The Poisson Equation for Electrostatics
|
|
|
- Beatrice Mosley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Puerto Rico - Mayagüez
2 Table of Contents 1 Derivation from Maxwell s Equations 2 3 4
3 Derivation from Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s Equations for Electrodynamics in differential form are: E = 1 ɛ 0 ρ( r, t) B = 0 E = B t B = µ 0 E J( r, t) + µ0 ɛ 0 t (Gauss s Law for Electricity) (1a) (Gauss s Law for Magnetism)(1b) (Faraday s Law of Induction) (1c) (Ampère-Maxwell s Law) (1d).
4 Using the Helmholtz Theorem and that B is divergenceless, the magnetic field can be expressed in terms of a vector potential, A: B = A (2) From this and Faraday s Law, Eq. (1c), the electric field can be expressed as: E = V A (3) t
5 Substiting into Gauss Law, Eq. (1a), results in: In the electrostatic case, it reduces to 2 V + t ( A) = 1 ɛ 0 ρ (4) V 2 V = 1 ɛ 0 ρ( r), (5) which is Poisson s equation. For a region of space in which there is no charge, we obtain Laplace s equation: V 2 V = 0 (6)
6 The Laplace equation in rectangular coordinates is 2 V x V y V z 2 = 0 (7) To solve by separation of variables we assume that: V (x, y, z) = X (x)y (y)z(z) (8) After substituting and diving, this results in: 1 d 2 X X (x) dx d 2 Y Y (y) dy d 2 Z Z(z) dz 2 = 0 (9)
7 In order for the result to hold for arbitrary values of the coordinates, each of the terms must be individually constant: where α 2 + β 2 = γ 2. 1 d 2 X X (x) dx 2 = α 2 (10a) 1 d 2 Y Y (y) dy 2 = β 2 (10b) 1 d 2 Z Z(z) dz 2 = γ 2, (10c)
8 If α 2 and β 2 are arbitrarily chosen to be positive, the solutions to the set of ODEs are then: X (x) = e ±iαx (11a) Y (y) = e ±iβy (11b) Z(z) = e ± α 2 +β 2z. (11c)
9 Derivation from Maxwell s Equations In order to determine α and β, we impose the boundary conditions on the potential. An example is shown in the figure. Yese J. Felipe
10 Since V = 0, for x = 0, y = 0, z = 0, we obtain that X (x) = sin(αx) (12a) Y (y) = sin(βy) (12b) Z(z) = sinh( α 2 + β 2 z), (12c) From V = 0, for x = a, and y = b, we must have that α(a) = nπ, and β(b) = mπ. Therefore, α n = nπ a β m = mπ b n γ nm = π 2 α 2 + m2 β 2, (13a) (13b) (13c)
11 So, the partial potential that satisfies the above boundary conditions is V nm = sin(α n x)sin(β m y)sinh(γ nm z) (14) The potential can then be expanded in terms of V nm with arbitrary coefficients that will be chosen to fulfill the final boundary condition: V (x, y, z) = n,m=1 A nm sin(α n x)sin(β m y)sinh(γ nm z) (15)
12 Evaluating the final boundary condition, V (x, y, c) = V 0 (x, y) at z = c: V 0 (x, y) = n,m=1 A nm sin(α n x)sin(β m y)sinh(γ nm c) (16) Which is a double Fourier series for the function V 0 (x, y). Here the coefficients A nm are given by A nm = 4 ab sinh γ nm c a 0 dx b 0 dyv 0 (x, y)sin(α n x)sin(β m y) (17)
13 If the box has potentials different from zero on all six sides, the solution for the potential inside the box can be obtained by linear superposition of six solutions, one for each side, equivalent to Eqs.(17) and (15). In the case of the potential inside the box with a charge distribution inside, Poisson s equation with prescribed boundary conditions on the surface, requires the construction of the appropiate Green function, whose discussion shall be ommited.
14 First uniqueness theorem: The solution to Laplace s equation in some volume τ is uniquely determined if V is specified on the boundary surface S. This theorem guarantees that the solution found for the previous example is unique. Corollary: The potential in a volume τ is uniquely determined if (a) the charge density throughout the region and (b) the value of V on all boundaries, are specified. This corollary is crucial for the validity of the solutions obtained with another method used for finding the electric potential, known as The Method of Images.
15 Derivation from Maxwell s Equations Second uniqueness theorem: In a volume τ surrounded by conductors and containing a specified charge density ρ,p the electric field is uniquely determined if the total charge, Qtot = i Qi, on each conductor is given (as ilustrated below). Yese J. Felipe
16 J.D. Jackson Classical Electrodynamics. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 3rd edition, D.J. Griffiths Introduction to Electrodynamics. Prentice-Hall, 3rd edition, 1999.
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRODYNAMICS
 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRODYNAMICS Second Edition DAVID J. GRIFFITHS Department of Physics Reed College PRENTICE HALL, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS Preface xi Advertisement 1 1 Vector Analysis
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRODYNAMICS Second Edition DAVID J. GRIFFITHS Department of Physics Reed College PRENTICE HALL, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS Preface xi Advertisement 1 1 Vector Analysis
Summary of time independent electrodynamics
 hapter 10 Summary of time independent electrodynamics 10.1 Electrostatics Physical law oulomb s law charges as origin of electric field Superposition principle ector of the electric field E(x) in vacuum
hapter 10 Summary of time independent electrodynamics 10.1 Electrostatics Physical law oulomb s law charges as origin of electric field Superposition principle ector of the electric field E(x) in vacuum
Electrodynamics PHY712. Lecture 4 Electrostatic potentials and fields. Reference: Chap. 1 & 2 in J. D. Jackson s textbook.
