Physical Solution of Poisson-Boltzmann Equation. Abstract
|
|
|
- Alfred Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physical Solution of Poisson-Boltzmann Equation Rajib Chakraborty 89/3 Tanupukur Road, Dhakuria, Calcutta 7 3, West Bengal, India (Dated: August 5, 24) Abstract We correct the solution of Poisson-Boltzmann equation regarding charge distribution in an electrolytic solution bounded by walls. Considering charge conservation principle properly, we show that the gradient of electrostatic potential at different walls are strictly related, and cannot be assigned independent values, unlike old theory. It clarifies some cause and effect ideas: distribution turns out to be independent of the initial polarity of walls; the accumulated charges in liquid usually induce opposite polarity on the wall surface, forms Electric Double Layer (EDL), contrary to the common belief that a charged wall attracts counter-ions to form EDL. Distribution depends only on the potential difference between walls and the net charge present in the solution, apart from Debye length. PACS numbers: 4.2.Cv, h, 82.6.Lf, y mecrajib@gmail.com
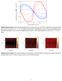
2 Let s find the charge density distribution ρ e within an electrolytic solution bounded by walls. A rectangular geometry, with very small width 2a compared to its length and height, makes it essentially a simple -D problem []; although keeps important physics we are interested in. Here, ρ e varies only along the direction of the shortest side of domain, say in x-direction. Let s define a few parameters, κ a/λ D ; x/a; ψ ψ/ζ () Where, λ D is Debye length; ψ is electrostatic potential and ζ is a suitable scale for it (ζ > ). Now, ρ e and ψ are related through Boltzmann distribution [, 2] [ ] ρ e = ɛκ2 ɛκ 2 a ψ = ζ ψ (2) 2 a 2 = ψ (3) Where, ρ ρ e /ρ, and ρ ( ɛκ 2 ζ/a 2) (4) ψ and ρ e are also related by Poisson s equation; for -D: d 2 ψ dx = ρ e 2 ɛ (5) (using Eq. and Eq. 4) d2 ψ d = 2 κ2 (6) If Q is the net charge present in liquid, in a cross-section, + d = ρ + ρ e d = Q ρ q (7) Integrating both sides of Eq. 6 w.r.t and using Eq. 7, dψ d dψ =+ d = q κ 2 (8) = Hence, we cannot assign independent values to dψ /d at two walls, which was done earlier [3] and is not acceptable. Eq. 3 and Eq. 6 gives Poisson-Boltzmann equation, It s general solution is (with arbitrary constants A, B), d 2 ψ d 2 = κ2 ψ (9) ψ = A exp(κ) + B exp( κ) () dψ = κ[a exp(κ) B exp( κ)] () d dψ d = κ[a exp(κ) B exp( κ)] (2) =+ dψ d = κ[a exp( κ) B exp(κ)] (3) = 2
3 Subtracting Eq. 3 from Eq. 2, and using Eq. 8 we get, A + B = q κ 2 sinh(κ) (4) Let, δ be the potential difference between walls at = + and =. From Eq., ψ =+ = A exp(κ) + B exp( κ) (5) ψ = = A exp( κ) + B exp(κ) (6) Subtracting Eq. 6 from Eq. 5 we get, A B = δ 2 sinh(κ) (7) From Eq. 4 and Eq. 7 we solve for A and B, Using Eq. 8, Eq. 9, Eq., and rearranging terms, From Eq. 3 we get, ψ = = A = 4 sinh(κ) [δ q κ] (8) B = 4 sinh(κ) [δ + q κ] (9) 2 sinh(κ) [δ sinh(κ) q κ cosh(κ)] (2) 2 sinh(κ) [q κ cosh(κ) δ sinh(κ)] (2) From Eq. 2 we can see many interesting things that are described below. If the walls are at the same potential i.e. δ =, and also the solution is neutral as a whole i.e. q =, then the solution is neutral everywhere. Suppose δ =. If liquid contains a net charge, say, for definiteness q >, the excess charges accumulate mostly near the walls (see Fig. (a)) and it does not depend on the initial polarity of the walls i.e. before walls come into contact with liquid. The accumulated charge in liquid must induce opposite charge of necessary amount on the wall surface, if it was already not present. It is contrary to the common belief that a charged surface, when exposed to a solution, induces counter-ions near it; actually this belief led this author to attempt forming erroneous Electric Triple Layer (ETL) theory [4], that says when a neutral solution exposed to a charged wall, the counter-ions form layer near walls leaving behind co-ion abundant layer away from wall. But, for electrostatics, ψ can attain minima 3
4 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) FIG.. Charge density distribution (normalized) along the domain cross-section, in an electrolytic solution enclosed by walls; potential difference between right and left walls is δ; the net charge in the cross-section is q (normalized). For each case, inverse of scaled Debye length κ = 25. (a): q =. and δ =. (b): q =. and δ = 2. (c): q = and δ = (d): q = and δ = (e): q =.3 and δ = 2 or maxima only at boundaries, not inside domain [5], so formation of co-ion abundant layer away from the wall is not possible according to Poisson-Boltzmann model. For δ >, the charges re-distribute (Fig. (b)); higher potential at right wall pushes some +ve charges towards left. Suppose q = and δ >. We see from Fig. (c) +ve ( ve) charges accumulate near the wall of lower (higher) potential (eventually induces opposite polarity on the walls). Reversing sign of δ reverses distribution (Fig. (d)). From Fig. (e),we see, even for q >, some ve charges accumulate at one wall, because δ. Before their exposure to solution, two surfaces can contain same type of charges but have potential difference due to difference in charge density, but when brought in contact with the solution, they acquire different polarities because δ. We see that when δ, charge separation occurs even if q =. Where ρ changes sign, dψ /d =, but it is not an extrema, but a point of inflection; d 2 ψ /d 2 =, too. In some physical systems, the solution acquires a net charge by chemical interaction with the wall, or as a result of adsorption of ions by walls [6 9]. In this case wall automatically acquires a polarity opposite to that of q. If we add some neutral salt to solution, it changes concentration and hence changes κ, but q should not change if there is no further adsorption by walls. It can be checked from Eq. 2 that + ρ ed produces q indeed i.e. it does not change with κ. But in old theories 4
