Maxwell s equations. Kyoto. James Clerk Maxwell. Physics 122. James Clerk Maxwell ( ) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions
|
|
|
- Francine Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Maxwell s equations Physics /5/ Lecture XXIV Kyoto /5/ Lecture XXIV James Clerk Maxwell James Clerk Maxwell (83 879) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions /5/ Lecture XXIV 3
2 Φ = da = Q ε Gauss s law the number of field lines that go in = the number of field lines that go out, unless there are sinks (negative charges) or sources (positive charges) /5/ Lecture IV 4 Gauss s law for magnetic field Can you guess: Φ = da =? /5/ Lecture XXIV 5 Gauss s law for magnetic field You can never separate north end of the magnet from south end à There are no magnetic charges (monopoles) - no sinks or sources à magnetic field lines are always closed à magnetic flux through any is always zero Φ = da = /5/ Lecture XXIV 6
3 Faraday s law of induction: Changing Φ generates Magnetic flux is increasing è induced emf: emf = dφ = V l = l = V lectric current in the circuit, but What makes stationary charges moves? Induced electric field: dφ Integral of the electric field over a is equal to negative derivative of the magnetic flux over time: /5/ Lecture XXI 7 dφ dl = Ampere s Law Current = moving electric charges produce magnetic field dl = µ I encl Integral of the magnetic field over a is equal to the enclosed current /5/ Lecture XII 8 Known phenomena Currents produce magnetic field Changing magnetic field produces electricity (induction) M theory Assumptions Changing electric field is equivalent to current and also produces magnetic field Unification James Clark Maxwell (83-879): one field electromagnetic (M). /5/ Lecture XXI 9 3
4 Displacement currents A Moving charged particles Q = CV = ( ε )( d) = ε A = ε Φ d (current) create magnetic field Charged particles create dq dφ " I D"= = ε electric field lectric field is changing when particles move Changing electric field is equivalent to current displacement current I D No charges jump across the capacitor à No charges are actually moving in the displacement current I I D /5/ Lecture XXI Modified Ampere s Law Current = moving electric charges + displacement current (changing electric field) produce magnetic field dl = µ ( I + I dl = µ I encl displ ) encl dφ + µ ε dq dφ " I D"= = ε /5/ Lecture XII Gauss s Law Maxwell s equations Gauss s law for magnetic field == there no magnetic charges == magnetic filed lines are always closed Faraday s law Changing magnetic field can create electric field Amper s law + extra term introduced by Maxwell displacement current Changing electric field can create magnetic field closed Q da = ε da = dφ dl = path dφ dl = µ I + µ ε /5/ Lecture XXIV 4
5 Maxwell s equations in vacuum No charges, no currents Changing magnetic field creates electric field Changing electric field creates magnetic field closed da = da = dφ dl = path dφ dl = µ ε /5/ Lecture XXIV 3 dφ dl = path M wave dφ dl = µ ε dl = ( + d) dy dy = ddy dφ d = dxdy d d = x dx dl = ddz dφ d = µ ε = µ ε dxdz t ε µ x y y d d = v = µ ε t dx t x 8 v = = = 3. m / s ε µ π closed 7 /5/ Lecture XXIV 4 M wave v v = sin( kx ϖt) = sin( kx ϖt) v = v x y z / = v π k = λ ϖ = πf ϖ fλ = = v k /5/ Lecture XXIV 5 5
6 nergy in M wave M waves transport energy nergy density: u = ε + µ Poynting vector (energy transported by M wave per unit time per unit area) S = µ Average energy per unit time per unit area S = rms rms µ /5/ Lecture XXIV 6 Intensity of waves nergy of oscillation U is proportional to amplitude squared U Intensity I, W/m energy / time power I = = area area Intensity I is proportional to amplitude squared, inversely proportional to r : I I r r /5/ Lecture XXIV 7 Average intensity lectric fields follows harmonic oscillation: = sin( ϖt) Intensity (brightness for light) I is proportional to electric field squared I Average over time (one period of oscillation) I: = I π T I = I T π sin ( ϖt) = I sin ϖt xdx = I π ϖt π /5/ Lecture XXIV 8 I = I sin ( ϖt) sin ( ϖt) dϖt = I ( cos x) dx = 6
7 λ M spectrum f c = fλ c speed of light (m/s) f frequency (Hz=/s) λ wavelength (m) /5/ Lecture XXIV 9 Radiation from an AC antenna Changing electric field creates magnetic field Changing magnetic field creates electric field Change propagates with a finite velocity lectromagnetic wave proof of unification /5/ Lecture XXIV Transmission and reception Antennas are used to transmit and to receive M waves Rod antennas transmit and receive component to rod Loop antennas component (use induction) loop /5/ Lecture XXIV 7
8 Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Frequency modulation (FM) /5/ Lecture XXIV 8
Motional Electromotive Force
 Motional Electromotive Force The charges inside the moving conductive rod feel the Lorentz force The charges drift toward the point a of the rod The accumulating excess charges at point a create an electric
Motional Electromotive Force The charges inside the moving conductive rod feel the Lorentz force The charges drift toward the point a of the rod The accumulating excess charges at point a create an electric
Maxwell s equations and EM waves. From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law
 Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
PHYS 1441 Section 001 Lecture #24 Wednesday, Dec. 6, 2017 Dr. Animesh Chatterjee
 PHYS 1441 Section 1 Lecture #4 Dr. Animesh Chatterjee Chapter 3: Inductance AC Circuit W/ LRC Chapter 31: Maxwell s Equations Expansion of Ampere s Law Gauss Law for Magnetism Production of EM Waves Light
PHYS 1441 Section 1 Lecture #4 Dr. Animesh Chatterjee Chapter 3: Inductance AC Circuit W/ LRC Chapter 31: Maxwell s Equations Expansion of Ampere s Law Gauss Law for Magnetism Production of EM Waves Light
Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory
 Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory Lecture topics Laws of magnetism and electricity Meaning of Maxwell s equations Solution of Maxwell s equations Electromagnetic radiation: wave model James Clerk
Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory Lecture topics Laws of magnetism and electricity Meaning of Maxwell s equations Solution of Maxwell s equations Electromagnetic radiation: wave model James Clerk
Maxwell s Equations & Electromagnetic Waves. The Equations So Far...
