Reactive Transport & Biodegradation Model (Part I)
|
|
|
- Darlene Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Projet no.: (STREP) SEDBARCAH SEDiment BioBARriers for Chlorinated Aliphati Hydroarbons in ground water reahing surfae water Reative Transport & Biodegradation Model (Part I) Harald Kalka Short Leture at the Meeting Wageningen, January 006 Start date of projet: 01/01/005 Lead ontrator for Work Pakage 5 (Modeling): Duration: years UIT GmbH Dresden
2 Reative Transport and CAH-Biodegradation Model SEDBARCAH 1 Basi Equations Transport Phenomena 3 Enzyme Kinetis 4 Model Parameters 5 Software Presentation / Examples H. Kalka, UIT Gmbh Dresden, Germany Wageningen / January 006
3 Main Proesses Advetion Dispersion Sorption Enzyme Kinetis Population Dynamis Wageningen / January Thermodynamis CO- Equilibrium ph, ORP Transport Biodegradation Geohemistry Multi-Layer Model (Compartment Model) redutive dehlorination obi oxidation PhreeqC Mass & Charge onservation
4 Multi-Layer Model (Compartments) Layer A Layer B Layer C inflow F(t) Transport & Reations along a flow line 1 Model for Tasks Column Experiments Field-Sale Appliations Zenne Site Bath Reations (only kinetis) Pelhrimov Site Wageningen / January
5 Basi Equation (ADR) multi-speies model i CAH s, Cl -, DOC, O, CO... R t i v i x D L x i Φ bio ( i, j ) sorption advetion dispersion biodegradation Set of Partial Differential Equations (PDE) PCE TCE TCE DCE Wageningen / January
6 Operator Splitting t Φ Φ Φ adv Φ disp Φ bio n n1 n 1/ 3 n / 3 n 3/ 3 ~ Φ ~ Φ ~ Φ adv disp bio ( ( ( n, t) n 1/ 3 n / 3, t), t) FD method m intermediate steps k intermediate steps t / m t / k Runge-Kutta for ODE Wageningen / January
7 Cell size & Time step Layer A Layer B Layer C N A ells N B ells N C ells Vpore onst εaa x A εba x B... x L L N L L flow: pore veloity: V Q t Q vl ε A L pore x t onst L t V Q pore AεL x Q L onst Wageningen / January
8 Wageningen / January Analytial Solution x D x v t L λ 4Dt w) x(v erf D w) x(v exp 4Dt w) x(v erf D w) x(v exp t) (x, 0 λ D 4 v w π x ) t ( exp x erf 0 t, x for 0 0 t 0, x for 0 x 0, t for 0 0 > > >
9 Numerial Test N 40 ells v 9.8 mm/h t.56 h L 1 m 0 mm onentration [mm],1,0 1,9 1,8 1,7 α L 5 mm α L 50 mm 1,6 1,5 λ 0 λ 0 1,4 1,3 1, 1,1 1,0 0,9 α L 50 mm 0,8 0,7 λ 5 h -1 0,6 0,5 0,4 0,3 0, 0,1 0, Model versus Analytial Solution time [h] Wageningen / January
10 Degradation Pathways PCE Cl - TCE Cl - redutive dehlorination (erobi) DCE Cl - CO Cl - VC Cl - obi oxidation CO Cl - CO ETH Wageningen / January
11 Eletron Transfer e-donor e-aeptor DCE VC Cl - Mirobe e - ½CH O ½ CO O Mirobe H O 4e - ½DCE CO Cl - redutive dehlorination obi oxidation Wageningen / January
12 Eletron Balane CHCl CH O HO CO 4H 4e CHCl H e CHCl CH Cl DCE Corg H O VC CO H Cl erobi obi CHCl CHCl 4H O CO 10H 8e Cl O 4H 4e H O DCE O CO H Cl Wageningen / January
13 Biodegradation ODE (part I) d [PCE] Λ d [TCE] Λ P d [DCE] Λ d [VC] d [ETH] Λ Λ P T T T D D V V E Λ Λ Λ Λ T D D V V E E C Λ Λ D C V C d [CAH] abbreviations: Λ Λ Λ Λ P T D C Λ Λ T D V C ( Λ Λ ) Λ Λ V E D V are E C V C Λ V E Wageningen / January
14 Biodegradation ODE (part II) d [Cl d [C org d [O ] d [CO ] ] Λ y Corg Λ Λ D C Λ V C 5 Λ D C Λ V C 3 ] yco Λ Λ Λ E C for CH O as C org y Corg y CO stoihiometri oeffiients CO ΗCO HCO 3 - d [H ] d [Cl ] ( CO equilibiurm ) PhreeqC Wageningen / January
15 Population Dynamis biomass populations dx dx Y Y Λ Λ k k d d X X stationarity yield oeffiient death rate dx 0 Wageningen / January
16 Environmental Fators Temperature (ARRHENIUS behavior) ph miroorgs prefer ph ORP Moisture Content but: prodution of org. aids, HCl ( erobi / obi ) Nutrients C:N:P 10:10:1 Inhibiting or Toxi Compounds Wageningen / January
17 Enzyme Kinetis (part I) transition rates Λ Λ biomass i j i j X f i j (CAH) f temperature dependene (C org ) f 3 (T) f 4 (ph) F X fi j(cah) f (O) f3(t) f4(ph) ph dependene inh MICHAELIS-MENTEN and HALDANE f () [] K [] F inh K inh K inh [O non-ompetitive inhibition ] Wageningen / January
18 MICHAELIS-MENTEN Kinetis E S k k ES k E P steady state E S ES E P d[p] v K max S [S] [S] v max d[p]/ ½v max K S k k k [ E0 ] [E] [ES] vmax k[e0] K S [S] Wageningen / January
19 Enzyme Inhibition E H EH ompetitive inhibition v K I [S] [S] I 1 [H] K max 1 S 1 1 E S ESS self-inhibition (HALDANE) v K [S] I 1 [S] K max S [S]I E S G ESG non-ompetitive inhibition v K [S] 1 I [G] I 1 max 3 S [S] 3 K3 Wageningen / January
20 Enzyme Kinetis (part II) k i v (i) max / X CAH speies f i j K I i i k i[i] [i] [i] / K H i many kineti parameters! I i ompetitive inhibition 1 j i [j] K inh ij assumption: self-inhibition (HALDANE) K inh ij K j Wageningen / January
21 Software (1st version 0.40) User Interfae fast C ode inl. PhreeqC high flexibility Online Visualization Data Interpretation Wageningen / January
22 High Flexibility number of layers (ompartments) number of ells per layer number of hemial elements (PhreeqC) number of inflow ompositions unlimited unlimited unlimited unlimited Clearly arranged Input / Output struture Stop-and-Go (alulation with interrupts) Open for future extensions Wageningen / January
23 Input Data (part I) time-step wih t h ell number Ν end time T h ell length x m ross setion area A m porosity ε number of layers N L dispersity α L m inflow solution inp.sol bulk density ρ b g/m 3 Global Data org. arbon ontentent biomass for t0 f o X µg/l Data for eah Layer biomass for t0 initial solution fot t0 X µg/l file: ell.sol Wageningen / January
