Printing Colour at the Optical Diffraction Limit
|
|
|
- Noreen Dixon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: /NNANO Printing Colour at the Optical Diffraction Limit Karthik Kumar 1,#, Huigao Duan 1,#, Ravi S. Hegde 2, Samuel C.W. Koh 1, Jennifer N. Wei 1 and Joel K.W. Yang 1 * NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY 1
2 Figure S1. Simulated reflectance spectra of nanodisks in the presence of Si in vacuum Figure S1. Simulated spectra of Ag/Au nanodisks hovering above a reflective Si surface. The spectra for both (A) 140 nm disks and (B) 50 nm disks in periodic arrays with gaps of 30 nm are presented here. When the disks are placed directly on a reflective surface (0 nm), all visible wavelengths appear to be reflected almost equally, which would result in a dull gray colour. As soon as the nanodisks are allowed to hover above the surface even at a distance of 20 nm, the spectrum shifts drastically; plasmonic scattering is observed for the larger nanodisks, while certain wavelengths are absorbed of the smaller nanodisks. At a distance of 180 nm, more of the low wavelength regions are reflected, resulting in a bluish tinge to the colours observed. 2
3 The behavior of nanodisks in the vicinity of a back-reflector can be explained via the existence of a screening dipole, which is a mirror dipole, and thus has the opposite effect the orginal dipole. The dipoles are thus cancelled out. The cancellation is most effective when the dipoles are closest to each other. Thus when resting right on top, there is almost full cancellation and as we start hovering the disk, the cancellation becomes less effective. The role of the HSQ structures can thus be hypothesized to be due to the reduction of the effects of the screening charges. 1,2 It is highly likely that once the nanodisks are separated far enough from the surface, the configuration of nanodisk and reflective surface will produce a superposed response of the individual spectra from the nanodisk and the silicon surface. 3
4 Figure S2. Experimental Microspectrophotometry Data Figure S2. Selected experimentally obtained spectra with varying D and g. The corresponding colours observed in reflection brightfield microscopy are also displayed. 4
5 Figure S3. Simulation results for an array of nanopillar structures with separations of 120 nm. Figure S3. Simulation results, electric field and Poynting vector plots for an array of nanopillar structures with separations of 120 nm. (a) 140 nm disks: A peak at 590 nm (i) and a dip at 710 nm (ii) are observed. The corresponding E-field amplitude enhancement plot (ci) shows that a dipole resonance is present in the disk at this point, while the Poynting vector plot (di) shows that most of the power is reflected away towards the observer. At the dip at 710 nm, the corresponding E-field plot (cii) shows a strong 5
6 resonance within the disk, while the Poynting vector plot (dii) shows how the power flows around the nanodisk into the nanohole. (b) 50 nm disks: A single dip at 440 nm (iii) is observed. The corresponding E-field plot (ciii) shows that a strong dipole resonance is set up within the nanodisk, while the Poynting vector plot (diii) shows how the power flows mostly into the nanodisk and towards the nanohole. To investigate the observed spectral features in the reflectance plots, we looked at the simulated electric field amplitude enhancement (E-field) plots and Poynting vector plots at the peaks and dips for 140 and 50 nm disks (Figures S3a and S3b, reproduced for clarity from Figure 2cii). Two key features for disks with a diameter of 140 nm (Figure S3a), i.e. a clear peak at ~590 nm, and a dip at ~710 nm are observable. At the peak, we see strong E-fields around the disk (Figure S3c(i)) and Poynting vector plots (Figure S3d(i)) showing energy flow into the disk, both signifying the condition of a disk plasmon resonance, which re-radiates light back to the viewer. 3 On the other hand, at the dip (~710 nm), we observe both a strong E-field (Figure S3c(ii)) around the disk and through the hole of the back-reflector. The Poynting vector plot (Figure S3d(ii)) shows that power is being channeled sharply around the disk and into the hole. Hence, the peak of reflectance occurs at the plasmon resonance of the disk, whereas the dip in reflectance corresponds to the antenna-assisted EOT mode. As the disk size is reduced to between 90 nm to 50 nm, we note the disappearance of the peak, and a blue-shifting in the position of the dip (Figures 2c(ii), S3b). Observing the field plots (Figure S3c(iii)) and Poynting vector plots (Figure S3d(iii)) at this dip at 6
7 ~440 nm, we see the strong E-fields around the disk and energy being channeled into the disk and hole suggesting the behavior of the nanostructures as an anti-reflection stack. 7
8 Figure S4. Simulated reflectance spectra of nanodisks in vacuum Figure S4. Simulation of the reflectances of an array of disks with a separation of 120 nm in vacuum. The peak position of the reflectance red-shifts from 430 nm to 580 nm with increasing diameters of the nanodisk. The reflectance intensity also increases with increasing diameter of the nanodisks. 8
9 Figure S5. Simulation of the reflectances of an array of nanoholes in an Ag/Au stack Figure S5. Simulation of the reflectances of an array of nanoholes in an Ag/Au stack. The fill factor is kept constant at 0.5 [D/(D+g)] with the diameter and the gap being equal to each other. EOT modes are detected for these cases which redshifts from 850 nm to 1050 nm with increase in periodicity as indicated by the gray arrow. The dip position of the reflectance stays fairly constant at ~ 450 nm, indicating that the absorbance at this region is independent of periodicity. This dip may be attributed to the anti-reflection coating stack of Au/Ag on Si at this wavelength. 9
10 Figure S6: Effect of holes at the base of the nanoposts in the backplane Figure S6. Numerical simulations of the structures with and without the presence of a hole in the backreflector plane. The periodicity was kept constant at 120 nm and simulations were done for the cases of D = 50 nm and 90 nm to compare with those in Figure 3. The inflexion points at 900 nm disappear for the case of the planar backreflector, due to the absence of Fano resonances. For D = 90 nm, the nanoholes reduce reflectance in the red part of the spectrum and at longer wavelengths thus accentuating the blue and green colors. 10
