SCALING OF THE ADHESION BETWEEN PARTICLES AND SURFACES FROM MICRON-SCALE TO THE NANOMETER SCALE FOR PHOTOMASK CLEANING APPLICATIONS
|
|
|
- Melanie Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCALING OF THE ADHESION BETWEEN PARTICLES AND SURFACES FROM MICRON-SCALE TO THE NANOMETER SCALE FOR PHOTOMASK CLEANING APPLICATIONS Gautam Kumar, Shanna Smith, Florence Eschbach, Arun Ramamoorthy, Michael Salib, Sean Eichenlaub, and Stephen Beaudoin Purdue University School of Chemical Engineering Forney Hall of Chemical Engineering 480 Stadium Mall Dr. West Lafayette, Indiana Phone: (765)
2 Rationale Mask cleaning processes can be more quickly optimized if the magnitude of particle-mask adhesion forces known Mask layers and contaminants offering most difficult cleaning challenge can be identified Effects of solution properties on contaminant adhesion can be evaluated Range of adhesion forces for given contaminant/mask layer can be determined
3 Particle Characteristics The Academic System Polystyrene Latex Sphere (PSL sphere) 5 μm The Real World Alumina Particle Ideal geometries 5 μm Can model contact area using classic approaches Contact mechanics (JKR, DMT ) DLVO Uniform microscopic morphology Empirical, semi-empirical approaches Unusual geometry Random microscopic morphology Compression/deformation of surface asperities Chemical heterogeneities Settling (tilting, shifting) Statistical information
4 Macroscopic Adhesion Model: DLVO Theory F = F + A Total Adhesion Force vdw van der Waals Force F F vdw = f ( A,d,a,h) EDL A = System Hamaker constant d = Particle diameter a = Contact radius h = Particle-surface separation distance ε = Medium dielectric constant ζ = Zeta potential κ = Reciprocal double-layer thickness I = Medium ionic strength Electrostatic Double Layer Force F EDL = f ( ε, ζ, κ,d,h) ζ = f (I,pH ) κ = f (I ) F A Particle d a Surface
5 Electrostatic Double Layer (EDL) Force S u r f a c e Potential ψ ψ s ζ Outer Helmholtz Plane + Shear Plane - Diffuse Double Layer - Distance + F EDL = εε Negative Co-Ion Positive Counter-Ion Zeta Potential, ζ Stern Layer Diffuse Layer Ions in Bulk Solution ( ψ + ψ ) 0d p s κh κh 4 κe 1 e ψ pψ s ψ p + ψ s ψ approximated by ζ e κh
6 van der Waals (vdw) Force F vdw = F Keesom + F Debye + F London induced-permanent permanent-permanent induced-induced Electrons Lithium atom -q l μ = ql (instantaneous dipole moment) +q Electric field lines Surface Surface Induced dipole moment μ 1 μ Surface
7 Particle Adhesion Measurements AFM Schematic Distribution of Forces Mounted particle cantilever Sample Sample holder and translation stage Frequency Adhesion Force Particles Mounted on AFM Cantilevers PSL Particle a AFM Force Curve Al O 3 Particle b c d e Deflection d c b e Position a Adhesion Force
8 Surface Roughness and Adhesion Removal Force (nn) Modified vdw for a rough silicon surface 5 μm PSL spheres in contact with a silicon substrate in 0.03 M KNO 3 Removal Force = Adhesion Force Modified vdw for a smooth silicon surface Transition Region ph
9 Geometry and Adhesion Interaction Force (N) Interaction Forces 3.E-09.E-09 1.E-09 0.E+00-1.E-09 -.E-09-3.E-09-4.E-09 (b) (c) Ideal Surfaces particle double layer Dominant dominant interaction region surface (a) van der Waals Electrostatic Combined DLVO Interaction Force (N) Interaction Forces Irregular Particles 1.E-08 5.E E+00-5.E-09-1.E-08 (b) (c) van der Waals Electrostatic Combined DLVO (a) -5.E-09 0E+00 E-09 4E-09 6E-09 8E-09 1E-08 Separation Distance (m) -.E-08 0E+00 E-09 4E-09 6E-09 8E-09 1E-08 Separation Distance (m)
10 Alumina Interactions with SiO Alumina Adhesion Force (nn) vdw Model Predictions Model Predictions Experimental Measurements ph (Constant Ionic Strength 0.01 M) Electrostatic interactions do affect the adhesion force, which varies with ph Large area between particle and wafer out of contact Small contact area
11 How to Describe? du 1 = van der Waals Point-by-point additivity {( x x ) + ( y y ) + ( z z ) } 3 1 C 1 ρ ρ dv dv μm Electrostatics Poisson-Boltzmann Equation κ = ψ = κ ψ e z n i i ε ε k T 0 r B io Hamaker Constant, A 1 Approximate Solutions A R F = 6h A R1R F = 6h R + R + 1 A F = 1πh 1 3 Computational Solutions Combination of ideal shapes κh εε d κe ( ψ + ) ( ) ( ) p ψ s ψ pψ 0 s = κh F + e κh e sphere-plate 4 1 ψ p + ψ s + + sphere-sphere plate-plate Approximate Solutions + ε r ( ψ 1ψ cosh( κ ) ψ1 ψ ) ( κh) κ ε 0 F = h sinh + ε r ( ψ 1ψ cosh( κ ) ψ1 ψ ) ( κh) κ ε 0 F = h sinh Computational Solutions
12 Combined vdw, ES Interaction Models Generate Mathematical Surface Representations SEM (Geometry) 3-D Reconstruction Surface Potential ζ (mv) ph IEP vdw + EDL Model Contact Surfaces AFM (Topographic Data) Compression/Deformation Load (mn) Applied Load force/depth profile Removal Force Statistics AFM Force Measurements
13 Geometric Models School of Chemical Engineering
14 Fourier transform of surface profile Reconstruction of surfaces generated with random phase angles FFT Roughness Model F(x) x π AFM scan of actual Cu surface FFT model Cu surface FFT with random phase
15 Validation: PSL Adhesion to Evolving Surfaces Only vdw forces needed to describe adhesion Average Measured Value 10 nn Removal Force = Adhesion Force Average Measured Value 17 nn Frequency Range of Observed Values Range of Observed Values Rough Silicon Surface Smooth Silicon Surface Removal Force (nn)
16 PSL Interactions with SiO 300 PSL Adhesion Force (nn) vdw Model Predictions Model Predictions Experimental Measurements ph (Constant Ionic Strength 0.01 M) Electrostatic interactions do not have a significant effect at different phs Large contact area between sphere and wafer dominated by vdw
