DEFORMATION PATTERN IN ELASTIC CRUST
|
|
|
- Martin Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEFORMATION PATTERN IN ELASTIC CRUST Stress and force in 2D Strain : normal and shear Elastic medium equations Vertical fault in elastic medium => arctangent General elastic dislocation (Okada s formulas) Fault examples 1
2 Stress (σ) in 2D -Normal stress =σ ii - Shear stress = σij - Force = σ x surface - no rotation => σxy = σyx - only 3 independent.components :..σxx, σyy, σxy 2
3 Applied forces Normal forces on x axis : = σxx(x). δy σxx(x+δx). δy = δy [σxx(x). σxx(x+δx)] = δy d σ xx/ dx. δx (1) Shear forces on x axis : = σyx(y). δx σyx(y+δy). δx = δx d σ yx/ dy. δy (2) 3 Total on x axis = (1)+(2) = [ d σ xx/ dx + d σ yx/ dy] δx δy
4 Forces Equilibrium Total on x axis = [ d σ xx/ dx + d σ yx/ dy] δx δy Total on y axis = [ d σ yy/ dy + d σ yx/ dx] δy δx Equilibrium => [ d σ yy/ dy + d σ yx/ dx] = 0 [ d σ xx/ dx + d σ yx/ dy] = 0 4
5 Normal strain : change length (not angles) - Change of length proportional to length - εxx, εyy, εzz are normal component of strain 5 nb : If deformation is small, change of volume is εxx + εyy + εzz (neglecting quadratic terms)
6 Shear strain : change angles εxy = - 1 / 2 (Φ1 + Φ2) = 1 / 2 ( dω y/ d x + dω x/ d y ) 6 εxy = εyx (obvious)
7 Solid elastic deformation (1) Stresses are proportional to strains No preferred orientations σxx = (λ+2g) εxx + λ εyy + λ εzz σyy = λ εxx + (λ+2g) εyy + λ εzz σzz = λ εxx + λ εyy + (λ+2g) εzz λ and G are Lamé parameters The material properties are such that a principal strain component ε produces a stress (λ+2g)ε in the same direction 7 and stresses λε in mutually perpendicular directions
8 Solid elastic deformation (2) Inversing stresses and strains give : εxx = 1 ν ν ν / E σxx - / E σyy - / E σzz εyy = - / E σxx + 1 ν ν ν / E σyy - / E σzz εzz = - / E σxx - / E σyy + 1 / E σzz E and ν are Young s modulus and Poisson s ratio a principal stress component σ produces a strain 1 / E σ in the same direction and 8 strains ν / E σ in mutually perpendicular directions
9 Elastic deformation across a locked fault Two plates (red and green) are separated by a vertical strike-slip fault. If the fault was slick then the two plates would slide freely along each other with no deformation. But because its surface is rough and there is some friction, the fault is locked. So because the plates keep moving far away from the fault, and don t move on the fault, they have to deform. 9 What is the shape of the accumulated deformation?
10 Mathematical formulation The plates are made of elastic crust above a viscous mantle. The viscous flow localizes the deformation in a narrow band just beneath the elastic layer We can compute the deformation of the elastic layer using the elastic equations detailed before 10
11 Mathematical formulation Symetry => all derivative with y = 0 εyy = 0 No gravity => σzz = 0 What is the displacement field U in the elastic layer? 11
12 Mathematical formulation Elastic equations : (1) σxx = (λ+2g) εxx + λ εzz (2) σyy = λ εxx + λ εzz σxy = 2G εxy σxz = 2G εxz (3) σzz = λ εxx + (λ+2g) εzz σyz = 2G εyz (3) + σzz = 0 => λ εxx + λ εzz = -2G εzz and (2) => σyy = λ εxx + λ εzz = -2 G εzz => εxx = - (2G + λ)/ λ εzz 12 and (1) => σxx = [- ( λ+2g) 2 / λ + λ ] εzz
13 Mathematical formulation Force equilibrium along the 3 axis x (x) dσxx / dx + dσyx / dy + dσxz / dz = 0 (y) dσxy / dx + dσyy / dy + dσyz / dz = 0 x (z) dσxz / dx + dσyz / dy + dσzz / dz = 0 Derivation of eq. 1 with x and eq. 3 give : d 2 σxx / dx 2 = 0 equation 2 becomes : dσxy / dx + dσyz / dz = 0 13
14 Mathematical formulation relations between stress (σ) and displacement vector (U) σxy = 2G εxy = 2G [dux / dy + duy / dx]. 1 / 2 σyz = 2G εyz = 2G [duz / dy + duy / dz]. 1 / 2 Using dσxy / dx + dσyz / dz = 0 we obtain : x x duy/dx] duy/dz] d/dx[dux/dy + + d/dz[duz/dy + = 0 14 d 2 Uy / dx 2 + d 2 Uy / dz 2 = 0
15 Mathematical formulation d 2 Uy / dx 2 + d 2 Uy / dz 2 = 0 What is U y, function of x and z, solution of this equation? Guess : U y = K arctang ( x / z ) works fine! Nb. datan(α)/ dα = 1 / (1+α2 ) duy/dx= K /z(1+x 2 /z 2 ) => d 2 Uy/dx 2 = -2Kxz/(z 2 +x 2 ) duy/dz= -Kx /z 2 (1+x 2 /z 2 ) => d 2 Uy/dz 2 = 2Kxz/(x 2 +z 2 ) 15
16 Mathematical formulation U y = K arctang ( x / z ) Boundary condition at the base of the crust (z=0) U y = K. Π/2 if x > 0 = K. Π/2 if x < 0 And also : U y = +V 0 if x > 0 = V if x < 0 0 => K = 2. V 0/ Π 16
17 Mathematical formulation U y = K arctang ( x / z ) at the surface (z=h) U y = 2. V 0/ Π arctang ( x / h ) 17 The expected profile of deformation across a strike slip fault we should see at the surface of the earth (if the crust is elastic) is shape like an arctangant function. The exact shape depends on the thickness of the elastic crust, also called the locking depth.
