical Parameters of KID 6131659, a Low-Mass, Double- Lined Eclipsing Binary Gideon Bass Jerome Orosz, William Welsh, Gur Windmiller, Trevor Gregg, Tara Fetherolf, Richard Wade, Samuel Quinn Paper available
Date of delivery: 29 June 2011 Journal and vol/article ref: IAU Number of pages (not including this page): 5
 Date of delivery: 29 June 2011 Journal and vol/article ref: IAU 1101538 Number of pages (not including this page): 5 Author queries: Typesetter queries: Non-printed material: The Physics of the Sun and
Date of delivery: 29 June 2011 Journal and vol/article ref: IAU 1101538 Number of pages (not including this page): 5 Author queries: Typesetter queries: Non-printed material: The Physics of the Sun and
Validation of Transiting Planet Candidates with BLENDER
 Validation of Transiting Planet Candidates with BLENDER Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Planet Validation Workshop, Marseille, 14 May 2013 2013 May 14 Planet Validation Workshop,
Validation of Transiting Planet Candidates with BLENDER Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Planet Validation Workshop, Marseille, 14 May 2013 2013 May 14 Planet Validation Workshop,
Chapter 13 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Alternative Pre- Observation Catalogue for Photometric Follow- Up of Transiting Exoplanets
 Alternative Pre- Observation Catalogue for Photometric Follow- Up of Transiting Exoplanets Terreka S Hart Tennessee State University Advisor: Dr John A Johnson University of Hawai i - Institute for Astronomy
Alternative Pre- Observation Catalogue for Photometric Follow- Up of Transiting Exoplanets Terreka S Hart Tennessee State University Advisor: Dr John A Johnson University of Hawai i - Institute for Astronomy
Planets and Brown Dwarfs
 Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Professional / Amateur collaborations in exoplanetary science
 Professional / Amateur collaborations in exoplanetary science Alexandre Santerne Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço, Universidade do Porto alexandre.santerne@astro.up.pt Outline Exoplanets:
Professional / Amateur collaborations in exoplanetary science Alexandre Santerne Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço, Universidade do Porto alexandre.santerne@astro.up.pt Outline Exoplanets:
Young Solar-like Systems
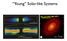 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems. The New Science of Distant Worlds
 Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Extrasolar Planets Our goals for learning Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? How do we detect
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Extrasolar Planets Our goals for learning Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? How do we detect
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space
 The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems. Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? Size Difference. Brightness Difference
 Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? Size Difference Planets are small compared to interstellar distances 10 billion to 1 scale Sun is size of
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? Size Difference Planets are small compared to interstellar distances 10 billion to 1 scale Sun is size of
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets. Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto
 Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results
 The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results Thomas N. Gautier, Kepler Project Scientist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology 3 July 2012 SAO STScI 2012
The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results Thomas N. Gautier, Kepler Project Scientist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology 3 July 2012 SAO STScI 2012
Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars
 Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
Habitability in the Upsilon Andromedae System
 Habitability in the Upsilon Andromedae System Adrienne Dove University of Missouri Columbia Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii Mentor: Nader Haghighipour ABSTRACT We investigate the habitability
Habitability in the Upsilon Andromedae System Adrienne Dove University of Missouri Columbia Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii Mentor: Nader Haghighipour ABSTRACT We investigate the habitability
Finding Other Earths. Jason H. Steffen. Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009
 Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Why Should We Expect to Find Other Planets? Planetary system formation is a natural by-product of star formation
 1 Why Should We Expect to Find Other Planets? Planetary system formation is a natural by-product of star formation 2 Why Should We Expect to Find Other Planets? Observations show young stars are surrounded