11 Figures S7 and S8: Layout Generation Red, green, and blue (RGB) values for each combination of disk size (D), and gap size (g) were first extracted from the optical micrograph of the colour palette of Figure 2(b), as presented in Figure S7. A code was written in Matlab to generate pattern layouts for the electron-beam lithography tool based on a bitmap image. The code then extracts RGB values for each pixel and finds a closest match to a combination of D and g from the colour palette using a least-squares error method. Each pixel was defined to occupy an area, which could be set to an arbitrary value, e.g. 250 nm by 250 nm square (as presented in the main text). To fit disks into this pixel array, two approaches were used. The first, which was used to create the bowtie image (Figure S7a-c) simply used the exact D and g obtained from the closest match and fitted a 2x2 array of disks into the square area. The 2x2 array would fit inside this square array if the condition 2*(D+g) < 250 nm was satisfied, but if a situation arose such that 2*(D+g) > 250 nm, only a single disk of size D was positioned at the center of the square. This approach could lead to inaccuracies in the colour reproduction. In the second approach, used in the main text, we make use of the fact that lines of almost equal colour exists on the D vs g plot. This approach was used to create the Lena image (Figure 4a-c). It would first find the closest match for D and g just like the first method, but would then scale D and g to D and g along lines of nearly equal colours on the D vs g plot. These lines were approximately defined to be lines of equal slopes such that (D D)/(g g) = ½, which should also satisfy the equation 2*(D + g ) = 250 nm. The resulting disks would be a periodic array of disks with varying D and g values. In 11
12 cases where a single disk would suffice, e.g. in the rendering of blue/purple colour in the Lena image, the code would decide this by comparing the fractional change in D and g for both cases to the original D and g and choosing the case with the smaller fractional change. The code would then create an entry in the layout file for the coordinates of these 4 disks within the pixel area. Further improvements in the code can be obtained by including the ability of colour prediction, interpolating between data points, and by feeding in more data points for a larger range of D and g values. Figure S7. Plots of R, G, and B values on a D vs g axis extracted from the optical micrograph of the colour palette in Figure 2(b). These RGB values with their corresponding D and g combinations were used by the code to find a closest colour match for every pixel in a given bitmap image. The closest match for D and g, or modified D and g values were then used to calculate the coordinates and sizes of each disk in the layout. 12
13 Figure S8: Arbitrary full-colour image printing. (a) A colour image prior to deposition of the metal layers, the optical micrograph shows at best grayscale variations (cf. Figure 2a). (b) Upon deposition of the uniform metal layers, the various solid colours emerge. (c) SEM image of a selected area in 4a, showing the structures array, with the exact two bright dots that appear in 4b as circled. Dotted lines were drawn in to show boundaries between the different colors. 13
14 Figure S9. Demonstration of nanoimprint lithography for scaling up the throughput Figure S9. Photograph and SEM images showing results obtained with nanoimprint lithography. To investigate the feasibility of scaling-up the throughput of such plasmonic micro-images, we used thermal nanoimprint lithography to create a 1 x 1 cm area of nanopillars in polycarbonate (see Methods section). The nanopillars were subsequently coated with a metal layer. The patterned areas had a blue colour, while the unpatterned areas retained the bulk metal layer colour. 14
15 Acknowledgements R.S.H acknowledges useful discussion with Peter Nordlander, Rice University. 1 Dimitriev, A. et al. Enhanced nanoplasmonic optical sensors with reduced substrate effect. Nano Lett. 8, (2008). 2 Zhang, S., Bao, K., Halas, N.J., Xu, H. & Nordlander, P. Substrate-induced fano resonances of a plasmonic nanocube: A route to increased-sensitivity localized surface plasmon resonance sensors revealed. Nano Lett. 11, (2011). 3 Liu, N. et al. Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the drude damping limit. Nature Mater. 8, (2009). 15
Full-color Subwavelength Printing with Gapplasmonic
 Supporting information for Full-color Subwavelength Printing with Gapplasmonic Optical Antennas Masashi Miyata, Hideaki Hatada, and Junichi Takahara *,, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University,
Supporting information for Full-color Subwavelength Printing with Gapplasmonic Optical Antennas Masashi Miyata, Hideaki Hatada, and Junichi Takahara *,, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University,
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Large-scale lithography-free metasurface with spectrally tunable super
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Large-scale lithography-free metasurface with spectrally tunable super
Biosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities
 iosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities. Sepulveda, 1, Y. Alaverdyan,. rian, M. Käll 1 Nanobiosensors and Molecular Nanobiophysics Group Research Center on Nanoscience and Nanotechnolog (CIN)CSIC-ICN
iosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities. Sepulveda, 1, Y. Alaverdyan,. rian, M. Käll 1 Nanobiosensors and Molecular Nanobiophysics Group Research Center on Nanoscience and Nanotechnolog (CIN)CSIC-ICN
Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances
 Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances T. J. Davis, D. E. Gómez and K. C. Vernon CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering Localized surface plasmon (LSP)
Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances T. J. Davis, D. E. Gómez and K. C. Vernon CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering Localized surface plasmon (LSP)
Supplementary Figure S1 Anticrossing and mode exchange between D1 (Wood's anomaly)
 Supplementary Figure S1 Anticrossing and mode exchange between D1 (Wood's anomaly) and D3 (Fabry Pérot cavity mode). (a) Schematic (top) showing the reflectance measurement geometry and simulated angle-resolved
Supplementary Figure S1 Anticrossing and mode exchange between D1 (Wood's anomaly) and D3 (Fabry Pérot cavity mode). (a) Schematic (top) showing the reflectance measurement geometry and simulated angle-resolved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Nano-scale plasmonic motors driven by light Ming Liu 1, Thomas Zentgraf 1, Yongmin Liu 1, Guy Bartal 1 & Xiang Zhang 1,2 1 NSF Nano-scale Science and Engineering Center (NSEC),
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Nano-scale plasmonic motors driven by light Ming Liu 1, Thomas Zentgraf 1, Yongmin Liu 1, Guy Bartal 1 & Xiang Zhang 1,2 1 NSF Nano-scale Science and Engineering Center (NSEC),
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Light emission near a gradient metasurface Leonard C. Kogos and Roberto Paiella Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston,
Supporting Information Light emission near a gradient metasurface Leonard C. Kogos and Roberto Paiella Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston,
Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics)
 Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Unterpoerlitzer
Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Unterpoerlitzer
Supplementary information for. plasmonic nanorods interacting with J-aggregates.