5 [], the integral of ρ e i.e the net charge in liquid turned out to be depend upon κ; it means when we add neutral solution the net charge changes, it clearly violates the principle of conservation of charge, which got corrected in this work. Now, see from Eq. 2, ψ = = q κ/(2 sinh(κ)), which is not zero in general. It is well known that adding a constant to ψ should not change the physics [ 2]. But, from Eq. 3 we see that, in the Poisson-Boltzmann model, ψ is related to a definite quantity, which cannot vary for a given problem. So, ψ gets fixed at all the points in a way that is consistent with Eq. 7; we cannot change ψ further by adding constant, without changing the physics. Thanks to Anthony Leggett and Wolfgang Ketterle for their valuable comments, they pointed out that my earlier attempt to generalize charge distribution through Electric Triple Layer theory was not satisfying Poisson s equation, and then I reformulated the theory here. [] S. Chakraborty and D. Paul, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 39, 5364 (26). [2] H. Bruus, Theoretical Microfluidics (Oxford University Press Inc., New York, United States, 28). [3] A. Ajdari, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 755 (995). [4] R. Chakraborty, Electric triple-layer theory, (24). [5] L. Landau, E. Lifshitz, and L. Pitaevskii, Electrodynamics of Continuous Media, 2nd Edition (Butterworth-Heinemann, Linacre House, Jordan Hill, Oxford OX2 8DP, 984). [6] H. Stone, A. Stroock, and A. Ajdari, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 36, 38 (24). [7] J. Lyklema, Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science,, Vol. 2 (Academic, London, 99). [8] C. Zhao and C. Yang, Microfluid Nanofluid (22),.7/s [9] G. E. Brown-Jr., Science 294, 67 (2). [] D. J. Griffiths, Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3rd ed. (Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi, India, 25) Section 2.3.2, p. 8. [] R. Feynman, R. B. Leighton, and M. Sands, The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol. 2 (Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, India, 964). [2] E. M. Purcell, Berkeley Physics Course Volume 2: Electricity and Magnetism, 2nd ed. (Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limitied., New Delhi, India, 28) Section 2.2, p
Electric Triple Layer Theory. Abstract
 Electric Triple Layer Theory Rajib Chakraborty Department of Physical Sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Kolkata, Mohanpur Campus, Mohanpur-74 5, West Bengal, India (Dated:
Electric Triple Layer Theory Rajib Chakraborty Department of Physical Sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Kolkata, Mohanpur Campus, Mohanpur-74 5, West Bengal, India (Dated:
Plug-flow does not exist in electro-osmosis. Abstract
 Plug-flow does not exist in electro-osmosis Rajib Chakraborty Department of Physical Sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Kolkata, Mohanpur Campus, Mohanpur-74 5, West Bengal,
Plug-flow does not exist in electro-osmosis Rajib Chakraborty Department of Physical Sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Kolkata, Mohanpur Campus, Mohanpur-74 5, West Bengal,
Electro-osmotic Flow Through a Rotating Microchannel
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 306 Electro-osmotic Flow Through a Rotating Microchannel Cheng
Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 306 Electro-osmotic Flow Through a Rotating Microchannel Cheng
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 38: "" The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c )
 The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces
 Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Potential changes of the cross section for rectangular microchannel with different aspect ratios
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(1), 186-190 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Potential changes of the cross section for rectangular microchannel with different aspect ratios Hyo Song Lee, Ki Ho Kim, Jae Keun Yu, Soon
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(1), 186-190 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Potential changes of the cross section for rectangular microchannel with different aspect ratios Hyo Song Lee, Ki Ho Kim, Jae Keun Yu, Soon
Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels Jarrod Schiffbauer *,1, Josh Fernandez 2,
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels Jarrod Schiffbauer *,1, Josh Fernandez 2,
Viscoelastic Effects on Dispersion due to Electroosmotic Flow with Variable Zeta Potential
 Proceedings of the 3 rd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'17) Rome, Italy June 8 10, 2017 Paper No. HTFF 147 ISSN: 2369-8136 DOI: 10.11159/htff17.147 Viscoelastic Effects
Proceedings of the 3 rd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'17) Rome, Italy June 8 10, 2017 Paper No. HTFF 147 ISSN: 2369-8136 DOI: 10.11159/htff17.147 Viscoelastic Effects
Colloid Chemistry. La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross.
 Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1 Analytical Derivation of Diffusio-osmosis Electric Potential and Velocity Distribution of an Electrolyte in a Fine Capillary
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1 Analytical Derivation of Diffusio-osmosis Electric Potential and Velocity Distribution of an Electrolyte in a Fine Capillary
Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
Anindya Aparajita, Ashok K. Satapathy* 1.
