Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer
|
|
|
- Sharon Allison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water
2 LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column chromatography, HPLC, Paper Chromatography, TLC They are examples of the adsorption of solutes at the liquid solid interface. Liquid solid interfaces can be found everywhere and in any form and size, from electrode surfaces to ship hulls.
3 LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Not so obvious examples for a solidliquid liquid interface is a colloid particle. Colloids are widely spread in daily use: Paint Blood Air pollution
4 LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids A very sensitive method to measure the amount of adsorbed material is by using a QCM (quartz crystal microbalance)
5 LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Adsorption at low solute concentration: These isotherms can be either fitted by the langmuir isotherm Or the freundlich isotherm
6 LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Stearic acid is adsorbed onto carbon black differently in different solvents:
7 LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Different chain lengthes will show differences in adsorption behaviour:
8 LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Traube s s rule:
9 LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Composite adsorption isotherms:
10 Intermolecular Forces Interaction Force/Radius (mn/m) van der Waals Electrostatic Steric Depletion Hydrophobic Solvation Separation Distance (nm) Repulsive Forces (Above Xaxis) Attractive Forces (Below Xaxis)
11 Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Flagella EColi demonstrate tumbling & locomotive modes of motion in the cell to align themselves with the cell s rear portion Flagella motion is propelled by a molecular motor made of proteins Influencing proton release through protein is a key molecular approach to prevent EColi induced diarrhea Mingming Wu, Cornell University (animation) Berg, Howard, C. Nature 249: 7879, 1974.
12 Electrostatic Forces & van der Waals Forces jointly influence Flocculation / Coagulation Suspension of Al 2 O 3 at different solution ph Critical for Water Treatment Processes
13 Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer 1) Sources of interfacial charge 2) Electrostatic theory: The electrical double layer 3) Electrokinetic Phenomena 4) Electrostatic forces
14 SOURCES OF INTERFACIAL CHARGE Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Direct Ionization of surface groups. H O M H O O O H O O M O H O O O H M H O 2 O O O (2) Specific ion adsorption OH O M O O
15 SURFACE CHARGE GENERATION (cont.) (3) Differential ion solubility Some ionic crystals have a slight imbalance in number of lattice cations or anions on surface, eg. AgI, BaSO 4, CaF 2, NaCl, KCl (4) Substitution of surface ions eg. lattice substitution in kaolin HO Si HO O Al O O Si O O OH Si O OH
16 ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYERS Ψ 0 SOLVENT MOLECULES COUNTER IONS x OHP CO IONS Helmholtz (100 years ago) proposed that surface charge is balanced by a layer of oppositely charged ions
17 Ψ 0 GouyChapman Model ( ) x Diffusion plane Assumed PoissonBoltzmann distribution of ions from surface ions are point charges ions do not interact with each other Assumed that diffuse layer begins at some distance from the surface
18 Ψ ζ Ψ 0 Stern (1924) / Grahame (1947) Model Gouy/Chapman diffuse double layer and layer of adsorbed charge. Linear decay until the Stern plane. Stern Plane Difusion layer Shear Plane Gouy Plane Bulk Solution x
19 Stern (1924) / Grahame (1947) Model In different approaches the linear decay is assumed to be until the shear plane, since there is the barrier where the charges considered static. In this courese however we will assume that the decay is linear until the Stern plane. Ψ ζ Ψ 0 OHP Difusion layer Shear Plane Gouy Plane Bulk Solution x
20 POISSONBOLTZMANN DISTRIBUTION 1 st Maxwell law (Gauss law): The total of the electric flux out of a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed divided by the permittivity E = ( r) ρ ε ε Electric field is the differential of the electric potential E ( r) = Ψ Combining the two equations we get: Ψ r Which for one dimension becomes: () 0 r () r ρ( r = ε ε 2 ) 2 d Ψ dx Assuming Boltzmann ion distribution: 0 ( x) ρ( x) 2 = n ( x) ρ( x) 1 Z eψ kt Zen ( ZΨe kt Z e kt = = Z nee = e e ) 2 d Ψ i Ψ 2 i dx εε 0 εε 0 i εε 0 εε 0 r ρ Definitions E: Electric filed Ψ: Electric potential ρ: Charge density E Q : Energy of the ion x, r : Distance Boltzmann ion distribution E ezψ Q kt kt ( x) e = n Zee = ρ 0 0
21 POISSONBOLTZMANN DISTRIBUTION d 2 dx ψ 2 = 2Zen sinh ε ε r 0 Zeψ kt Z = electrolyte valence, e = elementary charge (C) n = electrolyte concentration(#/m 3 ) ε r = dielectric constant of medium ε 0 = permittivity of a vacuum (F/m) k = Boltzmann constant (J/K) T = temperature (K) PoissonBoltzmann distribution describes the EDL Defines potential as a function of distance from a surface ions are point charges ions do not interact with each other
22 POISSONBOLTZMANN DISTRIBUTION DebyeHückel approximation ZeΨ kt <<1 2Zen Zeψ sinh ε ε kt For then: 2 d ψ = 2 dx r 0 2Zen ε ε r 0 Zeψ = kt ( Ze) 2n ε ε kt 2 ( x) = κ Ψ( x) The solution is a simple exponential decay (assuming Ψ(0)=Ψ 0 and Ψ( )=0): Ψ( x)= Ψ 0 e κx DebyeHückel parameter (κ) describes the decay length κ = ( Ze) 2n ε ε kt r 0 2 r 0 2 Ψ
23 DOUBLE LAYER FOR MULTIVALENT ELECTROLYTE: DEBYE LENGTH DebyeHückel parameter (κ) describes the decay length 1/ 2 2 n e 2 κ = C iz i ε rε 0kT i= 1 Z i = electrolyte valence e = elementary charge (C) C i = ion concentration (#/m 3 ) n = number of ions ε r = dielectric constant of medium ε 0 = permittivity of a vacuum (F/m) k = Boltzmann constant (J/K) T = temperature (K) κ 1 (Debye length) has units of length
24 POISSONBOLTZMANN DISTRIBUTION Exact Solution For M 11 electrolyte Surface Potential (mv) Surface Potential (mv) ZeΨ kt <1 ZeΨ kt >1
25 DEBYE LENGTH AND VALENCY Debye Length κ 1, (nm) electrolyte 22 electrolyte 33 electrolyte Electrolyte Concentration (M) Ions of higher valence are more effective in screening surface charge.