17 Alumina Interactions with SiO Alumina Adhesion Force (nn) ph (Constant Ionic Strength 0.01 M) vdw Model Predictions Model Predictions Experimental Measurements Electrostatic interactions do affect the adhesion force, which varies with ph Large area between particle and wafer out of contact Small contact area
18 Nanoscale Adhesion Approach Measure, model micronscale adhesion Extract vdw, ES constants Measure nano-scale adhesion Model adhesion using constants from micron-scale Can measure nano-scale adhesion Can model roughness and geometry effects Can predict nano-scale adhesion
19 School of Chemical Engineering Silicon Dioxide Surface AFM Image FFT model Regeneration 50
20 Silicon Nitride Particle: Micron-Scale FESEM image of a Si 3 N 4 particle mounted on an AFM cantilever Photomodeler Pro model for the nitride particle
21 Silicon Nitride Cantilevers: Nanoscale Sharpened silicon nitride probe Max ROC ~ 40nm Region considered in force calculations ~10nm ~ μm Geometry considered in modeling the force between nanoscale cantilevers and substrates
22 Silicon Nitride Adhesion to Silicon Dioxide in Air Tip ROC=1nm Tip ROC=36nm
23 Silicon Nitride Adhesion to Silicon Dioxide in Water Tip ROC=10nm Tip ROC=41nm
24 Silicon Nitride Adhesion to Quartz in Air Tip ROC=14nm Tip ROC=3nm
25 Silicon Nitride Adhesion to Quartz in Water Tip ROC=14nm Tip ROC=3nm
26 Theory and Experiment: Silicon Nitride Adhesion to Silicon Dioxide in Air Particle System MSCT OTR8 Tip ROC=36nm Tip ROC=1nm Force (nn)
27 Theory and Experiment: Silicon Nitride Adhesion to Silicon Dioxide in Water Particle System MSCT Tip ROC=41nm OTR8 Tip ROC=10nm Force (nn)
28 Theory and Experiment: Silicon Nitride Adhesion to Quartz in Air Particle System MSCT Tip ROC=3nm OTR8 Tip ROC=14nm Force (nn)
29 Theory and Experiment: Silicon Nitride Adhesion to Quartz in Water Particle System MSCT Tip ROC=3nm OTR8 Tip ROC=14nm Force (nn)
30 Conclusions Micron- and nano-scale particle adhesion can be described by vdw and electrostatic force models Proper accounting for roughness and geometry is required Particle adhesion characterized by a distribution of adhesion forces Reflective of the interaction of two rough surfaces Particles with highly nonuniform geometry can be influenced by electrostatic forces even when in contact with a substrate
31 Acknowledgements Financial support National Science Foundation CAREER grant (CTS ) NSF/SRC ERC for Environmentally-Benign Semiconductor Manufacturing State of Indiana 1 st Century Fund Intel Praxair Microelectronics SEZ America Stefan Myhajlenko Arizona State University Center for Solid State Electronics Research Ann Gelb Arizona State University Mathematics
Basic Laboratory. Materials Science and Engineering. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
 Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) M108 Stand: 20.10.2015 Aim: Presentation of an application of the AFM for studying surface morphology. Inhalt 1.Introduction...
Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) M108 Stand: 20.10.2015 Aim: Presentation of an application of the AFM for studying surface morphology. Inhalt 1.Introduction...
Contents. Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII. 1 Introduction 1
 V Contents Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII 1 Introduction 1 2 Van der Waals Forces 5 2.1 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 5 2.1.1 Coulomb Interaction 5 2.1.2 Monopole Dipole Interaction
V Contents Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII 1 Introduction 1 2 Van der Waals Forces 5 2.1 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 5 2.1.1 Coulomb Interaction 5 2.1.2 Monopole Dipole Interaction
Simulation of the Adhesion of Particles to Surfaces
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 234, 284 292 (2001) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.7276, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Simulation of the Adhesion of Particles to Surfaces Kevin Cooper,,1
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 234, 284 292 (2001) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.7276, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Simulation of the Adhesion of Particles to Surfaces Kevin Cooper,,1
! Importance of Particle Adhesion! History of Particle Adhesion! Method of measurement of Adhesion! Adhesion Induced Deformation
 ! Importance of Particle Adhesion! History of Particle Adhesion! Method of measurement of Adhesion! Adhesion Induced Deformation! JKR and non-jkr Theory! Role of Electrostatic Forces! Conclusions Books:
! Importance of Particle Adhesion! History of Particle Adhesion! Method of measurement of Adhesion! Adhesion Induced Deformation! JKR and non-jkr Theory! Role of Electrostatic Forces! Conclusions Books:
MEGASONIC CLEANING OF WAFERS IN ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS: POSSIBLE ROLE OF ELECTRO-ACOUSTIC AND CAVITATION EFFECTS. The University of Arizona, Tucson
 MEGASONIC CLEANING OF WAFERS IN ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS: POSSIBLE ROLE OF ELECTRO-ACOUSTIC AND CAVITATION EFFECTS Manish Keswani 1, Srini Raghavan 1, Pierre Deymier 1 and Steven Verhaverbeke 2 1 The University
MEGASONIC CLEANING OF WAFERS IN ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS: POSSIBLE ROLE OF ELECTRO-ACOUSTIC AND CAVITATION EFFECTS Manish Keswani 1, Srini Raghavan 1, Pierre Deymier 1 and Steven Verhaverbeke 2 1 The University
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces
 Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Post Tungsten CMP Cleaner Development with Improved Organic and Particle Residue Removal on Silicon Nitride and Excellent Tungsten Compatibility