24 Input Data (part II) temperature temp C ph-value ORP PCE TCE CAH s is-dce VC ETH C org (dissolved organi arbon) ph pe mm mm mm mm mm mm Aqueous Solution Data DIC (dissolved inorgani arbon) mm Cl mm DO (dissolved oxygen) mm file: ell.sol other anions: S(VI), S(-II), N(V),... mm file: inp.sol other ations: Ca, Mg, Na, N(-III),... mm Wageningen / January
25 Input Data (part III) obi erobi max. speifi dehlor. rate half-veloity oeffiient HALDANE oeffiint max. speifi oxid. rate half-veloity oeffiient HALDANE oeffiint O inhibition K inh k i K i K Hi k i K i K Hi µm µmol/µg/d µmol/µg/d µmol/µg/d µmol/µg/d µmol/µg/d µmol/µg/d PCE TCE TCE DCE DCE VC VC ETH DCE CO VC CO ETH CO C org half-veloity oeffiient K Corg µm Population Dynamis yield Y, Y µg/µmol 7 Kineti Parameters death rate k d, k d d 1 Wageningen / January
26 Example Calulations A B C D E F pure advetion advetion dispersion biodegradation with onstant inflow biodegradation with time-dependent inflow biodegradation with population dynamis... other examples Software Presentation Wageningen / January
27 Kineti Parameter Set (Example) erobi k i µmol/mgp/d K i µm K Hi µm λ k i X/ K i d -1 PCE TCE TCE DCE DCE VC VC ETH X mgp/l 30 Y mgp/µm Cl k death d data: Yu & Semprini 004 Data in literature varies strongly! Wageningen / January
28 Demo (3 Example Configurations) onst inflow onst inflow t 0: t 0: 1 Layer (40 ells) A without CAH 3 Layers A B C without with CAH without A B C no X with X no X Wageningen / January
29 Open Questions e - donor C org : CH O, CH 4 or other? fration of DOC? population dynamis: stationarity? obi oxidation? role of other oxidants (NO3 et.)?... and many other questions Wageningen / January
30 WP5 - Next Steps PC-Program end version D11 Model / Software desription Feb month UIT Simulation Column Tests Simulation Zenne & Pelhrimov sites WP1, WP, WP3 ode updating 3 month Statistial Modelling (AUA) WP6 Guidlines Wageningen / January
31 More Info: SEDBARCAH projet Deliverable D11 End of presentation. Wageningen / January
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #11: Solute Transport in Groundwater
 1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. harles Harvey Leture Paket #11: Solute Transport in Groundwater Importane of Solute Transport in Groundwater Geologi questions: ion migration, ore deposition. Environmental
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. harles Harvey Leture Paket #11: Solute Transport in Groundwater Importane of Solute Transport in Groundwater Geologi questions: ion migration, ore deposition. Environmental
Chapter 14. The Concept of Equilibrium and the Equilibrium Constant. We have for the most part depicted reactions as going one way.
 Chapter 14 The Conept of Equilibrium and the Equilibrium Constant In hapter 1 we dealt with Physial Equilibrium Physial Changes HO 2 (l) HO 2 (g) In hapter 14 we will learn about Chemial Equilibrium. We
Chapter 14 The Conept of Equilibrium and the Equilibrium Constant In hapter 1 we dealt with Physial Equilibrium Physial Changes HO 2 (l) HO 2 (g) In hapter 14 we will learn about Chemial Equilibrium. We
9.4 Determination of the reaction order
 0,1 0,2 0,3 r 0,1 r 0,2 r 0,3 t Signifiane r = k [A] [B] [C] One we determine the order of a reation, we an write out the rate equation of the reation and tell the details of the kineti harateristis of
0,1 0,2 0,3 r 0,1 r 0,2 r 0,3 t Signifiane r = k [A] [B] [C] One we determine the order of a reation, we an write out the rate equation of the reation and tell the details of the kineti harateristis of
CEE 670 TRANSPORT PROCESSES IN ENVIRONMENTAL AND WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING. Kinetics Lecture #1
 Updated: 8 Deember 0 Print version CEE 670 TRNSPORT PROCESSES IN ENVIRONMENTL ND WTER RESOURCES ENGINEERING Kinetis Leture # Introdution: Simple Rate Laws Clark, 9.-9.6 Brezonik, pp.-39 Introdution Kinetis
Updated: 8 Deember 0 Print version CEE 670 TRNSPORT PROCESSES IN ENVIRONMENTL ND WTER RESOURCES ENGINEERING Kinetis Leture # Introdution: Simple Rate Laws Clark, 9.-9.6 Brezonik, pp.-39 Introdution Kinetis
Chapter 15: Chemical Equilibrium
 Chapter 5: Chemial Equilibrium ahoot!. At eq, the rate of the forward reation is the rate of the reverse reation. equal to, slower than, faster than, the reverse of. Selet the statement that BEST desribes
Chapter 5: Chemial Equilibrium ahoot!. At eq, the rate of the forward reation is the rate of the reverse reation. equal to, slower than, faster than, the reverse of. Selet the statement that BEST desribes
2. Failure to submit this paper in its entirety at the end of the examination may result in disqualification.
 Memorial University of Newfoundland St. John s, Newfoundland and Labrador Chemistry 101 Intersession 007 Midterm Exam May 8 th, 007 Time: 0 Minutes Name: MUN #: Dr. Peter Warburton READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY!
Memorial University of Newfoundland St. John s, Newfoundland and Labrador Chemistry 101 Intersession 007 Midterm Exam May 8 th, 007 Time: 0 Minutes Name: MUN #: Dr. Peter Warburton READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY!