26 ZETA POTENTIAL Point of Zero Charge (PZC) ph at which surface potential = 0 Isoelectric Point (IEP) ph at which zeta potential = 0 Question: What will happen to a mixed suspension of Alumina and Si3N4 particles in water at ph 4, 7 and 9?
27 ZETA POTENTIAL Effect of Ionic Strength Zeta Potential (mv) Alumina Increasing I.S ph
28 SPECIFIC ADSORPTION Free energy decrease upon adsorption greater than predicted by electrostatics Have the ability to shift the isoelectric point v and reverse zeta potential Multivalent ions: Ca 2, Mg 2, La 3, hexametaphosphate, sodium silicate Selfassembling organic molecules: surfactants, polyelectrolytes 2
29 SPECIFIC ADSORPTION Ca 2 PO 4 3 ph Multivalent cations shift IEP to right (calcite supernatant) Multivalent anions shift IEP to left (apatite supernatant) Amankonah and Somasundaran, Colloids and Surfaces, 15, 335 (1985).
30 ELECTROKINETIC PHENOMENA Electrophoresis Movement of particle in a stationary fluid by an applied electric field. Electroosmosis Movement of liquid past a surface by an applied electric field Streaming Potential Creation of an electric field as a liquid moves past a stationary charged surface Sedimentation Potential Creation of an electric field when a charged particle moves relative to stationary fluid
31 ZETA POTENTIAL MEASUREMENT Electrophoresis ζ determined by the rate of diffusion (electrophoretic mobility) of a charged particle in an applied DC electric field. PCS ζ determined by diffusion of particles as measured by photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS) in applied field Acoustophoresis ζ determined by the potential created by a particle vibrating in its double layer due to an acoustic wave Streaming Potential ζ determined by measuring the potential created as a fluid moves past macroscopic surfaces or a porous plug
32 ZETA POTENTIAL MEASUREMENT Electrophoresis Smoluchowski Formula (1921) assumed κa >> 1 κ = Debye parameter a = particle radius electrical double layer thickness much smaller than particle v = µ Ε ε = r ε η ε 0 r ζ ε η 0 Ε ζ v = velocity, ε r = media dielectric constant ε 0 = permittivity of free space ζ = zeta potential, E = electric field η = medium viscosity µ E = electrophoretic mobility
33 ZETA POTENTIAL MEASUREMENT Electrophoresis Henry Formula (1931) expanded for arbitrary κa, assumed E field does not alter surface charge low σ 0 v µ 2εrε = 3η Ε 0 ζ f 2εrε = 3η 0 1 ζ f ( κa) Ε 1 ( κa) v = velocity ε r = media dielectric constant ε 0 = permittivity of free space ζ = zeta potential η = medium viscosity E = electric field µ E = electrophoretic mobility Hunter, Foundations of Colloid Science, p. 560
34 ZETA POTENTIAL MEASUREMENT Streaming Potential exp(zeζ / κa 2kT) << 1 κ = Debye parameter a = particle radius ζ = zeta potential Ε = Potential over capillary (V) ε r = media dielectric constant ε 0 = permittivity of free space (F/m) η = medium viscosity (Pa s) K E = solution conductivity (S/m) p = pressure drop across capillary (Pa) E = ε r ε 0 ηk ζ E p
35 Combined Effects of van der Waals and Electrostatic Forces DLVO Theory DLVO Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey and Overbeek Based on the sum of van der Waals attractive potential and a screened electrostatic repulsion potential arising between the double layer potential screened by ions in solution. The total interaction energy U of the system is: 2 AR 64πkTRnγ U ( x) = exp 2 12x κ Van der Waals (Attractive force) Electrostatics (Repulsive force) ( κx)
36 DLVO Theory 2 AR 64πkTRnγ U ( x) = exp 2 12x κ ( κx) A = Hamakar s constant R = Radius of particle x = Distance of Separation k = Boltzmann s constant T = Temperature n = bulk ion concentration κ= Debye parameter γ = tanh zeψ 4kT z = valency of ion e = Charge of electron Ψ = Surface potential
37 DLVO Theory 100 nm Alumina, 0.01 M NaCl, Ψ zeta =20 mv For short distances of separation between particles
38 DLVO Theory Hard Sphere Repulsion (< 0.5 nm) No Salt added J/m Energy Barrier x (distance) Secondary Minimum (Flocculation) Primary Minimum (Coagulation)
39 Discussion: Flocculation vs. Coagulation The DLVO theory defines formally (and distinctly), the often interused terms flocculation and coagulation Flocculation: Corresponds to the secondary energy minimum at large distances of separation The energy minimum is shallow (weak attractions, 12 kt units) Attraction forces may be overcome by simple shaking Coagulation: Corresponds to the primary energy minimum at short distances of separation upon overcoming the energy barrier The energy minimum is deep (strong attractions) Once coagulated, particle separation is almost impossible
40 Hard Sphere Repulsion (< 0.5 nm) J/m Effect of Salt Energy Barrier No Salt added Upon Salt addition x (distance) Secondary Minimum (Flocculation) Primary Minimum (Coagulation) Addition of salt reduces the energy barrier of repulsion. How?