18 Arctang profiles U y = 2. V 0/ Π arctang ( x / h ) 18
19 dipping fault If the fault is not vertical but dipping with a given angle, then the profile at the surface is just the same. Only the center of the profile is shifted to be at the vertical of the shear flow in the viscous layer. 19 Then, the geological trace of the fault is not the place where the shear gradient is maximum
20 Elastic dislocation (Okada, 1985) Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half space, BSSA vol75, n 4, , The displacement field u i (x 1,x 2,x 3 ) due to a dislocation u j (ξ 1,ξ 2,ξ 3 ) across a surface Σ in an isotropic medium is given by : 20 Where δ jk is the Kronecker delta, λ and µ are Lamé s parameters, ν k is the direction cosine of the normal to the surface element dσ. u ij is the i th component of the displacement at (x 1,x 2,x 3 ) due to the j th direction point force of magnitude F at (ξ 1,ξ 2,ξ 3 )
21 Elastic dislocation (Okada, 1985) (1) displacements For strike-slip For dip-slip For tensile fault 21
22 Elastic dislocation (Okada, 1985) Where : 22
23 Sagaing Fault, Myanmar GPS measurement on the Sagaing fault fit well the arctang profile 23 but with an offset of 1015 km
24 Palu Fault, Sulawesi 24 Part of the GPS data on Palu fault fits well an arctang profile. But wee need a second fault to explain all the data
25 AltynTaghFault, China 25
26 Altyn Tagh Fault, China (INSAR) Interferogram Nov. 1995/ Nov Fault-parallel velocity : Slip rate V 0 = 1.4 cm/yr Locking depth D = 15 km v = v 0 /π atan(x/d) 26 1 color cycle = 28 mm LOS displacement
27 San Andreas Fault, USA (INSAR) 27
28 Subduction in south America 28
29 Subduction modeling Velocity component // to convergence direction In the case of a subduction (dippping fault with downward slip) we use Okada s formulas. We find a very large deformation area (> 500 km) because the dipping angle is only With oblique slip we predict the surface vector will start to rotate at the vertical of the end of the subduction plane The profile of the velocity component // to the convergence shows this with a flat portion at this location
30 Subduction parameter adjustments 30 Model and data Residuals
DEFORMATION PATTERN IN ELASTIC CRUST
 DEFORMATION PATTERN IN ELASTIC CRUST Stress and force in 2D Strain : normal and shear Elastic medium equations Vertical fault in elastic medium => arctangent General elastic dislocation (Okada s formulas)
DEFORMATION PATTERN IN ELASTIC CRUST Stress and force in 2D Strain : normal and shear Elastic medium equations Vertical fault in elastic medium => arctangent General elastic dislocation (Okada s formulas)
Deformable Materials 2 Adrien Treuille. source: Müller, Stam, James, Thürey. Real-Time Physics Class Notes.
 Deformable Materials 2 Adrien Treuille source: Müller, Stam, James, Thürey. Real-Time Physics Class Notes. Goal Overview Strain (Recap) Stress From Strain to Stress Discretization Simulation Overview Strain
Deformable Materials 2 Adrien Treuille source: Müller, Stam, James, Thürey. Real-Time Physics Class Notes. Goal Overview Strain (Recap) Stress From Strain to Stress Discretization Simulation Overview Strain
3.2 Hooke s law anisotropic elasticity Robert Hooke ( ) Most general relationship
 3.2 Hooke s law anisotropic elasticity Robert Hooke (1635-1703) Most general relationship σ = C ε + C ε + C ε + C γ + C γ + C γ 11 12 yy 13 zz 14 xy 15 xz 16 yz σ = C ε + C ε + C ε + C γ + C γ + C γ yy
3.2 Hooke s law anisotropic elasticity Robert Hooke (1635-1703) Most general relationship σ = C ε + C ε + C ε + C γ + C γ + C γ 11 12 yy 13 zz 14 xy 15 xz 16 yz σ = C ε + C ε + C ε + C γ + C γ + C γ yy
3D Elasticity Theory
 3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Strain Strain is the formal description of the change in shape of a
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Strain Strain is the formal description of the change in shape of a
Stress Integration for the Drucker-Prager Material Model Without Hardening Using the Incremental Plasticity Theory
 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. / No., 008 / pp. 80-89 UDC: 59.74:004.0 Stress Integration for the Drucker-rager Material Model Without Hardening Using the Incremental
Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. / No., 008 / pp. 80-89 UDC: 59.74:004.0 Stress Integration for the Drucker-rager Material Model Without Hardening Using the Incremental
Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation.
 Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation. In the process zone, stress amplitudes are poorly determined and much
Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation. In the process zone, stress amplitudes are poorly determined and much
Shear stresses around circular cylindrical openings
 Shear stresses around circular cylindrical openings P.C.J. Hoogenboom 1, C. van Weelden 1, C.B.M. Blom 1, 1 Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Gemeentewerken Rotterdam, the Netherlands In
Shear stresses around circular cylindrical openings P.C.J. Hoogenboom 1, C. van Weelden 1, C.B.M. Blom 1, 1 Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Gemeentewerken Rotterdam, the Netherlands In
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
RHEOLOGY & LINEAR ELASTICITY
 GG303 Lecture 20 10/25/09 1 RHEOLOGY & LINEAR ELASTICITY I Main Topics A Rheology: Macroscopic deformation behavior B Importance of fluids and fractures in deformation C Linear elasticity for homogeneous
GG303 Lecture 20 10/25/09 1 RHEOLOGY & LINEAR ELASTICITY I Main Topics A Rheology: Macroscopic deformation behavior B Importance of fluids and fractures in deformation C Linear elasticity for homogeneous
RHEOLOGY & LINEAR ELASTICITY. B Importance of fluids and fractures in deformation C Linear elasticity for homogeneous isotropic materials
 GG303 Lecture 2 0 9/4/01 1 RHEOLOGY & LINEAR ELASTICITY I II Main Topics A Rheology: Macroscopic deformation behavior B Importance of fluids and fractures in deformation C Linear elasticity for homogeneous
GG303 Lecture 2 0 9/4/01 1 RHEOLOGY & LINEAR ELASTICITY I II Main Topics A Rheology: Macroscopic deformation behavior B Importance of fluids and fractures in deformation C Linear elasticity for homogeneous
1. classic definition = study of deformed rocks in the upper crust
 Structural Geology I. Introduction 1. classic definition = study of deformed rocks in the upper crust deformed includes translation, rotation, and strain (change of shape) All rocks are deformed in some
Structural Geology I. Introduction 1. classic definition = study of deformed rocks in the upper crust deformed includes translation, rotation, and strain (change of shape) All rocks are deformed in some
Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension
 Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension Module. General Field Equations General Field Equations [] Equilibrium Equations in Elastic bodies xx x y z yx zx f x 0, etc [2] Kinematics xx u x x,etc. [3]
Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension Module. General Field Equations General Field Equations [] Equilibrium Equations in Elastic bodies xx x y z yx zx f x 0, etc [2] Kinematics xx u x x,etc. [3]
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
Topics. GG612 Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST 805 Lecture 4 Mechanics: Stress and Elas3city Theory
 GG612 Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 4 Mechanics: Stress and Elas3city Theory 11/6/15 GG611 1 Topics 1. Stress vectors (trac3ons) 2. Stress at a point 3. Cauchy
GG612 Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 4 Mechanics: Stress and Elas3city Theory 11/6/15 GG611 1 Topics 1. Stress vectors (trac3ons) 2. Stress at a point 3. Cauchy
Data Repository Hampel et al., page 1/5
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2138 Data Repositor Hampel et al., page 1/5 SETUP OF THE FINITE-ELEMENT MODEL The finite-element models were created with the software ABAQUS and consist of a 1-km-thick lithosphere,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2138 Data Repositor Hampel et al., page 1/5 SETUP OF THE FINITE-ELEMENT MODEL The finite-element models were created with the software ABAQUS and consist of a 1-km-thick lithosphere,
Chapter 2 Governing Equations
 Chapter Governing Equations Abstract In this chapter fundamental governing equations for propagation of a harmonic disturbance on the surface of an elastic half-space is presented. The elastic media is
Chapter Governing Equations Abstract In this chapter fundamental governing equations for propagation of a harmonic disturbance on the surface of an elastic half-space is presented. The elastic media is
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805
 GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 5 Mechanics Stress, Strain, and Rheology 11/6/16 GG611 1 Stresses Control How Rock Fractures hkp://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/kilauea/update/images.html
GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 5 Mechanics Stress, Strain, and Rheology 11/6/16 GG611 1 Stresses Control How Rock Fractures hkp://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/kilauea/update/images.html
(b) What is the amplitude at the altitude of a satellite of 400 km?