A Simple Formula to Estimate the Maximum Contaminant Plume Length
 Simple Formula to Estimate the Maximum Contaminant Plume ength P. Dietrih (),. J. Valohi (), R. iedl (), P. Grathwohl () () Center for pplied Geosiene, University of Tuebingen () Dept. of Civil and Environmental
Simple Formula to Estimate the Maximum Contaminant Plume ength P. Dietrih (),. J. Valohi (), R. iedl (), P. Grathwohl () () Center for pplied Geosiene, University of Tuebingen () Dept. of Civil and Environmental
Mechanistic Model for Reactive Transport of Radionuclides on Iron-(Oxy)Hydroxide Colloids at the Yucca Mountain Repository
 U.S. Department of Energy Offie of Civilian Radioative Waste Management Mehanisti Model for Reative Transport of Radionulides on Iron-(Oxy)Hydroxide Colloids at the Yua Mountain Repository Presented to:
U.S. Department of Energy Offie of Civilian Radioative Waste Management Mehanisti Model for Reative Transport of Radionulides on Iron-(Oxy)Hydroxide Colloids at the Yua Mountain Repository Presented to:
Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium
 Chapter 5 Chemial Equilibrium 5. The Conept of Equilibrium Figure: 3. from Chemistry by MMurray & Fey Figure 3.(a) NO 4( g) NO( g) olorless brown we start with reatant, N O 4, so the solution is olorless
Chapter 5 Chemial Equilibrium 5. The Conept of Equilibrium Figure: 3. from Chemistry by MMurray & Fey Figure 3.(a) NO 4( g) NO( g) olorless brown we start with reatant, N O 4, so the solution is olorless
POROUS CARBON PARTICLE COMBUSTION IN AIR
 MCS 7 Chia Laguna, Cagliari, Sardinia, taly, 11-15, 11 POOUS CABON PATCLE COMBUSTON N A V. M. Gremyahkin grema@ipmnet.ru nstitute for Problems in Mehanis, AS, Mosow, ussia Abstrat Theoretial investigation
MCS 7 Chia Laguna, Cagliari, Sardinia, taly, 11-15, 11 POOUS CABON PATCLE COMBUSTON N A V. M. Gremyahkin grema@ipmnet.ru nstitute for Problems in Mehanis, AS, Mosow, ussia Abstrat Theoretial investigation
Determination of the reaction order
 5/7/07 A quote of the wee (or amel of the wee): Apply yourself. Get all the eduation you an, but then... do something. Don't just stand there, mae it happen. Lee Iaoa Physial Chemistry GTM/5 reation order
5/7/07 A quote of the wee (or amel of the wee): Apply yourself. Get all the eduation you an, but then... do something. Don't just stand there, mae it happen. Lee Iaoa Physial Chemistry GTM/5 reation order
Chapter 15 Equilibrium. Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium. Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium. Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium 5/27/2014
 Amount of reatant/produt 5/7/01 quilibrium in Chemial Reations Lets look bak at our hypothetial reation from the kinetis hapter. A + B C Chapter 15 quilibrium [A] Why doesn t the onentration of A ever
Amount of reatant/produt 5/7/01 quilibrium in Chemial Reations Lets look bak at our hypothetial reation from the kinetis hapter. A + B C Chapter 15 quilibrium [A] Why doesn t the onentration of A ever
Chapter 15 Equilibrium. Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium. Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium. Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium 2/3/2014
 Amount of reatant/produt //01 quilibrium in Chemial Reations Lets look bak at our hypothetial reation from the kinetis hapter. A + B C Chapter 15 quilibrium [A] Why doesn t the onentration of A ever go
Amount of reatant/produt //01 quilibrium in Chemial Reations Lets look bak at our hypothetial reation from the kinetis hapter. A + B C Chapter 15 quilibrium [A] Why doesn t the onentration of A ever go
9.4 Determination of the reaction order
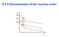 0,1 0,2 0,3 r 0,1 r 0,2 r 0,3 t Signifiane r = k [A] [B] [C] One we determine the order of a reation, we an write out the rate equation of the reation and tell the details of the kineti harateristis of
0,1 0,2 0,3 r 0,1 r 0,2 r 0,3 t Signifiane r = k [A] [B] [C] One we determine the order of a reation, we an write out the rate equation of the reation and tell the details of the kineti harateristis of
Lecture 6 Design of ESP
 Leture 6 Design of ES DESIGN OF ELECTROSTATIC RECIITATOR Introdution An eletrostati preipitator (ES) is a partile ontrol devie that uses eletrial fores to move the partiles out of the flowing gas stream
Leture 6 Design of ES DESIGN OF ELECTROSTATIC RECIITATOR Introdution An eletrostati preipitator (ES) is a partile ontrol devie that uses eletrial fores to move the partiles out of the flowing gas stream
JF Physical Chemistry JF CH 1101: Introduction to Physical Chemistry.
 JF Physial Chemistry 010-011. JF CH 1101: Introdution to Physial Chemistry. Dr Mike Lyons. Shool of Chemistry Trinity College Dublin. melyons@td.ie A ompendium of past examination questions set on Physial
JF Physial Chemistry 010-011. JF CH 1101: Introdution to Physial Chemistry. Dr Mike Lyons. Shool of Chemistry Trinity College Dublin. melyons@td.ie A ompendium of past examination questions set on Physial
Chemistry (Physical chemistry) Lecture 10.
 Chemistry (Physial hemistry) Leture 0. EPM, semester II by Wojieh Chrzanowsi, PhD, DS Wyłady współfinansowane ze środów Unii Europejsiej w ramah EFS, UDA-POKL 04.0.02.-00-37/-00 Absolwent Wydziału Chemiznego
Chemistry (Physial hemistry) Leture 0. EPM, semester II by Wojieh Chrzanowsi, PhD, DS Wyłady współfinansowane ze środów Unii Europejsiej w ramah EFS, UDA-POKL 04.0.02.-00-37/-00 Absolwent Wydziału Chemiznego
Module 4 Lesson 2 Exercises Answer Key squared square root
 Module Lesson Eerises Answer Key 1. The volume is 1 L so onentrations an be done by inspetion. Just substitute values and solve for K [ CO][ HO] K CO H (0.8)(0.8) (0.55) (0.55) K 0.659. [CH ][HS] K [H
Module Lesson Eerises Answer Key 1. The volume is 1 L so onentrations an be done by inspetion. Just substitute values and solve for K [ CO][ HO] K CO H (0.8)(0.8) (0.55) (0.55) K 0.659. [CH ][HS] K [H
Lecture 4. Kinetics and Transport in Sorption (1)
 Leture 4. Kinetis and Transport in Sorption () Mass-Transport Proesses in Adsorption Convetion-Dispersion Model Modes of Time-Dependent Sorption Operation Chromatogram Solute Conentration Distriution Separation
Leture 4. Kinetis and Transport in Sorption () Mass-Transport Proesses in Adsorption Convetion-Dispersion Model Modes of Time-Dependent Sorption Operation Chromatogram Solute Conentration Distriution Separation
Mass Transfer (Stoffaustausch) Fall 2012
 Mass Transfer (Stoffaustaush) Fall Examination 9. Januar Name: Legi-Nr.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussler: none nd rd Test Duration: minutes The following materials are not permitted at your table and
Mass Transfer (Stoffaustaush) Fall Examination 9. Januar Name: Legi-Nr.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussler: none nd rd Test Duration: minutes The following materials are not permitted at your table and
Chapter 13, Chemical Equilibrium
 Chapter 13, Chemial Equilibrium You may have gotten the impression that when 2 reatants mix, the ensuing rxn goes to ompletion. In other words, reatants are onverted ompletely to produts. We will now learn
Chapter 13, Chemial Equilibrium You may have gotten the impression that when 2 reatants mix, the ensuing rxn goes to ompletion. In other words, reatants are onverted ompletely to produts. We will now learn
Line Radiative Transfer
 http://www.v.nrao.edu/ourse/astr534/ineradxfer.html ine Radiative Transfer Einstein Coeffiients We used armor's equation to estimate the spontaneous emission oeffiients A U for À reombination lines. A
http://www.v.nrao.edu/ourse/astr534/ineradxfer.html ine Radiative Transfer Einstein Coeffiients We used armor's equation to estimate the spontaneous emission oeffiients A U for À reombination lines. A
Fluorescence Correlation
 Theory setions of the leture Studying dynami proesses in ells and model membranes with Fluoresene Correlation Spetrosopy () and FCS-urves LSM (3D projetion) Confoal Laser Sanning Mirosopy presented at
Theory setions of the leture Studying dynami proesses in ells and model membranes with Fluoresene Correlation Spetrosopy () and FCS-urves LSM (3D projetion) Confoal Laser Sanning Mirosopy presented at
Homework Set 4. gas B open end
 Homework Set 4 (1). A steady-state Arnold ell is used to determine the diffusivity of toluene (speies A) in air (speies B) at 298 K and 1 atm. If the diffusivity is DAB = 0.0844 m 2 /s = 8.44 x 10-6 m
Homework Set 4 (1). A steady-state Arnold ell is used to determine the diffusivity of toluene (speies A) in air (speies B) at 298 K and 1 atm. If the diffusivity is DAB = 0.0844 m 2 /s = 8.44 x 10-6 m
KINETICS OF IRON OXIDE DIRECT REDUCTION BY COAL E.R. ABRIL 1
 KINETICS OF IRON OXIDE DIRECT REDUCTION BY COAL E.R. ABRIL 1 CIMM- Av.Velez Sarsfield 1561 C.P.5000 Córdoba, Argentina. aabril@intiemor.gov.ar Abstrat - A new interpretation to the kinetis of iron oxide
KINETICS OF IRON OXIDE DIRECT REDUCTION BY COAL E.R. ABRIL 1 CIMM- Av.Velez Sarsfield 1561 C.P.5000 Córdoba, Argentina. aabril@intiemor.gov.ar Abstrat - A new interpretation to the kinetis of iron oxide
Part II SECTION I : One or more options correct Type
 [1] JEE Advaned 2013/ Paper -2 Part II SECTION I : One or more options orret Type This setion ontains 8 multiple hoie questions. Eah question has four hoies (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of whih ONE or MORE
[1] JEE Advaned 2013/ Paper -2 Part II SECTION I : One or more options orret Type This setion ontains 8 multiple hoie questions. Eah question has four hoies (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of whih ONE or MORE
General Equilibrium. What happens to cause a reaction to come to equilibrium?
