CMB Foreground and separation methods. Astro 448 Yuxi Zhao 12/5/2018
|
|
|
- Kory Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMB Foreground and separation methods Astro 448 Yuxi Zhao 12/5/2018
2 Outline CMB foreground overview Thermal Dust AME (spin dust, spinning nanodiamonds? ) Synchrotron Free-free CO Zodiacal light, CIB Component separation methods Template fitting Parametric method: Commander Non-parametric methods: NILC, FastICA, SMICA,ABS
3 Various types of foregrounds Dickinson, 2016
4 What does foregrounds look like? Temperature maps Planck 2015 results. I
5 What does foregrounds look like? Polarization maps An intuitive conclusion: Galactic component dominate the foreground. Polarization fraction: Π = # $ Planck 2015 results. I
6 temperature polarization Spectral characteristics of foregrounds and CMB Galactic radiation are most notably foregrounds, and dominating at the lower and higher frequencies. The foreground minimum is at 70 GHz The foregrounds in temperature are more complex but the brightness is acceptable While in polarization, the situation is quite on the contrary Planck 2015 results. I
7 Power spectrum of foreground Left: frequency spectra,! = 200 ( first peak ) Right: angular power spectra, % = 100'() Solid lines show where the spectra are estimated from data, and dashed lines are extrapolations Planck 2013 results. I
8 At frequencies 70 GHz, thermal emission from the interstellar dust grains mostly made of graphites, silicates, and PAHs (Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons) dominates the foreground. Blackbody emission modified by opacity effects, which is a modified blackbody spectrum Thermal dust gray body! " = $ %& % % & ' ( )(",!, )., : emissivity index $ : dust optical depth
9 Thermal dust Planck 2013 results. XI.
10 Thermal dust twocomponent model Dust radiance Planck 2013 results. XI. Single-component model may introduce systematic errors at lower frequency. Different-sized grains intrinsically require multicomponent model. Famous SFD dust model (Schlegel, Finkbeiner & Davis, 1998) : two components! ",$ = 9.4, 16 +,, ",$ = (1.67,2.70)
11 Thermal dust Grains will emit (or absorb) photons most efficiently along the shortest axis. Long grain axis tend to align by the local magnetic fields. So the polarization is perpendicular to magnetic fields. Degree of alignment rely on the size of grain, leading to frequency-dependent polarization. polarization A large fraction of the sky has polarization fractions > 5 % At high latitudes, thermal dust polarized up to 20% Planck intermediate results. XIX.
12 Planck 2015 results. I. Thermal dust polarization Left: angle of polarization at 353 GHz, rotated by 90 to indicate the direction of the Galactic magnetic field projected on the plane of the sky Right: dust polarization amplitude map, $ = & ' + ) ', at 353 GHz
13 E mode, B mode angular power spectrum Planck 2015 results. X. The dashed lines: best-fit power-law models to each case The solid and dashed black lines: best-fit Λ"#$ power spectrum as fitted to temperature observations only r: tensor-to-scalar ratio B mode signal is really hard to extract!
14 Bennet et al. (2013) Spin dust Anomalous emission at GHz, firstly recognized as freefree, but lack of correlation with Hα line. Spatial distribution is closely related to the thermal dust. Spin dust emission: smallest ( 10 #$ m) dust grains with electric dipole moment, they rotate at GHz frequencies.
15 Spin dust twocomponent model Planck collaboration et al. (2011) The anomalous emission spectrum is consistent with the spinning dust model of Draine et al. (1998) Two-component model : dense molecular gas and lowdensity atomic gas. [ Ali-Haïmoud et al. 2009]
16 Spinning diamonds? Anomalous microwave emission from spinning nanodiamonds around stars, Nature Astronomy (2018). spin dust Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) used thought to be the candidate source of AME Found AME in three protoplanetary disk Both PAHs and nanodiamonds emit infrared light Other protoplanetary disks with infrared signature of PAHs show no signs of AME
17 Synchrotron radiation is emitted by relativistic cosmic ray (CR) electrons, which are accelerated by the Galactic magnetic field. Synchrotron modeling CR Number density and energy spectrum,! " = $" %& Strength of the magnetic field, ' Spatial dependence Spectrum of antenna temperature T(*) ' -./ 0 * 1, where 2 = &%4. [G. B. Rybicki and A. P. Lightman, Radiative Processes in 5 Astrophysics] Full-sky realization model: Haslam et al. (1982) map at 408 MHz, used by WMAP map at 1.4 GHz by Reich and Reich (1986) Global Sky Model (GSM) by de Oliveira-Costa et al. (2008) GALPROP model, Orlando & Strong (2013 ), used by Planck
18 Larmor formula only acting force is the (relativistic) Lorentz force Synchrotron modeling Then we have the energy loss rate Average over the solid angle Due to the beaming effect, some detailed calculation is needed to get the expression of it s power spectrum.
