EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9. Maxwell s Equations. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
|
|
|
- Erick Rice
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik
2 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields produced by stationary charges. Magnetostatic Fields produced by steady (DC) currents or stationary magnet materials. Electrostatic Fields and Magnetostatic Fields do not vary with time (time invariant). Electromagnetic Fields produced by time-varying currents. 2
3 Maxwell s Equations for static fields 3
4 9.2 Faraday s Law Michael Faraday ( ) Michael Faraday's ideas about conservation of energy led him to believe that since an electric current could cause a magnetic field, a magnetic field should be able to produce an electric current. He demonstrated this principle of induction in
5 Faraday s Law In 1831, Farady discovered that a time-varying magnetic field would produce an induced voltage (called electromotive force or emf). According to Faraday s experiments, a static magnetic field produces no current flow. Faraday discovered that the induced Vemf (in volts) in any closed circuit is equal to the time rate of change of the magnetic flux linkage by the circuit. 5
6 Faraday s Law V emf dλ = = N dt dψ dt where λ = NΨ is the flux linkage N is the number of turns in the circuit. Ψ is the flux through each turn. 6
7 Faraday s Law Change flux due to moving permanent magnet V emf dψ = N dt 7
8 Faraday s Law 8
9 Minus Sign? Lenz s Law Induced EMF is in direction that opposes the change in flux that caused it 9
10 9.3 Transformer and motional electromotive forces For a circuit with a single turn, N = 1 dψ Vemf = dt In terms of E and B d Vemf = E. dl = B. ds dt L where S is the surface area of the circuit bounded by the closed path L Notice that in time varying situation, both electric and S magnetic fields are present and interrelated. 10
11 The variation of flux with time may be caused in three ways: 1) By having a stationary loop in a time-varying B field. (Transformer induction) 2) By having a time-varying loop area in static B field. (motional induction) 3) By having a time-varying loop area in a time-varying B field. (general case, transformer and motional induction) 11
12 Application: DC Generators 12
13 Application: AC Generator Water turns wheel rotates magnet changes flux induces emf drives current 13
14 A. Stationary loop in Time-Varying B field (Transformer EMF) =. B V. emf E dl = ds t L S 14
15 A. Stationary loop in Time-Varying B field (Transformer EMF) =. B V. emf E dl = ds t L By applying Stoke's theorem S B E. ds =. ds t ( ) S S B E = t This is one of Maxwell s equations for time-varying fields. Note that E 0 (time-varying E field is non-conservative) 15
16 B. Moving loop in static B field (Motional EMF) Consider a conducting loo moving with uniform velocity u, the emf induced in the loop is V =. ( ). emf Em dl = u B dl L L This type of emf is called motional emf or flux-cutting emf (due to motion action). 16
17 B. Moving loop in static B field (Motional EMF) It is kind of emf found in electrical machines such as motors and generators. Given below is in example of dc machine, where voltage is generated as the coil rotates within the magnetic field. 17
18 B. Moving loop in static B field (Motional EMF) Another example of motional emf is illustrated below, where a conducting bar is moving between a pair of rails. 18
19 B. Moving loop in static B field (Motional EMF) Recall that the force on a charge moving with uniform velocity u in a a magnetic field B is: F = Qu B We define the motional electric field E as Fm Em = = u B Q V = E. dl = ( u B). dl emf L m By applying Stoke's theorem, S ( ) = ( ) L E. ds u B. ds m m S ( ) or E = u B m m V =. ( ). emf Em dl = u B dl L L 19
20 B. Moving loop in static B field (Motional EMF) V =. ( ). emf Em dl = u B dl L L Notes: The integral is zero along the portion of the loop where u=0. (e.g. dl is taken along the rod in the shown figure. The direction of the induced current is the same that of Em or uxb. The limits of integration are selected in the direction opposite to the direction of u x B to satisfy Lenz s law. (e.g. induced current flows in the rod along ay, the integration over L is along -ay). 20
21 C. Moving loop in Time Varying Field Both Transformer emf and motional emf are present. B Vemf = Ed.l =.S d + ( u B).l d t L S L Transformer Motional or B E= + u B t ( ) Note that eq. V emf dψ = dt equations in cases A, B, and C. can always be applied in place of the 21
22 a conducting bar can slide freely over two conducting rails as shown in the figure. Calculate the induced voltage in the bar ( a) If the bar is staioned at y=8 cm and B = 4 cos 10 t a mwb/m ( 6 t y) z 6 2 z 2 z ( b) If the bar slides at a velocity u = 20 a m/s and B=4a mwb/m ( c) If the bar slided at a velocity u = 20 a m/s and B=4 cos 10 a Example mwb/m y y 22
23 ( a) we have transformer emf B Vemf=-. ds = 4(10 )(10 )sin10 t y= 0 x= =4(10 )(0.08)(0.06)sin =19.2 sin 10 V ( b) This is motional emf ( ) = ( ) Vemf= u B. dl ua Ba. dx a 0 x= l t t dx dy 3 = - 20(4.10 )(0.06) ubl =- 4.8 mv y z x = t 23
24 ( c) Both transformer emf and motional emf are present in this case. this problem can be solved in two ways: Method 1: B Vemf= -. ds + ( u B ). dl t 0.06 x= 00 y (10 )(10 )sin(10 t ) = y dy dx a y 4.10 cos(10 t y) az. dx a x 0.06 ( 6 ) y cos 10 t y 80(10 )(0.06) cos(10 t y) 0 = ( 6 ) 6 3 ( 6 t y t t y) = 240cos cos10 4.8(10 ) cos cos 10 ( ) t y 240cos10 t
25 Method 2: Ψ Vemf=-, where Ψ= B. ds t y = 4 cos(10 ) y= 0 x= 0 6 =-40(0.06)sin(10 ) t t y dx dy y y y= = -0.24sin(10 t y)+0.24 sin10 t mwb But dy = u y = ut = 20t dt Hence, sin(10 20 ) 0.24sin10 mwb Ψ= t t + t Ψ Vemf=- = 0.24(10 20) cos(10 t 20 t) 0.24(10 ) cos10 t mv t 240cos 10 ( ) t y 240cos10 t
26 Example 9.2 The loop shown in the figure is inside a uniform magnetic field B=50 a x mw/m 2. If side DC of the loop cuts the flux lines at the frequency of 50 Hz and the loop lies in the yz-plane at the time t=0, find (a) The induced emf at at t=1 ms. (b) The induced current at t=3 ms. 26
27 The B field is time invariant, the induced emf is motional ρφ Vemf= ( u B). dl, where dl = d zaz, u= aφ = ρωa t ρ = AD = 4 cm, ω = 2π f = 100π Transform B into cylindrical corrdinates: 0 x 0 ( φa φa ) B=B a = B cos sin, where B =0.05 ρ u B = 0 ρω 0 = ρωb cos φ a B cosφ B sinφ ( ) = = ( ) u B. dl ρωb cos φ dz 0.04(100 π ) 0.05 cos φ dz Vemf 0.03 z= 0 a a a ρ 0 φ φ = 0.2π cos φ dz 0.2π cos φ dz 6π cos φ mv = = z 0 0 z φ 27