 Post Tungsten CMP Cleaner Development with Improved Organic and Particle Residue Removal on Silicon Nitride and Excellent Tungsten Compatibility Ching-Hsun Chao, Chi Yen, Ping Hsu, Eugene Lee, Paul Bernatis
Post Tungsten CMP Cleaner Development with Improved Organic and Particle Residue Removal on Silicon Nitride and Excellent Tungsten Compatibility Ching-Hsun Chao, Chi Yen, Ping Hsu, Eugene Lee, Paul Bernatis
Particle removal in linear shear flow: model prediction and experimental validation
 Particle removal in linear shear flow: model prediction and experimental validation M.L. Zoeteweij, J.C.J. van der Donck and R. Versluis TNO Science and Industry, P.O. Box 155, 600 AD Delft, The Netherlands
Particle removal in linear shear flow: model prediction and experimental validation M.L. Zoeteweij, J.C.J. van der Donck and R. Versluis TNO Science and Industry, P.O. Box 155, 600 AD Delft, The Netherlands
NANO AND MICROSCALE PARTICLE REMOVAL
 NANO AND MICROSCALE PARTICLE REMOVAL Ahmed A. Busnaina William Lincoln Smith Professor and Director of the oratory Northeastern University, Boston, MA 2115-5 OUTLINE Goals and Objectives Approach Preliminary
NANO AND MICROSCALE PARTICLE REMOVAL Ahmed A. Busnaina William Lincoln Smith Professor and Director of the oratory Northeastern University, Boston, MA 2115-5 OUTLINE Goals and Objectives Approach Preliminary
Atomic Force Microscopy imaging and beyond
 Atomic Force Microscopy imaging and beyond Arif Mumtaz Magnetism and Magnetic Materials Group Department of Physics, QAU Coworkers: Prof. Dr. S.K.Hasanain M. Tariq Khan Alam Imaging and beyond Scanning
Atomic Force Microscopy imaging and beyond Arif Mumtaz Magnetism and Magnetic Materials Group Department of Physics, QAU Coworkers: Prof. Dr. S.K.Hasanain M. Tariq Khan Alam Imaging and beyond Scanning
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Analysis Method for Quantifying the Morphology of Nanotube Networks Dusan Vobornik*, Shan Zou and Gregory P. Lopinski Measurement Science and Standards, National Research Council
Supporting Information Analysis Method for Quantifying the Morphology of Nanotube Networks Dusan Vobornik*, Shan Zou and Gregory P. Lopinski Measurement Science and Standards, National Research Council
Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer
 Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column
Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column
PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS
 PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS George Adams, Ahmed A. Busnaina and Sinan Muftu the oratory Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Eng. Department Northeastern University, Boston,
PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS George Adams, Ahmed A. Busnaina and Sinan Muftu the oratory Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Eng. Department Northeastern University, Boston,
STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope
 STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope Basic idea STM working principle Schematic representation of the sample-tip tunnel barrier Assume tip and sample described by two infinite plate electrodes Φ t +Φ s =
STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope Basic idea STM working principle Schematic representation of the sample-tip tunnel barrier Assume tip and sample described by two infinite plate electrodes Φ t +Φ s =
Multimedia : Boundary Lubrication Podcast, Briscoe, et al. Nature , ( )
 3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces
 CHEM-E150 Interfacial Phenomena in Biobased Systems Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces Monika Österberg Spring 018 Content Colloidal stability van der Waals Forces Surface Forces and their
CHEM-E150 Interfacial Phenomena in Biobased Systems Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces Monika Österberg Spring 018 Content Colloidal stability van der Waals Forces Surface Forces and their
Atomic and molecular interactions. Scanning probe microscopy.
 Atomic and molecular interactions. Scanning probe microscopy. Balázs Kiss Nanobiotechnology and Single Molecule Research Group, Department of Biophysics and Radiation Biology 27. November 2013. 2 Atomic
Atomic and molecular interactions. Scanning probe microscopy. Balázs Kiss Nanobiotechnology and Single Molecule Research Group, Department of Biophysics and Radiation Biology 27. November 2013. 2 Atomic
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications. CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications
 CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications History of Nanotechnology: Time Line Democritus in ancient Greece: concept of atom 1900 : Rutherford : discovery of atomic nucleus The first TEM was
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications History of Nanotechnology: Time Line Democritus in ancient Greece: concept of atom 1900 : Rutherford : discovery of atomic nucleus The first TEM was
L8: The Mechanics of Adhesion used by the Gecko
 L8: The Mechanics of Adhesion used by the Gecko With help from Bo He Overview Gecko s foot structure Intermolecular force Measurement: 2-D MEMS sensor Gecko s adhesive mechanism Measurement results discussion
L8: The Mechanics of Adhesion used by the Gecko With help from Bo He Overview Gecko s foot structure Intermolecular force Measurement: 2-D MEMS sensor Gecko s adhesive mechanism Measurement results discussion
Non-contact removal of 60-nm latex particles from silicon wafers with laser-induced plasma
 J. Adhesion Sci. Technol., Vol. 18, No. 7, pp. 795 806 (2004) VSP 2004. Also available online - www.vsppub.com Non-contact removal of 60-nm latex particles from silicon wafers with laser-induced plasma