 General Equilibrium Chemial Equilibrium Most hemial reations that are enountered are reversible. In other words, they go fairly easily in either the forward or reverse diretions. The thing to remember
General Equilibrium Chemial Equilibrium Most hemial reations that are enountered are reversible. In other words, they go fairly easily in either the forward or reverse diretions. The thing to remember
2 How far? Equilibrium Answers
 How far? Equilibrium Answers ratie: pages 37 39 1 Answer is D. Only a hange in temperature harges the value of the equilibrium onstant. Answer is D. [B] /[A] so [B] [A] or [B] [A] 1/ 3 Answer is B. Amounts
How far? Equilibrium Answers ratie: pages 37 39 1 Answer is D. Only a hange in temperature harges the value of the equilibrium onstant. Answer is D. [B] /[A] so [B] [A] or [B] [A] 1/ 3 Answer is B. Amounts
MODULE 3: MASS TRANSFER COEFFICIENTS
 MOULE 3: MASS TRASFER COEFFICIETS LECTURE O. 6 3.5. Penetration theory Most of the industrial proesses of mass transfer is unsteady state proess. In suh ases, the ontat time between phases is too short
MOULE 3: MASS TRASFER COEFFICIETS LECTURE O. 6 3.5. Penetration theory Most of the industrial proesses of mass transfer is unsteady state proess. In suh ases, the ontat time between phases is too short
THALES Project No. 65/1181
 THALES Projet No. 65/8 Time distribution of adsorption ative sites on heterogeneous solid surfaes through experimental measurements of adsorption energies, loal adsorption isotherms and the energy distribution
THALES Projet No. 65/8 Time distribution of adsorption ative sites on heterogeneous solid surfaes through experimental measurements of adsorption energies, loal adsorption isotherms and the energy distribution
(\4. liz. jl2. ci3?( iu1 q. Oft) ojo. 1 r %FN. x L. - i t <. a0
 7, p. A Il i II (A L A 1 > D i t
7, p. A Il i II (A L A 1 > D i t
Chapter 8 Thermodynamic Relations
 Chapter 8 Thermodynami Relations 8.1 Types of Thermodynami roperties The thermodynami state of a system an be haraterized by its properties that an be lassified as measured, fundamental, or deried properties.
Chapter 8 Thermodynami Relations 8.1 Types of Thermodynami roperties The thermodynami state of a system an be haraterized by its properties that an be lassified as measured, fundamental, or deried properties.
Mass Transfer 2. Diffusion in Dilute Solutions
 Mass Transfer. iffusion in ilute Solutions. iffusion aross thin films and membranes. iffusion into a semi-infinite slab (strength of weld, tooth deay).3 Eamples.4 ilute diffusion and onvetion Graham (85)
Mass Transfer. iffusion in ilute Solutions. iffusion aross thin films and membranes. iffusion into a semi-infinite slab (strength of weld, tooth deay).3 Eamples.4 ilute diffusion and onvetion Graham (85)
Advanced Computational Fluid Dynamics AA215A Lecture 4
 Advaned Computational Fluid Dynamis AA5A Leture 4 Antony Jameson Winter Quarter,, Stanford, CA Abstrat Leture 4 overs analysis of the equations of gas dynamis Contents Analysis of the equations of gas
Advaned Computational Fluid Dynamis AA5A Leture 4 Antony Jameson Winter Quarter,, Stanford, CA Abstrat Leture 4 overs analysis of the equations of gas dynamis Contents Analysis of the equations of gas
Laboratory exercise No. 2 Basic material parameters of porous building materials
 Laboratory exerise No. Basi material parameters of porous building materials Materials (building materials) an be lassified aording to the different riteria, e.g. based on their properties, funtion, hemial
Laboratory exerise No. Basi material parameters of porous building materials Materials (building materials) an be lassified aording to the different riteria, e.g. based on their properties, funtion, hemial
Chemical Reaction Engineering
 Leture 6 Chemial Reation Engineering (CRE) is the field that studies the rates and mehanisms of hemial reations and the design of the reators in whih they tae plae. Web Leture 6 Class Leture Course Information
Leture 6 Chemial Reation Engineering (CRE) is the field that studies the rates and mehanisms of hemial reations and the design of the reators in whih they tae plae. Web Leture 6 Class Leture Course Information
Perspective of environmental impact modelling of CO2 leakage for public acceptance
 Perspetive of environmental impat modelling of CO2 leakage for publi aeptane Toru Sato Dept of Oean Tehnology, Poliy, and Environment University of Tokyo CO2 Leakage Risk CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage)
Perspetive of environmental impat modelling of CO2 leakage for publi aeptane Toru Sato Dept of Oean Tehnology, Poliy, and Environment University of Tokyo CO2 Leakage Risk CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage)
Heat exchangers: Heat exchanger types:
 Heat exhangers: he proess of heat exhange between two fluids that are at different temperatures and separated by a solid wall ours in many engineering appliations. he devie used to implement this exhange
Heat exhangers: he proess of heat exhange between two fluids that are at different temperatures and separated by a solid wall ours in many engineering appliations. he devie used to implement this exhange
In this problem, we are given the following quantities: We want to find: Equations and basic calculations:
 .1 It takes. million tons of oal per year to a 1000-W power plant that operates at a apaity fator of 70%. If the heating value of the oal is 1,000 /lb, alulate the plant s effiieny and the heat rate. In
.1 It takes. million tons of oal per year to a 1000-W power plant that operates at a apaity fator of 70%. If the heating value of the oal is 1,000 /lb, alulate the plant s effiieny and the heat rate. In
THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE?
 THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE? The stars are spheres of hot gas. Most of them shine beause they are fusing hydrogen into helium in their entral parts. In this problem we use onepts of
THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE? The stars are spheres of hot gas. Most of them shine beause they are fusing hydrogen into helium in their entral parts. In this problem we use onepts of
A First Course on Kinetics and Reaction Engineering. Class 9 on Unit 9
 A First Course on Kinetics and Reaction Engineering Class 9 on Unit 9 Part I - Chemical Reactions Part II - Chemical Reaction Kinetics Where We re Going A. Rate Expressions - 4. Reaction Rates and Temperature
A First Course on Kinetics and Reaction Engineering Class 9 on Unit 9 Part I - Chemical Reactions Part II - Chemical Reaction Kinetics Where We re Going A. Rate Expressions - 4. Reaction Rates and Temperature
IV Transport Phenomena. Lecture 21: Solids and Concentrated Solutions
 IV Transport Phenomena Leture 21: Solids and Conentrated Solutions MIT Student (and MZB) Marh 28, 2011 1 Transport in Solids 1.1 Diffusion The general model of hemial reations an also be used for thermally
IV Transport Phenomena Leture 21: Solids and Conentrated Solutions MIT Student (and MZB) Marh 28, 2011 1 Transport in Solids 1.1 Diffusion The general model of hemial reations an also be used for thermally
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Lecture/Lession Plan -1
 Chapter 4 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Leture/Lession Plan -1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 4.1 Conept of eletrohemistry Eletrohemistry is a branh of hemistry where we will study how hemial energy an be transformed into eletrial
Chapter 4 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Leture/Lession Plan -1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 4.1 Conept of eletrohemistry Eletrohemistry is a branh of hemistry where we will study how hemial energy an be transformed into eletrial
Moisture transport in seasoned wood
 in seasoned wood Coupled diffusion model and model sensitivity Staffan Svensson 1976 Syrause Univ. press Wood struture and identifiation H. A.. Core, et al. Wood, a open porous material Softwood has a
in seasoned wood Coupled diffusion model and model sensitivity Staffan Svensson 1976 Syrause Univ. press Wood struture and identifiation H. A.. Core, et al. Wood, a open porous material Softwood has a
IMPACT MODELLING OF THE COEFFICIENT OF RESTITUTION OF POTATOES BASED ON THE KELVIN- VOIGHT PAIR
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agriultural Food Engineering Vol. 9 (58) No. - 06 IMPACT MODELLING OF THE COEFFICIENT OF RESTITUTION OF POTATOES BASED
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agriultural Food Engineering Vol. 9 (58) No. - 06 IMPACT MODELLING OF THE COEFFICIENT OF RESTITUTION OF POTATOES BASED
Relativistic Dynamics
 Chapter 7 Relativisti Dynamis 7.1 General Priniples of Dynamis 7.2 Relativisti Ation As stated in Setion A.2, all of dynamis is derived from the priniple of least ation. Thus it is our hore to find a suitable
Chapter 7 Relativisti Dynamis 7.1 General Priniples of Dynamis 7.2 Relativisti Ation As stated in Setion A.2, all of dynamis is derived from the priniple of least ation. Thus it is our hore to find a suitable
Process engineers are often faced with the task of
 Fluids and Solids Handling Eliminate Iteration from Flow Problems John D. Barry Middough, In. This artile introdues a novel approah to solving flow and pipe-sizing problems based on two new dimensionless
Fluids and Solids Handling Eliminate Iteration from Flow Problems John D. Barry Middough, In. This artile introdues a novel approah to solving flow and pipe-sizing problems based on two new dimensionless
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Def n: Reactions in which one or more electrons is shifted from one element to another (In acid/base, gas transfer, and precipitation reactions discussed previously,
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Def n: Reactions in which one or more electrons is shifted from one element to another (In acid/base, gas transfer, and precipitation reactions discussed previously,
Improvements in the Modeling of the Self-ignition of Tetrafluoroethylene
 Exerpt from the Proeedings of the OMSOL onferene 010 Paris Improvements in the Modeling of the Self-ignition of Tetrafluoroethylene M. Bekmann-Kluge 1 *,. errero 1, V. Shröder 1, A. Aikalin and J. Steinbah
Exerpt from the Proeedings of the OMSOL onferene 010 Paris Improvements in the Modeling of the Self-ignition of Tetrafluoroethylene M. Bekmann-Kluge 1 *,. errero 1, V. Shröder 1, A. Aikalin and J. Steinbah
Modeling of Threading Dislocation Density Reduction in Heteroepitaxial Layers
 A. E. Romanov et al.: Threading Disloation Density Redution in Layers (II) 33 phys. stat. sol. (b) 99, 33 (997) Subjet lassifiation: 6.72.C; 68.55.Ln; S5.; S5.2; S7.; S7.2 Modeling of Threading Disloation
A. E. Romanov et al.: Threading Disloation Density Redution in Layers (II) 33 phys. stat. sol. (b) 99, 33 (997) Subjet lassifiation: 6.72.C; 68.55.Ln; S5.; S5.2; S7.; S7.2 Modeling of Threading Disloation
Metal: a free electron gas model. Drude theory: simplest model for metals Sommerfeld theory: classical mechanics quantum mechanics
 Metal: a free eletron gas model Drude theory: simplest model for metals Sommerfeld theory: lassial mehanis quantum mehanis Drude model in a nutshell Simplest model for metal Consider kinetis for eletrons
Metal: a free eletron gas model Drude theory: simplest model for metals Sommerfeld theory: lassial mehanis quantum mehanis Drude model in a nutshell Simplest model for metal Consider kinetis for eletrons
Optimization of In-Situ Chemical Oxidation Design Parameters
 Optimization of In-Situ Chemical Oxidation Design Parameters by Amine Dahmani, PhD Director, Site Assessment & Remediation Laboratories Ken Huang, PhD Remediation Laboratory Manager Environmental Research
Optimization of In-Situ Chemical Oxidation Design Parameters by Amine Dahmani, PhD Director, Site Assessment & Remediation Laboratories Ken Huang, PhD Remediation Laboratory Manager Environmental Research
Characterizing Pure and Undefined Petroleum Components
 International Journal of Engineering & ehnology IJE-IJENS Vol:10 No:0 8 Charaterizing Pure and Undefined Petroleum Components Hassan S. Naji King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Website: http://hnaji.au.edu.sa
International Journal of Engineering & ehnology IJE-IJENS Vol:10 No:0 8 Charaterizing Pure and Undefined Petroleum Components Hassan S. Naji King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Website: http://hnaji.au.edu.sa
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(10): Research Article
 Available online www.jopr.om Journal of Chemial and Pharmaeutial Researh, 014, 6(10:441-449 Researh Artile ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA : JCPRC5 Modeling and simulation of a wetted-wall olumn for SO absorption
Available online www.jopr.om Journal of Chemial and Pharmaeutial Researh, 014, 6(10:441-449 Researh Artile ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA : JCPRC5 Modeling and simulation of a wetted-wall olumn for SO absorption
Evaluation of Organoclays for Use in Landfill Liners
 The Open Waste Management Journal, 29, 2, 37-42 37 Evaluation of Organolays for Use in Landfill Liners Open Aess Bharat Jhamnani * and S.K. Singh Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Delhi
The Open Waste Management Journal, 29, 2, 37-42 37 Evaluation of Organolays for Use in Landfill Liners Open Aess Bharat Jhamnani * and S.K. Singh Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Delhi
Stochastic boundary conditions to the convection-diffusion equation including chemical reactions at solid surfaces.