28 To determine φ recall that dφ ω= φ = ωt+ C0 ( C0 is the integration constant) dt At t=0, φ = π / 2 beacause the loop is in the yz-plane at that time, C 0 = π / 2. Hence, φ = ωt+ π / 2 ( ) Vemf = 6π cos ωt + π / 2 =6πsin(100 πt) mv At t=1 ms, Vemf=6πsin(0.1 π) =5.825 mv (b) The current induced is Vemf i = = 60πsin(100 πt) ma R At t=3ms, i=60πsin(0.3 π) ma= A ( ) Note that for sides AD and BC u B. dl = 0 since az. a ρ = 0 28
29 9.4 Displacement current Here we will consider Maxwell's curl equation for magnetic fields (Ampere's Law) for time-varying conditions. For static EM fields, recall that H = J (1) But the divergence of the curl is zero: ( H) = 0 = J (2) However, the equation of continuity requires that ρv J = (3) t Thus, equations (2) and (3) are incompatible for time varying conditions!! 29
30 Here We must modify equation (1) to consider time-varying situation: J d To do this, add a term to eq. (1): H = J+ J (4) again, taking the divergence, we have: ( H ) d = 0 = J + J (5) ρv Since J =, hen, t Jd = t Since D = ρ V Displacement current d ρv t D D J d = ( D) = J d= t t t (6) Substituting eq (6) into eq (4) results in, D H = J + t (7) 30
31 Displacement current D H = J + t This is Maxwell's equation ( based on Ampere's circuit law) for a time varying field. The term J = d D t is known as displacement current density. This is the third type of current density we have met: Conduction current density: (motion of charge in a conductor) Convection Current Density: J= σ E J= ρvu (doesn t involve conductors, current flows through an insulating medium, such as liquid, or vacuum). D Displacement Current Density: J d = t (is a result of time-varying electric field). 31
32 Displacement current The insertion of Jd into Ampere s equation was one of the major contributions of Maxwell. Without the term Jd, the propagation of electromagnetic waves (e.g., radio or TV) would be impossible. Displacement current is the mechanism which allows electromagnetic waves to propagate in a non-conducting medium. The displacement current is defined as: D I= J.S d d d =.S t d 32
33 Displacement current A typical example of displacement current is the current through a capacitor when alternating voltage source is applied to its plates. The total current density is J+Jd. Take Amperian path as shown. Consider 2 surfaces bounded by path L. If surface S1 is chosen: Jd=0 L H. dl= J. ds= I = I S 1 enc If surface S2 is chosen: J=0 d dq H. dl= J.S= d D.S d = = I dt d dt L S S 2 2 So we obtain the same current for either surface. A time-varying electric field induces magnetic field inside the capacitor. 33
34 Conduction to Displacement Current Ratio The conduction current density is given by The displacement current density is given by Assume that the electric field is a sinusoidal function of time: Then, E = E cosωt 0 J = σ E cos ωt, J = ωε E sinωt c 0 d 0 J J c d = σ E E = ε t We have Therefore J = σ E, J = ωε E J J c d c max max max = σ ωε 0 d max 0 σ >> ωε σ << ωε Good Conductor ( Id neglible) Good Insulator ( I neglible) c Note: In free space (or other perfect dielectric), the conduction current is zero and only displacement current can exist. 34
35 Example 9.4 A parallel plate capacitor with plate area of 5 cm 2 and plate separation of 3 mm has a voltage 50 sin 10 3 t V applied to its plates. Calculate the displacement current assuming ε=2 ε 0. D Id = J d. S, J d= t V D ε dv but D = εe = ε J d = = d t d dt ε S dv dv Id = = C ( same as conduction current Ic). d dt dt Id = cos(10 t) 3 36π I = cos(10 t) na d 35
36 9.5 Maxwell s Equations in Final Forms 36
37 The concepts of linearity, isotropy, and homogeneity of a material medium still apply for time varying fields. In a linear, homogeneous, and isotropic medium characterized by σ, ε, and μ, the following relations hold for time varying fields: D= εe = ε E+ P B = µ H = µ (H + M) Consequently, the boundary conditions remain valid for time 0 0 J = σe+ ρ u V varying fields. E E = 0, D - D = ρ 1t 2t 1n 2n S H H = K, B -B = 0 1t 2t 1n 2n 37
38 Electromagnetic flow diagrams Figure 9.11 Electromagnetic flow diagrams showing the relationship between the potentials and vector fields: (a) electrostatic system, (b) magnetostatic system, (c) electromagnetic system. 38
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9. Maxwell s Equations. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2012 1 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s Equations Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 2012 1 Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics Electrostatic Fields
Maxwell s Equations 5/9/2016. EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 9. Maxwell s Equations for static fields. Review Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Generate by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit oftware 5/9/216 3332 lectromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s quations Islamic University of Gaza lectrical ngineering Department Prof. Dr. Hala J l-khozonar 216 1 2 Review
Generate by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit oftware 5/9/216 3332 lectromagnetic II Chapter 9 Maxwell s quations Islamic University of Gaza lectrical ngineering Department Prof. Dr. Hala J l-khozonar 216 1 2 Review
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 25
 Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 25 1) Transformer and Motional EMFs 2) Displacement Current 3) Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Waves & Applications Time Varying Fields Until now, we have
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 25 1) Transformer and Motional EMFs 2) Displacement Current 3) Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Waves & Applications Time Varying Fields Until now, we have
UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields)
 UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields) Faraday s law, transformer emf &inconsistency of ampere s law Displacement current density Maxwell s equations in final form Maxwell s equations in word
UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields) Faraday s law, transformer emf &inconsistency of ampere s law Displacement current density Maxwell s equations in final form Maxwell s equations in word
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
 UNIT-III INTRODUCTION: In our study of static fields so far, we have observed that static electric fields are produced by electric charges, static magnetic fields are produced by charges in motion or by
UNIT-III INTRODUCTION: In our study of static fields so far, we have observed that static electric fields are produced by electric charges, static magnetic fields are produced by charges in motion or by
Magnetostatic fields! steady magnetic fields produced by steady (DC) currents or stationary magnetic materials.