J. Adhesion Sci. Technol., Vol. 18, No. 7, pp. 795 806 (2004) VSP 2004. Also available online - www.vsppub.com Non-contact removal of 60-nm latex particles from silicon wafers with laser-induced plasma
Supporting Information: Slippery and Sticky Graphene in Water
 Supporting Information: Slippery and Sticky in Water Yijue Diao 1, Gus Greenwood 1, Michael Cai Wang 2,3, SungWoo Nam 2, Rosa M. Espinosa-Marzal* 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Supporting Information: Slippery and Sticky in Water Yijue Diao 1, Gus Greenwood 1, Michael Cai Wang 2,3, SungWoo Nam 2, Rosa M. Espinosa-Marzal* 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Influence of Enterococcal Surface Protein (esp) on the Transport of Enterococcus faecium within Saturated Quartz Sands
 Influence of Enterococcal Surface Protein (esp) on the Transport of Enterococcus faecium within Saturated Quartz Sands Jennifer J. Johanson, Lucia Feriancikova, Shangping Xu* Department of Geosciences
Influence of Enterococcal Surface Protein (esp) on the Transport of Enterococcus faecium within Saturated Quartz Sands Jennifer J. Johanson, Lucia Feriancikova, Shangping Xu* Department of Geosciences
Effects of Size, Humidity, and Aging on Particle Removal
 LEVITRONIX Ultrapure Fluid Handling and Wafer Cleaning Conference 2009 February 10, 2009 Effects of Size, Humidity, and Aging on Particle Removal Jin-Goo Park Feb. 10, 2009 Department t of Materials Engineering,
LEVITRONIX Ultrapure Fluid Handling and Wafer Cleaning Conference 2009 February 10, 2009 Effects of Size, Humidity, and Aging on Particle Removal Jin-Goo Park Feb. 10, 2009 Department t of Materials Engineering,
Experimental and Analytical Study of Submicrometer Particle Removal from Deep Trenches
 0013-4651/2006/153 9 /C603/5/$20.00 The Electrochemical Society Experimental and Analytical Study of Submicrometer Particle Removal from Deep Trenches Kaveh Bakhtari, a Rasim O. Guldiken, a Ahmed A. Busnaina,
0013-4651/2006/153 9 /C603/5/$20.00 The Electrochemical Society Experimental and Analytical Study of Submicrometer Particle Removal from Deep Trenches Kaveh Bakhtari, a Rasim O. Guldiken, a Ahmed A. Busnaina,
Specific ion effects on the interaction of. hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled
 Supporting Information Specific ion effects on the interaction of hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled monolayers T. Rios-Carvajal*, N. R. Pedersen, N. Bovet, S.L.S. Stipp, T. Hassenkam. Nano-Science
Supporting Information Specific ion effects on the interaction of hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled monolayers T. Rios-Carvajal*, N. R. Pedersen, N. Bovet, S.L.S. Stipp, T. Hassenkam. Nano-Science
Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces
 Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Outline Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM)
 AFM Outline Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM) A family of microscopy forms where a sharp probe is scanned across a surface and some tip/sample interactions are monitored Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM)
AFM Outline Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM) A family of microscopy forms where a sharp probe is scanned across a surface and some tip/sample interactions are monitored Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM)
Nanoparticle Contamination Control and Metrology for the EUVL Systems
 Nanoparticle Contamination Control and Metrology for the EUVL Systems David Y. H. Pui Distinguished McKnight University Professor Mechanical Engineering Department University of Minnesota Jing Wang Assistant
Nanoparticle Contamination Control and Metrology for the EUVL Systems David Y. H. Pui Distinguished McKnight University Professor Mechanical Engineering Department University of Minnesota Jing Wang Assistant
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Graphene transfer method 1 : Monolayer graphene was pre-deposited on both
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Graphene transfer method 1 : Monolayer graphene was pre-deposited on both
Lecture: P1_Wk1_L1 IntraMolecular Interactions. Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University 2012
 Lecture: IntraMolecular Interactions Distinguish between IntraMolecular (within a molecule) and InterMolecular (between molecules) Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University 2012 1
Lecture: IntraMolecular Interactions Distinguish between IntraMolecular (within a molecule) and InterMolecular (between molecules) Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University 2012 1
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol Materials Research Society
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 738 2003 Materials Research Society G7.26.1 Determination of the Plastic Behavior of Low Thermal Expansion Glass at the Nanometer Scale Richard Tejeda, 1 Roxann Engelstad,
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 738 2003 Materials Research Society G7.26.1 Determination of the Plastic Behavior of Low Thermal Expansion Glass at the Nanometer Scale Richard Tejeda, 1 Roxann Engelstad,
Friction, Adhesion, and Deformation: Dynamic Measurements with the Atomic Force Microscope
 Friction, Adhesion, and Deformation: Dynamic Measurements with the Atomic Force Microscope Phil Ian Wark Research Institute, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes SA 595 Australia (J. Adhesion Sci.
Friction, Adhesion, and Deformation: Dynamic Measurements with the Atomic Force Microscope Phil Ian Wark Research Institute, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes SA 595 Australia (J. Adhesion Sci.