 Maxwell s Equations & Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations contain the wave equation Velocity of electromagnetic waves c = 2.99792458 x 1 8 m/s Relationship between E and B in an EM wave Energy in
Maxwell s Equations & Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations contain the wave equation Velocity of electromagnetic waves c = 2.99792458 x 1 8 m/s Relationship between E and B in an EM wave Energy in
PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #22
 PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #22 Monday, April 23, 2012 Dr. Extension of Ampere s Law Gauss Law of Magnetism Maxwell s Equations Production of Electromagnetic Waves Today s homework is #13, due 10pm,
PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #22 Monday, April 23, 2012 Dr. Extension of Ampere s Law Gauss Law of Magnetism Maxwell s Equations Production of Electromagnetic Waves Today s homework is #13, due 10pm,
Transformers. slide 1
 Transformers an alternating emf V1 through the primary coil causes an oscillating magnetic flux through the secondary coil and, hence, an induced emf V2. The induced emf of the secondary coil is delivered
Transformers an alternating emf V1 through the primary coil causes an oscillating magnetic flux through the secondary coil and, hence, an induced emf V2. The induced emf of the secondary coil is delivered
PHYS 1444 Section 003 Lecture #23
 PHYS 1444 Section 3 Lecture #3 Monday, Nov. 8, 5 EM Waves from Maxwell s Equations Speed of EM Waves Light as EM Wave Electromagnetic Spectrum Energy in EM Waves Energy Transport The epilogue Today s homework
PHYS 1444 Section 3 Lecture #3 Monday, Nov. 8, 5 EM Waves from Maxwell s Equations Speed of EM Waves Light as EM Wave Electromagnetic Spectrum Energy in EM Waves Energy Transport The epilogue Today s homework
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
EMF Notes 11; Maxwell s Equations. MAXWELL S EQUATIONS Maxwell s four equations
 MAXWELL S EQUATONS Maxwell s four equations n the 870 s, James Clerk Maxwell showed that four equations constitute a complete description of the electric and magnetic fields, or THE ELECTROMAGNETC FELD
MAXWELL S EQUATONS Maxwell s four equations n the 870 s, James Clerk Maxwell showed that four equations constitute a complete description of the electric and magnetic fields, or THE ELECTROMAGNETC FELD
INTRODUCTION ELECTRODYNAMICS BEFORE MAXWELL MAXWELL S DISPLACEMENT CURRENT. Introduction Z B S. E l = Electrodynamics before Maxwell
 Chapter 14 MAXWELL S EQUATONS ntroduction Electrodynamics before Maxwell Maxwell s displacement current Maxwell s equations: General Maxwell s equations in vacuum The mathematics of waves Summary NTRODUCTON
Chapter 14 MAXWELL S EQUATONS ntroduction Electrodynamics before Maxwell Maxwell s displacement current Maxwell s equations: General Maxwell s equations in vacuum The mathematics of waves Summary NTRODUCTON
EM Waves. From previous Lecture. This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization. Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves
 EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
Chapter 31. Faraday s Law
 Chapter 31 Faraday s Law 1 Ampere s law Magnetic field is produced by time variation of electric field dφ B ( I I ) E d s = µ o + d = µ o I+ µ oεo ds E B 2 Induction A loop of wire is connected to a sensitive
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law 1 Ampere s law Magnetic field is produced by time variation of electric field dφ B ( I I ) E d s = µ o + d = µ o I+ µ oεo ds E B 2 Induction A loop of wire is connected to a sensitive
Problem Fig
 Problem 9.53 A flexible circular loop 6.50 cm in diameter lies in a magnetic field with magnitude 0.950 T, directed into the plane of the page, as shown. The loop is pulled at the points indicated by the
Problem 9.53 A flexible circular loop 6.50 cm in diameter lies in a magnetic field with magnitude 0.950 T, directed into the plane of the page, as shown. The loop is pulled at the points indicated by the
Lecture 36: WED 18 NOV CH32: Maxwell s Equations I
 Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 36: WED 18 NOV H32: Maxwell s Equations I James lerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Maxwell I: Gauss Law for E-Fields: charges produce electric fields, field lines start and
Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 36: WED 18 NOV H32: Maxwell s Equations I James lerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Maxwell I: Gauss Law for E-Fields: charges produce electric fields, field lines start and
Electromagnetic Induction and Waves (Chapters 33-34)
 Electromagnetic nduction and Waves (Chapters 33-34) The laws of emf induction: Faraday s and Lenz s laws Concepts of classical electromagnetism. Maxwell equations nductance Mutual inductance M Self inductance
Electromagnetic nduction and Waves (Chapters 33-34) The laws of emf induction: Faraday s and Lenz s laws Concepts of classical electromagnetism. Maxwell equations nductance Mutual inductance M Self inductance
Electromagnetism Physics 15b
 Electromagnetism Physics 15b Lecture #18 Maxwell s Equations Electromagnetic Waves Purcell 9.1 9.4 What We Did Last Time Impedance of R,, and L Z R = V R = R Z I = V = 1 Z R I iω L = V L = iωl I L Generally
Electromagnetism Physics 15b Lecture #18 Maxwell s Equations Electromagnetic Waves Purcell 9.1 9.4 What We Did Last Time Impedance of R,, and L Z R = V R = R Z I = V = 1 Z R I iω L = V L = iωl I L Generally
Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance
 Lesson 7 Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance Oscillations in an LC Circuit The RLC Circuit Alternating Current Electromagnetic