 Practice final quiz 2015 Geodynamics 2015 1 a) Complete the following table. parameter symbol units temperature T C or K thermal conductivity heat capacity density coefficient of thermal expansion volumetric)
Practice final quiz 2015 Geodynamics 2015 1 a) Complete the following table. parameter symbol units temperature T C or K thermal conductivity heat capacity density coefficient of thermal expansion volumetric)
Basic Equations of Elasticity
 A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake. EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole
 Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole Content Earthquakes and faults Examples of SAR interferograms of earthquakes
Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole Content Earthquakes and faults Examples of SAR interferograms of earthquakes
Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth
 Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth References: Turcotte and Schubert, Geodynamics, Sections 2.1,-2.4, 2.7, 3.1-3.8, 6.1, 6.2, 6.8, 7.1-7.4. Jaeger and Cook, Fundamentals of
Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth References: Turcotte and Schubert, Geodynamics, Sections 2.1,-2.4, 2.7, 3.1-3.8, 6.1, 6.2, 6.8, 7.1-7.4. Jaeger and Cook, Fundamentals of
CONSTITUTIVE RELATIONS FOR LINEAR ELASTIC SOLIDS
 Chapter 9 CONSTITUTIV RLATIONS FOR LINAR LASTIC SOLIDS Figure 9.1: Hooke memorial window, St. Helen s, Bishopsgate, City of London 211 212 CHAPTR 9. CONSTITUTIV RLATIONS FOR LINAR LASTIC SOLIDS 9.1 Mechanical
Chapter 9 CONSTITUTIV RLATIONS FOR LINAR LASTIC SOLIDS Figure 9.1: Hooke memorial window, St. Helen s, Bishopsgate, City of London 211 212 CHAPTR 9. CONSTITUTIV RLATIONS FOR LINAR LASTIC SOLIDS 9.1 Mechanical
Continuum mechanism: Stress and strain
 Continuum mechanics deals with the relation between forces (stress, σ) and deformation (strain, ε), or deformation rate (strain rate, ε). Solid materials, rigid, usually deform elastically, that is the
Continuum mechanics deals with the relation between forces (stress, σ) and deformation (strain, ε), or deformation rate (strain rate, ε). Solid materials, rigid, usually deform elastically, that is the
ELASTICITY (MDM 10203)
 ELASTICITY () Lecture Module 3: Fundamental Stress and Strain University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Normal Stress inconstant stress distribution σ= dp da P = da A dimensional Area of σ and A σ A 3 dimensional
ELASTICITY () Lecture Module 3: Fundamental Stress and Strain University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Normal Stress inconstant stress distribution σ= dp da P = da A dimensional Area of σ and A σ A 3 dimensional
} based on composition
 Learning goals: Predict types of earthquakes that will happen at different plate boundaries based on relative plate motion vector vs. strike (vector subtraction) Understand interseismic and coseismic deformation,
Learning goals: Predict types of earthquakes that will happen at different plate boundaries based on relative plate motion vector vs. strike (vector subtraction) Understand interseismic and coseismic deformation,
Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics
 Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements
 Title Page Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements Brendan Meade and Bradford Hager Three basic questions Large historical earthquakes One basic question How
Title Page Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements Brendan Meade and Bradford Hager Three basic questions Large historical earthquakes One basic question How
Physics of Continuous media
 Physics of Continuous media Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Classical Mechanics 2012 October 26, 2012 Deformations of continuous media If a body is deformed, we say that the point which originally had
Physics of Continuous media Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Classical Mechanics 2012 October 26, 2012 Deformations of continuous media If a body is deformed, we say that the point which originally had
CH.3. COMPATIBILITY EQUATIONS. Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics
 CH.3. COMPATIBILITY EQUATIONS Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics Overview Introduction Lecture 1 Compatibility Conditions Lecture Compatibility Equations of a Potential Vector Field Lecture 3 Compatibility
CH.3. COMPATIBILITY EQUATIONS Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics Overview Introduction Lecture 1 Compatibility Conditions Lecture Compatibility Equations of a Potential Vector Field Lecture 3 Compatibility
Introduction to Displacement Modeling
 Introduction to Displacement Modeling Introduction Deformation on the Earth surface informs us about processes and material properties below surface Observation tools: GPS (static-dynamic) InSAR (static)
Introduction to Displacement Modeling Introduction Deformation on the Earth surface informs us about processes and material properties below surface Observation tools: GPS (static-dynamic) InSAR (static)
Elastoplastic Deformation in a Wedge-Shaped Plate Caused By a Subducting Seamount
 Elastoplastic Deformation in a Wedge-Shaped Plate Caused By a Subducting Seamount Min Ding* 1, and Jian Lin 2 1 MIT/WHOI Joint Program, 2 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution *Woods Hole Oceanographic
Elastoplastic Deformation in a Wedge-Shaped Plate Caused By a Subducting Seamount Min Ding* 1, and Jian Lin 2 1 MIT/WHOI Joint Program, 2 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution *Woods Hole Oceanographic
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
20. Rheology & Linear Elasticity
 I Main Topics A Rheology: Macroscopic deformation behavior B Linear elasticity for homogeneous isotropic materials 10/29/18 GG303 1 Viscous (fluid) Behavior http://manoa.hawaii.edu/graduate/content/slide-lava
