Supplementary Information
|
|
|
- Earl Bruce Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Large-scale lithography-free metasurface with spectrally tunable super absorption Kai Liu 1, Xie Zeng 1, Suhua Jiang 2, Dengxin Ji 1, Haomin Song 1, Nan Zhang 1, Qiaoqiang Gan 1 * 1. Department of Electrical Engineering, The State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY Department of Materials Science, Fudan University, Shanghai , China * qqgan@buffalo.edu. 1. Diameter distribution of directly-sputtered Ag NPs According to SEM images shown in Fig. 1, randomly distributed Ag NPs were obtained from the direct sputtering process. The statistic distribution of the NPs can be controlled by changing the deposited mass thickness, as shown in Fig. S1. According to previous reports S1-S3, the resonant peak wavelength of MDM super absorbers strongly depends on the lateral dimension (i.e. diameter/length) of the periodic or random distributed nanopatterns. Here, the spectral position of the resonant peak is mainly determined by the dominant diameter of Ag NPs. One can see from Fig. S1 that the dominant diameter ranges from nm to nm as the deposited mass thickness increases from 0.8 to 4.0 nm, and therefore resulting in the red-shift of the absorption peaks for samples MA1-MA5 (see Fig. 2a). Moreover, due to the relatively wide distribution of the particle diameter, broader band optical absorption resonances were obtained in these directly-sputtered samples compared with their periodically patterned counterparts S4- S6. 1
2 Figure S1. Size distributions of direct-deposited Ag NPs with different nominal mass thicknesses of (a) 0.8 nm, (b) 1.6 nm, (c) 2.4 nm, (d) 3.2 nm, and (e) 4.0 nm, respectively. The size distribution percentage is calculated by the ratio of particle counts in a specific diameter range to the total number of Ag NPs from the SEM images shown in Fig. 1. The red lines are Gaussian fittings of the size distribution of NPs. 2. Scattering effect of the directly-deposited metasurfaces The reflection spectra of metasurfaces were characterized by a microscopic FTIR with a 15X objective lens (NA=0.4), which can only collect the reflected/scattered light within the spatial angle of To demonstrate the accuracy of the measured reflection and absorption spectrum, we employed another three objective lenses (NA=0.3, 0.6 and 0.95, corresponding to the collection angles of 17.4, 36.9 and 71.8 o, respectively) in an optical microscope (OLYMPUS IX81) coupled with a compact spectrometer (Ocean Optics, Jaz) to measure the reflection spectrum of sample MA4, as shown in Fig. S2a. One can see that the measured reflection spectra under the collection angles of 36.9 and 71.8 are approximately identical, indicating that all the scattered signals can be safely collected within the angle of Although the reflection spectrum observed by the microscopic FTIR system is slightly different from the one observed within the collection angle of 36.9, the spectral position and the absolute intensity at the resonance position is almost identical, indicating the absorption spectra observed in the microscopic FTIR system is accurate to demonstrate the resonant super absorption. Figure S2. (a) Reflection spectra of sample MA4 measured by four objective lenses with NA=0.3, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.95, respectively. (b) and (c) are measured angle-dependent reflection/scattering spectra of sample MA4 with a fixed incident angle at (b) 15 and (c) 50, respectively. To reveal the direction of the scattered light, we employed an angular-tunable stage (Bruker, A513/Q) to measure the angle-dependent reflection/scattering spectra of sample MA4 with a fixed incident angle. As shown in Fig. S2b, the incident angle is fixed at 15 o and the collection angle is tuned to 20, 25, 30, 2
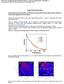
3 and 35, respectively. One can see that little reflection signal can be measured beyond the angle of 30. For a large incident angle of 50, when the collection angle is tuned to 55, 60, 65, and 70, more scattering signal can be observed at longer wavelengths, explaining the slight difference in this spectral region observed in Fig. S2a. Due to the omnidirectional absorption feature of the meta-absorber (see Fig. S3d), there is little scattering signal observed at the resonant wavelength. Consequently, the absorption spectra observed by the microscopic FTIR system can represent the optical properties of the proposed metasurface accurately at the resonant wavelength. 3. Modeling of optical properties of metasurface structures Figure S3. (a) Conceptual illustration of the three-layered metamaterial absorber structure. (b) Absorption spectra as the function of NP diameters, D, from 10 nm to 40 nm. Four bars indicate the NP diameter ranges of samples MA2-MA5 obtained from Fig. S1. (c) Modeled displacement current density of sample NM3 (i.e. D=20 nm). (d) Simulated absorption spectra of NM3 as the function of the incident angle. Fig. S3a illustrates the inverted 2D meta-absorber structure modeled using COMSOL Multiphysics. The structure consists of a top glass layer, a semicircular Ag nanoparticle, a 10-nm-thick Al 2 O 3 film and 3
4 an optically thick Ag ground plate. A TM-polarized plane wave is employed to illuminate the structure from the glass side at normal or oblique incident directions. The absorption spectra are plotted in Fig. S3b as the function of the NP diameter, showing that the resonant wavelength is tuned from 494 nm to 732 nm as the particle diameter increases from 10 nm to 40 nm. The observed resonant peak positions of samples MA2-MA5 were marked with vertical bars to indicate dominant diameter ranges for each sample (see Fig. S3b), showing reasonably good agreement with the theoretical modeling. The resonant position of sample MA1 was not plotted since it is beyond the spectral region available for our measurement system. To demonstrate the nature of the absorption resonance explicitly, the displacement current density of model NM3 (i.e. D=20 nm) is plotted in Fig. S3c. A circulation of current is excited between the Ag nanopattern and the ground plate, forming the magnetic resonance S2, S7- S9. To further reveal the angular dependence of the optical response of NM3, we modeled its absorption resonance as the function of the incident angle as shown in Fig. S3d. Due to the angle-independent coupling between the incident magnetic field and the excited magnetic resonance mode S7, the super absorption peak over 85% can be retained up to 70. Therefore, the spectrally tunable perfect absorption resonance supported by the metasurface structure is also omnidirectional, as revealed by experimental characterizations shown in Figs. 2e and 