19 Synchrotron modeling For the emission from many electrons emissivity is the power per unit solid angle produced within 1"# $
20 Synchrotron spectral index Planck 2015 results. X Planck 2015 results. XXV b : Galactic latitude $ 2.7 at radio frequency Steeper values $ 3.0 around 10 GHz, spatial variation ±0.2 Steepening: CR aging effect Flattening : multiple components
21 Synchrotron polarization Planck 2015 results. X Polarized perpendicular to the magnetic field lines Degree of polarization Π = # + 1 /(# + 7/3) Low frequency, low S/N, no accurate spectral index Simple power-law +, = 3; or frequency dependence index, - = ± 0.3 (Kogut et al. 2007)
22 Synchrotron polarization WMAP results. Gold et al.(2011) Planck 2015 results. I Left: WMAP nine-years data, 23 GHz Right: angle of polarization at 30 GHz, dominated by synchrotron, indicate the direction of magnetic field, No precise polarization degree, but it s smaller at low latitude, because of superposition of different polarization angle
23 Free-free emission, also known as thermal bremsstrahlung, arises from electron ion scattering in interstellar plasma. Intensity of free-free emission is given by an integration along the line of sight as I " = % " &', where % " is emissivity ( power radiated per unit frequency, per unit volume, per steradian) Free-free derive the spectrum Gaunt factor: For h) +,, only Gaunt factor is frequency dependent Observed intensity - " is often expressed in terms of brightness temperature:,. = /0-12" 0 ",. ) [Bruce T. Draine, Physics of the Interstellar and Intergalactic Medium]
24 Free free absorption, using the Kirchoff law From bremsstrahlung to black body At Raleigh Jeans limit Source function (which is tend to be! " at optical thick case):
25 Delabrouille et al. (2013) Free-free Planck 2015 results. XXV Dickinsion et al.(2003) The close correlation with the optical!" line, at 22.8 GHz At high Galactic latitudes, free-free emission is relatively weak At higher frequencies, the spectrum steepens slightly
26 Planck early results. VI. Planck 2015 results. X CO line emission Rotational transitions of carbon monoxide (CO) in the molecular cloud: CO rotation energy is quantized. The most effective tracer of molecular interstellar matter. Empirical relationship:! " # = 3 10 #) +,,. /0 12[45 6# ]
27 Inter Planetary dust (IPD) in our Solar system, concentrated within the orbit of Jupiter. Zodiacal light, Cosmic Infrared Background Planck 2013 results. XIV
28 Template fitting Component separation methods Parametric methods: Commander Non-parametric method: Needlet Internal linear combination (NILC) Independent Component Analysis (FastICA) Spectral Matching Independent Component Analysis (SMICA). Analytical Blind Separation ( ABS )
29 Assume sky at given pixel!" and frequency # is a superposition of various components and noise. Template fitting where $ % # is the template coefficients, the frequency dependence Then fit the combination of templates in a least-squares sense to the observation sky map WMAP: synchrotron template from lowest channels + free-free template from &$ + dust template from Schlegel,Finkbeiner and Davis(SFD)
30 WMAP diffuse foreground templates Template fitting Bennett et al. (2013)
31 Templates are no need to be real physical components: SFD can represent both thermal dust at high frequencies and AME at low frequencies simultaneously Template fitting Pros: statistical properties of noise in the foregroundcleaning map is unaffected Cons: assumes a separable nature for frequency and spatial positions, which is not true for real sky (spectral index of synchrotron emissions varies over the sky, and even have curvature)
32 COMMANDER: Bayesian parametric pixel-by-pixel fitting with MCMC Gibbs sampling MCMC sampling(metropolis-hastings algorithm): if!(# $%& ) >! # $, the proposed step is always accepted; COMMANDER otherwise, the step is accepted with probability!(# $%& )/! # $ Gibbs sampling: When we sample multivariate probability distributions *(#), start with + (,) = + & (,),, +0 (,), draw + & (&) from *(+& + 2,,, + 0, ), then + 2 (&) from * +2 + &,, + 3,,, + 0,, etc
33 COMMANDER The maximum of joint posterior distribution!(#, % &, ' ( *) can tell us the best fit parameter & and CMB power spectrum ' (, where # is the signal, % & is the foreground, * is observed data. This is a very high-dimensional distribution, to study its characteristics, MCMC sampling is needed. But firstly, sampling joint pdf is difficult,use Gibbs sampling to reduce the problem: sampling two conditional density.
34 Assuming the conditional distributions are Gaussian likelihoods, and using Bayes theorem COMMANDER! " : noise covariance at frequency # $ : signal covariance, Multivariate Gaussian for % " + ' ", inverse gamma for ( ) Simplify version of detailed % " + ' " parametric treatment:
35 summary of main parametric model COMMANDER Planck 2015 results. X
36 COMMANDER Planck 2015 results. X
37 COMMANDER Pros: best estimate of the power spectrum with posterior probability best estimate of foreground parameters with errors component separation method can apply our knowledge of physical processes and additional observational constrain as priors Cons: sensitive to the assumed priors on the foreground model parameters computationally intensive, so the resolution is the lowest (though the high resolution may not be necessary for inflationary B-mode detection on large scale)
38 Minimum-variance internal linear combination in needlet space. NILC Advantage of spherical needlets over spherical harmonics : spherical harmonics are global functions, suffers from Gibbs phenomenon needlets are localized at a certain region and a finite number of frequencies, also decay quasi-exponentially D.Marinucci et al. (2018)
39 Main idea: signal and foregrounds are uncorrelated + signal is the same in every maps + foreground components are canceled out linearly combined map have the total minimum variance NILC Pros: Localization in pixel space allows the weight to adapt local conditions. Localization in harmonic space allows to reject foreground on large scales and noise on small scales. Cons: Relies on the independence between signal and foreground, can not separate each Galactic foreground component
40 Detection contains CMB signal and contamination Estimate signal as weighted internal linear combination NILC to be of minimum variance Where is the covariance matrix average over a certain domain surrounding pixel p.
41 Unbiased estimate of CMB and minimized residual foreground Solution: the resulting weight to meet the minimum variance NILC!: frequency channel ": scale #: pixel Needlet coefficient: Covariance matrix: average of product over some space domain Reconstruction :
42 The ICA (independent component analysis) model is given by!: frequency, ": mixing matrix, # $ : signal including foregrounds Assume signal components are independent, then for FastICA we can find a % & $ to maximize the independency of ' $. Which is equivalent to maximize non-gaussianity. Key point is to find a suitable measure of non-gaussianity of ' $ Need no assumption about the spatial distribution and frequency dependence of foreground components Many application in COBE, BEAST, WMAP, 21cm map, CO map in PLANCK
43 Power spectra fitting approach in harmonic space, also no need of prior assumption of foreground SMICA here! " ($) is the cross band power with $ contains whatever parameters are needed to determine the model above. & : CMB spectrum, ' : foreground spectrum, ( " : foreground covariance matrix, ) " : diagonal noise matrix Sample spectral covariance matrix Best-fit parameters $: equivalent to maximizing the likelihood under condition that they follow Gaussian isotropic distribution characterized by the spectra and cross band matrix.