 Electrodynamics PHY712 Lecture 4 Electrostatic potentials and fields Reference: Chap. 1 & 2 in J. D. Jackson s textbook. 1. Complete proof of Green s Theorem 2. Proof of mean value theorem for electrostatic
Electrodynamics PHY712 Lecture 4 Electrostatic potentials and fields Reference: Chap. 1 & 2 in J. D. Jackson s textbook. 1. Complete proof of Green s Theorem 2. Proof of mean value theorem for electrostatic
Mathematical Notes for E&M Gradient, Divergence, and Curl
 Mathematical Notes for E&M Gradient, Divergence, and Curl In these notes I explain the differential operators gradient, divergence, and curl (also known as rotor), the relations between them, the integral
Mathematical Notes for E&M Gradient, Divergence, and Curl In these notes I explain the differential operators gradient, divergence, and curl (also known as rotor), the relations between them, the integral
Notes 19 Gradient and Laplacian
 ECE 3318 Applied Electricity and Magnetism Spring 218 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 19 Gradient and Laplacian 1 Gradient Φ ( x, y, z) =scalar function Φ Φ Φ grad Φ xˆ + yˆ + zˆ x y z We can
ECE 3318 Applied Electricity and Magnetism Spring 218 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 19 Gradient and Laplacian 1 Gradient Φ ( x, y, z) =scalar function Φ Φ Φ grad Φ xˆ + yˆ + zˆ x y z We can
TENTATIVE CONTENTS OF THE COURSE # EE-271 ENGINEERING ELECTROMAGNETICS, FS-2012 (as of 09/13/12) Dr. Marina Y. Koledintseva
 TENTATIVE CONTENTS OF THE COURSE # EE-271 ENGINEERING ELECTROMAGNETICS, FS-2012 (as of 09/13/12) Dr. Marina Y. Koledintseva Part 1. Introduction Basic Physics and Mathematics for Electromagnetics. Lecture
TENTATIVE CONTENTS OF THE COURSE # EE-271 ENGINEERING ELECTROMAGNETICS, FS-2012 (as of 09/13/12) Dr. Marina Y. Koledintseva Part 1. Introduction Basic Physics and Mathematics for Electromagnetics. Lecture
Electrodynamics PHY712. Lecture 3 Electrostatic potentials and fields. Reference: Chap. 1 in J. D. Jackson s textbook.
 Electrodynamics PHY712 Lecture 3 Electrostatic potentials and fields Reference: Chap. 1 in J. D. Jackson s textbook. 1. Poisson and Laplace Equations 2. Green s Theorem 3. One-dimensional examples 1 Poisson
Electrodynamics PHY712 Lecture 3 Electrostatic potentials and fields Reference: Chap. 1 in J. D. Jackson s textbook. 1. Poisson and Laplace Equations 2. Green s Theorem 3. One-dimensional examples 1 Poisson
CHAPTER 2. COULOMB S LAW AND ELECTRONIC FIELD INTENSITY. 2.3 Field Due to a Continuous Volume Charge Distribution
 CONTENTS CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ANALYSIS 1. Scalars and Vectors 2. Vector Algebra 3. The Cartesian Coordinate System 4. Vector Cartesian Coordinate System 5. The Vector Field 6. The Dot Product 7. The Cross
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ANALYSIS 1. Scalars and Vectors 2. Vector Algebra 3. The Cartesian Coordinate System 4. Vector Cartesian Coordinate System 5. The Vector Field 6. The Dot Product 7. The Cross
Maxwell s equations for electrostatics
 Maxwell s equations for electrostatics October 6, 5 The differential form of Gauss s law Starting from the integral form of Gauss s law, we treat the charge as a continuous distribution, ρ x. Then, letting
Maxwell s equations for electrostatics October 6, 5 The differential form of Gauss s law Starting from the integral form of Gauss s law, we treat the charge as a continuous distribution, ρ x. Then, letting
Time-Varying Systems; Maxwell s Equations
 Time-Varying Systems; Maxwell s Equations 1. Faraday s law in differential form 2. Scalar and vector potentials; the Lorenz condition 3. Ampere s law with displacement current 4. Maxwell s equations 5.
Time-Varying Systems; Maxwell s Equations 1. Faraday s law in differential form 2. Scalar and vector potentials; the Lorenz condition 3. Ampere s law with displacement current 4. Maxwell s equations 5.
PHY103A: Lecture # 9
 Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 9 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 20-Jan-2018 Summary of Lecture # 8: Force per unit
Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 9 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 20-Jan-2018 Summary of Lecture # 8: Force per unit
Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 2, 3, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap. 2. 2π nx i a. ( ) = G n.
 Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
3. Calculating Electrostatic Potential
 3. Calculating Electrostatic Potential 3. Laplace s Equation 3. The Method of Images 3.3 Separation of Variables 3.4 Multipole Expansion 3.. Introduction The primary task of electrostatics is to study
3. Calculating Electrostatic Potential 3. Laplace s Equation 3. The Method of Images 3.3 Separation of Variables 3.4 Multipole Expansion 3.. Introduction The primary task of electrostatics is to study
송석호 ( 물리학과 )
 http://optics.hanyang.ac.kr/~shsong 송석호 ( 물리학과 ) Introduction to Electrodynamics, David J. Griffiths Review: 1. Vector analysis 2. Electrostatics 3. Special techniques 4. Electric fields in mater 5. Magnetostatics
http://optics.hanyang.ac.kr/~shsong 송석호 ( 물리학과 ) Introduction to Electrodynamics, David J. Griffiths Review: 1. Vector analysis 2. Electrostatics 3. Special techniques 4. Electric fields in mater 5. Magnetostatics
Joel A. Shapiro January 21, 2010
 Joel A. shapiro@physics.rutgers.edu January 21, 20 rmation Instructor: Joel Serin 325 5-5500 X 3886, shapiro@physics Book: Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) Web home page: www.physics.rutgers.edu/grad/504
Joel A. shapiro@physics.rutgers.edu January 21, 20 rmation Instructor: Joel Serin 325 5-5500 X 3886, shapiro@physics Book: Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) Web home page: www.physics.rutgers.edu/grad/504
Today in Physics 217: electric potential
 Today in Physics 17: electric potential Finish Friday s discussion of the field from a uniformly-charged sphere, and the gravitational analogue of Gauss Law. Electric potential Example: a field and its
Today in Physics 17: electric potential Finish Friday s discussion of the field from a uniformly-charged sphere, and the gravitational analogue of Gauss Law. Electric potential Example: a field and its
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
 Phys 311 Fall 2014 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY Phys 311 Fall 2014 Instructor: Office: Professor David Collins WS 228B Phone: 248-1787 email: Office Hours: dacollin@coloradomesa.edu MT 9:00 9:50am, MWF 2:00
Phys 311 Fall 2014 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY Phys 311 Fall 2014 Instructor: Office: Professor David Collins WS 228B Phone: 248-1787 email: Office Hours: dacollin@coloradomesa.edu MT 9:00 9:50am, MWF 2:00
ELECTROMAGNETISM. Second Edition. I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips. John Wiley & Sons. Department of Physics University of Manchester
 ELECTROMAGNETISM Second Edition I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips Department of Physics University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Flow diagram inside front cover
ELECTROMAGNETISM Second Edition I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips Department of Physics University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Flow diagram inside front cover
CLASSICAL ELECTRODYNAMICS I Physics 6/75203 SPRING 2013
 INSTRUCTOR: CLASSICAL ELECTRODYNAMICS I Physics 6/75203 SPRING 2013 Dr. Mark Manley manley@kent.edu 220 Smith Hall http://www.kent.edu/cas/physics/people/manley.cfm 330-672-2407 CLASS HOURS: 1:10-2:00
INSTRUCTOR: CLASSICAL ELECTRODYNAMICS I Physics 6/75203 SPRING 2013 Dr. Mark Manley manley@kent.edu 220 Smith Hall http://www.kent.edu/cas/physics/people/manley.cfm 330-672-2407 CLASS HOURS: 1:10-2:00
page 78, Problem 2.19:... of Sect Refer to Prob if you get stuck.
 Some corrections in blue to Pearson New International Edition Introduction to Electrodynamics David J. Griffiths Fourth Edition Chapter 2 page 78, Problem 2.19:... of Sect. 2.2.2. Refer to Prob. 1.63 if
Some corrections in blue to Pearson New International Edition Introduction to Electrodynamics David J. Griffiths Fourth Edition Chapter 2 page 78, Problem 2.19:... of Sect. 2.2.2. Refer to Prob. 1.63 if
Selected electrostatic problems (Lecture 14)
 Selected electrostatic problems (Lecture 14) February 1, 2016 236/441 Lecture outline In this lecture, we demonstrate how to solve several electrostatic problems related to calculation of the fields generated
Selected electrostatic problems (Lecture 14) February 1, 2016 236/441 Lecture outline In this lecture, we demonstrate how to solve several electrostatic problems related to calculation of the fields generated
Chapter 2. Electrostatics. Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3 rd or 4 rd Edition, David J. Griffiths
 Chapter 2. Electrostatics Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3 rd or 4 rd Edition, David J. Griffiths 2.3 Electric Potential 2.3.1 Introduction to Potential E 0 We're going to reduce a vector problem (finding
Chapter 2. Electrostatics Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3 rd or 4 rd Edition, David J. Griffiths 2.3 Electric Potential 2.3.1 Introduction to Potential E 0 We're going to reduce a vector problem (finding
LESSON PLAN EE0205 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
 LESSON PLAN EE0205 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF EEE Course Code : EE0205 Course Title : ELECTROMAGNETIC
LESSON PLAN EE0205 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF EEE Course Code : EE0205 Course Title : ELECTROMAGNETIC
fiziks Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 Content-ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 1. Electrostatics (1-58) 1.1 Coulomb s Law and Superposition Principle 1.1.1 Electric field 1.2 Gauss s law 1.2.1 Field lines and Electric flux 1.2.2 Applications 1.3
Content-ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 1. Electrostatics (1-58) 1.1 Coulomb s Law and Superposition Principle 1.1.1 Electric field 1.2 Gauss s law 1.2.1 Field lines and Electric flux 1.2.2 Applications 1.3
A Brief Revision of Vector Calculus and Maxwell s Equations
 A Brief Revision of Vector Calculus and Maxwell s Equations Debapratim Ghosh Electronic Systems Group Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay e-mail: dghosh@ee.iitb.ac.in
A Brief Revision of Vector Calculus and Maxwell s Equations Debapratim Ghosh Electronic Systems Group Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay e-mail: dghosh@ee.iitb.ac.in
Second Year Electromagnetism Summer 2018 Caroline Terquem. Vacation work: Problem set 0. Revisions
 Second Year Electromagnetism Summer 2018 Caroline Terquem Vacation work: Problem set 0 Revisions At the start of the second year, you will receive the second part of the Electromagnetism course. This vacation
Second Year Electromagnetism Summer 2018 Caroline Terquem Vacation work: Problem set 0 Revisions At the start of the second year, you will receive the second part of the Electromagnetism course. This vacation