 Stohasti boundary onditions to the onvetion-diffusion equation inluding hemial reations at solid surfaes. P. Szymzak and A. J. C. Ladd Department of Chemial Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville,
Stohasti boundary onditions to the onvetion-diffusion equation inluding hemial reations at solid surfaes. P. Szymzak and A. J. C. Ladd Department of Chemial Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville,
STATIC SIMULATION PROGRAM OF COPPER SOLVENT EXTRACTION CONFIGURATIONS USING MICROSOFT EXCEL SOLVER
 STATIC SIMULATION PROGRAM OF COPPER SOLVENT EXTRACTION CONFIGURATIONS USING MICROSOFT EXCEL SOLVER Joseph Kafumbila This textbook provides the proedure for design stati simulation programs using Exel Solver
STATIC SIMULATION PROGRAM OF COPPER SOLVENT EXTRACTION CONFIGURATIONS USING MICROSOFT EXCEL SOLVER Joseph Kafumbila This textbook provides the proedure for design stati simulation programs using Exel Solver
III. SURFACE PROPERTIES III.A. SURFACE TENSION SURFACE PROPERTIES
 III. SURFACE PROPERTIES III.A. SURFACE TENSION GOAL: To investigate the influene of the solution onentration and/or the kind of the solute on the surfae tension INTRODUCTION Liquids tend to adopt shapes
III. SURFACE PROPERTIES III.A. SURFACE TENSION GOAL: To investigate the influene of the solution onentration and/or the kind of the solute on the surfae tension INTRODUCTION Liquids tend to adopt shapes
Phase Field Method. From fundamental theories to a phenomenological simulation method. Nele Moelans 24 June 2003
 Phase Field Method From fundamental theories to a phenomenologial simulation method Nele Moelans 4 June 003 Outline Introdution Important onepts: Diffuse interphase-phase field variables Thermodynamis
Phase Field Method From fundamental theories to a phenomenologial simulation method Nele Moelans 4 June 003 Outline Introdution Important onepts: Diffuse interphase-phase field variables Thermodynamis
Gyrokinetic calculations of the neoclassical radial electric field in stellarator plasmas
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 8, NUMBER 6 JUNE 2001 Gyrokineti alulations of the neolassial radial eletri field in stellarator plasmas J. L. V. Lewandowski Plasma Physis Laboratory, Prineton University, P.O.
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 8, NUMBER 6 JUNE 2001 Gyrokineti alulations of the neolassial radial eletri field in stellarator plasmas J. L. V. Lewandowski Plasma Physis Laboratory, Prineton University, P.O.
Electronic Supplementary information
 Eletroni Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Siene & Tehnology. This journal is The Royal Soiety of Chemistry 2017 Eletroni Supplementary information Conversion of n-utane and produt seletivity
Eletroni Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Siene & Tehnology. This journal is The Royal Soiety of Chemistry 2017 Eletroni Supplementary information Conversion of n-utane and produt seletivity
Review of classical thermodynamics
 Review of lassial thermodynamis Fundamental Laws, roperties and roesses () First Law - Energy Balane hermodynami funtions of state Internal energy, heat and work ypes of paths (isobari, isohori, isothermal,
Review of lassial thermodynamis Fundamental Laws, roperties and roesses () First Law - Energy Balane hermodynami funtions of state Internal energy, heat and work ypes of paths (isobari, isohori, isothermal,
PROOST: Object oriented approach to multiphase reactive transport. modeling in porous media.
 1 2 3 PROOST: Objet oriented approah to multiphase reative transport modeling in porous media. P. Gamazo a, L.J. Slooten b,e, J. Carrera b,e, M.W. Saaltink,e, S. Bea d and J. Soler a 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12
1 2 3 PROOST: Objet oriented approah to multiphase reative transport modeling in porous media. P. Gamazo a, L.J. Slooten b,e, J. Carrera b,e, M.W. Saaltink,e, S. Bea d and J. Soler a 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12
CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS
 Updated: 19 November 2013 1 Print version CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS Lecture #19 Chloramines Cont: Primary Literature Enzyme Kinetics: basics Brezonik, pp. 419-450 Introduction Conclusions
Updated: 19 November 2013 1 Print version CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS Lecture #19 Chloramines Cont: Primary Literature Enzyme Kinetics: basics Brezonik, pp. 419-450 Introduction Conclusions
Shrinking core model for the reaction-diffusion problem in thermo-chemical heat storage Lan, S.; Zondag, H.A.; Rindt, C.C.M.
 Shrinking ore model for the reation-diffusion problem in thermo-hemial heat storage Lan, S.; Zondag, H.A.; Rindt, C.C.M. Published in: Proeedings of The 13th International Conferene on Energy Storage,
Shrinking ore model for the reation-diffusion problem in thermo-hemial heat storage Lan, S.; Zondag, H.A.; Rindt, C.C.M. Published in: Proeedings of The 13th International Conferene on Energy Storage,
CE 329, Fall 2015 Assignment 16, Practice Exam
 CE 39, Fall 15 Assignment 16, Practice Exam You may only use pencils, pens and erasers while taking this exam. You may NO use a calculator. You may not leave the room for any reason if you do, you must
CE 39, Fall 15 Assignment 16, Practice Exam You may only use pencils, pens and erasers while taking this exam. You may NO use a calculator. You may not leave the room for any reason if you do, you must
DYNAMICS OF CAPILLARY FLOW AND TRANSPORT PROPERTIES IN CARBONATE SEDIMENTARY FORMATION BY TIME-CONTROLLED POROSIMETRY
 SCA4-44 /5 DYNAMICS OF CAPILLARY FLOW AND TRANSPORT PROPERTIES IN CARBONATE SEDIMENTARY FORMATION BY TIME-CONTROLLED POROSIMETRY A. Cerepi, Institut EGID-Bordeaux 3, Université Mihel de Montaigne,, allée
SCA4-44 /5 DYNAMICS OF CAPILLARY FLOW AND TRANSPORT PROPERTIES IN CARBONATE SEDIMENTARY FORMATION BY TIME-CONTROLLED POROSIMETRY A. Cerepi, Institut EGID-Bordeaux 3, Université Mihel de Montaigne,, allée
Sample Teaching Sequence (Hong Kong Secondary 4 6 Chemistry)
 Revised (1 Sept 009 Sample Teahing Suene (Hong Kong Seondary 4 6 Chemistry Topi: Chemial Equilibrium Teahing Suene Content 1.1 Reversible reations Examples of reversible reation; forward reation; reverse
Revised (1 Sept 009 Sample Teahing Suene (Hong Kong Seondary 4 6 Chemistry Topi: Chemial Equilibrium Teahing Suene Content 1.1 Reversible reations Examples of reversible reation; forward reation; reverse