I Main Topics A Rheology: Macroscopic deformation behavior B Linear elasticity for homogeneous isotropic materials 10/29/18 GG303 1 Viscous (fluid) Behavior http://manoa.hawaii.edu/graduate/content/slide-lava
Mechanical Properties of Materials
 Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
Geodynamics Lecture 5 Basics of elasticity
 Geodynamics Lecture 5 Basics of elasticity Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi! 16.9.2014 Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Introduce linear elasticity! Look at the
Geodynamics Lecture 5 Basics of elasticity Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi! 16.9.2014 Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Introduce linear elasticity! Look at the
Strain Transformation equations
 Strain Transformation equations R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 8 Table of Contents 1. Stress transformation
Strain Transformation equations R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 8 Table of Contents 1. Stress transformation
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
Earthquake and Volcano Deformation
 Earthquake and Volcano Deformation Paul Segall Stanford University Draft Copy September, 2005 Last Updated Sept, 2008 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: To be published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, c
Earthquake and Volcano Deformation Paul Segall Stanford University Draft Copy September, 2005 Last Updated Sept, 2008 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: To be published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, c
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression. 1. Introduction
 Journal of Control Science and Engineering 1 (2015) 40-47 doi: 10.17265/2328-2231/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression Mitsuru
Journal of Control Science and Engineering 1 (2015) 40-47 doi: 10.17265/2328-2231/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression Mitsuru
Stress and Strain. Stress is a force per unit area. Strain is a change in size or shape in response to stress
 Geologic Structures Geologic structures are dynamically-produced patterns or arrangements of rock or sediment that result from, and give information about, forces within the Earth Produced as rocks change
Geologic Structures Geologic structures are dynamically-produced patterns or arrangements of rock or sediment that result from, and give information about, forces within the Earth Produced as rocks change
Stress equilibrium in southern California from Maxwell stress function models fit to both earthquake data and a quasi-static dynamic simulation
 Stress equilibrium in southern California from Maxwell stress function models fit to both earthquake data and a quasi-static dynamic simulation Peter Bird Dept. of Earth, Planetary, and Space Sciences
Stress equilibrium in southern California from Maxwell stress function models fit to both earthquake data and a quasi-static dynamic simulation Peter Bird Dept. of Earth, Planetary, and Space Sciences
12. Stresses and Strains
 12. Stresses and Strains Finite Element Method Differential Equation Weak Formulation Approximating Functions Weighted Residuals FEM - Formulation Classification of Problems Scalar Vector 1-D T(x) u(x)
12. Stresses and Strains Finite Element Method Differential Equation Weak Formulation Approximating Functions Weighted Residuals FEM - Formulation Classification of Problems Scalar Vector 1-D T(x) u(x)
Dynamics of the Mantle and Lithosphere ETH Zürich Continuum Mechanics in Geodynamics: Equation cheat sheet
 Dynamics of the Mantle and Lithosphere ETH Zürich Continuum Mechanics in Geodynamics: Equation cheat sheet or all equations you will probably ever need Definitions 1. Coordinate system. x,y,z or x 1,x
Dynamics of the Mantle and Lithosphere ETH Zürich Continuum Mechanics in Geodynamics: Equation cheat sheet or all equations you will probably ever need Definitions 1. Coordinate system. x,y,z or x 1,x
Useful Formulae ( )
 Appendix A Useful Formulae (985-989-993-) 34 Jeremić et al. A.. CHAPTER SUMMARY AND HIGHLIGHTS page: 35 of 536 A. Chapter Summary and Highlights A. Stress and Strain This section reviews small deformation
Appendix A Useful Formulae (985-989-993-) 34 Jeremić et al. A.. CHAPTER SUMMARY AND HIGHLIGHTS page: 35 of 536 A. Chapter Summary and Highlights A. Stress and Strain This section reviews small deformation
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by
 SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
Exercise: concepts from chapter 8
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Exercise: concepts from chapter 5
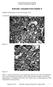 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
ANALYSIS OF STRAINS CONCEPT OF STRAIN
 ANALYSIS OF STRAINS CONCEPT OF STRAIN Concept of strain : if a bar is subjected to a direct load, and hence a stress the bar will change in length. If the bar has an original length L and changes by an
ANALYSIS OF STRAINS CONCEPT OF STRAIN Concept of strain : if a bar is subjected to a direct load, and hence a stress the bar will change in length. If the bar has an original length L and changes by an
Deformation of Rocks. Orientation of Deformed Rocks
 Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design
 MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
Numerical modeling of rock deformation: 03 Analytical methods - Folding. Stefan Schmalholz LEB D3
 Numerical modeling of rock deformation: 0 Analytical methods - Folding Stefan Schmalholz schmalholz@erdw.ethz.ch LEB D S008, Thursday 0-, CAB 5 Overview Derive a thin-plate equation for bending, folding
Numerical modeling of rock deformation: 0 Analytical methods - Folding Stefan Schmalholz schmalholz@erdw.ethz.ch LEB D S008, Thursday 0-, CAB 5 Overview Derive a thin-plate equation for bending, folding
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen?