4b. 4. Post thermal treatment To overcome the percolation threshold limitation of the directly deposited Ag films, post thermal annealing processes can be introduced to transform the mesh network back to isolated Ag NPs and further broaden the tunability of NP dimensions. Here we first deposited Ag layers with mass thicknesses of 9.6, 11.2, 12.8 and 14.4 nm on top of microscope glass substrates, as shown in the left panels of Figs. S4a-S4d (denoted as M6-M9). One can see that connected metal networks were obtained. When these metal mesh networks were covered by 20-nm-thick Al 2 O 3 spacer films and optically thick Ag ground plates to form the three-layered MDM structures (denoted as RA6-RA9 in Fig. S4), their optical absorption properties are relatively weak as shown by the dashed lines in Fig. S4e, indicating that the magnetic resonances were not excited efficiently or the critical coupling condition was not met. We then employed the post thermal annealing to further manipulate the morphologies of these connected metal meshes. As shown in Fig. S4, samples M6-M9 were annealed in a N 2 ambient at the temperature of 300 C for 30 minutes. As a result, the connected mesh networks were transformed into isolated NPs (see SEM images of samples MA6- MA9). The optical absorption spectra of the three-layered MDM structure based on these annealed NPs were characterized as shown by solid lines in Fig. S4e. One can see that obvious absorption resonances were obtained with the absorption peaks of 60.9%, 62.4%, 66.9%, and 63.9% in the near infrared spectral 4
5 region from 921 nm to 1339 nm, respectively. The relatively low absorption is potentially related to the non-uniform shape of the metal particles. Further exploration and optimization of IR super absorbers are still under investigation using oblique angle depositions S10, S11. Figure S4. (a)-(d) Left corners show SEM images of the directly-deposited metal films (i.e. samples M6-M9) with nominal mass thicknesses of (a) 9.6 nm, (b) 11.2 nm, (c) 12.8 nm and (d) 14.4 nm, respectively. Right corners show the surface morphologies of NPs after the thermal treatment. The scale bar is 400 nm. (e) Absorption spectra of three-layered MDM structures based on the connected metal mesh networks (see dotted lines, i.e. samples RA6-RA9) and thermal annealed NPs (see solid lines, i.e. samples MA6-MA9). 5. Fabrication of graded metasurface absorbers The sputtering system configuration for the directional deposition of graded metasurfaces is illustrated in Fig. S5a. The distance between the Ag target center and the substrate stage is H=8.2 cm, while the central axis of the sputtering beam is aligned with the substrate surface at an angle of θ=70. The local mass thickness increases gradually from the left edge to the right edge and form the graded variable NP layers (i.e. samples GR1 and GR2 in Fig. 3a). In our experiment, the nominal mass thickness of the deposited metal film is 2.4 nm and 3.2 nm for samples GR1 and GR2, respectively. Figs. S5b and S5c are measured absorption spectra for samples GR1 and GR2, respectively, showing the best optical absorption of ~37% (indicated by the empty circles), which is relatively weak. 5
6 Figure S5. (a) Configuration schematic of the sputtering chamber for the graded NP deposition. In our system, H=8.4 cm and θ=70. (b) and (c) show the measured spatial-dependent absorption spectra of reference graded samples (b) GR1 and (c) GR2, respectively. Empty circles indicate the highest absorption peaks of GR1 and GR2. 6. Optical characterization of glass and flexible PEN substrates As shown in Fig. 4, the optical absorption of flexible metasurface absorbers are slightly lower than those fabricated on glass substrates shown in Figs. 2 and 3 due to the higher reflection of the PEN material. As shown in Fig. S6, we measured the optical reflection and transmission spectra of a glass slide and a PEN substrate. One can see that the reflection from the flexible substrate (red dashed line) is 10-16% in the visible to near-ir spectral region, which is 6-11% higher than that for a glass substrate (blue dashed line). This higher reflection at the air-pen interface results in the reduced peak absorption, and therefore degrading the visual contrast of the uniform and graded flexible meta-absorbers. Figure S6. Transmission (solid curves) and reflection (dashed curves) properties of a glass slide (blue lines) and a flexible PEN substrate (red lines). 6
7 References [S1] Kumar, K., Duan, H., Hegde, R. S., Koh, S. C., Wei, J. N. & Yang, J. K. Printing colour at the optical diffraction limit. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, (2012). [S2] Tittl, A., Mai, P., Taubert, R., Dregely, D., Liu, N. & Giessen, H. Palladium-based plasmonic perfect absorber in the visible wavelength range and its application to hydrogen sensing. Nano Lett. 11, (2011). [S3] Cheng, C., Abbas, M. N., Chiu, C., Lai, K. Shih, M. & Chang, Y. Wide-angle polarization independent infrared broadband absorbers based on metallic multi-sized disk arrays. Opt. Express 20, (2012). [S4] Wu, C. & Shvets, G. Design of metamaterial surfaces with broadband absorbance. Opt. Lett. 37, (2012). [S5] Bouchon, P., Koechlin, C., Pardo, F., Haidar, R. & Pelouard, J. Wideband omnidirectional infrared absorber with a patchwork of plasmonic nanoantennas. Opt. Lett. 37, (2012). [S6] Cui, Y., Xu, J., Fung, K. H., Jin, Y., Kumar, A., He, S. & Fang, N. X. A thin film broadband absorber based on multi-sized nanoantennas. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, (2011). [S7] Liu, N., Mesch, M., Weiss, T., Hentschel, M. & Giessen, H. Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett. 10, (2010). [S8] Wu, C., Neuner, B. & Shvets, G. Large-area wide-angle spectrally selective plasmonic absorber. Phys. Rev. B 84, (2011). [S9] Hao, J., Zhou, L. & Qiu, M. Nearly total absorption of light and heat generation by plasmonic metamaterials. Phys. Rev. B 83, (2011). [S10] Fu, J., Collins, A. & Zhao, Y. Optical properties and biosensor application of ultrathin silver films prepared by obique angle deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, (2008). [S11] He, Y., Fu, J. & Zhao, Y. Oblique angle deposition and its application in plasmonics. Front. Phys. DOI /s
Subcell misalignment in vertically cascaded metamaterial absorbers
 Subcell misalignment in vertically cascaded metamaterial absorbers Qin Chen, 1,2,* Fuhe Sun, 1 and Shichao Song 1 1 Key Laboratory of Nanodevices and Applications, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics,
Subcell misalignment in vertically cascaded metamaterial absorbers Qin Chen, 1,2,* Fuhe Sun, 1 and Shichao Song 1 1 Key Laboratory of Nanodevices and Applications, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics,