2. Mass transfer takes place in the two contacting phases as in extraction and absorption.
 PRT 11- CONVECTIVE MSS TRNSFER 2.1 Introdution 2.2 Convetive Mass Transfer oeffiient 2.3 Signifiant parameters in onvetive mass transfer 2.4 The appliation of dimensional analysis to Mass Transfer 2.4.1
PRT 11- CONVECTIVE MSS TRNSFER 2.1 Introdution 2.2 Convetive Mass Transfer oeffiient 2.3 Signifiant parameters in onvetive mass transfer 2.4 The appliation of dimensional analysis to Mass Transfer 2.4.1
Inter-fibre contacts in random fibrous materials: experimental verification of theoretical dependence on porosity and fibre width
 J Mater Si (2006) 41:8377 8381 DOI 10.1007/s10853-006-0889-7 LETTER Inter-fibre ontats in random fibrous materials: experimental verifiation of theoretial dependene on porosity and fibre width W. J. Bathelor
J Mater Si (2006) 41:8377 8381 DOI 10.1007/s10853-006-0889-7 LETTER Inter-fibre ontats in random fibrous materials: experimental verifiation of theoretial dependene on porosity and fibre width W. J. Bathelor
Modeling of Corrosion Kinetics of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid in the Presence and Absence of a Drug Inhibitor
 Portugaliae Eletrohimia Ata 2016, 34(6), 407-416 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201606407 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Modeling of Corrosion Kinetis of Mild Steel in Hydrohlori Aid in the Presene and
Portugaliae Eletrohimia Ata 2016, 34(6), 407-416 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201606407 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Modeling of Corrosion Kinetis of Mild Steel in Hydrohlori Aid in the Presene and
Supporting information
 Eletroni Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Cemistry A. Tis journal is Te Royal Soiety of Cemistry 017 Supporting information Simultaneous improvement of power fator and termal ondutivity
Eletroni Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Cemistry A. Tis journal is Te Royal Soiety of Cemistry 017 Supporting information Simultaneous improvement of power fator and termal ondutivity
RT3D Double Monod Model
 GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS RT3D Double Monod Model 1 Introduction This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in using GMS and RT3D to model the reaction between an electron donor and an electron acceptor, mediated
GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS RT3D Double Monod Model 1 Introduction This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in using GMS and RT3D to model the reaction between an electron donor and an electron acceptor, mediated
v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial RT3D Double Monod Model Prerequisite Tutorials None Time minutes Required Components Grid MODFLOW RT3D
 v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial Objectives Use GMS and RT3D to model the reaction between an electron donor and an electron acceptor, mediated by an actively growing microbial population that exists in both soil
v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial Objectives Use GMS and RT3D to model the reaction between an electron donor and an electron acceptor, mediated by an actively growing microbial population that exists in both soil
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SEA ICE GROWTH AND DESALINATION
 17th International Symposium on Ie Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1-5 June 004 International Assoiation of Hydrauli Engineering and Researh Session I NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SEA ICE GROWTH AND DESALINATION
17th International Symposium on Ie Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1-5 June 004 International Assoiation of Hydrauli Engineering and Researh Session I NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SEA ICE GROWTH AND DESALINATION
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SEA ICE GROWTH AND DESALINATION
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SEA ICE GROWTH AND DESALINATION Chris Petrih 1, Pat J. Langhorne 1, Zhifa Sun 1 ABSTRACT We present a numerial model based on the finite volume method to simulate sea ie growth
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SEA ICE GROWTH AND DESALINATION Chris Petrih 1, Pat J. Langhorne 1, Zhifa Sun 1 ABSTRACT We present a numerial model based on the finite volume method to simulate sea ie growth
Section 3. Interstellar absorption lines. 3.1 Equivalent width
 Setion 3 Interstellar absorption lines 3.1 Equivalent width We an study diuse interstellar louds through the absorption lines they produe in the spetra of bakground stars. Beause of the low temperatures
Setion 3 Interstellar absorption lines 3.1 Equivalent width We an study diuse interstellar louds through the absorption lines they produe in the spetra of bakground stars. Beause of the low temperatures
Where as discussed previously we interpret solutions to this partial differential equation in the weak sense: b
 Consider the pure initial value problem for a homogeneous system of onservation laws with no soure terms in one spae dimension: Where as disussed previously we interpret solutions to this partial differential
Consider the pure initial value problem for a homogeneous system of onservation laws with no soure terms in one spae dimension: Where as disussed previously we interpret solutions to this partial differential
High Energy Astrophysics
 High Energ Astrophsis Essentials Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophsis - Uniersit of Manhester giampaolo.pisano@manhester.a.uk - http://www.jb.man.a.uk/~gp/ Februar 01 Essentials - Eletromagneti
High Energ Astrophsis Essentials Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophsis - Uniersit of Manhester giampaolo.pisano@manhester.a.uk - http://www.jb.man.a.uk/~gp/ Februar 01 Essentials - Eletromagneti
Answer: Easiest way to determine equilibrium concentrations is to set up a table as follows: 2 SO 2 + O 2 2 SO 3 initial conc change
 Problem #1 6 mol of SO and 4 mol of O are plaed into a 1 L flask at temperature, T. The equilibrium onentration of SO is found to be 4 mol/l. Determine K. SO (g) + O (g) SO (g) K = [SO ] / [SO ] [O ] Answer:
Problem #1 6 mol of SO and 4 mol of O are plaed into a 1 L flask at temperature, T. The equilibrium onentration of SO is found to be 4 mol/l. Determine K. SO (g) + O (g) SO (g) K = [SO ] / [SO ] [O ] Answer:
NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ONE-DIMENSIONAL REACTIVE FLOWS IN ROCKET ENGINES WITH REGENERATIVE COOLING
 Proeedings of the 11 th Brazilian Congress of Thermal Sienes and Engineering -- ENCIT 2006 Braz. So. of Mehanial Sienes and Engineering -- ABCM, Curitiba, Brazil, De. 5-8, 2006 Paper CIT06-0353 NUMERICAL
Proeedings of the 11 th Brazilian Congress of Thermal Sienes and Engineering -- ENCIT 2006 Braz. So. of Mehanial Sienes and Engineering -- ABCM, Curitiba, Brazil, De. 5-8, 2006 Paper CIT06-0353 NUMERICAL
MICROSCALE SIMULATIONS OF CONDUCTIVE / RADIATIVE HEAT TRANSFERS IN POROUS MEDIA
 MICROCALE IMULAION OF CONDUCIVE / RADIAIVE HEA RANFER IN POROU MEDIA J.-F. hovert, V.V. Mourzenko, C. Roudani Institut PPRIME-CNR Context, motivation moldering in porous media 400K (measured) Mirosale
MICROCALE IMULAION OF CONDUCIVE / RADIAIVE HEA RANFER IN POROU MEDIA J.-F. hovert, V.V. Mourzenko, C. Roudani Institut PPRIME-CNR Context, motivation moldering in porous media 400K (measured) Mirosale
Asphaltene Deposition Modeling during Natural Depletion and Developing a New Method for Multiphase Flash Calculation
 Iranian Journal of Oil & Gas Siene and Tehnology, Vol. 5 (2016), No. 2, pp. 45-65 http://ijogst.put.a.ir Asphaltene Deposition Modeling during Natural Depletion and Developing a New Method for Multiphase
Iranian Journal of Oil & Gas Siene and Tehnology, Vol. 5 (2016), No. 2, pp. 45-65 http://ijogst.put.a.ir Asphaltene Deposition Modeling during Natural Depletion and Developing a New Method for Multiphase
Three-dimensional morphological modelling in Delft3D-FLOW
 Three-dimensional morphologial modelling in Delft3D-FLOW G. R. Lesser, J. van Kester, D.J.R. Walstra and J.A. Roelvink WL delft hydraulis email: giles.lesser@ldelft.nl Abstrat Computer modelling of sediment
Three-dimensional morphologial modelling in Delft3D-FLOW G. R. Lesser, J. van Kester, D.J.R. Walstra and J.A. Roelvink WL delft hydraulis email: giles.lesser@ldelft.nl Abstrat Computer modelling of sediment
Natural Convection Experiment Measurements from a Vertical Surface
 OBJECTIVE Natural Convetion Experiment Measurements from a Vertial Surfae 1. To demonstrate te basi priniples of natural onvetion eat transfer inluding determination of te onvetive eat transfer oeffiient.
OBJECTIVE Natural Convetion Experiment Measurements from a Vertial Surfae 1. To demonstrate te basi priniples of natural onvetion eat transfer inluding determination of te onvetive eat transfer oeffiient.