 San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
The Frictional Regime
 The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
Basic Concepts of Strain and Tilt. Evelyn Roeloffs, USGS June 2008
 Basic Concepts of Strain and Tilt Evelyn Roeloffs, USGS June 2008 1 Coordinates Right-handed coordinate system, with positions along the three axes specified by x,y,z. x,y will usually be horizontal, and
Basic Concepts of Strain and Tilt Evelyn Roeloffs, USGS June 2008 1 Coordinates Right-handed coordinate system, with positions along the three axes specified by x,y,z. x,y will usually be horizontal, and
Geodynamics. Brittle deformation and faulting Lecture Predicting fault orientations. Lecturer: David Whipp
 Geodynamics Brittle deformation and faulting Lecture 11.6 - Predicting fault orientations Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Introduce
Geodynamics Brittle deformation and faulting Lecture 11.6 - Predicting fault orientations Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Introduce
Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault
 Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault Introduction Duncan Agnew, Andy Michael We propose the PBO instrument, with GPS and borehole strainmeters, the creeping section of
Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault Introduction Duncan Agnew, Andy Michael We propose the PBO instrument, with GPS and borehole strainmeters, the creeping section of
PLAXIS 3D TUNNEL. Material Models Manual version 2
 PLAXIS 3D TUNNEL Material Models Manual version 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...1-1 1.1 On the use of different models...1-1 1.2 Limitations...1-2 2 Preliminaries on material modelling...2-1
PLAXIS 3D TUNNEL Material Models Manual version 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...1-1 1.1 On the use of different models...1-1 1.2 Limitations...1-2 2 Preliminaries on material modelling...2-1
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress?
 When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
Earth Deformation Homework 1
 Earth Deformation Homework 1 Michal Dichter October 7, 14 Problem 1 (T+S Problem -5) We assume the setup of Figure -4 from Turcotte and Schubert: We are given the following values: hcc = 5 km hsb = 7 km
Earth Deformation Homework 1 Michal Dichter October 7, 14 Problem 1 (T+S Problem -5) We assume the setup of Figure -4 from Turcotte and Schubert: We are given the following values: hcc = 5 km hsb = 7 km
Wave and Elasticity Equations
 1 Wave and lasticity quations Now let us consider the vibrating string problem which is modeled by the one-dimensional wave equation. Suppose that a taut string is suspended by its extremes at the points
1 Wave and lasticity quations Now let us consider the vibrating string problem which is modeled by the one-dimensional wave equation. Suppose that a taut string is suspended by its extremes at the points
Module-4. Mechanical Properties of Metals
 Module-4 Mechanical Properties of Metals Contents ) Elastic deformation and Plastic deformation ) Interpretation of tensile stress-strain curves 3) Yielding under multi-axial stress, Yield criteria, Macroscopic
Module-4 Mechanical Properties of Metals Contents ) Elastic deformation and Plastic deformation ) Interpretation of tensile stress-strain curves 3) Yielding under multi-axial stress, Yield criteria, Macroscopic
DETAILS ABOUT THE TECHNIQUE. We use a global mantle convection model (Bunge et al., 1997) in conjunction with a
 DETAILS ABOUT THE TECHNIQUE We use a global mantle convection model (Bunge et al., 1997) in conjunction with a global model of the lithosphere (Kong and Bird, 1995) to compute plate motions consistent
DETAILS ABOUT THE TECHNIQUE We use a global mantle convection model (Bunge et al., 1997) in conjunction with a global model of the lithosphere (Kong and Bird, 1995) to compute plate motions consistent
Analytic and Numeric Tests of Fourier Deformation Model (Copyright 2003, Bridget R. Smith and David T. Sandwell)
 Analytic and Numeric Tests of Fourier Deformation Model (Copyright 2003, Bridget R. Smith and David T. Sandwell) Although the solutions of our Fourier deformation model have been checked using computer
Analytic and Numeric Tests of Fourier Deformation Model (Copyright 2003, Bridget R. Smith and David T. Sandwell) Although the solutions of our Fourier deformation model have been checked using computer
0- Numerical methods / Finite differences 1- Deformation and Estress, tensors 2- Basic equations of Solid Mechanics 3- Constitutive laws 4-
 0- Numerical methods / Finite differences 1- Deformation and Estress, tensors 2- Basic equations of Solid Mechanics 3- Constitutive laws 4- Orientation of faults on Earth (Anderson) 5- Critical shape of
0- Numerical methods / Finite differences 1- Deformation and Estress, tensors 2- Basic equations of Solid Mechanics 3- Constitutive laws 4- Orientation of faults on Earth (Anderson) 5- Critical shape of
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/ngeo739 Supplementary Information to variability and distributed deformation in the Marmara Sea fault system Tobias Hergert 1 and Oliver Heidbach 1,* 1 Geophysical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/ngeo739 Supplementary Information to variability and distributed deformation in the Marmara Sea fault system Tobias Hergert 1 and Oliver Heidbach 1,* 1 Geophysical