44 Get the CMB power spectrum where: SMICA SMICA can not blindly separate the components with similar angular power spectrum Fortunately, CMB s is distinct with other foregrounds But component separation between foreground can be difficult (same with NICL)
45 Analytical method of blind separation on harmonic space Based on PJ Zhang, J. Zhang, L. Zhang; arxiv: and Jian Yao, Le Zhang, Yuxi Zhao, et al; arxiv: Cross band power spectrum ABS! "# $%&' has order of frequency channel number ($, but rank ) depends on the number of independent foreground Without noise + ) < ( $, there is unique analytical solution of! +,-. Achieved by Sylvester s determinant theorem..-th eigenvector of! "# is / (1)
46 In the case with noise: normalize the data + discard the eigenvector that is dominated by the noise %&#'(!" ) #$ = + %&#'(,,# + %&#'(,,$ (1 +! #$ )/2 ABS Then only use eigenmodes with 4 5 > noise level 7 is a free parameter to reduce the systematic error and stabilize the computation
47 Resulting eigenvalue ABS Yao et al. (2018)
48 Resulting eigenvector, a mixture of several astrophysical components ABS The other two eigenvectors are noise dominated Yao et al. (2018)
49 Recovered CMB power spectrum ABS Yao et al. (2018)
50 Robustness test: reverse the mask ABS still have <1% deviation on average Yao et al. (2018)
51 ABS Using simulation sky maps, so real-world instrument effects : beam shape, correlated non-gaussian noise may affected the result Additional complex foreground and point sources may complicate the removal process
52 Thanks! Q&A
Cosmic Microwave Background
 Cosmic Microwave Background Carlo Baccigalupi,, SISSA CMB lectures at TRR33, see the complete program at darkuniverse.uni-hd.de/view/main/winterschoollecture5 These lectures are available in pdf format
Cosmic Microwave Background Carlo Baccigalupi,, SISSA CMB lectures at TRR33, see the complete program at darkuniverse.uni-hd.de/view/main/winterschoollecture5 These lectures are available in pdf format
DES Galaxy Clusters x Planck SZ Map. ASTR 448 Kuang Wei Nov 27
 DES Galaxy Clusters x Planck SZ Map ASTR 448 Kuang Wei Nov 27 Origin of Thermal Sunyaev-Zel'dovich (tsz) Effect Inverse Compton Scattering Figure Courtesy to J. Carlstrom Observables of tsz Effect Decrease
DES Galaxy Clusters x Planck SZ Map ASTR 448 Kuang Wei Nov 27 Origin of Thermal Sunyaev-Zel'dovich (tsz) Effect Inverse Compton Scattering Figure Courtesy to J. Carlstrom Observables of tsz Effect Decrease
Polarized Foregrounds and the CMB Al Kogut/GSFC
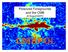 Polarized Foregrounds and the CMB Al Kogut/GSFC The Problem In A Nutshell Galactic foregrounds are 2 orders of magnitude brighter than primordial B-mode polarization from 30 to 200 GHz Polarized vs Unpolarized
Polarized Foregrounds and the CMB Al Kogut/GSFC The Problem In A Nutshell Galactic foregrounds are 2 orders of magnitude brighter than primordial B-mode polarization from 30 to 200 GHz Polarized vs Unpolarized
The microwave sky as seen by Planck
 The microwave sky as seen by Planck Ingunn Kathrine Wehus Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology on behalf of the Planck Collaboration Bayesian component separation We adopt a parametric
The microwave sky as seen by Planck Ingunn Kathrine Wehus Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology on behalf of the Planck Collaboration Bayesian component separation We adopt a parametric
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 22 Feb 1999
 Anomalous Microwave Emission arxiv:astro-ph/9902307v1 22 Feb 1999 A. Kogut Laboratory for Astronomy and Solar Physics, Code 685, Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 Abstract. Improved knowledge
Anomalous Microwave Emission arxiv:astro-ph/9902307v1 22 Feb 1999 A. Kogut Laboratory for Astronomy and Solar Physics, Code 685, Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 Abstract. Improved knowledge
Polarised foregrounds (synchrotron, dust and AME) and their effect on the detection of primordial CMB B-modes
 Polarised foregrounds (synchrotron, dust and AME) and their effect on the detection of primordial CMB B-modes Ricardo T. Génova Santos Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias Cosmology School in the Canary
Polarised foregrounds (synchrotron, dust and AME) and their effect on the detection of primordial CMB B-modes Ricardo T. Génova Santos Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias Cosmology School in the Canary
Galactic radio loops. Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar. The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017
 Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
Challenges of foreground subtraction for (primordial) CMB B-modes
 Challenges of foreground subtraction for (primordial) CMB B-modes Clive Dickinson Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics University of Manchester Bennett et al. (2013) CMB2013, OIST, Okinawa, Japan, 10-14
Challenges of foreground subtraction for (primordial) CMB B-modes Clive Dickinson Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics University of Manchester Bennett et al. (2013) CMB2013, OIST, Okinawa, Japan, 10-14
Dust emission. D.Maino. Radio Astronomy II. Physics Dept., University of Milano. D.Maino Dust emission 1/24
 Dust emission D.Maino Physics Dept., University of Milano Radio Astronomy II D.Maino Dust emission 1/24 New insight on Dust Emission Before WMAP and Planck with only COBE-DMR, dust is well described by
Dust emission D.Maino Physics Dept., University of Milano Radio Astronomy II D.Maino Dust emission 1/24 New insight on Dust Emission Before WMAP and Planck with only COBE-DMR, dust is well described by
Polarized Galactic foregrounds: a review
 Polarized Galactic foregrounds: a review Joanna Dunkley University of Oxford CMBPol Chicago, July 1 2009 Foreground Working Groups Removal: Alex Amblard, Carlo Baccigalupi, Marc Betoule, David Chuss, Asantha
Polarized Galactic foregrounds: a review Joanna Dunkley University of Oxford CMBPol Chicago, July 1 2009 Foreground Working Groups Removal: Alex Amblard, Carlo Baccigalupi, Marc Betoule, David Chuss, Asantha
WMAP Excess Interpreted as WIMP Annihilation
 WMAP Excess Interpreted as WIMP Annihilation idm2004, Edinburgh September 9, 2004 Douglas Finkbeiner Princeton University Outline " " " WMAP ISM emission (expected) The Galactic synchrotron Haze (unexpected)
WMAP Excess Interpreted as WIMP Annihilation idm2004, Edinburgh September 9, 2004 Douglas Finkbeiner Princeton University Outline " " " WMAP ISM emission (expected) The Galactic synchrotron Haze (unexpected)
3/1/18 LETTER. Instructors: Jim Cordes & Shami Chatterjee. Reading: as indicated in Syllabus on web
 Astro 2299 The Search for Life in the Universe Lecture 9 Last time: Star formation Formation of protostars and planetary systems This time A few things about the epoch of reionization and free fall times
Astro 2299 The Search for Life in the Universe Lecture 9 Last time: Star formation Formation of protostars and planetary systems This time A few things about the epoch of reionization and free fall times
Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM
 Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale on behalf of the Planck Consortium Outline The Planck data
Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale on behalf of the Planck Consortium Outline The Planck data
Really, really, what universe do we live in?
 Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium
 The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth
 Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
BipoSH Representation: Modulation & Systematics
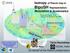 Isotropy of Planck map in C l L=0 BipoSH Representation: Modulation & Systematics Planck 2013 results. XXIII. Isotropy and statistics of the CMB L=10 Spherical harmonic l Planck unveils the Cosmic Microwave
Isotropy of Planck map in C l L=0 BipoSH Representation: Modulation & Systematics Planck 2013 results. XXIII. Isotropy and statistics of the CMB L=10 Spherical harmonic l Planck unveils the Cosmic Microwave
Dark Matter searches with radio observations
 Marco Taoso Dpt. of Physics and Astronomy UBC Vancouver Dark Matter searches with radio observations IDM 2012 Chicago, 23-27 July Search for DM with astrophysical observations Gamma- rays Microwave Radio
Marco Taoso Dpt. of Physics and Astronomy UBC Vancouver Dark Matter searches with radio observations IDM 2012 Chicago, 23-27 July Search for DM with astrophysical observations Gamma- rays Microwave Radio
Correlation of the South Pole 94 data with 100 µm and 408 MHz maps
 A&A 368, 760 765 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010061 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Correlation of the South Pole 94 data with 100 µm and 408 MHz maps J.-Ch. Hamilton 1 and K. M. Ganga 1,2 1 Physique
A&A 368, 760 765 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010061 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Correlation of the South Pole 94 data with 100 µm and 408 MHz maps J.-Ch. Hamilton 1 and K. M. Ganga 1,2 1 Physique
CHAPTER 27. Continuum Emission Mechanisms
 CHAPTER 27 Continuum Emission Mechanisms Continuum radiation is any radiation that forms a continuous spectrum and is not restricted to a narrow frequency range. In what follows we briefly describe five
CHAPTER 27 Continuum Emission Mechanisms Continuum radiation is any radiation that forms a continuous spectrum and is not restricted to a narrow frequency range. In what follows we briefly describe five
FOUR-YEAR COBE 1 DMR COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND OBSERVATIONS: MAPS AND BASIC RESULTS
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 464 : L1 L4, 1996 June 10 1996. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. FOUR-YEAR COBE 1 DMR COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND OBSERVATIONS: MAPS
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 464 : L1 L4, 1996 June 10 1996. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. FOUR-YEAR COBE 1 DMR COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND OBSERVATIONS: MAPS
EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
 EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Luis C. Reyes KICP The Extragalactic Background Light (EBL) What is it? Accumulation of all energy releases in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Luis C. Reyes KICP The Extragalactic Background Light (EBL) What is it? Accumulation of all energy releases in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 21 Nov 2006
 Evidence for Inverted Spectrum 20 GHz Emission in the Galactic Plane arxiv:astro-ph/0611655 v1 21 Nov 2006 S. P. Boughn and J. C. Pober Department of Astronomy, Haverford College, Haverford, PA 19041;
Evidence for Inverted Spectrum 20 GHz Emission in the Galactic Plane arxiv:astro-ph/0611655 v1 21 Nov 2006 S. P. Boughn and J. C. Pober Department of Astronomy, Haverford College, Haverford, PA 19041;
- Potentials. - Liénard-Wiechart Potentials. - Larmor s Formula. - Dipole Approximation. - Beginning of Cyclotron & Synchrotron
 - Potentials - Liénard-Wiechart Potentials - Larmor s Formula - Dipole Approximation - Beginning of Cyclotron & Synchrotron Maxwell s equations in a vacuum become A basic feature of these eqns is the existence
- Potentials - Liénard-Wiechart Potentials - Larmor s Formula - Dipole Approximation - Beginning of Cyclotron & Synchrotron Maxwell s equations in a vacuum become A basic feature of these eqns is the existence
MICROWAVE EMISSION AT HIGH GALACTIC LATITUDES IN THE FOUR-YEAR DMR SKY MAPS
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 464 : L5 L9, 1996 June 10 1996. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. MICROWAVE EMISSION AT HIGH GALACTIC LATITUDES IN THE FOUR-YEAR DMR SKY
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 464 : L5 L9, 1996 June 10 1996. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. MICROWAVE EMISSION AT HIGH GALACTIC LATITUDES IN THE FOUR-YEAR DMR SKY
Cosmic Microwave Background
 Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
BINGO simulations and updates on the performance of. the instrument
 BINGO simulations and updates on the performance of BINGO telescope the instrument M.-A. Bigot-Sazy BINGO collaboration Paris 21cm Intensity Mapping Workshop June 2014 21cm signal Observed sky Credit:
BINGO simulations and updates on the performance of BINGO telescope the instrument M.-A. Bigot-Sazy BINGO collaboration Paris 21cm Intensity Mapping Workshop June 2014 21cm signal Observed sky Credit:
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 7 Apr 2006
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 () Printed 5 February 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) A determination of the Spectra of Galactic components observed by WMAP arxiv:astro-ph/0511384v2 7 Apr 2006 R.D.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 () Printed 5 February 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) A determination of the Spectra of Galactic components observed by WMAP arxiv:astro-ph/0511384v2 7 Apr 2006 R.D.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 10 Feb 2003
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 () Printed 5 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Reappraising foreground contamination in the COBE-DMR data arxiv:astro-ph/0302181v1 10 Feb 2003 A. J. Banday, 1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 () Printed 5 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Reappraising foreground contamination in the COBE-DMR data arxiv:astro-ph/0302181v1 10 Feb 2003 A. J. Banday, 1
THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS ASTROPHYSICS VERSUS. Greg Dobler. Harvard/CfA July 14 th, TeV09
 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Greg Dobler Harvard/CfA July 14 th, 2009 - TeV09 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Doug Finkbeiner (CfA) Dan Hooper (FNAL) Gabrijela
THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Greg Dobler Harvard/CfA July 14 th, 2009 - TeV09 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Doug Finkbeiner (CfA) Dan Hooper (FNAL) Gabrijela
Dust polarization observations towards interstellar filaments as seen by Planck: Signature of the magnetic field geometry
 Dust (total) emission of the ISM as seen by Planck Dust polarization observations towards interstellar filaments as seen by Planck: Signature of the magnetic field geometry Doris Arzoumanian (IAS, Orsay)
Dust (total) emission of the ISM as seen by Planck Dust polarization observations towards interstellar filaments as seen by Planck: Signature of the magnetic field geometry Doris Arzoumanian (IAS, Orsay)
Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations
 Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations In collaboration with E.Borriello and G.Miele, University of Naples Federico II Alessandro Cuoco, Institute for Physics and Astronomy University
Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations In collaboration with E.Borriello and G.Miele, University of Naples Federico II Alessandro Cuoco, Institute for Physics and Astronomy University