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: Achieving Strong Field Enhancement and Light Absorption Simultaneously with Plasmonic Nanoantennas Exploiting Film-Coupled Triangular Nanodisks Yang Li, Dezhao Li, Cheng Chi, and
Supporting Information: Achieving Strong Field Enhancement and Light Absorption Simultaneously with Plasmonic Nanoantennas Exploiting Film-Coupled Triangular Nanodisks Yang Li, Dezhao Li, Cheng Chi, and
Full-color Subwavelength Printing with Gapplasmonic
 Supporting information for Full-color Subwavelength Printing with Gapplasmonic Optical Antennas Masashi Miyata, Hideaki Hatada, and Junichi Takahara *,, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University,
Supporting information for Full-color Subwavelength Printing with Gapplasmonic Optical Antennas Masashi Miyata, Hideaki Hatada, and Junichi Takahara *,, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University,
Volume 3, Number 2, 2017 Pages Jordan Journal of Electrical Engineering ISSN (Print): , ISSN (Online):
 JJEE Volume 3, Number 2, 2017 Pages 126-137 Jordan Journal of Electrical Engineering ISSN (Print): 2409-9600, ISSN (Online): 2409-9619 Reduced Cell Size Metamaterial Based Wideband Infrared Absorber Hamzeh
JJEE Volume 3, Number 2, 2017 Pages 126-137 Jordan Journal of Electrical Engineering ISSN (Print): 2409-9600, ISSN (Online): 2409-9619 Reduced Cell Size Metamaterial Based Wideband Infrared Absorber Hamzeh
Broadband Absorption in the Cavity Resonators with Changed Order
 Broadband Absorption in the Cavity Resonators with Changed Order Agata Roszkiewicz Institute of Fundamental Technological Research, Polish Academy of Sciences, Adolfa Pawińskiego 5b, 02-106 Warsaw, Poland
Broadband Absorption in the Cavity Resonators with Changed Order Agata Roszkiewicz Institute of Fundamental Technological Research, Polish Academy of Sciences, Adolfa Pawińskiego 5b, 02-106 Warsaw, Poland
U-Shaped Nano-Apertures for Enhanced Optical Transmission and Resolution
 U-Shaped Nano-Apertures for Enhanced Optical Transmission and Resolution Mustafa Turkmen 1,2,3, Serap Aksu 3,4, A. Engin Çetin 2,3, Ahmet A. Yanik 2,3, Alp Artar 2,3, Hatice Altug 2,3,4, * 1 Electrical
U-Shaped Nano-Apertures for Enhanced Optical Transmission and Resolution Mustafa Turkmen 1,2,3, Serap Aksu 3,4, A. Engin Çetin 2,3, Ahmet A. Yanik 2,3, Alp Artar 2,3, Hatice Altug 2,3,4, * 1 Electrical
A Broadband Flexible Metamaterial Absorber Based on Double Resonance
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 46, 73 78, 2014 A Broadband Flexible Metamaterial Absorber Based on Double Resonance ong-min Lee* Abstract We present a broadband microwave metamaterial
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 46, 73 78, 2014 A Broadband Flexible Metamaterial Absorber Based on Double Resonance ong-min Lee* Abstract We present a broadband microwave metamaterial
Design and Characterization of a Dual-Band Metamaterial Absorber Based on Destructive Interferences
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 47, 95, 24 Design and Characterization of a Dual-Band Metamaterial Absorber Based on Destructive Interferences Saeid Jamilan, *, Mohammad N. Azarmanesh, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 47, 95, 24 Design and Characterization of a Dual-Band Metamaterial Absorber Based on Destructive Interferences Saeid Jamilan, *, Mohammad N. Azarmanesh, and
Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in a Schottky junction consisted of single CdS nanoparticles and a planar gold film
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in
Electronic Supplementary Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Electronic Supplementary Information for Broadband Photoresponse Based on
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Electronic Supplementary Information for Broadband Photoresponse Based on
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information In situ and real-time ToF-SIMS analysis of light-induced chemical changes
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information In situ and real-time ToF-SIMS analysis of light-induced chemical changes
Supplementary Figure 1 SEM images and corresponding Fourier Transformation of nanoparticle arrays before pattern transfer (left), after pattern
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEM images and corresponding Fourier Transformation of nanoparticle arrays before pattern transfer (left), after pattern transfer but before pattern shrinkage (middle), and after
Supplementary Figure 1 SEM images and corresponding Fourier Transformation of nanoparticle arrays before pattern transfer (left), after pattern transfer but before pattern shrinkage (middle), and after
Design principles for infrared wide-angle perfect absorber based on plasmonic structure
 Design principles for infrared wide-angle perfect absorber based on plasmonic structure Mingbo Pu, Chenggang Hu, Min Wang, Cheng Huang, Zeyu Zhao, Changtao Wang, Qin Feng, and Xiangang Luo* State Key Laboratory
Design principles for infrared wide-angle perfect absorber based on plasmonic structure Mingbo Pu, Chenggang Hu, Min Wang, Cheng Huang, Zeyu Zhao, Changtao Wang, Qin Feng, and Xiangang Luo* State Key Laboratory
AFRL-RY-WP-TP
 AFRL-RY-WP-TP-2013-0193 MULTI-SPECTRAL NEAR PERFECT METAMATERIAL ABSORBERS USING SPATIALLY MULTIPLEXED PLASMON RESONANCE METAL SQUARE STRUCTURES (PREPRINT) Joshua Hendrickson Optoelectronic Technology
AFRL-RY-WP-TP-2013-0193 MULTI-SPECTRAL NEAR PERFECT METAMATERIAL ABSORBERS USING SPATIALLY MULTIPLEXED PLASMON RESONANCE METAL SQUARE STRUCTURES (PREPRINT) Joshua Hendrickson Optoelectronic Technology
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Highly Sensitive, Reproducible, and Stable SERS Sensors Based on Well-Controlled Silver Nanoparticles Decorated Silicon Nanowire Building Blocks Xue Mei Han, Hui Wang, Xue Mei Ou,
Supporting Information Highly Sensitive, Reproducible, and Stable SERS Sensors Based on Well-Controlled Silver Nanoparticles Decorated Silicon Nanowire Building Blocks Xue Mei Han, Hui Wang, Xue Mei Ou,
Printing Colour at the Optical Diffraction Limit
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.128 Printing Colour at the Optical Diffraction Limit Karthik Kumar 1,#, Huigao Duan 1,#, Ravi S. Hegde 2, Samuel C.W. Koh 1, Jennifer N. Wei 1 and Joel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.128 Printing Colour at the Optical Diffraction Limit Karthik Kumar 1,#, Huigao Duan 1,#, Ravi S. Hegde 2, Samuel C.W. Koh 1, Jennifer N. Wei 1 and Joel
Supplementary Figure S1 SEM and optical images of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. a, SEM image of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. b, The size distribution of Si 0.