RESEARCH ON RANDOM FOURIER WAVE-NUMBER SPECTRUM OF FLUCTUATING WIND SPEED
 The Seventh Asia-Paifi Conferene on Wind Engineering, November 8-1, 9, Taipei, Taiwan RESEARCH ON RANDOM FORIER WAVE-NMBER SPECTRM OF FLCTATING WIND SPEED Qi Yan 1, Jie Li 1 Ph D. andidate, Department
The Seventh Asia-Paifi Conferene on Wind Engineering, November 8-1, 9, Taipei, Taiwan RESEARCH ON RANDOM FORIER WAVE-NMBER SPECTRM OF FLCTATING WIND SPEED Qi Yan 1, Jie Li 1 Ph D. andidate, Department
A Novel Process for the Study of Breakage Energy versus Particle Size
 Geomaterials, 2013, 3, 102-110 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/gm.2013.33013 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.sirp.org/journal/gm) A Novel Proess for the Study of Breakage Energy versus Partile Size Elias
Geomaterials, 2013, 3, 102-110 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/gm.2013.33013 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.sirp.org/journal/gm) A Novel Proess for the Study of Breakage Energy versus Partile Size Elias
Surface tension in a reactive binary mixture of incompressible fluids
 Surfae tension in a reative binary mixture of inompressible fluids Henning Struhtrup Institute for Mathematis and its Appliations, 400 Lind Hall, 07 Churh Street S.E, Minneapolis MN55455 John Dold Mathematis
Surfae tension in a reative binary mixture of inompressible fluids Henning Struhtrup Institute for Mathematis and its Appliations, 400 Lind Hall, 07 Churh Street S.E, Minneapolis MN55455 John Dold Mathematis
Enhanced Energy Harvesting by Concentration. Gradient-Driven Ion Transport in SBA-15 Mesoporous
 Eletroni Supplementary aterial (ESI) for ab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Soiety of Chemistry 016 Eletroni supplementary information (ESI) Enhaned Energy arvesting by Conentration Gradient-Driven
Eletroni Supplementary aterial (ESI) for ab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Soiety of Chemistry 016 Eletroni supplementary information (ESI) Enhaned Energy arvesting by Conentration Gradient-Driven
Replacement of gas phase with liquid, for hexamine production
 Proeedings of the International Conferene on Ciruits, Systems, Signals Replaement of gas phase with liquid, for hexamine prodution Anita Kovač Kralj¹ Davorin Kralj² Faulty of Chemistry and Chemial Engineering,
Proeedings of the International Conferene on Ciruits, Systems, Signals Replaement of gas phase with liquid, for hexamine prodution Anita Kovač Kralj¹ Davorin Kralj² Faulty of Chemistry and Chemial Engineering,
STATISTICAL MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
 UVA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHD QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEM FILE STATISTICAL MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS UPDATED: NOVEMBER 14, 212 1. a. Explain what is meant by the density of states, and give an expression for
UVA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHD QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEM FILE STATISTICAL MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS UPDATED: NOVEMBER 14, 212 1. a. Explain what is meant by the density of states, and give an expression for
Notes on Implementation of Colloid Transport and Colloid-Facilitated Solute Transport into HYDRUS-1D
 Note on Implementation of Colloid Tranport and Colloid-Failitated Solute Tranport into HYDRUS-1D (a text implified from van Genuhten and Šimůnek (24) and Šimůnek et al. (26)) Jirka Šimůnek Department of
Note on Implementation of Colloid Tranport and Colloid-Failitated Solute Tranport into HYDRUS-1D (a text implified from van Genuhten and Šimůnek (24) and Šimůnek et al. (26)) Jirka Šimůnek Department of
RT3D Double Monod Model
 GMS TUTORIALS RT3D Double Monod Model This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in using GMS and RT3D to model the reaction between an electron donor and an electron acceptor, mediated by an actively
GMS TUTORIALS RT3D Double Monod Model This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in using GMS and RT3D to model the reaction between an electron donor and an electron acceptor, mediated by an actively
REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 15
 hemistry 10 ANSWER EY REVIEW QUESTIONS hapter 15 1. A mixture of 0.10 mol of NO, 0.050 mol of H and 0.10 mol of HO is plaed in a 1.0-L flask and allowed to reah equilibrium as shown below: NO (g) + H (g)
hemistry 10 ANSWER EY REVIEW QUESTIONS hapter 15 1. A mixture of 0.10 mol of NO, 0.050 mol of H and 0.10 mol of HO is plaed in a 1.0-L flask and allowed to reah equilibrium as shown below: NO (g) + H (g)
Problem Set 11: Angular Momentum, Rotation and Translation
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department o Physis Physis 80T Fall Term 004 Problem Set : Angular Momentum, Rotation and Translation Available on-line November ; Due: November 3 at 4:00 pm Please
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department o Physis Physis 80T Fall Term 004 Problem Set : Angular Momentum, Rotation and Translation Available on-line November ; Due: November 3 at 4:00 pm Please
Mean Activity Coefficients of Peroxodisulfates in Saturated Solutions of the Conversion System 2NH 4. H 2 O at 20 C and 30 C
 Mean Ativity Coeffiients of Peroxodisulfates in Saturated Solutions of the Conversion System NH 4 Na S O 8 H O at 0 C and 0 C Jan Balej Heřmanova 5, 170 00 Prague 7, Czeh Republi balejan@seznam.z Abstrat:
Mean Ativity Coeffiients of Peroxodisulfates in Saturated Solutions of the Conversion System NH 4 Na S O 8 H O at 0 C and 0 C Jan Balej Heřmanova 5, 170 00 Prague 7, Czeh Republi balejan@seznam.z Abstrat:
Computer simulation and verification of deliming process mathematical model
 Computer simulation and verifiation of deliming proess mathematial model Hana Charvátová, Dagmar Janáčová, ladimír ašek, Pavel Mokrejš, Karel Kolomazník Abstrat The paper deals with hemial deliming proess
Computer simulation and verifiation of deliming proess mathematial model Hana Charvátová, Dagmar Janáčová, ladimír ašek, Pavel Mokrejš, Karel Kolomazník Abstrat The paper deals with hemial deliming proess
Electrokinetics in Nanochannels: Part I. Electric double layer overlap and channel-to-well equilibrium
 letrokinetis in Nanohannels: Part I. letri double layer overlap and hannel-to-well equilibrium Fabio Baldessari and Juan G. Santiago Department of Mehanial ngineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
letrokinetis in Nanohannels: Part I. letri double layer overlap and hannel-to-well equilibrium Fabio Baldessari and Juan G. Santiago Department of Mehanial ngineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
CHEM-E3205 BIOPROCESS OPTIMIZATION AND SIMULATION
 CHEM-E3205 BIOPROCESS OPTIMIZATION AND SIMULATION TERO EERIKÄINEN ROOM D416d tero.eerikainen@aalto.fi COURSE LECTURES AND EXERCISES Week Day Date Time Place Lectures/Execises 37 Mo 12.9.2016 10:15-11:45
CHEM-E3205 BIOPROCESS OPTIMIZATION AND SIMULATION TERO EERIKÄINEN ROOM D416d tero.eerikainen@aalto.fi COURSE LECTURES AND EXERCISES Week Day Date Time Place Lectures/Execises 37 Mo 12.9.2016 10:15-11:45
(Chapter 10) EE 403/503 Introduction to Plasma Processing
 (Chapter 10) EE 403/503 Introdution to Plasma Proessing November 9, 011 Average Eletron Energy, [ev] P = 100 Hz P = 10 KHz P = 1 MHz P = 13.56 MHz P = 100 MHz P =.45 GHz P = 10 GHz P = 1 THz T e,mw > T
(Chapter 10) EE 403/503 Introdution to Plasma Proessing November 9, 011 Average Eletron Energy, [ev] P = 100 Hz P = 10 KHz P = 1 MHz P = 13.56 MHz P = 100 MHz P =.45 GHz P = 10 GHz P = 1 THz T e,mw > T