The Morphology of the Anomalous Microwave Emission in the Planck 2015 data release
 Prepared for submission to JCAP arxiv:1507.05171v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Jul 2015 The Morphology of the Anomalous Microwave Emission in the Planck 2015 data release S. von Hausegger a,1 H. Liu a,b a The Niels
Prepared for submission to JCAP arxiv:1507.05171v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Jul 2015 The Morphology of the Anomalous Microwave Emission in the Planck 2015 data release S. von Hausegger a,1 H. Liu a,b a The Niels
Dust Polarization. J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse
 Dust Polarization J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse 1 Layout - Dust polarization (Extinction) - Dust polarization (Emission) - Dust polarization observational
Dust Polarization J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse 1 Layout - Dust polarization (Extinction) - Dust polarization (Emission) - Dust polarization observational
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 26 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 26 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 26 Feb 2013](/thumbs/95/125081310.jpg) FERMILAB-PUB-13-52-A Two Emission Mechanisms in the Fermi Bubbles: A Possible Signal of Annihilating Dark Matter Dan Hooper 1, 2 and Tracy R. Slatyer 3 1 Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, Theoretical
FERMILAB-PUB-13-52-A Two Emission Mechanisms in the Fermi Bubbles: A Possible Signal of Annihilating Dark Matter Dan Hooper 1, 2 and Tracy R. Slatyer 3 1 Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, Theoretical
Using training sets and SVD to separate global 21-cm signal from foreground and instrument systematics
 Using training sets and SVD to separate global 21-cm signal from foreground and instrument systematics KEITH TAUSCHER*, DAVID RAPETTI, JACK O. BURNS, ERIC SWITZER Aspen, CO Cosmological Signals from Cosmic
Using training sets and SVD to separate global 21-cm signal from foreground and instrument systematics KEITH TAUSCHER*, DAVID RAPETTI, JACK O. BURNS, ERIC SWITZER Aspen, CO Cosmological Signals from Cosmic
The Extragalactic Radio Background
 The Extragalactic Radio Background Challenges and Opportunities Al Kogut Goddard Space Flight Center Extragalactic Backgrounds Early Background Estimates T ex From Spectral Index Variations T ex = 30 80
The Extragalactic Radio Background Challenges and Opportunities Al Kogut Goddard Space Flight Center Extragalactic Backgrounds Early Background Estimates T ex From Spectral Index Variations T ex = 30 80
- Synchrotron emission: A brief history. - Examples. - Cyclotron radiation. - Synchrotron radiation. - Synchrotron power from a single electron
 - Synchrotron emission: A brief history - Examples - Cyclotron radiation - Synchrotron radiation - Synchrotron power from a single electron - Relativistic beaming - Relativistic Doppler effect - Spectrum
- Synchrotron emission: A brief history - Examples - Cyclotron radiation - Synchrotron radiation - Synchrotron power from a single electron - Relativistic beaming - Relativistic Doppler effect - Spectrum
Measurements of Degree-Scale B-mode Polarization with the BICEP/Keck Experiments at South Pole
 Measurements of Degree-Scale B-mode Polarization with the BICEP/Keck Experiments at South Pole Benjamin Racine for the BICEP/Keck Collaboration March 18th, 2018 53 èmes Rencontres de Moriond La Thuile
Measurements of Degree-Scale B-mode Polarization with the BICEP/Keck Experiments at South Pole Benjamin Racine for the BICEP/Keck Collaboration March 18th, 2018 53 èmes Rencontres de Moriond La Thuile
Recap Lecture + Thomson Scattering. Thermal radiation Blackbody radiation Bremsstrahlung radiation
 Recap Lecture + Thomson Scattering Thermal radiation Blackbody radiation Bremsstrahlung radiation LECTURE 1: Constancy of Brightness in Free Space We use now energy conservation: de=i ν 1 da1 d Ω1 dt d
Recap Lecture + Thomson Scattering Thermal radiation Blackbody radiation Bremsstrahlung radiation LECTURE 1: Constancy of Brightness in Free Space We use now energy conservation: de=i ν 1 da1 d Ω1 dt d
Astrochemistry (2) Interstellar extinction. Measurement of the reddening
 Measurement of the reddening The reddening of stellar colours casts light on the properties of interstellar dust Astrochemistry (2) Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo The reddening is measured
Measurement of the reddening The reddening of stellar colours casts light on the properties of interstellar dust Astrochemistry (2) Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo The reddening is measured
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields
 Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering
 Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Primordial and Doppler modulations with Planck Antony Lewis On behalf of the Planck collaboration
 Primordial and Doppler modulations with Planck Antony Lewis On behalf of the Planck collaboration http://cosmologist.info/ Outline Primordial modulations and power asymmetry τ NL trispectrum Kinematic
Primordial and Doppler modulations with Planck Antony Lewis On behalf of the Planck collaboration http://cosmologist.info/ Outline Primordial modulations and power asymmetry τ NL trispectrum Kinematic
Midterm Results. The Milky Way in the Infrared. The Milk Way from Above (artist conception) 3/2/10
 Lecture 13 : The Interstellar Medium and Cosmic Recycling Midterm Results A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath The Milky Way in the Infrared View from the Earth: Edge On Infrared light penetrates the clouds and shows
Lecture 13 : The Interstellar Medium and Cosmic Recycling Midterm Results A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath The Milky Way in the Infrared View from the Earth: Edge On Infrared light penetrates the clouds and shows
The CMB sky observed at 43 and 95 GHz with QUIET
 The CMB sky observed at 43 and 95 GHz with QUIET Hans Kristian Eriksen for the QUIET collaboration University of Oslo Munich, November 28th, 2012 QUIET (Q/U Imaging ExperimenT) QUIET is a ground-based
The CMB sky observed at 43 and 95 GHz with QUIET Hans Kristian Eriksen for the QUIET collaboration University of Oslo Munich, November 28th, 2012 QUIET (Q/U Imaging ExperimenT) QUIET is a ground-based
A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy
 A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy (The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 231:21 (16pp), 2017 August) November 14, 2017 Young-Soo Jo Young-Soo
A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy (The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 231:21 (16pp), 2017 August) November 14, 2017 Young-Soo Jo Young-Soo
Consistency tests for Planck and WMAP in the low multipole domain
 PREPARED FOR SUBMISSION TO JCAP arxiv:1305.4033v1 [astro-ph.co] 17 May 2013 Consistency tests for Planck and WMAP in the low multipole domain A. Frejsel, M. Hansen and H. Liu Niels Bohr Institute and Discovery
PREPARED FOR SUBMISSION TO JCAP arxiv:1305.4033v1 [astro-ph.co] 17 May 2013 Consistency tests for Planck and WMAP in the low multipole domain A. Frejsel, M. Hansen and H. Liu Niels Bohr Institute and Discovery
Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations. Joern Geisbuesch
 Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations In collaboration with Paul Alexander, Rosie Bolton, Martin Krause April 2008 University of Cambridge Department of Physics Motivation and
Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations In collaboration with Paul Alexander, Rosie Bolton, Martin Krause April 2008 University of Cambridge Department of Physics Motivation and