 Supplementary Figure S1 SEM and optical images of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. a, SEM image of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. b, The size distribution of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. The standard derivation is 4.4 %. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure S1 SEM and optical images of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. a, SEM image of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. b, The size distribution of Si 0.6 H 0.4 colloids. The standard derivation is 4.4 %. Supplementary
Lithography-Free Broadband Ultrathin Film. Photovoltaics
 Supporting Information Lithography-Free Broadband Ultrathin Film Absorbers with Gap Plasmon Resonance for Organic Photovoltaics Minjung Choi 1, Gumin Kang 1, Dongheok Shin 1, Nilesh Barange 2, Chang-Won
Supporting Information Lithography-Free Broadband Ultrathin Film Absorbers with Gap Plasmon Resonance for Organic Photovoltaics Minjung Choi 1, Gumin Kang 1, Dongheok Shin 1, Nilesh Barange 2, Chang-Won
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.72 Tunable Subradiant Lattice Plasmons by Out-of-plane Dipolar Interactions Wei Zhou and Teri W. Odom Optical measurements. The gold nanoparticle arrays
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.72 Tunable Subradiant Lattice Plasmons by Out-of-plane Dipolar Interactions Wei Zhou and Teri W. Odom Optical measurements. The gold nanoparticle arrays
Modulation of Negative Index Metamaterials in the Near-IR Range
 Modulation of Negative Index Metamaterials in the Near-IR Range Evgenia Kim (1), Wei Wu ( 2) (2, Ekaterina Ponizovskaya ), Zhaoning Yu ( 2) ( 2, Alexander M. Bratkovsky ) (2), Shih-Yuang Wang, R. Stanley
Modulation of Negative Index Metamaterials in the Near-IR Range Evgenia Kim (1), Wei Wu ( 2) (2, Ekaterina Ponizovskaya ), Zhaoning Yu ( 2) ( 2, Alexander M. Bratkovsky ) (2), Shih-Yuang Wang, R. Stanley
Fluorescence Enhancement on Silver Nanoplate at the. Single- and Sub-Nanoparticle Level
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Supporting 2015 Information Fluorescence Enhancement on Silver Nanoplate at the Single- and Sub-Nanoparticle
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Supporting 2015 Information Fluorescence Enhancement on Silver Nanoplate at the Single- and Sub-Nanoparticle
Metamaterials & Plasmonics
 Metamaterials & Plasmonics Exploring the Impact of Rotating Rectangular Plasmonic Nano-hole Arrays on the Transmission Spectra and its Application as a Plasmonic Sensor. Abstract Plasmonic nano-structures
Metamaterials & Plasmonics Exploring the Impact of Rotating Rectangular Plasmonic Nano-hole Arrays on the Transmission Spectra and its Application as a Plasmonic Sensor. Abstract Plasmonic nano-structures
Plasmonic metamaterial as broadband absorptive linear polarizer
 Plasmonic metamaterial as broadband absorptive linear polarizer Chunrui Han and Wing Yim Tam* Department of Physics and William Mong Institute of Nano Science and Technology The Hong Kong University of
Plasmonic metamaterial as broadband absorptive linear polarizer Chunrui Han and Wing Yim Tam* Department of Physics and William Mong Institute of Nano Science and Technology The Hong Kong University of
Two-Photon Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Metallic Nanostructures for Plasmonic Metamaterials
 Two-Photon Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Metallic Nanostructures for Plasmonic Metamaterials Atsushi ISHIKAWA 1 and Takuo TANAKA 1,2 1- Metamaterials Laboratory, RIKEN, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198,
Two-Photon Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Metallic Nanostructures for Plasmonic Metamaterials Atsushi ISHIKAWA 1 and Takuo TANAKA 1,2 1- Metamaterials Laboratory, RIKEN, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198,
A POLARIZATION-INDEPENDENT WIDE-ANGLE DUAL DIRECTIONAL ABSORPTION METAMATERIAL AB- SORBER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 27, 191 201, 2012 A POLARIZATION-INDEPENDENT WIDE-ANGLE DUAL DIRECTIONAL ABSORPTION METAMATERIAL AB- SORBER Lei Lu 1, *, Shaobo Qu 1, Hua Ma 1, Fei Yu 1, Song
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 27, 191 201, 2012 A POLARIZATION-INDEPENDENT WIDE-ANGLE DUAL DIRECTIONAL ABSORPTION METAMATERIAL AB- SORBER Lei Lu 1, *, Shaobo Qu 1, Hua Ma 1, Fei Yu 1, Song
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Coupling Effects in 3D Plasmonic Structures Templated by Morpho Butterfly
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Coupling Effects in 3D Plasmonic Structures Templated by Morpho Butterfly
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Supramolecular interactions via hydrogen bonding contributing to
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Supramolecular interactions via hydrogen bonding contributing to
Efficient Hydrogen Evolution. University of Central Florida, 4000 Central Florida Blvd. Orlando, Florida, 32816,
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 MoS 2 /TiO 2 Heterostructures as Nonmetal Plasmonic Photocatalysts for Highly
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 MoS 2 /TiO 2 Heterostructures as Nonmetal Plasmonic Photocatalysts for Highly
Light Absorber with an Ultra-Broad Flat Band Based on Multi-Sized Slow-Wave Hyperbolic Metamaterial Thin-Films
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 147, 69 79, 2014 Light Absorber with an Ultra-Broad Flat Band Based on Multi-Sized Slow-Wave Hyperbolic Metamaterial Thin-Films Sailing He 1, 2, 3, *, Fei Ding
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 147, 69 79, 2014 Light Absorber with an Ultra-Broad Flat Band Based on Multi-Sized Slow-Wave Hyperbolic Metamaterial Thin-Films Sailing He 1, 2, 3, *, Fei Ding
Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation
 Supporting Information Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation Yuanmu Yang, Wenyi Wang, Parikshit Moitra, Ivan I. Kravchenko, Dayrl P. Briggs,
Supporting Information Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation Yuanmu Yang, Wenyi Wang, Parikshit Moitra, Ivan I. Kravchenko, Dayrl P. Briggs,
Supporting Information. Molecular Selectivity of. Graphene-Enhanced Raman Scattering
 1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Molecular Selectivity of Graphene-Enhanced Raman Scattering Shengxi Huang,, Xi Ling,,, * Liangbo Liang, ǁ Yi Song,
1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Molecular Selectivity of Graphene-Enhanced Raman Scattering Shengxi Huang,, Xi Ling,,, * Liangbo Liang, ǁ Yi Song,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Trifunctional NiO Ag NiO Electrodes
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Trifunctional NiO Ag NiO Electrodes
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Light emission near a gradient metasurface Leonard C. Kogos and Roberto Paiella Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston,
Supporting Information Light emission near a gradient metasurface Leonard C. Kogos and Roberto Paiella Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston,
Sub-wavelength focusing meta-lens
 Sub-wavelength focusing meta-lens Tapashree Roy, 1 Edward T. F. Rogers, 1 and Nikolay I. Zheludev 1,2,* 1 Optoelectronics Research Centre & Centre for Photonic Metamaterials, University of Southampton,
Sub-wavelength focusing meta-lens Tapashree Roy, 1 Edward T. F. Rogers, 1 and Nikolay I. Zheludev 1,2,* 1 Optoelectronics Research Centre & Centre for Photonic Metamaterials, University of Southampton,
Supporting Infromation
 Supporting Infromation Transparent and Flexible Self-Charging Power Film and Its Application in Sliding-Unlock System in Touchpad Technology Jianjun Luo 1,#, Wei Tang 1,#, Feng Ru Fan 1, Chaofeng Liu 1,
Supporting Infromation Transparent and Flexible Self-Charging Power Film and Its Application in Sliding-Unlock System in Touchpad Technology Jianjun Luo 1,#, Wei Tang 1,#, Feng Ru Fan 1, Chaofeng Liu 1,
Super-reflection and Cloaking Based on Zero Index Metamaterial
 Super-reflection and Cloaking Based on Zero Index Metamaterial Jiaming Hao, Wei Yan, and Min Qiu Photonics and Microwave ngineering, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), lectrum 9, 164 4, Kista, Sweden
Super-reflection and Cloaking Based on Zero Index Metamaterial Jiaming Hao, Wei Yan, and Min Qiu Photonics and Microwave ngineering, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), lectrum 9, 164 4, Kista, Sweden