Elements of Rock Mechanics
 Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
2 Introduction to mechanics
 21 Motivation Thermodynamic bodies are being characterized by two competing opposite phenomena, energy and entropy which some researchers in thermodynamics would classify as cause and chance or determinancy
21 Motivation Thermodynamic bodies are being characterized by two competing opposite phenomena, energy and entropy which some researchers in thermodynamics would classify as cause and chance or determinancy
Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions
 Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions State of stress in Three Dimensions References Punmia B.C.,"Theory of Structures" (SMTS) Vol II, Laxmi Publishing Pvt Ltd, New Delhi 2004. Rattan.S.S., "Strength
Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions State of stress in Three Dimensions References Punmia B.C.,"Theory of Structures" (SMTS) Vol II, Laxmi Publishing Pvt Ltd, New Delhi 2004. Rattan.S.S., "Strength
Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum'
 Elasticity and Seismic Waves Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum' Elastic body is deformed in response to stress Two types of deformation: Change in volume and shape Equations of motion Wave
Elasticity and Seismic Waves Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum' Elastic body is deformed in response to stress Two types of deformation: Change in volume and shape Equations of motion Wave
INVERSE ANALYSIS METHODS OF IDENTIFYING CRUSTAL CHARACTERISTICS USING GPS ARRYA DATA
 Problems in Solid Mechanics A Symposium in Honor of H.D. Bui Symi, Greece, July 3-8, 6 INVERSE ANALYSIS METHODS OF IDENTIFYING CRUSTAL CHARACTERISTICS USING GPS ARRYA DATA M. HORI (Earthquake Research
Problems in Solid Mechanics A Symposium in Honor of H.D. Bui Symi, Greece, July 3-8, 6 INVERSE ANALYSIS METHODS OF IDENTIFYING CRUSTAL CHARACTERISTICS USING GPS ARRYA DATA M. HORI (Earthquake Research
Learning Objectives (LO) What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Distributed: Wednesday, March 17, 2004
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.00 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II QUIZ I SOLUTIONS Distributed: Wednesday, March 17, 004 This quiz consists
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.00 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II QUIZ I SOLUTIONS Distributed: Wednesday, March 17, 004 This quiz consists
c) Plot stability diagrams (Figure 11, p 10 of notes) for cases i) - iv), all on the same graph.
 12.520 Problem Set 4 Due 10/25/06 1) (90%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ;
12.520 Problem Set 4 Due 10/25/06 1) (90%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ;
Lecture 14: Strain Examples. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller
 Lecture 14: Strain Examples GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller A Worked Example Consider this case of pure shear deformation, and two vectors dx 1 and dx 2. How do they rotate? We ll look at vector
Lecture 14: Strain Examples GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller A Worked Example Consider this case of pure shear deformation, and two vectors dx 1 and dx 2. How do they rotate? We ll look at vector
A short review of continuum mechanics
 A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
Crustal Deformation. Earth Systems 3209
 Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Azimuth with RH rule. Quadrant. S 180 Quadrant Azimuth. Azimuth with RH rule N 45 W. Quadrant Azimuth
 30 45 30 45 Strike and dip notation (a) N30 E, 45 SE ("Quadrant"): the bearing of the strike direction is 30 degrees east of north and the dip is 45 degrees in a southeast (SE) direction. For a given strike,
30 45 30 45 Strike and dip notation (a) N30 E, 45 SE ("Quadrant"): the bearing of the strike direction is 30 degrees east of north and the dip is 45 degrees in a southeast (SE) direction. For a given strike,
Rock mechanics. Master 1, Course PAX7STAD. University of Grenoble I Mai-Linh Doan
 Rock mechanics Master 1, Course PAX7STAD University of Grenoble I 2015-2016 Mai-Linh Doan 2016-09-19 Chapter I : Stress & Strain (M.-L. Doan) 2016-09-21 Tutorial I : Stress & Strain (M.-L. Doan) 2016-09-23
Rock mechanics Master 1, Course PAX7STAD University of Grenoble I 2015-2016 Mai-Linh Doan 2016-09-19 Chapter I : Stress & Strain (M.-L. Doan) 2016-09-21 Tutorial I : Stress & Strain (M.-L. Doan) 2016-09-23
Advanced Structural Analysis EGF Cylinders Under Pressure
 Advanced Structural Analysis EGF316 4. Cylinders Under Pressure 4.1 Introduction When a cylinder is subjected to pressure, three mutually perpendicular principal stresses will be set up within the walls
Advanced Structural Analysis EGF316 4. Cylinders Under Pressure 4.1 Introduction When a cylinder is subjected to pressure, three mutually perpendicular principal stresses will be set up within the walls
Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses
 Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses Shear stresses in a Newtonian fluid A fluid at rest can not resist shearing forces. Under the action of such forces it deforms continuously, however small
Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses Shear stresses in a Newtonian fluid A fluid at rest can not resist shearing forces. Under the action of such forces it deforms continuously, however small