 Supplementary information for Approaching the strong coupling limit in single plasmonic nanorods interacting with J-aggregates. by Gülis Zengin, Göran Johansson, Peter Johansson, Tomasz J. Antosiewicz,
Supplementary information for Approaching the strong coupling limit in single plasmonic nanorods interacting with J-aggregates. by Gülis Zengin, Göran Johansson, Peter Johansson, Tomasz J. Antosiewicz,
Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.31 Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature Chang-Hua Liu 1, You-Chia Chang 2, Ted Norris 1.2* and Zhaohui
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.31 Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature Chang-Hua Liu 1, You-Chia Chang 2, Ted Norris 1.2* and Zhaohui
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: Achieving Strong Field Enhancement and Light Absorption Simultaneously with Plasmonic Nanoantennas Exploiting Film-Coupled Triangular Nanodisks Yang Li, Dezhao Li, Cheng Chi, and
Supporting Information: Achieving Strong Field Enhancement and Light Absorption Simultaneously with Plasmonic Nanoantennas Exploiting Film-Coupled Triangular Nanodisks Yang Li, Dezhao Li, Cheng Chi, and
Large Area Plasmonic Color Palettes with Expanded Gamut Using. Colloidal Self-Assembly
 Large Area Plasmonic Color Palettes with Expanded Gamut Using Colloidal Self-Assembly Liancheng Wang 1, Ray J. H. Ng 1, Saman Safari Dinachali 1, Mahsa Jalali 1, Ye Yu 1, and Joel K.W. Yang 1,2 1 Engineering
Large Area Plasmonic Color Palettes with Expanded Gamut Using Colloidal Self-Assembly Liancheng Wang 1, Ray J. H. Ng 1, Saman Safari Dinachali 1, Mahsa Jalali 1, Ye Yu 1, and Joel K.W. Yang 1,2 1 Engineering
l* = 109 nm Glycerol Clean Water Glycerol l = 108 nm Wavelength (nm)
 1/ (rad -1 ) Normalized extinction a Clean 0.8 Water l* = 109 nm 0.6 Glycerol b 2.0 1.5 500 600 700 800 900 Clean Water 0.5 Glycerol l = 108 nm 630 660 690 720 750 Supplementary Figure 1. Refractive index
1/ (rad -1 ) Normalized extinction a Clean 0.8 Water l* = 109 nm 0.6 Glycerol b 2.0 1.5 500 600 700 800 900 Clean Water 0.5 Glycerol l = 108 nm 630 660 690 720 750 Supplementary Figure 1. Refractive index
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Trilayer graphene is a semimetal with a gate-tuneable band overlap M. F. Craciun, S. Russo, M. Yamamoto, J. B. Oostinga, A. F. Morpurgo and S. Tarucha
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Trilayer graphene is a semimetal with a gate-tuneable band overlap M. F. Craciun, S. Russo, M. Yamamoto, J. B. Oostinga, A. F. Morpurgo and S. Tarucha
Symmetry Breaking in Oligomer Surface Plasmon Lattice Resonances
 Supporting Information Symmetry Breaking in Oligomer Surface Plasmon Lattice Resonances Marco Esposito 1, Francesco Todisco 2, Said Bakhti 3, Adriana Passaseo* 1, Iolena Tarantini 4, Massimo Cuscunà 1,
Supporting Information Symmetry Breaking in Oligomer Surface Plasmon Lattice Resonances Marco Esposito 1, Francesco Todisco 2, Said Bakhti 3, Adriana Passaseo* 1, Iolena Tarantini 4, Massimo Cuscunà 1,
Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials
 Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials Shuang Zhang 1, Wenjun Fan 1, N. C. Panoiu 2, K. J. Malloy 1, R. M. Osgood 2 and S. R. J. Brueck 2 1. Center for High Technology Materials and Department
Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials Shuang Zhang 1, Wenjun Fan 1, N. C. Panoiu 2, K. J. Malloy 1, R. M. Osgood 2 and S. R. J. Brueck 2 1. Center for High Technology Materials and Department
Multiple-Patterning Nanosphere Lithography for Fabricating Periodic Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Nanostructures
 Supporting Information Multiple-Patterning Nanosphere Lithography for Fabricating Periodic Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Nanostructures Xiaobin Xu, 1,2 Qing Yang, 1,2 Natcha Wattanatorn, 1,2 Chuanzhen
Supporting Information Multiple-Patterning Nanosphere Lithography for Fabricating Periodic Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Nanostructures Xiaobin Xu, 1,2 Qing Yang, 1,2 Natcha Wattanatorn, 1,2 Chuanzhen
Supporting information. Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via
 Supporting information Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via Photonic Fano Resonances Xingwang Zhang, Shinhyuk Choi, Dake Wang, Carl H. Naylor, A. T. Charlie Johnson, and Ertugrul Cubukcu,,*
Supporting information Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via Photonic Fano Resonances Xingwang Zhang, Shinhyuk Choi, Dake Wang, Carl H. Naylor, A. T. Charlie Johnson, and Ertugrul Cubukcu,,*
Shadow Overlap Ion-beam Lithography for Nanoarchitectures
 Shadow Overlap Ion-beam Lithography for Nanoarchitectures NANO LETTERS XXXX Vol. xx, No. x - Yeonho Choi, Soongweon Hong, and Luke P. Lee* Biomolecular Nanotechnology Center, Berkeley Sensor and Actuator
Shadow Overlap Ion-beam Lithography for Nanoarchitectures NANO LETTERS XXXX Vol. xx, No. x - Yeonho Choi, Soongweon Hong, and Luke P. Lee* Biomolecular Nanotechnology Center, Berkeley Sensor and Actuator
Simulated Study of Plasmonic Coupling in Noble Bimetallic Alloy Nanosphere Arrays
 CHAPTER 4 Simulated Study of Plasmonic Coupling in Noble Bimetallic Alloy Nanosphere Arrays 4.1 Introduction In Chapter 3, the noble bimetallic alloy nanosphere (BANS) of Ag 1-x Cu x at a particular composition
CHAPTER 4 Simulated Study of Plasmonic Coupling in Noble Bimetallic Alloy Nanosphere Arrays 4.1 Introduction In Chapter 3, the noble bimetallic alloy nanosphere (BANS) of Ag 1-x Cu x at a particular composition
Multiple Fano Resonances Structure for Terahertz Applications
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 50, 1 6, 2014 Multiple Fano Resonances Structure for Terahertz Applications Hadi Amarloo *, Daniel M. Hailu, and Safieddin Safavi-Naeini Abstract A new
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 50, 1 6, 2014 Multiple Fano Resonances Structure for Terahertz Applications Hadi Amarloo *, Daniel M. Hailu, and Safieddin Safavi-Naeini Abstract A new
Supporting Information for: Photo-induced force mapping of plasmonic. nanostructures
 Supporting Information for: Photo-induced force mapping of plasmonic nanostructures Thejaswi U. Tumkur,* # Xiao Yang,* # Benjamin Cerjan, Naomi J. Halas,*,,,, Peter Nordlander,*, Isabell Thomann*,,,, Corresponding
Supporting Information for: Photo-induced force mapping of plasmonic nanostructures Thejaswi U. Tumkur,* # Xiao Yang,* # Benjamin Cerjan, Naomi J. Halas,*,,,, Peter Nordlander,*, Isabell Thomann*,,,, Corresponding
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.72 Tunable Subradiant Lattice Plasmons by Out-of-plane Dipolar Interactions Wei Zhou and Teri W. Odom Optical measurements. The gold nanoparticle arrays
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.72 Tunable Subradiant Lattice Plasmons by Out-of-plane Dipolar Interactions Wei Zhou and Teri W. Odom Optical measurements. The gold nanoparticle arrays
Nanophysics: Main trends
 Nano-opto-electronics Nanophysics: Main trends Nanomechanics Main issues Light interaction with small structures Molecules Nanoparticles (semiconductor and metallic) Microparticles Photonic crystals Nanoplasmonics