Supporting Information Quantitative 3D phase imaging of plasmonic metasurfaces
 Supporting Information Quantitative 3D phase imaging of plasmonic metasurfaces Jiří Babocký 1,2, Aneta Křížová 1,2, Lenka Štrbková 1, Lukáš Kejík 1, Filip Ligmajer 1,3, Martin Hrtoň 1,3, Petr Dvořák 1,3,
Supporting Information Quantitative 3D phase imaging of plasmonic metasurfaces Jiří Babocký 1,2, Aneta Křížová 1,2, Lenka Štrbková 1, Lukáš Kejík 1, Filip Ligmajer 1,3, Martin Hrtoň 1,3, Petr Dvořák 1,3,
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 1 May 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 1 May 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 1 May 2011](/thumbs/74/70729533.jpg) Robust method to determine the resolution of a superlens by analyzing the near-field image of a two-slit object B. D. F. Casse, W. T. Lu, Y. J. Huang, and S. Sridhar Electronic Materials Research Institute
Robust method to determine the resolution of a superlens by analyzing the near-field image of a two-slit object B. D. F. Casse, W. T. Lu, Y. J. Huang, and S. Sridhar Electronic Materials Research Institute
Engineering heavily doped silicon for broadband absorber in the terahertz regime
 Engineering heavily doped silicon for broadband absorber in the terahertz regime Mingbo Pu, Min Wang, Chenggang Hu, Cheng Huang, Zeyu Zhao, Yanqin Wang, and Xiangang Luo * State Key Laboratory of Optical
Engineering heavily doped silicon for broadband absorber in the terahertz regime Mingbo Pu, Min Wang, Chenggang Hu, Cheng Huang, Zeyu Zhao, Yanqin Wang, and Xiangang Luo * State Key Laboratory of Optical
Flexible, Transparent and Highly Sensitive SERS. Substrates with Cross-nanoporous Structures for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 supplementary information Flexible, Transparent and Highly Sensitive SERS Substrates with Cross-nanoporous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 supplementary information Flexible, Transparent and Highly Sensitive SERS Substrates with Cross-nanoporous
Highly efficient SERS test strips
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Highly efficient SERS test strips 5 Ran Zhang, a Bin-Bin Xu, a Xue-Qing Liu, a Yong-Lai Zhang, a Ying Xu, a Qi-Dai Chen, * a and Hong-Bo Sun* a,b 5 10 Experimental
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Highly efficient SERS test strips 5 Ran Zhang, a Bin-Bin Xu, a Xue-Qing Liu, a Yong-Lai Zhang, a Ying Xu, a Qi-Dai Chen, * a and Hong-Bo Sun* a,b 5 10 Experimental
Plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in ultra-thin film solar cells by rear located aluminum nanodisk arrays
 Opt Quant Electron (2017)49:161 DOI 10.1007/s11082-017-0930-x Plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in ultra-thin film solar cells by rear located aluminum nanodisk arrays Debao Zhang 1 Yawei Kuang
Opt Quant Electron (2017)49:161 DOI 10.1007/s11082-017-0930-x Plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in ultra-thin film solar cells by rear located aluminum nanodisk arrays Debao Zhang 1 Yawei Kuang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances Y. Cheng, 1,2 C. Zhou, 1 B.G. Yuan, 1 D.J. Wu, 3 Q. Wei, 1 X.J. Liu 1,2* 1 Key Laboratory of Modern
Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances Y. Cheng, 1,2 C. Zhou, 1 B.G. Yuan, 1 D.J. Wu, 3 Q. Wei, 1 X.J. Liu 1,2* 1 Key Laboratory of Modern
[Electronic Supplementary Information]
![[Electronic Supplementary Information] [Electronic Supplementary Information]](/thumbs/95/123080639.jpg) [Electronic Supplementary Information] Tuning the Interparticle Distance in Nanoparticle Assemblies in Suspension via DNA-Triplex Formation: Correlation Between Plasmonic and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering
[Electronic Supplementary Information] Tuning the Interparticle Distance in Nanoparticle Assemblies in Suspension via DNA-Triplex Formation: Correlation Between Plasmonic and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering
Surface Plasmon Resonance in Metallic Nanoparticles and Nanostructures
 Surface Plasmon Resonance in Metallic Nanoparticles and Nanostructures Zhi-Yuan Li Optical Physics Laboratory, Institute of Physics, CAS Beijing 18, China January 5-9, 7, Fudan University, Shanghai Challenges
Surface Plasmon Resonance in Metallic Nanoparticles and Nanostructures Zhi-Yuan Li Optical Physics Laboratory, Institute of Physics, CAS Beijing 18, China January 5-9, 7, Fudan University, Shanghai Challenges
A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On
 Supplementary Information A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On an Organic Solid Matrix in the Presence of Gold Single Crystals Khaleda Banu,,,*
Supplementary Information A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On an Organic Solid Matrix in the Presence of Gold Single Crystals Khaleda Banu,,,*
Supplementary Information. Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye. Nanostructures
 Supplementary Information Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye Nanostructures Lei Zhou, Qing-Dong Ou, Jing-De Chen, Su Shen, Jian-Xin Tang,* Yan-Qing Li,* and Shuit-Tong
Supplementary Information Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye Nanostructures Lei Zhou, Qing-Dong Ou, Jing-De Chen, Su Shen, Jian-Xin Tang,* Yan-Qing Li,* and Shuit-Tong
Supporting information:
 Supporting information: Wavevector-Selective Nonlinear Plasmonic Metasurfaces Kuang-Yu Yang, 1,# Ruggero Verre, 2, # Jérémy Butet, 1,#, * Chen Yan, 1 Tomasz J. Antosiewicz, 2,3 Mikael Käll, 2 and Olivier
Supporting information: Wavevector-Selective Nonlinear Plasmonic Metasurfaces Kuang-Yu Yang, 1,# Ruggero Verre, 2, # Jérémy Butet, 1,#, * Chen Yan, 1 Tomasz J. Antosiewicz, 2,3 Mikael Käll, 2 and Olivier
transmission reflection absorption
 Optical Cages V. Kumar*, J. P. Walker* and H. Grebel The Electronic Imaging Center and the ECE department at NJIT, Newark, NJ 0702. grebel@njit.edu * Contributed equally Faraday Cage [], a hollow structure
Optical Cages V. Kumar*, J. P. Walker* and H. Grebel The Electronic Imaging Center and the ECE department at NJIT, Newark, NJ 0702. grebel@njit.edu * Contributed equally Faraday Cage [], a hollow structure
Supplementary Information. depending on the atomic thickness of intrinsic and chemically doped. MoS 2
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Confocal absorption spectral imaging of MoS 2 : Optical transitions
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Confocal absorption spectral imaging of MoS 2 : Optical transitions
Study of Surface Plasmon Excitation on Different Structures of Gold and Silver
 Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2015, 5(4): 71-81 DOI: 10.5923/j.nn.20150504.01 Study of Surface Plasmon Excitation on Different Structures of Gold and Silver Anchu Ashok 1,*, Arya Arackal 1, George Jacob
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2015, 5(4): 71-81 DOI: 10.5923/j.nn.20150504.01 Study of Surface Plasmon Excitation on Different Structures of Gold and Silver Anchu Ashok 1,*, Arya Arackal 1, George Jacob
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2013.97 Supplementary Information Far-field Imaging of Non-fluorescent Species with Sub-diffraction Resolution Pu Wang et al. 1. Theory of saturated transient absorption microscopy
DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2013.97 Supplementary Information Far-field Imaging of Non-fluorescent Species with Sub-diffraction Resolution Pu Wang et al. 1. Theory of saturated transient absorption microscopy
Surface Plasmon Polariton Assisted Metal-Dielectric Multilayers as Passband Filters for Ultraviolet Range
 Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the International School and Conference on Optics and Optical Materials, ISCOM07, Belgrade, Serbia, September 3 7, 2007 Surface Plasmon Polariton
Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the International School and Conference on Optics and Optical Materials, ISCOM07, Belgrade, Serbia, September 3 7, 2007 Surface Plasmon Polariton
Supporting Information. 1T-Phase MoS 2 Nanosheets on TiO 2 Nanorod Arrays: 3D Photoanode with Extraordinary Catalytic Performance
 Supporting Information 1T-Phase MoS 2 Nanosheets on Nanorod Arrays: 3D Photoanode with Extraordinary Catalytic Performance Yuxi Pi, Zhen Li, Danyun Xu, Jiapeng Liu, Yang Li, Fengbao Zhang, Guoliang Zhang,
Supporting Information 1T-Phase MoS 2 Nanosheets on Nanorod Arrays: 3D Photoanode with Extraordinary Catalytic Performance Yuxi Pi, Zhen Li, Danyun Xu, Jiapeng Liu, Yang Li, Fengbao Zhang, Guoliang Zhang,