Geophysics Departmental Exam: 2004 Part 1
 2004 Geophysics Departmental Exam: 2004 Part 1 This section is 90 minutes, closed book, and consists of questions designed to test your knowledge of facts and figures in the geosciences. The focus will
2004 Geophysics Departmental Exam: 2004 Part 1 This section is 90 minutes, closed book, and consists of questions designed to test your knowledge of facts and figures in the geosciences. The focus will
Continuum Mechanics. Continuum Mechanics and Constitutive Equations
 Continuum Mechanics Continuum Mechanics and Constitutive Equations Continuum mechanics pertains to the description of mechanical behavior of materials under the assumption that the material is a uniform
Continuum Mechanics Continuum Mechanics and Constitutive Equations Continuum mechanics pertains to the description of mechanical behavior of materials under the assumption that the material is a uniform
Aircraft Structures Kirchhoff-Love Plates
 University of Liège erospace & Mechanical Engineering ircraft Structures Kirchhoff-Love Plates Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/ Chemin
University of Liège erospace & Mechanical Engineering ircraft Structures Kirchhoff-Love Plates Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/ Chemin
Consider an elastic spring as shown in the Fig.2.4. When the spring is slowly
 .3 Strain Energy Consider an elastic spring as shown in the Fig..4. When the spring is slowly pulled, it deflects by a small amount u 1. When the load is removed from the spring, it goes back to the original
.3 Strain Energy Consider an elastic spring as shown in the Fig..4. When the spring is slowly pulled, it deflects by a small amount u 1. When the load is removed from the spring, it goes back to the original
UNIT-I Introduction & Plane Stress and Plane Strain Analysis
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY:: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Advanced Solid Mechanics (18CE1002) Year
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY:: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Advanced Solid Mechanics (18CE1002) Year
3 2 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) 3. a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1
 Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Code_Aster. HSNV120 - Tension hyper elastic of a bar under thermal loading
 Titre : HSNV - Traction hperélastique d'un barreau sou[...] Date : 4/8/ Page : / HSNV - Tension hper elastic of a bar under thermal loading Abstract: This quasi-static thermomechanical test consists in
Titre : HSNV - Traction hperélastique d'un barreau sou[...] Date : 4/8/ Page : / HSNV - Tension hper elastic of a bar under thermal loading Abstract: This quasi-static thermomechanical test consists in
EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS
 EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS Francis Nimmo Last Week Global gravity variations arise due to MoI difference (J 2 ) We can also determine C, the moment of inertia, either by observation (precession) or by
EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS Francis Nimmo Last Week Global gravity variations arise due to MoI difference (J 2 ) We can also determine C, the moment of inertia, either by observation (precession) or by
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry. Planetary Surfaces
 Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Plane and axisymmetric models in Mentat & MARC. Tutorial with some Background
 Plane and axisymmetric models in Mentat & MARC Tutorial with some Background Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Piet J.G. Schreurs Lambèrt C.A. van Breemen March 6,
Plane and axisymmetric models in Mentat & MARC Tutorial with some Background Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Piet J.G. Schreurs Lambèrt C.A. van Breemen March 6,
Regional Geodesy. Shimon Wdowinski. MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region. University of Miami
 MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
Unit 13 Review of Simple Beam Theory
 MIT - 16.0 Fall, 00 Unit 13 Review of Simple Beam Theory Readings: Review Unified Engineering notes on Beam Theory BMP 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 T & G 10-15 Paul A. Lagace, Ph.D. Professor of Aeronautics & Astronautics
MIT - 16.0 Fall, 00 Unit 13 Review of Simple Beam Theory Readings: Review Unified Engineering notes on Beam Theory BMP 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 T & G 10-15 Paul A. Lagace, Ph.D. Professor of Aeronautics & Astronautics
Linear Elasticity ( ) Objectives. Equipment. Introduction. ε is then
 Linear Elasticity Objectives In this lab you will measure the Young s Modulus of a steel wire. In the process, you will gain an understanding of the concepts of stress and strain. Equipment Young s Modulus
Linear Elasticity Objectives In this lab you will measure the Young s Modulus of a steel wire. In the process, you will gain an understanding of the concepts of stress and strain. Equipment Young s Modulus
c) Plot stability diagrams (Figure 11, p 10 of notes) for cases i) - iv), all on the same graph.
 12.520 Problem Set 4 1) (100%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ; ii) φ = 30,
12.520 Problem Set 4 1) (100%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ; ii) φ = 30,