Lesson 7 Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance Oscillations in an LC Circuit The RLC Circuit Alternating Current Electromagnetic
1 Maxwell s Equations
 PHYS 280 Lecture problems outline Spring 2015 Electricity and Magnetism We previously hinted a links between electricity and magnetism, finding that one can induce electric fields by changing the flux
PHYS 280 Lecture problems outline Spring 2015 Electricity and Magnetism We previously hinted a links between electricity and magnetism, finding that one can induce electric fields by changing the flux
Maxwell Equations: Electromagnetic Waves
 Maxwell Equations: Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s Equations contain the wave equation The velocity of electromagnetic waves: c = 2.99792458 x 10 8 m/s The relationship between E and B in an EM wave Energy
Maxwell Equations: Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s Equations contain the wave equation The velocity of electromagnetic waves: c = 2.99792458 x 10 8 m/s The relationship between E and B in an EM wave Energy
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 38/Page 1
 PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 38/Page 1 Today: Start last chapter 32 - Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Scottish mathematical physicist. He united all observations, experiments
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 38/Page 1 Today: Start last chapter 32 - Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Scottish mathematical physicist. He united all observations, experiments
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields
 Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 23 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION, AC CIRCUITS, AND ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGIES
 COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 23 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION, AC CIRCUITS, AND ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGIES Induced emf: Faraday s Law and Lenz s Law We observe that, when a magnet is moved near a conducting loop,
COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 23 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION, AC CIRCUITS, AND ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGIES Induced emf: Faraday s Law and Lenz s Law We observe that, when a magnet is moved near a conducting loop,
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I)
 Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
CHAPTER 32: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 CHAPTER 32: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES For those of you who are interested, below are the differential, or point, form of the four Maxwell s equations we studied this semester. The version of Maxwell s equations
CHAPTER 32: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES For those of you who are interested, below are the differential, or point, form of the four Maxwell s equations we studied this semester. The version of Maxwell s equations
Course Updates. 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves +
 Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr1/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #11 due Wednesday 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves + 3) In the home stretch [review schedule]
Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr1/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #11 due Wednesday 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves + 3) In the home stretch [review schedule]
MCQs E M WAVES. Physics Without Fear.
 MCQs E M WAVES Physics Without Fear Electromagnetic Waves At A Glance Ampere s law B. dl = μ 0 I relates magnetic fields due to current sources. Maxwell argued that this law is incomplete as it does not
MCQs E M WAVES Physics Without Fear Electromagnetic Waves At A Glance Ampere s law B. dl = μ 0 I relates magnetic fields due to current sources. Maxwell argued that this law is incomplete as it does not
Introduction to Electromagnetism
 Introduction to Electromagnetism Electric Field Lines If a charge feels an electrostatic force (Coulombic Force), it is said to be in an electric field. We like to represent electric fields with lines.
Introduction to Electromagnetism Electric Field Lines If a charge feels an electrostatic force (Coulombic Force), it is said to be in an electric field. We like to represent electric fields with lines.
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9. Maxwell s Equations. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2012 1 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2012 1 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields
AC Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
 AC Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves Physics 102 Lecture 5 7 March 2002 MIDTERM Wednesday, March 13, 7:30-9:00 pm, this room Material: through next week AC circuits Next week: no lecture, no labs, no
AC Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves Physics 102 Lecture 5 7 March 2002 MIDTERM Wednesday, March 13, 7:30-9:00 pm, this room Material: through next week AC circuits Next week: no lecture, no labs, no
Principles of Mobile Communications
 Communication Networks 1 Principles of Mobile Communications University Duisburg-Essen WS 2003/2004 Page 1 N e v e r s t o p t h i n k i n g. Wave Propagation Single- and Multipath Propagation Overview:
Communication Networks 1 Principles of Mobile Communications University Duisburg-Essen WS 2003/2004 Page 1 N e v e r s t o p t h i n k i n g. Wave Propagation Single- and Multipath Propagation Overview:
Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy.
 Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy. Outline: Self-induction and self-inductance. Inductance of a solenoid. The energy of a magnetic field. Alternative definition of inductance. Mutual Inductance.
Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy. Outline: Self-induction and self-inductance. Inductance of a solenoid. The energy of a magnetic field. Alternative definition of inductance. Mutual Inductance.
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9. Maxwell s Equations. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2013 1 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2013 1 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields
1830s Michael Faraday Joseph Henry. Induced EMF
 1830s Michael Faraday Joseph Henry Induced EMF There can be EMF produced in a number of ways: A time varying magnetic field An area whose size is varying A time varying angle between r and Any combination
1830s Michael Faraday Joseph Henry Induced EMF There can be EMF produced in a number of ways: A time varying magnetic field An area whose size is varying A time varying angle between r and Any combination
Lecture Sound Waves EM Waves. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org. The Doppler Effect 11/11/2014
 Lecture 1102 Sound Waves EM Waves Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift) is the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave for an observer moving
Lecture 1102 Sound Waves EM Waves Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift) is the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave for an observer moving
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
 UNIT-III INTRODUCTION: In our study of static fields so far, we have observed that static electric fields are produced by electric charges, static magnetic fields are produced by charges in motion or by
UNIT-III INTRODUCTION: In our study of static fields so far, we have observed that static electric fields are produced by electric charges, static magnetic fields are produced by charges in motion or by
Electromagnetic Induction
 Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 8_4_2008 Topics for Chapter
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 8_4_2008 Topics for Chapter
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
ε induced Review: Self-inductance 20.7 RL Circuits Review: Self-inductance B induced Announcements
 Announcements WebAssign HW Set 7 due this Friday Problems cover material from Chapters 20 and 21 We re skipping Sections 21.1-21.7 (alternating current circuits) Review: Self-inductance induced ε induced
Announcements WebAssign HW Set 7 due this Friday Problems cover material from Chapters 20 and 21 We re skipping Sections 21.1-21.7 (alternating current circuits) Review: Self-inductance induced ε induced
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Electromagnetic Oscillations Physics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 8! We have been working with circuits that have a constant current a current that increases to a constant current
Electromagnetic Oscillations Physics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 8! We have been working with circuits that have a constant current a current that increases to a constant current
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
Chapter 31. Faraday s Law
 Chapter 31 Faraday s Law 1 Ampere s law Magnetic field is produced by time variation of electric field B s II I d d μ o d μo με o o E ds E B Induction A loop of wire is connected to a sensitive ammeter
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law 1 Ampere s law Magnetic field is produced by time variation of electric field B s II I d d μ o d μo με o o E ds E B Induction A loop of wire is connected to a sensitive ammeter
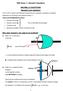
Along with C1 the magnetic field is also observed at location C 2 though no current is threading through this loop.
 Displacement current British physicist James C. Maxwell gave final shape to all phenomenon connecting electricity and magnetism. He noticed an inconsistency in Ampere s Law connecting Electric current
Displacement current British physicist James C. Maxwell gave final shape to all phenomenon connecting electricity and magnetism. He noticed an inconsistency in Ampere s Law connecting Electric current
UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields)
 UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields) Faraday s law, transformer emf &inconsistency of ampere s law Displacement current density Maxwell s equations in final form Maxwell s equations in word
UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields) Faraday s law, transformer emf &inconsistency of ampere s law Displacement current density Maxwell s equations in final form Maxwell s equations in word
Lecture 33. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 33 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Faraday s law of induction When the magnetic flux through a single closed loop changes with time, there is an induced emf that can drive a current around the loop: Recall
Lecture 33 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Faraday s law of induction When the magnetic flux through a single closed loop changes with time, there is an induced emf that can drive a current around the loop: Recall
CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION So far we have seen that electric charges are the source for both electric and magnetic fields. We have also seen that these fields can exert forces on other electric
CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION So far we have seen that electric charges are the source for both electric and magnetic fields. We have also seen that these fields can exert forces on other electric
Where k = 1. The electric field produced by a point charge is given by
 Ch 21 review: 1. Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of a matter. There are two kinds of charges, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other. Charges of opposite sign attract.
Ch 21 review: 1. Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of a matter. There are two kinds of charges, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other. Charges of opposite sign attract.