B. Zhu, Z. Wang, C. Huang, Y. Feng, J. Zhao, and T. Jiang Department of Electronic Science and Engineering Nanjing University Nanjing , China
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, 231 239, 2010 POLARIZATION INSENSITIVE METAMATERIAL ABSORBER WITH WIDE INCIDENT ANGLE B. Zhu, Z. Wang, C. Huang, Y. Feng, J. Zhao, and T. Jiang Department
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, 231 239, 2010 POLARIZATION INSENSITIVE METAMATERIAL ABSORBER WITH WIDE INCIDENT ANGLE B. Zhu, Z. Wang, C. Huang, Y. Feng, J. Zhao, and T. Jiang Department
Research Article Si Substrate-Based Metamaterials for Ultrabroadband Perfect Absorption in Visible Regime
 Nanomaterials, Article ID 893202, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/893202 Research Article Si Substrate-Based Metamaterials for Ultrabroadband Perfect in Visible Regime Qi Han, Lei Jin, Yongqi Fu, and
Nanomaterials, Article ID 893202, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/893202 Research Article Si Substrate-Based Metamaterials for Ultrabroadband Perfect in Visible Regime Qi Han, Lei Jin, Yongqi Fu, and
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Mesoporous C-coated SnO x nanosheets
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Mesoporous C-coated SnO x nanosheets
Influence of Plasmonic Array Geometry on Energy Transfer from a. Quantum Well to a Quantum Dot Layer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Influence of Plasmonic Array Geometry on Energy Transfer from a Quantum Well to a Quantum Dot
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Influence of Plasmonic Array Geometry on Energy Transfer from a Quantum Well to a Quantum Dot
Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni foam for solar thermal water evaporation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 The supporting information for Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 The supporting information for Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni
Supplementary Information. Experimental Evidence of Exciton Capture by Mid-Gap Defects in CVD. Grown Monolayer MoSe2
 Supplementary Information Experimental Evidence of Exciton Capture by Mid-Gap Defects in CVD Grown Monolayer MoSe2 Ke Chen 1, Rudresh Ghosh 2,3, Xianghai Meng 1, Anupam Roy 2,3, Joon-Seok Kim 2,3, Feng
Supplementary Information Experimental Evidence of Exciton Capture by Mid-Gap Defects in CVD Grown Monolayer MoSe2 Ke Chen 1, Rudresh Ghosh 2,3, Xianghai Meng 1, Anupam Roy 2,3, Joon-Seok Kim 2,3, Feng
Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure
 Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure Xiaofei Xu, Yijun Feng, Yu Hao, Juming Zhao, Tian Jiang Department of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing Univerisity, Nanjing,
Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure Xiaofei Xu, Yijun Feng, Yu Hao, Juming Zhao, Tian Jiang Department of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing Univerisity, Nanjing,
Proceedings Metasurface-Based THz Dual-Band Absorber Sensor for the Measurement of Refractive Index Variations of Chemical and Biological Substances
 Proceedings Metasurface-Based THz Dual-Band Absorber Sensor for the Measurement of Refractive Index Variations of Chemical and Biological Substances Mohammed Janneh 1, Andrea De Marcellis 1, *, Elia Palange
Proceedings Metasurface-Based THz Dual-Band Absorber Sensor for the Measurement of Refractive Index Variations of Chemical and Biological Substances Mohammed Janneh 1, Andrea De Marcellis 1, *, Elia Palange
Compact Acoustic Retroreflector Based on A Mirrored Luneburg Lens I. INTRODUCTION
 Compact Acoustic Retroreflector Based on A Mirrored Luneburg Lens Yangyang Fu 1,2,3,*, Junfei Li 1, *, Yangbo Xie 1, *, Chen Shen 1, Yadong Xu 3, Huanyang Chen 2, and Steven A. Cummer 1, 1. Department
Compact Acoustic Retroreflector Based on A Mirrored Luneburg Lens Yangyang Fu 1,2,3,*, Junfei Li 1, *, Yangbo Xie 1, *, Chen Shen 1, Yadong Xu 3, Huanyang Chen 2, and Steven A. Cummer 1, 1. Department
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information CW-Laser-Induced Morphological Changes of
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information CW-Laser-Induced Morphological Changes of
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information An Anode Buffer Layer with Size-Controlled Ag Nanoparticles for Polymer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information An Anode Buffer Layer with Size-Controlled Ag Nanoparticles for Polymer
Interfacial Polymerization with Electrosprayed Micro-droplets: Towards Controllable and Ultrathin Polyamide Membranes
 1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Interfacial Polymerization with Electrosprayed Micro-droplets: Towards Controllable and Ultrathin Polyamide Membranes 5 6 Xiao-Hua Ma,, Zhe Yang, Zhi-Kan Yao, Hao Guo, Zhen-Liang
1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Interfacial Polymerization with Electrosprayed Micro-droplets: Towards Controllable and Ultrathin Polyamide Membranes 5 6 Xiao-Hua Ma,, Zhe Yang, Zhi-Kan Yao, Hao Guo, Zhen-Liang
Thermo-responsive mechano-optical plasmonic nano-antenna. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University of Michigan,
 Supporting Information: Thermo-responsive mechano-optical plasmonic nano-antenna Yunbo Liu 1,, Younggeun Park 3, and Somin Eunice Lee 1,,4,5 1 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
Supporting Information: Thermo-responsive mechano-optical plasmonic nano-antenna Yunbo Liu 1,, Younggeun Park 3, and Somin Eunice Lee 1,,4,5 1 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM characterizations and topographical defects of h- BN films on silica substrates. (a) (c) show the AFM height
 Supplementary Figure S1. AFM characterizations and topographical defects of h- BN films on silica substrates. (a) (c) show the AFM height topographies of h-bn film in a size of ~1.5µm 1.5µm, 30µm 30µm
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM characterizations and topographical defects of h- BN films on silica substrates. (a) (c) show the AFM height topographies of h-bn film in a size of ~1.5µm 1.5µm, 30µm 30µm
A Photonic Crystal Laser from Solution Based. Organo-Lead Iodide Perovskite Thin Films
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION A Photonic Crystal Laser from Solution Based Organo-Lead Iodide Perovskite Thin Films Songtao Chen 1, Kwangdong Roh 2, Joonhee Lee 1, Wee Kiang Chong 3,4, Yao Lu 5, Nripan Mathews
SUPPORTING INFORMATION A Photonic Crystal Laser from Solution Based Organo-Lead Iodide Perovskite Thin Films Songtao Chen 1, Kwangdong Roh 2, Joonhee Lee 1, Wee Kiang Chong 3,4, Yao Lu 5, Nripan Mathews
Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances
 Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances T. J. Davis, D. E. Gómez and K. C. Vernon CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering Localized surface plasmon (LSP)
Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances T. J. Davis, D. E. Gómez and K. C. Vernon CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering Localized surface plasmon (LSP)
SENSITIVITY ENHANCEMENT OF A D-SHAPE SPR-POF LOW-COST SENSOR USING GRAPHENE
 International Journal of Education and Research Vol. No. November 03 SENSITIVITY ENHANCEMENT OF A D-SHAPE SPR-POF LOW-COST SENSOR USING GRAPHENE Ramona GALATUS, Lorant SZOLGA, Emil VOICULESCU Technical
International Journal of Education and Research Vol. No. November 03 SENSITIVITY ENHANCEMENT OF A D-SHAPE SPR-POF LOW-COST SENSOR USING GRAPHENE Ramona GALATUS, Lorant SZOLGA, Emil VOICULESCU Technical
Terahertz antireflection coating enabled by a subwavelength metallic mesh capped with a thin dielectric film
 Invited Paper Terahertz antireflection coating enabled by a subwavelength metallic mesh capped with a thin dielectric film Li Huang 1*, Beibei Zeng 2, Chun-Chieh Chang 2 and Hou-Tong Chen 2* 1 Physics
Invited Paper Terahertz antireflection coating enabled by a subwavelength metallic mesh capped with a thin dielectric film Li Huang 1*, Beibei Zeng 2, Chun-Chieh Chang 2 and Hou-Tong Chen 2* 1 Physics
Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering with enhanced mass transport
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table, Supplementary Notes and Supplementary References
 Description of Supplementary Files File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table, Supplementary Notes and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1.