 ECE 3313 Electromagnetics I! Static (time-invariant) fields Electrostatic or magnetostatic fields are not coupled together. (one can exist without the other.) Electrostatic fields! steady electric fields
ECE 3313 Electromagnetics I! Static (time-invariant) fields Electrostatic or magnetostatic fields are not coupled together. (one can exist without the other.) Electrostatic fields! steady electric fields
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields
 Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
r r 1 r r 1 2 = q 1 p = qd and it points from the negative charge to the positive charge.
 MP204, Important Equations page 1 Below is a list of important equations that we meet in our study of Electromagnetism in the MP204 module. For your exam, you are expected to understand all of these, and
MP204, Important Equations page 1 Below is a list of important equations that we meet in our study of Electromagnetism in the MP204 module. For your exam, you are expected to understand all of these, and
ECE 107: Electromagnetism
 ECE 107: Electromagnetism Set 7: Dynamic fields Instructor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 1 Maxwell s equations Maxwell
ECE 107: Electromagnetism Set 7: Dynamic fields Instructor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 1 Maxwell s equations Maxwell
toroidal iron core compass switch battery secondary coil primary coil
 Fundamental Laws of Electrostatics Integral form Differential form d l C S E 0 E 0 D d s V q ev dv D ε E D qev 1 Fundamental Laws of Magnetostatics Integral form Differential form C S dl S J d s B d s
Fundamental Laws of Electrostatics Integral form Differential form d l C S E 0 E 0 D d s V q ev dv D ε E D qev 1 Fundamental Laws of Magnetostatics Integral form Differential form C S dl S J d s B d s
Maxwell s Equations. In the previous chapters we saw the four fundamental equations governging electrostatics and magnetostatics. They are.
 Maxwell s Equations Introduction In the previous chapters we saw the four fundamental equations governging electrostatics and magnetostatics. They are D = ρ () E = 0 (2) B = 0 (3) H = J (4) In the integral
Maxwell s Equations Introduction In the previous chapters we saw the four fundamental equations governging electrostatics and magnetostatics. They are D = ρ () E = 0 (2) B = 0 (3) H = J (4) In the integral
Unit-1 Electrostatics-1
 1. Describe about Co-ordinate Systems. Co-ordinate Systems Unit-1 Electrostatics-1 In order to describe the spatial variations of the quantities, we require using appropriate coordinate system. A point
1. Describe about Co-ordinate Systems. Co-ordinate Systems Unit-1 Electrostatics-1 In order to describe the spatial variations of the quantities, we require using appropriate coordinate system. A point
Course no. 4. The Theory of Electromagnetic Field
 Cose no. 4 The Theory of Electromagnetic Field Technical University of Cluj-Napoca http://www.et.utcluj.ro/cs_electromagnetics2006_ac.htm http://www.et.utcluj.ro/~lcret March 19-2009 Chapter 3 Magnetostatics
Cose no. 4 The Theory of Electromagnetic Field Technical University of Cluj-Napoca http://www.et.utcluj.ro/cs_electromagnetics2006_ac.htm http://www.et.utcluj.ro/~lcret March 19-2009 Chapter 3 Magnetostatics
While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations
 Unit 2 Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equations While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields,
Unit 2 Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equations While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields,
CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION So far we have seen that electric charges are the source for both electric and magnetic fields. We have also seen that these fields can exert forces on other electric
CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION So far we have seen that electric charges are the source for both electric and magnetic fields. We have also seen that these fields can exert forces on other electric
Prof. Krishna Vasudevan, Prof. G. Sridhara Rao, Prof. P. Sasidhara Rao
 2 Basic Principles As mentioned earlier the transformer is a static device working on the principle of Faraday s law of induction. Faraday s law states that a voltage appears across the terminals of an
2 Basic Principles As mentioned earlier the transformer is a static device working on the principle of Faraday s law of induction. Faraday s law states that a voltage appears across the terminals of an
Chapter 7. Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equations
 Chapter 7. Time-arying Fields and Maxwell s Equations Electrostatic & Time arying Fields Electrostatic fields E, D B, H =J D H 1 E B In the electrostatic model, electric field and magnetic fields are not
Chapter 7. Time-arying Fields and Maxwell s Equations Electrostatic & Time arying Fields Electrostatic fields E, D B, H =J D H 1 E B In the electrostatic model, electric field and magnetic fields are not
Revision Guide for Chapter 15
 Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents tudent s Checklist Revision otes Transformer... 4 Electromagnetic induction... 4 Generator... 5 Electric motor... 6 Magnetic field... 8 Magnetic flux... 9 Force on
Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents tudent s Checklist Revision otes Transformer... 4 Electromagnetic induction... 4 Generator... 5 Electric motor... 6 Magnetic field... 8 Magnetic flux... 9 Force on
Revision Guide for Chapter 15
 Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents Revision Checklist Revision otes Transformer...4 Electromagnetic induction...4 Lenz's law...5 Generator...6 Electric motor...7 Magnetic field...9 Magnetic flux...
Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents Revision Checklist Revision otes Transformer...4 Electromagnetic induction...4 Lenz's law...5 Generator...6 Electric motor...7 Magnetic field...9 Magnetic flux...