Oscillations and Electromagnetic Waves. March 30, 2014 Chapter 31 1
 Oscillations and Electromagnetic Waves March 30, 2014 Chapter 31 1 Three Polarizers! Consider the case of unpolarized light with intensity I 0 incident on three polarizers! The first polarizer has a polarizing
Oscillations and Electromagnetic Waves March 30, 2014 Chapter 31 1 Three Polarizers! Consider the case of unpolarized light with intensity I 0 incident on three polarizers! The first polarizer has a polarizing
W15D1: Poynting Vector and Energy Flow. Today s Readings: Course Notes: Sections 13.6,
 W15D1: Poynting Vector and Energy Flow Today s Readings: Course Notes: Sections 13.6, 13.12.3-13.12.4 1 Announcements Final Math Review Week 15 Tues from 9-11 pm in 32-082 Final Exam Monday Morning May
W15D1: Poynting Vector and Energy Flow Today s Readings: Course Notes: Sections 13.6, 13.12.3-13.12.4 1 Announcements Final Math Review Week 15 Tues from 9-11 pm in 32-082 Final Exam Monday Morning May
Lecture 35. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 35 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Induced electric fields A long, thin solenoid is encircled by a circular conducting loop. Electric field in the loop is what must drive the current. When the solenoid current
Lecture 35 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Induced electric fields A long, thin solenoid is encircled by a circular conducting loop. Electric field in the loop is what must drive the current. When the solenoid current
Part 4: Electromagnetism. 4.1: Induction. A. Faraday's Law. The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is
 1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
where the last equality follows from the divergence theorem. Now since we did this for an arbitrary volume τ, it must hold locally:
 8 Electrodynamics Read: Boas Ch. 6, particularly sec. 10 and 11. 8.1 Maxwell equations Some of you may have seen Maxwell s equations on t-shirts or encountered them briefly in electromagnetism courses.
8 Electrodynamics Read: Boas Ch. 6, particularly sec. 10 and 11. 8.1 Maxwell equations Some of you may have seen Maxwell s equations on t-shirts or encountered them briefly in electromagnetism courses.
W13D2: Displacement Current, Maxwell s Equations, Wave Equations. Today s Reading Course Notes: Sections
 W13D2: Displacement Current, Maxwell s Equations, Wave Equations Today s Reading Course Notes: ections 13.1-13.4 1 Announcements Math Review Tuesday May 6 from 9 pm-11 pm in 26-152 Pset 10 due May 6 at
W13D2: Displacement Current, Maxwell s Equations, Wave Equations Today s Reading Course Notes: ections 13.1-13.4 1 Announcements Math Review Tuesday May 6 from 9 pm-11 pm in 26-152 Pset 10 due May 6 at
Magnetic Fields Part 3: Electromagnetic Induction
 Magnetic Fields Part 3: Electromagnetic Induction Last modified: 15/12/2017 Contents Links Electromagnetic Induction Induced EMF Induced Current Induction & Magnetic Flux Magnetic Flux Change in Flux Faraday
Magnetic Fields Part 3: Electromagnetic Induction Last modified: 15/12/2017 Contents Links Electromagnetic Induction Induced EMF Induced Current Induction & Magnetic Flux Magnetic Flux Change in Flux Faraday
Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecture 20 Chapter 34 Physics II Electromagnetic Waves Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Let s finish climbing our EM mountain. Maxwell s equations Let s revisit
Lecture 20 Chapter 34 Physics II Electromagnetic Waves Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Let s finish climbing our EM mountain. Maxwell s equations Let s revisit
Yell if you have any questions
 Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 efore Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 efore Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy.
 Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy. Outline: Self-induction and self-inductance. Inductance of a solenoid. The energy of a magnetic field. Alternative definition of inductance. Mutual Inductance.
Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy. Outline: Self-induction and self-inductance. Inductance of a solenoid. The energy of a magnetic field. Alternative definition of inductance. Mutual Inductance.
Physics 2102 Gabriela González. Marathon review of the course: 15 weeks in ~60 minutes!
 Physics 2102 Gabriela González Marathon review of the course: 15 weeks in ~60 minutes! Fields: electric & magnetic electric and magnetic forces on electric charges potential energy, electric potential,
Physics 2102 Gabriela González Marathon review of the course: 15 weeks in ~60 minutes! Fields: electric & magnetic electric and magnetic forces on electric charges potential energy, electric potential,
Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves. Slide 29-1
 Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves Slide 29-1 Equations of electromagnetism: a review We ve now seen the four fundamental equations of electromagnetism, here listed together for the first time.
Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves Slide 29-1 Equations of electromagnetism: a review We ve now seen the four fundamental equations of electromagnetism, here listed together for the first time.
Exam 3 Solutions. The induced EMF (magnitude) is given by Faraday s Law d dt dt The current is given by
 PHY049 Spring 008 Prof. Darin Acosta Prof. Selman Hershfield April 9, 008. A metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity of 60 cm/s [or 90 cm/s] along two parallel metal rails, which are connected
PHY049 Spring 008 Prof. Darin Acosta Prof. Selman Hershfield April 9, 008. A metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity of 60 cm/s [or 90 cm/s] along two parallel metal rails, which are connected
While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations
 Unit 2 Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equations While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields,
Unit 2 Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equations While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields,
Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits
 Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits Inductance Temporarily storage of energy by the magnetic field When the switch is closed, the current does not immediately reach its maximum value. Faraday s law of electromagnetic
Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits Inductance Temporarily storage of energy by the magnetic field When the switch is closed, the current does not immediately reach its maximum value. Faraday s law of electromagnetic
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 21 Chapter 30 sec. 1-4 Fall 2012 Semester Matthew Jones Question An LC circuit has =100 and =100. If it oscillates with an amplitude of 100 mv, what is the amplitude
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 21 Chapter 30 sec. 1-4 Fall 2012 Semester Matthew Jones Question An LC circuit has =100 and =100. If it oscillates with an amplitude of 100 mv, what is the amplitude
Chapter 31: Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law All sections covered.