Description of Supplementary Files File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table, Supplementary Notes and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Information for. Vibrational Spectroscopy at Electrolyte Electrode Interfaces with Graphene Gratings
 Supplementary Information for Vibrational Spectroscopy at Electrolyte Electrode Interfaces with Graphene Gratings Supplementary Figure 1. Simulated from pristine graphene gratings at different Fermi energy
Supplementary Information for Vibrational Spectroscopy at Electrolyte Electrode Interfaces with Graphene Gratings Supplementary Figure 1. Simulated from pristine graphene gratings at different Fermi energy
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Inverted Planar Solar Cell with 13% Efficiency and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Inverted Planar Solar Cell with 13% Efficiency and
Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 551 Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter Y. Y. Li, P. F. Gu, M. Y. Li,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 551 Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter Y. Y. Li, P. F. Gu, M. Y. Li,
Very large plasmon band shift in strongly coupled metal nanoparticle chain arrays.
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 797 2004 Materials Research Society W4.6.1 Very large plasmon band shift in strongly coupled metal nanoparticle chain arrays. L. A. Sweatlock 1, J. J. Penninkhof 2, S. A.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 797 2004 Materials Research Society W4.6.1 Very large plasmon band shift in strongly coupled metal nanoparticle chain arrays. L. A. Sweatlock 1, J. J. Penninkhof 2, S. A.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Longqing Cong, 1,2 Yogesh Kumar Srivastava, 1,2 Ankur Solanki, 1 Tze Chien Sum, 1 and Ranjan Singh 1,2,* 1 Division of Physics and Applied Physics, School of Physical and Mathematical
Supporting Information Longqing Cong, 1,2 Yogesh Kumar Srivastava, 1,2 Ankur Solanki, 1 Tze Chien Sum, 1 and Ranjan Singh 1,2,* 1 Division of Physics and Applied Physics, School of Physical and Mathematical
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium with thickness L. Supplementary Figure Measurement of
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium with thickness L. Supplementary Figure Measurement of
A Plasmonic Photocatalyst Consisting of Silver Nanoparticles Embedded in Titanium Dioxide. Ryan Huschka LANP Seminar February 19, 2008
 A Plasmonic Photocatalyst Consisting of Silver Nanoparticles Embedded in Titanium Dioxide Ryan Huschka LANP Seminar February 19, 2008 TiO 2 Applications White Pigment Photocatalyst Previous methods to
A Plasmonic Photocatalyst Consisting of Silver Nanoparticles Embedded in Titanium Dioxide Ryan Huschka LANP Seminar February 19, 2008 TiO 2 Applications White Pigment Photocatalyst Previous methods to
Supporting Information. Plasmon Ruler for Measuring Dielectric Thin Films
 Supporting Information Single Nanoparticle Based Hetero-Nanojunction as a Plasmon Ruler for Measuring Dielectric Thin Films Li Li, *a,b Tanya Hutter, c Wenwu Li d and Sumeet Mahajan *b a School of Chemistry
Supporting Information Single Nanoparticle Based Hetero-Nanojunction as a Plasmon Ruler for Measuring Dielectric Thin Films Li Li, *a,b Tanya Hutter, c Wenwu Li d and Sumeet Mahajan *b a School of Chemistry
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/4/e1501227/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Self-assembly of highly efficient, broadband plasmonic absorbers for solar steam generation Lin Zhou, Yingling Tan,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/4/e1501227/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Self-assembly of highly efficient, broadband plasmonic absorbers for solar steam generation Lin Zhou, Yingling Tan,
Supplementary Information for. Origin of New Broad Raman D and G Peaks in Annealed Graphene
 Supplementary Information for Origin of New Broad Raman D and G Peaks in Annealed Graphene Jinpyo Hong, Min Kyu Park, Eun Jung Lee, DaeEung Lee, Dong Seok Hwang and Sunmin Ryu* Department of Applied Chemistry,
Supplementary Information for Origin of New Broad Raman D and G Peaks in Annealed Graphene Jinpyo Hong, Min Kyu Park, Eun Jung Lee, DaeEung Lee, Dong Seok Hwang and Sunmin Ryu* Department of Applied Chemistry,
Optimizing the performance of metal-semiconductor-metal photodetectors by embedding nanoparticles in the absorption layer
 Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2015; 3(2-1): 78-82 Published online February 10, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/jeee) doi: 10.11648/j.jeee.s.2015030201.27 ISSN: 2329-1613
Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2015; 3(2-1): 78-82 Published online February 10, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/jeee) doi: 10.11648/j.jeee.s.2015030201.27 ISSN: 2329-1613
Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials
 Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials Shuang Zhang 1, Wenjun Fan 1, N. C. Panoiu 2, K. J. Malloy 1, R. M. Osgood 2 and S. R. J. Brueck 2 1. Center for High Technology Materials and Department
Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials Shuang Zhang 1, Wenjun Fan 1, N. C. Panoiu 2, K. J. Malloy 1, R. M. Osgood 2 and S. R. J. Brueck 2 1. Center for High Technology Materials and Department
Ultra-Wide-Band Microwave Composite Absorbers Based on Phase Gradient Metasurfaces
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 4, 9 18, 214 Ultra-Wide-Band Microwave Composite Absorbers Based on Phase Gradient Metasurfaces Yongfeng Li 1, Jiafu Wang 1, *, Jieqiu Zhang 1, Shaobo Qu 1,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 4, 9 18, 214 Ultra-Wide-Band Microwave Composite Absorbers Based on Phase Gradient Metasurfaces Yongfeng Li 1, Jiafu Wang 1, *, Jieqiu Zhang 1, Shaobo Qu 1,
Reversibly tunable coupled and decoupled super absorbing structures