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
Chapter 7. Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equation
 Chapter 7. Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equation Electrostatic & Time Varying Fields Electrostatic fields E, D B, H =J D H 1 E B In the electrostatic model, electric field and magnetic fields are
Chapter 7. Time-Varying Fields and Maxwell s Equation Electrostatic & Time Varying Fields Electrostatic fields E, D B, H =J D H 1 E B In the electrostatic model, electric field and magnetic fields are
Chapter 20: Electromagnetic Induction. PHY2054: Chapter 20 1
 Chapter 20: Electromagnetic Induction PHY2054: Chapter 20 1 Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic flux Induced emf Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Motional emf Magnetic energy Inductance RL circuits Generators and
Chapter 20: Electromagnetic Induction PHY2054: Chapter 20 1 Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic flux Induced emf Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Motional emf Magnetic energy Inductance RL circuits Generators and
PHYS Fields and Waves
 PHYS 2421 - Fields and Waves Idea: We have seen: currents can produce fields We will now see: fields can produce currents Facts: Current is produced in closed loops when the magnetic flux changes Notice:
PHYS 2421 - Fields and Waves Idea: We have seen: currents can produce fields We will now see: fields can produce currents Facts: Current is produced in closed loops when the magnetic flux changes Notice:
Field and Wave Electromagnetic
 Field and Wave Electromagnetic Chapter7 The time varying fields and Maxwell s equation Introduction () Time static fields ) Electrostatic E =, id= ρ, D= εe ) Magnetostatic ib=, H = J, H = B μ note) E and
Field and Wave Electromagnetic Chapter7 The time varying fields and Maxwell s equation Introduction () Time static fields ) Electrostatic E =, id= ρ, D= εe ) Magnetostatic ib=, H = J, H = B μ note) E and
Magnetostatic Fields. Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Palestine
 Magnetostatic Fields Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Palestine 01 Introduction In chapters 4 to 6, static electric fields characterized by E or D (D=εE) were discussed. This chapter considers
Magnetostatic Fields Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Palestine 01 Introduction In chapters 4 to 6, static electric fields characterized by E or D (D=εE) were discussed. This chapter considers
Lecture 12. Time Varying Electromagnetic Fields
 Lecture. Time Varying Electromagnetic Fields For static electric and magnetic fields: D = ρ () E = 0...( ) D= εe B = 0...( 3) H = J H = B µ...( 4 ) For a conducting medium J =σ E From Faraday s observations,
Lecture. Time Varying Electromagnetic Fields For static electric and magnetic fields: D = ρ () E = 0...( ) D= εe B = 0...( 3) H = J H = B µ...( 4 ) For a conducting medium J =σ E From Faraday s observations,
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 16 Chapter 28 sec. 1-3 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Magnetic Flux We define magnetic flux in the same way we defined electric flux: φ e = n E da φ m =
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 16 Chapter 28 sec. 1-3 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Magnetic Flux We define magnetic flux in the same way we defined electric flux: φ e = n E da φ m =
Sliding Conducting Bar
 Motional emf, final For equilibrium, qe = qvb or E = vb A potential difference is maintained between the ends of the conductor as long as the conductor continues to move through the uniform magnetic field
Motional emf, final For equilibrium, qe = qvb or E = vb A potential difference is maintained between the ends of the conductor as long as the conductor continues to move through the uniform magnetic field
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY SIRUVACHUR-621113 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT 2 MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS SUBJECT CODE: EE 6302 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY SIRUVACHUR-621113 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT 2 MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS SUBJECT CODE: EE 6302 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
Chapters 34,36: Electromagnetic Induction. PHY2061: Chapter
 Chapters 34,36: Electromagnetic Induction PHY2061: Chapter 34-35 1 Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic flux Induced emf Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Motional emf Magnetic energy Inductance RL circuits Generators
Chapters 34,36: Electromagnetic Induction PHY2061: Chapter 34-35 1 Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic flux Induced emf Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Motional emf Magnetic energy Inductance RL circuits Generators
Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Induction
 Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Induction Recall: right hand rule 2 10/28/2013 Units of Chapter 23 Induced Electromotive Force Magnetic Flux Faraday s Law of Induction Lenz s Law Mechanical
Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Induction Recall: right hand rule 2 10/28/2013 Units of Chapter 23 Induced Electromotive Force Magnetic Flux Faraday s Law of Induction Lenz s Law Mechanical
Last time. Gauss' Law: Examples (Ampere's Law)
 Last time Gauss' Law: Examples (Ampere's Law) 1 Ampere s Law in Magnetostatics iot-savart s Law can be used to derive another relation: Ampere s Law The path integral of the dot product of magnetic field
Last time Gauss' Law: Examples (Ampere's Law) 1 Ampere s Law in Magnetostatics iot-savart s Law can be used to derive another relation: Ampere s Law The path integral of the dot product of magnetic field
Lecture 6: Maxwell s Equations, Boundary Conditions.
 Whites, EE 382 Lecture 6 Page 1 of 7 Lecture 6: Maxwell s Equations, Boundar Conditions. In the last four lectures, we have been investigating the behavior of dnamic (i.e., time varing) electric and magnetic
Whites, EE 382 Lecture 6 Page 1 of 7 Lecture 6: Maxwell s Equations, Boundar Conditions. In the last four lectures, we have been investigating the behavior of dnamic (i.e., time varing) electric and magnetic
1830s Michael Faraday Joseph Henry. Induced EMF
 1830s Michael Faraday Joseph Henry Induced EMF There can be EMF produced in a number of ways: A time varying magnetic field An area whose size is varying A time varying angle between r and Any combination
1830s Michael Faraday Joseph Henry Induced EMF There can be EMF produced in a number of ways: A time varying magnetic field An area whose size is varying A time varying angle between r and Any combination
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 1
 EE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of EE Notes 1 1 Maxwell s Equations E D rt 2, V/m, rt, Wb/m T ( ) [ ] ( ) ( ) 2 rt, /m, H ( rt, ) [ A/m] B E = t (Faraday's Law) D H
EE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of EE Notes 1 1 Maxwell s Equations E D rt 2, V/m, rt, Wb/m T ( ) [ ] ( ) ( ) 2 rt, /m, H ( rt, ) [ A/m] B E = t (Faraday's Law) D H
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad Electronics and Communicaton Engineering
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 Electronics and Communicaton Engineering Question Bank Course Name : Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission Lines (EMTL) Course Code :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 Electronics and Communicaton Engineering Question Bank Course Name : Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission Lines (EMTL) Course Code :
Slide 1 / 24. Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger
 Slide 1 / 24 Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 24 Induced Currents If we have a galvanometer attached to a coil of wire we can induce a current simply by changing the magnetic
Slide 1 / 24 Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 24 Induced Currents If we have a galvanometer attached to a coil of wire we can induce a current simply by changing the magnetic
Magnetic inductance & Solenoids. P.Ravindran, PHY041: Electricity & Magnetism 22 February 2013: Magnetic inductance, and Solenoid
 Magnetic inductance & Solenoids Changing Magnetic Flux A changing magnetic flux in a wire loop induces an electric current. The induced current is always in a direction that opposes the change in flux.