 About Exam 3 When and where (same as before) Monday Nov. 22 rd 5:30-7:00 pm Bascom 272: Sections 301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 311,322, 327, 329 Ingraham B10: Sections 306, 307, 312, 321, 323, 324, 325, 328,
About Exam 3 When and where (same as before) Monday Nov. 22 rd 5:30-7:00 pm Bascom 272: Sections 301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 311,322, 327, 329 Ingraham B10: Sections 306, 307, 312, 321, 323, 324, 325, 328,
Pretty electromagnetic waves: a rainbow over the Potala Palace, Lhasa, Tibet; photo by Galen Rowell. 27 November 2012 Physics 122, Fall
 Today in Physics 122: the Maxwell equations Ampère s law is broken, and Maxwell fixes it. Gauss s law for magnetic fields. The Maxwell equations. The Maxwell equations in vacuum lead to a wave equation.
Today in Physics 122: the Maxwell equations Ampère s law is broken, and Maxwell fixes it. Gauss s law for magnetic fields. The Maxwell equations. The Maxwell equations in vacuum lead to a wave equation.
ELECTRO MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SET - 1 1. a) State and explain Gauss law in differential form and also list the limitations of Guess law. b) A square sheet defined by -2 x 2m, -2 y 2m lies in the = -2m plane. The charge density on the
SET - 1 1. a) State and explain Gauss law in differential form and also list the limitations of Guess law. b) A square sheet defined by -2 x 2m, -2 y 2m lies in the = -2m plane. The charge density on the
 E.M.WAVES 1. Taller the antenna longer is the coverage of television broadcast. Justify this statement with the help of a figure. 2.If v g, v x v m represents the speed of gamma rays, X-rays microwaves
E.M.WAVES 1. Taller the antenna longer is the coverage of television broadcast. Justify this statement with the help of a figure. 2.If v g, v x v m represents the speed of gamma rays, X-rays microwaves
Driven RLC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions
 Driven LC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions Problem : Using the same circuit as in problem 6, only this time leaving the function generator on and driving below resonance, which in the following pairs
Driven LC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions Problem : Using the same circuit as in problem 6, only this time leaving the function generator on and driving below resonance, which in the following pairs
Slide 1 / 24. Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger
 Slide 1 / 24 Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 24 Induced Currents If we have a galvanometer attached to a coil of wire we can induce a current simply by changing the magnetic
Slide 1 / 24 Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 24 Induced Currents If we have a galvanometer attached to a coil of wire we can induce a current simply by changing the magnetic
Last Homework. Reading: Chap. 33 and Chap. 33. Suggested exercises: 33.1, 33.3, 33.5, 33.7, 33.9, 33.11, 33.13, 33.15,
 Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic induction is the scientific principle that underlies many modern technologies, from the generation of electricity to communications and data storage.
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic induction is the scientific principle that underlies many modern technologies, from the generation of electricity to communications and data storage.
toroidal iron core compass switch battery secondary coil primary coil
 Fundamental Laws of Electrostatics Integral form Differential form d l C S E 0 E 0 D d s V q ev dv D ε E D qev 1 Fundamental Laws of Magnetostatics Integral form Differential form C S dl S J d s B d s
Fundamental Laws of Electrostatics Integral form Differential form d l C S E 0 E 0 D d s V q ev dv D ε E D qev 1 Fundamental Laws of Magnetostatics Integral form Differential form C S dl S J d s B d s
Exam 3: Tuesday, April 18, 5:00-6:00 PM
 Exam 3: Tuesday, April 18, 5:-6: PM Test rooms: Instructor Sections Room Dr. Hale F, H 14 Physics Dr. Kurter, N 15 CH Dr. Madison K, M 199 Toomey Dr. Parris J, L -1 ertelsmeyer Mr. Upshaw A, C, E, G G-3
Exam 3: Tuesday, April 18, 5:-6: PM Test rooms: Instructor Sections Room Dr. Hale F, H 14 Physics Dr. Kurter, N 15 CH Dr. Madison K, M 199 Toomey Dr. Parris J, L -1 ertelsmeyer Mr. Upshaw A, C, E, G G-3
Lecture 22 Chapter 31 Maxwell s equations
 Lecture 22 Chapter 31 Maxwell s equations Finally, I see the goal, the summit of this Everest Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 31: Section 31.2-4 Let s revisit Ampere s Law a straight wire with current
Lecture 22 Chapter 31 Maxwell s equations Finally, I see the goal, the summit of this Everest Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 31: Section 31.2-4 Let s revisit Ampere s Law a straight wire with current
Maxwell s Omission #1
 Absttractt: :: By Robert J Distinti B.S. EE 46 Rutland Ave. Fairfield Ct 06825. (203) 331-9696 Maxwell s Omission #1 Maxwell went to great length to derive point equations from the classical models that
Absttractt: :: By Robert J Distinti B.S. EE 46 Rutland Ave. Fairfield Ct 06825. (203) 331-9696 Maxwell s Omission #1 Maxwell went to great length to derive point equations from the classical models that
Sliding Conducting Bar
 Motional emf, final For equilibrium, qe = qvb or E = vb A potential difference is maintained between the ends of the conductor as long as the conductor continues to move through the uniform magnetic field
Motional emf, final For equilibrium, qe = qvb or E = vb A potential difference is maintained between the ends of the conductor as long as the conductor continues to move through the uniform magnetic field
Magnetostatic fields! steady magnetic fields produced by steady (DC) currents or stationary magnetic materials.