Uniform Plane Waves. Ranga Rodrigo. University of Moratuwa. November 7, 2008
 Uniform Plane Waves Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa November 7, 2008 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Uniform Plane Waves November 7, 2008 1 / 51 Summary of Last Week s Lecture Basic Relations
Uniform Plane Waves Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa November 7, 2008 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Uniform Plane Waves November 7, 2008 1 / 51 Summary of Last Week s Lecture Basic Relations
Class 11 : Magnetic materials
 Class 11 : Magnetic materials Magnetic dipoles Magnetization of a medium, and how it modifies magnetic field Magnetic intensity How does an electromagnet work? Boundary conditions for B Recap (1) Electric
Class 11 : Magnetic materials Magnetic dipoles Magnetization of a medium, and how it modifies magnetic field Magnetic intensity How does an electromagnet work? Boundary conditions for B Recap (1) Electric
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
Part IB Electromagnetism
 Part IB Electromagnetism Theorems Based on lectures by D. Tong Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IB Electromagnetism Theorems Based on lectures by D. Tong Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS
 UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
Electromagnetic waves in free space
 Waveguide notes 018 Electromagnetic waves in free space We start with Maxwell s equations for an LIH medum in the case that the source terms are both zero. = =0 =0 = = Take the curl of Faraday s law, then
Waveguide notes 018 Electromagnetic waves in free space We start with Maxwell s equations for an LIH medum in the case that the source terms are both zero. = =0 =0 = = Take the curl of Faraday s law, then
Chapter 4. Higher-Order Differential Equations
 Chapter 4 Higher-Order Differential Equations i THEOREM 4.1.1 (Existence of a Unique Solution) Let a n (x), a n,, a, a 0 (x) and g(x) be continuous on an interval I and let a n (x) 0 for every x in this
Chapter 4 Higher-Order Differential Equations i THEOREM 4.1.1 (Existence of a Unique Solution) Let a n (x), a n,, a, a 0 (x) and g(x) be continuous on an interval I and let a n (x) 0 for every x in this
Unit-1 Electrostatics-1
 1. Describe about Co-ordinate Systems. Co-ordinate Systems Unit-1 Electrostatics-1 In order to describe the spatial variations of the quantities, we require using appropriate coordinate system. A point
1. Describe about Co-ordinate Systems. Co-ordinate Systems Unit-1 Electrostatics-1 In order to describe the spatial variations of the quantities, we require using appropriate coordinate system. A point
Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, ISBN:
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, ISBN:
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
Helmholtz Wave Equation TE, TM, and TEM Modes Rect Rectangular Waveguide TE, TM, and TEM Modes Cyl Cylindrical Waveguide.
 Waveguides S. R. Zinka zinka@vit.ac.in School of Electronics Engineering Vellore Institute of Technology April 26, 2013 Outline 1 Helmholtz Wave Equation 2 TE, TM, and TEM Modes Rect 3 Rectangular Waveguide
Waveguides S. R. Zinka zinka@vit.ac.in School of Electronics Engineering Vellore Institute of Technology April 26, 2013 Outline 1 Helmholtz Wave Equation 2 TE, TM, and TEM Modes Rect 3 Rectangular Waveguide
Comment about Didactical formulation of the
 Comment about Didactical formulation of the Ampère law Hendrik van Hees Institute for Theoretical Physics, Goethe University Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue-Str. 1, D-60438 Frankfurt, Germany Frankfurt Institute
Comment about Didactical formulation of the Ampère law Hendrik van Hees Institute for Theoretical Physics, Goethe University Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue-Str. 1, D-60438 Frankfurt, Germany Frankfurt Institute
Maxwell s Equations. In the previous chapters we saw the four fundamental equations governging electrostatics and magnetostatics. They are.
 Maxwell s Equations Introduction In the previous chapters we saw the four fundamental equations governging electrostatics and magnetostatics. They are D = ρ () E = 0 (2) B = 0 (3) H = J (4) In the integral
Maxwell s Equations Introduction In the previous chapters we saw the four fundamental equations governging electrostatics and magnetostatics. They are D = ρ () E = 0 (2) B = 0 (3) H = J (4) In the integral
Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-242: ( Monday, Wednesday, Rutherford 115)
 Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-242: (1135-1225 Monday, Wednesday, Rutherford 115) Instructor: Shaun Lovejoy, Rutherford Physics, rm. 213, local 6537, email: lovejoy@physics.mcgill.ca Teaching assistants:
Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-242: (1135-1225 Monday, Wednesday, Rutherford 115) Instructor: Shaun Lovejoy, Rutherford Physics, rm. 213, local 6537, email: lovejoy@physics.mcgill.ca Teaching assistants:
Chapter 5. Magnetostatics
 Chapter 5. Magnetostatics 5.4 Magnetic Vector Potential 5.1.1 The Vector Potential In electrostatics, E Scalar potential (V) In magnetostatics, B E B V A Vector potential (A) (Note) The name is potential,
Chapter 5. Magnetostatics 5.4 Magnetic Vector Potential 5.1.1 The Vector Potential In electrostatics, E Scalar potential (V) In magnetostatics, B E B V A Vector potential (A) (Note) The name is potential,
Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions
 Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions Ranga Rodrigo June 23, 2010 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis [?]. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents 1 The Vector
Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions Ranga Rodrigo June 23, 2010 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis [?]. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents 1 The Vector
City University of Hong Kong. Course Syllabus. offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2016/17
 City University of Hong Kong offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2016/17 Part I Course Overview Course Title: Electromagnetism Course Code: AP3205 Course
City University of Hong Kong offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2016/17 Part I Course Overview Course Title: Electromagnetism Course Code: AP3205 Course
Course no. 4. The Theory of Electromagnetic Field
 Cose no. 4 The Theory of Electromagnetic Field Technical University of Cluj-Napoca http://www.et.utcluj.ro/cs_electromagnetics2006_ac.htm http://www.et.utcluj.ro/~lcret March 19-2009 Chapter 3 Magnetostatics