Japan. Keywords: wet etching, nanoscale region, dhf (dilute hydrofluoric acid solution), electric double layer, solid-liquid interface
 Solid State Phenomena Online: 24926 ISSN: 6629779, Vol. 29, pp 58 doi:.428/www.scientific.net/ssp.29.5 25 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Impact of electrostatic effects on wet etching phenomenon
Solid State Phenomena Online: 24926 ISSN: 6629779, Vol. 29, pp 58 doi:.428/www.scientific.net/ssp.29.5 25 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Impact of electrostatic effects on wet etching phenomenon
Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial
 Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial M. Ruths Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Lowell Presented at the Nanotribology Tutorial/Panel Session, STLE/ASME International
Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial M. Ruths Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Lowell Presented at the Nanotribology Tutorial/Panel Session, STLE/ASME International
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Scanning Direction References: Classical Tunneling Quantum Mechanics Tunneling current Tunneling current I t I t (V/d)exp(-Aφ 1/2 d) A = 1.025 (ev) -1/2 Å -1 I t = 10 pa~10na
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Scanning Direction References: Classical Tunneling Quantum Mechanics Tunneling current Tunneling current I t I t (V/d)exp(-Aφ 1/2 d) A = 1.025 (ev) -1/2 Å -1 I t = 10 pa~10na
Quiz #1 Practice Problem Set
 Name: Student Number: ELEC 3908 Physical Electronics Quiz #1 Practice Problem Set? Minutes January 22, 2016 - No aids except a non-programmable calculator - All questions must be answered - All questions
Name: Student Number: ELEC 3908 Physical Electronics Quiz #1 Practice Problem Set? Minutes January 22, 2016 - No aids except a non-programmable calculator - All questions must be answered - All questions
PY5020 Nanoscience Scanning probe microscopy
 PY500 Nanoscience Scanning probe microscopy Outline Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) - Quantum tunnelling - STM tool - Main modes of STM Contact probes V bias Use the point probes to measure the local
PY500 Nanoscience Scanning probe microscopy Outline Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) - Quantum tunnelling - STM tool - Main modes of STM Contact probes V bias Use the point probes to measure the local
Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
Module 26: Atomic Force Microscopy. Lecture 40: Atomic Force Microscopy 3: Additional Modes of AFM
 Module 26: Atomic Force Microscopy Lecture 40: Atomic Force Microscopy 3: Additional Modes of AFM 1 The AFM apart from generating the information about the topography of the sample features can be used
Module 26: Atomic Force Microscopy Lecture 40: Atomic Force Microscopy 3: Additional Modes of AFM 1 The AFM apart from generating the information about the topography of the sample features can be used
The Removal of Nanoparticles from Nanotrenches Using Megasonics
 NSF Center for Micro and Nanoscale Contamination Control The Removal of Nanoparticles from Nanotrenches Using Megasonics Pegah Karimi 1, Tae Hoon Kim 1, Ahmed A. Busnaina 1 and Jin Goo Park 2 1 NSF Center
NSF Center for Micro and Nanoscale Contamination Control The Removal of Nanoparticles from Nanotrenches Using Megasonics Pegah Karimi 1, Tae Hoon Kim 1, Ahmed A. Busnaina 1 and Jin Goo Park 2 1 NSF Center
Integrating MEMS Electro-Static Driven Micro-Probe and Laser Doppler Vibrometer for Non-Contact Vibration Mode SPM System Design
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 399 407 (2009) 399 Integrating MEMS Electro-Static Driven Micro-Probe and Laser Doppler Vibrometer for Non-Contact Vibration Mode SPM System
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 399 407 (2009) 399 Integrating MEMS Electro-Static Driven Micro-Probe and Laser Doppler Vibrometer for Non-Contact Vibration Mode SPM System
Colloid Chemistry. La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross.
 Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
HYDROPHOBIC FORCES IN FLOTATION. Rajesh Pazhianur ABSTRACT
 HYDROPHOBIC FORCES IN FLOTATION Rajesh Pazhianur ABSTRACT An atomic force microscope (AFM) has been used to conduct force measurements to better understand the role of hydrophobic forces in flotation.
HYDROPHOBIC FORCES IN FLOTATION Rajesh Pazhianur ABSTRACT An atomic force microscope (AFM) has been used to conduct force measurements to better understand the role of hydrophobic forces in flotation.
AFM Imaging In Liquids. W. Travis Johnson PhD Agilent Technologies Nanomeasurements Division
 AFM Imaging In Liquids W. Travis Johnson PhD Agilent Technologies Nanomeasurements Division Imaging Techniques: Scales Proteins 10 nm Bacteria 1μm Red Blood Cell 5μm Human Hair 75μm Si Atom Spacing 0.4nm
AFM Imaging In Liquids W. Travis Johnson PhD Agilent Technologies Nanomeasurements Division Imaging Techniques: Scales Proteins 10 nm Bacteria 1μm Red Blood Cell 5μm Human Hair 75μm Si Atom Spacing 0.4nm
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian. which is given in spherical coordinates by (2)
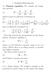 1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential. David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd
 An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd Fundamental Parameters that control the Nature and Behavior of all Particulate
An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd Fundamental Parameters that control the Nature and Behavior of all Particulate
Chapter 10. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Quasi-periodic nanostructures grown by oblique angle deposition
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 94, NUMBER 12 15 DECEMBER 2003 Quasi-periodic nanostructures grown by oblique angle deposition T. Karabacak, a) G.-C. Wang, and T.-M. Lu Department of Physics, Applied
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 94, NUMBER 12 15 DECEMBER 2003 Quasi-periodic nanostructures grown by oblique angle deposition T. Karabacak, a) G.-C. Wang, and T.-M. Lu Department of Physics, Applied
Nanoparticle Technology. Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting April 9 10, 2008 New Orleans
 Nanoparticle Technology Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting April 9 10, 2008 New Orleans Wetting in nano ACS National Meeting April 9 10, 2008 New Orleans 10
Nanoparticle Technology Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting April 9 10, 2008 New Orleans Wetting in nano ACS National Meeting April 9 10, 2008 New Orleans 10
Supporting Information for. Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene
 Supporting Information for Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene oxide colloidal stability in aquatic environment Binbin Sun, Yinqing Zhang, Wei Chen, Kunkun Wang, Lingyan
Supporting Information for Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene oxide colloidal stability in aquatic environment Binbin Sun, Yinqing Zhang, Wei Chen, Kunkun Wang, Lingyan
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes Fabrication of the scanning thermal microscopy (SThM) probes is summarized in Supplementary Fig. 1 and proceeds
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes Fabrication of the scanning thermal microscopy (SThM) probes is summarized in Supplementary Fig. 1 and proceeds
2.76/2.760 Multiscale Systems Design & Manufacturing
 2.76/2.760 Multiscale Systems Design & Manufacturing Fall 2004 MOEMS Devices for Optical communications system Switches and micromirror for Add/drops Diagrams removed for copyright reasons. MOEMS MEMS
2.76/2.760 Multiscale Systems Design & Manufacturing Fall 2004 MOEMS Devices for Optical communications system Switches and micromirror for Add/drops Diagrams removed for copyright reasons. MOEMS MEMS
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information for Manuscript: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction Supplementary Methods For each wear increment, the diamond indenter was slid laterally relative to the silicon
Supplementary Information for Manuscript: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction Supplementary Methods For each wear increment, the diamond indenter was slid laterally relative to the silicon
Forces Acting on Particle
 Particle-Substrate Interactions: Microscopic Aspects of Adhesion Don Rimai NexPress Solutions LLC. Rochester, NY 14653-64 Email: donald_rimai@nexpress.com (Edited for course presentation by ) Part Role
Particle-Substrate Interactions: Microscopic Aspects of Adhesion Don Rimai NexPress Solutions LLC. Rochester, NY 14653-64 Email: donald_rimai@nexpress.com (Edited for course presentation by ) Part Role
Simulating the Electrical Double Layer Guigen Zhang, Ph.D.