 Reversibly tunable coupled and decoupled super absorbing structures Nan Zhang 1, Ziye Dong 2, Dengxin Ji 1, Haomin Song 1, Xie Zeng 1, Zhejun Liu 3, Suhua Jiang 3, Yun Xu 4, Ayrton Bernussi 5, Wei Li 2,
Reversibly tunable coupled and decoupled super absorbing structures Nan Zhang 1, Ziye Dong 2, Dengxin Ji 1, Haomin Song 1, Xie Zeng 1, Zhejun Liu 3, Suhua Jiang 3, Yun Xu 4, Ayrton Bernussi 5, Wei Li 2,
Polarization insensitive metamaterial absorber based on E-shaped all-dielectric structure
 JOURNAL OF ADVANCED DIELECTRICS Vol. 5, No. 1 (2015) 1550009 (6 pages) The Authors DOI: 10.1142/S2010135X15500095 Polarization insensitive metamaterial absorber based on E-shaped all-dielectric structure
JOURNAL OF ADVANCED DIELECTRICS Vol. 5, No. 1 (2015) 1550009 (6 pages) The Authors DOI: 10.1142/S2010135X15500095 Polarization insensitive metamaterial absorber based on E-shaped all-dielectric structure
Biosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities
 iosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities. Sepulveda, 1, Y. Alaverdyan,. rian, M. Käll 1 Nanobiosensors and Molecular Nanobiophysics Group Research Center on Nanoscience and Nanotechnolog (CIN)CSIC-ICN
iosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities. Sepulveda, 1, Y. Alaverdyan,. rian, M. Käll 1 Nanobiosensors and Molecular Nanobiophysics Group Research Center on Nanoscience and Nanotechnolog (CIN)CSIC-ICN
A LOW-FREQUENCY METASURFACE ABSORBER BASED ON HELMHOLTZ RESONATORS
 A LOW-FREQUENCY METASURFACE ABSORBER BASED ON HELMHOLTZ RESONATORS Honggang Zhao )), Yang Wang ), Dan Zhao ), and Jihong Wen ) email: zhhg963@sina.com Yiu Wai Lam ), Olga Umnova ) ) Vibration and Acoustics
A LOW-FREQUENCY METASURFACE ABSORBER BASED ON HELMHOLTZ RESONATORS Honggang Zhao )), Yang Wang ), Dan Zhao ), and Jihong Wen ) email: zhhg963@sina.com Yiu Wai Lam ), Olga Umnova ) ) Vibration and Acoustics
Supplementary information for. plasmonic nanorods interacting with J-aggregates.
 Supplementary information for Approaching the strong coupling limit in single plasmonic nanorods interacting with J-aggregates. by Gülis Zengin, Göran Johansson, Peter Johansson, Tomasz J. Antosiewicz,
Supplementary information for Approaching the strong coupling limit in single plasmonic nanorods interacting with J-aggregates. by Gülis Zengin, Göran Johansson, Peter Johansson, Tomasz J. Antosiewicz,
sgsp agsp W=20nm W=50nm Re(n eff (e) } Re{E z Im{E x Supplementary Figure 1: Gap surface plasmon modes in MIM waveguides.
 (a) 2.4 (b) (c) W Au y Electric field (a.u) x SiO 2 (d) y Au sgsp x Energy (ev) 2. 1.6 agsp W=5nm W=5nm 1.2 1 2 3 4.1.1 1 1 Re(n eff ) -1-5 5 1 x (nm) W = 2nm E = 2eV Im{E x } Re{E z } sgsp Electric field
(a) 2.4 (b) (c) W Au y Electric field (a.u) x SiO 2 (d) y Au sgsp x Energy (ev) 2. 1.6 agsp W=5nm W=5nm 1.2 1 2 3 4.1.1 1 1 Re(n eff ) -1-5 5 1 x (nm) W = 2nm E = 2eV Im{E x } Re{E z } sgsp Electric field
Superconductivity Induced Transparency
 Superconductivity Induced Transparency Coskun Kocabas In this paper I will discuss the effect of the superconducting phase transition on the optical properties of the superconductors. Firstly I will give
Superconductivity Induced Transparency Coskun Kocabas In this paper I will discuss the effect of the superconducting phase transition on the optical properties of the superconductors. Firstly I will give
Noise Shielding Using Acoustic Metamaterials
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 53 (2010) pp. 560 564 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 53, No. 3, March 15, 2010 Noise Shielding Using Acoustic Metamaterials LIU Bin ( Ê) and
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 53 (2010) pp. 560 564 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 53, No. 3, March 15, 2010 Noise Shielding Using Acoustic Metamaterials LIU Bin ( Ê) and
A negative permeability material at red light
 A negative permeability material at red light Hsiao-Kuan Yuan, Uday K. Chettiar, Wenshan Cai, Alexander V. Kildishev, Alexandra Boltasseva*, Vladimir P. Drachev, and Vladimir M. Shalaev Birck Nanotechnology
A negative permeability material at red light Hsiao-Kuan Yuan, Uday K. Chettiar, Wenshan Cai, Alexander V. Kildishev, Alexandra Boltasseva*, Vladimir P. Drachev, and Vladimir M. Shalaev Birck Nanotechnology
A new concept of charging supercapacitors based on a photovoltaic effect
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic supporting information (ESI) A new concept of charging supercapacitors based on a photovoltaic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic supporting information (ESI) A new concept of charging supercapacitors based on a photovoltaic
Photothermal Spectroscopy Lecture 2 - Applications
 Photothermal Spectroscopy Lecture 2 - Applications Aristides Marcano Olaizola (PhD) Research Professor Department of Physics and Engineering Delaware State University, US 1 Outlook 1. Optical characterization
Photothermal Spectroscopy Lecture 2 - Applications Aristides Marcano Olaizola (PhD) Research Professor Department of Physics and Engineering Delaware State University, US 1 Outlook 1. Optical characterization
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) variable light emission created via direct ultrasonic exfoliation of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) High quantum-yield luminescent MoS 2 quantum dots
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) High quantum-yield luminescent MoS 2 quantum dots
Nanochannel-Assisted Perovskite Nanowires: Growth Mechanisms. to Photodetector Applications
 Supplementary Information: Nanochannel-Assisted Perovskite Nanowires: Growth Mechanisms to Photodetector Applications Qitao Zhou, Jun Gyu Park, Riming Nie, Ashish Kumar Thokchom, Dogyeong Ha, Jing Pan,
Supplementary Information: Nanochannel-Assisted Perovskite Nanowires: Growth Mechanisms to Photodetector Applications Qitao Zhou, Jun Gyu Park, Riming Nie, Ashish Kumar Thokchom, Dogyeong Ha, Jing Pan,