 μflu12-2012/24 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF COMBINED ELECTROOSMOTIC AND PRESSURE-DRIVEN FULLY DEVELOPED FLOW OF POWER LAW NANOFLUIDS IN MICROCHANNELS Anindya Aparajita, Ashok
μflu12-2012/24 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF COMBINED ELECTROOSMOTIC AND PRESSURE-DRIVEN FULLY DEVELOPED FLOW OF POWER LAW NANOFLUIDS IN MICROCHANNELS Anindya Aparajita, Ashok
Multimedia : Boundary Lubrication Podcast, Briscoe, et al. Nature , ( )
 3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
Band-bending. EE 436 band-bending 1
 Band-bending In the p-n junction and BJT, we saw that the semiconductor band edges were bent in the depletion layers. We used the depletion approximation and Poisson s equation to relate the band-bending
Band-bending In the p-n junction and BJT, we saw that the semiconductor band edges were bent in the depletion layers. We used the depletion approximation and Poisson s equation to relate the band-bending
Electroviscous Effects in Low Reynolds Number Flow through a Microfluidic Contraction with Rectangular Cross-Section
 PROCEEDINGS OF WORLD ACADEMY OF SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 3 JULY 28 ISSN 37-6884 Electroviscous Effects in Low Reynolds Number Flow through a Microfluidic Contraction with Rectangular
PROCEEDINGS OF WORLD ACADEMY OF SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 3 JULY 28 ISSN 37-6884 Electroviscous Effects in Low Reynolds Number Flow through a Microfluidic Contraction with Rectangular
Symmetry breakdown in binary elastic collisions in classical dynamics
 1 Symmetry breakdown in binary elastic collisions in classical dynamics Abstract Radhakrishnamurty Padyala #282, Duo Marvel Layout, Yelahanka, Bangalore 560064, India. Email: padyala1941@yahoo.com In classical
1 Symmetry breakdown in binary elastic collisions in classical dynamics Abstract Radhakrishnamurty Padyala #282, Duo Marvel Layout, Yelahanka, Bangalore 560064, India. Email: padyala1941@yahoo.com In classical
The Poisson Equation for Electrostatics
 University of Puerto Rico - Mayagüez Table of Contents 1 Derivation from Maxwell s Equations 2 3 4 Derivation from Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s Equations for Electrodynamics in differential form are:
University of Puerto Rico - Mayagüez Table of Contents 1 Derivation from Maxwell s Equations 2 3 4 Derivation from Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s Equations for Electrodynamics in differential form are:
Energy and Equations of Motion
 Energy and Equations of Motion V. Tanrıverdi tanriverdivedat@googlemail.com Physics Department, Middle East Technical University, Ankara / TURKEY Abstract. From the total time derivative of energy an equation
Energy and Equations of Motion V. Tanrıverdi tanriverdivedat@googlemail.com Physics Department, Middle East Technical University, Ankara / TURKEY Abstract. From the total time derivative of energy an equation
V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes MIT Student 1. Poisson-Nernst-Planck Equations The Nernst-Planck Equation is a conservation of mass equation that describes the influence of
V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes MIT Student 1. Poisson-Nernst-Planck Equations The Nernst-Planck Equation is a conservation of mass equation that describes the influence of
Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic
 Lecture Note #7 Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic phenomena Reading: Shaw, ch. 7 Origin of the charge at colloidal surfaces 1. Ionization Proteins acquire their charge by ionization of COOH and NH 2
Lecture Note #7 Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic phenomena Reading: Shaw, ch. 7 Origin of the charge at colloidal surfaces 1. Ionization Proteins acquire their charge by ionization of COOH and NH 2
Initial position, x p (0)/L
 .4 ) xp().2 ) ( 2L 2 xp Dc ( Displacement, /L.2.4.5.5 Initial position, x p ()/L Supplementary Figure Computed displacements of (red) positively- and (blue) negatively-charged particles at several CO 2
.4 ) xp().2 ) ( 2L 2 xp Dc ( Displacement, /L.2.4.5.5 Initial position, x p ()/L Supplementary Figure Computed displacements of (red) positively- and (blue) negatively-charged particles at several CO 2
Electrohydromechanical analysis based on conductivity gradient in microchannel
 Vol 17 No 12, December 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(12)/4541-06 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Electrohydromechanical analysis based on conductivity gradient in microchannel
Vol 17 No 12, December 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(12)/4541-06 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Electrohydromechanical analysis based on conductivity gradient in microchannel
GRAVITY. David J. Jeffery. Department of Physics, University of Idaho, PO Box , Moscow, Idaho , U.S.A January 1 ABSTRACT
 GRAVITY David J. Jeffery Department of Physics, University of Idaho, PO Box 440903, Moscow, Idaho 83844-0903, U.S.A. 2008 January 1 ABSTRACT Lecture notes on what the title says. Subject headings: keywords
GRAVITY David J. Jeffery Department of Physics, University of Idaho, PO Box 440903, Moscow, Idaho 83844-0903, U.S.A. 2008 January 1 ABSTRACT Lecture notes on what the title says. Subject headings: keywords
 Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer
 Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column
Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column
Electrodynamics PHY712. Lecture 3 Electrostatic potentials and fields. Reference: Chap. 1 in J. D. Jackson s textbook.