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV
 The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
Simulations of polarised dust emission
 Simulations of polarised dust emission Flavien Vansyngel - Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Collaborators: François Boulanger, Tuhin Ghosh, Andrea Bracco, Jonathan Aumont CMB-S4 meeting 03/016 Dust contamination
Simulations of polarised dust emission Flavien Vansyngel - Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Collaborators: François Boulanger, Tuhin Ghosh, Andrea Bracco, Jonathan Aumont CMB-S4 meeting 03/016 Dust contamination
The incident energy per unit area on the electron is given by the Poynting vector, '
 ' ' # Thompson Scattering Consider a beam of radiation moving in the direction, and being scattered by an electron through an angle in the plane. The electron experiences the following electric fields
' ' # Thompson Scattering Consider a beam of radiation moving in the direction, and being scattered by an electron through an angle in the plane. The electron experiences the following electric fields
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Toward an Understanding of Foregrounds in the BICEP2 Region
 Toward an Understanding of Foregrounds in the BICEP2 Region Raphael Flauger JCAP08(2014)039 (arxiv:1405.7351) w/ Colin Hill and David Spergel Status and Future of Inflationary Theory, KICP, August 22,
Toward an Understanding of Foregrounds in the BICEP2 Region Raphael Flauger JCAP08(2014)039 (arxiv:1405.7351) w/ Colin Hill and David Spergel Status and Future of Inflationary Theory, KICP, August 22,
Interstellar gamma rays. New insights from Fermi. Andy Strong. on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration. COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010
 Interstellar gamma rays New insights from Fermi Andy Strong on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010 Session E110: ' The next generation of ground-based Cerenkov
Interstellar gamma rays New insights from Fermi Andy Strong on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010 Session E110: ' The next generation of ground-based Cerenkov
1 Monday, November 7: Synchrotron Radiation for Beginners
 1 Monday, November 7: Synchrotron Radiation for Beginners An accelerated electron emits electromagnetic radiation. The most effective way to accelerate an electron is to use electromagnetic forces. Since
1 Monday, November 7: Synchrotron Radiation for Beginners An accelerated electron emits electromagnetic radiation. The most effective way to accelerate an electron is to use electromagnetic forces. Since
The Dusty Universe. Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy
 The Dusty Universe Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy To astronomers, dust means: sub micron solid grains (1 micron = 1 m = 10 6 m = one millionth of a meter) Typical
The Dusty Universe Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy To astronomers, dust means: sub micron solid grains (1 micron = 1 m = 10 6 m = one millionth of a meter) Typical
First scientific results from QUIJOTE. constraints on radio foregrounds
 First scientific results from QUIJOTE constraints on radio foregrounds Flavien Vansyngel, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias @ CMB Foregrounds, UCSD, 2017/11/29 The QUIJOTE experiment Tenerife experiment
First scientific results from QUIJOTE constraints on radio foregrounds Flavien Vansyngel, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias @ CMB Foregrounds, UCSD, 2017/11/29 The QUIJOTE experiment Tenerife experiment
Planck 2014 The Microwave Sky in Temperature and Polarisation Ferrara, 1 5 December The Planck mission
 Planck 2014 The Microwave Sky in Temperature and Polarisation Ferrara, 1 5 December 2014 The Planck mission Marco Bersanelli Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano Planck-LFI Deputy PI
Planck 2014 The Microwave Sky in Temperature and Polarisation Ferrara, 1 5 December 2014 The Planck mission Marco Bersanelli Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano Planck-LFI Deputy PI
Photodissociation Regions Radiative Transfer. Dr. Thomas G. Bisbas
 Photodissociation Regions Radiative Transfer Dr. Thomas G. Bisbas tbisbas@ufl.edu Interstellar Radiation Field In the solar neighbourhood, the ISRF is dominated by six components Schematic sketch of the
Photodissociation Regions Radiative Transfer Dr. Thomas G. Bisbas tbisbas@ufl.edu Interstellar Radiation Field In the solar neighbourhood, the ISRF is dominated by six components Schematic sketch of the
Polarised synchrotron simulations for EoR experiments
 Centre for Radio Cosmology Polarised synchrotron simulations for EoR experiments The broad impact of Low Frequency Observing Bologna, 19-23 June 2017 Marta Spinelli in collaboration with M. Santos and
Centre for Radio Cosmology Polarised synchrotron simulations for EoR experiments The broad impact of Low Frequency Observing Bologna, 19-23 June 2017 Marta Spinelli in collaboration with M. Santos and
8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust
 8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust James Graham UC, Berkeley 1 Reading Tielens, Interstellar Medium, Ch. 5 Mathis, J. S. 1990, AARA, 28, 37 Draine, B. T., 2003, AARA, 41, 241 2 Nature
8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust James Graham UC, Berkeley 1 Reading Tielens, Interstellar Medium, Ch. 5 Mathis, J. S. 1990, AARA, 28, 37 Draine, B. T., 2003, AARA, 41, 241 2 Nature
High latitude Galactic dust emission in the BOOMERanG maps
 High latitude Galactic dust emission in the BOOMERanG maps S. Masi 1, P.A.R. Ade 2,J.J Bock 3,4, A. Boscaleri 5, B.P. Crill 3, P. de Bernardis 1, M. Giacometti 1, E. Hivon 3, V.V. Hristov 3, A.E. Lange
High latitude Galactic dust emission in the BOOMERanG maps S. Masi 1, P.A.R. Ade 2,J.J Bock 3,4, A. Boscaleri 5, B.P. Crill 3, P. de Bernardis 1, M. Giacometti 1, E. Hivon 3, V.V. Hristov 3, A.E. Lange
Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction
 Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction Matt Chasse chasse@hawaii.edu Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, HI 96816 Matt Chasse, CMB Intro, May 3, 2005 p. 1/2 Outline CMB, what
Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction Matt Chasse chasse@hawaii.edu Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, HI 96816 Matt Chasse, CMB Intro, May 3, 2005 p. 1/2 Outline CMB, what
Primordial B-modes: Foreground modelling and constraints
 Primordial B-modes: Foreground modelling and constraints Carlo Contaldi Imperial College London Model Polarisation Amplitude 40 60-180 160 140 120 100 20 80 0 60 40 20 0-20 -40-60 -80-100 -120-140 -160-20
Primordial B-modes: Foreground modelling and constraints Carlo Contaldi Imperial College London Model Polarisation Amplitude 40 60-180 160 140 120 100 20 80 0 60 40 20 0-20 -40-60 -80-100 -120-140 -160-20
CMB Polarization and Cosmology
 CMB Polarization and Cosmology Wayne Hu KIPAC, May 2004 Outline Reionization and its Applications Dark Energy The Quadrupole Gravitational Waves Acoustic Polarization and Initial Power Gravitational Lensing
CMB Polarization and Cosmology Wayne Hu KIPAC, May 2004 Outline Reionization and its Applications Dark Energy The Quadrupole Gravitational Waves Acoustic Polarization and Initial Power Gravitational Lensing
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 12 Jan 1996
 COBE Preprint 96-01, Submitted To ApJ Letters 4-Year COBE 1 DMR Cosmic Microwave Background Observations: Maps and Basic Results arxiv:astro-ph/9601067v1 12 Jan 1996 C. L. Bennett 2,3, A. Banday 4, K.