41 Secondary Minimum: Real System 100 nm Alumina, Ψ zeta =30 mv
42 Discussion on the Effect of Salt The salt reduces the EDL thickness by charge screening Reduces the energy barrier (may induce coagulation) Also increases the distance at which secondary minimum occurs (aids flocculation) Since increased salt concentration decreases κ 1 (or decreases electrostatics), at the Critical Salt Concentration U(x) = 0
43 Effect of Salt Concentration and Type AR 12H 64πkTRnγ 2 κ 2 exp( κh ) = 0 H: Distance of separation at critical salt concentration At critical salt concentration, κh = 1. Upon simplification, we get: nα 1 z 6 Schultz Hardy Rule: n: Concentration Z: Valence Concentration to induce rapid coagulation varies inversely with charge on cation
44 Effect of Salt Concentration and Type For As 2 S 3 sol, KCl: MgCl 2 : AlCl 3 required to induce flocculation and coagulation varies by a simple proportion 1: 0.014: The DLVO theory thus explains why alum (AlCl 3 ) and polymers are effective (functionality and cost wise) to induce flocculation and coagulation
45 ph and Salt Concentration Effect Agglomerate Dispersion Dispersion Stability diagram for Si3N4(M11) particles as produced from calculations (IEP 4.4) assuming 90% probability of coagulation for solid formation.
46 REMARKS hydrophobic and solvation forces Due to the number of fitting parameters (ψ 0, A 132, spring constant, I.S.) and uncertainty in force laws (C.C. vs C.P., retardation) hydrophobic forces often invoked to explain differences between theory and experiment. Because hydrophobic forces involve the structure of the solvent, the number of molecules to be considered in the interaction is large and computer simulation has only begun to approach this problem. Widely accepted phenomenological models of hydrophobic forces still need to be developed.
Stability of colloidal systems
 Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
*blood and bones contain colloids. *milk is a good example of a colloidal dispersion.
 Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces
 Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids.
 Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids. Lyophilic and lyophobic sols Sols (lyosols) are dispersed colloidal size particles in a liquid medium (=solid/liquid dispersions) These sols
Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids. Lyophilic and lyophobic sols Sols (lyosols) are dispersed colloidal size particles in a liquid medium (=solid/liquid dispersions) These sols
Electrical double layer
 Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Multimedia : Boundary Lubrication Podcast, Briscoe, et al. Nature , ( )
 3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 37: "" The Lecture Contains: DLVO Theory. Effect of Concentration. Objectives_template
 The Lecture Contains: DLVO Theory Effect of Concentration file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture37/37_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:02:12 PM] Studying the stability of colloids is an important topic
The Lecture Contains: DLVO Theory Effect of Concentration file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture37/37_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:02:12 PM] Studying the stability of colloids is an important topic
Contents. Preface XIII
 V Contents Preface XIII 1 General Introduction 1 1.1 Fundamental Knowledge Required for Successful Dispersion of Powders into Liquids 1 1.1.1 Wetting of Powder into Liquid 1 1.1.2 Breaking of Aggregates
V Contents Preface XIII 1 General Introduction 1 1.1 Fundamental Knowledge Required for Successful Dispersion of Powders into Liquids 1 1.1.1 Wetting of Powder into Liquid 1 1.1.2 Breaking of Aggregates
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview
 Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Single action pressing (from top)
 www.komage.de Single action pressing (from top) Double action pressing with fixed die Typical course of the pressure during pressing and ejection (Single action) Upper punch Pressure Lower punch Time Green
www.komage.de Single action pressing (from top) Double action pressing with fixed die Typical course of the pressure during pressing and ejection (Single action) Upper punch Pressure Lower punch Time Green
István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry
 Colloid stability István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry www.kolloid.unideb.hu (Stability of lyophilic colloids see: macromolecular solutions) Stabilities 1.
Colloid stability István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry www.kolloid.unideb.hu (Stability of lyophilic colloids see: macromolecular solutions) Stabilities 1.