 Electrodynamics PHY712 Lecture 3 Electrostatic potentials and fields Reference: Chap. 1 in J. D. Jackson s textbook. 1. Poisson and Laplace Equations 2. Green s Theorem 3. One-dimensional examples 1 Poisson
Electrodynamics PHY712 Lecture 3 Electrostatic potentials and fields Reference: Chap. 1 in J. D. Jackson s textbook. 1. Poisson and Laplace Equations 2. Green s Theorem 3. One-dimensional examples 1 Poisson
TWO-STEP LORENTZ TRANSFORMATION OF FORCE. AMON ILAKOVAC and LUKA POPOV
 Printed ISSN 1330 0008 Online ISSN 1333 9125 CD ISSN 1333 8390 CODEN FIZAE4 TWO-STEP LORENTZ TRANSFORMATION OF FORCE AMON ILAKOVAC and LUKA POPOV Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of
Printed ISSN 1330 0008 Online ISSN 1333 9125 CD ISSN 1333 8390 CODEN FIZAE4 TWO-STEP LORENTZ TRANSFORMATION OF FORCE AMON ILAKOVAC and LUKA POPOV Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of
RELATIVISTIC TRANSFORMATION OF MAGNETIC DIPOLE MOMENT
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 47, 63 78, 013 RELATIVISTIC TRANSFORMATION OF MAGNETIC DIPOLE MOMENT Alexander Kholmetskii 1, *, Oleg Missevitch, and Tolga Yarman 3, 4 1 Belarus State University,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 47, 63 78, 013 RELATIVISTIC TRANSFORMATION OF MAGNETIC DIPOLE MOMENT Alexander Kholmetskii 1, *, Oleg Missevitch, and Tolga Yarman 3, 4 1 Belarus State University,
Observable Electric Potential and Electrostatic Potential in Electrochemical Systems
 658 J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 658-662 Observable Electric Potential and Electrostatic Potential in Electrochemical Systems Javier Garrido* and José A. Manzanares Departamento de Termodinámica, UniVersitat
658 J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 658-662 Observable Electric Potential and Electrostatic Potential in Electrochemical Systems Javier Garrido* and José A. Manzanares Departamento de Termodinámica, UniVersitat
Maxwell s equations for electrostatics
 Maxwell s equations for electrostatics October 6, 5 The differential form of Gauss s law Starting from the integral form of Gauss s law, we treat the charge as a continuous distribution, ρ x. Then, letting
Maxwell s equations for electrostatics October 6, 5 The differential form of Gauss s law Starting from the integral form of Gauss s law, we treat the charge as a continuous distribution, ρ x. Then, letting
An Improved Method of Determining the ζ -Potential and Surface Conductance
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 232, 186 197 (2000) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.7153, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on An Improved Method of Determining the ζ -Potential and Surface
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 232, 186 197 (2000) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.7153, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on An Improved Method of Determining the ζ -Potential and Surface
Lecture 8 - Carrier Drift and Diffusion (cont.) September 21, 2001
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Fall 2001 Lecture 8-1 Lecture 8 - Carrier Drift and Diffusion (cont.) September 21, 2001 Contents: 1. Non-uniformly doped semiconductor in thermal equilibrium
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Fall 2001 Lecture 8-1 Lecture 8 - Carrier Drift and Diffusion (cont.) September 21, 2001 Contents: 1. Non-uniformly doped semiconductor in thermal equilibrium
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muhammad Rashid Usman
 Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muhammad Rashid Usman Institute of Chemical Engineering and Technology University of the Punjab, Lahore. Figure taken from: http://heatexchanger-design.com/2011/10/06/heat-exchangers-6/
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muhammad Rashid Usman Institute of Chemical Engineering and Technology University of the Punjab, Lahore. Figure taken from: http://heatexchanger-design.com/2011/10/06/heat-exchangers-6/
Electrical double layer interactions between dissimilar oxide surfaces with charge regulation and Stern Grahame layers
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 296 (2006) 150 158 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis Electrical double layer interactions between dissimilar oxide surfaces with charge regulation and Stern Grahame
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 296 (2006) 150 158 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis Electrical double layer interactions between dissimilar oxide surfaces with charge regulation and Stern Grahame
The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview
 Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer
 1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
Electrical double layer
 Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
ELECTROSTATICS. the study of electric charges, forces and fields Static Electricity is Stationary Electricity or Accumulation of charge
 Electrostatics 1 ELECTROSTATICS the study of electric charges, forces and fields Static Electricity is Stationary Electricity or Accumulation of charge Fundamental Rule Opposites attract, Likes Repel Things
Electrostatics 1 ELECTROSTATICS the study of electric charges, forces and fields Static Electricity is Stationary Electricity or Accumulation of charge Fundamental Rule Opposites attract, Likes Repel Things
Stability of colloidal systems
 Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Discipline Course-I. Semester-II. Paper No: Electricity and Magnetism. Lesson: Polarization and Dielectric Materials
 Discipline CourseI SemesterII Paper No: Electricity and Magnetism Lesson: Polarization and Dielectric Materials Lesson Developer: Dr. Amit Choudhary College/ Department: Physics Department, Deshbandhu
Discipline CourseI SemesterII Paper No: Electricity and Magnetism Lesson: Polarization and Dielectric Materials Lesson Developer: Dr. Amit Choudhary College/ Department: Physics Department, Deshbandhu
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background
 The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 40: "" The Lecture Contains: Slow Coagulation. Other Factors affecting Kinetics of Coagulation
 The Lecture Contains: Slow Coagulation Other Factors affecting Kinetics of Coagulation file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture40/40_1.htm[6/16/2012 12:55:50 PM] Slow Coagulation As shown in
The Lecture Contains: Slow Coagulation Other Factors affecting Kinetics of Coagulation file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture40/40_1.htm[6/16/2012 12:55:50 PM] Slow Coagulation As shown in
Electrostatic Double Layer Force between Two Spherical Particles in a Straight Cylindrical Capillary: Finite Element Analysis
 4162 Langmuir 2003, 19, 4162-4172 Electrostatic Double Layer Force between Two Spherical Particles in a Straight Cylindrical Capillary: Finite Element Analysis Prodip K. Das, Subir Bhattacharjee,* and