Cose no. 4 The Theory of Electromagnetic Field Technical University of Cluj-Napoca http://www.et.utcluj.ro/cs_electromagnetics2006_ac.htm http://www.et.utcluj.ro/~lcret March 19-2009 Chapter 3 Magnetostatics
Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves
 CARL T. A. JOHNK Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore CHAPTER
CARL T. A. JOHNK Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore CHAPTER
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
ELECTRO MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SET - 1 1. a) State and explain Gauss law in differential form and also list the limitations of Guess law. b) A square sheet defined by -2 x 2m, -2 y 2m lies in the = -2m plane. The charge density on the
SET - 1 1. a) State and explain Gauss law in differential form and also list the limitations of Guess law. b) A square sheet defined by -2 x 2m, -2 y 2m lies in the = -2m plane. The charge density on the
21 Laplace s Equation and Harmonic Functions
 2 Laplace s Equation and Harmonic Functions 2. Introductory Remarks on the Laplacian operator Given a domain Ω R d, then 2 u = div(grad u) = in Ω () is Laplace s equation defined in Ω. If d = 2, in cartesian
2 Laplace s Equation and Harmonic Functions 2. Introductory Remarks on the Laplacian operator Given a domain Ω R d, then 2 u = div(grad u) = in Ω () is Laplace s equation defined in Ω. If d = 2, in cartesian
arxiv: v2 [physics.gen-ph] 20 Mar 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.gen-ph] 20 Mar 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.gen-ph] 20 Mar 2013](/thumbs/96/127587291.jpg) arxiv:129.3449v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Mar 213 Potential Theory in Classical Electrodynamics W. Engelhardt 1, retired from: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-85741 Garching, Germany Abstract In Maxwell
arxiv:129.3449v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Mar 213 Potential Theory in Classical Electrodynamics W. Engelhardt 1, retired from: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-85741 Garching, Germany Abstract In Maxwell
Physics 506 Winter 2004
 Physics 506 Winter 004 G. Raithel January 6, 004 Disclaimer: The purpose of these notes is to provide you with a general list of topics that were covered in class. The notes are not a substitute for reading
Physics 506 Winter 004 G. Raithel January 6, 004 Disclaimer: The purpose of these notes is to provide you with a general list of topics that were covered in class. The notes are not a substitute for reading
Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves
 9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
송석호 ( 물리학과 )
 http://optics.hanyang.ac.kr/~shsong 송석호 ( 물리학과 ) Field and Wave Electromagnetics, David K. Cheng Reviews on (Week 1). Vector Analysis 3. tatic Electric Fields (Week ) 4. olution of Electrostatic Problems
http://optics.hanyang.ac.kr/~shsong 송석호 ( 물리학과 ) Field and Wave Electromagnetics, David K. Cheng Reviews on (Week 1). Vector Analysis 3. tatic Electric Fields (Week ) 4. olution of Electrostatic Problems
Joel A. Shapiro January 20, 2011
 Joel A. shapiro@physics.rutgers.edu January 20, 2011 Course Information Instructor: Joel Serin 325 5-5500 X 3886, shapiro@physics Book: Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) Web home page: www.physics.rutgers.edu/grad/504
Joel A. shapiro@physics.rutgers.edu January 20, 2011 Course Information Instructor: Joel Serin 325 5-5500 X 3886, shapiro@physics Book: Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) Web home page: www.physics.rutgers.edu/grad/504
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 1. Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 1. Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt =
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt =
Electromagnetism HW 1 math review
 Electromagnetism HW math review Problems -5 due Mon 7th Sep, 6- due Mon 4th Sep Exercise. The Levi-Civita symbol, ɛ ijk, also known as the completely antisymmetric rank-3 tensor, has the following properties:
Electromagnetism HW math review Problems -5 due Mon 7th Sep, 6- due Mon 4th Sep Exercise. The Levi-Civita symbol, ɛ ijk, also known as the completely antisymmetric rank-3 tensor, has the following properties:
Physics 610: Electricity & Magnetism I
 Physics 610: Electricity & Magnetism I [i.e. relativistic EM, electro/magneto-(quasi)statics] [lin12.triumph.ca] [J-lab accelerator] [ixnovi.people.wm.edu] [Thywissen group, U. of Toronto] [nanotechetc.com]
Physics 610: Electricity & Magnetism I [i.e. relativistic EM, electro/magneto-(quasi)statics] [lin12.triumph.ca] [J-lab accelerator] [ixnovi.people.wm.edu] [Thywissen group, U. of Toronto] [nanotechetc.com]
Partial Differential Equations - part of EM Waves module (PHY2065)
 Partial Differential Equations - part of EM Waves module (PHY2065) Richard Sear February 7, 2013 Recommended textbooks 1. Mathematical methods in the physical sciences, Mary Boas. 2. Essential mathematical
Partial Differential Equations - part of EM Waves module (PHY2065) Richard Sear February 7, 2013 Recommended textbooks 1. Mathematical methods in the physical sciences, Mary Boas. 2. Essential mathematical
Electromagnetic. G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Jefferson Lab Professor of Physics Old Dominion University TAADI Electromagnetic Theory
 TAAD1 Electromagnetic Theory G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Jefferson Lab Professor of Physics Old Dominion University 8-31-12 Classical Electrodynamics A main physics discovery of the last half of the 2 th
TAAD1 Electromagnetic Theory G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Jefferson Lab Professor of Physics Old Dominion University 8-31-12 Classical Electrodynamics A main physics discovery of the last half of the 2 th
UNIT-I INTRODUCTION TO COORDINATE SYSTEMS AND VECTOR ALGEBRA
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : EMF(16EE214) Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech - EEE Year
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : EMF(16EE214) Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech - EEE Year
arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008](/thumbs/77/76689828.jpg) Can Maxwell s equations be obtained from the continuity equation? José A. Heras arxiv:0812.4785v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008 Departamento de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Iberoamericana, Prolongación
Can Maxwell s equations be obtained from the continuity equation? José A. Heras arxiv:0812.4785v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008 Departamento de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Iberoamericana, Prolongación
Lecture notes for ELECTRODYNAMICS.