 ECE 3313 Electromagnetics I! Static (time-invariant) fields Electrostatic or magnetostatic fields are not coupled together. (one can exist without the other.) Electrostatic fields! steady electric fields
ECE 3313 Electromagnetics I! Static (time-invariant) fields Electrostatic or magnetostatic fields are not coupled together. (one can exist without the other.) Electrostatic fields! steady electric fields
INDUCTANCE Self Inductance
 NDUTANE 3. Self nductance onsider the circuit shown in the Figure. When the switch is closed the current, and so the magnetic field, through the circuit increases from zero to a specific value. The increasing
NDUTANE 3. Self nductance onsider the circuit shown in the Figure. When the switch is closed the current, and so the magnetic field, through the circuit increases from zero to a specific value. The increasing
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
Poynting Vector and Energy Flow W14D1
 Poynting Vector and Energy Flow W14D1 1 Announcements Week 14 Prepset due online Friday 8:30 am PS 11 due Week 14 Friday at 9 pm in boxes outside 26-152 Sunday Tutoring 1-5 pm in 26-152 2 Outline Poynting
Poynting Vector and Energy Flow W14D1 1 Announcements Week 14 Prepset due online Friday 8:30 am PS 11 due Week 14 Friday at 9 pm in boxes outside 26-152 Sunday Tutoring 1-5 pm in 26-152 2 Outline Poynting
Physics 201. Professor P. Q. Hung. 311B, Physics Building. Physics 201 p. 1/3
 Physics 201 p. 1/3 Physics 201 Professor P. Q. Hung 311B, Physics Building Physics 201 p. 2/3 What are electromagnetic waves? Electromagnetic waves consist of electric fields and magnetic fields which
Physics 201 p. 1/3 Physics 201 Professor P. Q. Hung 311B, Physics Building Physics 201 p. 2/3 What are electromagnetic waves? Electromagnetic waves consist of electric fields and magnetic fields which
Physics 4. Magnetic Induction. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 4 Magnetic Induction Before we can talk about induction we need to understand magnetic flux. You can think of flux as the number of field lines passing through an area. Here is the formula: flux
Physics 4 Magnetic Induction Before we can talk about induction we need to understand magnetic flux. You can think of flux as the number of field lines passing through an area. Here is the formula: flux
About Exam 3. When and where
 When and where About Exam 3 Tuesday Nov 27th 5:30-7:00 pm (same location as Midterms 1 and 2) Format Closed book One 8x11 formula sheet allowed, must be self prepared, no photo copying/download-printing
When and where About Exam 3 Tuesday Nov 27th 5:30-7:00 pm (same location as Midterms 1 and 2) Format Closed book One 8x11 formula sheet allowed, must be self prepared, no photo copying/download-printing
E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective
 E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective Alec sees a moving charge, and he knows that this creates a magnetic field. From Brittney s perspective, the charge is at rest, so the magnetic field is zero. Is
E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective Alec sees a moving charge, and he knows that this creates a magnetic field. From Brittney s perspective, the charge is at rest, so the magnetic field is zero. Is
SUMMARY Phys 2523 (University Physics II) Compiled by Prof. Erickson. F e (r )=q E(r ) dq r 2 ˆr = k e E = V. V (r )=k e r = k q i. r i r.
 SUMMARY Phys 53 (University Physics II) Compiled by Prof. Erickson q 1 q Coulomb s Law: F 1 = k e r ˆr where k e = 1 4π =8.9875 10 9 N m /C, and =8.85 10 1 C /(N m )isthepermittivity of free space. Generally,
SUMMARY Phys 53 (University Physics II) Compiled by Prof. Erickson q 1 q Coulomb s Law: F 1 = k e r ˆr where k e = 1 4π =8.9875 10 9 N m /C, and =8.85 10 1 C /(N m )isthepermittivity of free space. Generally,
Yell if you have any questions
 Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 Before Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 Before Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Handout 10: Inductance. Self-Inductance and inductors
 1 Handout 10: Inductance Self-Inductance and inductors In Fig. 1, electric current is present in an isolate circuit, setting up magnetic field that causes a magnetic flux through the circuit itself. This
1 Handout 10: Inductance Self-Inductance and inductors In Fig. 1, electric current is present in an isolate circuit, setting up magnetic field that causes a magnetic flux through the circuit itself. This
Lecture 38: FRI 24 APR Ch.33 Electromagnetic Waves
 Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Heinrich Hertz (1857 1894) Lecture 38: FRI 24 APR Ch.33 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell Equations in Empty Space: E da = 0 S B da = 0 S C C B ds = µ ε 0 0 E ds = d dt d dt S
Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Heinrich Hertz (1857 1894) Lecture 38: FRI 24 APR Ch.33 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell Equations in Empty Space: E da = 0 S B da = 0 S C C B ds = µ ε 0 0 E ds = d dt d dt S
Chapter Three: Propagation of light waves
 Chapter Three Propagation of Light Waves CHAPTER OUTLINE 3.1 Maxwell s Equations 3.2 Physical Significance of Maxwell s Equations 3.3 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 3.4 Constitutive Relations 3.5
Chapter Three Propagation of Light Waves CHAPTER OUTLINE 3.1 Maxwell s Equations 3.2 Physical Significance of Maxwell s Equations 3.3 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 3.4 Constitutive Relations 3.5
Lecture notes for ELECTRODYNAMICS.