Nano-opto-electronics Nanophysics: Main trends Nanomechanics Main issues Light interaction with small structures Molecules Nanoparticles (semiconductor and metallic) Microparticles Photonic crystals Nanoplasmonics
Color Science Light & Spectra
 COLOR Visible Light Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by it s wavelength Most light sources produce contributions over many wavelengths, contributions
COLOR Visible Light Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by it s wavelength Most light sources produce contributions over many wavelengths, contributions
Large-Area and Uniform Surface-Enhanced Raman. Saturation
 Supporting Information Large-Area and Uniform Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Substrate Optimized by Enhancement Saturation Daejong Yang 1, Hyunjun Cho 2, Sukmo Koo 1, Sagar R. Vaidyanathan 2, Kelly
Supporting Information Large-Area and Uniform Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Substrate Optimized by Enhancement Saturation Daejong Yang 1, Hyunjun Cho 2, Sukmo Koo 1, Sagar R. Vaidyanathan 2, Kelly
A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars
 Nanoscale Res Lett (2008) 3: 127 DOI 10.1007/s11671-008-9124-6 NANO EXPRESS A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars Wei Wu Æ Dibyendu
Nanoscale Res Lett (2008) 3: 127 DOI 10.1007/s11671-008-9124-6 NANO EXPRESS A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars Wei Wu Æ Dibyendu
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped
 Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped gold substrate. (a) Spin coating of hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) resist onto the silicon substrate with a thickness
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped gold substrate. (a) Spin coating of hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) resist onto the silicon substrate with a thickness
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Coupling of Plasmonic Nanopore Pairs: Facing Dipoles Attract Each Other Takumi Sannomiya 1, Hikaru Saito 2, Juliane Junesch 3, Naoki Yamamoto 1. 1 Department of Innovative and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Coupling of Plasmonic Nanopore Pairs: Facing Dipoles Attract Each Other Takumi Sannomiya 1, Hikaru Saito 2, Juliane Junesch 3, Naoki Yamamoto 1. 1 Department of Innovative and
Nanoplasmonics: Classical down to the Nanometer Scale
 Supporting Information Nanoplasmonics: Classical down to the Nanometer Scale Huigao Duan #, Antonio I. Fernández-Domínguez 2#, Michel Bosman #, Stefan A. Maier 2* & Joel K. W. Yang * Institute of Materials
Supporting Information Nanoplasmonics: Classical down to the Nanometer Scale Huigao Duan #, Antonio I. Fernández-Domínguez 2#, Michel Bosman #, Stefan A. Maier 2* & Joel K. W. Yang * Institute of Materials
Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation
 Supporting Information Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation Yuanmu Yang, Wenyi Wang, Parikshit Moitra, Ivan I. Kravchenko, Dayrl P. Briggs,
Supporting Information Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation Yuanmu Yang, Wenyi Wang, Parikshit Moitra, Ivan I. Kravchenko, Dayrl P. Briggs,
Metamaterials & Plasmonics
 Metamaterials & Plasmonics Exploring the Impact of Rotating Rectangular Plasmonic Nano-hole Arrays on the Transmission Spectra and its Application as a Plasmonic Sensor. Abstract Plasmonic nano-structures
Metamaterials & Plasmonics Exploring the Impact of Rotating Rectangular Plasmonic Nano-hole Arrays on the Transmission Spectra and its Application as a Plasmonic Sensor. Abstract Plasmonic nano-structures
Invited Paper ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Invited Paper Numerical Prediction of the Effect of Nanoscale Surface Roughness on Film-coupled Nanoparticle Plasmon Resonances Chatdanai Lumdee and Pieter G. Kik *,, CREOL, the College of Optics and Photonics;
Invited Paper Numerical Prediction of the Effect of Nanoscale Surface Roughness on Film-coupled Nanoparticle Plasmon Resonances Chatdanai Lumdee and Pieter G. Kik *,, CREOL, the College of Optics and Photonics;
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematics of light transmission and reflection from a slab confined between
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure. Schematics of light transmission and reflection from a slab confined between two infinite media. Supplementary Figure. Reflectivity of a magneto-electric slab
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure. Schematics of light transmission and reflection from a slab confined between two infinite media. Supplementary Figure. Reflectivity of a magneto-electric slab
Al-Pd Nanodisk Heterodimers as Antenna-Reactor Photocatalysts
 Al-Pd Nanodisk Heterodimers as Antenna-Reactor Photocatalysts Chao Zhang 1, 4, Hangqi Zhao 1, 4, Linan Zhou 2, 4, Andrea E. Schlather 2, 4, Liangliang Dong 2, 4, Michael J. McClain 2, 4, Dayne F. Swearer
Al-Pd Nanodisk Heterodimers as Antenna-Reactor Photocatalysts Chao Zhang 1, 4, Hangqi Zhao 1, 4, Linan Zhou 2, 4, Andrea E. Schlather 2, 4, Liangliang Dong 2, 4, Michael J. McClain 2, 4, Dayne F. Swearer
Strong Light Confinement in Metal-Coated Si Nanopillars: Interplay of Plasmonic Effects and Geometric Resonance
 Kim et al. Nanoscale Research Letters (2017) 12:151 DOI 10.1186/s11671-017-1932-0 NANO EXPRESS Open Access Strong Light Confinement in Metal-Coated Si Nanopillars: Interplay of Plasmonic Effects and Geometric
Kim et al. Nanoscale Research Letters (2017) 12:151 DOI 10.1186/s11671-017-1932-0 NANO EXPRESS Open Access Strong Light Confinement in Metal-Coated Si Nanopillars: Interplay of Plasmonic Effects and Geometric
Surface Plasmon Polariton Assisted Metal-Dielectric Multilayers as Passband Filters for Ultraviolet Range
 Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the International School and Conference on Optics and Optical Materials, ISCOM07, Belgrade, Serbia, September 3 7, 2007 Surface Plasmon Polariton
Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the International School and Conference on Optics and Optical Materials, ISCOM07, Belgrade, Serbia, September 3 7, 2007 Surface Plasmon Polariton
Supplementary Information for. Fano resonance Rabi splitting of surfaces plasmons
 Supplementary Information for Fano resonance Rabi splitting of surfaces plasmons Zhiguang Liu, 1,4,# Jiafang Li, 1,#,* Zhe Liu, 1,# Wuxia Li, 1 Junjie Li, 1 Changzhi Gu, 1,2 and Zhi-Yuan Li 3,1,* 1 Institute
Supplementary Information for Fano resonance Rabi splitting of surfaces plasmons Zhiguang Liu, 1,4,# Jiafang Li, 1,#,* Zhe Liu, 1,# Wuxia Li, 1 Junjie Li, 1 Changzhi Gu, 1,2 and Zhi-Yuan Li 3,1,* 1 Institute
Symmetry breaking and strong coupling in planar optical metamaterials
 Symmetry breaking and strong coupling in planar optical metamaterials Koray Aydin 1*, Imogen M. Pryce 1, and Harry A. Atwater 1,2 1 Thomas J. Watson Laboratories of Applied Physics California Institute
Symmetry breaking and strong coupling in planar optical metamaterials Koray Aydin 1*, Imogen M. Pryce 1, and Harry A. Atwater 1,2 1 Thomas J. Watson Laboratories of Applied Physics California Institute
Supplementary Figure S1 SEM and optical images of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. a, SEM image of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. b, The size distribution of Si 0.