It is the size of the
 Chapter 2: Literature Review (Note: A modified form of this chapter will be published as Rheology and Colloidal Stability in Paints and Coatings, Proceedings of the Association of Formulation Chemists,
Chapter 2: Literature Review (Note: A modified form of this chapter will be published as Rheology and Colloidal Stability in Paints and Coatings, Proceedings of the Association of Formulation Chemists,
Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic
 Lecture Note #7 Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic phenomena Reading: Shaw, ch. 7 Origin of the charge at colloidal surfaces 1. Ionization Proteins acquire their charge by ionization of COOH and NH 2
Lecture Note #7 Charged Interfaces & electrokinetic phenomena Reading: Shaw, ch. 7 Origin of the charge at colloidal surfaces 1. Ionization Proteins acquire their charge by ionization of COOH and NH 2
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 38: "" The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c )
 The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential. David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd
 An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd Fundamental Parameters that control the Nature and Behavior of all Particulate
An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd Fundamental Parameters that control the Nature and Behavior of all Particulate
ISO Colloidal systems Methods for zetapotential. Part 1: Electroacoustic and electrokinetic phenomena
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13099-1 First edition 2012-06-15 Colloidal systems Methods for zetapotential determination Part 1: Electroacoustic and electrokinetic phenomena Systèmes colloïdaux Méthodes de
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13099-1 First edition 2012-06-15 Colloidal systems Methods for zetapotential determination Part 1: Electroacoustic and electrokinetic phenomena Systèmes colloïdaux Méthodes de
Zeta potential - An introduction in 30 minutes
 Zeta potential - An introduction in 30 minutes ZETA POTENTIAL Introduction Zeta potential is a physical property which is exhibited by any particle in suspension, macromolecule or material surface. It
Zeta potential - An introduction in 30 minutes ZETA POTENTIAL Introduction Zeta potential is a physical property which is exhibited by any particle in suspension, macromolecule or material surface. It
Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces
 CHEM-E150 Interfacial Phenomena in Biobased Systems Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces Monika Österberg Spring 018 Content Colloidal stability van der Waals Forces Surface Forces and their
CHEM-E150 Interfacial Phenomena in Biobased Systems Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces Monika Österberg Spring 018 Content Colloidal stability van der Waals Forces Surface Forces and their
SOLUTIONS TO CHAPTER 5: COLLOIDS AND FINE PARTICLES
 SOLUTIONS TO CHAPTER 5: COLLOIDS AND FINE PARTICLES EXERCISE 5.1: Colloidal particles may be either dispersed or aggregated. (a) What causes the difference between these two cases? Answer in terms of interparticle
SOLUTIONS TO CHAPTER 5: COLLOIDS AND FINE PARTICLES EXERCISE 5.1: Colloidal particles may be either dispersed or aggregated. (a) What causes the difference between these two cases? Answer in terms of interparticle
Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry
 Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry Lyophilic and lyophobic sols Sols (lyosols) are dispersed colloidal
Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry Lyophilic and lyophobic sols Sols (lyosols) are dispersed colloidal
Supporting Information for. Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene
 Supporting Information for Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene oxide colloidal stability in aquatic environment Binbin Sun, Yinqing Zhang, Wei Chen, Kunkun Wang, Lingyan
Supporting Information for Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene oxide colloidal stability in aquatic environment Binbin Sun, Yinqing Zhang, Wei Chen, Kunkun Wang, Lingyan
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions
 Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions 6.1 Kinetic Stability of Colloidal Suspensions o G = A f sl sl interfacial surface tension (sol/liq) [J/m 2 ] sol/liq surface change [m 2 ] γ sl > 0 colloid
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions 6.1 Kinetic Stability of Colloidal Suspensions o G = A f sl sl interfacial surface tension (sol/liq) [J/m 2 ] sol/liq surface change [m 2 ] γ sl > 0 colloid
Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications
 Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications Tadros, Tharwat F. ISBN-13: 9783527306299 Table of Contents Preface. 1 Introduction. 1.1 General Classification of Surface Active Agents. 1.2 Anionic Surfactants.
Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications Tadros, Tharwat F. ISBN-13: 9783527306299 Table of Contents Preface. 1 Introduction. 1.1 General Classification of Surface Active Agents. 1.2 Anionic Surfactants.
Foundations of. Colloid Science SECOND EDITION. Robert J. Hunter. School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions
 Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions 6.1 Kinetic Stability of Colloidal Suspensions o G = A f sl sl interfacial surface tension (sol/liq) [J/m 2 ] sol/liq surface change [m 2 ] γ sl > 0 colloid
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions 6.1 Kinetic Stability of Colloidal Suspensions o G = A f sl sl interfacial surface tension (sol/liq) [J/m 2 ] sol/liq surface change [m 2 ] γ sl > 0 colloid
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1 Analytical Derivation of Diffusio-osmosis Electric Potential and Velocity Distribution of an Electrolyte in a Fine Capillary
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1 Analytical Derivation of Diffusio-osmosis Electric Potential and Velocity Distribution of an Electrolyte in a Fine Capillary
The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background
 The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
Contents. Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII. 1 Introduction 1
 V Contents Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII 1 Introduction 1 2 Van der Waals Forces 5 2.1 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 5 2.1.1 Coulomb Interaction 5 2.1.2 Monopole Dipole Interaction
V Contents Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII 1 Introduction 1 2 Van der Waals Forces 5 2.1 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 5 2.1.1 Coulomb Interaction 5 2.1.2 Monopole Dipole Interaction
ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2
 Unclassified ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2 ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2 Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
Unclassified ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2 ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2 Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
Electrophoretic Deposition. - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode
 Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications. CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications
 CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications History of Nanotechnology: Time Line Democritus in ancient Greece: concept of atom 1900 : Rutherford : discovery of atomic nucleus The first TEM was
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications History of Nanotechnology: Time Line Democritus in ancient Greece: concept of atom 1900 : Rutherford : discovery of atomic nucleus The first TEM was
Colloid Chemistry. La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross.
 Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
DLVO Theory and Non-DLVO Forces
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 5 DLVO Theory and Non-DLVO Forces Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 5 DLVO Theory and Non-DLVO Forces Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039
South pacific Journal of Technology and Science
 Zetasizer Technique Dr. Nagham Mahmood Aljamali Abstract: Assist. Professor in Organic Chemistry, Chemistry Department.,College of Education.,Kufa University.,IRAQ. In this review study., zetasizer technique
Zetasizer Technique Dr. Nagham Mahmood Aljamali Abstract: Assist. Professor in Organic Chemistry, Chemistry Department.,College of Education.,Kufa University.,IRAQ. In this review study., zetasizer technique
Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial
 Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial M. Ruths Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Lowell Presented at the Nanotribology Tutorial/Panel Session, STLE/ASME International
Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial M. Ruths Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Lowell Presented at the Nanotribology Tutorial/Panel Session, STLE/ASME International
Introduction to Zeta Potential Measurement with the SZ-100
 Introduction to Zeta Potential Measurement with the SZ100 Jeffrey Bodycomb, Ph.D. HORIBA Scientific www.horiba.com/us/particle What is Zeta Potential? Zeta potential is the charge on a particle at the
Introduction to Zeta Potential Measurement with the SZ100 Jeffrey Bodycomb, Ph.D. HORIBA Scientific www.horiba.com/us/particle What is Zeta Potential? Zeta potential is the charge on a particle at the
Review: ISO Colloidal systems Methods for zeta potential determination
 Review: ISO 13099 Colloidal systems Methods for zeta potential determination Mark Bumiller mark.bumiller@horiba.com www.horiba.com/particle New ISO Standards www.iso.org Outline ISO standards Zeta potential
Review: ISO 13099 Colloidal systems Methods for zeta potential determination Mark Bumiller mark.bumiller@horiba.com www.horiba.com/particle New ISO Standards www.iso.org Outline ISO standards Zeta potential
1044 Lecture #14 of 18
 Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
 Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
Colloidal dispersion
 Dispersed Systems Dispersed systems consist of particulate matter, known as the dispersed phase, distributed throughout a continuous or dispersion medium. The dispersed material may range in size from
Dispersed Systems Dispersed systems consist of particulate matter, known as the dispersed phase, distributed throughout a continuous or dispersion medium. The dispersed material may range in size from
Porous Media Induced Aggregation of Protein- Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles
 Supporting Information 3 Porous Media Induced Aggregation of Protein- Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles 4 Matthew Y. Chan, and Peter J. Vikesland* Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Virginia
Supporting Information 3 Porous Media Induced Aggregation of Protein- Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles 4 Matthew Y. Chan, and Peter J. Vikesland* Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Virginia
Sanitary Engineering. Coagulation and Flocculation. Week 3
 Sanitary Engineering Coagulation and Flocculation Week 3 1 Coagulation and Flocculation Colloidal particles are too small to be removed by sedimentation or by sand filtration processes. Coagulation: Destabilization
Sanitary Engineering Coagulation and Flocculation Week 3 1 Coagulation and Flocculation Colloidal particles are too small to be removed by sedimentation or by sand filtration processes. Coagulation: Destabilization
Physical chemistry of surfaces
 Physical chemistry of surfaces Nanostructures possess a large fraction of surface atoms per unit volume. The physical and chemical properties of surfaces have great importance when describing general properties
Physical chemistry of surfaces Nanostructures possess a large fraction of surface atoms per unit volume. The physical and chemical properties of surfaces have great importance when describing general properties
Surface Forces & Liquid Films (Answers to Exercise Problems)
 //5 Surface Forces & Liquid Films (nswers to Exercise Problems) Wuge H. Briscoe wuge.briscoe@bris.ac.uk URL: wugebrisco7.wix.com/briscoegroup Exercise : van der Waals forces & liquid films When octane
//5 Surface Forces & Liquid Films (nswers to Exercise Problems) Wuge H. Briscoe wuge.briscoe@bris.ac.uk URL: wugebrisco7.wix.com/briscoegroup Exercise : van der Waals forces & liquid films When octane
Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces
 Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
TECHNOLOGIES THAT TRANSFORM POLLUTANTS TO INNOCUOUS COMPONENTS: CHEMICAL AND PHYSICOCHEMICAL METHODS
 TECHNOLOGIES THAT TRANSFORM POLLUTANTS TO INNOCUOUS COMPONENTS: CHEMICAL AND PHYSICOCHEMICAL METHODS HUANG Xia Tsinghua University, Beijing, P.R. China Keywords: Pollutants, Innocuous Components, Chemical
TECHNOLOGIES THAT TRANSFORM POLLUTANTS TO INNOCUOUS COMPONENTS: CHEMICAL AND PHYSICOCHEMICAL METHODS HUANG Xia Tsinghua University, Beijing, P.R. China Keywords: Pollutants, Innocuous Components, Chemical
Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important Mats Larsson 1, Adrian Hill 2, and John Duffy 2 1 Malvern
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important Mats Larsson 1, Adrian Hill 2, and John Duffy 2 1 Malvern
Particle Characterization Laboratories, Inc.
 Analytical services Particle size analysis Dynamic Light Scattering Static Light Scattering Sedimentation Diffraction Zeta Potential Analysis Single Point Titration Isoelectric point determination Aqueous
Analytical services Particle size analysis Dynamic Light Scattering Static Light Scattering Sedimentation Diffraction Zeta Potential Analysis Single Point Titration Isoelectric point determination Aqueous
Contents XVII. Preface
 V Preface XVII 1 General Introduction 1 1.1 Suspensions 1 1.2 Latexes 2 1.3 Emulsions 2 1.4 Suspoemulsions 3 1.5 Multiple Emulsions 3 1.6 Nanosuspensions 4 1.7 Nanoemulsions 4 1.8 Microemulsions 5 1.9
V Preface XVII 1 General Introduction 1 1.1 Suspensions 1 1.2 Latexes 2 1.3 Emulsions 2 1.4 Suspoemulsions 3 1.5 Multiple Emulsions 3 1.6 Nanosuspensions 4 1.7 Nanoemulsions 4 1.8 Microemulsions 5 1.9
Overview of DLVO Theory
 Overview of DLVO Theory Gregor Trefalt and Michal Borkovec Email. gregor.trefalt@unige.ch, michal.borkovec@unige.ch September 29, 214 Direct link www.colloid.ch/dlvo Derjaguin, Landau, Vervey, and Overbeek
Overview of DLVO Theory Gregor Trefalt and Michal Borkovec Email. gregor.trefalt@unige.ch, michal.borkovec@unige.ch September 29, 214 Direct link www.colloid.ch/dlvo Derjaguin, Landau, Vervey, and Overbeek
Jean-François Dufrêche. Ions at Interfaces
 Jean-François Dufrêche Ions at Interfaces 2014-2015 Electrical Double Layer Separation chemistry: liquid/liquid and solid/liquid interfaces? liquid/liquid extraction? diffusion in porous media (solid/
Jean-François Dufrêche Ions at Interfaces 2014-2015 Electrical Double Layer Separation chemistry: liquid/liquid and solid/liquid interfaces? liquid/liquid extraction? diffusion in porous media (solid/
Colloidal Materials: Part III
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 1: Lecture 4 Colloidal Materials: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 1: Lecture 4 Colloidal Materials: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039
Investigation of stabilization mechanisms for colloidal suspension using nanoparticles.