Magnetic inductance & Solenoids Changing Magnetic Flux A changing magnetic flux in a wire loop induces an electric current. The induced current is always in a direction that opposes the change in flux.
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR
 TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
AP Physics C - E & M
 AP Physics C - E & M Electromagnetic Induction 2017-07-14 www.njctl.org Table of Contents: Electromagnetic Induction Click on the topic to go to that section. Induced EMF Magnetic Flux and Gauss's Law
AP Physics C - E & M Electromagnetic Induction 2017-07-14 www.njctl.org Table of Contents: Electromagnetic Induction Click on the topic to go to that section. Induced EMF Magnetic Flux and Gauss's Law
Chapter 31. Faraday s Law
 Chapter 31 Faraday s Law 1 Ampere s law Magnetic field is produced by time variation of electric field dφ B ( I I ) E d s = µ o + d = µ o I+ µ oεo ds E B 2 Induction A loop of wire is connected to a sensitive
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law 1 Ampere s law Magnetic field is produced by time variation of electric field dφ B ( I I ) E d s = µ o + d = µ o I+ µ oεo ds E B 2 Induction A loop of wire is connected to a sensitive
Chapter 27, 28 & 29: Magnetism & Electromagnetic Induction. Magnetic flux Faraday s and Lenz s law Electromagnetic Induction Ampere s law
 Chapter 27, 28 & 29: Magnetism & Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic flux Faraday s and Lenz s law Electromagnetic Induction Ampere s law 1 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Electromagnetic Induction We
Chapter 27, 28 & 29: Magnetism & Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic flux Faraday s and Lenz s law Electromagnetic Induction Ampere s law 1 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Electromagnetic Induction We
Physics 11b Lecture #13
 Physics 11b Lecture #13 Faraday s Law S&J Chapter 31 Midterm #2 Midterm #2 will be on April 7th by popular vote Covers lectures #8 through #14 inclusive Textbook chapters from 27 up to 32.4 There will
Physics 11b Lecture #13 Faraday s Law S&J Chapter 31 Midterm #2 Midterm #2 will be on April 7th by popular vote Covers lectures #8 through #14 inclusive Textbook chapters from 27 up to 32.4 There will
Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]
![Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark] Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]](/thumbs/88/115570773.jpg) Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Part 4: Electromagnetism. 4.1: Induction. A. Faraday's Law. The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is
 1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
Physics / Higher Physics 1A. Electricity and Magnetism Revision
 Physics / Higher Physics 1A Electricity and Magnetism Revision Electric Charges Two kinds of electric charges Called positive and negative Like charges repel Unlike charges attract Coulomb s Law In vector
Physics / Higher Physics 1A Electricity and Magnetism Revision Electric Charges Two kinds of electric charges Called positive and negative Like charges repel Unlike charges attract Coulomb s Law In vector
Physics 202 Chapter 31 Oct 23, Faraday s Law. Faraday s Law
 Physics 202 Chapter 31 Oct 23, 2007 Faraday s Law Faraday s Law The final step to ignite the industrial use of electromagnetism on a large scale. Light, toasters, cars, TVs, telephones, ipods, industrial
Physics 202 Chapter 31 Oct 23, 2007 Faraday s Law Faraday s Law The final step to ignite the industrial use of electromagnetism on a large scale. Light, toasters, cars, TVs, telephones, ipods, industrial
Yell if you have any questions
 Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 Before Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 Before Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Faraday s Law. Underpinning of Much Technology
 Module 21: Faraday s Law 1 Faraday s Law Fourth (Final) Maxwell s Equation Underpinning of Much Technology 2 Demonstration: Falling Magnet 3 Magnet Falling Through a Ring Link to movie Falling magnet slows
Module 21: Faraday s Law 1 Faraday s Law Fourth (Final) Maxwell s Equation Underpinning of Much Technology 2 Demonstration: Falling Magnet 3 Magnet Falling Through a Ring Link to movie Falling magnet slows
General review: - a) Dot Product
 General review: - a) Dot Product If θ is the angle between the vectors a and b, then a b = a b cos θ NOTE: Two vectors a and b are orthogonal, if and only if a b = 0. Properties of the Dot Product If a,
General review: - a) Dot Product If θ is the angle between the vectors a and b, then a b = a b cos θ NOTE: Two vectors a and b are orthogonal, if and only if a b = 0. Properties of the Dot Product If a,
Faraday's Law ds B B G G ΦB B ds Φ ε = d B dt
 Faraday's Law ds ds ε= d Φ dt Φ Global Review Electrostatics» motion of q in external E-field» E-field generated by Σq i Magnetostatics» motion of q and i in external -field» -field generated by I Electrodynamics»
Faraday's Law ds ds ε= d Φ dt Φ Global Review Electrostatics» motion of q in external E-field» E-field generated by Σq i Magnetostatics» motion of q and i in external -field» -field generated by I Electrodynamics»
Class 11 : Magnetic materials
 Class 11 : Magnetic materials Magnetic dipoles Magnetization of a medium, and how it modifies magnetic field Magnetic intensity How does an electromagnet work? Boundary conditions for B Recap (1) Electric
Class 11 : Magnetic materials Magnetic dipoles Magnetization of a medium, and how it modifies magnetic field Magnetic intensity How does an electromagnet work? Boundary conditions for B Recap (1) Electric
Maxwell s equations. Kyoto. James Clerk Maxwell. Physics 122. James Clerk Maxwell ( ) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions
 Maxwell s equations Physics /5/ Lecture XXIV Kyoto /5/ Lecture XXIV James Clerk Maxwell James Clerk Maxwell (83 879) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions /5/ Lecture XXIV 3 Φ = da = Q ε
Maxwell s equations Physics /5/ Lecture XXIV Kyoto /5/ Lecture XXIV James Clerk Maxwell James Clerk Maxwell (83 879) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions /5/ Lecture XXIV 3 Φ = da = Q ε
n Higher Physics 1B (Special) (PHYS1241) (6UOC) n Advanced Science n Double Degree (Science/Engineering) n Credit or higher in Physics 1A
 Physics in Session 2: I n Physics / Higher Physics 1B (PHYS1221/1231) n Science, dvanced Science n Engineering: Electrical, Photovoltaic,Telecom n Double Degree: Science/Engineering n 6 UOC n Waves n Physical
Physics in Session 2: I n Physics / Higher Physics 1B (PHYS1221/1231) n Science, dvanced Science n Engineering: Electrical, Photovoltaic,Telecom n Double Degree: Science/Engineering n 6 UOC n Waves n Physical