 Lecture notes for 640-343 ELECTRODYNAMICS. 1 Summary of Electrostatics 1.1 Coulomb s Law Force between two point charges F 12 = 1 4πɛ 0 Q 1 Q 2ˆr 12 r 1 r 2 2 (1.1.1) 1.2 Electric Field For a charge distribution:
Lecture notes for 640-343 ELECTRODYNAMICS. 1 Summary of Electrostatics 1.1 Coulomb s Law Force between two point charges F 12 = 1 4πɛ 0 Q 1 Q 2ˆr 12 r 1 r 2 2 (1.1.1) 1.2 Electric Field For a charge distribution:
INTRODUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHODS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN
 INTROUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHOS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN CONTENTS 1. Poisson Equation 1 2. Outline of Topics 3 2.1. Finite ifference Method 3 2.2. Finite Element Method 3 2.3. Finite Volume
INTROUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHOS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN CONTENTS 1. Poisson Equation 1 2. Outline of Topics 3 2.1. Finite ifference Method 3 2.2. Finite Element Method 3 2.3. Finite Volume
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 1. Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 1. Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt
Virtual current density in magnetic flow meter
 Virtual current density in magnetic flow meter Problem presented by Claus Nygaard Rasmussen Siemens Flow Instruments Background Siemens Flow Instruments submits this problem for the 51st European Study
Virtual current density in magnetic flow meter Problem presented by Claus Nygaard Rasmussen Siemens Flow Instruments Background Siemens Flow Instruments submits this problem for the 51st European Study
Introduction to Electrostatics
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Electrostatics Problem Set #1: 1.5, 1.7, 1.12 (Due Monday Feb. 11th) 1.1 Electric field Coulomb showed experimentally that for two point charges the force is -proportionaltoeachofthecharges,
Chapter 1 Introduction to Electrostatics Problem Set #1: 1.5, 1.7, 1.12 (Due Monday Feb. 11th) 1.1 Electric field Coulomb showed experimentally that for two point charges the force is -proportionaltoeachofthecharges,
Chapter 5. Magnetostatics
 Chapter 5. Magnetostatics 5.1 The Lorentz Force Law 5.1.1 Magnetic Fields Consider the forces between charges in motion Attraction of parallel currents and Repulsion of antiparallel ones: How do you explain
Chapter 5. Magnetostatics 5.1 The Lorentz Force Law 5.1.1 Magnetic Fields Consider the forces between charges in motion Attraction of parallel currents and Repulsion of antiparallel ones: How do you explain
Holding Magnetic Field
 Holding Magnetic Field Abstract The design of a solenoid to produce the required rotating/holding magnetic field in the n- 3 He experiment is presented The solenoid is constructed using 19 currents which
Holding Magnetic Field Abstract The design of a solenoid to produce the required rotating/holding magnetic field in the n- 3 He experiment is presented The solenoid is constructed using 19 currents which
Gravitational Poynting theorem: interaction of gravitation and electromagnetism
 Graitational Poynting theorem 433 Journal of Foundations of Physics and Chemistry, 0, ol. (4) 433 440 Graitational Poynting theorem: interaction of graitation and electromagnetism M.W. Eans Alpha Institute
Graitational Poynting theorem 433 Journal of Foundations of Physics and Chemistry, 0, ol. (4) 433 440 Graitational Poynting theorem: interaction of graitation and electromagnetism M.W. Eans Alpha Institute
Physics Lecture: 09
 Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Physics 2113 Lecture: 09 Flux Capacitor (Schematic) Gauss Law II Carl Friedrich Gauss 1777 1855 Gauss Law: General Case Consider any ARBITRARY CLOSED surface S -- NOTE: this
Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Physics 2113 Lecture: 09 Flux Capacitor (Schematic) Gauss Law II Carl Friedrich Gauss 1777 1855 Gauss Law: General Case Consider any ARBITRARY CLOSED surface S -- NOTE: this
Theory of Electromagnetic Nondestructive Evaluation
 EE 6XX Theory of Electromagnetic NDE: Theoretical Methods for Electromagnetic Nondestructive Evaluation 1915 Scholl Road CNDE Ames IA 50011 Graduate Tutorial Notes 2004 Theory of Electromagnetic Nondestructive
EE 6XX Theory of Electromagnetic NDE: Theoretical Methods for Electromagnetic Nondestructive Evaluation 1915 Scholl Road CNDE Ames IA 50011 Graduate Tutorial Notes 2004 Theory of Electromagnetic Nondestructive
Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-340:
 Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-340: 2013 (2:35-3:25 Monday, Wednesday, Friday, Rutherford 114) http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/~gang/phys340/phys340.home.htm Instructor: Shaun Lovejoy, Rutherford Physics,
Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-340: 2013 (2:35-3:25 Monday, Wednesday, Friday, Rutherford 114) http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/~gang/phys340/phys340.home.htm Instructor: Shaun Lovejoy, Rutherford Physics,
Analysis III Solutions - Serie 12
 .. Necessary condition Let us consider the following problem for < x, y < π, u =, for < x, y < π, u y (x, π) = x a, for < x < π, u y (x, ) = a x, for < x < π, u x (, y) = u x (π, y) =, for < y < π. Find
.. Necessary condition Let us consider the following problem for < x, y < π, u =, for < x, y < π, u y (x, π) = x a, for < x < π, u y (x, ) = a x, for < x < π, u x (, y) = u x (π, y) =, for < y < π. Find
Spotlight on Laplace s Equation