 University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 8-2014 Investigation of stabilization mechanisms for colloidal suspension using
University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 8-2014 Investigation of stabilization mechanisms for colloidal suspension using
SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS. Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France
 SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France Outline IV - FORMATION OF SOLIDS FROM SOLUTIONS 1) Glass
SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France Outline IV - FORMATION OF SOLIDS FROM SOLUTIONS 1) Glass
The change in free energy on transferring an ion from a medium of low dielectric constantε1 to one of high dielectric constant ε2:
 The Born Energy of an Ion The free energy density of an electric field E arising from a charge is ½(ε 0 ε E 2 ) per unit volume Integrating the energy density of an ion over all of space = Born energy:
The Born Energy of an Ion The free energy density of an electric field E arising from a charge is ½(ε 0 ε E 2 ) per unit volume Integrating the energy density of an ion over all of space = Born energy:
Stern-layer parameters of alumina suspensions
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 26 (2003) 400 407 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis Stern-layer parameters of alumina suspensions E. Ruiz-Reina, A.I. Gómez-Merino, F.J. Rubio-Hernández, and P. García-Sánchez
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 26 (2003) 400 407 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis Stern-layer parameters of alumina suspensions E. Ruiz-Reina, A.I. Gómez-Merino, F.J. Rubio-Hernández, and P. García-Sánchez
Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP)
 Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP) Self-potential method (passive) Self-potential mechanism Measurement of self potentials and interpretation Induced polarization method (active)
Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP) Self-potential method (passive) Self-potential mechanism Measurement of self potentials and interpretation Induced polarization method (active)
Treatment Processes. Coagulation. Coagulation. Coagulation. Coagulation. Coagulation and Flocculation
 CIVL 1112 Water Treatment - and 1/7 Treatment Processes and and flocculation consist of adding a flocforming chemical reagent to a water to enmesh or combine with nonsettleable colloidal solids and slowsettling
CIVL 1112 Water Treatment - and 1/7 Treatment Processes and and flocculation consist of adding a flocforming chemical reagent to a water to enmesh or combine with nonsettleable colloidal solids and slowsettling
The Institute of Paper Chemistry
 The Institute of Paper Chemistry Appleton, Wisconsin Doctor's Dissertation The Role of Polyelectrolyte Charge Density and Molecular Weight on the Adsorption and Flocculation of Colloidal Silica with Polyethylenimine
The Institute of Paper Chemistry Appleton, Wisconsin Doctor's Dissertation The Role of Polyelectrolyte Charge Density and Molecular Weight on the Adsorption and Flocculation of Colloidal Silica with Polyethylenimine
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
Key Concepts for section IV (Electrokinetics and Forces)
 Key Concepts for section IV (Electrokinetics and Forces) 1: Debye layer, Zeta potential, Electrokinetics 2: Electrophoresis, Electroosmosis 3: Dielectrophoresis 4: InterDebye layer force, VanDer Waals
Key Concepts for section IV (Electrokinetics and Forces) 1: Debye layer, Zeta potential, Electrokinetics 2: Electrophoresis, Electroosmosis 3: Dielectrophoresis 4: InterDebye layer force, VanDer Waals
Determination of zeta potential by means of a rotating disk: planar, particulate, and porous samples!
 Determination of zeta potential by means of a rotating disk: planar, particulate, and porous samples! Paul J Sides! Zetametrix Inc! 5821 Kentucky Avenue! Pittsburgh, PA 15232! 1! ZetaSpin: universal tool
Determination of zeta potential by means of a rotating disk: planar, particulate, and porous samples! Paul J Sides! Zetametrix Inc! 5821 Kentucky Avenue! Pittsburgh, PA 15232! 1! ZetaSpin: universal tool
Complete and precise descriptions based on quantum mechanics exist for the Coulombic/Electrostatic force. These are used to describe materials.