4162 Langmuir 2003, 19, 4162-4172 Electrostatic Double Layer Force between Two Spherical Particles in a Straight Cylindrical Capillary: Finite Element Analysis Prodip K. Das, Subir Bhattacharjee,* and
AP Physics C - E & M
 AP Physics C - E & M Gauss's Law 2017-07-08 www.njctl.org Electric Flux Gauss's Law Sphere Table of Contents: Gauss's Law Click on the topic to go to that section. Infinite Rod of Charge Infinite Plane
AP Physics C - E & M Gauss's Law 2017-07-08 www.njctl.org Electric Flux Gauss's Law Sphere Table of Contents: Gauss's Law Click on the topic to go to that section. Infinite Rod of Charge Infinite Plane
Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential
 Physics 342 Lecture 11 Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential Lecture 11 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, February 20th, 2008 We understand that free particle solutions are meant
Physics 342 Lecture 11 Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential Lecture 11 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, February 20th, 2008 We understand that free particle solutions are meant
Mathematical Notes for E&M Gradient, Divergence, and Curl
 Mathematical Notes for E&M Gradient, Divergence, and Curl In these notes I explain the differential operators gradient, divergence, and curl (also known as rotor), the relations between them, the integral
Mathematical Notes for E&M Gradient, Divergence, and Curl In these notes I explain the differential operators gradient, divergence, and curl (also known as rotor), the relations between them, the integral
The de Haas van Alphen Oscillation in Two-Dimensional QED at Finite Temperature and Density
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 35 (21) pp. 673 678 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 35, No. 6, June 15, 21 The de Haas van Alphen Oscillation in Two-Dimensional QED at Finite Temperature
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 35 (21) pp. 673 678 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 35, No. 6, June 15, 21 The de Haas van Alphen Oscillation in Two-Dimensional QED at Finite Temperature
Todd Squires Aditya Khair
 The Francois Frenkiel Award Lecture: Fundamental aspects of Concentration Polarization Todd Squires Aditya Khair Chemical Engineering University of California, Santa Barbara Electrokinetic effects Diffuse
The Francois Frenkiel Award Lecture: Fundamental aspects of Concentration Polarization Todd Squires Aditya Khair Chemical Engineering University of California, Santa Barbara Electrokinetic effects Diffuse
II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics
 II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics Notes by ChangHoon Lim (and MZB) Open circuit voltage of galvanic cell is To understand compositional effects on, we need to consider
II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics Notes by ChangHoon Lim (and MZB) Open circuit voltage of galvanic cell is To understand compositional effects on, we need to consider
1044 Lecture #14 of 18
 Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
An electrokinetic LB based model for ion transport and macromolecular electrophoresis
 An electrokinetic LB based model for ion transport and macromolecular electrophoresis Raffael Pecoroni Supervisor: Michael Kuron July 8, 2016 1 Introduction & Motivation So far an mesoscopic coarse-grained
An electrokinetic LB based model for ion transport and macromolecular electrophoresis Raffael Pecoroni Supervisor: Michael Kuron July 8, 2016 1 Introduction & Motivation So far an mesoscopic coarse-grained
FINITE-VOLUME SOLUTION OF DIFFUSION EQUATION AND APPLICATION TO MODEL PROBLEMS
 IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eissn: 39-63 pissn: 3-738 FINITE-VOLUME SOLUTION OF DIFFUSION EQUATION AND APPLICATION TO MODEL PROBLEMS Asish Mitra Reviewer: Heat
IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eissn: 39-63 pissn: 3-738 FINITE-VOLUME SOLUTION OF DIFFUSION EQUATION AND APPLICATION TO MODEL PROBLEMS Asish Mitra Reviewer: Heat
Fundamentals of Plasma Physics
 Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Definition of Plasma: A gas with an ionized fraction (n i + + e ). Depending on density, E and B fields, there can be many regimes. Collisions and the Mean Free Path (mfp)
Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Definition of Plasma: A gas with an ionized fraction (n i + + e ). Depending on density, E and B fields, there can be many regimes. Collisions and the Mean Free Path (mfp)
Quasi-neutral limit for Euler-Poisson system in the presence of plasma sheaths
 in the presence of plasma sheaths Department of Mathematical Sciences Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) joint work with Masahiro Suzuki (Nagoya) and Chang-Yeol Jung (Ulsan) The
in the presence of plasma sheaths Department of Mathematical Sciences Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) joint work with Masahiro Suzuki (Nagoya) and Chang-Yeol Jung (Ulsan) The
Landau-Fermi liquid theory
 Landau-Fermi liquid theory Shreyas Patankar Chennai Mathematical Institute Abstract We study the basic properties of Landau s theory of a system of interacting fermions (a Fermi liquid). The main feature
Landau-Fermi liquid theory Shreyas Patankar Chennai Mathematical Institute Abstract We study the basic properties of Landau s theory of a system of interacting fermions (a Fermi liquid). The main feature
Lecture Note 1. 99% of the matter in the universe is in the plasma state. Solid -> liquid -> Gas -> Plasma (The fourth state of matter)
 Lecture Note 1 1.1 Plasma 99% of the matter in the universe is in the plasma state. Solid -> liquid -> Gas -> Plasma (The fourth state of matter) Recall: Concept of Temperature A gas in thermal equilibrium
Lecture Note 1 1.1 Plasma 99% of the matter in the universe is in the plasma state. Solid -> liquid -> Gas -> Plasma (The fourth state of matter) Recall: Concept of Temperature A gas in thermal equilibrium
Lecture 5: Electrostatic Interactions & Screening
 Lecture 5: Electrostatic Interactions & Screening Lecturer: Prof. Brigita Urbanc (brigita@drexel.edu) PHYS 461 & 561, Fall 2009-2010 1 A charged particle (q=+1) in water, at the interface between water
Lecture 5: Electrostatic Interactions & Screening Lecturer: Prof. Brigita Urbanc (brigita@drexel.edu) PHYS 461 & 561, Fall 2009-2010 1 A charged particle (q=+1) in water, at the interface between water
File ISM04. Properties of Colloids I
 File ISM04 Properties of Colloids I 1 Colloids Small things, but much bigger than a molecule Background: Foundations of Colloid Science Vol I & II, R.J. Hunter Physical Chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Chapter
File ISM04 Properties of Colloids I 1 Colloids Small things, but much bigger than a molecule Background: Foundations of Colloid Science Vol I & II, R.J. Hunter Physical Chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Chapter