 16 Spotlight on Laplace s Equation Reference: Sections 1.1,1.2, and 1.5. Laplace s equation is the undriven, linear, second-order PDE 2 u = (1) We defined diffusivity on page 587. where 2 is the Laplacian
16 Spotlight on Laplace s Equation Reference: Sections 1.1,1.2, and 1.5. Laplace s equation is the undriven, linear, second-order PDE 2 u = (1) We defined diffusivity on page 587. where 2 is the Laplacian
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS SUBJECT CODE : EC 2253 YEAR / SEMESTER : II / IV UNIT- I - STATIC ELECTRIC
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS SUBJECT CODE : EC 2253 YEAR / SEMESTER : II / IV UNIT- I - STATIC ELECTRIC
Inductance - Lecture 3
 Inductance - Lecture 3 1 Further Discussion of Faraday s Law In Lecture 2 Faraday s law was developed using the Lorentz force on a charge within a moving, conducting loop with the magnetic field is at
Inductance - Lecture 3 1 Further Discussion of Faraday s Law In Lecture 2 Faraday s law was developed using the Lorentz force on a charge within a moving, conducting loop with the magnetic field is at
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : Electro Magnetic fields : A00 : II B. Tech I
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : Electro Magnetic fields : A00 : II B. Tech I
Solutions to Laplace s Equations
 Solutions to Laplace s Equations Lecture 14: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We have seen that in the region of space where there are no sources of charge,
Solutions to Laplace s Equations Lecture 14: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We have seen that in the region of space where there are no sources of charge,
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 1
 EE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of EE Notes 1 1 Maxwell s Equations E D rt 2, V/m, rt, Wb/m T ( ) [ ] ( ) ( ) 2 rt, /m, H ( rt, ) [ A/m] B E = t (Faraday's Law) D H
EE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of EE Notes 1 1 Maxwell s Equations E D rt 2, V/m, rt, Wb/m T ( ) [ ] ( ) ( ) 2 rt, /m, H ( rt, ) [ A/m] B E = t (Faraday's Law) D H
Eddy Current Testing using the Bode 100
 Page 1 of 12 using the Bode 100 Lukas Heinzle Abstract: (ET) is a commonly used technique surface inspections of conducting materials. An eddy current sensor, namely a probe coil that produces an alternating
Page 1 of 12 using the Bode 100 Lukas Heinzle Abstract: (ET) is a commonly used technique surface inspections of conducting materials. An eddy current sensor, namely a probe coil that produces an alternating
Physical Solution of Poisson-Boltzmann Equation. Abstract
 Physical Solution of Poisson-Boltzmann Equation Rajib Chakraborty 89/3 Tanupukur Road, Dhakuria, Calcutta 7 3, West Bengal, India (Dated: August 5, 24) Abstract We correct the solution of Poisson-Boltzmann
Physical Solution of Poisson-Boltzmann Equation Rajib Chakraborty 89/3 Tanupukur Road, Dhakuria, Calcutta 7 3, West Bengal, India (Dated: August 5, 24) Abstract We correct the solution of Poisson-Boltzmann
Problem Set #3: 2.11, 2.15, 2.21, 2.26, 2.40, 2.42, 2.43, 2.46 (Due Thursday Feb. 27th)
 Chapter Electrostatics Problem Set #3:.,.5,.,.6,.40,.4,.43,.46 (Due Thursday Feb. 7th). Coulomb s Law Coulomb showed experimentally that for two point charges the force is - proportional to each of the
Chapter Electrostatics Problem Set #3:.,.5,.,.6,.40,.4,.43,.46 (Due Thursday Feb. 7th). Coulomb s Law Coulomb showed experimentally that for two point charges the force is - proportional to each of the
ENGI 4430 Gauss & Stokes Theorems; Potentials Page 10.01
 ENGI 443 Gauss & tokes heorems; Potentials Page.. Gauss Divergence heorem Let be a piecewise-smooth closed surface enclosing a volume in vector field. hen the net flux of F out of is F d F d, N 3 and let
ENGI 443 Gauss & tokes heorems; Potentials Page.. Gauss Divergence heorem Let be a piecewise-smooth closed surface enclosing a volume in vector field. hen the net flux of F out of is F d F d, N 3 and let
Time-varying electromagnetic field
 Chapter 5 Time-varying electromagnetic field In this chapter we take up the time-varying electromagnetic field. By this study, we will be able to understand in a systematic way that actually the electric
Chapter 5 Time-varying electromagnetic field In this chapter we take up the time-varying electromagnetic field. By this study, we will be able to understand in a systematic way that actually the electric
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Chapter 1. Electric Fields 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Triboelectric Effect 1.3 Experiments with Pith Balls 1.4 Experiments with a Gold-leaf Electroscope 1.5 Coulomb s Law 1.6 Electric
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Chapter 1. Electric Fields 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Triboelectric Effect 1.3 Experiments with Pith Balls 1.4 Experiments with a Gold-leaf Electroscope 1.5 Coulomb s Law 1.6 Electric
Hydroelastic vibration of a rectangular perforated plate with a simply supported boundary condition
 Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems IV 63 Hydroelastic vibration of a rectangular perforated plate with a simply supported boundary condition K.-H. Jeong, G.-M. Lee, T.-W. Kim & J.-I.
Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems IV 63 Hydroelastic vibration of a rectangular perforated plate with a simply supported boundary condition K.-H. Jeong, G.-M. Lee, T.-W. Kim & J.-I.