1 Why Should We Expect to Find Other Planets? Planetary system formation is a natural by-product of star formation 2 Why Should We Expect to Find Other Planets? Observations show young stars are surrounded
Dynamic Exoplanets. Alexander James Mustill
 Dynamic Exoplanets Alexander James Mustill Exoplanets: not (all) like the Solar System Exoplanets: not (all) like the Solar System Solar System Lissauer et al 14 Key questions to bear in mind What is role
Dynamic Exoplanets Alexander James Mustill Exoplanets: not (all) like the Solar System Exoplanets: not (all) like the Solar System Solar System Lissauer et al 14 Key questions to bear in mind What is role
Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission
 Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Member, TESS Follow-up Observing Program Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2018 1 Copyright Dennis
Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Member, TESS Follow-up Observing Program Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2018 1 Copyright Dennis
ECLIPSING BINARIES: THE ROYAL ROAD. John Southworth (Keele University)
 ECLIPSING BINARIES: THE ROYAL ROAD John Southworth (Keele University) Astrometric binaries: distant friends? William Herschel (1802) christened the term binary star Félix Savary (in 1827) established the
ECLIPSING BINARIES: THE ROYAL ROAD John Southworth (Keele University) Astrometric binaries: distant friends? William Herschel (1802) christened the term binary star Félix Savary (in 1827) established the
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground
 The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
Dynamical properties of the Solar System. Second Kepler s Law. Dynamics of planetary orbits. ν: true anomaly
 First Kepler s Law The secondary body moves in an elliptical orbit, with the primary body at the focus Valid for bound orbits with E < 0 The conservation of the total energy E yields a constant semi-major
First Kepler s Law The secondary body moves in an elliptical orbit, with the primary body at the focus Valid for bound orbits with E < 0 The conservation of the total energy E yields a constant semi-major
Interferometry & Asteroseismology of Solar-like Stars
 Interferometry & Asteroseismology of Solar-like Stars (+ their Connection to Exoplanets) Daniel Huber NASA Ames Research Center Feb 11 2014 Supergiants Giants Hot Dwarfs White Dwarfs Cool Dwarfs Griffith
Interferometry & Asteroseismology of Solar-like Stars (+ their Connection to Exoplanets) Daniel Huber NASA Ames Research Center Feb 11 2014 Supergiants Giants Hot Dwarfs White Dwarfs Cool Dwarfs Griffith
Exoplanet Pursuit. PLANet B. Kalpaxis Georgios Vasilainas Athanasios Vatistas Andreas
 Exoplanet Pursuit PLANet B Kalpaxis Georgios Vasilainas Athanasios Vatistas Andreas We must continue to go into space for the future of humanity. I do not think we will survive another 1,000 years without
Exoplanet Pursuit PLANet B Kalpaxis Georgios Vasilainas Athanasios Vatistas Andreas We must continue to go into space for the future of humanity. I do not think we will survive another 1,000 years without
Ay 20: Basic Astronomy and the Galaxy Fall Term Solution Set 4 Kunal Mooley (based on solutions by Swarnima Manohar, TA 2009)
 Ay 20: Basic Astronomy and the Galaxy Fall Term 2010 Solution Set 4 Kunal Mooley (based on solutions by Swarnima Manohar, TA 2009) Reporting an answer to unnecesary number of decimal places should be avoided.
Ay 20: Basic Astronomy and the Galaxy Fall Term 2010 Solution Set 4 Kunal Mooley (based on solutions by Swarnima Manohar, TA 2009) Reporting an answer to unnecesary number of decimal places should be avoided.
Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets
 Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets Until 1996, astronomers only knew about planets orbiting our sun. Though other planetary systems were suspected to exist, none had been found. Now, thirteen years
Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets Until 1996, astronomers only knew about planets orbiting our sun. Though other planetary systems were suspected to exist, none had been found. Now, thirteen years
hd b greg laughlin jonathan langton ucsc
 hd 80606 b greg laughlin jonathan langton ucsc The success of the planet detection programs has enabled the comparative study of populations of planets, as well as the detailed investigation of individual
hd 80606 b greg laughlin jonathan langton ucsc The success of the planet detection programs has enabled the comparative study of populations of planets, as well as the detailed investigation of individual
Planets are plentiful
 Extra-Solar Planets Planets are plentiful The first planet orbiting another Sun-like star was discovered in 1995. We now know of 209 (Feb 07). Including several stars with more than one planet - true planetary
Extra-Solar Planets Planets are plentiful The first planet orbiting another Sun-like star was discovered in 1995. We now know of 209 (Feb 07). Including several stars with more than one planet - true planetary