COBE Preprint 96-01, Submitted To ApJ Letters 4-Year COBE 1 DMR Cosmic Microwave Background Observations: Maps and Basic Results arxiv:astro-ph/9601067v1 12 Jan 1996 C. L. Bennett 2,3, A. Banday 4, K.
Chapter 2 Bremsstrahlung and Black Body
 Chapter 2 Bremsstrahlung and Black Body 2.1 Bremsstrahlung We will follow an approximate derivation. For a more complete treatment see [2] and [1]. We will consider an electron proton plasma. Definitions:
Chapter 2 Bremsstrahlung and Black Body 2.1 Bremsstrahlung We will follow an approximate derivation. For a more complete treatment see [2] and [1]. We will consider an electron proton plasma. Definitions:
Dust in the Diffuse Universe
 Dust in the Diffuse Universe Obscuring Effects Chemical Effects Thermal Effects Dynamical Effects Diagnostic Power Evidence for Grains: Chemical Effects Catalyzes molecular hydrogen formation. Depletion
Dust in the Diffuse Universe Obscuring Effects Chemical Effects Thermal Effects Dynamical Effects Diagnostic Power Evidence for Grains: Chemical Effects Catalyzes molecular hydrogen formation. Depletion
HOW TO GET LIGHT FROM THE DARK AGES
 HOW TO GET LIGHT FROM THE DARK AGES Anthony Smith Lunar Seminar Presentation 2/2/2010 OUTLINE Basics of Radio Astronomy Why go to the moon? What should we find there? BASICS OF RADIO ASTRONOMY Blackbody
HOW TO GET LIGHT FROM THE DARK AGES Anthony Smith Lunar Seminar Presentation 2/2/2010 OUTLINE Basics of Radio Astronomy Why go to the moon? What should we find there? BASICS OF RADIO ASTRONOMY Blackbody
Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way
 Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way Wolfgang Reich Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie Bonn Why is the Galactic B-field of interest? highest spatial resolution of B-fields clarify its role in spiral galaxies
Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way Wolfgang Reich Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie Bonn Why is the Galactic B-field of interest? highest spatial resolution of B-fields clarify its role in spiral galaxies
An Introduction to Radio Astronomy
 An Introduction to Radio Astronomy Second edition Bernard F. Burke and Francis Graham-Smith CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the second edition page x 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The role of radio
An Introduction to Radio Astronomy Second edition Bernard F. Burke and Francis Graham-Smith CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the second edition page x 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The role of radio
Rayleigh scattering:
 Rayleigh scattering: blue sky thinking for future CMB observations arxiv:1307.8148; previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Rayleigh scattering: blue sky thinking for future CMB observations arxiv:1307.8148; previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Anisotropy in the CMB
 Anisotropy in the CMB Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Hanson & Lewis: 0908.0963 Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu &
Anisotropy in the CMB Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Hanson & Lewis: 0908.0963 Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu &
C-BASS: The C-Band All-Sky Survey. Luke Jew
 C-BASS: The C-Band All-Sky Survey Luke Jew The C-Band All-Sky Survey All-sky map 5GHz (bandwidth 1GHz) Resolution ~0.73 degrees Stokes I, Q & U High S/N (0.1mK beam -1 ) 1. Overview of project 2. Current
C-BASS: The C-Band All-Sky Survey Luke Jew The C-Band All-Sky Survey All-sky map 5GHz (bandwidth 1GHz) Resolution ~0.73 degrees Stokes I, Q & U High S/N (0.1mK beam -1 ) 1. Overview of project 2. Current
Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets. Loïc Verdier DDAYS 2015
 Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets Loïc Verdier SPP DDAYS 2015 Loïc Verdier (SPP) Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets DDAYS 2015 1 / 21 Cluster Abell 520; Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/UVic./A.Mahdavi
Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets Loïc Verdier SPP DDAYS 2015 Loïc Verdier (SPP) Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets DDAYS 2015 1 / 21 Cluster Abell 520; Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/UVic./A.Mahdavi
Constraining the topology of the Universe using CMB maps
 Constraining the topology of the Universe using CMB maps P. Bielewicz, A.J. Banday K.M. Górski, JPL Outline topology of the Universe signatures of topology in the CMB maps search for signatures of topology
Constraining the topology of the Universe using CMB maps P. Bielewicz, A.J. Banday K.M. Górski, JPL Outline topology of the Universe signatures of topology in the CMB maps search for signatures of topology
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era. François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale
 Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
Data analysis of massive data sets a Planck example
 Data analysis of massive data sets a Planck example Radek Stompor (APC) LOFAR workshop, Meudon, 29/03/06 Outline 1. Planck mission; 2. Planck data set; 3. Planck data analysis plan and challenges; 4. Planck
Data analysis of massive data sets a Planck example Radek Stompor (APC) LOFAR workshop, Meudon, 29/03/06 Outline 1. Planck mission; 2. Planck data set; 3. Planck data analysis plan and challenges; 4. Planck
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Feb 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Feb 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Feb 2016](/thumbs/91/107334121.jpg) Astronomische Nachrichten, 1 October 2018 Excess B-modes extracted from the Planck polarization maps H. U. Nørgaard - Nielsen National Space Institute (DTU Space), Technical University of Denmark, Elektrovej,
Astronomische Nachrichten, 1 October 2018 Excess B-modes extracted from the Planck polarization maps H. U. Nørgaard - Nielsen National Space Institute (DTU Space), Technical University of Denmark, Elektrovej,
Review: Properties of a wave
 Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Scientific results from QUIJOTE. constraints on CMB radio foregrounds
 Scientific results from QUIJOTE constraints on CMB radio foregrounds Flavien Vansyngel, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, on the behalf of the QUIJOTE collaboration @ 53rd rencontres de Moriond The
Scientific results from QUIJOTE constraints on CMB radio foregrounds Flavien Vansyngel, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, on the behalf of the QUIJOTE collaboration @ 53rd rencontres de Moriond The