CHAPTER 5 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 CHAPTER 5 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION 1 Quick Summary on Previous Concepts Electrostatics Magnetostatics Electromagnetic Induction 2 Cases of Changing Magnetic Field Changing Field Strength in a Loop A Loop
CHAPTER 5 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION 1 Quick Summary on Previous Concepts Electrostatics Magnetostatics Electromagnetic Induction 2 Cases of Changing Magnetic Field Changing Field Strength in a Loop A Loop
Electromagnetism. 1 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless
 Electromagnetism 1 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless Radio Spectrum use for Communications 2 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless 3 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless Electromagnetism I Gauss
Electromagnetism 1 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless Radio Spectrum use for Communications 2 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless 3 ENGN6521 / ENGN4521: Embedded Wireless Electromagnetism I Gauss
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction
 Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction In this chapter we investigate how changing the magnetic flux in a circuit induces an emf and a current. We learned in Chapter 25 that an electromotive force (E) is
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction In this chapter we investigate how changing the magnetic flux in a circuit induces an emf and a current. We learned in Chapter 25 that an electromotive force (E) is
EECS 117 Lecture 19: Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Eq.
 University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 19 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 19: Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Eq. Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS
University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 19 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 19: Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Eq. Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS
Worked Examples Set 2
 Worked Examples Set 2 Q.1. Application of Maxwell s eqns. [Griffiths Problem 7.42] In a perfect conductor the conductivity σ is infinite, so from Ohm s law J = σe, E = 0. Any net charge must be on the
Worked Examples Set 2 Q.1. Application of Maxwell s eqns. [Griffiths Problem 7.42] In a perfect conductor the conductivity σ is infinite, so from Ohm s law J = σe, E = 0. Any net charge must be on the
Problem Fig
 Problem 9.53 A flexible circular loop 6.50 cm in diameter lies in a magnetic field with magnitude 0.950 T, directed into the plane of the page, as shown. The loop is pulled at the points indicated by the
Problem 9.53 A flexible circular loop 6.50 cm in diameter lies in a magnetic field with magnitude 0.950 T, directed into the plane of the page, as shown. The loop is pulled at the points indicated by the
Electromagnetic Induction (Chapters 31-32)
 Electromagnetic Induction (Chapters 31-3) The laws of emf induction: Faraday s and Lenz s laws Inductance Mutual inductance M Self inductance L. Inductors Magnetic field energy Simple inductive circuits
Electromagnetic Induction (Chapters 31-3) The laws of emf induction: Faraday s and Lenz s laws Inductance Mutual inductance M Self inductance L. Inductors Magnetic field energy Simple inductive circuits
EMF Notes 11; Maxwell s Equations. MAXWELL S EQUATIONS Maxwell s four equations
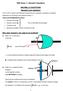 MAXWELL S EQUATONS Maxwell s four equations n the 870 s, James Clerk Maxwell showed that four equations constitute a complete description of the electric and magnetic fields, or THE ELECTROMAGNETC FELD
MAXWELL S EQUATONS Maxwell s four equations n the 870 s, James Clerk Maxwell showed that four equations constitute a complete description of the electric and magnetic fields, or THE ELECTROMAGNETC FELD
Electromagnetic Theory PHYS 402. Electrodynamics. Ohm s law Electromotive Force Electromagnetic Induction Maxwell s Equations
 Electromagnetic Theory PHYS 4 Electrodynamics Ohm s law Electromotive Force Electromagnetic Induction Maxwell s Equations 1 7.1.1 Ohms Law For the EM force Usually v is small so J = J = σ Current density
Electromagnetic Theory PHYS 4 Electrodynamics Ohm s law Electromotive Force Electromagnetic Induction Maxwell s Equations 1 7.1.1 Ohms Law For the EM force Usually v is small so J = J = σ Current density
Motional Electromotive Force
 Motional Electromotive Force The charges inside the moving conductive rod feel the Lorentz force The charges drift toward the point a of the rod The accumulating excess charges at point a create an electric
Motional Electromotive Force The charges inside the moving conductive rod feel the Lorentz force The charges drift toward the point a of the rod The accumulating excess charges at point a create an electric
Magnetic Induction Faraday, Lenz, Mutual & Self Inductance Maxwell s Eqns, E-M waves. Reading Journals for Tuesday from table(s)
 PHYS 2015 -- Week 12 Magnetic Induction Faraday, Lenz, Mutual & Self Inductance Maxwell s Eqns, E-M waves Reading Journals for Tuesday from table(s) WebAssign due Friday night For exclusive use in PHYS
PHYS 2015 -- Week 12 Magnetic Induction Faraday, Lenz, Mutual & Self Inductance Maxwell s Eqns, E-M waves Reading Journals for Tuesday from table(s) WebAssign due Friday night For exclusive use in PHYS
Physics 1302W.400 Lecture 33 Introductory Physics for Scientists and Engineering II
 Physics 1302W.400 Lecture 33 Introductory Physics for Scientists and Engineering II In today s lecture, we will discuss generators and motors. Slide 30-1 Announcement Quiz 4 will be next week. The Final
Physics 1302W.400 Lecture 33 Introductory Physics for Scientists and Engineering II In today s lecture, we will discuss generators and motors. Slide 30-1 Announcement Quiz 4 will be next week. The Final
Chapter 31. Faraday s Law
 Chapter 31 Faraday s Law 1 Ampere s law Magnetic field is produced by time variation of electric field B s II I d d μ o d μo με o o E ds E B Induction A loop of wire is connected to a sensitive ammeter
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law 1 Ampere s law Magnetic field is produced by time variation of electric field B s II I d d μ o d μo με o o E ds E B Induction A loop of wire is connected to a sensitive ammeter
Maxwell s equations and EM waves. From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law
 Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
Dynamic Fields, Maxwell s Equations (Chapter 6)
 Dynamic Fields, Maxwell s Equations (Chapter 6) So far, we have studied static electric and magnetic fields. In the real world, however, nothing is static. Static fields are only approximations when the
Dynamic Fields, Maxwell s Equations (Chapter 6) So far, we have studied static electric and magnetic fields. In the real world, however, nothing is static. Static fields are only approximations when the
Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors
 Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors 1 Revision of Electromagnetic Induction and Inductors (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Magnetic Field
Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors 1 Revision of Electromagnetic Induction and Inductors (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Magnetic Field
Exam 3 Solutions. The induced EMF (magnitude) is given by Faraday s Law d dt dt The current is given by
 PHY049 Spring 008 Prof. Darin Acosta Prof. Selman Hershfield April 9, 008. A metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity of 60 cm/s [or 90 cm/s] along two parallel metal rails, which are connected
PHY049 Spring 008 Prof. Darin Acosta Prof. Selman Hershfield April 9, 008. A metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity of 60 cm/s [or 90 cm/s] along two parallel metal rails, which are connected
Yell if you have any questions
 Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 efore Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 efore Starting All of your grades should now be posted
UNIT-I Static Electric fields
 UNIT-I Static Electric fields In this chapter we will discuss on the followings: Coulomb's Law Electric Field & Electric Flux Density Gauss's Law with Application Electrostatic Potential, Equipotential
UNIT-I Static Electric fields In this chapter we will discuss on the followings: Coulomb's Law Electric Field & Electric Flux Density Gauss's Law with Application Electrostatic Potential, Equipotential
EECS 117. Lecture 17: Magnetic Forces/Torque, Faraday s Law. Prof. Niknejad. University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 17 p. 1/? EECS 117 Lecture 17: Magnetic Forces/Torque, Faraday s Law Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 17 p. 1/? EECS 117 Lecture 17: Magnetic Forces/Torque, Faraday s Law Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
Chapter 2 Basics of Electricity and Magnetism
 Chapter 2 Basics of Electricity and Magnetism My direct path to the special theory of relativity was mainly determined by the conviction that the electromotive force induced in a conductor moving in a
Chapter 2 Basics of Electricity and Magnetism My direct path to the special theory of relativity was mainly determined by the conviction that the electromotive force induced in a conductor moving in a
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
14 Faraday s law and induced emf
 14 Faraday s law and induced emf Michael Faraday discovered (in 1831, less than 200 years ago)thatachanging current in a wire loop induces current flows in nearby wires today we describe this phenomenon
14 Faraday s law and induced emf Michael Faraday discovered (in 1831, less than 200 years ago)thatachanging current in a wire loop induces current flows in nearby wires today we describe this phenomenon
remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields, the remaining two
 Unit 2 Maxwell s Equations Time-Varying Form While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields, the
Unit 2 Maxwell s Equations Time-Varying Form While the Gauss law forms for the static electric and steady magnetic field equations remain essentially unchanged for the case of time-varying fields, the
FARADAY S AND LENZ LAW B O O K P G
 FARADAY S AND LENZ LAW B O O K P G. 4 3 6-438 MOTIONAL EMF AND MAGNETIC FLUX (DERIVIATION) Motional emf = vbl Let a conducting rod being moved through a magnetic field B During time t 0 the rod has been
FARADAY S AND LENZ LAW B O O K P G. 4 3 6-438 MOTIONAL EMF AND MAGNETIC FLUX (DERIVIATION) Motional emf = vbl Let a conducting rod being moved through a magnetic field B During time t 0 the rod has been
Faraday s Law. Faraday s Law of Induction Motional emf. Lenz s Law. Motors and Generators. Eddy Currents
 Faraday s Law Faraday s Law of Induction Motional emf Motors and Generators Lenz s Law Eddy Currents Induced EMF A current flows through the loop when a magnet is moved near it, without any batteries!
Faraday s Law Faraday s Law of Induction Motional emf Motors and Generators Lenz s Law Eddy Currents Induced EMF A current flows through the loop when a magnet is moved near it, without any batteries!
Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems:
 Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems: 5,7,9,10,11,13,15,17,20,21,28,29,31,32,33,34,49,50,52,58,63,64. Faraday's Law of Induction We learned that e. current produces magnetic field. Now we want
Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems: 5,7,9,10,11,13,15,17,20,21,28,29,31,32,33,34,49,50,52,58,63,64. Faraday's Law of Induction We learned that e. current produces magnetic field. Now we want
Electrical polarization. Figure 19-5 [1]
![Electrical polarization. Figure 19-5 [1] Electrical polarization. Figure 19-5 [1]](/thumbs/81/84036296.jpg) Electrical polarization Figure 19-5 [1] Properties of Charge Two types: positive and negative Like charges repel, opposite charges attract Charge is conserved Fundamental particles with charge: electron
Electrical polarization Figure 19-5 [1] Properties of Charge Two types: positive and negative Like charges repel, opposite charges attract Charge is conserved Fundamental particles with charge: electron
14 Faraday s law and induced emf
 14 Faraday s law and induced emf Michael Faraday discovered (in 1831, less than 200 years ago)thatachanging current in a wire loop induces current flows in nearby wires today we describe this phenomenon
14 Faraday s law and induced emf Michael Faraday discovered (in 1831, less than 200 years ago)thatachanging current in a wire loop induces current flows in nearby wires today we describe this phenomenon
Induction. Chapter 29. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by James Pazun
 Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun 29. Electromagnetic induction 1. Magnetic flux/faraday
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun 29. Electromagnetic induction 1. Magnetic flux/faraday
/R = If we take the surface normal to be +ẑ, then the right hand rule gives positive flowing current to be in the +ˆφ direction.