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference Boston Simulating the Electrical Double Layer Guigen Zhang, Ph.D. Dept. of Bioengineering, Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Institute for Biological Interfaces
Presented at the COMSOL Conference Boston Simulating the Electrical Double Layer Guigen Zhang, Ph.D. Dept. of Bioengineering, Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Institute for Biological Interfaces
Crystalline Surfaces for Laser Metrology
 Crystalline Surfaces for Laser Metrology A.V. Latyshev, Institute of Semiconductor Physics SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract: The number of methodological recommendations has been pronounced to describe
Crystalline Surfaces for Laser Metrology A.V. Latyshev, Institute of Semiconductor Physics SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract: The number of methodological recommendations has been pronounced to describe
Surface Chemical Analysis Using Scanning Probe Microscopy
 STR/03/067/ST Surface Chemical Analysis Using Scanning Probe Microscopy A. L. K. Tan, Y. C. Liu, S. K. Tung and J. Wei Abstract - Since its introduction in 1986 as a tool for imaging and creating three-dimensional
STR/03/067/ST Surface Chemical Analysis Using Scanning Probe Microscopy A. L. K. Tan, Y. C. Liu, S. K. Tung and J. Wei Abstract - Since its introduction in 1986 as a tool for imaging and creating three-dimensional
ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2
 Unclassified ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2 ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2 Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
Unclassified ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2 ENV/JM/MONO(2015)17/PART1/ANN2 Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
Van der Waals Interaction between Polymer Aggregates and Substrate Surface Analyzed by Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
 Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology Volume 15,Number 1(2002)127-132 2002TAPJ L Van der Waals Interaction between Polymer Aggregates and Substrate Surface Analyzed by Atomic Force Microscope
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology Volume 15,Number 1(2002)127-132 2002TAPJ L Van der Waals Interaction between Polymer Aggregates and Substrate Surface Analyzed by Atomic Force Microscope
File ISM04. Properties of Colloids I
 File ISM04 Properties of Colloids I 1 Colloids Small things, but much bigger than a molecule Background: Foundations of Colloid Science Vol I & II, R.J. Hunter Physical Chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Chapter
File ISM04 Properties of Colloids I 1 Colloids Small things, but much bigger than a molecule Background: Foundations of Colloid Science Vol I & II, R.J. Hunter Physical Chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Chapter
What we observe is not nature herself, But nature exposed to our method of questioning.
 What we observe is not nature herself, But nature exposed to our method of questioning. --Werner Heisenberg Lord, grant me the Serenity to accept the things I cannot change, Courage to change the things
What we observe is not nature herself, But nature exposed to our method of questioning. --Werner Heisenberg Lord, grant me the Serenity to accept the things I cannot change, Courage to change the things
Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels Jarrod Schiffbauer *,1, Josh Fernandez 2,
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels Jarrod Schiffbauer *,1, Josh Fernandez 2,
07: Intermolecular and surface forces
 Nanomanufacturing University of Michigan ME599-002 Winter 2010 07: Intermolecular and surface forces February 3, 2010 John Hart ajohnh@umich.edu hfp://www.umich.edu/~ajohnh 2010 A.J. Hart 1 Announcements
Nanomanufacturing University of Michigan ME599-002 Winter 2010 07: Intermolecular and surface forces February 3, 2010 John Hart ajohnh@umich.edu hfp://www.umich.edu/~ajohnh 2010 A.J. Hart 1 Announcements
Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and wetting
 Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and Contact angle phenomena and wetting Young s equation Drop on the surface complete spreading Establishing finite contact angle γ cosθ = γ γ L S SL γ S γ > 0 partial
Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and Contact angle phenomena and wetting Young s equation Drop on the surface complete spreading Establishing finite contact angle γ cosθ = γ γ L S SL γ S γ > 0 partial
Electro-osmotic Flow Through a Rotating Microchannel
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 306 Electro-osmotic Flow Through a Rotating Microchannel Cheng
Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 306 Electro-osmotic Flow Through a Rotating Microchannel Cheng
Instrumentation and Operation
 Instrumentation and Operation 1 STM Instrumentation COMPONENTS sharp metal tip scanning system and control electronics feedback electronics (keeps tunneling current constant) image processing system data
Instrumentation and Operation 1 STM Instrumentation COMPONENTS sharp metal tip scanning system and control electronics feedback electronics (keeps tunneling current constant) image processing system data
Defects Panel Discussion
 Defects Panel Discussion David Y. H. Pui Distinguished McKnight University Professor LM Fingerson/TSI Inc Chair in Mechanical Engineering Director of the Particle Technology Laboratory University of Minnesota
Defects Panel Discussion David Y. H. Pui Distinguished McKnight University Professor LM Fingerson/TSI Inc Chair in Mechanical Engineering Director of the Particle Technology Laboratory University of Minnesota
Supporting Information. Metallic Adhesion Layer Induced Plasmon Damping and Molecular Linker as a Non-Damping Alternative
 Supporting Information Metallic Adhesion Layer Induced Plasmon Damping and Molecular Linker as a Non-Damping Alternative Terefe G. Habteyes, Scott Dhuey, Erin Wood, Daniel Gargas, Stefano Cabrini, P. James
Supporting Information Metallic Adhesion Layer Induced Plasmon Damping and Molecular Linker as a Non-Damping Alternative Terefe G. Habteyes, Scott Dhuey, Erin Wood, Daniel Gargas, Stefano Cabrini, P. James
Supplementary Information. Omnidispersible Hedgehog Particles with Multilayer Coatings for. Multiplexed Biosensing
 Supplementary Information Omnidispersible Hedgehog Particles with Multilayer Coatings for Multiplexed Biosensing Douglas G. Montjoy 1, Joong Hwan Bahng 1,2, Aydin Eskafi 1, Harrison Hou 1, Nicholas A.