 Supplementary Figure S1 SEM and optical images of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. a, SEM image of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. b, The size distribution of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. The standard derivation is 4.4 %. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure S1 SEM and optical images of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. a, SEM image of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. b, The size distribution of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. The standard derivation is 4.4 %. Supplementary
Accurate Modeling of Dark-Field Scattering Spectra
 Accurate Modeling of Dark-Field Scattering Spectra of Plasmonic Nanostructures (Supporting Information) Liyong Jiang 1,2,, Tingting Yin 2,, Zhaogang Dong 3,, Mingyi Liao 4, Shawn J. Tan 3, Xiao Ming Goh
Accurate Modeling of Dark-Field Scattering Spectra of Plasmonic Nanostructures (Supporting Information) Liyong Jiang 1,2,, Tingting Yin 2,, Zhaogang Dong 3,, Mingyi Liao 4, Shawn J. Tan 3, Xiao Ming Goh
U-Shaped Nano-Apertures for Enhanced Optical Transmission and Resolution
 U-Shaped Nano-Apertures for Enhanced Optical Transmission and Resolution Mustafa Turkmen 1,2,3, Serap Aksu 3,4, A. Engin Çetin 2,3, Ahmet A. Yanik 2,3, Alp Artar 2,3, Hatice Altug 2,3,4, * 1 Electrical
U-Shaped Nano-Apertures for Enhanced Optical Transmission and Resolution Mustafa Turkmen 1,2,3, Serap Aksu 3,4, A. Engin Çetin 2,3, Ahmet A. Yanik 2,3, Alp Artar 2,3, Hatice Altug 2,3,4, * 1 Electrical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/nPHYS1804 Supplementary Information J. Zhu 1, J. Christensen 2, J. Jung 2,3, L. Martin-Moreno 4, X. Yin 1, L. Fok 1, X. Zhang 1 and F. J. Garcia-Vidal 2 1 NSF Nano-scale
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/nPHYS1804 Supplementary Information J. Zhu 1, J. Christensen 2, J. Jung 2,3, L. Martin-Moreno 4, X. Yin 1, L. Fok 1, X. Zhang 1 and F. J. Garcia-Vidal 2 1 NSF Nano-scale
Two-Photon Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Metallic Nanostructures for Plasmonic Metamaterials
 Two-Photon Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Metallic Nanostructures for Plasmonic Metamaterials Atsushi ISHIKAWA 1 and Takuo TANAKA 1,2 1- Metamaterials Laboratory, RIKEN, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198,
Two-Photon Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Metallic Nanostructures for Plasmonic Metamaterials Atsushi ISHIKAWA 1 and Takuo TANAKA 1,2 1- Metamaterials Laboratory, RIKEN, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198,
Collective effects in second-harmonic generation from plasmonic oligomers
 Supporting Information Collective effects in second-harmonic generation from plasmonic oligomers Godofredo Bautista,, *, Christoph Dreser,,, Xiaorun Zang, Dieter P. Kern,, Martti Kauranen, and Monika Fleischer,,*
Supporting Information Collective effects in second-harmonic generation from plasmonic oligomers Godofredo Bautista,, *, Christoph Dreser,,, Xiaorun Zang, Dieter P. Kern,, Martti Kauranen, and Monika Fleischer,,*
Continuous-wave biexciton lasing at room temperature using solution-processed quantum wells
 CORRECTION NOTICE Continuous-wave bieciton lasing at room temperature using solution-processed quantum wells Joel Q. Grim, Sotirios Christodoulou, Francesco Di Stasio, Roman Krahne, Roberto Cingolani,
CORRECTION NOTICE Continuous-wave bieciton lasing at room temperature using solution-processed quantum wells Joel Q. Grim, Sotirios Christodoulou, Francesco Di Stasio, Roman Krahne, Roberto Cingolani,
Optical recoil of asymmetric nano-optical antenna
 Optical recoil of asymmetric nano-optical antenna Jung-Hwan Song, 1 Jonghwa Shin, 1,* Hee-Jin Lim, 1 and Yong-Hee Lee 1,2 1 Department of Physics, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon
Optical recoil of asymmetric nano-optical antenna Jung-Hwan Song, 1 Jonghwa Shin, 1,* Hee-Jin Lim, 1 and Yong-Hee Lee 1,2 1 Department of Physics, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 XRD patterns and TEM image of the SrNbO 3 film grown on LaAlO 3(001) substrate. The film was deposited under oxygen partial pressure of 5 10-6 Torr. (a) θ-2θ scan, where * indicates
Supplementary Figure 1 XRD patterns and TEM image of the SrNbO 3 film grown on LaAlO 3(001) substrate. The film was deposited under oxygen partial pressure of 5 10-6 Torr. (a) θ-2θ scan, where * indicates
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Lateral heterojunctions within monolayer MoSe 2 -WSe 2 semiconductors Chunming Huang 1,#,*, Sanfeng Wu 1,#,*, Ana M. Sanchez 2,#,*, Jonathan J. P. Peters 2, Richard Beanland 2, Jason S. Ross 3, Pasqual
Lateral heterojunctions within monolayer MoSe 2 -WSe 2 semiconductors Chunming Huang 1,#,*, Sanfeng Wu 1,#,*, Ana M. Sanchez 2,#,*, Jonathan J. P. Peters 2, Richard Beanland 2, Jason S. Ross 3, Pasqual
Localized surface plasmons (Particle plasmons)
 Localized surface plasmons (Particle plasmons) ( Plasmons in metal nanostructures, Dissertation, University of Munich by Carsten Sonnichsen, 2001) Lycurgus cup, 4th century (now at the British Museum,
Localized surface plasmons (Particle plasmons) ( Plasmons in metal nanostructures, Dissertation, University of Munich by Carsten Sonnichsen, 2001) Lycurgus cup, 4th century (now at the British Museum,
Optimizing the performance of metal-semiconductor-metal photodetectors by embedding nanoparticles in the absorption layer
 Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2015; 3(2-1): 78-82 Published online February 10, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/jeee) doi: 10.11648/j.jeee.s.2015030201.27 ISSN: 2329-1613
Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2015; 3(2-1): 78-82 Published online February 10, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/jeee) doi: 10.11648/j.jeee.s.2015030201.27 ISSN: 2329-1613
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Facile Synthesis of High Quality Graphene Nanoribbons Liying Jiao, Xinran Wang, Georgi Diankov, Hailiang Wang & Hongjie Dai* Supplementary Information 1. Photograph of graphene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Facile Synthesis of High Quality Graphene Nanoribbons Liying Jiao, Xinran Wang, Georgi Diankov, Hailiang Wang & Hongjie Dai* Supplementary Information 1. Photograph of graphene
Supplementary Figure 1. Electron micrographs of graphene and converted h-bn. (a) Low magnification STEM-ADF images of the graphene sample before
 Supplementary Figure 1. Electron micrographs of graphene and converted h-bn. (a) Low magnification STEM-ADF images of the graphene sample before conversion. Most of the graphene sample was folded after
Supplementary Figure 1. Electron micrographs of graphene and converted h-bn. (a) Low magnification STEM-ADF images of the graphene sample before conversion. Most of the graphene sample was folded after
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications
 Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2013 Lecture 02 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Lecture 2: outline 2 Introduction to Nanophotonics Theoretical
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2013 Lecture 02 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Lecture 2: outline 2 Introduction to Nanophotonics Theoretical
Supplementary Information for Semiconductor Solar Superabsorbers
 Supplementary Information for Semiconductor Solar Superabsorbers Yiling Yu, Lujun Huang, Linyou Cao, * Department of Materials Science and Engineering, North Carolina State University, Raleigh NC 7695;
Supplementary Information for Semiconductor Solar Superabsorbers Yiling Yu, Lujun Huang, Linyou Cao, * Department of Materials Science and Engineering, North Carolina State University, Raleigh NC 7695;
Broadband Plasmonic Couplers for Light Trapping and Waveguiding
 Broadband Plasmonic Couplers for Light Trapping and Waveguiding F. Djidjeli* a, E. Jaberansary a, H. M. H. Chong a, and D. M. Bagnall a a Nano Research Group, School of Electronics and Computer Science,
Broadband Plasmonic Couplers for Light Trapping and Waveguiding F. Djidjeli* a, E. Jaberansary a, H. M. H. Chong a, and D. M. Bagnall a a Nano Research Group, School of Electronics and Computer Science,
A nano-plasmonic chip for simultaneous sensing with dual-resonance surface-enhanced Raman scattering and localized surface plasmon resonance
 Laser Photonics Rev. 8, No. 4, 610 616 (2014) / DOI 10.1002/lpor.201400029 ORIGINAL Abstract A dual-resonance surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) chip which also serves as a localized surface plasmon
Laser Photonics Rev. 8, No. 4, 610 616 (2014) / DOI 10.1002/lpor.201400029 ORIGINAL Abstract A dual-resonance surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) chip which also serves as a localized surface plasmon
Plasmonic eigenmodes in individual and bow-tie. graphene nanotriangles
 Plasmonic eigenmodes in individual and bow-tie graphene nanotriangles Weihua Wang,, Thomas Christensen,, Antti-Pekka Jauho,, Kristian S. Thygesen,, Martijn Wubs,, and N. Asger Mortensen,, DTU Fotonik,
Plasmonic eigenmodes in individual and bow-tie graphene nanotriangles Weihua Wang,, Thomas Christensen,, Antti-Pekka Jauho,, Kristian S. Thygesen,, Martijn Wubs,, and N. Asger Mortensen,, DTU Fotonik,
7. Localized surface plasmons (Particle plasmons)
 7. Localized surface plasmons (Particle plasmons) ( Plasmons in metal nanostructures, Dissertation, University of Munich by Carsten Sonnichsen, 2001) Lycurgus cup, 4th century (now at the British Museum,
7. Localized surface plasmons (Particle plasmons) ( Plasmons in metal nanostructures, Dissertation, University of Munich by Carsten Sonnichsen, 2001) Lycurgus cup, 4th century (now at the British Museum,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced thermoelectricity in High-temperature β-phase Copper (I) Selenides embedded with Cu 2 Te nanoclusters Sajid Butt, a,b, * Wei Xu, c,f, * Muhammad U. Farooq, d Guang K. Ren,
Supporting Information Enhanced thermoelectricity in High-temperature β-phase Copper (I) Selenides embedded with Cu 2 Te nanoclusters Sajid Butt, a,b, * Wei Xu, c,f, * Muhammad U. Farooq, d Guang K. Ren,
Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes
 Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes Supplemental Material L. Shi, T. K. Hakala, H. T. Rekola, J. -P.
Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes Supplemental Material L. Shi, T. K. Hakala, H. T. Rekola, J. -P.
Study of Surface Plasmon Excitation on Different Structures of Gold and Silver
 Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2015, 5(4): 71-81 DOI: 10.5923/j.nn.20150504.01 Study of Surface Plasmon Excitation on Different Structures of Gold and Silver Anchu Ashok 1,*, Arya Arackal 1, George Jacob
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2015, 5(4): 71-81 DOI: 10.5923/j.nn.20150504.01 Study of Surface Plasmon Excitation on Different Structures of Gold and Silver Anchu Ashok 1,*, Arya Arackal 1, George Jacob
Supporting Information to Multiband Plasmonic Sierpinski Carpet Fractal Antennas
 Supporting Information to Multiband Plasmonic Sierpinski Carpet Fractal Antennas Francesco De Nicola, 1, Nikhil Santh Puthiya Purayil, 1, 2 Davide Spirito, 3 Mario Miscuglio, 3, 4 Francesco Tantussi, 5
Supporting Information to Multiband Plasmonic Sierpinski Carpet Fractal Antennas Francesco De Nicola, 1, Nikhil Santh Puthiya Purayil, 1, 2 Davide Spirito, 3 Mario Miscuglio, 3, 4 Francesco Tantussi, 5