 Lecture notes for 640-343 ELECTRODYNAMICS. 1 Summary of Electrostatics 1.1 Coulomb s Law Force between two point charges F 12 = 1 4πɛ 0 Q 1 Q 2ˆr 12 r 1 r 2 2 (1.1.1) 1.2 Electric Field For a charge distribution:
Lecture notes for 640-343 ELECTRODYNAMICS. 1 Summary of Electrostatics 1.1 Coulomb s Law Force between two point charges F 12 = 1 4πɛ 0 Q 1 Q 2ˆr 12 r 1 r 2 2 (1.1.1) 1.2 Electric Field For a charge distribution:
The equations so far... Gauss Law for E Fields. Gauss Law for B Fields. B da. inside. d dt. n C 3/28/2018
 The equations so far... Gauss Law for E Fields E da S n 1 Q inside Gauss Law for B Fields B da S n C Faraday s Law d E dl dt S B da n Ampere s Law B dl I C 3/8/18 1 Ampere s Law B dl I inside _ path No
The equations so far... Gauss Law for E Fields E da S n 1 Q inside Gauss Law for B Fields B da S n C Faraday s Law d E dl dt S B da n Ampere s Law B dl I C 3/8/18 1 Ampere s Law B dl I inside _ path No
Electromagnetic Induction
 Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 29 Looking forward
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 29 Looking forward
Induced Electric Fields. You must understand how a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, and be able to calculate induced electric fields.
 Today s agenda: Induced lectric Fields. You must understand how a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, and be able to calculate induced electric fields. ddy Currents. You must understand how
Today s agenda: Induced lectric Fields. You must understand how a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, and be able to calculate induced electric fields. ddy Currents. You must understand how
r r 1 r r 1 2 = q 1 p = qd and it points from the negative charge to the positive charge.
 MP204, Important Equations page 1 Below is a list of important equations that we meet in our study of Electromagnetism in the MP204 module. For your exam, you are expected to understand all of these, and
MP204, Important Equations page 1 Below is a list of important equations that we meet in our study of Electromagnetism in the MP204 module. For your exam, you are expected to understand all of these, and
CEGE046 / GEOG3051 Principles & Practice of Remote Sensing (PPRS) 2: Radiation (i)
 CEGE046 / GEOG3051 Principles & Practice of Remote Sensing (PPRS) 2: Radiation (i) Dr. Mathias (Mat) Disney UCL Geography Office: 113, Pearson Building Tel: 7679 0592 Email: mdisney@ucl.geog.ac.uk www.geog.ucl.ac.uk/~mdisney
CEGE046 / GEOG3051 Principles & Practice of Remote Sensing (PPRS) 2: Radiation (i) Dr. Mathias (Mat) Disney UCL Geography Office: 113, Pearson Building Tel: 7679 0592 Email: mdisney@ucl.geog.ac.uk www.geog.ucl.ac.uk/~mdisney
Light. November 101 Lect 11 1
 Light What is light? To start, what are the observed properties of light? Describe the intrinsic properties of light light by itself. Later, what are the interactions of light? What happens when light
Light What is light? To start, what are the observed properties of light? Describe the intrinsic properties of light light by itself. Later, what are the interactions of light? What happens when light
Energy Carried by Electromagnetic Waves. Momentum and Radiation Pressure of an Electromagnetic Wave.
 Today s agenda: Electromagnetic Waves. Energy Carried by Electromagnetic Waves. Momentum and Radiation Pressure of an Electromagnetic Wave. Maxwell s Equations Recall: EdA Eds q enclosed o d dt B Bds=μ
Today s agenda: Electromagnetic Waves. Energy Carried by Electromagnetic Waves. Momentum and Radiation Pressure of an Electromagnetic Wave. Maxwell s Equations Recall: EdA Eds q enclosed o d dt B Bds=μ
Chapter 34. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves The Goal of the Entire Course Maxwell s Equations: Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell 1831 1879 Scottish theoretical physicist Developed the electromagnetic theory
Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves The Goal of the Entire Course Maxwell s Equations: Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell 1831 1879 Scottish theoretical physicist Developed the electromagnetic theory
Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 13 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves 13.1 The Displacement Current... 13. Gauss s Law for Magnetism... 4 13.3 Maxwell s Equations... 4 13.4 Plane Electromagnetic Waves... 6 13.4.1 One-Dimensional
Chapter 13 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves 13.1 The Displacement Current... 13. Gauss s Law for Magnetism... 4 13.3 Maxwell s Equations... 4 13.4 Plane Electromagnetic Waves... 6 13.4.1 One-Dimensional
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Review Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 34! The speed of an electromagnetic wave can be expressed in terms of two fundamental constants related to electric fields and magnetic
Review Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 34! The speed of an electromagnetic wave can be expressed in terms of two fundamental constants related to electric fields and magnetic