Supplementary Information Omnidispersible Hedgehog Particles with Multilayer Coatings for Multiplexed Biosensing Douglas G. Montjoy 1, Joong Hwan Bahng 1,2, Aydin Eskafi 1, Harrison Hou 1, Nicholas A.
A SCIENTIFIC APPROACH TO A STICKY PROBLEM
 A SCIENTIFIC APPROACH TO A STICKY PROBLEM Sticking, the adherence of granule to punch face or die bore, is one of the major issues affecting the manufacture of solid dose pharmaceuticals. As part of I
A SCIENTIFIC APPROACH TO A STICKY PROBLEM Sticking, the adherence of granule to punch face or die bore, is one of the major issues affecting the manufacture of solid dose pharmaceuticals. As part of I
Large-Scale and Precise Nanoparticle Placement via Electrostatic Funneling
 Large-Scale and Precise Nanoparticle Placement via Electrostatic Funneling August 21, 2007 Seong Jin Koh Materials Science and Engineering The University of Texas at Arlington Acknowledgement Vishva Ray
Large-Scale and Precise Nanoparticle Placement via Electrostatic Funneling August 21, 2007 Seong Jin Koh Materials Science and Engineering The University of Texas at Arlington Acknowledgement Vishva Ray
V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes MIT Student 1. Poisson-Nernst-Planck Equations The Nernst-Planck Equation is a conservation of mass equation that describes the influence of
V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes MIT Student 1. Poisson-Nernst-Planck Equations The Nernst-Planck Equation is a conservation of mass equation that describes the influence of
Point mass approximation. Rigid beam mechanics. spring constant k N effective mass m e. Simple Harmonic Motion.. m e z = - k N z
 Free end Rigid beam mechanics Fixed end think of cantilever as a mass on a spring Point mass approximation z F Hooke s law k N = F / z This is beam mechanics, standard in engineering textbooks. For a rectangular
Free end Rigid beam mechanics Fixed end think of cantilever as a mass on a spring Point mass approximation z F Hooke s law k N = F / z This is beam mechanics, standard in engineering textbooks. For a rectangular
Supplementary Information: Triggered self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles
 Supplementary Information: Triggered self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles L. Ye 1,3, T. Pearson 1, Y. Cordeau 2, O.T. Mefford 2, and T. M. Crawford 1 1 Smart State Center for Experimental Nanoscale
Supplementary Information: Triggered self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles L. Ye 1,3, T. Pearson 1, Y. Cordeau 2, O.T. Mefford 2, and T. M. Crawford 1 1 Smart State Center for Experimental Nanoscale
The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 38: "" The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c )
 The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
A General Equation for Fitting Contact Area and Friction vs Load Measurements
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 211, 395 400 (1999) Article ID jcis.1998.6027, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on A General Equation for Fitting Contact Area and Friction vs Load
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 211, 395 400 (1999) Article ID jcis.1998.6027, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on A General Equation for Fitting Contact Area and Friction vs Load
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions
 Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions 6.1 Kinetic Stability of Colloidal Suspensions o G = A f sl sl interfacial surface tension (sol/liq) [J/m 2 ] sol/liq surface change [m 2 ] γ sl > 0 colloid
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions 6.1 Kinetic Stability of Colloidal Suspensions o G = A f sl sl interfacial surface tension (sol/liq) [J/m 2 ] sol/liq surface change [m 2 ] γ sl > 0 colloid
Single-Molecule Recognition and Manipulation Studied by Scanning Probe Microscopy
 Single-Molecule Recognition and Manipulation Studied by Scanning Probe Microscopy Byung Kim Department of Physics Boise State University Langmuir (in press, 2006) swollen collapsed Hydrophilic non-sticky
Single-Molecule Recognition and Manipulation Studied by Scanning Probe Microscopy Byung Kim Department of Physics Boise State University Langmuir (in press, 2006) swollen collapsed Hydrophilic non-sticky
Foundations of. Colloid Science SECOND EDITION. Robert J. Hunter. School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Nanoscale IR spectroscopy of organic contaminants
 The nanoscale spectroscopy company The world leader in nanoscale IR spectroscopy Nanoscale IR spectroscopy of organic contaminants Application note nanoir uniquely and unambiguously identifies organic
The nanoscale spectroscopy company The world leader in nanoscale IR spectroscopy Nanoscale IR spectroscopy of organic contaminants Application note nanoir uniquely and unambiguously identifies organic
General concept and defining characteristics of AFM. Dina Kudasheva Advisor: Prof. Mary K. Cowman
 General concept and defining characteristics of AFM Dina Kudasheva Advisor: Prof. Mary K. Cowman Overview Introduction History of the SPM invention Technical Capabilities Principles of operation Examples
General concept and defining characteristics of AFM Dina Kudasheva Advisor: Prof. Mary K. Cowman Overview Introduction History of the SPM invention Technical Capabilities Principles of operation Examples
A Monte Carlo Simulator for Non-contact Mode Atomic Force Microscopy
 A Monte Carlo Simulator for Non-contact Mode Atomic Force Microscopy Lado Filipovic 1,2 and Siegfried Selberherr 1 1 Institute for Microelectronics, Technische Universität Wien, Gußhausstraße 27 29/E360,
A Monte Carlo Simulator for Non-contact Mode Atomic Force Microscopy Lado Filipovic 1,2 and Siegfried Selberherr 1 1 Institute for Microelectronics, Technische Universität Wien, Gußhausstraße 27 29/E360,
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions
 Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions 6.1 Kinetic Stability of Colloidal Suspensions o G = A f sl sl interfacial surface tension (sol/liq) [J/m 2 ] sol/liq surface change [m 2 ] γ sl > 0 colloid
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions 6.1 Kinetic Stability of Colloidal Suspensions o G = A f sl sl interfacial surface tension (sol/liq) [J/m 2 ] sol/liq surface change [m 2 ] γ sl > 0 colloid