6. Plasmon coupling between a flat gold interface and gold nanoparticles.
 6. Plasmon coupling between a flat gold interface and gold nanoparticles. 6.1. Introduction In this outlook oriented chapter the applicability of the multilayered system used in chapter 4.1., for the study
6. Plasmon coupling between a flat gold interface and gold nanoparticles. 6.1. Introduction In this outlook oriented chapter the applicability of the multilayered system used in chapter 4.1., for the study
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices
 Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
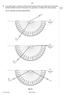 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information I. Schematic representation of the zero- n superlattices Schematic representation of a superlattice with 3 superperiods is shown in Fig. S1. The superlattice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information I. Schematic representation of the zero- n superlattices Schematic representation of a superlattice with 3 superperiods is shown in Fig. S1. The superlattice
[Electronic Supplementary Information]
![[Electronic Supplementary Information] [Electronic Supplementary Information]](/thumbs/95/123080639.jpg) [Electronic Supplementary Information] Tuning the Interparticle Distance in Nanoparticle Assemblies in Suspension via DNA-Triplex Formation: Correlation Between Plasmonic and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering
[Electronic Supplementary Information] Tuning the Interparticle Distance in Nanoparticle Assemblies in Suspension via DNA-Triplex Formation: Correlation Between Plasmonic and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering
Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 551 Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter Y. Y. Li, P. F. Gu, M. Y. Li,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 551 Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter Y. Y. Li, P. F. Gu, M. Y. Li,
Metamaterial-Induced
 Metamaterial-Induced Sharp ano Resonances and Slow Light Nikitas Papasimakis and Nikolay I. Zheludev Inspired by the study of atomic resonances, researchers have developed a new type of metamaterial. Their
Metamaterial-Induced Sharp ano Resonances and Slow Light Nikitas Papasimakis and Nikolay I. Zheludev Inspired by the study of atomic resonances, researchers have developed a new type of metamaterial. Their
transmission reflection absorption
 Optical Cages V. Kumar*, J. P. Walker* and H. Grebel The Electronic Imaging Center and the ECE department at NJIT, Newark, NJ 0702. grebel@njit.edu * Contributed equally Faraday Cage [], a hollow structure
Optical Cages V. Kumar*, J. P. Walker* and H. Grebel The Electronic Imaging Center and the ECE department at NJIT, Newark, NJ 0702. grebel@njit.edu * Contributed equally Faraday Cage [], a hollow structure
A normal-incident quantum well infrared photodetector enhanced by surface plasmon resonance
 Best Student Paper Award A normal-incident quantum well infrared photodetector enhanced by surface plasmon resonance Wei Wu a, Alireza Bonakdar, Ryan Gelfand, and Hooman Mohseni Bio-inspired Sensors and
Best Student Paper Award A normal-incident quantum well infrared photodetector enhanced by surface plasmon resonance Wei Wu a, Alireza Bonakdar, Ryan Gelfand, and Hooman Mohseni Bio-inspired Sensors and
Granular metal films on the surfaces of transparent dielectric materials studied and modified via optical means
 Invited Paper Granular metal films on the surfaces of transparent dielectric materials studied and modified via optical means Tigran A. Vartanyan*, Nikita B. Leonov, Valerii V. Khromov, Sergey G. Przhibelskii,
Invited Paper Granular metal films on the surfaces of transparent dielectric materials studied and modified via optical means Tigran A. Vartanyan*, Nikita B. Leonov, Valerii V. Khromov, Sergey G. Przhibelskii,
Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
 THE HARRIS SCIENCE REVIEW OF DOSHISHA UNIVERSITY, VOL. 56, No. 1 April 2015 Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
THE HARRIS SCIENCE REVIEW OF DOSHISHA UNIVERSITY, VOL. 56, No. 1 April 2015 Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
CURRENT STATUS OF NANOIMPRINT LITHOGRAPHY DEVELOPMENT IN CNMM
 U.S. -KOREA Forums on Nanotechnology 1 CURRENT STATUS OF NANOIMPRINT LITHOGRAPHY DEVELOPMENT IN CNMM February 17 th 2005 Eung-Sug Lee,Jun-Ho Jeong Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials U.S. -KOREA Forums
U.S. -KOREA Forums on Nanotechnology 1 CURRENT STATUS OF NANOIMPRINT LITHOGRAPHY DEVELOPMENT IN CNMM February 17 th 2005 Eung-Sug Lee,Jun-Ho Jeong Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials U.S. -KOREA Forums
Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator
 Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator Authors: Yang Xu 1,2, Ireneusz Miotkowski 1, Chang Liu 3,4, Jifa Tian 1,2, Hyoungdo
Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator Authors: Yang Xu 1,2, Ireneusz Miotkowski 1, Chang Liu 3,4, Jifa Tian 1,2, Hyoungdo
Enhanced spectral response of an AlGaN-based solar-blind ultraviolet photodetector with Al nanoparticles
 Enhanced spectral response of an AlGaN-based solar-blind ultraviolet photodetector with Al nanoparticles Guanghong Bao, 1,2 Dabing Li, 1,* Xiaojuan Sun, 1,3 Mingming Jiang, 1 Zhiming Li, 1 Hang Song, 1
Enhanced spectral response of an AlGaN-based solar-blind ultraviolet photodetector with Al nanoparticles Guanghong Bao, 1,2 Dabing Li, 1,* Xiaojuan Sun, 1,3 Mingming Jiang, 1 Zhiming Li, 1 Hang Song, 1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnano.21.29 Gammadion fabrication The gammadions were designed using CAD software with a line width of 8 nm and a periodicity of 8 nm, figure S1. They were arrayed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnano.21.29 Gammadion fabrication The gammadions were designed using CAD software with a line width of 8 nm and a periodicity of 8 nm, figure S1. They were arrayed
Plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in ultra-thin film solar cells by rear located aluminum nanodisk arrays
 Opt Quant Electron (2017)49:161 DOI 10.1007/s11082-017-0930-x Plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in ultra-thin film solar cells by rear located aluminum nanodisk arrays Debao Zhang 1 Yawei Kuang
Opt Quant Electron (2017)49:161 DOI 10.1007/s11082-017-0930-x Plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in ultra-thin film solar cells by rear located aluminum nanodisk arrays Debao Zhang 1 Yawei Kuang
Strong plasmon coupling between two gold nanospheres on a gold slab
 Strong plasmon coupling between two gold nanospheres on a gold slab H. Liu 1, *, J. Ng 2, S. B. Wang 2, Z. H. Hang 2, C. T. Chan 2 and S. N. Zhu 1 1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and
Strong plasmon coupling between two gold nanospheres on a gold slab H. Liu 1, *, J. Ng 2, S. B. Wang 2, Z. H. Hang 2, C. T. Chan 2 and S. N. Zhu 1 1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and
B.-Y. Lin et al., Opt. Express 17, (2009).