 The forces of nature: 1. Strong forces hold protons and neutrons together (exchange of mesons) 2. Weak interactions are involved in some kinds of radioactive decay (β-decay) 3. Coulombic or electrostatic
The forces of nature: 1. Strong forces hold protons and neutrons together (exchange of mesons) 2. Weak interactions are involved in some kinds of radioactive decay (β-decay) 3. Coulombic or electrostatic
Methods for charge and size characterization colloidal systems
 Methods for charge and size characterization colloidal systems Content General Basics Stabino Measurement basics Applications NANO-flex Measurement basics Applications Nanoparticles Bulkphase of gold gold
Methods for charge and size characterization colloidal systems Content General Basics Stabino Measurement basics Applications NANO-flex Measurement basics Applications Nanoparticles Bulkphase of gold gold
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions
 Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
13 Colloids and agglomeration
 13 Colloids and agglomeration The processing of fine particulate materials is becoming increasingly important and the term nanotechnology is typically used to describe any system with particle diameters
13 Colloids and agglomeration The processing of fine particulate materials is becoming increasingly important and the term nanotechnology is typically used to describe any system with particle diameters
Colloid Science Principles, methods and applications
 Colloid Science Principles, methods and applications Second Edition Edited by TERENCE COSGROVE School of Chemistry, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents
Colloid Science Principles, methods and applications Second Edition Edited by TERENCE COSGROVE School of Chemistry, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents
Next layer is called diffuse layer----ions not held tightly----thickness is > 1000 angstroms-- exact distance depends on ionic strength of soln
 What does double layer of IPE look like?-see Fig.1.2.3 Also called Electrified Inteface At no external E appl -- inner Stern layer or Inner Helmholz plane (IHP) contains mostly solvent solvent molecules
What does double layer of IPE look like?-see Fig.1.2.3 Also called Electrified Inteface At no external E appl -- inner Stern layer or Inner Helmholz plane (IHP) contains mostly solvent solvent molecules
Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles. Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles
 Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles 1 We now try to understand the nature of spontaneous instability in a confined
Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles 1 We now try to understand the nature of spontaneous instability in a confined
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian. which is given in spherical coordinates by (2)
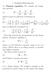 1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte. M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 009 Milan Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze Faculty of Informatics and Electrical Engineering Comsol Conference
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 009 Milan Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze Faculty of Informatics and Electrical Engineering Comsol Conference
An Improved Method of Determining the ζ -Potential and Surface Conductance
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 232, 186 197 (2000) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.7153, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on An Improved Method of Determining the ζ -Potential and Surface
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 232, 186 197 (2000) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.7153, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on An Improved Method of Determining the ζ -Potential and Surface
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Retention and Release of Graphene Oxide in Structured Heterogeneous Porous Media under Saturated and Unsaturated Conditions Shunan Dong 1, Xiaoqing Shi 1, Bin Gao 3, Jianfeng Wu
Supporting Information Retention and Release of Graphene Oxide in Structured Heterogeneous Porous Media under Saturated and Unsaturated Conditions Shunan Dong 1, Xiaoqing Shi 1, Bin Gao 3, Jianfeng Wu
 Number of pages in the question paper : 06 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Number of pages in the question paper : 06 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels Jarrod Schiffbauer *,1, Josh Fernandez 2,
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels Jarrod Schiffbauer *,1, Josh Fernandez 2,
The Utility of Zeta Potential Measurements in the Characterization of CMP Slurries David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd
 The Utility of Zeta Potential Measurements in the Characterization of CMP Slurries David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd HORIBA Scientific Webinar June 12 th 2013 Dispersed Systems An interface
The Utility of Zeta Potential Measurements in the Characterization of CMP Slurries David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd HORIBA Scientific Webinar June 12 th 2013 Dispersed Systems An interface
Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on flow and electrokinetic properties of Na-activated bentonite dispersions
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 27, No. 3, June 24, pp. 317 322. Indian Academy of Sciences. Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on flow and electrokinetic properties of Na-activated bentonite dispersions E GÜN STER,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 27, No. 3, June 24, pp. 317 322. Indian Academy of Sciences. Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on flow and electrokinetic properties of Na-activated bentonite dispersions E GÜN STER,
Initial position, x p (0)/L
 .4 ) xp().2 ) ( 2L 2 xp Dc ( Displacement, /L.2.4.5.5 Initial position, x p ()/L Supplementary Figure Computed displacements of (red) positively- and (blue) negatively-charged particles at several CO 2
.4 ) xp().2 ) ( 2L 2 xp Dc ( Displacement, /L.2.4.5.5 Initial position, x p ()/L Supplementary Figure Computed displacements of (red) positively- and (blue) negatively-charged particles at several CO 2
Engineering Nanomedical Systems. Zeta Potential
 BME 695 Engineering Nanomedical Systems Lecture 7 Zeta Potential James F. Leary, Ph.D. SVM Endowed Professor of Nanomedicine Professor of Basic Medical Sciences and Biomedical Engineering Member: Purdue
BME 695 Engineering Nanomedical Systems Lecture 7 Zeta Potential James F. Leary, Ph.D. SVM Endowed Professor of Nanomedicine Professor of Basic Medical Sciences and Biomedical Engineering Member: Purdue
Modeling the electrochemical properties and the complex conductivity of calcite
 Modeling the electrochemical properties and the complex conductivity of calcite Shuai Li Philippe Leroy Damien Jougnot André Revil Nicolas Devau Frank Heberling Mohamed Azaroual Complex conductivity in
Modeling the electrochemical properties and the complex conductivity of calcite Shuai Li Philippe Leroy Damien Jougnot André Revil Nicolas Devau Frank Heberling Mohamed Azaroual Complex conductivity in
SOIL COLLOIDS PROPERTIES AND ION RINDING. CRC Press. University of Bueno Aires Buenos Aires, Argentina. Taylor & Francis Croup
 SOIL COLLOIDS PROPERTIES AND ION RINDING Fernando V. Molina University of Bueno Aires Buenos Aires, Argentina CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the
SOIL COLLOIDS PROPERTIES AND ION RINDING Fernando V. Molina University of Bueno Aires Buenos Aires, Argentina CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the