nano-ta: Nano Thermal Analysis
 nano-ta: Nano Thermal Analysis Application Note #1 Failure Analysis - Identification of Particles in a Polymer Film Author: David Grandy Ph.D. Introduction Nano-TA is a local thermal analysis technique
nano-ta: Nano Thermal Analysis Application Note #1 Failure Analysis - Identification of Particles in a Polymer Film Author: David Grandy Ph.D. Introduction Nano-TA is a local thermal analysis technique
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview
 Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Probing the Hydrophobic Interaction between Air Bubbles and Partially. Hydrophobic Surfaces Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Supporting Information for Probing the Hydrophobic Interaction between Air Bubbles and Partially Hydrophobic Surfaces Using Atomic Force Microscopy Chen Shi, 1 Derek Y.C. Chan, 2.3 Qingxia Liu, 1 Hongbo
Supporting Information for Probing the Hydrophobic Interaction between Air Bubbles and Partially Hydrophobic Surfaces Using Atomic Force Microscopy Chen Shi, 1 Derek Y.C. Chan, 2.3 Qingxia Liu, 1 Hongbo
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES a b c Supplementary Figure 1 Fabrication of the near-field radiative heat transfer device. a, Main fabrication steps for the bottom Si substrate. b, Main fabrication steps for the
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES a b c Supplementary Figure 1 Fabrication of the near-field radiative heat transfer device. a, Main fabrication steps for the bottom Si substrate. b, Main fabrication steps for the
Structural and Mechanical Properties of Nanostructures
 Master s in nanoscience Nanostructural properties Mechanical properties Structural and Mechanical Properties of Nanostructures Prof. Angel Rubio Dr. Letizia Chiodo Dpto. Fisica de Materiales, Facultad
Master s in nanoscience Nanostructural properties Mechanical properties Structural and Mechanical Properties of Nanostructures Prof. Angel Rubio Dr. Letizia Chiodo Dpto. Fisica de Materiales, Facultad
Nanoparticle/AMC Contamination Control and Metrology for the EUVL Systems
 Nanoparticle/AMC Contamination Control and Metrology for the EUVL Systems David Y. H. Pui Distinguished McKnight University Professor Director of the Particle Technology Laboratory Mechanical Engineering
Nanoparticle/AMC Contamination Control and Metrology for the EUVL Systems David Y. H. Pui Distinguished McKnight University Professor Director of the Particle Technology Laboratory Mechanical Engineering
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context
 Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS
 MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS Christian L. Petersen, Rong Lin, Dirch H. Petersen, Peter F. Nielsen CAPRES A/S, Burnaby, BC, Canada CAPRES A/S, Lyngby, Denmark We
MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS Christian L. Petersen, Rong Lin, Dirch H. Petersen, Peter F. Nielsen CAPRES A/S, Burnaby, BC, Canada CAPRES A/S, Lyngby, Denmark We
Nano Particle Image Velocimetry (npiv); Data Reduction Challenges
 Nano Particle Image Velocimetry (npiv); Data Reduction Challenges Dr. Reza Sadr Micro Scale Thermo Fluids (MSTF) Laboratory Department of Mechanical Engineering Reza.sadr@qatar.tamu.edu P. O. Box 23874,
Nano Particle Image Velocimetry (npiv); Data Reduction Challenges Dr. Reza Sadr Micro Scale Thermo Fluids (MSTF) Laboratory Department of Mechanical Engineering Reza.sadr@qatar.tamu.edu P. O. Box 23874,
Nanometer-Scale Materials Contrast Imaging with a Near-Field Microwave Microscope
 Nanometer-Scale Materials Contrast Imaging with a Near-Field Microwave Microscope Atif Imtiaz 1 and Steven M. Anlage Center for Superconductivity Research, Department of Physics, University of Maryland,
Nanometer-Scale Materials Contrast Imaging with a Near-Field Microwave Microscope Atif Imtiaz 1 and Steven M. Anlage Center for Superconductivity Research, Department of Physics, University of Maryland,
EE C247B / ME C218 INTRODUCTION TO MEMS DESIGN SPRING 2016 C. NGUYEN PROBLEM SET #4
 Issued: Wednesday, March 4, 2016 PROBLEM SET #4 Due: Monday, March 14, 2016, 8:00 a.m. in the EE C247B homework box near 125 Cory. 1. This problem considers bending of a simple cantilever and several methods
Issued: Wednesday, March 4, 2016 PROBLEM SET #4 Due: Monday, March 14, 2016, 8:00 a.m. in the EE C247B homework box near 125 Cory. 1. This problem considers bending of a simple cantilever and several methods
Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids.
 Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids. Lyophilic and lyophobic sols Sols (lyosols) are dispersed colloidal size particles in a liquid medium (=solid/liquid dispersions) These sols
Colloid stability. Lyophobic sols. Stabilization of colloids. Lyophilic and lyophobic sols Sols (lyosols) are dispersed colloidal size particles in a liquid medium (=solid/liquid dispersions) These sols
Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy
 Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy Correlation Force Spectroscopy: Rationale In principle, the main advantage of correlation force spectroscopy (CFS) over onecantilever atomic force microscopy (AFM)
Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy Correlation Force Spectroscopy: Rationale In principle, the main advantage of correlation force spectroscopy (CFS) over onecantilever atomic force microscopy (AFM)
Supporting Information. Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films
 Supporting Information Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films Matthew Daly a,1, Changhong Cao b,1, Hao Sun b, Yu Sun b, *, Tobin Filleter b, *, and Chandra Veer Singh a, * a Department
Supporting Information Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films Matthew Daly a,1, Changhong Cao b,1, Hao Sun b, Yu Sun b, *, Tobin Filleter b, *, and Chandra Veer Singh a, * a Department
Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important Mats Larsson 1, Adrian Hill 2, and John Duffy 2 1 Malvern
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important Mats Larsson 1, Adrian Hill 2, and John Duffy 2 1 Malvern