Equilibrium orientation of an ellipsoidal particle inside a dielectric medium with a finite electric conductivity in the external electric field
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 71, 056611 005 Equilibrium orientation of an ellipsoidal particle inside a dielectric medium with a finite electric conductivity in the external electric field Yu. Dolinsky* and T. Elperin
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 71, 056611 005 Equilibrium orientation of an ellipsoidal particle inside a dielectric medium with a finite electric conductivity in the external electric field Yu. Dolinsky* and T. Elperin
Electrolytes. Chapter Basics = = 131 2[ ]. (c) From both of the above = = 120 8[
![Electrolytes. Chapter Basics = = 131 2[ ]. (c) From both of the above = = 120 8[ Electrolytes. Chapter Basics = = 131 2[ ]. (c) From both of the above = = 120 8[](/thumbs/83/88791608.jpg) Chapter 1 Electrolytes 1.1 Basics Here we consider species that dissociate into positively and negatively charged species in solution. 1. Consider: 1 H (g) + 1 Cl (g) + ()+ () = { } = (+ )+ ( ) = 167[
Chapter 1 Electrolytes 1.1 Basics Here we consider species that dissociate into positively and negatively charged species in solution. 1. Consider: 1 H (g) + 1 Cl (g) + ()+ () = { } = (+ )+ ( ) = 167[
Green s Function for Problems with Layers
 Chapter 9 Green s Function for Problems with Layers 9. Continuity conditions The medium comprises two or more straight or curved layers. The properties of the medium are constant within each layer; they
Chapter 9 Green s Function for Problems with Layers 9. Continuity conditions The medium comprises two or more straight or curved layers. The properties of the medium are constant within each layer; they
Electrostatic Double Layer Force between a Sphere and a Planar Substrate in the Presence of Previously Deposited Spherical Particles
 Langmuir 2005, 21, 4755-4764 4755 Electrostatic Double Layer Force between a Sphere and a Planar Substrate in the Presence of Previously Deposited Spherical Particles Prodip K. Das and Subir Bhattacharjee*
Langmuir 2005, 21, 4755-4764 4755 Electrostatic Double Layer Force between a Sphere and a Planar Substrate in the Presence of Previously Deposited Spherical Particles Prodip K. Das and Subir Bhattacharjee*
Educreator Research Journal (ERJ) ISSN :
 ESTIMATION OF GROUND-STATE ENERGY OF PARTICLE IN 1-D POTENTIAL WELL-VARIATION METHOD R.B. Ahirrao Uttamrao Patil College of Art s and Science, Dahivel (M. S.), Abstract: Quantum mechanics provides approximate
ESTIMATION OF GROUND-STATE ENERGY OF PARTICLE IN 1-D POTENTIAL WELL-VARIATION METHOD R.B. Ahirrao Uttamrao Patil College of Art s and Science, Dahivel (M. S.), Abstract: Quantum mechanics provides approximate
An Overview of Non-Newtonian Fluid
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 4(2): December, 2016: pp. 97-101 DOI: 10.5958/2322-0465.2016.00011.3 2016 New Delhi Publishers. All rights reserved An Overview of Non-Newtonian
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 4(2): December, 2016: pp. 97-101 DOI: 10.5958/2322-0465.2016.00011.3 2016 New Delhi Publishers. All rights reserved An Overview of Non-Newtonian
(Autonomous/ Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) COIMBATORE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 (Autonomous/ Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) COIMBATORE-641 032 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Semester III Academic Year: 2015-2016 Regulations 2014 COURSE PLAN Vision To
(Autonomous/ Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) COIMBATORE-641 032 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Semester III Academic Year: 2015-2016 Regulations 2014 COURSE PLAN Vision To
Effect of strength of gravitational field on electrode processes. Mirza Wasif Baig 1. CZ Prague 8, Czech Republic
 Effect of strength of gravitational field on electrode processes Mirza Wasif Baig 1 1 J. Heyrovský Institute of Physical Chemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, CZ-18223 Prague 8, Czech Republic
Effect of strength of gravitational field on electrode processes Mirza Wasif Baig 1 1 J. Heyrovský Institute of Physical Chemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, CZ-18223 Prague 8, Czech Republic
Chapter 17 & 18. Electric Field and Electric Potential
 Chapter 17 & 18 Electric Field and Electric Potential Electric Field Maxwell developed an approach to discussing fields An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a charged object
Chapter 17 & 18 Electric Field and Electric Potential Electric Field Maxwell developed an approach to discussing fields An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a charged object
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
Comment on Conjectures on exact solution of three-dimensional (3D) simple orthorhombic Ising lattices
 arxiv:0811.1802v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Nov 2008 Comment on Conectures on exact solution of three-dimensional (3D) simple orthorhombic Ising lattices Jacques H.H. Perk 145 Physical Sciences, Oklahoma
arxiv:0811.1802v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Nov 2008 Comment on Conectures on exact solution of three-dimensional (3D) simple orthorhombic Ising lattices Jacques H.H. Perk 145 Physical Sciences, Oklahoma
Module 6. Shear, Bond, Anchorage, Development Length and Torsion. Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 6 Shear, Bond, Anchorage, Development Length and Torsion Lesson 15 Bond, Anchorage, Development Length and Splicing Instruction Objectives: At the end of this lesson, the student should be able
Module 6 Shear, Bond, Anchorage, Development Length and Torsion Lesson 15 Bond, Anchorage, Development Length and Splicing Instruction Objectives: At the end of this lesson, the student should be able
Importance Sampling in Monte Carlo Simulation of Rare Transition Events
 Importance Sampling in Monte Carlo Simulation of Rare Transition Events Wei Cai Lecture 1. August 1, 25 1 Motivation: time scale limit and rare events Atomistic simulations such as Molecular Dynamics (MD)
Importance Sampling in Monte Carlo Simulation of Rare Transition Events Wei Cai Lecture 1. August 1, 25 1 Motivation: time scale limit and rare events Atomistic simulations such as Molecular Dynamics (MD)
Energy Conservation and Poynting Theorem in Electromagnetics: A Conceptual Perspective
 Energy Conservation and Poynting Theorem in Electromagnetics: A Conceptual Perspective Krishnasamy T. Selvan Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SSN College of Engineering, Kalavakkam,
Energy Conservation and Poynting Theorem in Electromagnetics: A Conceptual Perspective Krishnasamy T. Selvan Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SSN College of Engineering, Kalavakkam,
Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay. Poisson s and Laplace s Equations
 Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We will spend some time in looking at the mathematical foundations of electrostatics.
Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We will spend some time in looking at the mathematical foundations of electrostatics.
Primary Electroviscous Effect with a Dynamic Stern Layer: Low κa Results
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 226, 180 184 (2000) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.6804, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Primary Electroviscous Effect with a Dynamic Stern Layer: Low
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 226, 180 184 (2000) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.6804, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Primary Electroviscous Effect with a Dynamic Stern Layer: Low
Lecture 12: Finite Elements
 Materials Science & Metallurgy Part III Course M6 Computation of Phase Diagrams H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Lecture 2: Finite Elements In finite element analysis, functions of continuous quantities such as temperature
Materials Science & Metallurgy Part III Course M6 Computation of Phase Diagrams H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Lecture 2: Finite Elements In finite element analysis, functions of continuous quantities such as temperature
Lecture 7 - Carrier Drift and Diffusion (cont.) February 20, Non-uniformly doped semiconductor in thermal equilibrium
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 7-1 Lecture 7 - Carrier Drift and Diffusion (cont.) February 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-uniformly doped semiconductor in thermal equilibrium
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 7-1 Lecture 7 - Carrier Drift and Diffusion (cont.) February 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-uniformly doped semiconductor in thermal equilibrium
Capillary-gravity waves: The effect of viscosity on the wave resistance
 arxiv:cond-mat/9909148v1 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Sep 1999 Capillary-gravity waves: The effect of viscosity on the wave resistance D. Richard, E. Raphaël Collège de France Physique de la Matière Condensée URA
arxiv:cond-mat/9909148v1 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Sep 1999 Capillary-gravity waves: The effect of viscosity on the wave resistance D. Richard, E. Raphaël Collège de France Physique de la Matière Condensée URA
Fluid Mechanics Chapter 1 Effects of pressure
 Fluid Mechanics Chapter 1 Effects of pressure last edited eptember 10, 2017 1.1 Motivation 29 1.2 Concept of pressure 29 1.2.1 The direction of pressure 29 1.2.2 Pressure on an infinitesimal volume 30
Fluid Mechanics Chapter 1 Effects of pressure last edited eptember 10, 2017 1.1 Motivation 29 1.2 Concept of pressure 29 1.2.1 The direction of pressure 29 1.2.2 Pressure on an infinitesimal volume 30
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Retention and Release of Graphene Oxide in Structured Heterogeneous Porous Media under Saturated and Unsaturated Conditions Shunan Dong 1, Xiaoqing Shi 1, Bin Gao 3, Jianfeng Wu
Supporting Information Retention and Release of Graphene Oxide in Structured Heterogeneous Porous Media under Saturated and Unsaturated Conditions Shunan Dong 1, Xiaoqing Shi 1, Bin Gao 3, Jianfeng Wu
Formulae for Computing Logarithmic Integral Function ( )!
 Formulae for Computing Logarithmic Integral Function x 2 ln t Li(x) dt Amrik Singh Nimbran 6, Polo Road, Patna, INDIA Email: simnimas@yahoo.co.in Abstract: The prime number theorem states that the number
Formulae for Computing Logarithmic Integral Function x 2 ln t Li(x) dt Amrik Singh Nimbran 6, Polo Road, Patna, INDIA Email: simnimas@yahoo.co.in Abstract: The prime number theorem states that the number
An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential. David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd
 An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd Fundamental Parameters that control the Nature and Behavior of all Particulate
An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd Fundamental Parameters that control the Nature and Behavior of all Particulate
Electrostatic Field Calculations for Electrophoresis Using Surfaces
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1061 2008 Materials Research Society 1061-MM09-25 Electrostatic Field Calculations for Electrophoresis Using Surfaces Perumal Ramasamy 1, Raafat M Elmaghrabi 2, and Gary
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1061 2008 Materials Research Society 1061-MM09-25 Electrostatic Field Calculations for Electrophoresis Using Surfaces Perumal Ramasamy 1, Raafat M Elmaghrabi 2, and Gary
Sound Propagation through Media. Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Sound Propagation through Media Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur LECTURE-13 WAVE PROPAGATION IN SOLIDS Longitudinal Vibrations In Thin Plates Unlike 3-D solids, thin plates have surfaces
Sound Propagation through Media Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur LECTURE-13 WAVE PROPAGATION IN SOLIDS Longitudinal Vibrations In Thin Plates Unlike 3-D solids, thin plates have surfaces
PHY103A: Lecture # 9
 Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 9 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 20-Jan-2018 Summary of Lecture # 8: Force per unit
Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 9 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 20-Jan-2018 Summary of Lecture # 8: Force per unit
CONCEPTUAL TOOLS By: Neil E. Cotter CIRCUITS OHM'S LAW Physics
 Physics DERIV: Ohm's law is almost always derived from basic physics with a starting assumption that the electric field inside a resistor is constant. We first investigate this assumption. The electric
Physics DERIV: Ohm's law is almost always derived from basic physics with a starting assumption that the electric field inside a resistor is constant. We first investigate this assumption. The electric
arxiv: v2 [physics.gen-ph] 20 Mar 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.gen-ph] 20 Mar 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.gen-ph] 20 Mar 2013](/thumbs/96/127587291.jpg) arxiv:129.3449v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Mar 213 Potential Theory in Classical Electrodynamics W. Engelhardt 1, retired from: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-85741 Garching, Germany Abstract In Maxwell