 Problem 6.2 The loop in Fig. P6.2 is in the x y plane and B = ẑb 0 sinωt with B 0 positive. What is the direction of I (ˆφ or ˆφ) at: (a) t = 0 (b) ωt = π/4 (c) ωt = π/2 V emf y x I Figure P6.2: Loop of
Problem 6.2 The loop in Fig. P6.2 is in the x y plane and B = ẑb 0 sinωt with B 0 positive. What is the direction of I (ˆφ or ˆφ) at: (a) t = 0 (b) ωt = π/4 (c) ωt = π/2 V emf y x I Figure P6.2: Loop of
ElectroMagnetic Induction
 ElectroMagnetic Induction Physics 1 What is E/M Induction? Electromagnetic Induction is the process of using magnetic fields to produce voltage, and in a complete circuit, a current. Michael Faraday first
ElectroMagnetic Induction Physics 1 What is E/M Induction? Electromagnetic Induction is the process of using magnetic fields to produce voltage, and in a complete circuit, a current. Michael Faraday first
9-3 Inductance. * We likewise can have self inductance, were a timevarying current in a circuit induces an emf voltage within that same circuit!
 /3/004 section 9_3 Inductance / 9-3 Inductance Reading Assignment: pp. 90-86 * A transformer is an example of mutual inductance, where a time-varying current in one circuit (i.e., the primary) induces
/3/004 section 9_3 Inductance / 9-3 Inductance Reading Assignment: pp. 90-86 * A transformer is an example of mutual inductance, where a time-varying current in one circuit (i.e., the primary) induces
Magnetostatics III. P.Ravindran, PHY041: Electricity & Magnetism 1 January 2013: Magntostatics
 Magnetostatics III Magnetization All magnetic phenomena are due to motion of the electric charges present in that material. A piece of magnetic material on an atomic scale have tiny currents due to electrons
Magnetostatics III Magnetization All magnetic phenomena are due to motion of the electric charges present in that material. A piece of magnetic material on an atomic scale have tiny currents due to electrons
ELE 3310 Tutorial 10. Maxwell s Equations & Plane Waves
 ELE 3310 Tutorial 10 Mawell s Equations & Plane Waves Mawell s Equations Differential Form Integral Form Faraday s law Ampere s law Gauss s law No isolated magnetic charge E H D B B D J + ρ 0 C C E r dl
ELE 3310 Tutorial 10 Mawell s Equations & Plane Waves Mawell s Equations Differential Form Integral Form Faraday s law Ampere s law Gauss s law No isolated magnetic charge E H D B B D J + ρ 0 C C E r dl
Lecture 33. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 33 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Faraday s law of induction When the magnetic flux through a single closed loop changes with time, there is an induced emf that can drive a current around the loop: Recall
Lecture 33 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Faraday s law of induction When the magnetic flux through a single closed loop changes with time, there is an induced emf that can drive a current around the loop: Recall
Vector field and Inductance. P.Ravindran, PHY041: Electricity & Magnetism 19 February 2013: Vector Field, Inductance.
 Vector field and Inductance Earth s Magnetic Field Earth s field looks similar to what we d expect if 11.5 there were a giant bar magnet imbedded inside it, but the dipole axis of this magnet is offset
Vector field and Inductance Earth s Magnetic Field Earth s field looks similar to what we d expect if 11.5 there were a giant bar magnet imbedded inside it, but the dipole axis of this magnet is offset
Dr. Fritz Wilhelm page 1 of 13 C:\physics\230 lecture\ch31 Faradays law.docx; 5/3/2009
 Dr. Fritz Wilhelm page 1 of 13 C:\physics\3 lecture\ch31 Faradays law.docx; 5/3/9 Homework: See website. Table of Contents: 31.1 Faraday s Law of Induction, 31. Motional emf and Power, 4 31.a Transformation
Dr. Fritz Wilhelm page 1 of 13 C:\physics\3 lecture\ch31 Faradays law.docx; 5/3/9 Homework: See website. Table of Contents: 31.1 Faraday s Law of Induction, 31. Motional emf and Power, 4 31.a Transformation
CHAPTER 5: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 CHAPTER 5: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 5 5. An AC generator consists a coil of 30 turns with cross sectional area 0.05 m 2 and resistance 100 Ω. The coil rotates in a magnetic field
CHAPTER 5: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 5 5. An AC generator consists a coil of 30 turns with cross sectional area 0.05 m 2 and resistance 100 Ω. The coil rotates in a magnetic field
Where k = 1. The electric field produced by a point charge is given by
 Ch 21 review: 1. Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of a matter. There are two kinds of charges, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other. Charges of opposite sign attract.
Ch 21 review: 1. Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of a matter. There are two kinds of charges, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other. Charges of opposite sign attract.
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I)
 Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
Electromagnetic Induction
 Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 29 Looking forward
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 29 Looking forward
Yell if you have any questions
 Class 31: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions possible exam questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P31 1 Exam 3 Topics Faraday s Law Self Inductance Energy Stored
Class 31: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions possible exam questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P31 1 Exam 3 Topics Faraday s Law Self Inductance Energy Stored
October 23. Physics 272. Fall Prof. Philip von Doetinchem
 Physics 272 October 23 Fall 2014 http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~philipvd/pvd_14_fall_272_uhm.html Prof. Philip von Doetinchem philipvd@hawaii.edu Phys272 - Fall 14 - von Doetinchem - 170 Motional electromotive
Physics 272 October 23 Fall 2014 http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~philipvd/pvd_14_fall_272_uhm.html Prof. Philip von Doetinchem philipvd@hawaii.edu Phys272 - Fall 14 - von Doetinchem - 170 Motional electromotive
A Brief Revision of Vector Calculus and Maxwell s Equations
 A Brief Revision of Vector Calculus and Maxwell s Equations Debapratim Ghosh Electronic Systems Group Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay e-mail: dghosh@ee.iitb.ac.in
A Brief Revision of Vector Calculus and Maxwell s Equations Debapratim Ghosh Electronic Systems Group Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay e-mail: dghosh@ee.iitb.ac.in
Today in Physics 217: EMF, induction, and Faraday s Law
 Today in Physics 217: EMF, induction, and Faraday s Law Electromotive force v Motional EMF The alternating-current generator Induction, Faraday s Law, Lenz s Law I R h I Faraday s Law and Ampère s Law
Today in Physics 217: EMF, induction, and Faraday s Law Electromotive force v Motional EMF The alternating-current generator Induction, Faraday s Law, Lenz s Law I R h I Faraday s Law and Ampère s Law