 !!!! The Ag nanoparticle array can be considered Ag nanorods arranged in hexagonal pattern with an inter-nanorod gap (W). The rod diameter (D) is 25 nm and the rod length (L) is 100 nm. A series of curved
!!!! The Ag nanoparticle array can be considered Ag nanorods arranged in hexagonal pattern with an inter-nanorod gap (W). The rod diameter (D) is 25 nm and the rod length (L) is 100 nm. A series of curved
Transmission of Light Through Small Elliptical Apertures (Part 2)
 Transmission of Light Through Small Elliptical Apertures (Part 2) Masud Mansuripur, Armis R. Zakharian and Jerome V. Moloney Last month, in Part 1 of this column, we analyzed the interaction of light with
Transmission of Light Through Small Elliptical Apertures (Part 2) Masud Mansuripur, Armis R. Zakharian and Jerome V. Moloney Last month, in Part 1 of this column, we analyzed the interaction of light with
Plasmon-suppressed vertically-standing nanometal structures
 Plasmon-suppressed vertically-standing nanometal structures Jin-Kyu Yang 1,2*, In-Kag Hwang 3, Min-Kyo Seo 1, Se-Heon Kim 1, and Yong-Hee Lee 1 1 Department of Physics, Korea Advanced Institute of Science
Plasmon-suppressed vertically-standing nanometal structures Jin-Kyu Yang 1,2*, In-Kag Hwang 3, Min-Kyo Seo 1, Se-Heon Kim 1, and Yong-Hee Lee 1 1 Department of Physics, Korea Advanced Institute of Science
Near-Normal Incidence Dark-Field Microscopy: Applications to Nanoplasmonic Spectroscopy
 pubs.acs.org/nanolett Near-Normal Incidence Dark-Field Microscopy: Applications to Nanoplasmonic Spectroscopy Jonathan A. Fan,*,, Kui Bao, J. Britt Lassiter, Jiming Bao, Naomi J. Halas,, Peter Nordlander,
pubs.acs.org/nanolett Near-Normal Incidence Dark-Field Microscopy: Applications to Nanoplasmonic Spectroscopy Jonathan A. Fan,*,, Kui Bao, J. Britt Lassiter, Jiming Bao, Naomi J. Halas,, Peter Nordlander,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.123 Ultra-strong Adhesion of Graphene Membranes Steven P. Koenig, Narasimha G. Boddeti, Martin L. Dunn, and J. Scott Bunch* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.123 Ultra-strong Adhesion of Graphene Membranes Steven P. Koenig, Narasimha G. Boddeti, Martin L. Dunn, and J. Scott Bunch* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Supplementary material for High responsivity mid-infrared graphene detectors with antenna-enhanced photo-carrier generation and collection
 Supplementary material for High responsivity mid-infrared graphene detectors with antenna-enhanced photo-carrier generation and collection Yu Yao 1, Raji Shankar 1, Patrick Rauter 1, Yi Song 2, Jing Kong
Supplementary material for High responsivity mid-infrared graphene detectors with antenna-enhanced photo-carrier generation and collection Yu Yao 1, Raji Shankar 1, Patrick Rauter 1, Yi Song 2, Jing Kong
Low Loss and High Transmission Electromagnetically Induced Transparency (EIT) Effect in Cylindrical Through-Hole Dielectric Cubes
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 76, 207 215, 2018 Low Loss and High Transmission Electromagnetically Induced Transparency (EIT) Effect in Cylindrical Through-Hole Dielectric Cubes Lei Zhu
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 76, 207 215, 2018 Low Loss and High Transmission Electromagnetically Induced Transparency (EIT) Effect in Cylindrical Through-Hole Dielectric Cubes Lei Zhu
Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring 215 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators
Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring 215 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators
Size-Dependent Biexciton Quantum Yields and Carrier Dynamics of Quasi-
 Supporting Information Size-Dependent Biexciton Quantum Yields and Carrier Dynamics of Quasi- Two-Dimensional Core/Shell Nanoplatelets Xuedan Ma, Benjamin T. Diroll, Wooje Cho, Igor Fedin, Richard D. Schaller,
Supporting Information Size-Dependent Biexciton Quantum Yields and Carrier Dynamics of Quasi- Two-Dimensional Core/Shell Nanoplatelets Xuedan Ma, Benjamin T. Diroll, Wooje Cho, Igor Fedin, Richard D. Schaller,
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context
 Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
Nanosphere Lithography
 Nanosphere Lithography Derec Ciafre 1, Lingyun Miao 2, and Keita Oka 1 1 Institute of Optics / 2 ECE Dept. University of Rochester Abstract Nanosphere Lithography is quickly emerging as an efficient, low
Nanosphere Lithography Derec Ciafre 1, Lingyun Miao 2, and Keita Oka 1 1 Institute of Optics / 2 ECE Dept. University of Rochester Abstract Nanosphere Lithography is quickly emerging as an efficient, low
Enhanced Transmission by Periodic Hole. Arrays in Metal Films
 Enhanced Transmission by Periodic Hole Arrays in Metal Films K. Milliman University of Florida July 30, 2008 Abstract Three different square periodic hole arrays were manufactured on a silver film in order
Enhanced Transmission by Periodic Hole Arrays in Metal Films K. Milliman University of Florida July 30, 2008 Abstract Three different square periodic hole arrays were manufactured on a silver film in order
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Plasmonic colour laser printing Xiaolong Zhu 1, Christoph Vannahme 1, Emil Højlund-Nielsen 1, N. Asger Mortensen 2 & Anders Kristensen 1 Simulated reflection spectra. The plasmonic metasurfaces were simulated
Plasmonic colour laser printing Xiaolong Zhu 1, Christoph Vannahme 1, Emil Højlund-Nielsen 1, N. Asger Mortensen 2 & Anders Kristensen 1 Simulated reflection spectra. The plasmonic metasurfaces were simulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Simulations of the lm thickness dependence of plasmon modes on lms or disks on a 30 nm thick Si 3 N 4 substrate.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Simulations of the lm thickness dependence of plasmon modes on lms or disks on a 30 nm thick Si 3 N 4 substrate. (a) Simulated plasmon energy at k=30 µm 1 for the surface plasmon
Supplementary Figure 1 Simulations of the lm thickness dependence of plasmon modes on lms or disks on a 30 nm thick Si 3 N 4 substrate. (a) Simulated plasmon energy at k=30 µm 1 for the surface plasmon
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/NNANO.211.214 Control over topological insulator photocurrents with light polarization J.W. McIver*, D. Hsieh*, H. Steinberg, P. Jarillo-Herrero and N. Gedik SI I. Materials and device fabrication
DOI: 1.138/NNANO.211.214 Control over topological insulator photocurrents with light polarization J.W. McIver*, D. Hsieh*, H. Steinberg, P. Jarillo-Herrero and N. Gedik SI I. Materials and device fabrication
Nanostructures Fabrication Methods
 Nanostructures Fabrication Methods bottom-up methods ( atom by atom ) In the bottom-up approach, atoms, molecules and even nanoparticles themselves can be used as the building blocks for the creation of
Nanostructures Fabrication Methods bottom-up methods ( atom by atom ) In the bottom-up approach, atoms, molecules and even nanoparticles themselves can be used as the building blocks for the creation of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances Y. Cheng, 1,2 C. Zhou, 1 B.G. Yuan, 1 D.J. Wu, 3 Q. Wei, 1 X.J. Liu 1,2* 1 Key Laboratory of Modern
Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances Y. Cheng, 1,2 C. Zhou, 1 B.G. Yuan, 1 D.J. Wu, 3 Q. Wei, 1 X.J. Liu 1,2* 1 Key Laboratory of Modern
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information: Photocurrent generation in semiconducting and metallic carbon nanotubes Maria Barkelid 1*, Val Zwiller 1 1 Kavli Institute of Nanoscience, Delft University of Technology, Delft,
Supplementary Information: Photocurrent generation in semiconducting and metallic carbon nanotubes Maria Barkelid 1*, Val Zwiller 1 1 Kavli Institute of Nanoscience, Delft University of Technology, Delft,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.162 Selective Molecular Sieving Through Porous Graphene Steven P. Koenig, Luda Wang, John Pellegrino, and J. Scott Bunch* *email: jbunch@colorado.edu Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.162 Selective Molecular Sieving Through Porous Graphene Steven P. Koenig, Luda Wang, John Pellegrino, and J. Scott Bunch* *email: jbunch@colorado.edu Supplementary
Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures. based on a nano-obelisk
 Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures based on a nano-obelisk Je-Hyung Kim, Young-Ho Ko, Su-Hyun Gong, Suk-Min Ko, Yong-Hoon Cho Department of Physics, Graduate School of Nanoscience
Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures based on a nano-obelisk Je-Hyung Kim, Young-Ho Ko, Su-Hyun Gong, Suk-Min Ko, Yong-Hoon Cho Department of Physics, Graduate School of Nanoscience