LFI frequency maps: data analysis, results and future challenges
 LFI frequency maps: data analysis, results and future challenges Davide Maino Università degli Studi di Milano, Dip. di Fisica New Light in Cosmology from the CMB 22 July - 2 August 2013, Trieste Davide
LFI frequency maps: data analysis, results and future challenges Davide Maino Università degli Studi di Milano, Dip. di Fisica New Light in Cosmology from the CMB 22 July - 2 August 2013, Trieste Davide
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I. R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 2009
 Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 009 Light of the night sky We learn of the universe around us from EM radiation, neutrinos,
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 009 Light of the night sky We learn of the universe around us from EM radiation, neutrinos,
Interstellar Dust and Extinction
 University of Oxford, Astrophysics November 12, 2007 Outline Extinction Spectral Features Emission Scattering Polarization Grain Models & Evolution Conclusions What and Why? Dust covers a range of compound
University of Oxford, Astrophysics November 12, 2007 Outline Extinction Spectral Features Emission Scattering Polarization Grain Models & Evolution Conclusions What and Why? Dust covers a range of compound
Information Field Theory. Torsten Enßlin MPI for Astrophysics Ludwig Maximilian University Munich
 Information Field Theory Torsten Enßlin MPI for Astrophysics Ludwig Maximilian University Munich Information Field Theory signal field: degrees of freedom data set: finite additional information needed
Information Field Theory Torsten Enßlin MPI for Astrophysics Ludwig Maximilian University Munich Information Field Theory signal field: degrees of freedom data set: finite additional information needed
Planck. Ken Ganga. APC/CNRS/ University of Paris-Diderot
 Planck Ken Ganga APC/CNRS/ University of Paris-Diderot A Brief History of the Cosmos The CMB was emitted when the Universe was about 3 10-5 of its current age. 2 Planck/HFI Timeline The HFI builds on the
Planck Ken Ganga APC/CNRS/ University of Paris-Diderot A Brief History of the Cosmos The CMB was emitted when the Universe was about 3 10-5 of its current age. 2 Planck/HFI Timeline The HFI builds on the
High Energy Astrophysics
 High Energy Astrophysics Introduction Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk January 2012 Today s introduction - The sky at different
High Energy Astrophysics Introduction Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk January 2012 Today s introduction - The sky at different
Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons. and Light. Lecture 7
 Lecture 7 Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Theory, Photons. and Light Sources of light Emission of light by atoms The electromagnetic spectrum see supplementary material posted on the course website Electric
Lecture 7 Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Theory, Photons. and Light Sources of light Emission of light by atoms The electromagnetic spectrum see supplementary material posted on the course website Electric
Power spectrum exercise
 Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Discovery of TeV Gamma-ray Emission Towards Supernova Remnant SNR G Last Updated Tuesday, 30 July :01
 Background-subtracted gamma-ray count map of SNR G78.2+2.1 showing the VERITAS detection (VER2019+407). For details, see Figure 1 below. Reference: E. Aliu et al. (The VERITAS Collaboration), Astrophysical
Background-subtracted gamma-ray count map of SNR G78.2+2.1 showing the VERITAS detection (VER2019+407). For details, see Figure 1 below. Reference: E. Aliu et al. (The VERITAS Collaboration), Astrophysical
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 24. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
An Introduction to Radio Astronomy
 An Introduction to Radio Astronomy Bernard F. Burke Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Francis Graham-Smith Jodrell Bank, University of Manchester CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface Acknowledgements
An Introduction to Radio Astronomy Bernard F. Burke Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Francis Graham-Smith Jodrell Bank, University of Manchester CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface Acknowledgements
Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement
 Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement HEP seminar at Kyoto University April 13 th, 2007 Akito KUSAKA University of Tokyo Outline Physics of CMB and its Polarization What does WMAP shed light
Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement HEP seminar at Kyoto University April 13 th, 2007 Akito KUSAKA University of Tokyo Outline Physics of CMB and its Polarization What does WMAP shed light
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy
 Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
364 DE OLIVEIRA-COSTA ET AL. Vol. 567
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 567:363È369, 2002 March 1 ( 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A NEW SPIN ON GALACTIC DUST ANGE LICA DE OLIVEIRA-COSTA,1 MAX TEGMARK,1
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 567:363È369, 2002 March 1 ( 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A NEW SPIN ON GALACTIC DUST ANGE LICA DE OLIVEIRA-COSTA,1 MAX TEGMARK,1
THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe
 THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe Rodrigo Leonardi Planck Science Office ESTEC/ESA OVERVIEW Planck observational objective & science.
THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe Rodrigo Leonardi Planck Science Office ESTEC/ESA OVERVIEW Planck observational objective & science.
Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission
 Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission Masaki Mori ICRR CANGAROO group internal seminar, November 7, 2005 Adrian Cho S. Hunter, GLAST meeting, Oct.2004 The Galactic Diffuse Gamma-ray Emission...
Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission Masaki Mori ICRR CANGAROO group internal seminar, November 7, 2005 Adrian Cho S. Hunter, GLAST meeting, Oct.2004 The Galactic Diffuse Gamma-ray Emission...
Gas 1: Molecular clouds
 Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results. Alexander Schmah
 The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