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt =
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt =
Summary on Units, Dimensions and Conversions on Electrodynamics
 Summary on Units, Dimensions and Conversions on Electrodynamics Summary on Units, Dimensions and Conversions on Electrodynamics Dongwook Lee Abstract. In this short note, we summarize five different units
Summary on Units, Dimensions and Conversions on Electrodynamics Summary on Units, Dimensions and Conversions on Electrodynamics Dongwook Lee Abstract. In this short note, we summarize five different units
Chapter 1. Introduction to Electrostatics
 Chapter. Introduction to Electrostatics. Electric charge, Coulomb s Law, and Electric field Electric charge Fundamental and characteristic property of the elementary particles There are two and only two
Chapter. Introduction to Electrostatics. Electric charge, Coulomb s Law, and Electric field Electric charge Fundamental and characteristic property of the elementary particles There are two and only two
Measurement of electric potential fields
 Measurement of electric potential fields Matthew Krupcale, Oliver Ernst Department of Physics, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland Ohio, 44106-7079 18 November 2012 Abstract In electrostatics, Laplace
Measurement of electric potential fields Matthew Krupcale, Oliver Ernst Department of Physics, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland Ohio, 44106-7079 18 November 2012 Abstract In electrostatics, Laplace
Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-12) Solution 1 From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have.
 For 2 weeks course only Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-2 Solution From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have F e at2 e at2 e it dt e at2 +(it/a dt ( setting (
For 2 weeks course only Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-2 Solution From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have F e at2 e at2 e it dt e at2 +(it/a dt ( setting (
EECS 117. Lecture 25: Field Theory of T-Lines and Waveguides. Prof. Niknejad. University of California, Berkeley
 EECS 117 Lecture 25: Field Theory of T-Lines and Waveguides Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 25 p. 1/2 Waveguides and Transmission Lines
EECS 117 Lecture 25: Field Theory of T-Lines and Waveguides Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 25 p. 1/2 Waveguides and Transmission Lines
EM concept map. Field laws. No monopoles. Gauss s law. Conservation laws. equations (In vacuum) Ampere s law. radiation. Faraday s law.
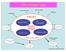 EM concept map radiation Conservation laws Special relativity EM waves Field laws Gauss s law No monopoles electrostatics Faraday s law Conservation Maxwell s laws equations (In vacuum) Ampere s law magnetostatics
EM concept map radiation Conservation laws Special relativity EM waves Field laws Gauss s law No monopoles electrostatics Faraday s law Conservation Maxwell s laws equations (In vacuum) Ampere s law magnetostatics
MATH 31BH Homework 1 Solutions
 MATH 3BH Homework Solutions January 0, 04 Problem.5. (a) (x, y)-plane in R 3 is closed and not open. To see that this plane is not open, notice that any ball around the origin (0, 0, 0) will contain points
MATH 3BH Homework Solutions January 0, 04 Problem.5. (a) (x, y)-plane in R 3 is closed and not open. To see that this plane is not open, notice that any ball around the origin (0, 0, 0) will contain points
Linearized theory of elasticity
 Linearized theory of elasticity Arie Verhoeven averhoev@win.tue.nl CASA Seminar, May 24, 2006 Seminar: Continuum mechanics 1 Stress and stress principles Bart Nowak March 8 2 Strain and deformation Mark
Linearized theory of elasticity Arie Verhoeven averhoev@win.tue.nl CASA Seminar, May 24, 2006 Seminar: Continuum mechanics 1 Stress and stress principles Bart Nowak March 8 2 Strain and deformation Mark
Electrical polarization. Figure 19-5 [1]
![Electrical polarization. Figure 19-5 [1] Electrical polarization. Figure 19-5 [1]](/thumbs/81/84036296.jpg) Electrical polarization Figure 19-5 [1] Properties of Charge Two types: positive and negative Like charges repel, opposite charges attract Charge is conserved Fundamental particles with charge: electron
Electrical polarization Figure 19-5 [1] Properties of Charge Two types: positive and negative Like charges repel, opposite charges attract Charge is conserved Fundamental particles with charge: electron
Introduction and Review Lecture 1
 Introduction and Review Lecture 1 1 Fields 1.1 Introduction This class deals with classical electrodynamics. Classical electrodynamics is the exposition of electromagnetic interactions between the develoment
Introduction and Review Lecture 1 1 Fields 1.1 Introduction This class deals with classical electrodynamics. Classical electrodynamics is the exposition of electromagnetic interactions between the develoment
Review of Electrostatics. Define the gradient operation on a field F = F(x, y, z) by;
 Review of Electrostatics 1 Gradient Define the gradient operation on a field F = F(x, y, z) by; F = ˆx F x + ŷ F y + ẑ F z This operation forms a vector as may be shown by its transformation properties
Review of Electrostatics 1 Gradient Define the gradient operation on a field F = F(x, y, z) by; F = ˆx F x + ŷ F y + ẑ F z This operation forms a vector as may be shown by its transformation properties
Reflection of Plane Electromagnetic Wave from Conducting Plane
 Reflection of Plane Electromagnetic Wave from Conducting Plane Zafar Turakulov August 19, 2014 Abstract The phenomenon of reflection from conducting surface is considered in terms of exact solutions of
Reflection of Plane Electromagnetic Wave from Conducting Plane Zafar Turakulov August 19, 2014 Abstract The phenomenon of reflection from conducting surface is considered in terms of exact solutions of
Lecture 20 Ampère s Law
 Lecture 20 Ampère s Law Sections: 7.2, partially 7.7 Homework: See homework file Ampère s Law in ntegral Form 1 the field of a straight wire with current (Lecture 19) B H = = a a φ φ µ, T 2πρ, A/m 2πρ
Lecture 20 Ampère s Law Sections: 7.2, partially 7.7 Homework: See homework file Ampère s Law in ntegral Form 1 the field of a straight wire with current (Lecture 19) B H = = a a φ φ µ, T 2πρ, A/m 2πρ