File ISM04. Properties of Colloids I
 File ISM04 Properties of Colloids I 1 Colloids Small things, but much bigger than a molecule Background: Foundations of Colloid Science Vol I & II, R.J. Hunter Physical Chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Chapter
File ISM04 Properties of Colloids I 1 Colloids Small things, but much bigger than a molecule Background: Foundations of Colloid Science Vol I & II, R.J. Hunter Physical Chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Chapter
Potential changes of the cross section for rectangular microchannel with different aspect ratios
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(1), 186-190 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Potential changes of the cross section for rectangular microchannel with different aspect ratios Hyo Song Lee, Ki Ho Kim, Jae Keun Yu, Soon
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(1), 186-190 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Potential changes of the cross section for rectangular microchannel with different aspect ratios Hyo Song Lee, Ki Ho Kim, Jae Keun Yu, Soon
The colloidal and rheological properties of bentonite suspensions
 ELSEVIER ADVANCES IN COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 82 (1999) 43-92 www.elsevier.nl/locate/cis The colloidal and rheological properties of bentonite suspensions
ELSEVIER ADVANCES IN COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 82 (1999) 43-92 www.elsevier.nl/locate/cis The colloidal and rheological properties of bentonite suspensions
Factors governing the tendency of colloidal particles to flocculate
 Brownian flocculation of polymer colloids in the presence of a secondary minimum William R. Schowalter* and Alec B. Eidsath Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Illinois, Urbana, IL 61801
Brownian flocculation of polymer colloids in the presence of a secondary minimum William R. Schowalter* and Alec B. Eidsath Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Illinois, Urbana, IL 61801
Monolayers. Factors affecting the adsorption from solution. Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support
 Monolayers Adsorption as process Adsorption of gases on solids Adsorption of solutions on solids Factors affecting the adsorption from solution Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support Adsorption
Monolayers Adsorption as process Adsorption of gases on solids Adsorption of solutions on solids Factors affecting the adsorption from solution Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support Adsorption
Overview. Lecture 5 Colloidal Dispersions
 Physical Pharmacy Lecture 5 Colloidal Dispersions Assistant Lecturer in Pharmaceutics Overview Dispersed Systems Classification Colloidal Systems Properties of Colloids Optical Properties Kinetic Properties
Physical Pharmacy Lecture 5 Colloidal Dispersions Assistant Lecturer in Pharmaceutics Overview Dispersed Systems Classification Colloidal Systems Properties of Colloids Optical Properties Kinetic Properties
Adsorption Processes. Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
Recap: Introduction 12/1/2015. EVE 402 Air Pollution Generation and Control. Adsorption
 EVE 402 Air Pollution Generation and Control Chapter #6 Lectures Adsorption Recap: Solubility: the extent of absorption into the bulk liquid after the gas has diffused through the interface An internal
EVE 402 Air Pollution Generation and Control Chapter #6 Lectures Adsorption Recap: Solubility: the extent of absorption into the bulk liquid after the gas has diffused through the interface An internal
Research Article A Modified Method to Calculate Critical Coagulation Concentration Based on DLVO Theory
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 215, rticle ID 317483, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/317483 Research rticle Modified Method to Calculate Critical Coagulation Concentration Based on DLVO
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 215, rticle ID 317483, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/317483 Research rticle Modified Method to Calculate Critical Coagulation Concentration Based on DLVO
Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants
 Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants Fuquan Tu, Bum Jun Park and Daeyeon Lee*. Description of the term notionally swollen droplets When particles are adsorbed
Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants Fuquan Tu, Bum Jun Park and Daeyeon Lee*. Description of the term notionally swollen droplets When particles are adsorbed
Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry
 Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry Volume 1: The Double Layer Edited by J. O'M. Bockris Texas A&M University College Station, Texas Brian E. Conway University of Ottawa Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry Volume 1: The Double Layer Edited by J. O'M. Bockris Texas A&M University College Station, Texas Brian E. Conway University of Ottawa Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
SCALING OF THE ADHESION BETWEEN PARTICLES AND SURFACES FROM MICRON-SCALE TO THE NANOMETER SCALE FOR PHOTOMASK CLEANING APPLICATIONS
 SCALING OF THE ADHESION BETWEEN PARTICLES AND SURFACES FROM MICRON-SCALE TO THE NANOMETER SCALE FOR PHOTOMASK CLEANING APPLICATIONS Gautam Kumar, Shanna Smith, Florence Eschbach, Arun Ramamoorthy, Michael
SCALING OF THE ADHESION BETWEEN PARTICLES AND SURFACES FROM MICRON-SCALE TO THE NANOMETER SCALE FOR PHOTOMASK CLEANING APPLICATIONS Gautam Kumar, Shanna Smith, Florence Eschbach, Arun Ramamoorthy, Michael
Specific ion effects on the interaction of. hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled
 Supporting Information Specific ion effects on the interaction of hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled monolayers T. Rios-Carvajal*, N. R. Pedersen, N. Bovet, S.L.S. Stipp, T. Hassenkam. Nano-Science
Supporting Information Specific ion effects on the interaction of hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled monolayers T. Rios-Carvajal*, N. R. Pedersen, N. Bovet, S.L.S. Stipp, T. Hassenkam. Nano-Science
Colloid & Interface Science Case Study Model Answers
 Colloid & Interface Science Case Study Model Answers Distance Learning Course in Cosmetic Science Society of Cosmetic Scientists Common Features Formulations were examples of lyophobic colloidal systems
Colloid & Interface Science Case Study Model Answers Distance Learning Course in Cosmetic Science Society of Cosmetic Scientists Common Features Formulations were examples of lyophobic colloidal systems
Correlation between rheological parameters and some colloidal properties of anatase dispersions
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 15, 7 Correlation between rheological parameters and some colloidal properties of anatase dispersions A.I. Gómez-Merino, F. J. Rubio-Hernández,
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 15, 7 Correlation between rheological parameters and some colloidal properties of anatase dispersions A.I. Gómez-Merino, F. J. Rubio-Hernández,
An electrokinetic LB based model for ion transport and macromolecular electrophoresis
 An electrokinetic LB based model for ion transport and macromolecular electrophoresis Raffael Pecoroni Supervisor: Michael Kuron July 8, 2016 1 Introduction & Motivation So far an mesoscopic coarse-grained
An electrokinetic LB based model for ion transport and macromolecular electrophoresis Raffael Pecoroni Supervisor: Michael Kuron July 8, 2016 1 Introduction & Motivation So far an mesoscopic coarse-grained