arxiv:129.3449v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Mar 213 Potential Theory in Classical Electrodynamics W. Engelhardt 1, retired from: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-85741 Garching, Germany Abstract In Maxwell
Linearized theory of elasticity
 Linearized theory of elasticity Arie Verhoeven averhoev@win.tue.nl CASA Seminar, May 24, 2006 Seminar: Continuum mechanics 1 Stress and stress principles Bart Nowak March 8 2 Strain and deformation Mark
Linearized theory of elasticity Arie Verhoeven averhoev@win.tue.nl CASA Seminar, May 24, 2006 Seminar: Continuum mechanics 1 Stress and stress principles Bart Nowak March 8 2 Strain and deformation Mark
Importance Sampling in Monte Carlo Simulation of Rare Transition Events
 Importance Sampling in Monte Carlo Simulation of Rare Transition Events Wei Cai Lecture 1. August 1, 25 1 Motivation: time scale limit and rare events Atomistic simulations such as Molecular Dynamics (MD)
Importance Sampling in Monte Carlo Simulation of Rare Transition Events Wei Cai Lecture 1. August 1, 25 1 Motivation: time scale limit and rare events Atomistic simulations such as Molecular Dynamics (MD)
History. The word electricity comes from the Greek elektron which means amber. The amber effect is what we call static electricity.
 Electrostatics 1 History The word electricity comes from the Greek elektron which means amber. The amber effect is what we call static electricity. 2 ELECTROSTATICS the study of electric charges, forces
Electrostatics 1 History The word electricity comes from the Greek elektron which means amber. The amber effect is what we call static electricity. 2 ELECTROSTATICS the study of electric charges, forces
( ) by D n ( y) 1.1 Mathematical Considerations. π e nx Dirac s delta function (distribution) a) Dirac s delta function is defined such that
 Chapter 1. Electrostatics I Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 1. Units from the Système International (SI) will be used in this chapter. 1.1 Mathematical
Chapter 1. Electrostatics I Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 1. Units from the Système International (SI) will be used in this chapter. 1.1 Mathematical
Moment of a force (scalar, vector ) Cross product Principle of Moments Couples Force and Couple Systems Simple Distributed Loading
 Chapter 4 Moment of a force (scalar, vector ) Cross product Principle of Moments Couples Force and Couple Systems Simple Distributed Loading The moment of a force about a point provides a measure of the
Chapter 4 Moment of a force (scalar, vector ) Cross product Principle of Moments Couples Force and Couple Systems Simple Distributed Loading The moment of a force about a point provides a measure of the
Foundations of Chemistry
 Name Foundations of Chemistry What is matter, and how does it change? Date Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about matter and how it changes Record three things that
Name Foundations of Chemistry What is matter, and how does it change? Date Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about matter and how it changes Record three things that
Module 14. Tension Members. Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 14 Tension Members Lesson 37 Numerical Problems Instructional Objectives: At the end of this lesson, the student should be able to: select the category of the problem if it is a liquid retaining
Module 14 Tension Members Lesson 37 Numerical Problems Instructional Objectives: At the end of this lesson, the student should be able to: select the category of the problem if it is a liquid retaining
PHYS102 - Gauss s Law.
 PHYS102 - Gauss s Law. Dr. Suess February 2, 2007 PRS Questions 2 Question #1.............................................................................. 2 Answer to Question #1......................................................................
PHYS102 - Gauss s Law. Dr. Suess February 2, 2007 PRS Questions 2 Question #1.............................................................................. 2 Answer to Question #1......................................................................
Sound Propagation through Media. Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Sound Propagation through Media Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur LECTURE-17 HARMONIC PLANE WAVES Introduction In this lecture, we discuss propagation of 1-D planar waves as they travel
Sound Propagation through Media Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur LECTURE-17 HARMONIC PLANE WAVES Introduction In this lecture, we discuss propagation of 1-D planar waves as they travel
Figure 1.1: Ionization and Recombination
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is a Plasma? 1.1.1 An ionized gas A plasma is a gas in which an important fraction of the atoms is ionized, so that the electrons and ions are separately free. When does
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is a Plasma? 1.1.1 An ionized gas A plasma is a gas in which an important fraction of the atoms is ionized, so that the electrons and ions are separately free. When does
Electrostatics Review A. A B. B C. C D. D
 Name: ate: 1. Which sketch best represents the charge distribution around a neutral electroscope when a positively charged strip is brought near, but does not touch, the electroscope? 4. In the diagram
Name: ate: 1. Which sketch best represents the charge distribution around a neutral electroscope when a positively charged strip is brought near, but does not touch, the electroscope? 4. In the diagram
Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation
 Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation Ion:ion interactions What is the free energy of ion:ion interactions ΔG i-i? Consider an ion in a solution
Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation Ion:ion interactions What is the free energy of ion:ion interactions ΔG i-i? Consider an ion in a solution
1. Comparison of stability analysis to previous work
 . Comparison of stability analysis to previous work The stability problem (6.4) can be understood in the context of previous work. Benjamin (957) and Yih (963) have studied the stability of fluid flowing
. Comparison of stability analysis to previous work The stability problem (6.4) can be understood in the context of previous work. Benjamin (957) and Yih (963) have studied the stability of fluid flowing
